Chernaya dyra
(I. D. Novikov, "Fizika Kosmosa", 1986,
26.03.2003 20:16, 22.4 KBait, otvetov: 659)
Chernaya dyra - oblast' prostranstva, v k-roi pole tyagoteniya nastol'ko sil'no, chto
vtoraya kosmich. skorost' (parabolicheskaya
skorost')
dlya nahodyashihsya v etoi oblasti tel dolzhna byla by prevyshat' skorost' sveta, t.e.
iz Ch.d. nichto ne mozhet vyletet' - ni izluchenie, ni chasticy, ibo v prirode nichto ne
mozhet
dvigat'sya so skorost'yu, bol'shei skorosti sveta. Granicu oblasti, za k-ruyu ne vyhodit
svet, naz. gorizontom Ch.d. Dlya togo chtoby pole tyagoteniya smoglo "zaperet'" izluchenie,
sozdayushee eto pole massa 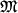 dolzhna szhat'sya do ob'ema s radiusom,
men'shim gravitacionnogo radiusa
dolzhna szhat'sya do ob'ema s radiusom,
men'shim gravitacionnogo radiusa 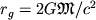 . Gravitac. radius chrezvychaino mal dazhe dlya bol'shih mass (napr., dlya
Solnca, imeyushego massu
. Gravitac. radius chrezvychaino mal dazhe dlya bol'shih mass (napr., dlya
Solnca, imeyushego massu 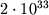 g,
g, 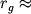 3 km).
3 km).
Pole tyagoteniya Ch.d. opisyvaetsya teoriei tyagoteniya Einshteina (sm. Tyagotenie).
Soglasno etoi teorii, vblizi Ch.d. geometrich. sv-va prostranstva
opisyvayutsya neevklidovoi (rimanovoi) geometriei, a vremya techet medlennee, chem vdali,
vne sil'nogo polya tyagoteniya.
Po sovr. predstavleniyam, massivnye zvezdy (s massoi v nesk.  i bol'she), zakanchivaya svoyu evolyuciyu, mogut v konce koncov szhat'sya (skollapsirovat')
i prevratit'sya v Ch.d. (sm. Evolyuciya zvezd,
Gravitacionnyi kollaps).
i bol'she), zakanchivaya svoyu evolyuciyu, mogut v konce koncov szhat'sya (skollapsirovat')
i prevratit'sya v Ch.d. (sm. Evolyuciya zvezd,
Gravitacionnyi kollaps).
Esli Ch.d. voznikaet pri szhatii nevrashayushegosya nezaryazhennogo tela, to ee vnesh. pole
tyagoteniya okazyvaetsya strogo sfericheskim i zavisyashim tol'ko ot polnoi massy tela
 . Vse otkloneniya ot sferichnosti v graivtac. pole pri obrazovanii Ch.d. izluchayutsya
v vide gravitac. voln (sm. Gravitacionnoe
izluchenie). Ostavsheesya pole ne zavisit ot raspredeleniya massy vnutri szhavshegosya
tela. T.o., hotya vnutri Ch.d. mozhet byt' "spryatano" ochen' nesimmetrichno szhimayusheesya
telo,
vnesh. pole tyagoteniya budet strogo sfericheski-simmetrichnym (t.n. pole Shvarcshil'da).
. Vse otkloneniya ot sferichnosti v graivtac. pole pri obrazovanii Ch.d. izluchayutsya
v vide gravitac. voln (sm. Gravitacionnoe
izluchenie). Ostavsheesya pole ne zavisit ot raspredeleniya massy vnutri szhavshegosya
tela. T.o., hotya vnutri Ch.d. mozhet byt' "spryatano" ochen' nesimmetrichno szhimayusheesya
telo,
vnesh. pole tyagoteniya budet strogo sfericheski-simmetrichnym (t.n. pole Shvarcshil'da).
Pri obrazovanii Ch.d. izluchayutsya takzhe vse fiz. polya, krome staticheskogo elektricheskogo
polya (esli kollapsiruyushee telo bylo elektricheski zaryazhennym).
Esli telo, obrazovavshee Ch.d., vrashalos', to vokrug Ch.d. sohranyaetsya "vihrevoe" gravitac.
pole, uvlekayushee vse tela vblizi Ch.d. vo vrashatel'noe dvizhenie vokrug nee. Eto pole
opredelyaetsya pomimo massy Ch.d. tol'ko ee polnym momentom impul'sa. Pole tyagoteniya
vrashayusheisya Ch.d. naz. polem Kerra.
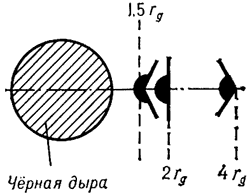
Dvizhenie tel v pole tyagoteniya Shvarcshil'da obladaet ryadom osobennostei. V teorii N'yutona
dvizhenie po okruzhnosti vokrug tyagoteyushego centra vozmozhno na lyubom rasstoyanii R
ot nego. V teorii Einshteina eto ne tak. Chem blizhe k Ch.d., tem bol'she skorost' krugovogo
dvizheniya. Na okruzhnosti s R=1,5 rg skorost'
dvizheniya dostigaet svetovoi. Blizhe k Ch.d. dvizhenie po okruzhnosti, ochevidno, voobshe
nevozmozhno. V deistvitel'nosti zhe dvizhenie po okruzhnosti stanovitsya neustoichivym
na znachitel'no
bol'shih rasstoyaniyah, a imenno: nachinaya s R=3 rg,
kogda skorost' dvizheniya sostavlyaet vsego polovinu svetovoi. Tol'ko na rasstoyaniyah,
prevyshayushih 3rg, vozmozhno ustoichivoe krugovoe dvizhenie.
Na predele ustoichivosti krugovyh orbit energiya
svyazi chasticy 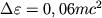 , gde m - massa
chasticy.
, gde m - massa
chasticy.
Osobyi interes predstavlyaet vozmozhnost' gravitac. zahvata chernoi dyroi tel, priletayushih
iz beskonechnosti k tyagoteyushei masse, opisyvaet okolo nee parabolu ili giperbolu i
(esli
ne ispytyvaet soudareniya s tyagoteyushei massoi) snova uletaet v beskonechnost'. Gravitac.
zahvat v etoi zadache nevozmozhen.
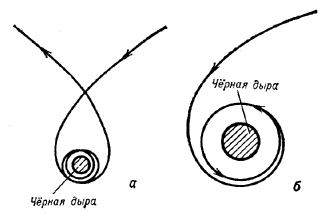
|
|
Ris. 1.
|
Inache obstoit delo v pole tyagoteniya Ch.d. Konechno, esli telo dvizhetsya na bol'shih rasstoyaniyah
ot Ch.d. (R>rg), gde pole tyagoteniya uzhe slabo i
spravedliva s bol'shoi tochnost'yu teoriya N'yutona, to traektoriya dvizheniya pochti tochno
sovpadaet s paraboloi ili giperboloi. V dostatochnoi blizosti ot Ch.d. traektoriya rezko
otlichaetsya
ot n'yutonovskoi. Tak, esli skorost' tela vdali ot Ch.d. mnogo men'shn svetovoi i traektoriya
ego dvizheniya podhodit blizko k okruzhnosti s R=2 rg,
to telo sovershit mnogo oborotov vokrug Ch.d., prezhde chem snova uletit v kosmos (ris.
1, a).
Nakonec, esli telo podoidet vplotnuyu k ukazannoi okruzhnosti, to ego orbita budet
neogranichenno navivats'ya na okruzhnost'. Telo okazhetsya gravitacionno zahvachennym Ch.d.
i nikogda
snova ne uletit v kosmos (ris. 1, b). Esli zhe telo podletit eshe blizhe k Ch.d., to
posle nesk. oborotov ili dazhe ne uspev sdelat' ni odnogo oborota, ono upadet v Ch.d.
|
|
Ris. 2.
|
V pole tyagoteniya Ch.d. vyrazhenie dlya parabolicheskoi skorosti zapisyvaetsya formal'no
tak zhe, kak i v teorii N'yutona. Odnako neobhodimo sdelat' sleduyushee utochnenie. Kogda
telo
dvizhetsya pryamo po radisu k Ch.d., to kakuyu by skorost' telo ne imelo, v t.ch. i bol'she
parabolicheskoi, ono upadet v Ch.d. Bolee togo, esli telo dvizhetsya hotya i ne pryamo
po radiusu
k Ch.d., no traektoriya ego dostatochno blizka k Ch.d., to ono tozhe budet zahvacheno Ch.d.
Sledovatel'no, dlya togo chtoby vyrvat'sya iz okrestnostei Ch.d., malo imet' skorost',
prevyshayushuyu
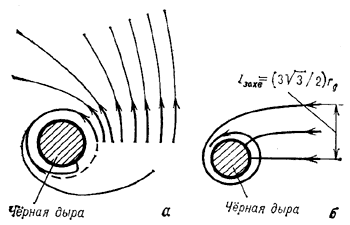
parabolicheskuyu, nado eshe, chtoby ugol 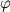 mezhdu napravleniem etoi
skorosti i napravleniem na Ch.d. prevyshal nek-roe kritich. znachenie
mezhdu napravleniem etoi
skorosti i napravleniem na Ch.d. prevyshal nek-roe kritich. znachenie 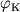 .
Pri
.
Pri 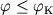 telo okazhetsya zahvachennym Ch.d., pri
telo okazhetsya zahvachennym Ch.d., pri 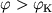 (i uslovii, chto skorost' bol'she ili ravna parabolicheskoi) telo uletit
ot Ch.d. Znachenie
(i uslovii, chto skorost' bol'she ili ravna parabolicheskoi) telo uletit
ot Ch.d. Znachenie 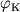 zavisit ot rasstoyaniya do Ch.d. Na ris. 2 chernym
cvetom zakrashen konus zahvata: esli vektor parabolicheskoi skorosti raspolagaetsya
v etom
konuse, to telo budet zahvacheno Ch.d.
zavisit ot rasstoyaniya do Ch.d. Na ris. 2 chernym
cvetom zakrashen konus zahvata: esli vektor parabolicheskoi skorosti raspolagaetsya
v etom
konuse, to telo budet zahvacheno Ch.d.
|
|
Ris. 3.
|
Pole tyagoteniya Ch.d. iskrivlyaet traektorii luchei sveta (i voobshe lyubyh ul'trarelyativistskih
chastic, k-rye dvizhutsya prakticheski po tem zhe traektoriyam, chto i fotony). Chem blizhe
k Ch.d. traektorii, tem sil'nee oni iskrivleny. Na ris. 3, a privedeny traektorii
luchei sveta, ispushennyh na raznyh rasstoyaniyah ot Ch.d. perpendikulyarno k radial'nomu
napravleniyu.
Dlya luchei sushestvuet kritich. okruzhnost' s R=1,5 rg.
Po etoi okruzhnosti mozhet dvigat'sya foton, uderzhivaemyi tyagoteniem Ch.d. Odnako eto
dvizhenie neustoichivo. Pri maleishem vozmushenii foton libo popadaet v Ch.d., libo uletaet
v kosmos.
Nalichie kritich. okruzhnosti vedet k tomu, chto vse luchi s pricel'nym parametrom na
beskonechnosti 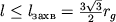 gravitacionno zahvatyvayutsya
(ris. 3, b).
gravitacionno zahvatyvayutsya
(ris. 3, b).
Okolo vrashayusheisya Ch.d., kak uzhe bylo skazano, dolzhno sushestvovat' "vihrevoe" gravitac.
pole. Vdali ot Ch.d. ono ochen' slabo, a vblizi vozrastaet nastol'ko, chto vedet k kachestvenno
novym effektam.
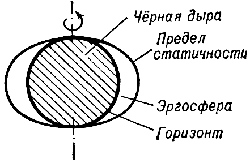
Tak, v okrestnosti vrashayusheisya Ch.d. voznikaet oblast', v k-roi vse tela i fotony
uvlekatsya v dvizhenie vokurg Ch.d. Vnesh. granica etoi oblasti naz. predelom statichnosti.
Odnako
vnutri predela statichnosti tela i fotony sovsem ne obyazatel'no dolzhny padat' k centru,
oni mogut i priblizhat'sya k Ch.d. i udalyat'sya ot nee, mogut vyhodit' za predel statichnosti.
T.o., predel statichnosti ne yavl. granicei Ch.d., ee gorizontom, iz-pod k-rogo nel'zya
vyiti. Lineinye razmery predela statichnosti po poryadku velichiny ravny rg.
Gorizont Ch.d. raspolozhen glubzhe, pod predelom statichnosti. Prostranstvo mezhdu gorizontom
i predelom statichnosti naz. ergosferoi (ris. 4). Predel statichnosti kasaetsya gorizonta
v polyusah vrashayusheisya Ch.d.
Pri padenii tela na vrashayushuyusya Ch.d. ono snachala otklonyaetsya v svoem dvizhenii v storonu
vrasheniya Ch.d., peresekaet granicu ergosfery i postepenno priblizhaetsya k gorizontu.
Dlya vnesh. nablyudatelya svet, ispuskaemyi padayushim telom, stanovitsya vse bolee krasnym
i menee intensivnym, zatem polnost'yu zatuhaet: telo, uidya pod gorizont, stanovitsya
nevidimym
dlya vnesh. nablyudatelya. Na gorizonte vse tela imeyut odnu tu zhe uglovuyu skorost' obrasheniya,
v kakoe by mesto gorizonta ni popadalo padayushee telo.
Obshaya dlya vseh padayushih tel uglovaya skorost' 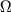 na gorizonte Ch.d.
i est' skorost' ee vrasheniya:
na gorizonte Ch.d.
i est' skorost' ee vrasheniya: 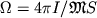 , gde I
-
moment impul'sa tela, iz k-rogo voznikla Ch.d.,
, gde I
-
moment impul'sa tela, iz k-rogo voznikla Ch.d., 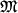 - massa,
S - ploshad' gorizonta Ch.d. Moment impul'sa Ch.d. zadannoi massy ne mozhet byt'
skol'
ugodno bol'shim. Maksimal'no vozmozhnye znacheniya I i
- massa,
S - ploshad' gorizonta Ch.d. Moment impul'sa Ch.d. zadannoi massy ne mozhet byt'
skol'
ugodno bol'shim. Maksimal'no vozmozhnye znacheniya I i 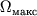 opredelyayutsya tem, chto pri obrazovanii Ch.d. lineinaya skorost' vrasheniya tochek ekvatora
tela
ne prevyshaet skorosti sveta. Po poryadku velichiny
opredelyayutsya tem, chto pri obrazovanii Ch.d. lineinaya skorost' vrasheniya tochek ekvatora
tela
ne prevyshaet skorosti sveta. Po poryadku velichiny 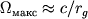 .
Dlya Ch.d. s massoi, ravnoi masse Solnca,
.
Dlya Ch.d. s massoi, ravnoi masse Solnca, 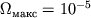 (1/s).
(1/s).
|
|
Ris. 4.
|
Gravitac. zahvat chastic Ch.d. s vrasheniem neskol'ko otlichaetsya ot zahvata nevrashayusheisya
Ch.d. Legche vsego zahvatyvayutsya chasticy, k-rye proletayut vblizi Ch.d. v storonu, protivopolozhnuyu
vrasheniyu, trudnee zahvatyvayutsya chasticy, letyashie mimo Ch.d. v storonu vrasheniya. Naglyadno
mozhno sebe predstavit', chto vihrevoe gravitac. pole vokrug Ch.d. deistvuet podobno
prashe,
uskoryaya, otbrasyvaya tem samym chasticy, dvizhushiesya mimo Ch.d. v tu zhe storonu, v k-ruyu
zakruchivaetsya "vihr'" etogo polya, i, naoborot, tormozya i zahvatyvaya chasticy, dvizhushiesya
protiv "vihrya".
Rassmotrim dlya primera zahvat fotona, dvizhushegosya v ploskosti ekvatora maksimal'no
bystro vrashayusheisya Ch.d.
Dlya fotona, dvizhushegosya v napravlenii vrasheniya Ch.d., pricel'nyi parametr lzahv,1=1/2
rg; dlya fotona, dvizhushegosya
protiv vrasheniya, pricel'nyi parametr namnogo bol'she: lzahv,2=4
rg. Izmenyaetsya situaciya i s krugovymi orbitami.
Dlya Ch.d. bez vrasheniya poslednyaya ustoichivaya krugovaya orbita imeet radius 3rg;
chastica, dvizhushayasya po nei, imeet skorost' c/2. I samoe
vazhnoe: chtoby popast' na etu orbitu, chastica s massoi m dolzhna otdat' energiyu
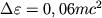 (energiyu svyazi) v vide, napr., gravitacionnogo
izlucheniya.
(energiyu svyazi) v vide, napr., gravitacionnogo
izlucheniya.
V sluchae maksimal'no bystro vrashayusheisya dyry poslednyaya krugovaya orbita lezhit v ekvatorial'noi
ploskosti blizko k gorizontu, gluboko vnutri ergosfery. No zdes' chastica mozhet
dvigat'sya tol'ko v storonu vrasheniya Ch.d. Energiya, k-ruyu vydelyaet chastica, popavshaya
na etu orbitu, gorazdo bol'she i sostavlyaet 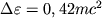 .
V to
zhe vremya poslednyaya ustoichivaya orbita chasticy, obrashayusheisya vokrug dyry v protivopolozhnom
napravlenii, lezhit vne ergosfery i chastica, popadayushaya v nee, vydelyaet energiyu
.
V to
zhe vremya poslednyaya ustoichivaya orbita chasticy, obrashayusheisya vokrug dyry v protivopolozhnom
napravlenii, lezhit vne ergosfery i chastica, popadayushaya v nee, vydelyaet energiyu 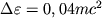 .
.
Polnaya massa vrashayusheisya Ch.d. opredelyaetsya kak ee razmerami (ploshad'yu S gorizonta),
tak i energiei vrasheniya:
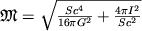 .
.
Esli vrashenie otsutstvuet (I=0), to 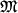 opredelyaetsya
tol'ko razmerami Ch.d. Pri maksimal'no vozmozhnoi skorosti vrasheniya Ch.d. vtoroe slagaemoe
pod kornem ravno pervomu.
opredelyaetsya
tol'ko razmerami Ch.d. Pri maksimal'no vozmozhnoi skorosti vrasheniya Ch.d. vtoroe slagaemoe
pod kornem ravno pervomu.
V ergosfere Ch.d. vozmozhny processy, privodyashie k umen'sheniyu energii vrasheniya Ch.d.,
t.e., kak okazyvaetsya, Ch.d. mozhet teryat' energiyu. V chastnosti, kogda v ergosferu
vletae
chastica, imevshaya vdali ot Ch.d. energiyu 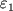 (vklyuchaya energiyu
pokoya), i raspadaetsya na dve chasticy, to raspad mozhet proizoiti takim obrazom, chto
odna
chastica upadet na Ch.d., a drugaya, sravnitel'no nemnogo uvelichiv svoyu skorost' v moment
raspada, pereidet na takuyu orbitu, chto vyletit iz ergosfery s ogromnoi skorost'yu.
Eta
skorost' mozhet namnogo prevyshat' i pervonachal'nuyu skorost' podleta chasticy k ergosfere,
i velichinu izmeneniya skorosti pri raspade. V rezul'tate polnaya energiya vyletevshei
chasticy
(vklyuchaya energiyu
pokoya), i raspadaetsya na dve chasticy, to raspad mozhet proizoiti takim obrazom, chto
odna
chastica upadet na Ch.d., a drugaya, sravnitel'no nemnogo uvelichiv svoyu skorost' v moment
raspada, pereidet na takuyu orbitu, chto vyletit iz ergosfery s ogromnoi skorost'yu.
Eta
skorost' mozhet namnogo prevyshat' i pervonachal'nuyu skorost' podleta chasticy k ergosfere,
i velichinu izmeneniya skorosti pri raspade. V rezul'tate polnaya energiya vyletevshei
chasticy
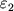 okazhetsya bol'she
okazhetsya bol'she 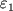 . Izbytok energii
. Izbytok energii
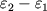 cherpaetsya iz energii vrasheniya Ch.d. Energiya
vrasheniya Ch.d. mozhet umen'shat'sya takzhe pri rasseyanii el.-magn. voln na Ch.d. Rasseyannaya
volna pri opredelennyh usloviyah mozhet okazat'sya intensivnee padayushei. Poterya energii
vrasheniya Ch.d. pri raspade chasticy v ergosfere dostigaet maksimuma, kogda raspad proishodit
na gorizonte. Pri etom ploshad' gorizonta ne menyaetsya. Vo vseh drugih sluchayah ploshad'
gorizonta neskol'ko uvelichivaetsya za schet energii chasticy, upavshei v Ch.d. Okazyvaetsya,
chto ploshad' gorizonta Ch.d. ne umen'shaetsya ni pri kakih processah voobshe (za isklyucheniem
medlennogo samoproizvol'nogo kvantovogo ispareniya Ch.d., o k-rom govoritsya dalee).
Napr., ch.d. mogut stolknut'sya i slit'sya v odnu. Chast' ih energii budet unesena pri
etom za
schet izlucheniya gravitac. voln, no gorizont voznikshei Ch.d. budet po ploshadi bol'she,
chem summa ploshadei gorizontov pervonachal'nyh dyr. Ni pri kakih vozdeistviyah (prilivnyh
i
drugih) Ch.d. ne mozhet razdelit'sya na dve ili bol'shee kolichestvo Ch.d.
cherpaetsya iz energii vrasheniya Ch.d. Energiya
vrasheniya Ch.d. mozhet umen'shat'sya takzhe pri rasseyanii el.-magn. voln na Ch.d. Rasseyannaya
volna pri opredelennyh usloviyah mozhet okazat'sya intensivnee padayushei. Poterya energii
vrasheniya Ch.d. pri raspade chasticy v ergosfere dostigaet maksimuma, kogda raspad proishodit
na gorizonte. Pri etom ploshad' gorizonta ne menyaetsya. Vo vseh drugih sluchayah ploshad'
gorizonta neskol'ko uvelichivaetsya za schet energii chasticy, upavshei v Ch.d. Okazyvaetsya,
chto ploshad' gorizonta Ch.d. ne umen'shaetsya ni pri kakih processah voobshe (za isklyucheniem
medlennogo samoproizvol'nogo kvantovogo ispareniya Ch.d., o k-rom govoritsya dalee).
Napr., ch.d. mogut stolknut'sya i slit'sya v odnu. Chast' ih energii budet unesena pri
etom za
schet izlucheniya gravitac. voln, no gorizont voznikshei Ch.d. budet po ploshadi bol'she,
chem summa ploshadei gorizontov pervonachal'nyh dyr. Ni pri kakih vozdeistviyah (prilivnyh
i
drugih) Ch.d. ne mozhet razdelit'sya na dve ili bol'shee kolichestvo Ch.d.
V ergosfere Ch.d. mogut protekat' kvantovye processy rozhdeniya chastic. V sil'nom pole
tyagoteniya Ch.d. vakuum (predstavlyaet soboi fiz. polya v nainizshem energeticheskom sostoyanii)
ne ustoichiv i iz nego mogut rozhdat'sya chasticy i antichasticy, v osnovnom bezmassovye:
fotony, neitrino, gravitony.
Rozhdennye chasticy, uletaya iz ergesfery na beskonechnost', unosyat energiyu Ch.d. Harakternaya
chastota 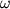 rozhdayushihsya fotonov po poryadku velichiny ravna
rozhdayushihsya fotonov po poryadku velichiny ravna 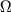 .
Skorost' poteri energii vrasheniya Ch.d. opredelyaetsya sootnosheniem:
.
Skorost' poteri energii vrasheniya Ch.d. opredelyaetsya sootnosheniem:
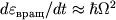 .
.
Chrezvychaino vazhno, chto vakuum neustoichiv v pole tyagoteniya ne tol'ko vrashayusheisya Ch.d.,
no i nevrashayusheisya. Eto oznachaet, chto za schet kvantovyh processov nevrashayushayasya Ch.d.
takzhe teryaet energiyu, umen'shayutsya ee massa i razmery. Nevrashayushayasya Ch.d. izluchaet
kak absolyutno chernoe telo s temp-roi T=1011(1015/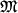 ) K, polnaya moshnost' el.-magn. izlucheniya L=1010(1015/
) K, polnaya moshnost' el.-magn. izlucheniya L=1010(1015/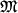 ) erg/s, a vremya sushestvennogo
umen'sheniya massy Ch.d.
) erg/s, a vremya sushestvennogo
umen'sheniya massy Ch.d. 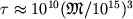 let,
gde
let,
gde 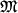 - znachenie massy Ch.d. v g. Privedennye sootnosheniya
pokazyvvayut,
chto kvantovye processy sovershenno nichtozhny dlya Ch.d., voznikshih iz zvezd s massami
- znachenie massy Ch.d. v g. Privedennye sootnosheniya
pokazyvvayut,
chto kvantovye processy sovershenno nichtozhny dlya Ch.d., voznikshih iz zvezd s massami
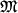 >1034 g. Odnako oni sushestvenny
dlya
malomassivnyh pervichnyh Ch.d., k-rye mogli voznikat' na rannih etapah rasshireniya Vselennoi.
>1034 g. Odnako oni sushestvenny
dlya
malomassivnyh pervichnyh Ch.d., k-rye mogli voznikat' na rannih etapah rasshireniya Vselennoi.
Po mere umen'sheniya massy Ch.d. moshnost' izlucheniya dolzhna rasti, i v konce koncov malen'kaya
Ch.d. porodit moshnuyu vspyshku zhestkogo gamma-izlucheniya (poslednie 109
g Ch.d. izluchaet za 0,1 s, chto podobno vzryvu milliona megatonnyh vodorodnyh bomb).
V real'nyh usloviyah Vselennoi ch.d., k-rye mogli vozniknut' iz zvezd, vse vremya uvelichivayut
svoyu massu za schet padeniya na nih gaza i izlucheniya, v t.ch. i reliktovogo izlucheniya
Vselennoi. Uvelichenie massy Ch.d. pri etom hotya obychno i malo, no sushestvenno prevyshaet
poteri za schet kvantovogo ispareniya.
Ch.d., voznikshie v rezul'tate kollapsa massivnyh zvezd, mogut vyzyvat' svoim sil'nym
gravitac. polem burnye processy pri padenii v nih gaza. Takie gazovye potoki mogut
byt'
osobenno moshnymi, kogda na Ch.d., vhodyashuyu v sostav tesnoi dvoinoi zvezdnoi sistemy,
gaz peretekaet ot zvezdy-giganta. Gaz, nagretyi pri padenii v pole tyagoteniya Ch.d.,
daet
rentg. izluchenie, i po etomu izlucheniyu Ch.d. mozhet byt' obnaruzhena. Veroyatno, odna
ch.d. uzhe obnaruzhena takim sposobom v rentg. istochnike Lebed' H-1 (sm. Rentgenovskaya astronomiya, Akkrecionnye
diski).
Vozmozhno, chto v centre yader galaktik i kvazarov sushestvuyut sverhmassivnye Ch.d., s
massoi do 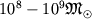 , v pole tyagoteniya k-ryh protekayut
burnye
processy, yavlyayushiesya prichinoi aktivnosti yader galaktik i kvazarov.
, v pole tyagoteniya k-ryh protekayut
burnye
processy, yavlyayushiesya prichinoi aktivnosti yader galaktik i kvazarov.
Lit.:
Zel'dovich Ya.B., Novikov I.D., Teoriya tyagoteniya i evolyuciya zvezd, M., 1971; Mizner
Ch., Torn K., Uiler Dzh., Gravitaciya, t. 3, per. s angl., M., 1977; Frolov V.P., Chernye
dyry
i kvantovye processy v nih, UFN, 1976, t. 118, v. 3, s. 473; Torn K., Poiski chernyh
dyr, per. s angl., tam zhe, s. 453.
(I.D. Novikov)
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(oliya Korobeinikova,
11.12.2010 20:41, 362 Bait, otvetov: 3)
Privet vsem!Pisala ,chto v "chernuyu dyru"sbrasyvayut planety,zvezdy potom dostayut.Chernaya dyra est' vo Vselennoi,galaktikah,v SS i na Zemle.Na Zemle Bermudskii treugol'nik.On
nahoditsya ryadom s Amerikoi,znachit ChD v SS nahoditsya ryadom s Marsom.Stoit li letet' na Mars?Tam nahoditsya Olimp.Na Zemle v treugol'niki ischezayut korabli,samolety.Kogda to poyavyatsya.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(s. a. veprev,
16.12.2010 12:38, 738 Bait)
| Citata: |
| Privet vsem!Pisala ,chto v "chernuyu dyru"sbrasyvayut planety,zvezdy potom
dostayut.Chernaya dyra est' vo Vselennoi,galaktikah,v SS i na Zemle.Na Zemle Bermudskii treugol'nik.On
nahoditsya ryadom s Amerikoi,znachit ChD v SS nahoditsya ryadom s Marsom.Stoit li letet' na Mars?Tam nahoditsya
Olimp.Na Zemle v treugol'niki ischezayut korabli,samolety.Kogda to poyavyatsya. |
Esli na Zemle ona est', togda pochemu nas vseh eshe tuda ne zasosalo? Kogda veshestvo popadaet tuda ot
treniya voznikaet izluchenie, pochemu ono v treugol'nike ne nablyudaetsya?
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(s. a. veprev,
16.12.2010 12:38, 738 Bait)
| Citata: |
| Privet vsem!Pisala ,chto v "chernuyu dyru"sbrasyvayut planety,zvezdy potom
dostayut.Chernaya dyra est' vo Vselennoi,galaktikah,v SS i na Zemle.Na Zemle Bermudskii treugol'nik.On
nahoditsya ryadom s Amerikoi,znachit ChD v SS nahoditsya ryadom s Marsom.Stoit li letet' na Mars?Tam nahoditsya
Olimp.Na Zemle v treugol'niki ischezayut korabli,samolety.Kogda to poyavyatsya. |
Esli na Zemle ona est', togda pochemu nas vseh eshe tuda ne zasosalo? Kogda veshestvo popadaet tuda ot
treniya voznikaet izluchenie, pochemu ono v treugol'nike ne nablyudaetsya?
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Vlad Loginov,
18.12.2010 21:58, 147 Bait)
A prichem tut chernaya dyra i bermudskii treugol'nik? I konechno, korabli i samolety poyavyatsya, kogda ih so dna dostanut. Pohozhe, sil'no mistificiruete.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A. V. Rykov,
12.12.2010 15:34, 3.7 KBait, otvetov: 1)
Radius chernyh dyr opredelyayutsya po formule N'yutona R(N)=sqrt(GM/g(max)) Minimal'naya dyra imeet
massu m(x)=1,859447219e9 kg. Ee radius sovpadaet s razmerom reshetki sredy (8). Privedennaya formula rezko otlichaetsya ot formuly Shvarcshil'da,
naidennaya iz resheniya OTO: R(gr)=2*GM/c^2, chto privodit k znachitel'noi raznice v ocenkah radiusa chernyh dyr. Shvarcshil'dovskii radius Solnca raven 3 km
R = 46 km po teorii struktury sredy), dlya Zemli - 1 sm79 mpo teorii
struktury sredy). Dlya chernyh dyr v centrah galaktik plotnost' po Shvarcshil'du mozhet byt' na urovne plotnosti
vody, po strukture sredy na 5-7 poryadkov bol'she. Sreda ravna strukture vakuuma.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(V. V. Komogorov,
13.12.2010 20:38, 956 Bait)
Dovol'no stranno, pochemu ponyatnoe triedinstvo, sushestvovaniya energii (Ek - Ep - Rab), vosprinimaetsya nami
zakonomernost'yu i vpolne ponyatnoi. A vot triedinstvo sushestvovaniya elektrichestva, kak tok - napryazhenie -
inuktivnost' (I - U - L), ne mozhem dazhe pomyslit'. V etom mire vse troistvenno, kak i nashe poyavlenie na svet: ot
zhelaniya otca i materi zemnyh, po soizvoleniyu sredy (odnih zhelanii mozhet byt' malo). Deistviya porozhdennye odnim
zhelaniem privodyat k myslyam o "chernyh dyrah i temnyh energiyah". Vsya beda v tom, chto my zakony vidimogo mira
primenyaem k miru "bezvidnomu". "Chernaya dyra" - nahoditsya v nauchnom mire, a ne v ideal'no sozdennom dlya cheloveka
mirozdanii, imya kotoromu - Tverd' Nebesnaya. Hvatit fantazii. Bednyi Kopernik dazhe ne znal o dopisannoi neradivym
uchenikom glavy s matematicheskoi model'yu "vokrug Solnca". On byl uzhe paralizovan i, uedinivshis' prekratil vsyakoe obshenie
s vneshnim mirom.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(G. V. Fiveiskii,
23.12.2010 15:19, 270 Bait)
Kazhdaya chernaya dyra imeet svoyu zvezdu i oni svyazany nekim tonnelem.Zabiraya iz prostranstva vse,chto popadaetsya v pole tyagoteniya, chernaya dyra postavlyaetzvezde goryuchee.Esli goryuchee
plohoe ili ego malo,to zvezda gasnet,esli goryuchee slishkom aktivnoe,zvezda mozhet vzorvat'sya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
25.12.2010 1:36, 635 Bait)
tovarish Novikov
pishet,chto pri
priblizhenii k
chernoi dyre
kosmonavtov
razorvet iz-za
prilivnyh
sil,raznosti
uskorenii.Pochemu
vse zabyvayut o
relyativistskom
sokrashenii
razmerov?Ved' pri
vlete v chernuyu
dyry vsya
vletayushaya v nee
materiya
szhimaetsya,umen'shaetsya
v razmerah.Potomu
raznost' uskorenii
v umen'shemsya tele
kosmonavta budet
nebol'shoi.I szhatiya
on takzhe ne
oshutit.Na moem
saite http://
genzubkov.narod.ru/
takzhe est' stat'ya
pro chernye dyry.
Pravda moi
vzglyady s nedavnih
por
izmenilis':schitayu
uzhe ,chto svet ne
podverzhen
inercii,gravitacii,ibo
ne imeet massy
pokoya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.12.2010 15:31, 756 Bait, otvetov: 1)
G.A.Zubkov
"Pochemu
vse zabyvayut o
relyativistskom
sokrashenii
razmerov?"
Mne priyatno vstretit' tolkovogo relyativista,
kotoryi v prakticheskom primenenii pol'zuetsya
relyativiskimi sokrasheniyami v bytu.
U menya vopros, - kosmonavt v kosmicheskom korable
derzhit v rukah futbol'nyi myach, korabl' razgonyaetsya
do dvukratnogo sokrasheniya dlinny, posle chego
kosmonavt
s myachom v rukah povorachivaetsya na 90
gradusov otnositel'no napravleniya dvizheniya,
so splyushennym myachom v rukah, posle chego korabl'
nachinaet tormozhenie, u kosmonavta
v rukah
v itoge okazalsya splyushennyi myach dlya regbi,
- vopros kakoi vneshnii vid kosmonavta?
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(A. V. Postnikov,
5.03.2016 14:41, 953 Bait)
| Citata: |
G.A.Zubkov
"Pochemu
vse zabyvayut o
relyativistskom
sokrashenii
razmerov?"
Mne priyatno vstretit' tolkovogo relyativista,
kotoryi v prakticheskom primenenii pol'zuetsya
relyativiskimi sokrasheniyami v bytu.
U menya vopros, - kosmonavt v kosmicheskom korable
derzhit v rukah futbol'nyi myach, korabl' razgonyaetsya
do dvukratnogo sokrasheniya dlinny, posle chego
kosmonavt
s myachom v rukah povorachivaetsya na 90
gradusov otnositel'no napravleniya dvizheniya,
so splyushennym myachom v rukah, posle chego korabl'
nachinaet tormozhenie, u kosmonavta
v rukah
v itoge okazalsya splyushennyi myach dlya regbi,
- vopros kakoi vneshnii vid kosmonavta?
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.12.2010 15:43, 318 Bait)
Estestvenno vopros voznikaet o edinicah izmereniya,
svyazannyh s sokrasheniyami ot skorosti.
Tak-zhe voznikaet vopros - a skoro postupyat v prodazhu
instrukcii i
rekomendacii po poletam na relyativiskih
skorostyah s cel'yu provedeniya relyativiskih
sokrashenii i rastyazhenii vmesto plasticheskoi hirurgii?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
26.12.2010 21:48, 1.5 KBait)
Chem blizhe k
centru
gravitacii,tem
tesnee shodyatsya v
tochku silovye
linii
gravitacionnogo
polya.Tak chto myach
budet plyushit' ne
tol'ko vdol',no i
poperek-potomu on
ostanetsya
kruglym.Voobshe
kogda na telo
nichego krome
gravitacii ne
deistvuet,to ono
nahoditsya v
nevesomosti,i net
nikakih
peregruzok.Mozhno
svyazat' sistemu
otscheta s
kosmonavtom-on v
nei nepodvizhen,a
chernaya dyra na
nego
nadvigaetsya.Chem
ona blizhe,tem ona
bol'she,shire,razrezhennee:vozle
i vnutri dyry
prostranstvo
sil'no szhato,tak
chto tam mozhet
pomestit'sya celaya
vselennaya(v
principe tam i
nahoditsya celaya
polovina nashei
vselennoi v
umen'shennom vide-
ta,v kotoruyu
letim). Ne myach,a
vsya kruglaya Chernaya
dyra stanet
splyusnutoi,ploskoi
i tonko-
efemernoi,kak
blin. Blagodarya
relyativistskoi
skorosti
sblizheniya vremya
vnutri rakety
techet
medlennee,chem
snaruzhi.Potomu
kosmonavt ''i
glazom morgnut'
ne uspeet'',kak
prolet skvoz'
tonnel' Chernoi
budet zavershen.
Chernaya dyra tem i
otlichaetsya ot
obychnoi ili
neitronnoi
zvezdy,chto te
prihoditsya
obletat', ogibat',a
skvoz' Chernuyu
DYRU mozhno
napryamik
skorotat' put' i
vremya. Naschet
radiusa
Shvarcshil'da est'
eshe takaya
gipoteza,chto on
dolzhen byt' v
chetyre raza
men'she,chtoby
raketa i dyra
uspeli uskorit'sya
do skorosti 2s -
eto otnositel'naya
skorost'
sblizheniya
fotonov.Tak chto
schitat' ne po
formule
R=2GM/(c^2),a tak:
R=GM/(2c^2)
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.12.2010 18:56, 1.5 KBait, otvetov: 1)
G.A.Zubkov
Ya smotryu Vy ne sovsem polnost'yu predstavlyaete
kartinu vliyaniya i vozdeistviya na nekotoroe telo,
v ramkah
zayavlennyh svoistv Chernoi dyry.
V pervuyu ochered' telo pod vliyaniem chernoi dyry,
nahoditsya pod postoyannym i uvelichivayushimsya uskoreniem.
Vtoroe -
chernaya dyra imeet zayavlennuyu bol'shuyu massu, i
ona ne mozhet v prostranstve dvigat'sya - ona - yakor'.
Tret'e - prostranstvo szhimat'sya i razzhimat'sya ne mozhet,
mogut izmenyat' svoi razmery ne kachestvennye izmeritel'nye
instrumenty, na osnovanii chego delaetsya vyvod o szhatii ili
razzhatii prostranstva.
V svyazi
s tem chto uskorenie postoyanno uvelichivaetsya,
to chem dlinnee probnoe telo, to ego chast' nahodyashaya blizhe
k chernoi dyre - prityagivaetsya sil'nee, i telo udlinyaetsya,
tak kak uvelichivayushayasya gravitaciya, pri priblizhenii k dyre,
vyzyvaet v dlinnom probnom tele rastyazhenie na razryv,
i uzh nikak probnoe telo ne nahoditsya v pokoe,
tak kak padenie
v chernuyu dyru - eto ne dvizhenie na orbite, i ne svobodnoe
padenie - eto prinuditel'noe padenie s postoyanno vozrastayushim
uskoreniem.
Chernaya dyra - ne yavlyaetsya tonnelem, po prichine togo chto
u nee est' massa, i lyuboi relyativist ochen' bystro i
doblestno razob'etsya v lepeshku o ee poverhnost',
tak kak ee razmer i radius
Vam izvesten, - fil'truite mysl', i inogda slegka popytaites'
obosnovat' - pered tem kak chto-to utverzhdat'.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
28.12.2010 21:38, 2.1 KBait)
Oi,ne smeshite
menya: chem eto
svobodnoe padenie
otlichaetsya ot
prinuditel'nogo?
Esli obrezat' tros
lifta(ili
vyklyuchit'
dvigatel'
samoleta),to my
budem padat'
vmeste s nim s
odnoi i toi zhe
skorost'yu,takim zhe
uskoreniem
svobodnogo
padeniya.Potomu
otnositel'no
lifta ili
samoleta my
budem v
nevesomosti.Eto
esli padat' v
vakuume
konechno.Vot esli
by my napravili
samolet vniz na
maksimal'noi
tyage,eto bylo by
prinuditel'noe
padenie,i my
prilipli by ''k
potolku''. Po
Einshteinu:
gravitaciya
real'no iskrivlyaet
prostranstvo,a ne
tol'ko
pribory.Uskorenie
izmeryaetsya v m/
s^2, a
sekundy,vremya v
relyativistskih
ob'ektah tekut po
drugomu.Pri
padenii na Zemlyu
uskorenie tozhe
rastet.I nikogo
eshe im ne
''porvalo'' i ne
rastyanulo hot' na
mikron.V fotone
skorost' s , vremya
nulevoe,zamorozhennoe,potomu
ni foton,ni chto-
libo dvizhusheesya
so skorost'yu
sveta,razrushit'
nel'zya-nikakim
uskoreniem ili
stolknoveniem.Zakon
sohraneniya
energii. Voz'mem
naprimer
annigilyaciyu:elektron
i pozitron
razgonyayutsya
vstrechno svoimi
polyami do
skorosti sveta i
prevrashayutsya v
dva celehon'kih
fotona po
511kEv.Bez vsyakih
oskolkov,chto bylo
by pri tverdom
stolknovenii. Vse
tela,i mozhet dazhe
chasticy sostoyat iz
elektronov i
pozitronov.Tak chto
tela mogut
naprimer
annigilirovat'
(pereiti v
volnovoe
sostoyanie) pri
podlete k chernoi
dyre,i
sobirat'sya,sintezirovat'sya
zanovo na drugom
konce dyry. Tak zhe
kak sinteziruyutsya
elektron i
pozitron pri
prolete fotona
1Mev skvoz' yadro
atoma. Ne vsegda
mozhno ponyat':my
dvigaemsya
navstrechu
ob'ektu,ili on k
nam dvigaetsya.Vot
ya i dopustil,chto
kosmonavt stoit na
meste,a dyra k
nemu
prityagivaetsya.Ne
vazhen istochnik
sily.Vazhna obshaya
otnositel'naya
skorost'. Hotya po
teorii
otnositel'nosti
vyhodit,chto esli
chasticu razognat'
do skorosti
sveta,to ee massa
stanet
beskonechnoi.I
togda chastica
smozhet celuyu
galaktiku k sebe
prityanut'.Absurd.Tak
chto skoree vsego
relyativistskie
chasticy naoborot
teryayut massu do
nulya,a ne tyazheleyut.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.12.2010 0:24, 1019 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Vy kak i vse astro fiziki, pishete o fizicheskih
svoistvah chego libo v stile -
"Tak spimpzdel chto azh sam poveril".
I Vy prosto ne ponimaete gde Vy
vrete gde drugie
privrali da i ne ponimaete sam predmet o kotorom
rassuzhdaete.
Vy kak labuh pripletaete Einshteina k chernym dyram.
Vy ya dumayu dazhe
ne znaete napisannoe na etom saite
odnoznachnoe opredelenie chernoi dyry - ot avtora.
A prochitali navernoe okolonauchnoi omosyatiny
na populyarnoi mehanike o chernyh
dyrah.
Oni tam i izluchayut i u nih vybrosy, i mnogo prochih svoistv.
Prichem iskrivlenie prostranstva ot Einshteina, k chernym dyram?
Chernye dyry pridumal
- odin avtor.
Kriviznu prostranstva pridumal - drugoi avtor.
Razmer chernoi dyry - pridumal tretii.
Kakoe otnoshenie imeet k chernoi dyre - annigilyaciya?
"Tak zhe kak sinteziruyutsya elektron i pozitron pri
prolete fotona 1Mev skvoz' yadro atoma."
---- eto gde Vy takuyu omosyatinu fizicheskuyu prochitali?,
v kakoi knizhke.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
30.12.2010 9:34, 744 Bait)
Nepriyatno
obshat'sya s takimi
priblatnennymi
negativistami,kak
vy. Net,chtob chto-to
svoe,konstruktivnoe
dobavit',zanimaetes'
odnim
kritikanstvom. Vash
uroven' znanii po
nekotorym
voprosam yavno
nizhe dazhe moego,a
vy naezzhaete na
menya, kak budto vy-
znatneishii
professor.
Nevazhno,kto
avtor.Vsyu teoriyu
Chernyh dyr mozhno
samomu vyvesti iz
formuly
gravitacii F=GmM/
r^2 . Ya bol'she sam
dumayu,chem izuchayu
chuzhie trudy.Pro
process,obratnyi
annigilyacii,napisano
naprimer v
''Elementarnom
uchebnike fiziki''
tom 3 s.553
G.S.Landsberga:
''obrazovanie pary
elektron-pozitron
proishodit v
rezul'tate
vzaimodeistviya
gamma-kvanta s
elektricheskim
polem odnogo iz
atomnyh yader
veshestva.''
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.12.2010 17:53, 1.8 KBait)
Ya Vam kul'turno vse vremya namekayu chto Vy v
svoih razmyshleniyah to v oblakah letaete,
to otbivaetes' ot obsheprinyatyh utverzhdenii,
to nesete v rukah bred sivoi
kobyly.
Esli Vam eto nravitsya - to eto lichno Vash vybor,
mogu Vas obradovat', chto takih mechtatelei niochem,
kak Vy - delayushih pri etom naukoemkii vid
i vyrabatyvaya
mysli pritenduyushem na aplodismenty, - tak takih
sredi astro-fizikov prakticheski absolyutnoe bol'shinstvo.
A to chto napisano naprimer na etom
saite o chernoi dyre,
Vy ya tak ponimayu vzyat' za standart ne hotite, i pri etom
otbrosit' vse vydumki. Opredelenie dostatochno prostoe,
- gravitaciya takaya chto
dazhe fotony ne mogut pokinut' -
zdes' nado togda priznat' vrunami vseh kto utverzhdaet
chto dyry izluchayut, - kak po mne - nado tak nado,
a Vam vybirat' .
U chernoi dyry est' radius sledovatel'no est' poverhnost',
i v etom sluchai s moei tochki zreniya, - vruny te kto utverzhdaet
chto skvoz' dyru est' tonnel',
- a Vam vybirat'.
Ya Vam vkratce pytayus' ob'yasnit' chto v fizike esli
avtor predostavlyaet chitatelyu pravo vybora - to eto
uzhe govorit o tom chto eto vran'e
ili neobosnovannaya
vydumka iznachal'no, i mne smeshno i zhal' Vas po
bessmyslenno potrachennomu Vami vremeni v razmyshleniyah
nad chernymi dyrami, esli by vy vnikli
v bazovye
avtorskie postanovki zadach i ob'yasnenii Vy by srazu
ponyali chto eto prostaya galimat'ya, ne imeyushaya nikakogo
otnosheniya k nablyudaemym ob'ektam.
Ya
Vam po druzheski skazhu pochemu na tekushii moment
nikto ne obnaruzhil chernoi dyry, a slyshny lish' utverzhdeniya
chto ona vot tam dolzhna byt', - potomu chto astro-fiziki
i sami ne znayut kak ona dolzhna vyglyadet', -
ya dumayu Vy dogadyvaetes', pochemu astronomiyu v shkolah
otmenili.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.12.2010 18:13, 507 Bait)
V astronomii krizis ochen' bol'shoi - iz za togo chto neudobno
uchenikam prerekat'sya s prepodavatelem, i v lico emu skazat'
ne mogut - mol hvatit nam bred sivoi kobyly
v mozg zalivat'.
A so vremenem ucheniki na zalitom v mosk brede i uverennosti
v otsutstvii kritiki - pishut takuyu galimat'yu, chto ushi
u odnih zavorachivayutsya,
a molodye vosprinimayut za "chistuyu monetu",
i vse idet po krugu - tak nazyvaemyi -
"avtoritarnyi krugovorot breda sivoi kobyly v astronomii".
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.12.2010 18:29, 397 Bait)
Prochitaite 16 otvet, i drugie otvety Samouchki
mozhet poimete drugie situacii, no kak pravilo srednemu
cheloveku dano ponyat' odnu teoriyu po teme, vtoroi teoriei
s drugimi ideyami ego obuchat' net smysla,
ibo nepoimets.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.12.2010 22:23, 911 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Vy vot dazhe ne znaete chto lichno Vy vot
yavlyaetes' fizikom-teoretikom.
Eto prosto fantasticheskaya anekdoticheskaya istoriya.
Bylo eto davnym davno -
zahodit sekretar'
ck kpss, v laboratoriyu i sprashivaet u svoego
pomoshnika - a na kakom meste nasha strana po
kolichestvu fizikov?
Ne na pervom, - otvechaet
pomoshnik.
Chtoby finansirovat' fizika nado mnogo deneg na
oborudovanie.
sekretar': -A eshe kakie-to varianty est'?
pomoshnik: -Da est' mozhno
pri nebol'shom finansirovanii
vyiti na pervoe mesto v mire esli finansirovat',
fiziko - matematicheskoe napravlenie ili teoreticheskuyu fiziku,
iz vseh priborov
i oborudovaniya im dostatochno pis'mennogo
stola karandasha i rezinki.
sekretar': - Da?
pomoshnik: - net, nu esli chetno to stiratel'naya rezinka
teoretiku ne nuzhna, dostatochno stola i karandasha,
- otovretsya esli oshibetsya.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
31.12.2010 18:32, 1.9 KBait)
Sfera,radius
chernoi dyry-
ponyatie
uslovnoe.Oni mogut
byt' dazhe
nulevymi-togda
Chernaya dyra stanet
Chernoi
tochkoi.Lyuboe telo
mozhno
rassmatrivat' kak
goloe silovoe
(gravitacionnoe
ili drugoe)
pole,uslovno
schitat' ego
razmery
nulevymi,chtoby te
padat' ne meshali :-
D,uskoryat'sya do
skorosti sveta. Do
skorosti sveta
takzhe razgonyayutsya
(esli verit' teorii
BV) vse galaktiki v
13 mlrd.svetovyh
let ot nas,tak chto
my okruzheny nekoi
skorlupoi-sferoi
Shvarcshil'da
navyvorot.A chto za
nei?
Sverhsvetovye
skorosti ili opyat'
zhe tunnel'nye
pereskoki,kak v
Chernoi dyre? Vot
naprimer,my
razgonemsya za god
do skorosti
sveta,esli nashe
uskorenie budet
ravno zemnomu -
10 m/s^2. Zametim
li my moment
sverhsveta?Vryad
li. Ved' tol'ko
otnositel'no
''pokoyashihsya'' zvezd
i mesta starta my
budem dvigat'sya so
skorost'yu sveta, a
otnositel'no
drugih zvezd
skorost' budet
raznoi. I dlya
pokoyashihsya zvezd
my budem videt'sya
i yavlyat'sya
fotonami
(nichto,krome
fotonov,ne
dvizhetsya so
skorost'yu sveta),a
dlya
drugih-raketoi.
Shmyaknemsya my ob
svetovoi bar'er?
Net.Znachit i ob
sferu
Shvarcshil'da ne
shmyaknemsya. Ved'
po effektu
Dopplera nasha
chastota,i chastota
dyry budut
beskonechnymi.A
gamma-luchi skvoz'
chto ugodno
proidut. Nevazhno
kak ono v
real'nosti.Glavnoe
predvidet'
vozmozhnye
varianty,avos' ch'ya-
nibud'
model',ideya
vyvedet kogo-
nibud' k novym
otkrytiyam.Ved'
takaya toska
beret,kogda vse
uchenye,vse
telekanaly podayut
tol'ko odin
variant kakogo-
nibud' yavleniya-
Razbeganie
galaktik,Chernaya
dyra i t.p. Pochital
ya otvety tovarisha
Samouchki.Chtoby ne
byt'
posmeshishem,emu
stoilo by pereiti
na novuyu
terminologiyu.Efir
zamenit'
neitrino,gravitonami,chasticami
s otricatel'noi
massoi,mikro-
chernymi dyrami i
t.p. Efirnaya
zvezda-eto po-
sovremennomu
Belaya dyra,-
ta,kotoraya vse
ottalkivaet,otrazhaet.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
31.12.2010 18:00, 571 Bait)
Da chut' ne zabyl chto Vy prosili vyskazat' chto-to konstruktivnoe,
- da v nauke byli podobnye vremena kogda nauka v raznyh oblastyah
ne opravdyvala vlozhennyh deneg,
i stanovilas' neponyatnaya dlya prostyh
lyudei, i ob'yasneniya uchennyh prostym lyudyam kazalis' bredovymi
- prakticheski analogichnaya situaciya v fizike i astronomii.
Tak vot, lechilos' eto tem chto na 50-100 let rekomendovalos' polnost'yu
prekrashat' finansirovanie dannyh napravlenii v nauke.
Posle chego finansirovanie vozobnovlyaetsya.
Pozdravlyayu vseh s nastupayushim Novym Godom!
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
31.12.2010 19:31, 2.2 KBait)
"(esli verit' teorii
BV)"
o - Vy delaete uspehi.
Ya etu teoriyu schitayu lozhnoi na 100%.
Chernye dyry vran'e 100% s moei tochki zreniya.
Teorii Einshteina neobosnovannaya
vydumka na 100%, - s
moei tochki zreniya.
Vy prosto ne ponimaete chto lyubaya teoriya po bol'shomu schetu vydumka.
Tam gde ne ob'yasnyaetsya teoriyami tekushie
voprosy no delayutsya predskazaniya -
tam Vas uzhe obmanuli.
"Glavnoe
predvidet'
vozmozhnye
varianty,avos' ch'ya-
nibud'
model',
ideya
vyvedet kogo-
nibud' k novym
otkrytiyam"
Zdes' Vy zabluzhdaetes' - v podtverzhdenie tomu sto let
relyativiskogo shestviya v nikuda, i milliardy lyudei na difektivnyh
teoriyah nikogda
i nizachto tratya lyubye den'gi, nichego ne dob'yutsya poleznogo.
Predvidet' kak raz nichego ne nuzhno, nado prosto ob'yasnit' prosto i ponyatno
to chto nablyudaetsya
seichas.
"Chtoby ne
byt'
posmeshishem,emu
stoilo by pereiti
na novuyu
terminologiyu.Efir
zamenit'
neitrino,gravitonami,chasticami
s otricatel'noi
massoi,mikro-
chernymi dyrami i
t.p"
Rasskazhu ya Vam odnu istoriyu, - davnym davno vse pol'zovalis' v fizike efirom,
v 1800 T.Yung, dobilsya vydayushihsya uspehov i na opytah obosnoval svetovoe
izluchenie
i interferenciyu kak kolebaniya sredy kotorye pri vozdeistvii sozdayut v atomarnoi strukture
svetovoe izluchenie, takzhe dlya izmereniya kolichestva kolebanii
dlya sred byl priduman
Doplerom - effekt Doplera - i obosnovan - dlya sred.
Posle chego Enshtein v molodosti - zayavlyaet chto v prostranstve pustota, i ne oprovergaet
ni Yunga ni Doplera, a prosto postuliruet .
Vot sobstvenno s etogo momenta vsya fizika poshla pod otkos, a astronomiya
poshla pod otkos s uskoreniem, - vot
takaya zhestokaya selyavi.
Tak chto efir po faktu - ostalsya, po prichine otsutstviya vnyatnyh oproverzhenii,
kotorye po ob'yasnitel'nym vozmozhnostyam prevoshodyat ob'yasneniya
Yunga i Doplera,
a raz takovyh za sto let relyativisty ne smogli obosnovat' to efir luchshe pustoty v prostranstve.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.01.2011 16:22, 1.0 KBait)
Vot yarkii primer kogda moderatory davyat avtoritetom i zamolachivayut
forum svoimi vstryavaniyami ne po teme.
Na fiz voprosah, obsuzhdayut ustroistvo kompyutera
i ego mat obespechenie
pri proektirovanii.
Mne zhal' Dmitriya Vibe .
Special'no perenes ego vyskazyvanie chtoby on ne ster,
on ochen' polyublyaet
poskandalit', a potom steret' gde on
vyglyadel ploho, i gde zateval skandal.
"Vy polagaete, chto komp'yuter sozdavalsya bez matematicheskoi modeli nablyudaemyh
yavlenii?"
, sovsem intellektual'no sdal, kazhdyi ego naezd
yarko vidno ego nameren'ya, vstryaet s voprosami ne po teme i provociruet skandaly
svoei
tupiznoi i neponimaniem, a vtoroi moderator, vstryaet s ochen' strogim
podhodom i horoshim ponimaniem togo chto otvety dolzhny byt' strogo
po nazvaniyu foruma, vot i
poluchaetsya odin moderator tupit na ego provokacionnye
voprosy esli otvetit' to vtoroi moderator zabanit tak kak razgovor ne po teme.
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,79788.720.html
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.01.2011 17:59, 1.2 KBait)
""Vy polagaete, chto komp'yuter sozdavalsya bez matematicheskoi modeli nablyudaemyh
yavlenii?"
Kstati vopros ne pravil'no postavlen, chto
sobstvenno govorit o tom chto zadavshii etot vopros prosto diletant
v oblasti osnov komp'yutera.
Ya bolee chem uveren chto nikto iz zdes'
prisutstvuyushih ne znaet otveta na etot vopros.
A dlya menya etot vopros proshe legkogo.
Tak vot - za osnovu
pri konstruirovanii komp'yutera, bylo
vzyato nekotoroe logicheskoe utverzhdenie, chto naprimer est' nekotoroe
arifmeticheskoe - logicheskoe ustroistvo, kotoroe mozhet
odnovremenno vypolnyat' komandu,
ustanavlivat' adresnye dannye, i po ustanovlennomu adresu mozhet proizvodit'
zapis' ili chtenie dannyh, (prinimat' ili peredavat'
dannye po
ukazannomu adresu, pri etom vypolnyaet komandu).
I nachinaet svoyu rabotu s ustanovki nulei po adresu i po etomu adresu delaet chtenie dannyh
i vypolnyaet
komandu zapisannuyu v nulevom adrese.
Kak pravilo kachestve istochnika zadanii (programm) ispol'zuetsya v mladshem adresnom prostranstve
postoyannaya pamyat' (tol'ko
chtenie) , v kotoroi i zapisana programma, v starshih adresah ispol'zuetsya
operativnaya pamyat' (zapis' i chtenie).
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.01.2011 20:23, 1.4 KBait, otvetov: 1)
VibeVy polagaete, chto komp'yuter sozdavalsya bez matematicheskoi
modeli nablyudaemyh yavlenii?
EVVNet. Ya tak ne polagayu.
VibeTo
est', Vy priznaete, chto dlya publikacii teksta o fantaziinosti
sovremennoi fiziki Vy ispol'zuete odnu (dazhe i ne odnu) iz ee fantazii?
V moe vremya teh kto zadaet voprosy , i pereviraet slova i otvechaet za ooponenta i potom
za svoi otvet za opponenta
uprekaet - takih nazyvali gnidami i chmoshnikami.
Vibe - sovsem oborzel moderatorom.
Vot esli tam na forume pravdu skazat'
moderatoru, to Vas zabanyat,
Vy podobnogo nikogda ne delaite, oni provokatory i dlya nih zabanit' kogo
tak eto im v radost'.
Ya rad - hot' vse vidyat metody
etogo chmoshnika.
A eto kak on sam na svoi vopros o kompyutere otvetil, ya zhe tochno govoril,
chto etot chmoshnik ne mog znat' bazovyh osnov kompyutero stroeniya,
a
vopros zadaet.
"Cirk. Ya ne ispol'zuyu. Ya tol'ko na knopochki zhmu. I tot, kto sozdal
komp'yuter,
tozhe ne ispol'zoval. On uchil chto-to gde-to kogda-to."
Ponimanie Vibe - o komp'yutere, yavno detskii lepet.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
1.01.2011 21:21, 886 Bait)
Vas voobshe nauka
interesuet?
Zanimaetes'
melkimi
dryazgami,vyyasneniem
otnoshenii.
Zabud'te ob
emociyah,lichnom i
vmeste so vsemi
ishite otvety na
eshe ne
razreshennye
chelovechestvom
voprosy.Na
astronomy.ru
voobshe-to eshe
dazhe terpimo,a vot
na dxdy.ru
moderaciya tochno
zhestochaishaya i ne
vsegda
ob'ektivnaya.I
davaite ne
uklonyat'sya ot
temy. Teoriya
Einshteina vse-
taki
podtverzhdaetsya
eksperimentami :
chem blizhe
skorost' chasticy k
skorosti sveta,tem
trudnee ee
uskorit' .Spornymi
mogut byt' lish'
detali:koefficienty,relyativizm
massy;prityazhenie,davlenie
sveta i t.d. Ya
nedavno po tv
Diskaveri videl
peredachu Wormhole
- Skvoz'
chervotochinu
,tak tam astronomy
celoe video
sklepali iz
fotografii
centra Mlechnogo
puti,kak tam
zvezdy vokrug
nevidimoi chernoi
dyry obrashayutsya.
Po raschetam tak u
nih vyhodit.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.01.2011 22:18, 1.3 KBait)
Vy uzh izvinite no v relyativiskom ... ya kovyryatsya ne sobirayus',
ibo cenyu svoe vremya, i uvazhayu zdravyi smysl.
Tak chto voprosy na relyativiskie temy ne vosprinimayu.
Rekomenduyu prochest' polnost'yu, tam est' vse otvety
na tipichnye voprosy.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/forums/1244628?page=1
Esli strogo
razbirat'sya s chernymi dyrami, - to zdes'
ya schitayu chto Zvezda Efira bolee podhodit na etu rol'.
Delo v tom chto ona reshaet ryad voprosov kotorye ne mozhet reshit'
chernaya dyra.
Ya davno govoril, eshe do pervyh teleskopov kotorye mogut obnaruzhivat'
holodnye uchastki , chto est' ochen' mnogo zvezd efira s temperaturoi nizhe
160gradusov
Cel'siya.
http://znaniya-sila.narod.ru/
Na etoi stranice napisano chto daveche obnaruzhili i takih ob'ektov
s temperaturoi vsego lish' na 10 gradusov
bol'she absolyutnogo nulya,
tol'ko v nashei galaktike bol'she milliona.
I eshe do togo kak obnaruzhili hvosty u dvizhushihsya v prostranstve zvezd,
- Reaktivnye
Zvezdy Fizikov, ya govoril chto u vseh zvezd kotorye dvizhutsya
ne v rukavah a sami po sebe s bol'shoi skorost'yu, to u nih budet reaktivnyi
vybros, i budet ostavat'sya
sled iz pyli.
Tak chto u menya tochnye znaniya i dostovernye v oblasti astronomii.
I vse prosto i vse shoditsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.01.2011 13:26, 189 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Vot eshe nashel "Predpolozhenie o zvezdah",
rekomenduyu prochest' prosto dlya obshego razvitiya.
http://forum.membrana.ru/forum/alternative.html?parent=1053369627#1053369627
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
3.01.2011 0:08, 708 Bait)
Po poslednei
ssylke prochital
takoe:chernaya dyra
pogloshaet
veshestvo i
izluchaet v
prostranstvo
efir.V drugom
meste tam zhe
napisano:vozmozhnno
efir mozhet
prevrashat'sya v
veshestvo.
Vot i vyhodit
togda v summe
takoe:veshestvo
padaet v chernuyu
dyru,potom
prevrashaetsya v
efir,a potom
materializuetsya-
opyat'
prevrashaetsya v
veshestvo. Tol'ko
vmesto efira
mozhno napisat' i
fotony,i
neitrino,i t.p.
Tol'ko po ssylke
vyhodit,chto chernaya
dyra
otfutbolivaet
chasticu
tuda,otkuda ta
prishla(belaya dyra
tak i delaet),a po
moemu mneniyu
chernaya dyra
teleportiruet
chasticu skvoz'
sebya dal'she-v tom
zhe
napravlenii,kuda
chastica dvigalas'
(padala)ran'she.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.01.2011 10:48, 2.8 KBait)
Ya ne ponimayu pochemu Vy vse vremya pytaetes'
naiti chto ugodno vmesto efira.
Ya ponimayu chto relyativisty otvergli efir
bolee sta let nazad, i teper' efir nado
vernut' na svoe
mesto, i chestno priznat'sya chto otkaz ot efira byl oshibkoi.
I sto let shestviya relyativizma byli bessmyslenny.
No eto bylo vidno srazu tak kak
otsutstvovala metodika
izmerenii i izmeritel'nye pribory na zayavlennye
relyativistami fizicheskie svoistva.
Chernaya dyra izluchayushaya efir v prostranstvo
- nazyvaetsya Zvezda efira.
Ispol'zovanie terminologii chernaya dyra, prosto
dlya obsheniya, i dalee ne primenima, tak kak
chernuyu dyru nichto ne mozhet
pokinut',
i v zayavlennyh svoistvah prostranstvo vokrug chernoi dyry
pustoe i ona vse vsasyvaet, zvezda efira naoborot - sozdaet
bol'shuyu plotnost' efira vokrug
sebya, i vse ottalkivaet.
Pogloshaet veshestvo zvezda efira kotoroe bol'she
poteri massy pri izluchenii efira v prostranstvo ,
nahodyas' vnutri zvezdy Fiziki,
ili vnutri cyfeidy.
Ya tak ponimayu chto Vy ne v kurse
togo chto al'fa beta i gamma, eto ne kolebaniya sredy,
eto chasticy - tak vot massa zvezdy efira uvelichivaetsya
za schet etih chastic.
Radio volny i do fotonov- eto kolebaniya sredy analogichnye
zvuku, a al'fa beta i gamma eto chasticy,
- delo v tom chto svetovoe
izluchenie kolebanie
sredy opredelyaemoe prosto po otrazheniyu
ot zerkala, ono otrazhaetsya pod uglom padeniya, - znachit
kolebaniya sredy, a al'fa beta i gamma,
pri stolknovenii
s zerkalom razletayutsya kuda ugodno, i chast' proletaet
skvoz' zerkalo.
Toist' - fotony eto ne chasticy.
Ochen' rekomenduyu pochitat'
Vam raboty T.Yunga.
"chernaya dyra teleportiruet chasticu skvoz' sebya
dal'she-v tom zhe napravlenii,kuda chastica
dvigalas' (padala)ran'she"
- eto Vashe svyashennoe pravo tak schitat',
tol'ko Vam ostalos' vypolnit' svyashennyi dolg fizika
- obosnovat' svoe utverzhdenie
i privesti prakticheskie
primery, - a inache
postulat bez prichiny - priznak durachiny.
Rekomenduyu sperva opredelitsya s -
prostranstvom i ego svoistvami,
so svoistvami chernoi
dyry, - i Vy dolzhny
pridumat' ei drugoe nazvanie tak kak ona
otlichaetsya ot zayavlennyh avtorom ChD svoistv,
tak-zhe vopros kakie chasticy,
mogut li byt'
ob'ekty i kakih razmerov,
mozhet li upast' v dyru portacii - zvezda,
planeta ili drugaya dyra portacii.
Kak vyglyadit dyra portacii v teleskop?
I kak
svyazanno eto s tem chto nasmotrelis' po
televizoru fantastiki, ili svyazanno s estestvennymi
chelovecheskimi chuvstvami i zhelaniyami halyavy, i
svyazannogo s etim
zhelaniem peremeshat'sya bystro
i besplatno, v svyazi s chem mozhno stroit' kollaider
novyi dlya poiska dyry teleportacii. S pomosh'yu kotoryh
mozhno budet peremeshat'sya
na halyavu po vsei planete.
Aferoi popahivaet.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.01.2011 11:52, 1.9 KBait, otvetov: 1)
Vy vot slishkom uzko smotrite na chernuyu dyru,
i ne mozhete obozret' myslenno vsei gluposti v
tekushei astronomii.
Iznachal'no chernaya dyra byla pridumana
dlya
utilizacii izbytochnogo izlucheniya zvezd.
Do etogo sdelali pervyi radio teleskop, na shum etogo
teleskopa sbezhalas' staya zhazhdushih halyavnoi slavy,
i bylo pridumano eho bol'shogo vzryva, da i
sam bol'shoi vzryv priduman nemnogim ran'she.
I relyativizm svyazyvali s atomnym oruzhiem.
Hotya konstrukciya atomnoi
bomby byla opublikovana v 1942
godu v ne sekretnom zhurnale. I relyativisty k etoi publikacii
ne imeli nikakogo otnosheniya.
Bol'shoi vzryv podtverzhdalsya
shumom v radioteleskope.
A to kuda devaetsya energiya ot zvezd, tak i ne poluchalos',
dlya etogo pridumali chernye dyry, a tak kak krugom pustota
to dyra dolzhna
prityagivat' i material'nye ob'ekty,
- vot zdes' bez efira vsya astrofizika proletela namnogo
sil'nee chem bez chernoi dyry.
Potomu chto poluchalos' chto vse tol'ko
prityagivaetsya, zvezdy
prityagivayut zvezdy i chernye dyry i planety, a chernye dyry
prityagivayut chernye dyry zvezdy i planety, - toist' poluchaetsya
chto vo vselennoi
vse tol'ko prityagivaetsya, a esli vse
prityagivaetsya znachit ne mozhet vse razletaetsya posle bol'shogo
vzryva, a mozhet tol'ko vse szhimat'sya.
Prolet galaktik odna
skvoz' druguyu, na nebol'shih skorostyah,
to dolzhno bylo vyzvat' stenu ognya i ogromnoe kolichestvo
stolknovenii - chego ne nablyudalos'.
Posle etogo srochno pridumali
temnuyu materiyu i temnuyu
energiyu , vmesto efira - zapolnyayushuyu prostranstvo, i
opredelili temnoi materii i temnoi energii massu ot
60 do 90 procentov, ot obshei
massy vo vselennoi, -
kak govoritsya ruchnymi postulatami, proveli imitaciyu
efira.
Tak chto Vashi poiski portala v chernoi dyre, - eto vashe
vremya priprovozhdenie,
po prichine togo chto nichego v
astrofizike ne byvaet prosto tak.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
3.01.2011 16:36, 2.1 KBait)
Vychislyat'
vzaimodeistviya
mezhdu potokami
efira namnogo
slozhnee,chem -
mezhdu otdel'nymi
ob'ektami.Potomu
efir tak
nepopulyaren.
Al'fa-chasticy-
eto atomy(ili
yadra) geliya,beta-
eto
elektrony,gamma-
eto
superpronikayushie
elektro-magnitnye
volny (samyi
vysokochastotnogo
diapazon). Zerkalo
ne otrazhaet
gamma-luchi,kak
svet,lish'
potomu,chto
rasstoyanie mezhdu
chasticami zerkala
bol'she dliny
volny gamma-
luchei.Chtoby
otrazhat' gamma-
luchi,nuzhno zerkalo
iz superplotnogo
provodyashego
materiala. Belaya
dyra(Chernaya dyra
otricatel'noi
massy) otrazhaet
lyubye luchi.
Primery chernyh
dyr(ChD)?
Elektrony.Ih massa
stabil'na.Oni
vedut sebya i kak
chasticy,i kak
volny.Ih radius
Shvarcshil'da-10^-57
m. Drugie nazvaniya
ChD-
Fotonizator,Graviteleport,Skvoznaya
massa,Sfera
prozrachnoi
Nevidimosti,Superlinza.
V chernuyu dyru
mogut padat' tela
lyuboi massy.Esli
na ChD budet padat'
drugaya ChD,to oni
ne sol'yutsya,a
proidut s
uskoreniem drug
skvoz' druga.Esli
massa planety
namnogo bol'she
massy ChD,to
planeta ostanetsya
na meste,a ChD
budet proletat'
skvoz'
planetu,vynyrivaya
iz nee ''to tut,to
tam''. V teleskop
ideal'naya ChD
budet vyglyadet'
kak prozrachnaya
(gravitacionnaya)
linza. Hotya mnogim
telam ne hvataet
inercionnoi
energii,chtoby,proletev
skvoz'
dyru,navsegda
pokinut' granicy
ee polya.Takzhe ne
vse tela padayut
strogo po
napravleniyu v
centr dyry.Potomu
real'naya ChD-eto
naprimer centr
galaktiki,vokrug
kotorogo kruzhitsya
uima materii.
Takzhe nekotorye
oblasti kosmosa
nastol'ko
plotny,chto ih
mozhno schitat'
global'noi ChD-oni
i vidny,kak linzy
ili fragmenty
linz .Kogda
stalkivayutsya
galaktiki,ih
centry vstrechno
teleportiruyutsya,a
ostal'naya massa
zvezd slishkom
rasseyanna,chtoby
chasto
stalkivat'sya.Kuda
devaetsya energiya
ot zvezd?Pochitaite
v poiskovikah pro
Fotonnuyu
sferu.Vse fotony
tipa tormozyatsya na
sfere
Metagalaktiki,i
potom eta
Fotonnaya sfera
gravitaciei
rasshiryaet nashe
prostranstvo.Ya
somnevayus',chto
seichas real'no
mozhno szhat'
materiyu do
sostoyaniya ChD.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.01.2011 17:25, 3.5 KBait, otvetov: 1)
"Vychislyat'
vzaimodeistviya
mezhdu potokami
efira namnogo
slozhnee,chem -
mezhdu otdel'nymi
ob'ektami.Potomu
efir tak
nepopulyaren."
Konechno vyuchit' ves' efir za mesyac i li uchitsya pyat' let relyativizmu,
ponyatno chto dlya prepodavatelei astronomii
i fiziki efir ne privlekatel'nyi,
- negde guby naduvat', i pal'cy zagibat'.
Po povodu sobstvenno vychislenii, tak Vashi slova lzhivy, ibo komp'yuteru
gluboko do lampochki lyubye vychisleniya, on ne ustanet.
Vy mozhet eshe v ruchnuyu vychislyaete, togda ya Vam rekomenduyu
ispol'zovat' tehnicheskie sredstva.
"Al'fa-chasticy-
eto atomy(ili
yadra) geliya,beta-
eto
elektrony,gamma-
eto
superpronikayushie
elektro-magnitnye
volny (samyi
vysokochastotnogo
diapazon)."
Da Vash uroven' znaniya fiziki menya shokiruet, a dumayu chto Vy eshe namnogo vyshe
srednego, Vy hot' kakie-to nazvaniya znaete.
Mne bol'she
vsego ponravilos'
"beta-
eto
elektrony" - toist' na kakom izluchenii vyrabatyvayut elektrichestvo
atomnye stancii u Vas somnenii net. I eti elektrony vyletayut po provodam iz
rozetki i ustayut
kogda komp'yuter gonyaet ih po processoru, smeshno.
"Esli
na ChD budet padat'
drugaya ChD,to oni
ne sol'yutsya,a
proidut s
uskoreniem
drug
skvoz' druga"
Mne vse ravno kak Vy traktuete, no Vy vybiraite - ili Vy idete v fizike po
puti chmoshnikov - tol'ko postuliruya, ili Vy kak normal'nyi
fizik -
obosnovyvaete prichiny vyskazannyh Vami yavlenii.
Vopros pochemu chernaya dyra prityagivaet chernuyu dyru, a ih yadra proletayut mimo.
Variant otveta,
- Mne tak hochetsya - nazyvaetsya postulat.
"Kogda
stalkivayutsya
galaktiki,ih
centry vstrechno
teleportiruyutsya,a
ostal'naya massa
zvezd
slishkom
rasseyanna,chtoby
chasto
stalkivat'sya."
Zdes' ya Vam hochu skazat', chto Vy inogda prizadumyvaites', nad skazannym, Vy sebe predstav'te
chernuyu dyru massoi v tysyachu solnechnyh,
kotoraya proletaet mimo drugoi,
i potom vsya eta massa peremeshaetsya s mgnovennoi skorost'yu v druguyu tochku prostranstva
ne ukazannuyu Vami , Vy dazhe ne dogadyvaetes'
skol'ko energii fizicheskoi nado zatratit',
i posle vyhoda iz tonnelya u chernoi dyry vesom v tysyachi mass solnca budet stol'ko kineticheskoi
energii i takaya skorost'
dvizheniya, chto proletaya ona budet probivat' zvezdy, i letet' dolzhna
so sverh svetovoi skorost'yu.
Tak chto ya dumayu Vy ne chmoshnik, i smozhete ob'yasnit' ot kuda beretsya
energiya dlya peremesheniya
tysyachi mass solnca, i kuda potom devaetsya.
"Takzhe nekotorye
oblasti kosmosa
nastol'ko
plotny,chto ih
mozhno schitat'
global'noi ChD-oni
i vidny,kak linzy
ili fragmenty
linz ."
Vy hot' ponimaete chto Vy v rukah nesete - Vy hot' dogadyvaetes' chto v kosmose
v ramkah tekushih teorii pustota, a u pustoty ne mozhet byt' plotnosti.
Vy ne ponimaete, chto tekushaya global'naya putanica i krizis v astronomii, kak raz
iz za togo chto pustote pripisyvayut svoistva sredy, i pri etom sredu otricayut.
"Vse fotony
tipa tormozyatsya na
sfere
Metagalaktiki,i
potom eta
Fotonnaya
sfera
gravitaciei
rasshiryaet nashe
prostranstvo"
A slabo obosnovat'?
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
3.01.2011 23:16, 3.2 KBait)
Naschet elektronov
ya chital takoe
oficial'noe
ob'yasnenie:kogda v
provode techet
tok,sami elektrony
dvizhutsya
medlenno-mm/
sekundu,zato oni
bystro peredayut
drug drugu svoimi
ottalkivayushimi
polyami energiyu
toka,zaryad,i tok
dvizhetsya pochti so
skorost'yu sveta. Vy
voobshe chitali
stat'yu pro chernye
dyry na moem
saite http://
genzubkov.narod.ru/ ?
Ya tam vse logichno
podrobno
ob'yasnil ,a do vas
nikak ne
''doidet'',skol'ko ya
tut ne pytayus'
ob'yasnit'. ChD
prohodit skvoz'
ChD,tak kak oni do
kasaniya-
stolknoveniya
uspevayut
razognat'sya do
skorosti s (ili 2s).
Pri skorosti s
vnutrennee vremya
ne idet,potomu
moment vhoda v
sferu ChD i vyhoda
iz nee dlya
kosmonavta
sol'yutsya v odin
mig. Naschet zakona
sohraneniya
energii:gravitaciya-
eto voobshe
sploshnoe ego
narushenie.Planeta
nas i predmety
prityagivaet,a
energiyu na eto ne
tratit (esli ne
vnikat' v nyuansy-
energiyu svyazi).
Chem bol'she massa
ChD,tem bol'she ee
gravitaciya,uskorenie,priobretennaya
kineticheskaya
energiya. Kuda
devaetsya energiya?
Kogda chernye dyry
proletyat drug
skvoz'
druga,svoimi
polyami oni drug
druga nachnut
tormozit'.Tak chto
skol'ko
gravitacionnoi
energii ushlo na ih
sblizhenie,stol'ko
zhe energii uidet
na ih tormozhenie.
I poluchitsya v
itoge,chto skorost'
(kineticheskaya
energiya) galaktik
ne
izmenitsya,prosto
oni perenesli drug
druga v
prostranstve.Naschet
gravitacionnyh
linz: est' mnogo
fotografii
kosmosa,na kotoryh
vidno iskrivlenie
sveta gravitaciei
(a mozhet byt' eto
prosto
prelomlenie-
imho) ,vidny kak by
chasti linz,serpy.
Formula radiusa
Shvarcshil'da
R=2GM/c^2.
Vyvedem
zavisimost'
radiusa
Shvarcshil'da ot
plotnosti sredy.
M=pV=p(4/3)PIR^3 .
R=[2Gp(4/3)PIR^3]/
c^2 .Sokrashaya
R,poluchaem: R=sqrt
[(3c^2)/(8GpPI)]
.Otsyuda vidno,chto
radius ChD obratno
proporcionalen
kvadratnomu kornyu
iz plotnosti ChD.
Znachit,chem bol'she
radius ChD,tem
men'shei mozhet
byt' ee plotnost'.
Nashi uchenye po
krasnomu
smesheniyu svoimi
metodami
vychislili,chto
plotnost' nashei
vidimoi Vselennoi
(Metagalaktiki)
1.773298*10^-28
m.Esli etu
plotnost'
podstavit' v
formulu vyshe,to
poluchim R=10^25
m,chto sovpadaet s
real'nym-
oficial'no
prinyatym
radiusom
Metagalaktiki.Vot
i vyhodit,chto nasha
vselennaya-
nevidimaya Chernaya
dyra,Graviteleport
dlya nablyudatelei
iz drugih,vneshnih
Vselennyh.Hotya po
moei teorii
veshestvo vnutri
ChD ne rasshiryaetsya.
Pro gravitaciyu
Fotonnoi
sfery,sovpadayushei
so sferoi
Metagalaktiki,pisal
na svoem saite
odin uchenyi,pozzhe
utochnyu.Smysl v
tom,chto
chasticy,pokidayushie
nashu Vselennuyu,po
relyativistskomu
zakonu,dostigaya
skorosti sveta(a
fotony-
uvelichivaya
chastotu),stanovyatsya
beskonechno
tyazhelymi,a znachit
obladayut sil'noi
gravitaciei,kotoraya
i rasshiryaet vo vse
storony nashu
vselennuyu. No est'
uchenye(naprimer
Grishaev http://
newfiz.narod.ru/ ),dokazyvayushie,chto
vse polya takzhe
imeyut predel
skorosti=s. Eto
nazyvaetsya tipa
Lorencevskoe
preobrazovanie
polya.Potomu polya
relyativistskih
chastic slabee,chem
pokoyashihsya.Takzhe
i polya potomu ne
pospevayut za
relyativistskimi
chasticami.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
4.01.2011 0:12, 253 Bait)
Utochnenie: pro
Fotonnuyu sferu
pishet Natanzon
D.D. na http://
www.sciteclibrary.ru/
rus/catalog/
pages/8894.html/ .
Tovarish pishet,chto
vse,chto vyletelo iz
nashei
Vselennoi,prevrashaetsya
v
sputniki,kruzhashiesya
vokrug nashei
Vselennoi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
4.01.2011 0:15, 253 Bait)
Utochnenie: pro
Fotonnuyu sferu
pishet Natanzon
D.D. na http://
www.sciteclibrary.ru/
rus/catalog/
pages/8894.html/ .
Tovarish pishet,chto
vse,chto vyletelo iz
nashei
Vselennoi,prevrashaetsya
v
sputniki,kruzhashiesya
vokrug nashei
Vselennoi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
4.01.2011 0:16, 253 Bait)
Utochnenie: pro
Fotonnuyu sferu
pishet Natanzon
D.D. na http://
www.sciteclibrary.ru/
rus/catalog/
pages/8894.html/ .
Tovarish pishet,chto
vse,chto vyletelo iz
nashei
Vselennoi,prevrashaetsya
v
sputniki,kruzhashiesya
vokrug nashei
Vselennoi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.01.2011 1:08, 1.3 KBait, otvetov: 1)
Vy ya smotryu nedoponimaete,
- Vy berete teoreticheskuyu chernuyu dyru massoi 1000
mass solnca, na kotoruyu dvizhetsya drugaya takaya-zhe teoreticheskaya
chernaya dyra, po
usloviyu o chernyh dyrah, oni uzhe drug
druga posle sblizheniya nikogda ne pokinut.
Vy vyvodite dyru portacii, i u Vas tysyacha
solnechnyh mass ne tochno prityagivaet
druguyu tysyachu,
- hotya zadacha chernyh dyr prityagivat' po samoe dal'she
nekuda.
Vy voz'mite dva sharika dlya nastol'nogo tennisa,
namazh'te rezinovym kleem,
i polozhite v tarelku s vodoi
i tolknite shariki drug na druga tak chtoby oni prilipli.
Ya dumayu chto Vy poimete chto esli teoreticheskie chernye dyry
ne stalkivayutsya,
a po opredeleniyu oni prityagivayut vse
s takoi siloi chto ni to chto material'nye ob'ekty imeyushie
massu ne mogut ego pokinut', a ego ne mozhet pokinut'
elektromagnitnoe
izluchenie - eto govorit o tom chto gravitaciya,
u dyry v sta metrah takaya chto proletayushuyu chernuyu dyru prosto
razorvet kogda ona budet mimo proletat'.
Ladno
ne rvite serdce, obosnovat' Vy nichego ne mozhete,
Vy mozhete prochitat' napisannoe i pereskazat' ego, a ponyat'
v prochitannom chto est' obosnovanie, gde porozhnyak,
gde vydumka, a gde vran'e - Vy poka ne mozhete.
Zhelayu uspehov v oblasti astrofiziki.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
4.01.2011 7:14, 1.7 KBait)
Gravitaciya i klei-
ponyatiya slishkom
raznye.Gravitaciyu
obychno izobrazhayut
v vide
potencial'noi
yamy.Pust' est'
nekaya ne ochen'
glubokaya yamka v
polu. I chtoby
shariku vykatit'sya
iz yamki,ego (vtoraya
kosmicheskaya)
skorost' na krayu
yamki dolzhna byt'
ne men'she 3 sm/s
(analog skorosti
sveta). Pust' u nas
est' kii,kotorym
nam razresheno 1
raz soobshat'
shariku skorost' ne
bol'she 3 sm/sek .
Togda esli sharik
budet lezhat' na
dne,ili nizhe kraya
yamy(vnutri sfery
Shvarcshil'da),to
impul'som v 3sm/s
my ne smozhem
vytolknut' sharik
iz yamy(potomu i
svet ne mozhet
pokinut' ChD).Zato
esli my soobshim
skorost' 3 sm/s
shariku,nahodyashemusya
na polu vne
yamy,to ,skativshis'
v yamu,sharik
blagodarya
gravitacii,na dne
yamy budet imet'
uzhe skorost' 6sm/
sek(v centre ChD
otnositel'naya
skorost' ravna 2s).
I prokativshis' po
inercii,sharik
vykatitsya s
drugogo kraya yamy
so skorost'yu 3sm/
sek(eto ne men'she
vtoroi
kosmicheskoi
skorosti) i s etoi
zhe skorost'yu
pokatitsya dal'she
po polu(vyletit
navsegda iz ChD).
Chernuyu dyru
mozhno postroit'
naprimer,esli
sobrat' rtut'yu
(plotnost' 13600 kg/
m^3) zapolnit'
sferu radiusom
1.08*10^11m-( eto
tochno ravno
radiusu orbity
Venery). Esli vzyat'
2 takih rtutnyh ChD
i soedinit' ih v
odnu kaplyu,to
poluchitsya sfera
iz rtuti massoi v
2 raza bol'she i
radiusom v (koren'
kubicheskii iz
2)1.26 raz
bol'she,chem to zhe u
1 kapli. Togda eta
bol'shaya kaplya
perestanet byt'
chernoi dyroi,ibo
ee radius budet
men'she radiusa
Shvarcshil'da(pri
udvoenii ChD ee
radius tozhe
dolzhen udvoit'sya).
A znachit iz etoi
obshei kapli v
principe ne tak
uzh slozhno budet
vyrvat'sya,i eta
kaplya budet menee
stabil'na,chem 2
men'shie otdel'nye
kapli(ChD).
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.01.2011 9:37, 1.4 KBait)
Mne Vashi vydumki ne interesny i ne interesny
neobosnovannye s fizicheskoi tochki zreniya
ob'yasneniya Vashih vydumok.
Vy odnu vydumku ob'yasnyaete drugoi vydumkoi
-
v luchshih tradiciyah Einshteinovskogo relyativizma.
Mne takaya klounada ne ponyatna i ne interesna.
U Vas net strategicheskogo ponimaniya, vcepilis' za kakuyu-to
melkuyu ... i chahnite nad nei.
Do lampochki vsei astrofizike portiruet ili net
chernaya dyra, kotoruyu eshe nikto i ne nablyudal, a tol'ko
rukoi mogut
ukazat' na nee napravlenie i skazat'
- vot mol, ona tam gde-to dolzhna byt'.
Tem bolee Vy ne ponimaete osnovnyh principov, peredachi
energii drugomu telu
imeyushemu massu. Ne ponimaya etogo
i ne opredeliv kak eto obosnovat' prostymi slovami -
to vse ostal'noe ne imeet smysla.
"Naschet zakona sohraneniya
energii:gravitaciya- eto
voobshe sploshnoe ego narushenie."
Vy vot tysyachu solnechnyh mass, razgonyali do dvuh svetovyh,
i pri gravitacii proletaete kak
fanera nad Parizhem, mol est'
takaya a kak ona gravitiruet azh neponyatno - tak eto
otvet chmoshnika. Esli Vy zanimaetes' dyroi portala, to Vy
dolzhny vse voprosy
obosnovat', i v pervuyu ochered' samye
trudnye a ne samye prostye, mol peremeshaetsya ...
znaet kuda v portale, vot takoi ya molodec, prosto "zvezdnye
vrata"
razregulirovannye poluchilis' u Vas.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.01.2011 10:27, 2.9 KBait)
Ya ponimayu chto mozhno doktorskuyu zashitit' na
razbore padenii v chernuyu dyru.
Pri padenii telo portiruetsya - daleko ili ryadyshkom.
Pri padenii v chernuyu szhimalku
telo szhimaetsya.
Pri padenii v chernuyu razrushilku telo razrushaetsya.
Pri padenii v chernuyu anigililku telo anigiliruetsya.
Pri padenii v chernuyu-rasdvoilko-portalo-anigililku,
telo sperva razdvaivaetsya potom portiruetsya posle chego
doblestno anigiliruetsya.
Vidite skol'ko bessmyslennyh napravlenii i tem mozhno
vysosat'
iz pal'ca za odnu minutu, tak ya takoi erundy
mogu pridumyvat' bez ustali, tol'ko tolku ot etogo
nikakogo. No zato chmoshnyh kandidatskih i doktorskih mozhno
zashitit'
kuchu i malen'kuyu gorku.
Rekomenduyu Vam chtoby vy esli nad chem-to dumaete, to delat'
eto zhelatel'no tak, chto-by vtoroi raz ni Vy i ni drugie nad etim
voprosom
ne napryagalis', - esli reshaete to vopros dolzhen
byt' reshen i odnoznachno, esli ne reshili znachit zrya potratili
vremya v dannom napravlenii, znachit nado iskat' prichinu
oshibki.
A potom vernutsya k voprosu i reshit' ego polnost'yu.
"""Sformirovavshiesya v predshestvuyushee stoletie korpuskulyarnaya
i volnovaya
koncepciya sveta v XIX veke prodolzhili ozhestochennuyu
bor'bu. Pervaya opiralas' na avtoritet N'yutona, vtoraya - na
avtoritet Guka, Gyuigensa, Eilera, Lomonosova. Storonniki
korpuskulyarnoi koncepcii nadeyalis' ob'yasnit' s ee pozicii
zatrudneniya s ob'yasneniem yavlenii difrakcii i interferencii.
T.Yung dal eto ob'yasnenie s pozicii
volnovoi koncepcii. Ishodya
iz vyskazannyh im gipotez o sushestvovanii razrezhennogo i uprugogo
svetonosnogo efira, zapolnyayushego Vselennuyu, o vozbuzhdenii
volnoobraznyh
dvizhenii v efire pri svechenii tela, o zavisimosti
oshusheniya razlichnyh cvetov ot razlichnoi chastoty kolebanii,
vozbuzhdaemyh svetom na setchatke glaza, o prityagivanii
vsemi
material'nymi telami efirnoi sredy, vsledstvie chego poslednyaya
nakaplivaetsya v veshestve etih tel i na malom rasstoyanii vokrug
nih v sostoyanii bol'shei
plotnosti (no ne bol'shei uprugosti),
Yung delaet vyvod o tom, chto izluchaemyi svet sostoit iz
volnoobraznyh dvizhenii svetonosnogo efira. Eto dalo vozmozhnost'
vse raznoobrazie cvetov svesti k kolebatel'nym dvizheniyam efira,
a razlichie cvetov ob'yasnit' razlichiem chastot kolebanii efira,
a takzhe sformulirovat' princip
interferencii. """
http://pda.coolreferat.com/%D0%9E%D1%81%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B5_%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%86%D0%B5%D0%BF%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B8_%D0%BA%D0%BB%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%81%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B9_%D1%84%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B8_XIX_%D0%B2%D0%B5%D0%BA%D0%B0
Zamet'te kak Tomas Yung delal utverzhdeniya, - sperva nahodil nekotorye
yavleniya i razbiralsya v nih a potom ih formuliroval.
A Vy kak delaete, berete
neobosnovannyi porozhnyak - ChD,
pridumyvaete dlya nee trassu s liftom i gabaritnye ogni.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.01.2011 14:35, 1.9 KBait, otvetov: 1)
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,79788.msg1436797.html#msg1436797
Vibe
prodolzhaet tupit' v polnyi rost,
etot chmoshnik sam ne znaet chto
on hochet,
etot kon' sporit s apgonentom na pravah moderatora,
etot kon' pedal'nyi dazhe ne mozhet sebe dlya spora drugoi nik
vzyat', togda by eto ... uznalo by
chto takoe spor,
i kak by ego ... za tupye voprosy drugie
moderatory.
On oboroten' moderatorskii, zashitnik relyativizma,
i on dumaet chto eto
ego prednaznachenie.
Pravilami foruma na skol'ko ya znayu ne zapresheno izoblichat'
moderatorov chmoshnikov s drugih forumov.
"Oh... Vy napisali,
chto slozhnost' i mnogoobrazie metodov
matematiki pozvolyaet pravdopodobno obosnovat' somnitel'nye
veshi v fizike. Ya poprosil ob'yasnit', kak imenno eto dolzhno
proishodit'.
Ya nigde ne utverzhdal (poka), chto "rezul'taty
raschetov, nesovpadayushie s nablyudeniyami, mogut postavit'
zadachu peresmotra matematicheskih metodov". Ya vsego
lish'
proshu Vas poyasnit' Vashi zhe utverzhdeniya. Poka Vy etogo ne
sdelaete, ya ne mogu dazhe byt' uveren, chto ne soglasen s nimi."
"Problema v tom,
chto u nas razdel -- fizicheskii.
Poetomu tut vazhno, chtoby utverzhdaemye polozheniya
ne protivorechili by fizicheskim principam. I voobshe,
otnosilis' by k fizike."
"U menya obshaya pros'ba. Davaite vse-taki suzim obsuzhdenie
do kriteriev istiny v sovremennoi fizike. Ne v matematike,
ne v religii, ne v zhizni. V fizike.
Ponimaya pod kriteriyami
istiny kriterii vybora toi ili inoi fizicheskoi modeli ili teorii."
Etot chmoshnik ranee interesovalsya kak ustroen komp'yuter,
i naezzhal s etim voprosom sam na nego ne znaya otveta,
- teper' "belka hitrosti" ego probila vesti razgovory
strogo v rusle fiziki, dlya togo chtoby eto
... moglo
steret' svoi-zhe voprosy ne po fizike.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(G. A. Zubkov,
5.01.2011 19:34, 627 Bait)
K sozhaleniyu na
etom forume
napisannye ssylki
ne klikabel'ny,a
vvodit' takuyu
bol'shuyu ssylku
pro Yunga vruchnuyu
malo kto zahochet.
Ob'yasnit' chto-to
teoriei-eto
''kazhdyi durak
mozhet''. Teoriya
eshe dolzhna byt'
prikladnOi-
pomogayushei
izobretat' chto-
nibud'
poleznoe.Smozhete
che-nit' iz efira
svarganit'-
dokazhete bol'she
svoyu pravotu! Ya
voobshe ne tol'ko
teoriyu ChD pytayus'
razvivat'.No
promezhutochnye
syrye rezul'taty
na svoem saite
poka razmeshat'
smysla ne vizhu.
Hotya v
fizike,''mozgovoi
atake'' chem bol'she
idei,tem
luchshe:avos' kakaya-
nibud' budet
vernoi ili
prigoditsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.01.2011 20:55, 2.3 KBait)
Vy v lyubom poiskovike naberite T. Yung, interferenciya,
samoe smeshnoe chto dlinu svetovoi volny on eshe v1800,
tochno opredelil ne ispol'zuya nikakih spec priborov
kotorye est' seichas.
Ya vse-taki schitayu chto esli lyuboi astronom v ramkah efirnoi
teorii smozhet osmyslenno i obosnovanno otvetit' na lyuboi
vopros tomu
kto ne znaet nichego o astronomii, i v ramkah efirnoi
teorii emu budut prosty i ponyatny prichiny vnutri zvezdnyh
processov, i prichiny formirovaniya galakticheskih
rukavov,
prichiny glavnoi posledovatel'no, ponyatny prichiny dvizhenii
zvezd v prostranstve, prosty i ponyatny lyubye vidimye
vzryvy zvezd i ih prichiny, to u astronomov
budet osmyslennyi
vzglyad na zvezdy.
A seichas oni smotryat bessmyslenno i vse zvezdnye teorii
na tekushii moment ne vzaimosvyazany, i vysosany iz pal'ca.
Odno to chto astronomy utverzhdayut konechnost' vselennoi,
i ne zamechayut togo chto eto uzhe dlitsya ne odnu sotnyu let,
i razmer vselennoi sootvetstvuet - tyutel'ka
v tyutel'ku
vozmozhnostyam teleskopov, eto sravnimo s moei tochki zreniya
s global'nym pozorom vseh astronomov.
Vy nedoponimaete, u astronomov ne tak mnogo
vremeni,
esli oni budut prodolzhat' bred nesti razroznennyi to
veroyatnost' polnogo prekrasheniya finansirovaniya dostatochno
vysoka, po toi prichine chto net
smysla finansirovat' togo
kto vnyatno i ob'yasnit ne mozhet - zachem i chto on ishet.
I gravitaciya - vot dazhe Vami traktuetsya na urovne chuda,
v efirnoi
teorii etot vopros reshaetsya pervym, i
proshe prostogo, pri etom reshayutsya vse voprosy
termodinamiki, dvizheniya po orbitam, sovpadaet
na sto procentov s effektom
Doplera, ob'yasnyaet za odno
stacionarnost' i beskonechnost' vselennoi, i krasnoe smeshenie.
Kogda ya slyshu slova "mozgovaya ataka", to u menya voznikaet
chuvstvo chto obshayus' s umstvenno nepolnocennym, po toi prichine
chto etot termin udel teh kto ekstrenno hochet chego-to dostich'.
V astrofizike ekstrennogo nichego
ne nuzhno, zdes' dostatochno
horosho obosnovannogo. Vy posmotrite hot' na relyativistov -
sto let chitayut odni i te-zhe knigi, i ih propoveduyut,
i im chto "mozgovoi
shturm", chto "mozgovaya ataka", chto "mozgovaya oborona"
chto "mozgovoe otstuplenie" im eto vse odinakovo - pustoi zvuk.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.01.2011 11:41, 1.8 KBait)
"chem bol'she idei,tem luchshe:avos' kakaya- nibud'
budet vernoi ili prigoditsya."
Kogda sam podhod k resheniyu zadach ne pravil'nyi,
- to uzhe vse
ravno skol'ko yuzerov zanimayutsya
resheniem i tem bolee vse ravno skol'ko u nih idei.
Vot yarkii primer nepravil'nogo podhoda,
analogichno portacii chernoi
dyroi.
V principe polnost'yu sovpadaet s Vashim podhodom
tol'ko v dannom sluchai drugoi ob'ekt.
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,73751.msg1438840.html#msg1438840
"""Nasha Vselennaya pochti navernyaka ogranichena po
ob'emu i masse. Tak govorit logika. Trudno
priznat' fakt vozniknoveniya mgnovennogo
beskonechnogo
ob'ema s beskonechnoi massoi.
Teoriya inflyacii govorit ob etom svoimi modelyami.
No granic net. Vselennaya, po-vidimomu zamknuta,
(prostranstvo-vremya) pri lyuboi
geometrii - ili
sfera, ili kub,tor, mnogogranniki i t.p..
Gomeomorfnost' "granic" """
V dannom primere yarko vidno
kak ne obosnovannyi
otvet i sploshnye postulaty i trebovaniya k vselennoi,
vstupayut v protivorechie s tekushei vselennoi.
U dannogo otveta dve tehnicheskie
trudnosti ,
odna iz nih ne sposobnost' ponyat' beskonechnost'.
V tekste dazhe net somneniya v vozmozhnosti
sushestvovaniya beskonechnosti, i net podhoda
k
fizicheskim metodam opredeleniya dannogo voprosa,
vopros reshen postulirovaniem.
Vtoraya tozhe global'naya trudnost' - popytka obosnovat'
prichinu vozniknoveniya
vselennoi, - sobstvenno
tam gde eto ne nuzhno, v dannom sluchai nado
ne obosnovyvat' prichinu, a konstatirovat' po
faktu, tak kak lyuboe obosnovanie prichinnosti
v dannom sluchai - neobosnovannaya vydumka,
- a eto teorii iz pal'ca,
po toi prichine chto otsutstvuet dazhe teoreticheskaya
vozmozhnost' podtverzhdeniya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.01.2011 13:46, 1.5 KBait)
Po povodu togo chto ya Vam rasskazyval chto za svetovym
izlucheniem s povysheniem kolebanii letyat chasticy, tak ya v etom voprose
razobralsya ochen' davno. Vot smotryu na
forume kak svoimi
silami pytayutsya razobrat'sya astronomy, (ya tam kak Vy ponyali ne
obshayus', zabanili, da i mnogie prosili prihodit' kogda-to potom - v budushem).
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,79500.msg1446226.html#msg1446226
I kak vsegda poyavlyaetsya chmoshnyi moderator udivlyayushii svoei tupiznoi,
i
ego naezdy nosyat trebovatel'nyi harakter, tak kak esli tot k komu on
obratilsya s voprosom
"""
Moderator: Eto otkuda izvestno? """
Etot gnidenysh ne utruzhdaet sebya dokazatel'stvom togo chtoby privesti primer.
Da, tak vot kogda on obrashaetsya s podobnym voprosom na kotoryi i on sam ne
znaet tochnogo otveta, tak eto normal'noe sostoyanie moderatora- gandol'era.
Samoe dikoe vozmozhno vperedi - eto kogda moderator- gandol'er, budet
trebovat' ne otvechat'
na drugie voprosy do teh por poka ne otvetyat emu na etot,
posle chego moderator - gandol'er zabanivaet togo s kem sporit.
http://bourabai.narod.ru/radio.htm
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.01.2011 14:13, 656 Bait, otvetov: 2)
Vot ob'yasnit' deistviya moderatora-gandol'era dostatochno legko,
on napisal nekotorye svoi vyskazyvaniya ot imeni vseh astronomov,
estestvenno on vedet moderaciyu tak
chtoby otvlekat' i ostanavlivat'
razvitie idei pri obshenii drugih, kotorye vyhodyat za predely togo
chto on oglasil samoproizvol'no (kak istinnyi gandol'er), ot imeni
vseh astronomov.
Ya dumayu chto vse astronomy obyazany sbrositsya den'gami na kursy
gandol'erov v Venecii , dlya togo chtoby u nih byl diplomirovannyi
moderator
- gandol'er.
http://elementy.ru/lib/430399
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(S. V. Semenov,
7.01.2013 10:26, 1.1 KBait, otvetov: 1)
| Citata: |
Vot ob'yasnit' deistviya moderatora-gandol'era dostatochno legko,
on napisal nekotorye svoi vyskazyvaniya ot imeni vseh astronomov,
estestvenno
on vedet moderaciyu tak
chtoby otvlekat' i ostanavlivat'
razvitie idei pri obshenii drugih, kotorye vyhodyat za predely togo
chto on oglasil samoproizvol'no (kak istinnyi gandol'er), ot imeni
vseh astronomov.
Ya dumayu chto vse astronomy obyazany sbrositsya den'gami na kursy
gandol'erov v Venecii , dlya togo chtoby u nih byl diplomirovannyi
moderator
- gandol'er.
http://elementy.ru/lib/430399 |
Ya-novichok. Veselo u vas, rebyata! A.P.Vasi, kak ya ponyal, dezhurnyi kloun. Hamovatyi (chto klounam proshayut), no nahvatavshiisya terminov (chto vselyaet uvazhenie u Mitrofanushek i veselit
ostal'nyh). Tak derzhat'! Vnesu etot sait v Izbrannoe.
- Re[3]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
7.01.2013 12:42, 583 Bait)
Fiziki,
chto
religioznye
fanatiki,
religiya
kotoryh
-
fizika.
I
vo
vsem
vidyat
fiziku,
vklyuchaya
astronomiyu.
No
s
astronomiei
takoe
ne
prohodit
potomu,
chto
pered
tem,
kak
sdelat'
"logicheskie
postroeniya"
fiziku
nuzhno
dogovorit'sya
s
astronomom
ob
astrob'ekte.
A
astronomu
nuzhny
sotni
(a
mozhet
tysyachi
let)
na
to,
chtoby
s
nim
opredelit'sya.
A
fizik
zhdat'
ne
mozhet,
porozhdaya
v
astronomii
massu
neproveryaemyh
gipotez,
smenyayushih
odna
druguyu.
A
gde
tochnaya
nauka ?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.01.2011 22:21, 1.7 KBait)
Hot' ya i uvlekayus' astronomiei, no ya ni razu ne smotrel
v teleskop, da i mne sovsem ne interesno smotret' na
kartinku.
Smotrel peredachu pro teleskop Habbla,
tak tam sploshnoe
hvastovstvo i svoditsya k tomu chto mol stalo luchshe vidno,
i postoyanno meryayutsya s drugimi teleskopami (na lineikah).
Ya ochen' sochuvstvuyu astronomam
kotorye raduyutsya
kachestvennoi nepodvizhnoi kartinke zvezdnogo neba.
I dazhe ne podozrevayut chto nichego prosto tak ne byvaet,
i tam na samom dele proishodit
takaya vpechatlyayushaya
dinamika vo vseh processah, ot malogo do bol'shogo.
Kak po mne kosmos so zvezdami na stol'ko interesen v
dinamike chto esli by astronomy
mogli v budushem predstavit'
sebe chto vo vselennoi prostranstvo zapolneno efirom,
to oni srazu by ponyali chto zvezdnye foto - kamennyi vek,
dolzhna byt' zvezdnaya
karta s ukazaniem - massy i vektora kazhdoi zvezdy,
i skorosti, plotnosti efira vozle nee, i plotnosti efira i temperatury
v raznyh napravleniyah na rasstoyanii svetovogo
goda.
Estestvenno chto dlya prosmotra takoi karty, zhelatel'no
ispol'zovat' "3d". Takzhe vnutrennyaya chast' zvezdy - imeet sovsem
druguyu strukturu i dinamiku
ot obsheprinyatoi, i ee esli
sdelat' v razreze s tochki zreniya uvlekaemogo efira, to prosto
za zvezdami budet nablyudat' na komp'yutere i pronikat' v nih
interesno
lyubomu, i posmotret' kak oni ustroenny, - hotya
eto idei takogo dalekogo budushego, uchityvaya kamennyi vek
tekushei paradigmy, chto ya prosto astronomam sochuvstvuyu
kogda oni smotryat v teleskop, ne to chto, na nepodvizhnuyu kartinku,
a na zvezdy - kotorye tol'ko i mogut - chto postoyanno udalyat'sya
ot bol'shogo vzryva, i krasnet'
.
- Re: Chernaya dyra kak super kollaedr
(L. L. luyko,
15.02.2011 14:47, 2.5 KBait)
Nachnu s togo chto ChD ne s'edaet materiyu, materiya kak u lyuboi zvezdy stremitsya na razryv, a uvelichivayushayasya
gravitaciya naest_enter_group,quest_add_left preobladaet poka ne dostignet ChD ravnovessiya sil,pochemu to vse zabyvayut o
techennii vremeni,ono v centre zamedlyaetsya,s nashei tochki zreniya ono voobshe stoit, raznost' techeniya vremen
sozdaet neprolaznuyu dlya sobytii i voobshe vsego: materii i.t.d. stenu.A vneshnyaya shvachennaya materiya
puskaetsya v smertel'nyi horovod rasshepleniya do chastic ne imeyushih zaryada i massy.Esli chastica ne imeet
massy i zaryada ona mozhet prinyat' lyubuyu formu.Shema diska vokrug ChD pohozha na vodu v vanne posle otkrytiya
zaglushki, primerno tak: vernyaya polovina ploskosti diska vyletaet ogibaya ChD vniz nizhnyaya ogibaya ChD vverh,
chem bol'she ChD (v chd super gigantah)tem ochevidnee eto pryavlyaetsya.Takim obrazom super chd nahodyashayasya v
centre galaktik nasyshaet postranstvo nevidimoi materiei i energiei, dazhe vidimoi energiei iz za etogo oni
razbegayutsya.Tak chto ChD sidit gluboko na zhestkoi diete,esli i proderetsya kakoi to kvant sveta cherez stenu
raznovremeniya, to ob etom ChD uznaet v daleeeeeeeekom budushem,ona bednaya kak cherepaha Tartila medlennaya do
nel'zya,kakie to giganskie zvezdy mel'kayut pered glazami kak muhi tol'ko seichas byla i uzhe net.Vopreki
uprekam vseh v adres ChD,ona prosto tak ne rastet, vnutri nee tish' da glad' kak v glazu u Ciklona.Ee sud'bu
mozhet izmenit' tol'ko drugaya ChD slivshis' s nei.Togda ona mozhet slest' s diety i nachat' obzhorstvo .Po
dostizhenii ravnovesiya vnutrennih sil ustakanivaniya, opyat' syadet na dietu. Okolo steny raznosti vremeni
est' oblast' szhatogo prostranstva, k primeru 1 mm raven rastoyaniya ot zemli do Siriusa{cifry ne tochny}
t.e.prostranstvo tut kakby zameneno raznost'yu vremeni t.e.vremeni v tochke H mnogo znachit prostranstva
navalom.Prostanstvo eshe i szhato a vremya v dobovok iskrivleno.Vnutri ChD ogromnoe prostranstvo,no ono ne dlya
bol'shih chastic kotoryh mozhno bez problem registrirovat' priborami.Kollaedr BAK v Cerne lomaetsya potomu chto
razgon chastic cherevat mehanicheskimi posletstviyami.Mozhet neizvestnye chasticy vzaimodeistvuyut s holodil'noi
ustanovkoi BAKa.Chastica pri bol'shoi plotnosti protranstva dolzhna priobretat' svoistva volny,a forma mozhet
byt' lyuboi,mozho dazhe pofantazirovat' chto karpuskulyarnaya chastica raplyushivaetsya-udlinyaetsya v strunu i ei
teper' nuzhno minimum usilii-kolebanii chtoby vse zahodilo hodunom v global'nom masshtabe-vo vselennoi.Vopros
nomer-1 OTO Eeinshteina rabotaet ili net? Kazhetsya ya svoei teoriei snyal mnozhestvo voposov,ili mozhet dobavil
izvenite esli chto ne tak.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.04.2011 12:00, 968 Bait)
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,73830.msg1534675.html#msg1534675
Moderatora na atroforume prodolzhaet zhestoko gandol'erit' s dvoinoi siloi, on
uzhe putaet - svoe mnenie i obosnovanie kotoroe vytekaet iz ob'yasneniya.
"Nablyudeniya
pokazali, chto Luna udalyaetsya ot Zemli na 3.6 - 3.8 sm v god...
Poschitaem, na skol'ko eti ob'ekty "udalyayutsya" pri izmerenii rasstoyanii s
pomosh'yu svetovogo signala pri uslovii snizheniya skorosti sveta...
vidimoe uvelichenie rasstoyaniya sostavit -- do Luny DR = 0.55 sm za god...
Vychislennye znacheniya na poryadok otlichayutsya ot nablyudaemyh... Dlya Luny
eto otlichie mozhno ob'yasnit' tem, chto vychislennoe znachenie tol'ko vklad v
nablyudaemoe. T.e. naryadu s vidimym uvelicheniem rasstoyaniya imeetsya i
fizicheskoe uvelichenie za schet teh zhe prilivnyh yavlenii."
Vibe argumentiruet
- Est' eshe odno ob'yasnenie -- Vashi vyvody ob umen'shenii skorosti
sveta neverny.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(s. s. pogosyan,
17.04.2011 10:15, 232 Bait)
www.armonpogosyan.com V sovremennoi nauke ustanovlenno nevernii rezhim vozniknoveniya i evolyucii Pervichnyh chernyh dyr.Ob etom i o karkase iz PChD smotri v knige-Armonnaia
struktura metavselennoi.S uvazheniem,S.Pogosyan.Armenia.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(L. L. Li,
24.05.2011 6:20, 2.5 KBait)
Uvazhaemye kollegi teoretiki davaite razberemsya s ChD kotoraya nahoditsya v centre galaktik, potomu chto oni
pervye formiruyutsya. Kogda ona byla zvezdoi gigantom. Pri szhatii zvezdy giganta pod siloi svoego prityazheniya
v centre izmenyaetsya techenie vremeni ono zamedlyaet hod. Vsya massa materii vokrug magnitnoi dosyagaemosti
zvezdy nachinaet vrashenie kak voda v vanne posle otkrytiya probki, centrobezhnaya sila vrasheniya gaza, pyli,
i.t.d. prizhimaet vse v spiral'nyi disk, uskoryayushiisya v centre. No ono uskoryaetsya v predelah dozvolyayushih
zamedlennym vremenem t.e. skorost' sveta ne prevyshaet svoyu zhe skorost', kak i vo vsem kosmose. No est' v
kosmose estestvennyi sposob oboiti etu zakonomernost'. Energeticheskie izlucheniya iz ChD v centre galaktiki
mogut ishodit' iz dvuh istochnikov. Pervyi iz vneshnei obolochki, t.e. v skvazhinu kak v rakovine, ogibaya no
ne popadaya v samu ChD, kak smerch uhodya daleko ot vliyaniya diska. Vtoroi iz gorizonta sobytii, iz samoi ChD.
Esli diskovoi materii okolo ChD stanovitsya ochen' mnogo, massa diska nachinaet budorazhit' ChD, pri tom
vrashat'sya ChD mozhet so skorost'yu i napravleniem sovershenno otlichnym ot vneshnego diska, esli voobshe ona
vrashaetsya. Pustota ili svobodnoe prostranstvo mezhdu ChD i diskom stanovitsya bol'she, veroyatnost'
proniknoveniya diskovoi materii vnutr' ChD isklyuchaetsya voobshe. Pustoty tem bolee zdes' ne mozhet byt', ona
zapolnena temnoi materiei, kotoraya rodilas' iz rasshepleniya v diske, normal'noi materii. Teper' ona
uskoryayas' udalyatsya ot centra ChD i dostigaet kraev galaktiki. Uskoryayas' temnaya materiya perehodit v temnuyu
volnovuyu energiyu prohodyashuyu cherez nas, my vosprinimaem ee, ne chto inoe kak techenie, hod Vremeni. V konce
puti na periferii v dal'nih rukavah galaktiki, temnaya energiya zamedlyaetsya prevrashayas' v temnuyu materiyu,
skaplivaetsya vozdeistvuya na dvizhenie rukavov. No TM mozhet prodolzhit' i obratnyi cikl, v silu togo zhe
skopleniya onoi na periferii, teper' uzhe k centru galaktiki. Eto oznachaet chto vremya mozhet tech' obratno,
otnositel'no nas, i s zaderzhkami. Pohozhe chto ChD za gorizontom sobytii zhivet svoei zhizn'yu,v ravnovesnom
sostoyanii ne pogloshaet poka ne vstretit druguyu ChD ili dr.supermassiv materii. Vyhodit chto ChD yavlyaetsya
svernutym v kokon vremeni, gigantskim hranilishem materii kotoryi v svoe vremya osvoboditsya iz tyagoteniya
lovushki. Kak? V moment szhatiya zvezdy, rozhdeniya ChD zadayutsya parametry na skol'ko daleko v budushee budet
deistvovat' Kokon vremeni. V budushem astrofiziki govoryat ostanutsya tol'ko holodnyi mrak i gigantskie
chernye dyry.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(s. s. pogosyan,
24.05.2011 10:32, 1.2 KBait)
Uvazhaemyi L.L.L.,Sverhmassivnye ChD voznikayut v processe sliyaniya ChD s men'shimi massami,do privrasheniya etih ob'ektov v obychnye galaktiki.No samoe glavnoe u sovremennoi nauki
ne pravil'noe predstavlenie o ChD-h.Razvivaemaya nami kosmologicheskaya model' vselennoi s strogo ploskim prastranstvom isklyuchaet,zaprishaet sushestvovonie absolyutnogo gravitacionnogo
kollapsa,absolyutnyh chernyh dyr.Ploskoe prastranstvo vselennoi prinuzhdaet otnositel'nye ChD ni kollapsirovat',a ob'edinyayas' uvelichivat' svoi massy i razmery.Takie otnositel'nye
ChD byvayut dvuh vidov: kosmologicheskie-eto Pervichnye ChD,i metagalakticheskie ChD-ih nazyvaem D-telami v chest' nashego sootechestvennika V.A.Ambarcumyana.Tak vot D-tela v processe
kosmoevolyucii,vprocesse rasshireniya vselennoi,ob'edinyayas' uvelichivayut svyu massu i razmer,dostegaya nekotorogo predela.Vse osnovnye processy kvantovo-gravitacionnoi evolyucii
materii proishodyat imenno v D-telah:narusheniya simetrii Velikogo i elektroslabogo ob'edinenii,kvark-glyuonnyi fazovyi perehod,yadernyi sintez,rekombinaciya i t. d.V dol'neishem
D-tela,sverhmassivnye ChD prevrashayut'sya v skopleniya galaktik,galaktiki...S uvazheniem,Samvel Pogosyan. www.armonpogosyan.com
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.05.2011 9:38, 1.3 KBait, otvetov: 2)
\davaite razberemsya s ChD kotoraya nahoditsya v centre galaktik\
---nikto ne nablyudal ni odnoi chernoi dyry,
vse oni raschetnye, tak kak matematika
ne shoditsya s real'nost'yu.
\ChD kotoraya nahoditsya v centre galaktik, potomu chto oni
pervye formiruyutsya\
--- pervye formirovalis' pri bol'shom vzryve, - kotoryi dokazyvaetsya chem?,
reliktovym izlucheniem, iz chego delaetsya vyvod o tom chto bylo 14mlrd
let tomu,
- eto bol'she pohozhe na lohotron, chem na nauchnoe obosnovanie.
A vash vopros ob'edenyaet tri lohotrona kotorye Vas prokatili.
1Bol'shoi vzryv
2chernaya
dyra
3formirovanie chernyh dyr pri bol'shom vzryve
\Pri szhatii zvezdy giganta pod siloi svoego prityazheniya
v centre izmenyaetsya techenie vremeni ono zamedlyaet hod\
- eto tozhe lohotron na kotorom Vy kataetes', po prichine otsutstviya
fizicheskoi prichiny kogda material'nye
tela
pri izmenenii svoih svoistv,
mogut vliyat' na vremennye processy v prostranstve.
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8971-nasledstvennyie-chernyie-dyiryi/#comments
prochtite vse kommentarii - Mimohodom,
polnost'yu razgromlena vsya myshinaya voznya vokrug chernyh dyr
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(M. Yu. Yakimov,
25.05.2011 10:56, 1.1 KBait, otvetov: 1)
Prezhde chem trepat', dorogoi gospodin Vasi, podumaite, kak otmyvat'sya-to budete. Ili ponyatie chesti u nas ne v chesti? Mozhno vrat' na kazhdom slove, i pri etom dazhe ne krasnet'?
Esli v centre nashei Galaktiki net chernoi dyry, kak zhe vy ob'yasnite, vokrug chego obrashayutsya blizhaishie k etomu centru zvezdy, razgonyayas' do 500 km/s i bolee http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1180936.
Kak
ob'yasnite aktivnost' radioistochnika Strelec A? Kak ob'yasnite nalichie harakternyh strui goryachego gaza vokrug ob'ekta strelec A? http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1227506
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sagittarius_A*
Kak vy otmahnetes' ot vsego etogo http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A1%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%B5%D1%86_A*?
Chernaya
dyra ne prosto govorit - vopiet o svoem sushestvovanii! Otricat' etot fakt (a eto uzhe nauchnyi fakt) po men'shei mere glupo.
- Re[3]: Chernaya dyra
(M. Yu. Yakimov,
25.05.2011 11:05, 539 Bait)
Vnimanie!
K sozhaleniyu, privedennye v moem predydushem soobshenii ssylki otobrazilis' nepravil'no - pri perehode po nim nuzhno obyazatel'no uchityvat'
zvezdochku v konce, kotoraya pochemu-to ignoriruetsya dvizhkom foruma!
Proshu eto uchest', i ne perehodit' po etim ssylkam avtomaticheski -
popadete ne tuda!!!
V svoyu ochered' postarayus' svyazat'sya s administraciei foruma, chtoby v ocherednoi - kotoryi uzhe! - raz pozhalovat'sya na sistemu.
Stoit
li udivlyat'sya tomu, chto forum ne populyaren, nesmotrya na izvestnost' saita.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.05.2011 22:22, 11.4 KBait, otvetov: 1)
M.Yu.Yakimov
Vy za menya ne perezhivaite,
Vy chitali vse posty mimohodom?
esli net to prochitaite.
A v centre galaktiki
bol'shoe kolichestvo
zvezd u kotoryh vzaimnaya gravitaciya, i esli by vy posmotreli
video to zametili by chto dvizheniya zvezd vokrug yavnogo centra
net.
I
esli Vy tak rezko vozmushaetes' to esli ne smozhete
dat' chetkoi formulirovki chernoi dyry i metodiki
ee obnaruzheniya to Vy prosto nedalekii i ne ponimaete
predmeta
razgovora, - trepach.
A to chto sovremennaya astrofizika ne mozhet proshitat'
gravitaciyu dlya bolee dvuh tel - to eto ne znachit
chto tam chernaya dyra.
Esli
net chetkogo odnoznachnogo predmeta razgovora s odnoznachnymi
harakteristikami i odnoznachnymi opredeleniyami, to razgovor
na etot predmet nazyvaetsya - boltovnya.
Chtoby Vy byli v kurse Zemlya letit po orbite 30km v sekundu,
a solnechnaya sistema dvizhetsya so skorost'yu 400km v sekundu.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1244775/07.html
(Stoit skazat', chto sozvezdiyu Kormy prinadlezhit eshe odin rekord - samaya
bystraya zvezda - RX J0822-4300, dvigayushayasya so skorost'yu 1300 km/s)
Zhdu formulirovku chernoi dyry i metody ee obnaruzheniya - uspehov.
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8971-nasledstvennyie-chernyie-dyiryi/page/2/
......Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie (gamma-luchi, γ-luchi)
vid elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s chrezvychaino maloi dlinoi volny
< 5×10−3 nm i, vsledstvie etogo, yarko vyrazhennymi korpuskulyarnymi
i slabo vyrazhennymi volnovymi svoistvami.
Gamma-kvantami yavlyayutsya fotony s vysokoi energiei. Obychno schitaetsya,
chto energii kvantov gamma-izlucheniya prevyshayut 105 eV, hotya rezkaya granica
mezhdu gamma- i rentgenovskim izlucheniem ne opredelena. Na shkale
elektromagnitnyh voln gamma-izluchenie granichit s rentgenovskim izlucheniem,
zanimaya diapazon bolee vysokih chastot i energii. V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu. Ochevidno,
fizicheski kvanty elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s odinakovoi energiei ne
otlichayutsya, poetomu takoe razdelenie uslovno.
Gamma-izluchenie ispuskaetsya pri perehodah mezhdu vozbuzhdennymi
sostoyaniyami atomnyh yader (sm. Izomernyi perehod, energii takih
gamma-kvantov lezhat v diapazone ot ~1 keV do desyatkov MeV),
pri yadernyh reakciyah (naprimer, pri annigilyacii elektrona i pozitrona,
raspade neitral'nogo piona i t.d.), a takzhe pri otklonenii energichnyh
zaryazhennyh chastic v magnitnyh i elektricheskih polyah (sm. Sinhrotronnoe izluchenie).....
Esli net poverhnosti ob kotoruyu proishodit tormozhenie.
Material iz Vikipedii
.....Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh
obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v rentgenovskih
trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok yavlyayutsya
metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe antikatodom).
V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom, uskoryayutsya
pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom i katodom
(pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak uskorenie slishkom malo)
i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe tormozhenie. Pri etom za schet
tormoznogo izlucheniya proishodit generaciya izlucheniya rentgenovskogo diapazona,
i odnovremenno vybivayutsya elektrony iz vnutrennih elektronnyh obolochek atomov
anoda. Pustye mesta v obolochkah zanimayutsya drugimi ....
To vstupaet v silu fraza -
V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.
sledovatel'no pri otsutstvii udara o poverhnost' - otsutstvuet sama vozmozhnost'
vozniknoveniya rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, a esli izluchenie est' to ono mozhet
byt' tol'ko rezul'tatom izlucheniya v yadernom perehode. A eto uzhe chasticy vysokih energii.
kosmogon
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188549
Polost' Rosha
Dlya sozdaniya akrecionnogo diska, - polost' Rosha dolzhna byt',
zdes' prakticheski polnaya nevozmozhnost' sushestvovaniya dannoi polosti u
zvezdy, uchityvaya tot zhe kvadrat vliyaniya gravitacii, zdes' vopros o
udel'noi plotnosti zvezdy - u kotoroi atmosfera soderzhit naprimer 30%
massy zvezdy, i eta massa popolnyaetsya pri ee potere iz nedr zvezdy -
feerichno.
Povtoryu - avtorskoe izluchenie iz chernoi dyry -
.Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash metod obnaruzheniya Chernoi Dyry
-Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
....Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo.
ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut. ....
Padaya na Chernuyu Dyru veshestvo ne
mozhet rezko tormozitsya ili rezko uskoryatsya,
a sledovatel'no - ne mozhet
byt' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya po etoi prichine.
V svyazi s tem chto dlya uskoreniya do skorosti sveta
pri kotorom vozmozhno izluchenie neobhodimo
ne bolee 10 sekund, a zvezda razmerom s
Solnce na takoi skorosti proletit cherez gorizont
sobytii maksimum za minutu.
Gorizont sobytii - eto skorost' sveta - esli
ob'ekt uletaet s etoi skorost'yu ot nablyudatelya, to
u nego vozniknet krasnoe smeshenie.
Esli by veshestvo dolgo padalo - godami na maloi skorosti
s uskoreniem to bylo by zametno izmenenie Z u padayushih
tel v chernuyu dyru so vremenem, no pri etom nevozmozhno
rentgenovskoe izluchenie - iz za slishkom medlennogo
uvelicheniya uskoreniya.
.... Material iz Vikipedii Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri
vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah.....
A rentgenovskoe izluchenie est' - sledovatel'no
ego istochnikom mozhet byt' tol'ko rezul'tat yadernoi
reakcii.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.....
A esli rezul'tat izlucheniya istochnik yadernoi reakcii -
i on dlitsya godami, - to eto neitronnaya zvezda.
Uvazhaemyi Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe -Padaya na Chernuyu Dyru veshestvo ne mozhet rezko tormozitsya ili rezko uskoryatsya,
Vashe - Razogrevat'sya mozhet? A to, chto nagretoe veshestvo izluchaet,
znaete? Imenno takov mehanizm izlucheniya pri akkrecii. Tam eshe drugie
processy, no dlya Vas, boyus', eto budet slishkom slozhno.
Nazovite pozhaluista fizicheskuyu prichinu,
- ili fizicheskie processy, pri kotoryh razogrevayutsya tela
v vakuume pri svobodnom padenii na drugie tela ?
kosmogon
...Pri padenii zvezdy (bol'shego na men'shee) veshestvo budet peretekat' po plotnoi spirali (akkrecionnyi disk)...
Ne hotel ya zatragivat' etot vopros, blazhenny veruyushie, Vam chestno skazhu -
ne mozhet veshestvo pri uskorennom padenii peretekat' v disk , v pervuyu
ochered' - etot disk tol'ko predpolozhenie i komp'yuternoe modelirovanie.
Nevozmozhnost' ob'yasnit'
legko - Vy govorili o uvelichenii s kvadratom rasstoyaniya - na praktike
pri izmenenii rasstoyaniya v 50 raz vliyanie gravitacii vozrastet v 2500
raz. Iz chego est' fizicheskaya analogiya chto chernaya dyra analogichna
pylesosu, v dannom sluchai pylesos yavlyaetsya chast'yu nekotorogo sektora
chernoi dyry, - tak vot zasoset, tochnee upadet vse v chernuyu dyru vmeste s
akrecionnym diskom i prakticheski mgnovenno. Ibo net prichiny u tela pri
padenii otklonyat'sya ot pryamolineinoi traektorii pri padenii i vyhodit'
na krugovuyu orbitu.
kosmogon
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1186352
Ris. 1
U chernoi dyry bol'shaya gravitaciya, na rasstoyanii naprimer
v 10 diametrov solnca, u chernoi dyry po sravneniyu so zvezdoi po masse kak Solnce gravitaciya naprimer v 1000 raz bol'she.
A na risunkah risuyut ne vziraya na razlichnuyu gravitaciyu, i odni i te-zhe
svoistva, chto dlya dvoinyh zvezd i tozhe samoe kogda zvezda i chernaya dyra.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(M. Yu. Yakimov,
27.05.2011 8:00, 746 Bait)
A.P.Vasi - vashe neponimanie chernoi dyry proishodit vsego navsego iz polnogo neznaniya ili neponimaniyafiziki - eto sovershenno ochevidno iz togo, chto tut u vas ponapisano.
Odin
perl naschet togo, chto veshestvo padaet v chernuyu dyru ne uskoryayas', chego stoit. Voz'mite orbital'nuyu skorost', radius i poschitaite hotya by centrostremitel'noe uskorenie. No
ya tak ponimayu, chto chto-to podschitat' dlya vas delo sovershenno nevozmozhnoe.
I teper' o forume. Pochemu ego tak lyubyat personazhi, podobnye Vasi? Vse prosto. Na lyubom uvazhayushem
sebya forume posty podobnyh avtorov udalyayut, a samih takih avtorov otluchayut ot foruma.
Chtoby na gryadke roslo chto-to krome sornyakov, ee nuzhno propalyvat', gospoda administratory
i moderatory!!!
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.05.2011 9:27, 922 Bait)
M.Yu.Yakimov
Vy ili otvet'te na vopros
- formulirovki chernoi dyry i metodiki
ee obnaruzheniya?
Esli ne mozhete, to Vy boltun, i pustortrep,
i izvineniya v stile - prostit' za nekompetentnost' - prinimayutsya.
Eshe raz Vam ob'yasnyayu, est' avtorskoe
izlozhenie
Chernyh Dyr - eto zakon dlya astrofizikov.
I ni odin astrofizik ne imeet prava izlagat' ili traktovat'
Chernye Dyry kak emu vzdumaetsya, po toi prichine
chto to uzhe ne Chernye Dyry o kotoryh govoril avtor -
a chto-to drugoe.
Vy kogda budete astrofiziku ponimat' a ne znat',
togda u Vas budet vozmozhnost'
obosnovat' pered
moderatorom prichinu Vashei pravoty. A na tekushii moment,
Vy dvuh slov svyazat' i obosnovat' ne mozhete,
i ne mozhete otvetit' na elementarnyi
vopros, tak chto
Vas nado blokirovat' na forume za nekompetentnost'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.05.2011 10:11, 627 Bait)
M.Yu.Yakimov
Vy opredelites' zachem prihodite na forum -
chtoby poobshat'sya s lyud'mi u kotoryh drugaya
tochka zreniya ili
poobshat'sya s takimi zhe kak Vy,
- esli pervoe, - to Vy dolzhny
i zadavat' voprosy i otvechat' obosnovanno na voprosy opponenta,
a esli
vtoroe - to Vam proshe pered zerkalom pogovorit' samim s soboyu.
Na attrakcionah veselo katat'sya,
- tam i ne tak mnogo pravil, - hvalit' i dopolnyat' attrakcion,
i horosho otzyvat'sya o attrakcione, dopolneniyah, i horosho otzyvat'sya o teh
kto na nih kataetsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.06.2011 20:14, 916 Bait)
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,85823.0.html
\\\
Dmitrii
Vibe Moderator
Tema zakryta.\\\
Moderator uzhe vnyatno obosnovat' prichinu
ne mozhet, sovsem mozgi poteryal bedolaga.
A avtor temy to prav, chto nauka lohotron
ustroila,
s gravitaciei, i na prostye voprosy kotorye
v zadachah dlya bolee chem dvuh tel - vsya gravitaciya
yaica vyedennogo ne stoit , i bessmyslennost'
formul vidna dazhe ne specialistam.
A moderator to formulam dlya dvuh tel - rukopleshet,
a zadachu tol'ko zablokirovat' u nego uma hvataet,
a reshit' zadachu
i vnyatno obosnovat' otvet - moderator ne v sostoyanii,
mozgov ne hvataet.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.08.2011 11:47, 1.3 KBait, otvetov: 1)
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,76585.msg1641461.html#msg1641461
Dmitrii Vibe prodolzhaet davit' na liniyu obsuzhdeniya.
\\\augustina, vot
zdes'
ya uzhe prosil Vas vozderzhat'sya ot publikacii novyh smelyh utverzhdenii,
poka Vy ne obosnuete uzhe sdelannye. Tam Vy pisat' perestali, i ya zakryl
na eto glaza. No Vy reshili prodolzhit' generaciyu gipotez, poetomu mne
prihoditsya napomnit' o tom svoem soobshenii.
Ostal'nym uchastnikam
napominayu, chto eta tema posvyashena vozmozhnosti stareniya sveta. Proshu
ogranichit'sya strogo etoi tematikoi. Esli vas volnuyut inye ili bolee
global'nye kosmologicheskie problemy, dlya ih obsuzhdeniya mozhno naiti uzhe
sushestvuyushuyu ili sozdat' novuyu temu.\\\
Ya ob'yasnyu chto proishodit - etot kloun imeet svoyu tochku zreniya kotoraya sovpadaet
s paradigmoi pered kotoroi on chelom
b'et, no v fizike Vibe ne razbiraetsya,
no on ponimaet chto esli sdelayut polnomasshtabnyi analiz vseh vzaimosvyazei,
to nakroetsya mednym tazom vsya paradigma, vot on
i zapreshaet provodit'
prichinnyi analiz, i trebuet govorit' i obsuzhdat' isklyuchitel'no starenie sveta,
a po pravilam foruma eto mozhno delat' tol'ko v ramkah paradigmy.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.08.2011 12:07, 3.1 KBait)
Ya lichno voobshe ne ponimayu togo s kakim userdiem
vse zanimayutsya krasnym smesheniem.
Kak glyadya s tochki zreniya fizika
vynuli zdravyi smysl
i polozhili ego na polku i poshli
zanimat'sya tret'estepennymi zadachami.
Dazhe s tochki zreniya fiziki eta zadacha reshatsya
cherez postanovku opytov fizicheskih s analogichnoi
analogiei - vot etogo nikto ne delaet.
A osnovnye zadachi nikto staraetsya ne zamechat', -
ono udobno polozhit' zdravyi smysl na polku i
zhdat' kogda
pridut lyubiteli i na halyavu
reshat astronomam vse trudnosti.
Vot osnovnye zadachi - kuda devaetsya teplo
i pochemu v kosmose holodno?
Pochemu vnutri
zvezdy net vodoroda?
A vse ostal'nye voprosy poka net otveta
na eti dva eto prosto klounada.
Povtoryu eshe pro BV.
\Esli u predmeta
obsuzhdeniya po fizike,
net odnoznachnogo obsheprinyatogo opredeleniya -
to rassuzhdeniya po etomu predmetu - boltovnya bessmyslennaya.
Boltovnya bessmyslennaya
- ona iz sostavlyayushih
neponyatnyh i neobosnovannyh teorii v fizike.
Kogda Vy soglashaetes' s podobnymi teoriyami
- bud'te bditel'ny, Vam v etom sluchai za Vashe
zhito budut
vechno neponyatno rasskazyvat' o neponyatnom, i
pri etom budete vyglyadet' glupo i ne sposobnym
ponyat' genial'noe.
Ladno chto budete vyglyadet' vsyu
zhizn' glupo,
tak Vy eshe i bessmyslenno potratite uimu vremeni,
a eto ne vremya, eto Vy svoyu zhizn' potratite
na to v chem ne mozhet byt' rezul'tata.
Temnaya
energiya i temnaya materiya iznachal'no
byli pridumany kak podporki paradigmy,
u kotoroi energiya zvezd neponyatno kuda devaetsya v
pustoi pustote, po etoi prichine
kogda v pustoi
pustote est' zvezdy, to pogloshat' teplovuyu energiyu
mogut tol'ko Chernye Dyry, no dlya poglosheniya
energii Chernyh Dyr okazalos' nedostatochno, tochnee
ih nado v tysyachu raz bol'she chem zvezd chtoby bylo,
a uchityvaya chto oficial'no ne obnaruzhili ne
odnoi dyry, po tem parametram o kotoryh govoril
avtor, a potom
avtor peredumal i pomenyal reshenie,
a potom astronomy poslali avtora s ego opredeleniyami
vdal' i stali iskat' i nazyvat' Chernymi Dyrami
to chto im nravitsya a
ne to o chem govoril avtor, vot
togda i stalo ponyatno chto obshestvo poshlet
v dalekuyu dal' esli skazat' chto chernyh
dyr v 1000 raz bol'she chem zvezd. I reshili
utilizirovat' rasshireniem vselennoi,
a potom reshili i uskorennoi, tol'ko ne uchli
chto i v etot lohotron mnogo tepla ot zvezd ne pomestitsya,
i potom na temnuyu
energiyu i temnuyu materiyu reshili
sprosit' vse teplo metodom perebrosa massy,
i skazali chto massa temnoi materii i temnoi
energii stol'ko to procentov. No pri
etom
opyat' ne skladyvaetsya - v bol'shom vzryve to eta
massa ne uchtena, a esli vsya massa materii
pri bol'shom vzryve razogreta do milliona gradusov,
to ohladit'sya
ona mozhet peredav energiyu
drugim telam, a v vakuume - pustoi
pustote drugih tel net, sledovatel'no
esli uchityvat' temnuyu materiyu i temnuyu energiyu
pri bol'shom
vzryve to posle vzryva veshestvo
ne smozhet v pustote ostyt' i budet goryachim vechno.\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A. P. Ivanov,
2.09.2011 13:29, 290 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Ya dumayu chto nikakih chernyh dyr netu.
Chernye dyry sushestvuyut v soznanii lyudei tol'ko iz-za ponyatiya gravitacii.
Pri detal'nom rassmotrenii etogo ponyatiya voznikaet
vopros.
Kak mogut prityagivat'sya dva tela, bez vneshnego vozdeistviya, esli oni uravnovesheny otnositel'no drug druga?
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(V. V. Komogorov,
5.09.2011 16:13, 554 Bait)
Vopros imeet obraz, no kak byt' s opredeleniyami? Chto takoe telo? Esli tela
uravnovesheny, chto yavlyaetsya centrom ravnovesiya? Mozhno poluchit' ravnovesie v
srede, no ukazat', chto yavlyaetsya sredoi. Matematiki i fiziki ob'edinivshis',
sozdali nechto tret'e, chego ne sushestvuet v real'nom mire. Fizik, razglyadyvaya
tochku na fotoplastinke, govorit: chastica. Matematik, stavya tochku na listike,
govorit elektron. Pri etom ponimayut drug druga, nesmotrya na to, chto odin,
risuet vid, a drugoi pytaetsya ponyat' deistvie. Potok v sechenii, tozhe tochkoi
predstavlyaetsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.09.2011 0:37, 1.0 KBait)
Gipotezy, teorii sozdayutsya, kogda net udovletvoritel'nogo ob'yasneniya yavlenii v ramkah deistvuyushei paradigmy.
Vibe
-Kakoe
imenno yavlenie ne imeet udovletvoritel'nogo ob'yasneniya v ramkah
deistvuyushei paradigmy i imeet udovletvoritel'noe ob'yasnenie v ramkah
Vashei "teorii"?\\\
Moderatora zvezdocheta opyat' nachinaet gandol'erit', opponet govorit o paradigme
a moderator peredergivaet svoyu gandollu i gandol'erit
na konflikt.
Vibe dolzhen slozhit' svoe moderatorstvo.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.09.2011 1:00, 544 Bait)
Paradigma dazhe prichiny skorosti sveta ne mozhet
obosnovat', i prichiny togo chto pustota vystupaet
liniei zaderzhki dlya elektromagnitnyh kolebanii
v tom chisle
i svetovyh - u prostranstva to-ist' pustoty
poyavilos' svoistvo. Pryam kak v sredah dlya signalov.
Effekt Doplera dlya sred - vopros pochemu ego
mozhno primenyat'
dlya signalov v pustote? A potomu
chto tam sreda, tol'ko relyativisty ee nikogda ne priznayut,
a svoistvami ee pol'zuyutsya s voplyami - mol volnovye svoistva
fotonov
kotorye chasticy.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.09.2011 18:42, 1.0 KBait, otvetov: 1)
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,88376.msg1675230.html#msg1675230
Nu i konechno, u menya est' pretenzii k samoi paradigme v chasti prostranstva i vremeni.
Ili eto
ne obsuzhdaetsya?
Vibe -Chto "eto"? Vashi personal'nye pretenzii k prostranstvu i vremeni?
Gonite etogo Vibe iz moderatorov, po prichine
togo chto etot moderator
sovsem oborzel, i zapreshaet dazhe somnevat'sya na forume v pravil'nosti paradigmy,
i etot moderator sporit s posetitelyami na pravah moderatora,
vyberite moderatora kotoryi ne lizhet paradigmu,
kotoryi prosto sledit za kul'turoi obsheniya.
Etot upyr' dumaet chto na forume tol'ko ego studenty okolachivayutsya,
- te metody kotorymi on studnei vospityvaet te on i na
forume primenyaet - gnat' v sheyu s moderatorov.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(A. S. Vishnevskii,
19.09.2011 3:13, 1.2 KBait)
<
tbody>| Citata: |
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,88376.msg1675230.html#msg1675230
Nu i konechno, u menya est' pretenz
ii k samoi paradigme v chasti prostranstva i vremeni.
Ili eto
ne obsuzhdaetsya?
Vibe -Chto "eto"? Vashi personal'nye pretenzii k
prostranstvu i vremeni?
Gonite etogo Vibe iz moderatorov, po prichine t
ogo chto etot moderator
sovsem oborzel, i zapreshaet dazhe somnevat'sya na forume v pravil'nosti p
aradigmy,
i etot moderator sporit s posetitelyami na pravah moderatora,
vyberite moderatora kotoryi ne lizhet paradigmu,
kotoryi prosto sledit za kul'turoi obsh
eniya.
Etot upyr' dumaet chto na forume tol'ko ego studenty okolachivayutsya,
- te metody kotorymi on studnei vospityvaet te on i na
forume primenyaet - gnat' v sheyu s moder
atorov.
|
O, e
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.09.2011 12:14, 4.7 KBait)
Ono taki ochen' udobno dlya storonnikov paradigmy
chtoby byli imenno takie pravila na forume kak tam est',
storonniki paradigmy dazhe ne napryagayutsya kogda im govoryat
chto vot tot i vot eto utverzhdenie ne verno.
Ne napryagayutsya po prichine togo chto ne oni eto
pridumali i po etomu ne im za eto otvechat'.
I v itoge poyavlyaetsya
zhelanie u uchastnikov vyglyadet'
krasivo i argumentirovanno i oni predpolozhitel'no
otkryvayut kuchu forumov na drugih saitah po etoi tematike
potom prihodyat
i "padayut na koleni" pered moderatorom
i kak studenty emu otvechayut, po prichine togo chto moderator
ne obosnovanno postavil im zadachu, - nichego ne pisat'
poka ne otvetit na etot vopros. V rezul'tate chego ot treti
do poloviny forumov na membrane byli analogichnye na zvezdochete.
Chto menya udivlyaet, - tak
eto to chto vsya astrofizika krasivaya i pushistaya,
i vse prekrasno.
No eto zhe ne tak, vot te-zhe chernye dyry - eto zhe
prosto pipec - i chto eto nikto ne zamechaet
ili nikto ne
ponimaet.
Hochu srazu sprosit', Vashe mnenie po
...Chernaya dyra...
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188232
Soglasny li Vy s etim?
Kakie iz perechislennyh statei sootvetstvuyut standartam Chernoi
Dyry?
1 Est' li zhizn' v chernoi dyre
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8822-est-li-zhizn-v-chernoy-dyire/
2[ssylka]
Ustanovlena massa samoi krupnoi iz sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr.
Takoe nam i ne snilos'.
3[ssylka]
Mifologiya chernyh dyr.V nashei Galaktike sushestvuyut milliony chernyh dyr
massoi v neskol'ko solnechnyh
4http://www.popmech.ru/article/8140-raspad-dyiryi/
Raspad dyry.
Vzryv sverhnovoi mozhet zakanchivat'sya obrazovaniem ne odnoi, a srazu
neskol'kih chernyh dyr.
5[ssylka]
Detstvo chernoi dyry
Vzryv, zafiksirovannyi v glubinah kosmosa 31 god nazad, sudya po vsemu,
znamenoval rozhdenie chernoi dyry samoi molodoi iz nam izvestnyh
6[ssylka]
Temnyi centr
Tainstvennyi centr nashei galaktiki,
mesto obitaniya sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyry i istochnik moshneishih potokov izlucheniya,
prepodnosit novye syurprizy.
7[ssylka]
Nebol'shoe zamechanie o prirode gravitacii privodit k sledstviyam
kosmicheskogo masshtaba k vyvodam o rozhdenii novyh mirov iz chernyh dyr
8[ssylka]
Obychnaya po razmeram chernaya dyra vybrasyvaet
kolossal'nye potoki izlucheniya i chastic.
9[ssylka]
Astrofiziki predlozhili sposob (teoreticheski) unichtozhit' chernuyu dyru
10[ssylka]
Iz vseh sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr lish' okolo 1% vybrasyvayut
znachitel'nye kolichestva energii
11[ssylka]
Vyzhivayushie dyry
Para redkih ekzemplyarov
V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
kakim-to chudom vyzhivayushih v sosedstve s etim monstrom.
12[ssylka]
Kak zhivetsya vnutri chernoi dyry? Vy i sami znaete,
kak: esli spravedlivy novye teoreticheskie vykladki,
vsya nasha Vselennaya mozhet nahodit'sya vnutri chernoi dyry,
raspolozhennoi v drugoi Vselennoi. Edakaya matreshka mirozdaniya.
13[ssylka]
Oni prosto predpolozhili, chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu. Eto dalo cifru v 10103, tozhe ogromnuyu, no vse-taki na mnogo
poryadkov nizhe.
14[ssylka]
Esli ochen', ochen' bystryi kosmicheskii korabl' razognat'
pochti do skorosti sveta, prevratitsya li on v chernuyu dyru?
15[ssylka]
Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.09.2011 12:38, 28.3 KBait)
1 Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
2
V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
3 Oni prosto predpolozhili,
chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu.
Material iz
Vikipedii
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/39/M87_jet.jpg/250px-M87_jet.jpg
Izobrazhenie, poluchennoe s pomosh'yu teleskopa Habbl: Aktivnaya galaktika
M87. V yadre galaktiki, predpolozhitel'no, nahoditsya chernaya dyra. Na
snimke vidna relyativistskaya struya dlinoi okolo 5 tysyach svetovyh let
Relyativistskie strui
, dzhety (angl. jet) strui plazmy, vyryvayushiesya iz centrov (yader) takih
astronomicheskih ob'ektov, kak aktivnye galaktiki, kvazary i
radiogalaktiki.
Obychno u ob'ekta nablyudaetsya dve strui, napravlennye v protivopolozhnye storony.
Na nastoyashii moment relyativistskie strui ostayutsya nedostatochno izuchennym
yavleniem. Prichinoi poyavleniya takih strui chasto nazyvayut vzaimodeistvie
magnitnyh polei s akkrecionnym diskom vokrug chernoi dyry ili neitronnoi
zvezdy.
V stat'e na Elementah metodom chislennogo modelirovaniya pokazano, chto
pri sliyanii dvuh neitronnyh zvezd obrazuetsya chernaya dyra, magnitnoe pole
kotoroi vytyanuto vdol' osi. Eto navodit na mysli, chto etot zhe process
mozhet formirovat' i relyativistskie strui. Tem ne menee, v stat'e
govoritsya, chto predlozhennaya avtorami nauchnoi raboty matematicheskaya
model' okazalas' ochen' slozhna, a vychislitel'nye vozmozhnosti sovremennyh
komp'yuterov okazalis' nedostatochny, chtoby s dolzhnoi tochnost'yu provesti
vse neobhodimye raschety i ubeditel'no dokazat' formirovanie strui.
V drugoi stat'e na Elementah provodyatsya paralleli mezhdu processami v
chernyh dyrah i boze-einshteinovskom kondensate. Otmechaetsya chto kondensat
mozhet kollapsirovat' (slipat'sya) i pri posleduyushem ego raspade tozhe
mogut voznikat' uzkonapravlennye vybrosy.
Dal'neishee izuchenie relyativistskih strui
Pri samyh pervyh popytkah ob'yasneniya sverhsvetovogo dvizheniya s pomosh'yu
relyativistskogo napravlennogo potoka chastic vozniklo oslozhnenie:
udivitel'no bol'shaya dolya kompaktnyh istochnikov pokazyvala sverhsvetovoe
dvizhenie, v to vremya kak na osnovanii prostyh geometricheskih dovodov
poluchalos', chto tol'ko neskol'ko procentov takih ob'ektov dolzhno byt'
sluchaino orientirovano pochti vdol' linii zreniya. Prisutstvie
simmetrichnyh protyazhennyh radiokomponent predpolagalo, chto oni
obespechivalis' energiei ot central'nogo istochnika dvuh simmetrichnyh
luchei. No trudno sravnit' svetimost' priblizhayusheisya i udalyayusheisya (ili
dazhe stacionarnoi) komponent. Eto ochevidnoe razlichie obychno obsuzhdaetsya v
kontekste modeli s dvoinym istecheniem [4], kogda izluchenie iz yadra
rassmatrivaetsya kak stacionarnaya tochka, gde priblizhayushiisya
relyativistskii potok stanovitsya neprozrachnym. Sverhsvetovoe dvizhenie
nablyudaetsya mezhdu etoi stacionarnoi tochkoi v sople i dvizhushimisya
volnovymi frontami ili drugimi neodnorodnostyami v vyhodyashem
relyativistskom potoke.......
.....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie (gamma-luchi, γ-luchi)
vid elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s chrezvychaino maloi dlinoi volny
< 5×10−3 nm i, vsledstvie etogo, yarko vyrazhennymi korpuskulyarnymi
i slabo vyrazhennymi volnovymi svoistvami.
Gamma-kvantami yavlyayutsya fotony s vysokoi energiei. Obychno schitaetsya,
chto energii kvantov gamma-izlucheniya prevyshayut 105 eV, hotya rezkaya granica
mezhdu gamma- i rentgenovskim izlucheniem ne opredelena. Na shkale
elektromagnitnyh voln gamma-izluchenie granichit s rentgenovskim izlucheniem,
zanimaya diapazon bolee vysokih chastot i energii. V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu. Ochevidno,
fizicheski kvanty elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s odinakovoi energiei ne
otlichayutsya, poetomu takoe razdelenie uslovno.
Gamma-izluchenie ispuskaetsya pri perehodah mezhdu vozbuzhdennymi
sostoyaniyami atomnyh yader (sm. Izomernyi perehod, energii takih
gamma-kvantov lezhat v diapazone ot ~1 keV do desyatkov MeV),
pri yadernyh reakciyah (naprimer, pri annigilyacii elektrona i pozitrona,
raspade neitral'nogo piona i t.d.), a takzhe pri otklonenii energichnyh
zaryazhennyh chastic v magnitnyh i elektricheskih polyah (sm. Sinhrotronnoe izluchenie).....
Esli net poverhnosti ob kotoruyu proishodit tormozhenie.
Material iz Vikipedii
.....Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh
obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v rentgenovskih
trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok yavlyayutsya
metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe antikatodom).
V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom, uskoryayutsya
pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom i katodom
(pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak uskorenie slishkom malo)
i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe tormozhenie. Pri etom za schet
tormoznogo izlucheniya proishodit generaciya izlucheniya rentgenovskogo diapazona,
i odnovremenno vybivayutsya elektrony iz vnutrennih elektronnyh obolochek atomov
anoda. Pustye mesta v obolochkah zanimayutsya drugimi ....
To vstupaet v silu fraza -
V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.
sledovatel'no pri otsutstvii udara o poverhnost' - otsutstvuet sama vozmozhnost'
vozniknoveniya rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, a esli izluchenie est' to ono mozhet
byt' tol'ko rezul'tatom izlucheniya v yadernom perehode. A eto uzhe chasticy vysokih energii.
avtorskoe izluchenie iz chernoi dyry -
.Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash metod obnaruzheniya Chernoi Dyry
-Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
....Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo.
ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut. ....
Padaya na Chernuyu Dyru veshestvo ne
mozhet rezko tormozitsya ili rezko uskoryatsya,
a sledovatel'no - ne mozhet
byt' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya po etoi prichine.
V svyazi s tem chto dlya uskoreniya do skorosti sveta
pri kotorom vozmozhno izluchenie neobhodimo
ne bolee 10 sekund, a zvezda razmerom s
Solnce na takoi skorosti proletit cherez gorizont
sobytii maksimum za minutu.
Gorizont sobytii - eto skorost' sveta - esli
ob'ekt uletaet s etoi skorost'yu ot nablyudatelya, to
u nego vozniknet krasnoe smeshenie.
Esli by veshestvo dolgo padalo - godami na maloi skorosti
s uskoreniem to bylo by zametno izmenenie Z u padayushih
tel v chernuyu dyru so vremenem, no pri etom nevozmozhno
rentgenovskoe izluchenie - iz za slishkom medlennogo
uvelicheniya uskoreniya.
.... Material iz Vikipedii Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri
vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah.....
A rentgenovskoe izluchenie est' - sledovatel'no
ego istochnikom mozhet byt' tol'ko rezul'tat yadernoi
reakcii.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.....
A esli rezul'tat izlucheniya istochnik yadernoi reakcii -
i on dlitsya godami, - to eto neitronnaya zvezda.
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8971-nasledstvennyie-chernyie-dyiryi/page/3/
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke, ya tak ponyal reshil -
zachem dobru propadat' - pust' izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi
dyry budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Vashe - Rentgenovskoe izluchenie ChD voznikaet pri akkrecii veshestva.
Izluchenie Hokinga - drugoi process. Stranno, chto za 7 let "uvlecheniya
astrofizikoi" Vy etogo ne ponyali.
Moe - S moei tochki zreniya - uvazhaemyi A.M.ChEREPAShUK imeet takoe zhe otnoshenie
k Chernym Dyram kak ya ili Vy.
My s Vami, i A.M.ChEREPAShUK mozhem tol'ko predpolagat' i vyskazyvat'
svoyu tochku zreniya, no obrashat' vnimaniya na podobnye vyskazyvaniya i brat'
ih na veru, ya ne vizhu smysla.
Drugoe delo avtor. Kak on skazal to - takie i Chernye Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vot ya naprimer govoryu chto veshestvo padaet na chernuyu dyru,
i posle udara o poverhnost' s protivopolozhnoi storony chernoi dyry voznikaet rentgenovskoe i svetovoe izluchenie.
Drugoi schitaet chto izluchenie na podlete.
V binokl' ne vidno - odni predpolozheniya, i ih mozhet byt'
bol'she sotni naprimer - komu verit'?
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vy zatragivaete vopros interpretacii avtorskih
idei bez soglasiya s avtorom.
A esli desyatok drugih avtorov opublikuyut po 300 nauchnyh rabot, a avtor o
Chernyh Dyrah govorit chto izluchenie v osnovnom iz fotonov - a vse drugie
govoryat, chto
izluchenie iz rentgenovskih chastic, drugoi govorit iz radio izlucheniya, a
tretii govorit iz gamma chastic - ya dolzhen slushat' isklyuchitel'no avtora
Chernyh Dyr,
a ne teh kto interpretiruet, i tem bolee teh kto plevat' hotel na avtorskii variant chernyh dyr.
Nikto ne meshaet pridumat' svoi - rentgenovskie chernye dyry, - tak net ne
hotyat, - tak na neudobnye voprosy otvechat' dolzhen budet avtor, a pri
interpretacii avtora - pisaka naprimer stat'i s levymi ideyami v oblasti
Chernyh Dyr, prikryvaetsya avtorstvom avtora
Chernyh Dyr, a sam so svoim bredom po otnosheniyu k avtorskomu izlozheniyu, kak-by i ne prichem.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
..Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii). Tochnee,
razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Vasha ssylka - tekst 11.05.11 20:36
....Kak otlichit' chernye dyry ot neitronnyh zvezd
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya chernaya dyra ne dolzhna proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. U nee mozhet nablyudat'sya lish' irregulyarnaya
peremennost' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya s harakternymi vremenami
$$Delta tapprox frac{r_g}{c}approx10^{-3} div 10^{-4}~mbox{rm s.}$$
I deistvitel'no, v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme Lebed' H-1, soderzhashei
chernuyu dyru s massoi okolo desyati solnechnyh, v sostoyanii, kogda
rentgenovskaya svetimost' ponizhena, a rentgenovskii spektr zhestkii i
stepennoi, nablyudaetsya bystraya irregulyarnaya peremennost' rentgenovskogo
potoka na vremenah poryadka millisekundy. Nablyudeniya, vypolnennye s
bortov sovremennyh rentgenovskih observatorii, takih, kak GINGA,
MIR-KVANT, GRANAT, ASKA, pokazali, chto rentgenovskie spektry
akkreciruyushih chernyh dyr sistematicheski bolee zhestkie, chem spektry
akkreciruyushih neitronnyh zvezd, i prostirayutsya do energii v neskol'ko
megaelektron-vol't.
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya neitronnaya zvezda mozhet proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. Odnako, esli neitronnaya zvezda obladaet
slabym magnitnym polem (napryazhennost'yu menee 1010 Gs) ili esli ee os'
vrasheniya neudachno orientirovana otnositel'no zemnogo nablyudatelya, pri
akkrecii na takuyu neitronnuyu zvezdu mogut ne nablyudat'sya regulyarnye
pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya. Poetomu otsutstvie strogo
periodicheskih pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya - eto lish' neobhodimyi,
no ne dostatochnyi priznak chernoi dyry. V to zhe vremya pri slabom
magnitnom pole neitronnoi zvezdy i nesil'nom tempe akkrecii veshestva na
ee poverhnosti mogut proishodit' termoyadernye vzryvy nakoplennogo
veshestva, privodyashie k yavleniyu rentgenovskogo barstera I tipa - korotkim
(dlitel'nost'yu poryadka 1-10 s) i moshnym vspyshkam intensivnosti
rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, chto takzhe yavlyaetsya harakternym priznakom
akkreciruyushei neitronnoi zvezdy, obladayushei tverdoi poverhnost'yu.
Poskol'ku chernaya dyra ne obladaet tverdoi poverhnost'yu, akkreciya
veshestva na nee ne dolzhna privodit' k fenomenu rentgenovskogo barstera I
tipa. Razumeetsya, otsutstvie etogo fenomena takzhe yavlyaetsya lish'
neobhodimym kriteriem nalichiya chernoi dyry. Takim obrazom, my mozhem
sformulirovat' vazhneishie priznaki akkreciruyushei chernoi dyry: eto moshnoe
rentgenovskoe izluchenie, bol'shaya massa (bolee treh solnechnyh),
otsutstvie fenomenov rentgenovskogo pul'sara ili rentgenovskogo barstera
I tipa. Pri etom vopros o nadezhnom opredelenii massy relyativistskogo
ob'ekta v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme yavlyaetsya reshayushim pri
identifikacii ego s chernoi dyroi....
Ya Vam prosto pokazyvayu proiivorechie u Vas i Vashei ssylke,
po otnosheniyu k napisannomu v Vikipedii o izluchenii iz Chernoi Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Leitenant Nemo
Chtoby proishodil razbros chastic rentgenovskogo
izlucheniya dlya etogo nado ili yadernoe gorenie zvezd,
chto k chernoi dyre ne primenimo, ili razgon materii
s posleduyushim udarom razognannoi chasticy o poverhnost'
kak eto proishodit v rentgen apparate.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Rentgenovskaya trubka
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v
elektronnyh obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok
yavlyayutsya metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe
antikatodom). V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom,
uskoryayutsya pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom
i katodom (pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak
uskorenie slishkom malo) i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe
tormozhenie. .....
Iz chego vytekaet sleduyushee chto dlya vozniknoveniya izlucheniya radioaktivnyh
chastic - neobhodim udar materii na skorosti odnoi desyatoi i bolee
skorosti sveta.
Iz chego sleduet nevozmozhnoe uslovie dlya izlucheniya materii pri padenii v
chernuyu dyru - tak kak dolzhna byt' poverhnost' dlya udara.
A poverhnosti to i net, veshestvo bez udara uhodit za gorizont sobytii,
sledovatel'no i ne mozhet chernaya dyra izluchat' radioaktivnye chasticy.
A.M.Cherepashyuk v dannom sluchai ne prav.
kosmogon
...Schitaetsya, chto pri padenii na ChD veshestvo razgonyaetsya do skorostei,
blizkih k s. V takom sluchae treniya bolee chem dostatochno dlya izlucheniya
vysokih energii. ...
Ya ne mogu ponyat' pochemu rassmatrivaetsya otdel'no vzyataya chast' i ne argumentiruetsya a postuliruetsya.
U Vas - postulat.
Vy voz'mite naprimer shar razmerom v kilometr v diametre, i bros'te ego v Chernuyu Dyru.
Nu i razognali Vy chto ugodno v pustote, - eshe raz povtoryayu - v pustote
proishodit padenie v chernuyu dyru - kakoe mozhet byt' trenie - prosto ne
ob chto teret'sya.
Voz'mite naprimer zvezdu, ei tozhe ne ob chto teret'sya kogda vokrug pustota,
letit padaet i ugasaet, tem bolee chto mne lichno
uvazhaemyi Dmitrii Mamontov raschety privodil chto zvezda na odnoi desyatoi
ili odnoi tretei skorosti sveta, mozhet prekrasno letat' na orbite
vokrug Chernoi Dyry, i s nei vse normal'no.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
,,,Chernaya dyra - oblast' prostranstva, v k-roi pole tyagoteniya nastol'ko
sil'no, chto vtoraya kosmich. skorost' (parabolicheskaya skorost') dlya
nahodyashihsya v etoi oblasti tel dolzhna byla by prevyshat' skorost' sveta,
t.e. iz Ch.d. nichto ne mozhet vyletet' - ni izluchenie, ni chasticy, ibo v
prirode nichto ne mozhet dvigat'sya so skorost'yu, bol'shei skorosti sveta.
Granicu oblasti, za k-ruyu ne vyhodit svet, naz. gorizontom Ch.d.,,,
Eto bazovoe opredelenie, dazhe esli predpolozhit' chto v chernuyu dyru padayut
zvezdy, pri etom izluchayut, i chto v centre galaktiki v chernyh dyrah
massa bol'she chem massa vseh zvezd v etoi galaktike, a s momenta bol'shogo
vzryva
togda mozhno poschitat' skol'ko milliardov zvezd v dyru v centre galaktiki
upalo. Tol'ko vot ne shoditsya s nablyudeniyami - zvezdy ne ischezayut v
chernyh dyrah - etogo nikto ne nablyudal, - ne nablyudali i to kak zvezda
prohodit cherez gorizont sobytii k chernoi dyre.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
...Ishodya iz klassiki, na kotoruyu Vy opiraetes', ChD dlya zemlyanina dolzhny svetit' kak kvazary....
Vashe - Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Moe - u menya vopros - esli v rentgen diapazone izluchayut nizhe privedennye
neitronnye zvezdy - kotorye
...V sluchae, kogda peretekanie veshestva prodolzhaetsya i posle
obrazovaniya N. z., ee massa mozhet so vremenem znachitel'no uvelichit'sya.
Pri ${mathfrak M}_{N.z.}>{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet
ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa
prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru. ...
To kak otlichit' neitronnuyu zvezdu ot chernoi dyry?
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188472
Neitronnye zvezdy
- gidrostaticheski ravnovesnye zvezdy, veshestvo k-ryh sostoit v osnovnom
iz neitronov. Sushestvovanie N. z. bylo predskazano v 30-h gg. 20
v.,vskore posle otkrytiya neitrona. Odnako tol'ko v 1967 g. oni byli
obnaruzheny v vide impul'snyh istochnikov radioizlucheniya - pul'sarov.
Zatem bylo ustanovleno, chto N. z. proyavlyayut sebya takzhe kak rentgenovskie
pul'sary (1971 g.) i vspyshechnye istochniki rentg. izlucheniya - barstery
(1975 g.). Ne isklyucheno, chto na odnoi iz stadii sushestvovaniya N. z. yavl.
istochnikami gamma-vspleskov. K 1984 g. otkryto ok. 400 N. z., iz nih
ok. 20 v vide rentg. pul'sarov, ok. 40 v vide barsterov, a ostal'nye v
vide obychnyh radiopul'sarov.
Druguyu vozmozhnost' poyavleniya N. z. predstavlyaet evolyuciya belyh karlikov v
tesnyh dvoinyh zvezdnyh sistemah. Peretekanie veshestva so
zvezdy-kompan'ona na belyi karlik postepenno uvelichivaet ego massu, i,
kogda ona dostigaet ${mathfrak M}_Ch$, belyi karlik prevrashaetsya v N. z. V
etom sluchae ${mathfrak M}_{N.z.}{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet
ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa
prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188644
Rentgenovskie pul'sary
- istochniki peremennogo periodicheskogo rentg. izlucheniya, predstavlyayushie
soboi vrashayushiesya neitronnye zvezdy s sil'nym magn. polem, izluchayushie za
schet akkrecii (padeniya veshestva na ih poverhnost'). Magn. polya na
poverhnosti R.p. ~ 1011-1014 Gs. Svetimosti bol'shinstva R.p. ot
1035-1039 erg/s. Periody sledovaniya impul'sov P ot 0,7 s do nesk. tysyach
s. R.p. vhodyat v tesnye dvoinye zvezdnye sistemy, vtorym komponentom
k-ryh yavl. normal'naya (nevyrozhdennaya) zvezda, postavlyayushaya veshestvo,
neobhodimoe dlya akkrecii i norm. funkcionirovaniya R.p. Esli vtoroi
komponent nahoditsya na stadii evolyucii, kogda skorost' poteri massy
(etim komponentom) mala (sm. Evolyuciya tesnyh dvoinyh zvezd), neitronnaya
zvezda ne proyavlyaet sebya kak R.p. Rentg. pul'sary vstrechayutsya kak v
massivnyh molodyh dvoinyh zvezdyh sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu I
Galaktiki i lezhashih v ee ploskosti, tak i v malomassivnyh dvoinyh
sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu II i prinadlezhashih k sferich.
sostavlyayushei Galaktiki. R.p. otkryty takzhe v Magellanovyh Oblakah. Vsego
otkryto ok. 20 R.p.
Na nachal'nom etape issledovanii otkryvaemym rentg. ob'ektam
prisvaivalis' naimenovaniya po sozvezdiyam, v k-ryh oni nahodyatsya. Napr.,
Gerkules X-1 oznachaet pervyi po rentg. yarkosti ob'ekt v sozvezdii
Gerkulesa, Kentavr H-3 - tretii po yarkosti v sozvezdii Kentavra. R.p. v
Malom Magellanovom Oblake oboznachaetsya kak SMC X-1, v Bol'shom
Magellanovom Oblake - LMC X-4. Obnaruzhenie so sputnikov bol'shogo chisla
rentg. istochnikov potrebovalo dr. sistemy oboznachenii.
Uskorenie i zamedlenie vrasheniya neitronnyh zvezd.
V otlichie ot radiopul'sarov (nek-rye iz k-ryh, v chastnosti pul'sary v
Krabe i Parusah, izluchayut i v rentg. diapazone, sm. Pul'sary),
izluchayushih za schet energii vrasheniya zamagnichennoi neitronnoi zvezdy i
uvelichivashih svoi period so vremenem, R.p., izluchayushie za schet akkrecii,
uskoryayut svoe vrashenie.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Spasibo za otvet.
Esli ya pravil'no ponyal, to istochnik
nepreryvnogo rentgenovskogo izlucheniya
so stabil'noi intensivnost'yu - nazyvaetsya
Chernoi Dyroi .
Esli rentgenovskoe izluchenie menyaet intensivnost'
to eto ili neitronnaya zvezda ili
rentgenovskii pul'sar.
Zdes' avtor chernyh dyr - sem' pyatnic na nedelyu,
sperva govoril vot tak -
...Chernaya dyrá oblast' v prostranstve-vremeni,
gravitacionnoe prityazhenie kotoroi nastol'ko veliko,
chto pokinut' ee ne mogut dazhe ob'ekty, dvizhushiesya
so skorost'yu sveta (v tom chisle i kvanty samogo sveta)....
Potom ego ozarilo v 1975 i on odaril chernye dyry i vseh
astrofizikom izlucheniem ot chernyh dyr.
---...Izluchénie Hókinga ...---
......Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi.
Predskazan teoreticheski Stivenom Hokingom v
1974 godu.[1] Rabote Hokinga predshestvoval
ego vizit v Moskvu v 1973 godu, gde on vstrechalsya
s sovetskimi uchenymi Yakovom Zel'dovichem i
Alekseem Starobinskim. Oni prodemonstrirovali
Hokingu, chto v sootvetstvii s principom
neopredelennosti kvantovoi mehaniki
vrashayushiesya chernye dyry dolzhny
porozhdat' i izluchat' chasticy.[2]
Isparenie chernoi dyry kvantovyi process.
Delo v tom, chto ponyatie o chernoi dyre kak ob'ekte,
kotoryi nichego ne izluchaet, a mozhet lish' pogloshat' materiyu,
spravedlivo do teh por, poka ne uchityvayutsya kvantovye effekty.
V kvantovoi zhe mehanike, blagodarya tunnelirovaniyu,
poyavlyaetsya vozmozhnost' preodolevat' potencial'nye bar'ery,
nepreodolimye dlya nekvantovoi sistemy. Utverzhdenie,
chto konechnoe sostoyanie chernoi dyry stacionarno,
pravil'no lish' v ramkah obychnoi, ne kvantovoi teorii
tyagoteniya. Kvantovye effekty vedut k tomu, chto na samom
dele chernaya dyra dolzhna nepreryvno izluchat', teryaya pri
etom svoyu energiyu.....
Itogo
...Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke,
ya tak ponyal reshil - zachem dobru propadat' - pust'
izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi dyry
budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A vot zdes' ya Vam mogu predlozhit' sdelat' u kazhdoi stat'i schetchik, - ponyal -ne ponyal,
Vashe - Dlya bazovogo ponimaniya nuzhno umet' chitat' i imet' nekotoruyu
podgotovku v ramkah hotya by shkoly. U Vas takaya podgotovka, sudya po
vsemu, hromaet na obe nogi, poetomu Vy ne ponimaete bol'shinstvo statei.
Dlya utochnyayushih voprosov est' kommentarii, dlya bazovoi podgotovki - shkola
i uchebniki.
- Vy dumaete chto vse uchennye pishut pravil'nye stat'i, i nikto stat'i ne
vysasyvaet iz pal'ca a potom ne rzhet nad chitatelyami, a Vash sait chtoby
chitat' - to nado byt' doktorom nauk, i v tozhe samoe vremya Vy lichno ne
mozhete otvetit' pryamo na pryamye voprosy, po etoi stat'e. Vy menya v
principe zaintrigovali, ya podumayu chtoby takoi puzyr' vysosat' iz pal'ca v
ramkah paradigmy, chtoby vse vokrug azh zaaplodirovali za isklyuchitel'no
vysokohudozhestvennyi idiotizm v ramkah breda sivoi kobyly.
Moe-Ne rasskazhete Vashe otnoshenie k vyskazyvaniyu, -
Esli opyt ne sovpadaet s teoriei to tem huzhe dlya opyta?
Napomnyu -
Moe - So vtorogo Vashego otveta ya ponyal - chto u Vas est' metody
dokazatel'stv kotorye pozvolyayut opredelit' kakimi byli v pervye momenty
bol'shogo vzryva zvezdy, chernye dyry , temperatura i drugie razlichnye
svoistva prostranstva i svoistva razlichnyh fizicheskih ob'ektov.
Vashe - Ne u menya. U astronomov, astrofizikov i kosmologov.
Moe- Esli mne ne mozhet opponent srazu vnyatno izlozhit' otvet na moi
prostoi vopros po obsuzhdaemoi stat'e, to ya ne obyazan verit' napisannomu,
a skoree naoborot - vynuzhden zasomnevat'sya.
Po povodu gromkih familii v astrofizike - to esli Vy proanaliziruete ih
biografiyu i trudovye zaslugi i proanaliziruete ih prichastnost' k
astrofizike, to oni vse v astrofizike - diletanty, kotorye idei
vbrasyvali v astrofiziku ot sluchaya k sluchayu, i ser'ezno ei ni kto ne
zanimalsya. Po etomu vsya astrofizika i sostoit iz razroznennyh idei, -
ozaryalok, kotorye posledovateli pytayutsya sostykovyvat' mezhdu soboi po
prichine poyavleniya novoi izmeritel'noi tehniki.
A astrofiziku u menya hobbi let 7, tak chto ya prochital stol'ko statei
raznyh, chto mogu delat' vyvody chto vysoska iz pal'ca, a chto i super
gramotno napisano .
Samoe smeshnoe chto super stat'i absolyutno neizvestny.
http://crydee.sai.msu.ru/Universe_and_us/4num/v4pap26.htm
-Ochen' horoshaya stat'ya.
http://www.anomaliy.ru/discovery/482
"Sverhnovye tipa I a, kak polagayut, formiruyutsya
posle vzryvov belyh karlikov, sverhplotnyh mertvyh zvezd razmerom s
nashu Zemlyu, kotorye kogda-to byli yadrom solncepodobnogo svetila, i
ch'ya vneshnyaya obolochka rastvorilas' v kosmose.
Odna iz osobennostei etogo tipa otsutstvie vodoroda, i eto
nesmotrya na to, chto vodorod yavlyaetsya samym rasprostranennym
himicheskim elementom."
Vot eta stat'ya - v principe dolzhna byla perevernut' vsyu astrofiziku,
po toi prichine chto net vodoroda vnutri zvezdy. A u tekushei paradigmy
vodorod vygoraet. I astrofiziki vnyatno otvetit' ne mogut prichinu po
kotoroi samyi legkii vodorod - preodolevaet gravitaciyu stanovitsya
tyazhelee vseh metallov i letit v yadro zvezdy pouchastvovat' v yadernoi
reakcii. I V to chto samyi legkii vodorod preodolevaet letit vnutr'
zvezdy -ya ne veryu, hot' v millione knizhek eto budet napisano, i tysyache
uchebnikov. Tak kak napisannoe ne podtverzhdeno fizicheskimi svoistvami a
protivorechit im.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.09.2011 15:51, 2.3 KBait)
http://www.wikiznanie.ru/ru-wz/index.php/%D0%AD%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%82%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BD-%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%8C%D1%82
Elektronvol't edinica izmereniya energii, ravnaya energii, neobhodimoi dlya perenosa elektrona mezhdu raznicei potencialov
1V, shiroko
primenyaemaya v atomnoi,
yadernoi
fizike i fizike
elementarnyh chastic.
Dlya teh kto ne ponyal - eto edenica izmereniya perenosa chasticy v uskoritele,
ukazyvayushaya kakoe uskoryayushee napryazhenie prilozheno dlya uskoreniya chasticy,
ili analogichnoe napryazhenie v rezul'tate tormoznogo izlucheniya,
povyletayut zaryazhennye oskolki.
"...
uchenye poluchili znacheniya mass verhnego kvarka - 2,01 0,14
megaelektronvol'ta - i nizhnego kvarka - 4,79 0,16 megaelektronvol'ta.
Eto sostavlyaet sootvetstvenno 0,214 i 0,510 procenta ot massy protona.
Takim obrazom, fiziki umen'shili pogreshnost' v opredelenii massy legkih
kvarkov s 30 do 1,5 procentov. " http://lenta.ru/news/2010/04/05/quarks/
.
Nu pri chem zdes' massa k prilozhennomu uskoryayushemu napryazheniyu na uskoritele,
dobavlyu naprugi bysree poletyat, i massa oskolka uvelichitsya - zaryad uvelichitsya,
tochnee dazhe ne zaryad uvelichitsya a energiya raskrutki oskolka atoma uvelichitsya,
kamera Vil'sona tomu podtverzhdenie, tak kak s povysheniem
uskoryayushego, pri tormozhenii
vyletayut s opredelennogo
napryazheniya - chasticy kotorye otklonyayutsya magnitnym polem,
chto govorit o tom chto oskolok vrashaetsya s opredelennogo napryazheniya uskoryayushego.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
20.09.2011 10:05, 1.8 KBait)
Otvet #4 : Segodnya v 06:44:07
Vibe - Net uzh, dostatochno temy pro starenie sveta. Etu temu ya zakryvayu.\\\
Gonite etogo star-pera v smysle zvezdnogo
tolkatelya.
Ya vot ne ponimayu kakoi umnik dodumalsya pustit' kozla v ogorod
http://elementy.ru/lib/430399
u Vibe est' svoe viden'e i emu gluboko ...
na mnenie drugih,
emu vazhnee ne obhezat'sya pered stud'nyami,
Vot ego tekst
\\\Takuyu vozmozhnost' nam predostavlyayut
zvezdnye skopleniya. (Zvezdy vnih, konechno, obrazuyutsya ne sovsem
odnovremenno, no vbol'shinstve sluchaev razbros vozrastov otdel'nyh zvezd
men'she srednego vozrasta skopleniya.) Teoriya zvezdnoi evolyucii
predskazyvaet, chto zvezdy razlichnyh mass evolyucioniruyut po-raznomu chem
massivnee zvezda, tem bystree ona zakanchivaet svoi zvezdnyi put'.
Poetomu chem starshe skoplenie, tem nizhe opuskaetsya planka maksimal'noi
massy naselyayushih ego zvezd. Naprimer, vochen' molodom zvezdnom skoplenii
Arches (Arki), raspolozhennom vblizi centra Galaktiki, est' zvezdy
smassoi vdesyatki solnechnyh mass. Takie zvezdy zhivut ne bolee
neskol'kih millionov let, stalo byt', imenno takov maksimal'nyi vozrast
etogo skopleniya. Avot vsharovyh skopleniyah naibolee tyazhelye zvezdy
imeyut massu ne bolee 2mass Solnca. Eto govorit otom, chto vozrasty
sharovyh skoplenii izmeryayutsya milliardami let.\\\
I nado byt' dyb_ilom, chtoby dumat' chto Vibe buduchi moderatorom
soglasitsya s vechnoi vselennoi. Ovna v tachku,
vse chto ne
sovpadaet so stat'ei napisannoi Vibe vse budet zabaneno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
20.09.2011 10:19, 952 Bait, otvetov: 1)
k Staticheskoi Vselennoi mozhno stavit' bol'she voprosov, chem k gipoteze stareniya sveta.
Vibe - Che, ya dumayu, chto
otkryvat' novuyu temu budet imet' smysl, kogda u Vas budut otvety na eti voprosy.\\\
Gonite v sheyu Vibe iz moderatorov, v dannom sluchai on govorit posetitelyu,
chtoby tot so svoei teoriei shel k sebe domoi na kuhnyu i tam ei zanimalsya,
a na forumah iskat' otvety i obsuzhdat' i konsul'tirovat'sya s drugimi mogut
tol'ko
te kto v paradigme - izbrannye i mahrovye relyativisty.
Vot teper' etot posetitel' poidet na skai teh ili membranu - i otkroet
tam obsuzhdeniya, chem sobstvenno budet
zamusorivat' te saity po prichine
togo chto tam do lampochki voprosy podnimaemye astronomami.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.10.2011 14:01, 2.2 KBait)
 S moei tochki zreniya osnovnaya trudnost' v fizike
- nalichie v nei geniev, po prichine togo chto krome
geniev v fizike mogut byt' nedoumki i difektivnye,
i nedogenii.
Grubo govorya fiziki delyatsya na dva osnovnyh klassa
genii i nedoumki, srednego ne dano.
Po skol'ku geniev edinicy - to vse vospityvayutsya v stile
nedoumkov, v principe ne sposobnyh svoimi slovami otvetit'
na voprosy po fizike, po skol'ku svoi mysli schitayut
myslyami nedoumkov, i sovetuyut pochitat' knizhki
geniev s ih tochki zreniya. Pri obshenii fizikov to i proishodit
vzaimoposylanie chitat' knizhki.
Vot takaya zhestokaya selyavi.
S moei tochki zreniya osnovnaya trudnost' v fizike
- nalichie v nei geniev, po prichine togo chto krome
geniev v fizike mogut byt' nedoumki i difektivnye,
i nedogenii.
Grubo govorya fiziki delyatsya na dva osnovnyh klassa
genii i nedoumki, srednego ne dano.
Po skol'ku geniev edinicy - to vse vospityvayutsya v stile
nedoumkov, v principe ne sposobnyh svoimi slovami otvetit'
na voprosy po fizike, po skol'ku svoi mysli schitayut
myslyami nedoumkov, i sovetuyut pochitat' knizhki
geniev s ih tochki zreniya. Pri obshenii fizikov to i proishodit
vzaimoposylanie chitat' knizhki.
Vot takaya zhestokaya selyavi.
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,79449.msg1722187.html#msg1722187
Vot Vibe naprimer zanimaetsya gandol'erizmom,
on voobshe nasazhdaet vsem podryad edinstvenno
pravil'nuyu tochku zreniya, ibo kak fizik on ne genii.
\\/Imenno chto po fizike. A Poisk Istiny -- eto filosofiya. Na filosofskom
forume Vas, veroyatno, privetili by i s oduvanchikami, i s apel'sinami. A v
fizike glavnoe -- chtoby rabotalo./\\
Sovsem otupel uzhe - kak rabotaet zamedlenie vremeni pust' rasskazhet, i kak rabotaet prityazhenie,
i krivizna prostranstva
- i kakimi izmeritel'nymi instrumentami eto izmeryaetsya.
Etomu ne geniyu dazhe ne ponyat' chto fizike do lampochki chtoby rabotalo,
- fizike nado ob'yasnit' prichinu, i
izmerit'.
\\\Konechno. No pochemu Vy reshili, chto zanimaetes' fizikoi? U menya vot,
naprimer, fizicheskoe obrazovanie, i po rabote ya, vrode kak, fizik. A
nichego, krome uprazhnenii v izyashnoi slovesnosti, ya v Vashih tekstah ne
vizhu. I u menya est' sil'noe podozrenie (osnovannoe na replikah drugih
uchastnikov), chto ya ne odinok v takom ih vospriyatii.\\\
Vot ocherednoe zhelanie probit'sya v genii mestnogo razliva, a pontov i pafosa kak budto ego
prepodavatel'
byl Tomas Yung, a na samom dele prohodilo gruppovoe chtenie
knig po relyativizmu s zauchivaniem naizust'.
\\\Eto ochen' horosho. No pochemu Vy tak stremites' navyazat'
eto ob'yasnenie drugim?\\\
Tol'ko gandol'er mahrovyi ne ponimaet chto lyubaya diskussiya, lekciya, prepodavanie eto navyazyvanie
drugoi tochki zreniya komu libo.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.11.2011 23:58, 1.6 KBait)
Shahsei-vahsei,
napishite, pozhaluista, zdes', zachem nuzhny Vashi izyskaniya. Ukazhite
konkretnye eksperimenty, kotorye Vy ob'yasnyaete luchshe, a takzhe podrobno
opishite novye eksperimenty, kotorye pozvolyat podtverdit' ili
oprovergnut' Vashu tochku zreniya. Do togo kak Vy eto sdelaete, proshu
drugie soobsheniya v razdele ne publikovat'.
Shahsei-vahsei, poskol'ku Vy moi slova demonstrativno ignoriruete, ya Vam zakryvayu vozmozhnost' publikacii
na nedelyu.\\\
\\\Tema zakryvaetsya do vyhoda avtora iz bana.\\\
U menya prosto segodnya prazdnik,
gandol'er vibe narushil vse prava moderatora,
on sozdal samovol'no novye pravila foruma, -
prinyal na sebya funkcii vladel'cev foruma,
zakonotvorchestvo ne ogovorennoe pravilami
foruma - sozdal tradicii,
posle etogo vystupil v kachestve poterpevshego
chmoshnika na vopros kotorogo ne bylo otveta
(po nepisannym pravilam novyh vibevskih tradicii),
posle etogo
vystupil v kachestve sud'i ot
imeni vozmushennogo chmoshnika (egozhe sobstvenno) kotoromu
ne otvetili na ego razvedyvatel'nyi vopros
kotoryi vynuzhdal otvechayushego
rasstat'sya so svoimi
avtorskim pravami - v pol'zu kakogo-to gandol'era.
Posle chego vibe sovsem oborzel i zakryl forum,
na osnovanii togo , sobstvenno
ponyatno chego, -
chto vse vokrug za bz dyat emu kak moderatoru perechit',
a knopki pozhalovat'sya na gandol'era
moderatora - hozyaevam foruma net.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.11.2011 1:17, 1.1 KBait)
Otvet #16 : 19.11.2011 [22:00:57]
lorein, otvet'te,
pozhaluista, na tradicionnyi vopros. Zachem nuzhno to, chto Vy pishete? Vy
luchshe ob'yasnyaete kakie-to eksperimenty? Mozhet byt', predskazyvaete
rezul'taty budushih eksperimentov?
Yarkii primer razvedyvatel'nogo tradicionnogo voprosa chtoby shopnut' ideyu
i avtorskie prava, ibo dlya togo chtoby zabrat' prava
est' osnovanie -
i prava mogut uiti s formulirovkoi - navodyashii vopros,
otvet na kotoryi byl dopolnen formuloi.
A otvet s formuloi i otvet bez formuly
- na segodnyashnii den'
eto dve raznye vesovye kategorii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.11.2011 13:17, 3.4 KBait)
Novaya situaciya na forume, uchastniki obsuzhdeniya
priblizhayutsya k tomu chtoby nagnut' relyativistov
i zdes' poyavlyaetsya "vibenok" i mashet pravilami
foruma
i ne daet prodolzhatsya diskussii.
S drugoi tochki zreniya "vibenok" prost kak kusok
..., emu nado chtoby avtor povedal emu nyuansy,
posle etogo mozhno
zapustit' poisk resheniya
metodom "ansamblya", dlya etogo nado imet'
ansambl', a u "vibenka" on est'.
Tak vot posle togo kak avtor rasskazyvaet
o nyuansah, "vibenok" na zakrytom obsuzhdenii
ot drugih, razdaet svoim studentam zadachi
s etimi nyuansami, posle chego rezul'taty
on budit svodit'
po srednemu, po luchshemu variantu
on ne smozhet tak kak on ne fizik, posle chego
pririsovyvaet formuly s pomosh'yu
programmy "matematika" i bezhit potom
zashishat'sya na novuyu stepen'.
------------------------------------------------------------
Da
mogu, konechno, odnako ne vizhu neobhodimosti obrushivat' srazu lavinu
novyh znanii na auditoriyu, slabo znakomuyu so specifikoi sploshnoi sredy.
Zachem "gnat' loshadei"?
"vibenok"
Zatem, chto takovy pravila, prinyatye v razdele.
O razdele Gorizonty nauki o Vselennoi.
Vvidu
ser'eznosti rassmatrivaemyh mirovozzrencheskih problem, u menya bol'shaya
pros'ba k Vam, gospodin moderator: pozvolit' diskussii razvivat'sya tak,
kak ona i razvivaetsya. Nespeshno, no v napravlenii korrelyacii s
Real'nost'yu i zakonami klassicheskoi fiziki.
"vibenok"
Vy special'no dlya menya srazu
napishite, zachem nuzhna Vasha teoriya, kak ee mozhno proverit'
eksperimental'no. Ya na etom uspokoyus', i diskussiya smozhet spokoino i
nespeshno razvivat'sya hot' v napravlenii real'nosti, hot' v napravlenii
klassicheskoi fiziki.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Vibenok narushaet pravila foruma i dazhe sam ne ponimaet
chto imenno narushaet
- marazm i star perenie beret svoe.
------------------------------
Dmitrii Vibe: To
est', poka dokazat' nuzhnost' svoei teorii Vy ne mozhete?
Chital gde-to, chto elektrodinamicheskaya teoriya Maksvella poluchila
priznanie daleko ne srazu. I glavnym vozrazheniem byl tezis o tom, chto,
"mozhet byt', matematicheski i vse verno - no eto sovershenno bespolezno, a potomu i obsuzhdat' fizikam nechego..."
"vibenok"
Interesno, kak Maksvell na eto reagiroval. Brodil po telegrafnym forumam i nyl, chto ego nikto ne ponimaet?
-----------------------------------------------------
Pravilami etogo foruma ne zapreshaetsya
vyskazyvat' svoe ob'ektivnoe mnenie o moderatore s drugogo foruma.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.11.2011 14:40, 3.8 KBait)
\\\"vibenok"
I eto obsuzhdenie tozhe ostanetsya nezavershennym. Potomu chto zavershenie
nauchnoi diskussii -- eto predlozheniya po eksperimental'noi proverke. Tak
chto vse-taki: kakie Vy vidite prespektivy po eksperimental'noi proverke
Vashih idei?\\\
Etomu ne geniyu dazhe ne ponyat' chto fizike do lampochki chtoby rabotalo,
- fizike nado ob'yasnit' prichinu, i
izmerit'.
Kstati hochu eshe raz akcentirovat'
vnimanie na to chto "vibenok" gonit golimyi
porozhnyak v svoih utverzhdeniyah ot imeni vsei
fiziki.
I vse dolzhny ponimat' chto esli gandol'er
utverzhdaet chto mol fizike glavnoe chtoby rabotalo -
to nado ponimat' - lyubaya rech' gandol'era iznachal'no
bespolezna dlya drugih i polezna dlya nego lichno.
----------------
Povtoryu tak kak aktual'no,
ibo vse delayut oshibki odni i te-zhe togo ne ponimaya.
S moei tochki zreniya osnovnaya trudnost' v fizike
- nalichie v nei geniev, po prichine togo chto krome
geniev v fizike mogut byt' nedoumki i difektivnye,
i nedogenii.
Grubo govorya fiziki delyatsya na dva osnovnyh klassa
genii i nedoumki, srednego ne dano.
Po skol'ku geniev edinicy - to vse vospityvayutsya v stile
nedoumkov, v principe ne sposobnyh svoimi slovami otvetit'
na voprosy po fizike, po skol'ku svoi mysli schitayut
myslyami nedoumkov, i sovetuyut pochitat' knizhki
geniev s ih tochki zreniya. Pri obshenii fizikov to i proishodit
vzaimoposylanie chitat' knizhki.
Vot takaya zhestokaya selyavi.
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,79449.msg1722187.html#msg1722187
Vot Vibe naprimer zanimaetsya gandol'erizmom,
on voobshe nasazhdaet vsem podryad edinstvenno
pravil'nuyu tochku zreniya, ibo kak fizik on ne genii.
\\/Imenno chto po fizike. A Poisk Istiny -- eto filosofiya. Na filosofskom
forume Vas, veroyatno, privetili by i s oduvanchikami, i s apel'sinami. A v
fizike glavnoe -- chtoby rabotalo./\\
Sovsem otupel uzhe - kak rabotaet zamedlenie vremeni pust' rasskazhet, i kak rabotaet prityazhenie,
i krivizna prostranstva
- i kakimi izmeritel'nymi instrumentami eto izmeryaetsya.
Etomu ne geniyu dazhe ne ponyat' chto fizike do lampochki chtoby rabotalo,
- fizike nado ob'yasnit' prichinu, i
izmerit'.
\\\Konechno. No pochemu Vy reshili, chto zanimaetes' fizikoi? U menya vot,
naprimer, fizicheskoe obrazovanie, i po rabote ya, vrode kak, fizik. A
nichego, krome uprazhnenii v izyashnoi slovesnosti, ya v Vashih tekstah ne
vizhu. I u menya est' sil'noe podozrenie (osnovannoe na replikah drugih
uchastnikov), chto ya ne odinok v takom ih vospriyatii.\\\
Vot ocherednoe zhelanie probit'sya v genii mestnogo razliva, a pontov i pafosa kak budto ego
prepodavatel'
byl Tomas Yung, a na samom dele prohodilo gruppovoe chtenie
knig po relyativizmu s zauchivaniem naizust'.
\\\Eto ochen' horosho. No pochemu Vy tak stremites' navyazat'
eto ob'yasnenie drugim?\\\
Tol'ko gandol'er mahrovyi ne ponimaet chto lyubaya diskussiya, lekciya, prepodavanie eto navyazyvanie
drugoi tochki zreniya komu libo.
"vibenok" prodolzhaet svoyu seriyu naglyh
razvedyvatel'nyh voprosov chtoby ukrast' chuzhie idei,
on prekrasno ponimaet chto zavtra esli on budet ostavat'sya
"relyativistom mahrovym", ego kormovaya baza budet
na skudnom racione, a vlez't' v al'ternativshiki
on mozhet tol'ko shopnuv idei al'tov.
Re: Mehanika sploshnoi sredy i Vselennaya"vibenok"\\\\Oh...
Esli Vy predlagaete novye vzglyady, znachit, starye Vas chem-to ne
ustraivayut. Chem? Esli Vy predlagaete novye vzglyady, znachit, oni v chem-to
luchshe staryh. V chem?\\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.11.2011 15:20, 687 Bait)
 Posmotrel fil'm ponravilsya, kak-by
Posmotrel fil'm ponravilsya, kak-by
fil'm
po astrofizike v hudozhestvennom variante.
V poiskah galaktiki / Galaxy Quest (1999) [BDRip 720p]
http://www.ex.ua/view/2039278?r=2
 Posmotrel klip, i slegka obnaruzhil temnuyu materiyu i temnuyu energiyu.
Posmotrel klip, i slegka obnaruzhil temnuyu materiyu i temnuyu energiyu.
The Rasmus - October
and April (2009)
http://www.ex.ua/view/208350?r=1991
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.11.2011 15:46, 1.7 KBait)
"vibenok"
\\\Net, konechno. Ya i ne proshu predstavit' dissertaciyu ili gotovuyu
nobelevskuyu rech'. U menya odna, vsego odna, ma-a-alen'kaya pros'ba.
Napisat' o perspektivah eksperimental'noi proverki.\\\
Gandol'er prodolzhaet razvedku sam togo ne podozrevaya chto trebuet
ot kazhdogo uchastnika foruma byt' akademikom.
A esli ne akademik - to ukrast' u nego ideyu i zabanit'.
Ob'yasnyu chto hochet etot gandol'er.
Delo v sleduyushem - chtoby razrabotat' prakticheskii opyt,
nado znat' vse analogi provodivshihsya opytov, posle etogo
nado ponyat' chto Fizikov na planete bylo edinicy, kotorye vnyatno
mogli ob'yasnit' svoi opyty. Sledovatel'no
nado samostoyatel'no
pereob'yasnit' vse opyty i naiti nekotoruyu global'nuyu
oshibku dlya vseh opytov.
Posle etogo nado razdelitsya na dva puti poiska,
odin
variant pridumat' metodiku izmereniya global'noi oshibki,
ili chastnoi dlya kakogo-to opyta.
Vtoroi variant metodiku vneshnego vozdeistviya na dannyi opyt.
Byvaet
tak chto nado budet zadeistvovat' i tretii variant,
poisk i analiz fiz analogov s cel'yu provesti opyt
na analogii, a potom provesti opyt po faktu, ili
dlya
dokazatel'stva analogiei.
Posle chego modeliruetsya sam opyt.
Tak vot tot kto smozhet eto vse sdelat',
tak tomu "vibenok" intellektom v
pup dyshit.
Sledovatel'no gandol'er on potomu i gandol'er
chto stavit nevypolnimye trebovaniya i posle
etogo ustraivaet proizvol.
Sobstvenno
konyu ponyatno chto takie trebovaniya mozhet
vypolnit' tol'ko gruppa fizikov s finansirovaniem
na urovne milliona evro (kazhdomu) v god kak minimum,
a umstvennye
sposobnosti dolzhny zashkalivat'
i pered nimi vse dolzhny prisedat' i delat' dva raza ku.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.11.2011 17:48, 1.7 KBait)
Kakie -to u Vas strannye predstavleniya o Poznanii...
"vibenok"
Uzh kakie est'. Chto glavnoe -- oni sovpadayut
s predstavleniyami vladel'cev foruma i ego administracii.\\\
Zadavili intellektom gandol'era s silovymi polnomoch'yami,
teper' on vklyuchaet duraka kogo-to zovet
zovet i na kogo-to ssylaetsya
i apeliruet na nesushestvuyushie
trebovaniya vladel'cev foruma k moderatoram, o kotoryh
nikto krome gandol'era vibenka ne znaet.
\\\
Vy
ponimaete, chto takoe eksperimental'naya proverka? Vy mozhete napisat'
chto-to v duhe: "Dlya proverki moego podhoda neobhodimo provesti sleduyushii
eksperiment..."?
Ponimaete, kakaya beda: krasivye rechi pro fizicheskii smysl, fundament, Miroponimanie, Poznanie menya sovershenno ne trogayut...\\\
Vot
chem sobstvenno otlichaetsya fizik ot gandol'era.
Gandol'er vidit i lyubit sebya (zvaniya, oplata za kazhdyi puk) v fizike,
a fizik lyubit fiziku vnutri sebya , i gandol'eru
nikogda ne ponyat' chto fizik zanimaetsya fizikoi potomu
chto ona emu prosto interesna, i mozhet 99.99 %
nikogda ne smogut pridumat' eksperimenta, no ih v fizike
interesuyut
vsyacheskie fizicheskie voprosy i trudnosti ,
i fizikam priyatno delat' hot' malen'kie no uverennye
shagi v osmyslenii fizicheskih situacii.
Da i gandol'er vibenok to i sam nikogda ne smozhet predlozhit'
nikakogo poverochnogo opyta, a ot drugih trebuet.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.11.2011 20:08, 1.4 KBait)
Mne zhalko smotret' na to kak muchayutsya yuzery s sinhronizaciei,
b'yutsya kak ryba ob led.
Sinhronizirovat'sya mozhno i s "nablyudatelyami" tol'ko
nado
nablyudatelyam pridat' fizicheskogo smysla, u "nablyudatelei"
dolzhna byt' tochka v prostranstve - fizicheskaya,
u nih dolzhny v karmane lezhat' chasy pokazyvayushee
global'noe vremya,
i u kazhdogo nablyudatelya v karmane 3 taimera.
Mezhdu nablyudatelyami izvestno rasstoyanie, i skorost' mezhdu nimi,
izvestno rasstoyanie i skorost'
mezhdu kazhdym iz nablyudatelei i nablyudaemym
ob'ektom.
V principe esli sdelat' "nablyudatelei" fizicheski gramotno
opisannymi, net prostora dlya
matematicheskih lohotronov,
a kak dlya fizicheskogo analiza "nablyudateli" fizicheski
gramotno opisannye i darom ne nuzhny,
tak kak pryamye izmereniya
budut analogichny nablyudaemym.
Priroda vsegda prepodnosit neozhidannye podarki,
po povodu togo kak v starinu sinhronizirovali vremya,
- ya vot chital chto
davnym davno sobake delali operaciyu, i vyrezali u nee
to-li kusochek kakogo-to organa to-li brali kakuyu-to
zhidkost', tochno ne pomnyu zabyl gde chital.
Tak vot
potom etu sobaku brali na korabl' i plyli s nei
kuda ugodno, a tam ot kuda vyshel korabl' brali
chast' veshestva nagrevali ego rovno v polden', i sobaka
v lyuboi
tochke zemli nachinala gavkat'.
Mozhno verit' etomu a mozhno i ne verit'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.12.2011 0:42, 1.3 KBait)
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,90464.msg1759427.html#msg1759427
Grishin S. G.:
Vmesto togo, chtoby chernuhu gnat',
posmotri v slovare, chto takoe "spekulyaciya".
Vrode na
"ty" ne perehodili.
Smotrim:
SPEKULYaCIYa
(ot lat. speculatio - vyslezhivanie, vysmatrivanie),1) kuplya-prodazha
cennostei (akcii, tovarov, valyuty i t. d.) s cel'yu polucheniya pribyli ot
raznicy mezhdu pokupnoi i prodazhnoi cenoi (kursom).2) V perenosnom smysle
- raschet, umysel, napravlennyi na ispol'zovanie chego-libo v korystnyh
celyah.
---------------------------------------------------------
Ocherednaya moderatorskaya tehnologiya, -
posetiteli na forume ustraivayut skandal, posle
chego moderator ne skandalistov udalyaet a forum zakryvaet.
Posle etogo mozhet byt' eshe odna moderatorskaya tehnologiya zakryt' forum,
eto kogda dva moderatora
zadayut voprosy
na kotorye otvety budut vzaimno protivorechivy, v rezul'tate
tozhe zakroyut forum.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.12.2011 10:29, 744 Bait)
Gandol'er vibenok za den'gi kotorye emu postoyanno platyat
gotov vechno
\\\Kopit' dannye, provodit' eksperimenty, kotorye
by postoyanno proveryali
sushestvuyushie teorii na prochnost'.
Rano ili pozdno etot put' obyazatel'no
privedet k uglubleniyu poznaniya Mira.\\\
Tol'ko gandol'er ne ponimaet chto skol'ko by on ne smotrel v teleskop,
i ne poluchal za eto zarplatu, to ot etogo
v durnoi golove umnyi opyt ne pridumaetsya,
ego deviz - lohotron, i on nikogda
ne smozhet pridumat' opyt, i kak
istinnyi gandol'er on obeshaet
chto kogda-to,
no ne govorit - kogda.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.12.2011 10:42, 346 Bait)
Vibenok - ballast nauki.
Kotoryi tol'ko mozhet krichat' chto on za novoe,
a na dele on i takie-zhe kak on star-pery
(zvezdnye tolkateli) blokiruyut vse novoe,
est' prichiny kak pravilo eto to chto vibenok
ne pereuchitsya drugoi teorii luchshe chem ego
student, a v etom sluchai prepodavatel' trebuet
nemedlennoi zameny.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.12.2011 20:45, 288 Bait)
Kak i sledovalo ozhidat' zakryty oba foruma.
V principe ponyatno pochemu, ne dat' prinyat' kollegial'nyh
reshenii, ibo kollegial'noe reshenie 10 lyubitelei,
s obosnovannymi vyskazyvaniyami kazhdogo,
ne tol'ko nagibaet geniya no i delaet kollegial'noe
reshenie zakonom.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.12.2011 16:57, 4.1 KBait)
Re: Deistvitel'no li skorost' sveta v vakuume - invariant?
Azh ponravilos' kak baryshya intelektual'no
nagnula relyativistov i otshmagala
intellektual'nym knutom pryamo po samoe - asyasyai.
I tak krepko
oshmagala, chto ne vidno dazhe v obozrimom
budushem relyativista kotoryi smog by otvet derzhat',
i prikryt' svoim umom chuzhie zadnicy.
\\\
Drobyshev pisal(a) Vchera :: 18:59:22:
Vot vasha ssylka. http://www.desy.de/user/projects/Physics/Relativity/SR/experiments.html.
Obeshaet "sotni opytov", dokazyvayushih postulaty STO.
Pri
vnimatel'nom rassmotrenii etih opytov vyyasnyaetsya, chto relyativisty
zhul'nicheski pytayutsya sozdat' vidimost' nalichiya u nih "mnozhestva
dokazatel'stv" postulatov STO i pod vidom "dokazatel'stv" samym
moshennicheskim obrazom ponataskali zdorovennuyu kuchu postoronnih opytov i
vsevozmozhnogo hlama, chtoby sozdat' vidimost' nalichiya dokazatel'stv i
chtoby vse normal'nye lyudi slomali nogu v etih psevdodokazatel'stvah.
Esli nabrat'sya terpeniya i razobrat' ves' etot hlam, to ochen' bystro i
legko obnaruzhivaetsya, chto nikakih dokazatel'stv u relyativistov net.
Davaite posmotrim povnimatel'nee na etu strannuyu kuchu. Chego zdes' tol'ko net!
Zdes'
est' i Bredli s ego aberraciei sveta. I Fizo s ego opredeleniem
skorosti sveta v dvizhusheisya vode. Zdes' upominaetsya Mikrovolnovoe
Fonovoe Kosmicheskoe izluchenie. I mnozhestvo prochih, sovershenno
POSTORONNIH OPYTOV, ne imeyushih ni maleishego otnosheniya k dokazatel'stvu
invariantnosti skorosti sveta! Zachem oni syuda vse eto pritashili? S cel'yu
sozdat' vidimost' monozhestva dokazatel'stv. 
Eshe
celaya seriya opytov - opyty po dokazatel'stvu "nezavisimosti skorosti
sveta ot skorosti istochnika". Eti opyty relyativisty raz za razom
pytayutsya podsunut' pod vidom dokazatel'stva "invariantnosti skorosti
sveta". Uvazhaemye relyativisty! My umeem razlichat' "invariantnost'
skorosti sveta" i "nezavisimost' skorosti sveta ot skorosti istochnika".
"Nezavisimost' skorosti sveta ot skorosti istochnika" invariantnosti
skorosti sveta ne dokazyvaet. Poetomu perestan'te moshennichat' i zhul'nicheskim obrazom podsovyvat' fal'shivye dokazatel'stva. 
Pro
mnogochislennye variacii opyta Maikel'sona my govorili uzhe tysyachi raz -
Maikel'son nepravil'no izobrazil traektoriyu poperechnogo lucha (ugol
otrazheniya narisoval neravnym uglu padeniya lucha), otkuda dosadnaya oshibka v
ego raschetah.
Lazery - mazery proveryayut effekt Doplera i tozhe podsunuty pod vidom dokazatel'stva "invariantnosti skorosti sveta".
I v takom
duhe.
Uv.
Drobyshev. Nam ne nuzhny spiski iz soten naimenovanii vsyakogo hlama.
Daite nam vsego lish' odnu ssylku, no ssylku ne na spiski musora
nenuzhnogo barahla, a ssylku na sam eksperiment, prichem takoi
eksperiment, kotoryi dokazyvaet imenno "invariantnost' skorosti sveta", a
ne nalichie effekta Dopplera, aberracii, fonovogo izlucheniya,
nezavisimosti skorosti sveta ot skorosti istochnika i prochih sovershenno
postoronnih veshei, ponataskannyh relyativistami ot bezyshodnosti iz-za
neimeniya nastoyashih dokazatel'stv.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.12.2011 17:02, 72 Bait)
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1319091586/390#390
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.12.2011 10:57, 1.4 KBait)
 Eksperiment Aleksandrova (i dr.) po podtverzhdeniyu nezavisimosti skorosti sveta ot dvizheniya istochnika
Eksperiment Aleksandrova (i dr.) po podtverzhdeniyu nezavisimosti skorosti sveta ot dvizheniya istochnika
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?action=dereferer;url=http://ufn.ru/ufn11/ufn11_12/Russian/r1112l.pdf
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1323760148/0#0
Prochital i vzgrustnulos' - kak relyativisty fizikoi stradayut,
no smogli hot' chto-to
sdelat' pri polnom
neponimanii to-go chto sdelali, ibo esli-by
ponimali to o nekotoryh n'yuansah by ne pisali.
Itogo chto imeem - vyletayut s kol'ca
sinhrofazotrona odinochnye razognannye atomy metalla,
iznachal'no ne sfokusirovannye, letyat i udaryayutsya ob sapfir,
i proishodit svetovaya vspyshka, v sleduyushem variante,
pered sapfirom stavyat steklo, tak kak steklo blizhe,
to na nego popadaet bol'she odinochno letyashih atomov
metalla i pri ih udare o steklo vspyshka estestvenno
budet yarche.
Vyvod-
Zayavlennye v opyte zadachi dannoe ustroistvo reshit' ne mozhet.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.12.2011 20:12, 959 Bait)
Vot dumal pro opyt Aleksandrova o tom kak ego sdelat' s zayavlennymi
vozmozhnostyami.
Zdes' chto nado ponimat', dvizhutsya odinochnye atomy po krugu, i oni
dolzhny
izluchat' - dlya etogo dolzhna byt' prichina.
V opyte izluchenie za schet tormoznogo uskoreniya, ili poprostu govorya
svetovye vspyshki proishodyat ot udarov o prepyatstvie,
to-li eto steklo ili sapfir.
Iznachal'no net strogoi fizicheskoi prichiny dlya svetovogo izlucheniya.
Esli dobavit' istochnik rentgenovskogo izlucheniya v tochku
potoka,
to dopolnitel'noe vozdeistvie vozmozhno privedet k svetovomu
izlucheniyu v potoke razognannyh chastic.
Vozmozhno na potok vozdeistvovat' lazernym luchom,
chtoby otrazhenie
lucha bylo ot chasticy, hot' eto ne odno i to-zhe kogda chastica sama izluchaet,
no vse-taki blizhe k zayavlennym svoistvam.
Estestvenno vse stenki
poverhnostei nado pokryt' chem-to pogloshayushim i
chernogo cveta, i vnutri rez'bu pered etim narezat'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.12.2011 17:17, 2.6 KBait)
Na populyarnoi kinematike menya zabanili po novoi,
ne nravitsya tam kogda im pravdu govoryat i vse nazyvayut
svoimi imenami, vot esli posle lekcii video v obrabotke
- to eto ili lekciya ne udalas' osvistali lektora,
a vtoroi variant eto zhadnost', ibo esli budet video
to kto-zh na platnye lekcii poidet.
Potom
vyskazalsya po temnoi materii. U kotoroi kak vse znayut
net opredeleniya, da i sama materiya nuzhna gruppe matematikov
stradayushih fizikoi,
u kotoryh drugie teorii
ne shodyatsya s realiyami, i oni
pridumyvayut novye, chtoby starye shodilis'.
---------
Moi lyubimye oshibki paradigmy na kotoryh ona
pokoitsya v kolybel'ke
gluposti.
Vodorod samyi legkii material so vremenem
prohodit skvoz' lyuboi metall, i vdrug s neponyatnogo
zhelaniya astrofizikov on sorval u sebya bashnyu
i poletel
v centry zvezd pouchavstvovat' v gorenii.
A kakaya krasota pogovorit' o tom u chego dazhe net opredeleniya,
temnaya materiya i temnaya energiya - eto
udel gigantov mysli,
razgovor vechnyi i becsmyslennyi, zato mozhno nagovoritsya
i pokazat' svoi intellekt.
Vot vzorvalas' zvezda i o chudo posle vzryva vodoroda
ne obnaruzheno - eto ne zvezda bez vodorodnaya okazalas'
eto vse knizhki po astrofizike oshibochnye i bessmyslennye.
A vot i vinovnica torzhestva iz izvestnogo
opyta razmerom
so spichechnyi korobok - kamera Vil'sona, blagodarya nepravil'noi
interpretacii nablyudaemogo sdelali samuyu bol'shuyu
i neponyatnuyu oshibku i ee uvekovechili
i ee ne zamechayut -
elektron, - etim slovom chto tol'ko ne nazyvayu.
Hotya elektro potenciala v prostranstve bez nositelya
ne byvaet, tak vot - zaryazhennyi ili raskruchennyi
atom
v prostranstve, ili oskolki atomov stali ot bol'shogo
uma nazyvat' elektronami, kak i to chto vnutri provodnikov
dvizhetsya.
Ya ochen' rad kak
kachestvenno fiziki i astrofiziki zagnali
sebya v gluhoi ugol.
=============
Potom pochital pro garpun dlya sputnikov chtoby komety garpunit'.
Na stol'ko
nedalekie chto dazhe ne znayut chto prakticheski u vseh
sputnikov vozle komet poluchilis' neshtatnye situacii.
-------------
Detvora dazhe ne ponimaet prichiny
neobhodimosti
garpuna, a ona prosta - komety ne prityagivayut,
im do lampochki knizhki po fizike.
Sputnik podletaet po programme na 50 metrov,
posle chego
dolzhen popast' pod vliyanie gravitacii
komety, a vliyaniya net, sputnik dreifuet kuda popalo,
no tol'ko ne na kometu.
Bol'shaya glupost' rasprostranit' padayushee
yabloko
na vsyu vselennuyu, vselennoi do lampochki kak yabloki
padayut u vselennoi dlya prityazheniya drugie prichiny.
--------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.01.2012 1:13, 2.0 KBait)
Rasskaz
Fantasticheskii son o gorode fizikov.
Prisnilsya gorod fizikov, on sostoyal iz odnoi central'noi ulicy,
kotoraya razdelyala pustynnye dikie prostory
klassicheskoi fiziki,
i plodonosyashie sady relyativistskoi fiziki.
Po pustynnym prostoram klassicheskoi fiziki skitalis' kakie-to
golodrancy neskol'ko bylo po
dvoe i po troe no v osnovnom odinochki,
hodili chto-to pisali na peske, koe kto iz al'ternativshikov provodil
kakie-to opyty na kostre poka gotovili edu.
Prakticheski
vse al'ternativshiki periodicheski i s raznym uspehom
uchastvovali v forumah
"skai-tyuh" i "zvezdomer".
Eti uchastki dorogi otlichalis' razmetkoi
ulicy, i nalichiem zabora
so storony relyativistov na "zvezdomere", zabor na "zvezdomere" ne
dlya togo chtoby al'ty ne lazili, a dlya togo chtoby
somnevayushiesya
relyativisty ne smogli ubezhat' ot moderatorskoi porki. Vozle forumnoi
razmetki s obeih storon periodicheski stoyali tolpy zevak i prihodili
oratory
to s toi a to s drugoi storony.
Na "skai-tyuhe" demokratii bylo pobol'she i vse orali drug na druga i periodicheski
rvali na sebe odezhdu i brosali cherez
dorogu, tam v nee vyshmarkivalis' i brosali
obratno.
Na "zvezdomere" reryativisty posle meryanii teleskopami i posle obeda v gos
stolovoi, pododvigalis'
i podkatyvalis' na svoih kreslah k doroge,
chtoby luchshe slyshat'.
Po sredine ulichnoi razmetki "zvezdomerovskogo" foruma stoyal - pletochnyh
shmaganii
master, - nesravnennyi moderator Bi-Be. On slavilsya tem chto ot
pryamyh voprosov uhodil svoimi otvetami v intellektual'noe begstvo.
Ot al'ternativshikov on treboval
dat' emu posmotret' teh pasport na efir,
i predostavit' opyty za kotorye mozhno nobelevskuyu poluchit' eshe vchera.
Estestvenno zapros na relyativistskii teh-pasport
na prichinu skorosti sveta vyzyvaet
shatanie v kreslah i bubnenie relyativistov o tom chto v nem net smysla,
a smysl est' v pasporte na efir.
Tak sobstvenno
v neponimanii i smotreli drug na druga.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.01.2012 1:43, 1.8 KBait)
Prodolzhenie
Rasskaz
Fantasticheskii son o gorode fizikov.
Dal'she u dorogi relyativisty postavili tribu svoih dostizhenii
s trubnymi fanfarami.
Na fanfarah
raznye nadpisi, - bez kotoryh relyativizm
byl by nevozmozhen.
Chtoby uiti ot efira pridumali fanfary ---- "vakuum"
Chtoby uiti ot sveta kotoryi byl
v efire, pridumali fanfary --- "foton"
Tak kak ne smogli pridumat'
kuda teplo devaetsya ot zvezd,
pridumali fanfary
- ---"bol'shoi vzryv",
tepla u zvezd okazalos' mnogo
i chtoby pogloshat' eshe teplo
ot zvezd pridumali fanfary -
--- "chernaya - dyra"
a energii okazalos' eshe bol'she,
pridumali fanfary ---" uskorennoe rasshirenie",
i neponyatno
chem prityagivaetsya
tokmo po dva tela pridumali fanfary --- "gravitaciya".
A na protiv tribuny s fanfarami raspolagalsya zritel'nyi zal
smeha
relyativistov, tak kak na tribunu s fanfarami periodicheski
zabegali odichavshie al'ty, oni pribegali s toi storony dorogi,
so storony klassicheskoi fiziki. I kogda
odichavshie al'ty v svoih
vozmushennyh rechah ispol'zovali slova isklyuchitel'no dlya
relyativistov, i oni sovpadali s nadpisyami na fanfarah, to vmesto
slov oni
duli v fanfary relyativistov.
Nekotorye dikie al'ty celye relyativistskie koncerty
ustraivali i vyduvali fugi , gorazdo
luchshe nekotoryh relyativistov. Relyativisty
osobo sil'no
smeyalis' kogda dikie al'ty ispol'zovali vse slova.
Vdrug zavisli v vozduhe udary plet'yu, master Bi-Be na "zvezdomere"
shmagal
vseh podryad a chtoby uvazhali.
Sobstvenno tak i zhili, klassicheskaya storona - pustynya bednosti,
i relyativistskie fruktovye sady s shokoladnymi kabinetami.
Po doroge to tam to tam probegali bobry, ih po druzheski bili
teleskopami s lyuboi storony ulicy.
Vot ya i prosnulsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(O. E. Korobeinikova,
24.01.2012 22:04, 1.1 KBait)
Kak pisalGermes Trismenist:"To,chto nahoditsya vnizu,sootvetstvuet tomu,chto prebyvaet vverhu, i to chto prebyvaet vverhu ,sootvetstvuet tomu,chto nahoditsya vnizu,chtoby osushestvit'
chudesa edinoi veshi." Izumrudnaya skrizhal'."Esli chernaya dyra est' v centre Vselennoi,. To i v Solnechnoi Sisteme est',i na Zemle,i u cheloveka. V Solnechnoi Sisteme nahoditsya
ot Poyasa Koipera do O'laka Oorta. Na Zemle ot Ural'skih gor do Tihogo okeana. Chernaya dyra,kak pylesos. Sibir' ot slova "mesti","podmetat'".Esli polozhit'
Sozvezdie Oriona na Zemlyu. To ego Poyas budet na Urale. Rossiya "serdce Oriona" Evropa "verhnyaya polovina tela,gde pravit golova,mech." Sibir' "chrevo,nutro"
Ameriki nogi. V cheloveke pravit seichas"chernaya nenasytnaya dyra". Ona postoyanno prosit pishi. Kinzhal/vspomnite sozvezdie/ tozhe pravit/Aziya/. Chut' -chto vonzyat v spinu,ispodtishka.
Postoyanno nekotorym udaryaet mocha v golovu. Golova tam ne pravit. Zahodite v moi dnevnik. Pravda ya tam s yanvarya. hppt.//www/liveinternet/ru/users/4652061/profile Ne znai pravil'no
nabrala?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(O. E. Korobeinikova,
4.02.2012 16:21, 31 Bait)
Spasibo!Chto pechatali moi posty.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.02.2012 18:59, 816 Bait)
Vy bol'ny fakticheski i ne ponimaete etogo,
zabros adrenalina privodit k perehodu organizma v sostoyanie ataki,
da tak potom i ostaetsya organizm v "atake".
Lechitsya eto ochen' dorogo.
http://top.rbc.ru/health/03/02/2012/636178.shtml
\\\Soprotivlyat'sya zhelaniyu proverit' obnovleniya v social'nyh setyah, naprimer
takih, kak Facebook i Twitter, namnogo slozhnee, chem otkazat'sya ot
alkogolya i sigaret. Takoi vyvod byl sdelan uchenymi iz Vysshei shkoly
biznesa imeni Buta Chikagskogo universiteta (University of Chicago Booth
School of Business, USA) na osnove oprosa 250 zhitelei SShA ob ih
povsednevnyh zhelaniyah, pishet The Telegraph.\\\
Chitat' polnost'yu: http://top.rbc.ru/health/03/02/2012/636178.shtml
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(O. E. Korobeinikova,
5.02.2012 22:49, 111 Bait)
Mne vse ravno,chto Vy pro menya pishete.Vy pokazyvaete svoe istinnoe lico.Skazhu znakomym,chtoby zaglyanuli pochitali.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.02.2012 0:34, 802 Bait)
http://www.psyclinic.ru/page_36.html
\\\Imenno vnezapnost' vozniknoveniya sostoyaniya straha ili fiziologicheskogo
diskomforta yavlyaetsya naibolee tochnym simptomom panicheskoi ataki. Nalichie
konkretnoi prichiny, kotoroi mozhet byt' vyzvan podobnyi epizod sovsem
neobyazatel'no. Odnako, cheloveku svoistvenno iskat' povod dlya neponyatnogo
yavleniya v okruzhayushih sobytiyah ili v samom sebe. Edinstvennaya prichina
panicheskoi ataki - vybros v krov' kolossal'nogo kolichestva adrenalina,
pri kotorom nastupaet sostoyanie peredozirovki etim biologicheski aktivnym
veshestvom. Lechenie panicheskih atak
na nachal'noi stadii napravleno imenno na regulyaciyu imenno kolichestva
adrenalina v krovi, a zatem uzhe na sami simptomy i boyazn' ih povtoreniya.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.02.2012 22:27, 885 Bait)
Segodnya prochital formulirovku absolyutno protivorechashuyu
avtorskomu ot Doplera.
Pal'mu pervenstva gluposti prodolzhayut nesti na plechah -
Kratko skazhu
prichinu legkogo idiotizma v razgovore tovarishei
kotorye dazhe ne ponimayut vsei gluposti rasskazhu kratko -
Effekt Doplera byl priduman avtorom isklyuchitel'no dlya sred,
i za dolgo do relyativizma, relyativisty ot ispol'zovaniya etogo
effekta otkazat'sya ne mogli tak kak on imeet mesto byt',
a chtoby prolohotronit' na okolosvetovyh
skorostyah oni
nachhav chto effekt dlya sred v avtorskom izlozhenii
pridumali novyi effekt dlya pustoty i nazvali ego
Relyativistskii effekt Doplera - metody gandol'erov.
Vot tekst ot nedalekih
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.02.2012 22:30, 2.2 KBait)
Uchityvaya chto moderatory tam periodicheski glupost' udalyayut
Skopiruyu pozor astrofizikov syuda.
Avtor
zamahnulsya na samoe svyatoe - na interpretaciyu kosmologicheskogo krasnogo
smesheniya kak na rezul'tat rasshireniya prostranstva. On polagaet, chto vse
svoditsya k dopleru i gravitacionnomu smesheniyu. Sootvetstvenno, govorit'
o tret'em tipe - nekorrektno.
Esli u avtora temy est' samoe ili ne samoe svyatoe, to chto on delaet v "Gorizonty nauki"?
Est' zhe mnozhestvo religioznyi
forumov.
Nu i glavnoe, Sergei Popov ne meshalo by nauchit'sya chitat', kak minimum poznakomit'sya, chto takoe Dopler effekt.
K svedeniyu:
Effékt
Dóplera izmenenie chastoty i dliny voln, registriruemyh priemnikom,
vyzvannoe dvizheniem ih istochnika i/ili dvizheniem priemnika.
Tak kak
dlya rasprostraneniya elektromagnitnyh voln ne trebuetsya material'naya
sreda, mozhno rassmatrivat' tol'ko otnositel'nuyu skorost' istochnika i
nablyudatelya.
To est', nikakogo smesheniya spektrov v sledstvie effekta
Doplera dlya vzaimno nepodvizhnyh istochnika i nablyudatelya ne budet. A esli
avtor (John Woodruff Simpson Fellow) upominaet o effekte Doplera, to eto
v lyubom raze oznachaet dvizhenie istochnika sveta otnositel'no
nablyudatelya, to est' ni o kakom "zamahnulsya na samoe svyatoe - na
interpretaciyu kosmologicheskogo krasnogo smesheniya kak na rezul'tat
rasshireniya prostranstva" rechi i blizko net.
Po samoi stat'e:
rassmatrivayutsya trivial'nye prostranstva s trivial'noi metrikoi i dokazyvaetsya glavnoe po mneniyu
avtora:
Whats
interesting, of course, is that because the two sets of coordinates are
different (one inertial, the other not), the two decompositions are
generally not equal, but the final results are the same, as they should
be because the underlying physics is identical. Tipa - bezrazlichno, chem
obuslovleno krasnoe smeshenie, oni oba privodyat k odnomu rezul'tatu
potomu chto osnovnaya fizika identichna.
Primerno tak u nego i poluchaetsya.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.02.2012 2:47, 1.6 KBait)
Po chernoi dyre eshe
http://siteua.org/system_category/330344
\\\"Do sih por nikto i nikogda ne fotografiroval
chernye
dyry, vvidu slozhnosti etogo meropriyatiya i ekzoticheskoi prirody samih
dyr", - govorit Dimitrios Psaltis, astronom iz Universiteta Arizony i
odin iz koordinatorov proekta.\\\
Sobirayutsya pervuyu fotografiyu chernoi dyry sdelat', i vsem do lampochki chto bez takovoi,
uzhe tysyachi statei o chernoi dyre napisali.
Delo ne v fotografii na samom dele, net obshei formulirovki chernoi dyry -
kazhdyi vidit v svoih izyskaniyah to chto on hochet i nazyvaet eto chernoi dyroi
- i eto
smeshno, - klassika zhanra.
\\\.Material
iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi.... \\\
-----------------------------------
http://www.lenta.ru/news/2012/01/19/prize/
Astronomicheskoi nagrady udostoilis' Reinhard
Gencel' (Reinhard Genzel) i
Andrea Gez (Andrea Ghez). Premiya byla prisuzhdena etim uchenym za
obnaruzhennye imi i ih sotrudnikami vesomye dokazatel'stva togo, chto v
centre Mlechnogo Puti nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya chernaya dyra. Oba astronoma
nablyudali zvezdy, obrashayushiesya vokrug centra Galaktiki i prishli k
odnomu i tomu zhe vyvodu nezavisimo drug ot druga.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.02.2012 17:42, 2.2 KBait)
http://www.popmech.ru/article/10479-dyira-kak-vyiklyuchatel/page/4/
\\\Skorost' rozhdeniya novyh zvezd v nekotoryh dalekih galaktikah tak velika, chto process etot nazyvayut
pryamo vspyshkoi
zvezdoobrazovaniya. Process etot, odnako, lish' vremennyi, i dovol'no skoro prekrashaetsya i sudya po vsemu, vinovaty v etom mogut byt'sverhmassivnye
chernye dyryv centrah etih galaktik.\\\
Vot tozhe stat'ya napolnennaya idiotizmom, i zhelaniem
ne s'est' tak po-nadkusyvat'.
Eto yarkii primer togo
do chego dovodit syusyukan'e
i potokatel'stvo. Vmesto togo chtoby otkryto skazat'
chto mol - pshel von dybil s takoi stat'ei
v kotoroi vse neponyatno i otsutstvuet
smyslovaya
vzaimosvyaz', - tak tak nikto ne pishet v kommentariyah,
a avtor dumaet chto pipl havaet, i emu nravitsya -
i avtor budet pisat' sleduyushuyu stat'yu s eshe
bol'shim
idiotizmom i neskladushkami.
A v normal'nom i zdravom vide stat'ya by vyglyadela
sleduyushaya -
obnaruzhili korotkie i yarkie vspyshki, zvezdo-obrazovanie
ili zvezdnye vspyshki neizvestno, pod ni odnu iz teorii
ne podhodit, ni v kakoi iz izvestnyh teorii podobnyi sluchai
ne opisyvalsya.
Kstati o chernyh
dyrah oni tozhe myamlili, ponadkusyvali
- v stile mol, chto esli u kakogo-to sleduyushego pisatelya budet
neshto podobnoe v pripadke genial'nosti, tak pust' on mol znaet
v nashem pripadke bessoznatel'nogo idiotizma bylo vpervye.
Eto pipec, no pipl havaet astronomam nravitsya, mne smeshno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.02.2012 15:35, 2.7 KBait)
Otvet #154 : Vchera v 16:04:25
A teper' Vy nam rasskazhite, kak v zakone Habbla V=H*R proyavlyayutsya kvantovye
svoistva fotona
polagayu - nikak. V etom i problema na moi vzglyad.
A teper' Vy nam rasskazhite, kak zakon Habbla vazhnee i vyshe kakih-to tam kvantovyh svoistv
fotona.
Polagayu, zakon Habbla v ramkah dannoi temy prosto vazhnee i vyshe, kakih-to tam kvantovyh svoistv fotona.
I
poka Vy ne ob'yasnite, kak v zakone Habbla proyavlyayutsya kvantovye
svoistva fotona, zdes' net smysla govorit' ob etih kvantovyh svoistvah.
Otvet #183 : Segodnya v 12:59:49
Stanislav Kravchenko, vnyatnyi
otvet daite, pozhaluista. Ne prosto predlozhenie so slovami "foton" i
"zakon Habbla", a vnyatnyi otvet. Prekrasnyi sluchai pokazat' drugim
primer adekvatnogo fizicheskogo podhoda.
--------------------------
Moderatoru v mosk udarilo zhelanie ne vyglyadet'
idiotom, a samyi gramotnyi relyativist, zatupil po polnoi,
i v itoge
zadali diletantu vopros sut' kotorogo v tom
pochemu relyativisty kogda hotyat, a kogda ne hotyat i v nekotoryh sluchayah
primenyayut odni fizicheskie svoistva, a na drugie
zabivayut,
a kogda im nado dlya chego-to drugogo oni na tozhe samoe
chihat' hoteli a akcentiruyutsya na drugom.
Vot i trebuyut ot diletanta im ob'yasnit' pochemu
oni inogda byvayut
bol'nye na vsyu golovu, i prosyat ih vvesti v sostoyanie zdravomysliya,
tochnee skazat' vyvesti iz sostoyaniya idiotizma.
Vot takaya zhestokaya
selyavi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.02.2012 16:24, 2.3 KBait)
Vse ravno slovo foton s fizicheskoi tochki zreniya
prostym fizicheskim opytom - slivaetsya v kanalizaciyu fiziki,
a tot kto ego primenyaet - budet
toptat'sya na meste
ibo ne provodit fizicheskii analiz ispol'zuemuyu
fizicheskuyu sushnost', a veryat opredeleniyam,
skazal naprimer odin matematik chto svet sostoit
iz chastic,
tak srazu lohi i zarukopleskali i poverili na slovo,
matematikami vysosannym iz pal'ca vydumkam radi
podtverzhdeniya svoih teorii nuzhny, a lohi dumayut
chto matematiki pal'cem v nebo popali, i chto fizika
takaya kak matematiki pridumali, i potom nachinayut
soedinyat' vydumannuyu matematiku s real'noi fizikoi,
i ne ponimayut pochemu oni zanimayutsya odnim i tem-zhe
stoletiyami - da udel nedalekih.
-------------
Kak ya ranee pisal - foton - ne imeet fizicheskogo smysla,
- obosnovat' eto, - bylo legko.
Dlya sushestvovaniya effekta Doplera, est' prichina - sreda i ee svoistva.
Dazhe esli ispol'zuetsya metod izmereniya dlya sred, a
govoritsya chto
vokrug pustota, to propadaet
prichinnost' vozniknoveniya dannogo
effekta kak svoistva prostranstva.
U relyativistov ne prostranstvo vystupaet v kachestve linii zaderzhki
signala, a vystupaet
- foton, kak dvizhushiisya ob'ekt, u kotorogo
ogranichena skorost' dvizheniya v pustote, po ne ponyatnoi prichine -
kotoraya postuliruetsya bez ob'yasneniya prichiny. Foton
v dannom sluchai
mozhet byt' tol'ko chasticei, - eto ne vozmozhno po prichine togo chto
chastica ne mozhet snizhat' i uvelichivat' svoyu skorost' chto
nablyudaetsya naprimer
pri dvizhenii sveta naprimer v vozduhe, potom
cherez steklo potom opyat' v vozduhe i potom v vakuum, tak kak
poluchaetsya chto v stekle letit foton medlennee chem v vozduhe
i
vakuume , a vyletaya iz stekla foton uvelichivaet svoyu skorost'. Tak
vot ne mozhet chastica kotoraya poteryala skorost', prosto tak vzyat' i
pri vylete iz stekla
uvelichit' skorost', - na podobnoe sposobny
tol'ko kolebaniya sredy v sredah s raznymi svoistvami. Tak chto foton
kak chastica - vydumka chistoi vody.
Vyvod -
v prostranstve rasprostranyayutsya kolebaniya sredy, i svetovoe
izluchenie ne dvizhetsya a obrazuetsya ot vzaimodeistviya kolebanii
sredy i materiala, kak v 1800 godu govoril
Tomas Yung.
Tak chto vse chto napisano v astrofizike bez ucheta sredy - k
sozhaleniyu ne pravil'no.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.02.2012 16:31, 469 Bait)
Iz predydushego sleduet chto ni odin relyativist
ne mozhet primenyat' dlya krasnogo smesheniya foton
ne uchityvaya to chto on chastica, i skorost' poleta
chasticy opredelyaet
skorost' sveta, i ne ispol'zovat'
foton kak chasticu - oni ne mogut. Tak kak
tol'ko dlya sredy zaderzhka sveta v prostranstve
mozhet ob'yasnyat'sya skorost'yu rasprostraneniya
vozmusheniya v srede. A u relyativistov sreda
pustaya, tam net nichego, i foton letit kak chastica.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.02.2012 19:24, 2.9 KBait)
\\\Polagayu, zakon Habbla v ramkah dannoi temy prosto vazhnee i vyshe, kakih-to tam kvantovyh svoistv fotona.\\\
Rasskazhu pravil'nyi otvet na
etot vopros, -
Iznachal'no byl obsheprinyatyi
efir, na osnovanii kolebatel'nyh svoistv sveta v
efire analogichnyh zvuku v vozduhe Tomas Yung ob'yasnil
interferenciyu sveta na dvuh ochen' blizko raspolozhennyh
shelyah. V svyazi s tem chto naprimer solnechnyi svet
prohodil cherez sheli, i bylo mesto gde nakladyvalos'
izobrazhenie solnca ot dvuh blizko raspolozhennyh shelei.
Opyt kogda risuyut tochechnyi istochnik sveta, a rasstoyanie
mezhdu shelyami bol'she diametra istochnika
sveta - ne korrektnyi,
on tol'ko na risunkah, na praktike on ne vozmozhen, tak
kak svetovye kolebaniya ne iskrivlyayutsya na shelyah, svet
prohodit skvoz' shel'
pryamo. Etomu podtverzhdenie
shkol'nyi opyt po fizike, kogda delaetsya malen'kaya dyrka
i beretsya chernyi yashik bez zadnei stenki i kal'ka,
v chernom yashike raspolagaetsya
naprotiv dyrki kal'ka,
i izobrazhenie poluchaetsya perevernutym,
i esli sdelat' ryadom eshe odnu dyrku, poluchitsya
dva izobrazheniya perevernutyh, kotorye nalozhatsya
drug
na druga - eto i nazyvaetsya interferenciya.
Tak vot, posle etogo nado bylo skazat' chto ob'yasnenie interferencii
Tomasa Yunga ne korrektno, i oprovergnut',
chego ne bylo sdelano.
Prosto za-postulirovali dlya pustoty chto dvizhutsya svetovye
chasticy. Za-postulirovali tak za-postulirovali, no poyavilsya
nyuans kotoryi
ne reshaetsya dlya chastic, tak kak nado ob'yasnit'
interferenciyu dlya solnca na dvuh shelyah na rasstoyanii naprimer
3mm mezhdu shelyami. I chto , i to chto dlya fotonov nado
pridumyvat'
dopolnitel'nye svoistva, na urovne potenciala, to-est' fotony
budut plyusovye i minusovye, pri etom vse proidet.
No zdes' voznikaet sleduyushii nyuans,
esli chastica so znakom
plyus ili minus to oni dolzhny otklonyatsya
magnitnym polem, - esli podnesti magnit k luchu,
naprimer minusom to plyusovye fotony dolzhny
prityagivat'sya
k magnitu a minusovye ottalkivat'sya, to-est' luch rasshiritsya,
- chego ne nablyudaetsya - vot takaya zhestokaya selyavi.
I chto v itoge poluchaem
dlya krasnogo smesheniya ili zakona Habbla,
azh nichego, tak kak esli rasshiryaetsya, to dolzhna umen'shat'sya
skorost' fotonov - eto nevozmozhno tak kak eto povliyaet na
skorost' sveta, a skorost' sveta za-postulirovana stabil'noi,
i ne zavisyashei ni ot chego. Chto delat' relyativistam? ob'yasnyat'
to nado, ostaetsya cherez poteryu napryazhennosti
fotonov,
tochnee elektro-potencialov, no delo v sleduyushem v
etom sluchai vse ravno ne mozhet izmenitsya chastota, mozhet
izmenitsya tol'ko amplituda raznosti, a
chastota ostanetsya.
Vot i prodolzhayut ogorod gorodit', i ochen' ne hotyat pri rasshirenii
schitat' chto fotony kak chasticy dolzhny skorost' menyat',
- s moei tochki
zreniya - shikarnyi samozaklin ot matematikov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.02.2012 2:12, 1.6 KBait)
U moderatora mosk poplyl po polnoi, ili starost'
svoe beret.
-------------------------------
Otvet #203 : Vchera v 17:24:20
Stanislav Kravchenko, ya zhdu obosnovaniya etogo utverzhdeniya:
Vernemsya k teme - interpretaciya kosmologicheskogo krasnogo smesheniya.
V
etom voprose nel'zya ignorirovat' tot eksperimental'nyi fakt, chto foton est' kvant deistviya.
Ne
ego otdel'nyh fragmentov, a celogo utverzhdeniya, so vsemi nyuansami. V
chastnosti, pochemu foton -- kvant deistviya, a ne prosto kvant. Esli
sleduyushee Vashe soobshenie ne budet takim obosnovaniem, dostup na forum
Vam budet zakryt na kakoe-to vremya.
---------------------------------
Povtoryayu dlya obtormozhennyh relyativistov - taki da, po Vashim
diffektivnym
teoriyam u Vas poluchaetsya chto foton eto kvant deistviya,
po toi prichine chto skorost' fotona -konstanta, a sam foton est' chastica.
Foton ne mozhet po relyativistskim
teoriyam letet' medlenno ili stoyat'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.02.2012 2:29, 409 Bait)
I moderator zabanil posetitelya za to chto relyativisty tupyat v fizike,
osobenno tormozit moderator.
Moderatoru nado pochitat' postulaty relyativizma, mozhet
on
i poimet ves' idiotizm relyativizma.
Vmesto togo
chtoby za relyativistskie paradoksy posetitelei banit'
nado luchshe fiziku uchit', - hotya kak my vidim na dannom
skandale chto mosk matematika fiziku ne vosprinimaet v principe.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.02.2012 16:46, 2.3 KBait)
A teper' ya poschitayu na skol'ko poluchaetsya
raznica pri opredelenii razmerov zvezd
metodami krasnogo smesheniya i Habbla.
--------------------
Udalennost'
Solnca ot Zemli, 149,6 mln km
diametr Solnca = 1 391 000 kilometrov.
A teper' posmotrim kak nedalekie astronomy
dazhe obladaya vysokokachestvennoi
tehnikoi
delayut vyvody o razmere SN1987a c
bol'shimi peregibami, chuvstvuetsya chto zdravyi
smysl oni polozhili na polku, no zato v teorii
vpisalis'.
http://planetologia.ru/sverhnova/1332--qq-sn-1987a.html
\\\Raspolagayas' na rasstoyanii 168 tys. svetovyh let ot
Zemli v galaktike Bol'shoe Magellanovoe
oblako, sverhnovaya
SN 1987A daet uchenym detal'nuyu informaciyu o tom, kak
dozhivayut svoi dni bol'shie zvezdy. Zvezdoi-predshestvennikom
SN 1987A byl goluboi sverhgigant
Sanduleak -69 202 s massoi
okolo 17 mass Solnca.\\\
\\\Oni izuchali vzaimodeistvie obrazovavshihsya ot vzryva zvezdy
diametrom okolo 9,6 trillionov kilometrov
kolec gaza,
okruzhayushego sverhnovuyu.\\\
Tak vot, ya dumayu chto razmer predshestvuyushei zvezdy byl
dva diametra solnca(17 mass Solnca), posle vzryva forma
zvezdy izmenilos',
ona priobrela diskoobraznyi vid, diametr diska s kraev
u kotorogo proishodyat vybrosy - posle vzryva razmer obrazovavshegosya diska
s vybrosami
po krayam raven dva s polovinoi diametra solnca.
Diametr diska s vybrosami po fotografii v dva raza men'she
diametra kolec i v traktovke sovremennoi paradigmy,
sledovatel'no diametr zvezdy v forme diska s vybrosami
po krayam ot astronomov v paradigme raven 4.8 trillionov
kilometrov.
Vot chto u menya poduchilos'
"diametr Solnca = 1 391 000 kilometrov"
dva s polovinoi diametra solnca i ravno 3.47 mln. km.
A u teh astronomov dazhe ne 4.8 milliardov kilometrov,
- diametr chto v tysyachu raz bylo by bol'she moego analiza,
u nih v million raz
razmer bol'she ne moego rascheta - a v million raz bol'she
zdravogo smysla.
I smeshno smotret' na etu klounadu,
i o kakih melkih voprosah vrasheniya mozhno rassuzhdat'
pri oshibke na rasstoyanii 168 tys.svetovyh let v - million- raz,
to
na skol'ko oni mogut oshibat'sya so svoimi zetami
dlya vysosannyh iz pal'ca fotonov na bol'shih rasstoyaniyah.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(O. E. Korobeinikova,
14.02.2012 19:58, 53 Bait)
Ya dala ssylku na Vash sait.Nichego. Na temu Sozvezdiya..
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.02.2012 22:56, 460 Bait)
http://elementy.ru/lib/430551
Risunok 1.
A vot za takie veshi ya schitayu chto fizikov fabrikuyushih
takie risunki bez opytov po kotorym oni provodilis'
nado
lishat' zvanii i zapreshat' pozhiznenno prepodavatel'skuyu
deyatel'nost', i rabotu v oblasti fiziki.
Eto zh nado do chego dodumalis', risuyut i im nas
rat' chto
eto obychnyi lohotron, oni schitayut chto eto horosho,
a pipl havaet optiki i astrofiziki dovol'ny, a mne smeshno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.02.2012 23:09, 804 Bait)
Po bol'shomu schetu astrofiziku i fiziku proshe
prostogo vylechit' ot idiotizma, lechitsya eto pri pomoshi
vrachei , prosto dostatochno chtoby byl zakon po kotoromu
fizik ili astrofizik obyazan prohodit' referirovanie
u psihiatra svoih statei, i esli psihiatr ne ponyal
izyskov fizikov i astrofizikov - to eto ne neznanie
i neponimanie fiziki psihiatrom, a eto skoree togo
chto fizik ili astrofizik vzyalsya za zadachu kotoraya
prevyshaet umstvennye sposobnosti avtora,
ili avtor
zavralsya po samoe dal'she nekuda,
ili avtor imeet otklonenie.
A tak chto poluchaetsya vezde est' otbor, a v fizike i astrofizike
kto napishet bol'she statei tot
i krassava, a to chto stat'i
perepolnenny idiotizmom i nestykovkami tak eto norma,
ibo eto nenakazuemo a naoborot pooshryaetsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.02.2012 23:18, 2.9 KBait)
Nu ladno ... s nim kak govoritsya otkazalis' ot
sredy pridumali foton, a skol'ko uma nado chtoby
formulu fotona napisat', i ot formuly fotona
plyasat', a ne
hotro zho pit' , mol hochu volnovye
svoistva efira primenyayu, hochu effekt Doplera
(kotoryi iznachal'no avtorom byl dlya efira priduman)
primenyayu, a hochu i korpuskulyarnyi
foton primenyayu,
- ya ne mogu ponyat' cinizm situacii, kogda psevdo fiziki
sami vybirayut i reshayut
chto im primenyat' i kogda, kak govoritsya a ne sil'no
li
obnagleli, esli skazali chto skorost' sveta konstanta,
tak i derzhites' za nee obeimi rukami, i skazhite chestno
chto rasshirenie prostranstva protivorechit uzhe etoi
situacii, a to im na vse ..., vizhu tol'ko zhelanie
... mozgi vsem podryad i obvinyat'
v etom drugih.
|
|
Re: Chernaya dyra
|
12.02.201215:35 |
|
Otvet #154 : Vchera v 16:04:25
A teper' Vy nam rasskazhite, kak v zakone Habbla V=H*R proyavlyayutsya kvantovye
svoistva fotona polagayu - nikak. V etom i problema na moi vzglyad.
A teper' Vy nam rasskazhite, kak zakon Habbla vazhnee i vyshe kakih-to tam kvantovyh svoistv
fotona.
Polagayu, zakon Habbla v ramkah dannoi temy prosto vazhnee i vyshe, kakih-to tam kvantovyh svoistv fotona. I
poka Vy ne ob'yasnite, kak v zakone Habbla proyavlyayutsya kvantovye
svoistva fotona, zdes' net smysla govorit' ob etih kvantovyh svoistvah. | |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.02.2012 2:11, 1.6 KBait)
Smotryu chto v prakticheskih voprosah fiziki
moderatory okazalis' nekompetentny
i vedut sebya tishe vody, periodicheski vylazyat
estestvenno pozoryatsya, i zatykayutsya,
Vibe voobshe
zatknulsya - eto emu ne iz-za spiny s dubinoi napadat'
na pravah moderatora, i Vibe v silu svoei nekompetentnosti
v fizike chtoby ne opozoritsya
nikogda ne vyskazyval
mnenie po voprosam, tak vot forumy nabrali oboroty s prakticheskim
ottenkom.
Chto mogu skazat' s odnoi storony horosho, s drugoi
storony - u neopredelennogo poiska ne mozhet
byt' sluchainoi celi,
ona dolzhna byt' produmanna i sproektirovana,
dolzhna byt' model', a
eshe s tret'ei storony - rekomenduyu vmenyaemym ne tratit'
svoe bescennoe vremya po toi prichine
chto ya na membrane
obsuzhdal eti voprosy 10 let nazad, i ya iz teh kto
prohodit dorogu tak - chto po nei vtoroi raz hodit'
ne nado, v otlichie ot relyativistov
- kotorye odni i te-zhe
voprosy reshali sto let i ostalis' tam-zhe - v nachale puti.
Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta
Rekomenduyu - chitat' nado vnimatel'no nikuda ne toropyas'
ot nachala i
do konca, mozhet pokazat'sya chto tam mnogo lishnego,
na samom dele eto ne tak - uspehov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.02.2012 2:15, 183 Bait)
http://www.astronet.ru/db/forums/1244628
"Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta."
V predydushem poste perehod ne
pravil'nyi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.02.2012 12:58, 1.4 KBait)
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,92644.msg1861215.html#msg1861215
Voobshe-to neploho bylo by razdelyat' elektromagnitnoe izluchenie po tipu
proishozhdeniya.
Zachem?
----------------------------------
Ya v principe rad chto ne obshayus' na tom forume, eto forum
s diktatom
gnid. ... oni-zhe moderatory.
Moderatory tam obshyayutsya kak cari, i im vse
posetiteli foruma dolzhny i obyazany kak zemlya kolhozu.
Ya mogu obosnovat'.
Vot gandol'er Vibe zadal vopros, na normal'nom forume
ego s takim voprosom poslali by na ....
Na normal'nom forume vperedi voprosa idet obosnovanie
voprosa.
Mol ya vot schitayu chto to-to to-to razdelyat' ne logichno, po prichine
takoi-to. A zdes' chto poluchaetsya chto dybil v dannom voprose
tupit, i v dannom
sluchai trebuet u specialista
provesti emu besplatnuyu lekciyu po tomu voprosu v kotorom
on dybil. Sobstvenno eti voprosy ot moderatorov i tormozyat
forum, po
toi prichine chto chelovek dumaet nad svoimi voprosami
a potom on dolzhen otvlekat'sya i dumat' o tom chto na
sto vosem'desyat gradusov otlichaetsya ot togo chem on seichas
zanyat,
specialist otvlekaetsya i teryaet nastroi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.02.2012 15:10, 1.3 KBait)
Slesar'-santehnik
\\\Vot mayatnik - universal'nyi pribor svyazyvayushii ponyatiya
massy, prostranstva i vremeni...\\\
Vibe \\\Ne mnogovato chesti mayatniku? A esli ego pruzhinoi zamenit'?\\\
Slesar'-santehnik
\\\
Poluchitsya pruzhinnyi mayatnik!
Koleblyushiisya to kak mayatnik, to kak gruz na uprugom podvese...\\\
Vibe \\\...dlina kotorogo izmenyaetsya. Mozhno li skazat',
chto pruzhina "rasshiryaetsya" v processe ee kolebanii?\\\
Vibe \\\Slesar'-santehnik, ya proshu argumentirovat' svoi vyskazyvaniya, a ne vydavat' ih v vide aksiom.\\\
A
vot za takoe neznanie fiziki professorskih zvanii lishit' Vibe prosto neobhodimo,
ya by po krainei mere svoemu rebenku ne razreshil by u nego uchitsya v svyazi s prof neprigodnost'yu
professora Vibe.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.02.2012 19:08, 817 Bait)
Otvet #233 : Segodnya v 17:34:02
Na minuse batareiki nakaplivayutsya elektrony,na plyuse-pozitrony.
Kto tam sprashival, gde iskat' antimateriyu? Vot ona -- v lyuboi batareike na plyuse.
---------------------------
I Vibe bashnyu sneslo ne po detski.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.02.2012 4:41, 932 Bait)
ZhPS zadeistvovali dlya tochnosti, vot kak
v dushu gadyat i ne stesnyayutsya, dumayut chto vokrug lohi
a oni velikie lohoboi.
Dlya zamera
rasstoyaniya mezhdu tochkami dostatochno VCh kabelya
analogichnogo dlya TV, chtoby uznat' skorost' v kabele nuzhen
generator impul'sov, i oscillograf. S vyhoda generatora
impul'sov,
kotoryi formiruet korotkie impul'sy s bol'shoi skvazhnost'yu,
podaetsya impul's na odin konec kabelya, i odnovremenno na vhod
vneshnei sinhronizacii
oscillografa, i na oscillografe opredelyaetsya
zaderzhka kabelya.
I esli est' istochnik sobytii i udalennyi ob'ekt, to znaya vremya zaderzhki v
kabele - proizvoditsya
sinhronizaciya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.02.2012 23:40, 1.1 KBait)
Effekt Vavilova Cherenkóva (izluchenie Vavilova Cherenkova)
svechenie, vyzyvaemoe v prozrachnoi srede zaryazhennoi chasticei, kotoraya
dvizhetsya so skorost'yu, prevyshayushei fazovuyu
skorost' rasprostraneniya sveta
v etoi srede. Cherenkovskoe izluchenie shiroko ispol'zuetsya v fizike
vysokih energii dlya registracii relyativistskih chastic i opredeleniya ih
skorostei.
--------------------
Vot ishut otvet na eto izluchenie, a ego iskat' ne nado,
ono bylo vsegda. I so skorost'yu prevyshayushuyu
skorost' sveta. Fiziki
fiziki ne znayut.
Nado prosto vzyat' i skazat' mol izvinite povelis'
na relyativistskii lohotron kotoryi nauke nichego ne dal,
dazhe net metodov i priborov dlya
izmereniya relyativistskih
effektov.
Ya lichno ne vizhu nichego zazornogo, s kem ne byvaet
luchshe spustya 100 let chtoby mosk osoznal, chem vechno obeshat' chto
vse sovpadaet - tol'ko nado postavit' ocherednoi opyt chtoby opredelit'
oblast' primeneniya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 2:52, 1.4 KBait)
Naprimer,
zakon vsemirnogo tyagoteniya N'yutona priemlem (no ne adekvaten dlya belee,
chem dvuh tel), poskol'ku pozvolyaet reshat' pochti vse nuzhnye zadachi
"cherez uho" teorii vozmushenii.
Ya
chasto primenyayu zakon tyagoteniya N'yutona v zadachah dlya nepreryvnoi sredy
(dlya beskonechnogo kolichestva tel). I ne ispol'zuyu pri etom teoriyu
vozmushenii. Chto ya delayu nepravil'no?
-----------------------------
Vot kak byvaet, gandol'er ispol'zuet v raschetah svoistva plotnosti efira,
pri etom ego zapreshaet, a propagandiruet
pustotu, i pri etom
sprashivaet - pochemu kogda on hitrit, to pochemu on pri etom ne
gandol'er v ego glazah, a drugie kogda govoryat o srede - oni duraki,
tak
kak sredy v prostranstve net u relyativistov.
Cinizm u gandol'era v dannom sluchai na kachestvenno vysokom urovne.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 11:27, 14.1 KBait)
Otvet #84 : Segodnya v 09:13:42
Ne sleduet li iz nego, chto absolyutno vse nashi priemy yavlyayutsya iskusstvennymi?
Iskusstvennost'
chashe vsego ponimaetsya ne kak model'nost', a kak podgonka pod
neobhodimyi rezul'tat. Po krainei mere ya ego primenil imenno v etom
smysle. Naprimer, v rassmatrivaemom myslennom eksperimente A-V, uznav,
chto S po svoim chasam na polet ot A do V zatratil 1 sekundu, zayavili:"Eto
u nego chasy zamedlili svoi hod". Eto ne model', otobrazhayushaya
deistvitel'nost', a iskusstvennyi priem, tak kak iz fizicheskih
soobrazhenii yasno, chto chasy ne mogli zamedlit' svoi hod ot togo, chto
gde-to kto-to letit s bol'shoi skorost'yu po otnosheniyu k etim chasam.
-------------------------------------------
Otvet #85 : Segodnya v 09:22:30
iz
fizicheskih soobrazhenii yasno, chto chasy ne mogli zamedlit' svoi hod ot
togo, chto gde-to kto-to letit s bol'shoi skorost'yu po otnosheniyu k etim
chasam.
Tak oni i ne zamedlili. S vnimatel'no sledil za nimi; on podtverdit.
------------------------------------------------------
S odnoi tochki zreniya vozmozhen cinizm.
A s drugoi tochki zreniya neschastnyi vibe, zanimaetsya fizikoi
i v fizike on ne polnyi nol' on v nei sushestvo bestolkovoe.
---
Dlya resheniya dannogo voprosa dlya fizika osobo dazhe ne
nado prilagat' umstvennyh zatrat,
etot vopros otnositsya k voprosu ili voprosam
nosyashim
obshee nazvanie - sinhronizaciya.
Rassmatrivaemyi primer odin iz sluchaev sinhronizacii,
uchityvaya chto zadacha iznachal'no stavitsya ne korrektno,
ona vse ravno
reshaetsya odnoznachno.
---
Iznachal'no
nado opredelitsya s nazvaniyami, - sravneniya i izmerenie.
Sravnenie
- kogda ya izmeryayu dlinu lineikoi, ya prosto sravnivayu razmernost' odnogo s
analogichnym.
Izmereniya
eto kogda iz dvuh raznyh sushnostei, no izvestnyh kolichestvenno opredelyaetsya
tret'ya sushnost'.
Naprimer,
- napryazhenie cherez tok i soprotivlenie, skorost' cherez dlinu i vremya.
Teper' o prostranstve - poluchaetsya dva metoda opredeleniya ego velichiny, odin
variant - prosto lineikoi, vtoroi skorost'yu sveta.
Lineikoi
logichno i prosto.
Skorost'yu
sveta - poluchaetsya chto pytaemsya priravnyat' izmeryaemuyu velichinu - zavisyashuyu
ot vremeni, (i tochnosti chasov ih schitayushih) lineiki izmeryayushei rasstoyanie (tochnee
svoistv lineiki i ee podverzhennosti deformaciyam), i skorost'yu rasprostraneniya
elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya.
Chto
sobstvenno poluchaetsya - pri izmereniyu prostranstva, skorost'yu sveta po
sravneniyu s priravnivaniem prostranstva k lineike.
U
nas poluchaetsya rasstoyanie dlinna,
tol'ko my zadeistvovali chasy lineiku, i elektromagnitnoe izluchenie.
Dlya izmereniya u nas est' tri sushnosti
skorost' vremya i rasstoyanie, i est' svoistvo prostranstva v kotorom rasprostranenie
elektromagnitnyh kolebanii ravno nekotoroi skorosti kotoruyu nazyvayut skorost'yu
sveta.
Zdes'
nado ponimat' sleduyushuyu situaciyu, - chto s odnoi tochki zreniya mozhno skazat', -
chto eta skorost' bystraya no mozhno skazat' chto ona medlennaya. No v lyubom sluchai
prostranstvo dlya kolebanii yavlyaetsya liniei zaderzhki, v kotoroi rasprostranyaetsya
signal. Vot, a zdes' uzhe poluchaetsya chto prostranstvo sostoit iz chego-to. Eto
proishodit potomu chto, prostranstvo my opredelili izmeryat' v metrah.
Dlya
svetovogo izlucheniya prostranstvo proyavilo eshe odno svoe svoistvo - zaderzhka
svetovogo lucha. Sledovatel'no - prostranstvo
zapolneno veshestvom, kotoroe zaderzhivaet svetovoi signal, analogichno tomu kak v
vozduhe ili vode zaderzhivaetsya zvuk. Zdes' mozhno nemnogo porazmyslit' o
skorosti signala v sredah, v vode zvuk vo stol'ko raz bystree - chem v vozduhe,
vo stol'ko na skol'ko blizhe rasstoyanie mezhdu molekulami v vode - chem v vozduhe. Iz chego sleduet - esli
podelit' skorost' sveta na skorost' zvuka v vozduhe my poluchim velichinu vo
skol'ko raz blizhe chastichki sredy,
kotorym zapolneno prostranstvo po
sravneniyu s chasticami vozduha.
Na samom dele skorost'yu
sveta izmeryat' prostranstvo nel'zya, potomu chto eto ne pravil'no, tak kak
skorost' sveta za sekundu ne yavlyaetsya meroi dlinny.
Eto
vse ravno, chto govorit', - chto ot Kieva do Moskvy tri tysyachi 75 sekund skorosti
zvuka.
---
Slozhenie so skorost'yu sveta
i vychitanie, pri dvizhenii
ob'ektov.
Est' ob'ekt, kotoryi otnositel'no drugogo ob'ekta mozhet dvigat'sya.
Est' skorost' sveta, s kotoroi
rasprostranyaetsya svetovoe izluchenie v prostranstve.
Poluchaetsya - chto nuzhno uiti ot generatora izlucheniya na issleduemom, a generator
vse ravno nuzhen.
Zdes' prinimaem volevoe reshenie, generator raspolagaetsya na uslovno nepodvizhnom
ob'ekte.
Na tom ob'ekte kotoryi dvizhetsya budem raspolagat' prostoe zerkalo.
V kachestve istochnika vybiraem svetovoi luch modulirovannyi s chastotoi 300MGc,
chto v prostranstve budet iz sebya predstavlyat' odno kolebanie na metr dlinny,
tochnee odin period na metr.
Ustanavlivaem na avtomobile zerkalo , na vzletnoi polose ustanavlivaem stend s
svetovym generatorom 300MGc s uzko napravlennym luchom, i priemnik s
chastotomerom.
Pervyi opyt zaklyuchaetsya v tom chto avtomobil' raspolozhen na rasstoyanii 1km, i
nepodvizhen, prinimaemaya otrazhennaya chastota budet ravna peredayushei.
Opyt vtoroi - avtomobil' edet k stendu so skorost'yu 20metrov v sekundu, o chudo
chastota uvelichilas' na 20Gc. Prichina svyazana s tem chto pri dvizhenii k
istochniku, mashina proezzhaet na 20 metrov blizhe, a poskol'ku u nas v odnom
metre odin period kolebaniya, to chastota pri priblizhenii so skorost'yu 20 metrov v sekundu
uvelichitsya na 20Gc.
Opyt vtoroi mashina udalyaetsya ot stenda so skorost'yu 30 metrov v sekundu, i chastota
prinimaemaya ot zerkala avtomobilya nizhe peredayushei na 30Gc.
Iz chego sleduet, chto svet proyavlyaet svoi svoistva po otnosheniyu k prostranstvu,
kotoroe i zaderzhivaet svet.
Prostranstvo dlya sveta yavlyaetsya liniei zaderzhki.
Esli est' v chem, - svetu rasprostranyatsya i zaderzhivat'sya, to svet nahoditsya v
srede kakoi-to, analogichno zvuku v vozduhe.
Po toi prichine chto dannoe slozhenie i vychitanie chastoty mozhno povtorit' primeniv
vmesto svetovogo istochnika moshnyi dinamik a na avtomobile ustanovim chastotomer
s mikrofonom.
Berem chastotu 300Gc, u nas poluchaetsya pri skorosti zvuka 300metrov v sekundu,
odno kolebanie na metr.
Avtomobil' priblizhaetsya k dinamiku so skorost'yu 20metrov v sekundu, chastota
prinimaemogo zvuka v avtomobile bol'she na 20Gc, posle chego avtomobil' dvizhetsya
ot stenda so skorost'yu 30metrov v sekundu i chastota prinimaemaya v avtomobile,
nizhe na 30Gc.
A zvuk tochno dvizhetsya v srede, - eto vozduh.
Vot ya sobstvenno i pokazal metod slozheniya skorostei v sravnenii s analogichnym.
Mogut byt' nekotorye netochnosti so skorost'yu sveta v vozduhe, no eto ne
principial'no v dannoi zadache.
Estestvenno mozhno ispol'zovat' dannyi metod s raspolozheniem zerkala pod uglom 45
gradusov, pri etom raspolagayutsya priemnik i generator v raznyh mestah, i
peredvigaetsya zerkalo k i ot priemnika, ili k i ot generatora.
Chto ya schitayu nedostatkom dannogo opyta?, - osobyh tehnicheskih nedostatkov ne
vizhu, tak kak opyt so svetovym luchom budet rezul'tativnym i pri okolo svetovyh
skorostyah.
Estestvenno dannyi opyt ne rekomenduyu provodit' samostoyatel'no bez konsul'tacii
so specialistami po pravilam soblyudeniya tehniki bezopasnosti.
---
Obshaya ideya predydushih opytov v naglyadnosti
togo, chto pri
dvizhenii avtomobilya k ob'ektu ili ot nego, chastota prinimaemaya na avtomobile, i
otrazhennaya im chastota, budut odinakovymi, sledovatel'no esli avtomobil'
posredine mezhdu dvuh generatorov, kotorye rabotayut na odinakovoi chastote, to
esli avtomobil' budet peremeshat'sya mezhdu nimi po pryamoi linii mezhdu
generatorami, to summa chastot delennaya na 2 vsegda budet ravna ishodnoi chastote
generatora.
---
Estestvennye vyvody kotorye poluchilis',-
esli
prostranstvo izmeryat' v metrah, to u
prostranstva obnaruzhivaetsya svoistvo po
zaderzhke elektromagnitnyh izluchenii.
---
Vot sobstvenno ispol'zuya bazovye ponyatiya o elektromagnitnom
izluchenii mozhno bolee detal'no pereiti k svetovomu izlucheniyu.
Svetovoe izluchenie - kolebanie zaryadov
v srede vokrug
drug druga primerno s chastotoi 100TGc, pri ih dvizhenii
v srede so skorost'yu kotoraya opredelyaetsya plotnost'yu sredy.
Nado uznat' skol'ko
kolebanii v metre u sveta, podelim
100TGc, na 300 tysyach km v sekundu, i podelim eshe na 1000,
i uznaem kolichestvo v metre = 333 333.
Ili - 333 kolebaniya na
millimetr.
Teper' nado ponyat' chto predstavlyaet iz sebya interferenciya.
Zdes' vse prosto. Svetovoi luch razdelyaetsya na dva lucha,
polu prozrachnym steklom,
vnutri kotorogo sloi metalla,
kotoryi propuskaet chast' luchei a druguyu chast' otrazhaet,
po prichine togo chto zaryady fotonov pri vzaimodeistvii vrashayas'
letyat,
i tak kak vrashenie ih haotichnoe, to podletayut k sloyu
po raznomu, chast' udaryaetsya odnovremenno plashmya, i otrazhaetsya,
a chast' prohodit mezhdu atomami metalla.
Posle chego iz dvuh luchei s pomosh'yu zerkala i poluprozrachnoi
linzy vostanavlivaetsya luch.
Zdes' poluchayutsya kol'cevye volny, o prichine togo chto u nas
raznaya
dlinna luchei, i fotony imeyut haotichnuyu raskrutku.
Esli v odno plecho razdelennogo lucha vvesti sosud s vodoi
- opyt Fizo, i voda budet dvigat'sya s nekotoroi
skorost'yu, to u nas
kol'ca nachnut shoditsya i rashoditsya.
Esli ya voz'mu fonarik i budu priblizhat'sya k stene,
so skorost'yu 10m/s, i pri etom
budu
svetit' na stenu, to chastota prinimaemyh signalov
na stene budet 333 333 umnozhit' na 10, to est' na 3,333MGc,
bol'she chem v fonarike, esli s takoi-zhe skorost'yu budu
udalyat'sya,
to na takuyu-zhe chastotu signal budet men'she.
Zdes' nado ponimat' prichinu, prichina ne v narushenii chastoty generatora,
i chastotomera, prichina
v tom chto kogda sozdayutsya
blagopriyatnye usloviya dlya sozdaniya fotonov na niti spirali fonarika,
oni vyletayut v prostranstvo, i dvizhutsya v nem,
a chastota menyaetsya
potomu chto posleduyushie fotony, vyletayut
iz fonarika v to vremya kogda fonarik menyaet svoe raspolozhenie
v prostranstve po otnosheniyu k stene, na kotoroi chastotomer.
---
Eshe raz vnimatel'no ---
Chastota
menyaetsya po prichine izmeneniya rasstoyaniya mezhdu priemnikom i peredatchikom.
---
Vyvod
- dannaya situaciya opredelyaet edinstvenno vozmozhnuyu fizicheskuyu situaciyu
dlya elektromagnitnyh kolebanii v prostranstve
- effekt Doplera dlya sredy "Efira".
V vysheizlozhennom tekste slovo "foton" - oshibka, vmesto nego
-"svet".
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 11:45, 972 Bait)
Estestvenno so smehom vspominaetsya opyt ot dybilov v fizike,
- svetovye chasy na orbite v kotoryh luch vverh vniz pod uglom
dvizhetsya.
Gde zdes' oshibka nedalekih
matematikov delayushih bessmyslennye
v svoei besposhadnosti
shagi v fizike.
Oshibka ona v tom chto proishodit pereprivyazka iz odnoi sistemy koordinat
k drugoi v voprosah izmereniya dlinny naklonnogo lucha, tak kak k dline
lucha dobavlyaetsya dlinna peremesheniya odnoi sistemy po otnosheniyu
k drugoi sisteme, - chego
na praktike ne to chto ne sushestvuet, a prosto
nevozmozhno. A v dannom sluchae nevozmozhnoe s fizicheskoi tochki
zreniya vydaetsya matematikami za deistvitel'nost'.
V svyazi s chem relyativistov ochen' legko nagnut', prostym povorotom
svetovogo generatora lucha,
svetovoi generator dostatochno povernut' na 90gradusov,
i letit
vsya naglyadnaya agitaciya.
Tochnee opyt nagibaet eshe kruche relyativistov, po toi prichine
chto rulit effekt Doplera dlya sredy.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 12:03, 1.2 KBait)
Vspomnilsya eshe odin opyt dlya matematikov v fizike,
opyt s poezdom.
V raznyh variaciyah mussiruetsya eta situaciya.
Est' perron, na perrone est' dvoe chasov,
chasy idut odinakovo.
Chasy postavili v centre perrona, na krayu platformy,
odni chasy postavili na vysote odin metr, a vtorye chasy
na vysote dva metra.
Na
poezde est' dva sachka, v pervom vagone sachok lovit na vysote
odin metr, v poslednem vagone na vysote dva metra.
Letit poezd gruzhennyi relyativistami vdol'
perrona,
i proezzhaya vdol' perrona pervyi vagon lovit sachkom
chasy - matematiki zapisyvayut pokazaniya pervyh chasov,
potom sachkom lovyatsya vtorye chasy i matematiki
zapisyvayut
pokazaniya vtoryh chasov, znaya dlinu mezhdu poezdami
oni opredelyayut skorost'.
No surovye al'ty dlya relyativistov reshili postavit'
chasy tak kak
relyativisty stavyat nablyudatelei,
i surovye al'ty raznesli chasy na kraya platformy,
- i relyativisty okazalis' v shoke, poezd proezzhal
so svetovoi skorost'yu,
tak kak pokazaniya chasov ne
otlichalis'.
A potom surovye al'ty chasy pomenyali mestami,
i relyativisty sdelali vyvod matematicheskii
chto dvizhutsya v obratnuyu
storonu - vot takaya zhestokaya
matematicheskaya selyavi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 12:20, 182 Bait)
http://physics.ru/courses/op25part2/content/chapter4/section/paragraph2/theory.html
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 12:59, 1.5 KBait)
Otvet #559 : 05.09.2009 [19:31:35]
Chto ya takogo skazal? Ne udalyaite bez obosnovyvanii. Esli ya ne prav, skazhite v chem. Pravila
foruma ya ne narushal.
Vy
narushili pravila razdela, opublikovav smeluyu gipotezu ob evolyucii
spiral'nogo uzora i galaktiki v celom, ne soprovodiv ee
"obosnovyvaniem".
---------------------
Vot ya vse ponimayu, no ne ponimayu pochemu matematicheskii kloun vseh lechit fizikoi,
i etot kloun
primenyaet raznye fizicheskie sluchai dlya sredy i pol'zuetsya
imi, i ne obosnovyvaet prichinu togo chto on ispol'zuet volnovye svoistva i svoistva
sredy, - hotya kak
relyativist on etogo ne to chto ne imeet prava delat',
i uzh tem bolee ne dolzhen etim hvastat'sya, mol vse vokrug duraki
a on mol zabil na obosnovanie on prosto pol'zuetsya,
emu klounu matematiku tak udobnei.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 13:12, 1.0 KBait)
Otvet #687 : 07.07.2010 [11:26:05]
\\\Vibe
"Vy vidite kartinku" -- eto i est' sovremennaya fizika
glazami al'tov.
Chelovek vidit kartinku i nachinaet delat' vyvody. Skachaet s saita
fotografiyu spiral'noi galaktiki, pomeditiruet nad nei i nachinaet pisat',
chto spiral'nye rukava yavno vyletayut iz centra galaktiki. Dlya ne-al'ta
kartinka sama po sebe neset minimum informacii.
Interferenciya -- eto ne
poloski, a vpolne opredelennaya zavisimost' intensivnosti sveta ot
koordinaty.\\\
Vot krendel' - dazhe ne znaet chto krome Tomasa Yunga, kotoryi ob'yasnil interferenciyu
s tochki zreniya efira kak sredy - nikto krome Tomasa Yunga
nichego vnyatnogo
na planete Zemlya vot uzhe 200 let skazat' ne mozhet, moska ne hvataet.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 13:19, 2.5 KBait)
A vot to chto ya iskal, - izbrannost' teh kto v paradigme,
kto pol'zuetsya pust' i nepravil'nymi trudami drugih
relyativistov, te kto za sto let novoi gaiki ne vytochili
v relyativizme - a aplomba kak u pervootkryvatelei.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
\\\
Otvet #721 : 09.07.2010 [15:38:48]
Riskuya
byt' udalennym s foruma, vyskazhu svoe mnenie. Al't - uchastnik dannogo
foruma, vzglyady kotorogo na fizicheskie yavleniya ne sovpadayut s vzglyadami
D.V.
\Vibe \-
Ya ob etom pisal ne odin raz, i ne tol'ko ya. Al't -- eto chelovek, kotoryi prenebregaet nauchnoi metodologiei.
Eto prenebrezhenie mozhet prinimat' raznye formy, ot global'nyh ("Brat'ya i
sestry! S nauchnoi tochki zreniya Vselennaya est' Bog!") do chastnyh
(naprimer, vydacha personal'nyh umozaklyuchenii za ustanovlennyi fakt), no
smysl imenno v etom. Vazhno, chto eto prenebrezhenie -- neosoznannoe. Al't
prenebregaet nauchnoi metodolgiei ne potomu, chto ona emu kazhetsya
nepravil'noi ili on po nature revolyucioner, net. On prenebregaet nauchnoi
metodolgiei, potomu chto ponyatiya ne imeet o ee sushestvovanii.
Vozmozhno,
ya ne prav. Svoe mnenie osnovyvayu na nedopustimosti naveshivaniya etogo
neopredelennogo termina (yarlyka?) na teh, suzhdeniya i opyt kotoryh
ispol'zovan v nauke Fizika. A ih suzhdeniya vsegda byli komu-to
al'ternativnymi. Popast' v ih kompaniyu ishodya iz samoocenki - verh
neskromnosti. Al'ternativnost' suzhdenii yavlyaetsya neobhodimost'yu. Ob etoi
neobhodimosti ukazal Li Smolin v svoei "Nepriyatnosti s fizikoi...".
Polozhitel'nyi effekt al'ternativnyh suzhdenii v ih obosnovannosti. Svoi
suzhdeniya osnovyvayu na priznannyh faktah, t.e. ispol'zuyu uzhe priznannye
suzhdeniya. Dazhe pri etom poluchayu tuk-tuk po temechku. No esli ne imeyu
svoih al't. suzhdenii, a tol'ko somnevayus' v nekotoryh uzhe prinyatyh, to ya
al't ili ne al't?\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 13:21, 1.7 KBait)
Otvet #724 : 09.07.2010 [16:10:04]
Al't
prenebregaet nauchnoi metodolgiei ne potomu, chto ona emu kazhetsya
nepravil'noi ili on po nature revolyucioner, net. On prenebregaet nauchnoi
metodolgiei, potomu chto ponyatiya ne imeet o ee sushestvovanii.
Esli by al'ty byli takimi tupymi, oni by tak ne razdrazhali.
\Vibe\-
Tupost'
tut ni pri chem. Prosto kogda ya smotryu, naprimer, na tokarya u stanka, ya
ponimayu, chto u nego est' opredelennye pravila raboty. Ya ne znayu etih
pravil, no ya znayu, chto oni est', i ponimayu: esli mne hochetsya samomu
vstat' k stanku, ya dolzhen snachala usvoit' eti pravila. (Inache budet v
luchshem sluchae: "Ya tehniku bezopasnosti kak svoi tri pal'ca znayu!").
Podobnye pravila est' i v nauke, no kto o nih znaet? Obshestvennyi obraz
uchenogo -- eto chelovek, kotoryi sidit v kresle i dumaet. Poetomu legko
poverit' v to, chto vot sam sel v kreslo, podumal, i uzhe tozhe stal
uchenym.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 13:24, 997 Bait)
Net slov .
---------------------------------------------------------------

Otvet #726 : 09.07.2010 [16:13:01]
Al't - eto prosto laskovyi namek na forumnyh grafomanov.
\Vibe/-
Da net, pochemu zhe. Ya sam grafoman, chto ya, ne znayu?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2012 13:53, 1.3 KBait)
Smeyalsya, ibo matematik zanimayushiisya fizikoi
dumaet chto on tvorit nauku, a poluchaetsya cirk na lopate.
---------------------------------------------------------------------
\\\
Otvet #1240 : 15.02.2011 [17:48:53]
Predvizhu vozrazhenie, mol, vozzrenii-to kak takovyh net. Est' "potok soznaniya", "literaturnoe
proizvedeniya", "fantaziya", nakonec.
\Vibe\
V
bol'shinstve sluchaev eto tak. Byvayut, konechno, i isklyucheniya. Che,
naprimer. No v bol'shinstve sluchaev -- da. I ya deistvitel'no starayus' eto
podcherkivat', chtoby chitateli (v tom chisle, i nezrimye) ponimali, chto
zanyatie naukoi -- eto rabota, a ne sochinenie krasivyh tekstov s umnymi slovami.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.02.2012 11:26, 598 Bait)
Vot eto zhestko astronomov sdelali,
da uzh kakaya paradigma, takoe k nei i otnoshenie.
---------------------------------------
\\\Dorogie druz'ya!
Chest' imeem priglasit' vas k uchastiyu vo Vseukrainskoi nauchnoi konferencii
Kosmologiya i Kosmonavtika: istoriya i perspektivy,
kotoraya sostoitsya v g. Kieve, v NTUU KPI18 maya 2012 goda\\\
\\\Kontakty:
g. Kiev, pr. Pobedy 37, korpus 7, Fakul'tet sociologii i prava\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(Masha Kovaleva,
28.02.2012 12:05, 25 Bait)
Kvazar - eto Chernaya dyra?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.02.2012 20:55, 10.4 KBait)
Kvazar lichno dlya menya zvezda u kotoroi est'
bol'shoi vybros ili vybrosy v prostranstvo,
tol'ko luch napravlen na nas.
A esli luch napravlen ne na
nas, to eto uzhe drugaya zvezda,
-SS 433- naprimer.
A u chernoi dyry v avtorskoi traktovke -
izluchenie
A vot spektr kvazarov
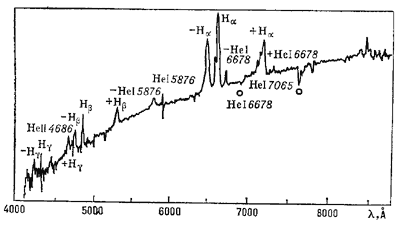
|
Ris. 1. Opticheskii spektr SS 433. Znakami plyus i minus
pomecheny podvizhnye emissionnye linii N , N , N , ,
N , Hel. Kruzhkami otmecheny
linii, obrazuyushiesya , Hel. Kruzhkami otmecheny
linii, obrazuyushiesya
pri pogloshenii izlucheniya v zemnoi atmosfere.
|
http://www.sdss.org/includes/sideimages/quasar_stack.html

I ot sebya dobavlyu, eto iz moego spora
s moderatorom pop mehaniki.
----------------------------------
Re: Chernaya dyra
19.09.201112:38
Material iz
Vikipedii
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/39/M87_jet.jpg/250px-M87_jet.jpg

Izobrazhenie, poluchennoe s pomosh'yu teleskopa Habbl: Aktivnaya galaktika
M87. V yadre galaktiki, predpolozhitel'no, nahoditsya chernaya dyra. Na
snimke vidna relyativistskaya struya dlinoi okolo 5 tysyach svetovyh let
Relyativistskie strui
, dzhety (angl. jet) strui plazmy, vyryvayushiesya iz centrov (yader) takih
astronomicheskih ob'ektov, kak aktivnye galaktiki, kvazary i
radiogalaktiki.
Obychno u ob'ekta nablyudaetsya dve strui, napravlennye v protivopolozhnye storony.
Na nastoyashii moment relyativistskie strui ostayutsya nedostatochno izuchennym
yavleniem. Prichinoi poyavleniya takih strui chasto nazyvayut vzaimodeistvie
magnitnyh polei s akkrecionnym diskom vokrug chernoi dyry ili neitronnoi
zvezdy.
V stat'e na Elementah metodom chislennogo modelirovaniya pokazano, chto
pri sliyanii dvuh neitronnyh zvezd obrazuetsya chernaya dyra, magnitnoe pole
kotoroi vytyanuto vdol' osi. Eto navodit na mysli, chto etot zhe process
mozhet formirovat' i relyativistskie strui. Tem ne menee, v stat'e
govoritsya, chto predlozhennaya avtorami nauchnoi raboty matematicheskaya
model' okazalas' ochen' slozhna, a vychislitel'nye vozmozhnosti sovremennyh
komp'yuterov okazalis' nedostatochny, chtoby s dolzhnoi tochnost'yu provesti
vse neobhodimye raschety i ubeditel'no dokazat' formirovanie strui.
V drugoi stat'e na Elementah provodyatsya paralleli mezhdu processami v
chernyh dyrah i boze-einshteinovskom kondensate. Otmechaetsya chto kondensat
mozhet kollapsirovat' (slipat'sya) i pri posleduyushem ego raspade tozhe
mogut voznikat' uzkonapravlennye vybrosy.
Dal'neishee izuchenie relyativistskih strui
Pri samyh pervyh popytkah ob'yasneniya sverhsvetovogo dvizheniya s pomosh'yu
relyativistskogo napravlennogo potoka chastic vozniklo oslozhnenie:
udivitel'no bol'shaya dolya kompaktnyh istochnikov pokazyvala sverhsvetovoe
dvizhenie, v to vremya kak na osnovanii prostyh geometricheskih dovodov
poluchalos', chto tol'ko neskol'ko procentov takih ob'ektov dolzhno byt'
sluchaino orientirovano pochti vdol' linii zreniya. Prisutstvie
simmetrichnyh protyazhennyh radiokomponent predpolagalo, chto oni
obespechivalis' energiei ot central'nogo istochnika dvuh simmetrichnyh
luchei. No trudno sravnit' svetimost' priblizhayusheisya i udalyayusheisya (ili
dazhe stacionarnoi) komponent. Eto ochevidnoe razlichie obychno obsuzhdaetsya v
kontekste modeli s dvoinym istecheniem [4], kogda izluchenie iz yadra
rassmatrivaetsya kak stacionarnaya tochka, gde priblizhayushiisya
relyativistskii potok stanovitsya neprozrachnym. Sverhsvetovoe dvizhenie
nablyudaetsya mezhdu etoi stacionarnoi tochkoi v sople i dvizhushimisya
volnovymi frontami ili drugimi neodnorodnostyami v vyhodyashem
relyativistskom potoke.......
.....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie (gamma-luchi, γ-luchi)
vid elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s chrezvychaino maloi dlinoi volny
< 5×10−3 nm i, vsledstvie etogo, yarko vyrazhennymi korpuskulyarnymi
i slabo vyrazhennymi volnovymi svoistvami.
Gamma-kvantami yavlyayutsya fotony s vysokoi energiei. Obychno schitaetsya,
chto energii kvantov gamma-izlucheniya prevyshayut 105 eV, hotya rezkaya granica
mezhdu gamma- i rentgenovskim izlucheniem ne opredelena. Na shkale
elektromagnitnyh voln gamma-izluchenie granichit s rentgenovskim izlucheniem,
zanimaya diapazon bolee vysokih chastot i energii. V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu. Ochevidno,
fizicheski kvanty elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s odinakovoi energiei ne
otlichayutsya, poetomu takoe razdelenie uslovno.
Gamma-izluchenie ispuskaetsya pri perehodah mezhdu vozbuzhdennymi
sostoyaniyami atomnyh yader (sm. Izomernyi perehod, energii takih
gamma-kvantov lezhat v diapazone ot ~1 keV do desyatkov MeV),
pri yadernyh reakciyah (naprimer, pri annigilyacii elektrona i pozitrona,
raspade neitral'nogo piona i t.d.), a takzhe pri otklonenii energichnyh
zaryazhennyh chastic v magnitnyh i elektricheskih polyah (sm. Sinhrotronnoe izluchenie).....
Esli net poverhnosti ob kotoruyu proishodit tormozhenie.
Material iz Vikipedii
.....Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh
obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v rentgenovskih
trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok yavlyayutsya
metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe antikatodom).
V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom, uskoryayutsya
pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom i katodom
(pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak uskorenie slishkom malo)
i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe tormozhenie. Pri etom za schet
tormoznogo izlucheniya proishodit generaciya izlucheniya rentgenovskogo diapazona,
i odnovremenno vybivayutsya elektrony iz vnutrennih elektronnyh obolochek atomov
anoda. Pustye mesta v obolochkah zanimayutsya drugimi ....
To vstupaet v silu fraza -
V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.
sledovatel'no pri otsutstvii udara o poverhnost' - otsutstvuet sama vozmozhnost'
vozniknoveniya rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, a esli izluchenie est' to ono mozhet
byt' tol'ko rezul'tatom izlucheniya v yadernom perehode. A eto uzhe chasticy vysokih energii.
avtorskoe izluchenie iz chernoi dyry -
.Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash metod obnaruzheniya Chernoi Dyry
-Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
....Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo.
ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut. ....
Padaya na Chernuyu Dyru veshestvo ne
mozhet rezko tormozitsya ili rezko uskoryatsya,
a sledovatel'no - ne mozhet
byt' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya po etoi prichine.
V svyazi s tem chto dlya uskoreniya do skorosti sveta
pri kotorom vozmozhno izluchenie neobhodimo
ne bolee 10 sekund, a zvezda razmerom s
Solnce na takoi skorosti proletit cherez gorizont
sobytii maksimum za minutu.
Gorizont sobytii - eto skorost' sveta - esli
ob'ekt uletaet s etoi skorost'yu ot nablyudatelya, to
u nego vozniknet krasnoe smeshenie.
Esli by veshestvo dolgo padalo - godami na maloi skorosti
s uskoreniem to bylo by zametno izmenenie Z u padayushih
tel v chernuyu dyru so vremenem, no pri etom nevozmozhno
rentgenovskoe izluchenie - iz za slishkom medlennogo
uvelicheniya uskoreniya.
.... Material iz Vikipedii Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri
vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah.....
A rentgenovskoe izluchenie est' - sledovatel'no
ego istochnikom mozhet byt' tol'ko rezul'tat yadernoi
reakcii.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.....
A esli rezul'tat izlucheniya istochnik yadernoi reakcii -
i on dlitsya godami, - to eto neitronnaya zvezda.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.02.2012 12:18, 6.2 KBait)
\\\Kvazar - eto Chernaya dyra?\\\
Uchityvaya nyuansy tekushei paradigmy kotoroi
po bol'shomu schetu do lampochki chto est' chernaya dyra,
dobavlyu
chto est' izluchenie.
Izlucheniya - elektromagnitnye, eto elektromagnitnye
kolebaniya kotorye yavlyayutsya izmeneniem plotnosti efira
v prostranstve analogichno zvuku
v vozduhe.
No est' nyuansy, esli posmotret' nizhe privedennuyu
tablicu to v nei ne hvataet neitrino.
Chto iz tablicy srazu vidno i ponyatno -
to chto elektro-manitnoe
izluchenie zakanchivaetsya na
ul'trafioletovom diapazone, i etot diapazon yavlyaetsya
perehodnym.
Posleduyushie izlucheniya - eto uzhe ne kolebaniya sredy,
eto
oskolki atomov, eto letyashie chasticy s opredelennoi
skorost'yu, a vyrazhenie \\\4 energiya fotona. \\\
sleduet ponimat' kak napryazhenie kotoroe prilagalos'
dlya uskoreniya chastic atomov, s posleduyushim razgonom
i udarom o mishen' i v rezul'tate udara poluchilis' oskolki
atoma.
I neitrino eto oskolki chastic
efira.
-------------------------------------

Klassifikaciya diapazonov spektra elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya
po-angliiski. Kolonki: 1 (chernaya) abbreviatury oboznacheniya diapazonov,
2 chastota, 3 dlina volny, 4 energiya fotona.
Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.02.2012 12:33, 916 Bait)
http://www.pravda.ru/science/eureka/hypotheses/29-02-2012/1109473-neitrino_falsh-0/
\\\Odnako pozzhe vyyasnilos', chto sam po sebe oscillyator ne vinovat. Delo v
tom, chto optovolokonnyi kabel', podayushii signaly ot GPS k nemu,
okazyvaetsya, oba raza byl prosto neplotno vstavlen. Voznikshee
elektricheskoe soprotivlenie v meste soedineniya privodilo k zaderzhke
signala. V rezul'tate vremya dvizheniya neitrino, soglasno raschetam,
umen'shalos', a ego skorost', sootvetstvenno, uvelichivalas'. Proshe
govorya, sensacionnye rezul'taty v eksperimentah OPERA obespechili
tehniki-razgil'dyai, kotorye prosto ne udosuzhilis' proverit', vseli v
poryadke.\\\
Dostatochno smeshno, osobenno -\\\Delo v
tom, chto optovolokonnyi kabel', podayushii signaly ot GPS k nemu,
okazyvaetsya, oba raza byl prosto neplotno vstavlen. Voznikshee
elektricheskoe soprotivlenie v meste soedineniya privodilo k zaderzhke
signala.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.02.2012 14:10, 2.6 KBait)
Vot esli pochitat' chto govorit zvezdo-bol po povodu
izluchenii - to iz ego teksta sleduet chto - chitatel' samostoyatel'no
dolzhen vo vsem sam razobrat'sya, i model'
sebe postroit'.
Kak mne ne nravyatsya takie klouny kotorye pishut
naukoobraznye stat'i v kotoryh poleznaya informaciya otsutstvuet,
i zadacha etih statei
- pokazat' kak avtor stat'i mnogo
znaet - no eti znaniya dutye, iz razryada - naduvatel'stvo.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://elementy.ru/lib/430399#radiowaves
Ot radiovoln do gamma-lucheiPredstavlenie
oedinstve fizicheskih zakonov
pozvolyaet sdelat' ochen' vazhnoe dopushenie. Pust' my ne mozhem, naprimer,
proniknut' vnedra zvezdy ili vyadro galaktiki, chtoby neposredstvenno
uvidet' proishodyashie tam processy. No my mozhem logicheski vyvesti
eti processy, nablyudaya proizvodimyi imi rezul'tat. Rezul'tatom etim
vpodavlyayushem bol'shinstve sluchaev okazyvaetsya svet, tochnee
elektromagnitnoe izluchenie vochen' shirokom diapazone chastot, kotoroe my
neposredstvenno i registriruem. Vse ostal'noe pomimo izlucheniya
predstavlyaet soboyu produkt teoreticheskoi interpretacii nablyudenii, sut'
kotoroi zaklyuchena dlya astronomov vprostoi formule OS, toest'
nablyudaemoe (observed) minus vychislennoe (computed). Chtoby ponyat' prirodu kakogo-libo ob'ekta, nuzhno postroit' ego model',
toest' fiziko-matematicheskoe opisanie proishodyashih vnem processov,
azatem spomosh'yu etoi modeli vychislit', kakoe izluchenie dolzhno
rozhdat'sya vetom ob'ekte. Dal'she ostaetsya sravnit' predskazaniya modeli s
rezul'tatami nablyudenii i, esli sravnenie okazalos' ne vpolne
ubeditel'nym, to libo izmenit' parametry imeyusheisya modeli, libo
pridumat' novuyu, bolee udachnuyu.
----------------------------
I etot matematicheskii kloun eshe lechit fizikov.
Za sto let relyativisty ne pridumali
nikakoi modeli, chego
oni zhdut, kogda perestanut mechtat', hotya s drugoi tochki zreniya,
fizicheskie modeli mogut pridumat' fiziki, a matematikam
estestvenno
takie modeli ne budut nravitsya, tak kak
matematikam pri adekvatnoi fiz modeli vhod v fiziku
budet zakryt na vechno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.02.2012 21:17, 1.2 KBait)
Otvet #486 : Segodnya v 18:54:20
Predlozhenie
- otkryt' otdel'nuyu vetku - i tam pust' vse al'ternativshiki drug s
drugom obshayutsya i sami otvechayut na sobstvennye voprosy.
A kak Vy ih tuda zagonite

-------------------------------------------------
Vot moderator ..., kak pravilo esli otkryvaetsya
takaya vetka to vsegda vopros v drugom, kak
s al'ternativnoi vetki vygnat' relyativistov s ih bredom.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.03.2012 14:12, 2.3 KBait)
Otvet #511 : Segodnya v 11:12:13
to, chto oto "ruhnet" - vopros vremeni, da i ne lozung eto.
Prezhde
chem govorit' ob etom, ili dazhe dumat'-rekomenduyu oznakomit'sya poka vas ne zabanili s Eksperimental'nye proverki obshei teorii otnositel'nosti: nedavnie uspehi
i budushie napravleniya issledovanii
http://www.mathnet.ru/php/getFT.phtml?jrnid=ufn&paperid=688&what=fullt&option_lang=rus
Posle oznakomleniya(a ono srazu otrezvlyaet) mozhno togda i k delu, t.e. obsuzhdeniyu pereiti

-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vse eti teorii yaica vyedennogo ne stoyat, oprovergayutsya v neskol'ko
minut.
1 Zayavlennoe pustoe prostranstvo oprovergaetsya tem, chto ono
obladaet svoistvom, kotoroe vystupaet liniei zaderzhki dlya sveta.
Chto delaet prichinu
dlya imenno takoi skorosti sveta?, -
prostranstvo pustoe, to skorost' ne mozhet byt' ogranichenna dlya chastic.
2 Zayavlennye fotony kak chasticy - glupost', lechitsya legko
-
letit foton so skorost'yu sveta, proletaet skvoz' steklo
v stekle snizhaet skorost' sveta v poltora raza, potom
vyletaet iz stekla i nabiraet skorost' - tak
vot
eto ne mozhet byt' svoistvom chastic, chasticy mogut zamedlyat'sya,
no uskoryatsya oni ne mogut, sledovatel'no svet analogichen
kolebaniyam zvuka v vozduhe.
Vyvod - i uzhe do lampochki vse proverki i eksperimenty,
tak kak oshibki global'nye.
Teorii gospodstvuyushei paradigmy -
bespoleznyi nabor formul.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.03.2012 18:42, 1.9 KBait)
Staryi relyativist obhezalsya po polnoi,
pered baryshnei, - vidno chto chto-to hochet smorozit',
no relyativistskii mosk privyk iskat' otvety v knizhkah,
a kogda
net v principe - na dannye voprosy dazhe opredelenii,
to chto on mozhet skazat', on mozhet sdelat' tol'ko umnyi vid
a po faktu vyglyadit glupee glupogo.
Sozdaet
vidimost' chto on mol vse znaet,
esli by znal to otvetil by po polnoi , a na poverku
ego znaniya - golimyi porozhnyak, i on ob etom
dogadyvaetsya.
-------------------------
Otvet #523 : Segodnya v 15:53:39
Neptun, neitrino, pozitron i mnogoe drugoe, vklyuchaya geliocentrizm, byli
snachala tol'ko gipotezoi na konchike pera teoretikov.
i ne tol'ko eto))
tema nazyvaetsya vyshe skorosti sveta.
pro gravitacionnoe pole - nichego ne
izvestno.
pro chernye dyry - tozhe
pro temnuyu materiyu - tozhe
pro elementarnye chasticy- nichego
pro zarozhdenie vselennoi- nichego
Uvy,
eto tol'ko podtverzhaet moi myagkii diagnoz. 
Vam neizvestno
- soglasen, no nado podpisyvat' IMHO.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.03.2012 5:12, 986 Bait)
Re: Chto takoe inerciya material'nogo tela?
Otvet #161 : Vchera v 19:48:50
Kakova cel' eksperimentov? Kakie vozmozhny ishody i chto oni budut oznachat'?
--------------------------
Moderator
tupit po polnoi, vsem ponyatno chto na lyuboi teme
esli predlagayutsya opyty, to dlya togo chtoby razobrat'sya
v fizicheskih voprosah dannoi temy.
Matematiku
ne ponyatno zachem nuzhny opyty
eli u nego i bez nih dvazhdy dva chetyre.
Gonite star pera, v smysle zvezdnogo tolkatelya iz moderatorov,
po prichine togo
chto on kruche vseh na forume tupit,
esli zametili, - vse spokoino obshayutsya i vsem vse ponyatno,
a moderator postoyanno tupit i zadaet dybil'nye voprosy.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.03.2012 15:13, 3.6 KBait)


Otvet #12 : Segodnya v 13:00:41
A razve na osnove planetarnoi modeli mozhno modelirovat' mnogoelektronnye
molekulyarnye obolochki?
Mozhno. No nuzhno uchityvat' kulonovskoe vzimodeistvie elektronov.
Strukturu molekuly benzola smodeliruete?
------------------------------------------------------------
Strukturu molekuly benzola smodeliruete?
Ya
ne imeyu vvidu tehnicheskuyu storonu voprosa - ved' i uravnenie Shredingera
odnochastichnoe. Mozhet byt' tehnicheski smodelirovat' molekulu benzola
ochen' trudno. Ya hochu skazat', chto principial'no uchet kulonovskogo
vzaimodeistviya rabotaet v planetarnoi modeli. Vecherom vylozhu raschet dlya
atoma geliya.
----------------------------------------
Otvet #14 : Segodnya v 13:44:27
Mozhet byt' tehnicheski smodelirovat' molekulu benzola ochen' trudno.
A mozhet byt', vovse nevozmozhno?
-------------------------------------------------------
Ya vot dumayu chto esli professor ne ponimaet chto esli emu
chto-to ne dano, to eto ne znachit chto
eto ne dano drugim,
dlya drugih eto vopros proshe prostogo.
Ya dumayu chto Vibe gde ne mozhet svoyu matematiku primenit'
to dumaet chto uzhe vse pipec - i eto
nevozmozhno.
Kak ya rad chto ya ne na etom forume s moderatorom
kotoryi professor v matematike i labuh v fizicheskih
zadachah, i kon' v pal'to v modelirovanii.
S drugoi storony ya rad za relyativistov, takie
kak Vibe derzhat eto stado v zagone, chto al'tov
izbavlyaet ot konkurencii.
I ya rad chto Vibe tak relyativistov
stroit - krassava.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.03.2012 21:06, 1.6 KBait)
Otvet #227 : Segodnya v 14:45:39
Ya proshu uchastnikov
sosredotochit'sya na obsuzhdaemoi teme. Teksty s lozungami i filosofskimi
obobsheniyami dalee budut udalyat'sya bez dopolnitel'nyh kommentariev.
---------------------------------------------------
Vot kakoi idiotizm na samom dele, a
moderator
professor k etomu idiotizmu nastoyatel'no ser'ezno trebuet
otnositsya.
---------
I vse relyativisty srazu po-vprygivali v mashiny vremeni,
i
nazhali na ruchnik i dali polnyi zadnii intellektual'nyi
tormoz, i ih klinonulo posle i poneslo nazad vo vremeni.
Zhdem vozvrasheniya, ot teh kto pobyval do bol'shogo
vzryva,
mnogie uzhe byvali v pervye minuty v pervye chasy i v pervye
sekundy bol'shogo vzryva.
Zdes' umesten deviz "ne obmanesh' - ne prozhivesh'".
Sovsem skoro lohoboi dolzhny vernutsya iz puteshestviya v proshloe,
ot tuda gde materii eshe ne bylo, a relyativisty tam uzhe byli,
i Dmitrii Vibe zhdet vozvrasheniya
geroev relyativistov
s dokladom, na polnom ser'eze.
A kak ya rad za relyativistov, molodcy - oni tak riskuyut puteshestvuya
v proshloe, nado po nobelevskoi
premii kazhdomu smel'chaku za
takoi geroizm i samopozhertvovanie davat'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
20.03.2012 15:56, 902 Bait)
http://www.computerra.ru/own/wiebe/660411/
\\\Solnechnyi veter vyduvaet vokrug nashei planetnoi sistemy gigantskii
puzyr' - geliosferu. Vnutri nee - mezhplanetnaya sreda, snaruzhi - uzhe
mezhzvezdnaya. Imenno mezhzvezdnaya sreda predstavlyaet soboyu tot komponent
Galaktiki, s kotorym Solnechnaya sistema kontaktiruet neposredstvenno.\\\
-------------------
Etot relyativistskii oboroten', vser'ez vzyalsya pisat' o srede
v prostranstve, - krassava.
Poluchaetsya vse relyativisty duraki chto dumayut chto kosmos pustoi,
a relyativist Vibe samyi umnyi, emu do lampochki chto relyativisty
postulirovali vakuum - pustotu, i otkazalis' ot sredy.
Zdes' est' odin variant Vibe dolzhen na gorizontah
v zagolovke sozdat' temu i izvinitsya pered
al'tami,
v stile " Prostite otcy "zas ranca" "
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.03.2012 17:55, 1.5 KBait)
Redkii sluchai, adekvatno rassuzhdayushii chelovek
na relyativistskom forume, i ne zabanennyi.
Kak eto moderatory proshelkali.
------------------------------------------------------------

\Uveryayu Vas, nikto dazhe ne zametil etoi kritiki. Mahisty (luchshe,
neopozitivisty) pohoronili materializm polnost'yu primerno do 1930 goda.
Pochitaite vnimatel'no Poppera i Kuna oni ochen' horoshie filosofy i
istoriki nauki.
Sovremennaya teoreticheskaya fizika po svoei
metodologii neopozitivistskaya (Popper nazyvaet ee to li
tehnologicheskoi, to li industiral'noi, uzhe ne pomnyu, podrazumevaya, chto
dlya sovremennyh teoretikov vazhno naiti okonchatel'nye uravneniya, no
sovsem ne vazhno, kakim putem oni polucheny). Ne mogu skazat', chtoby eto
mne ochen' nravilos', no, vo-pervyh, drugogo net, a vo-vtoryh, nauka
dobilas' takih uspehov na etom puti, chto mozhet byt' prav byl Feinman,
chto dlya nauki eto samaya luchshaya iz metodologii (nadeyus', Feinmana Vy ne
obvinite v tom, chto on ne znaet, chto govorit i delaet). \-
--------------------------------------------
Tak i poluchilos', formuly sami po sebe, - ne imeyushie
ne tol'ko fizicheskogo
ob'yasneniya no i fizicheskogo smysla.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A. I. Nezhivyh,
31.03.2012 21:08, 407 Bait)
V formule chernoi dyry net nikakih ogranichenii, kotorye mogla by prinimat' massa gravitiruyushego tela. Soglasno etoi formule
nasha Zemlya mogla ba prevratit'sya v chernuyu dyru radiusom 8,84 mm, a vmesto Solnca byla by chernaya dyra radiusom okolo 3-h km. Otsyuda sleduet vyvod, chto takih chernyh dyr, kotorye
opisyvaet tak nazyvaemaya teoriya, ne sushestvuet!!!
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.04.2012 19:16, 1014 Bait)
 [PDF] users.kpi.kharkov.ua/koef/Files/pr_c.files/Lab.../2.6_opt(Yung).pdf
[PDF] users.kpi.kharkov.ua/koef/Files/pr_c.files/Lab.../2.6_opt(Yung).pdf
----------------------
---------------------------
Obsuzhdayut geroicheski botaniki na forume.
S kakogo-to ul'ya pripisali Tomasu Yungu opyt na treh shelyah, kogda yasno
zhe napisano chto Tomas Yung prodelal ryadom dve dyrki igolkoi v kartone
i postavil kartonku pered solnechnym svetom.
A sovsem nedalekie fiziki dazhe ne ponimayut raznicu
v razognannyh chasticah
i svetom - eto pipec, - idiotizm v fizike.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.04.2012 19:22, 256 Bait)
Ya voobshe ne ponimayu zachem pisat' to chto ne vozmozhno,
i mne ne ponyatno kakoi baran pripisyvaet Tomasu Yungu opyt
na treh shelyah.
Tak-zhe ne ponyatno pochemu opyt
na dvuh shelyah i solnechnym svetom
ne prohodyat v shkole. Uzh opyt deshevle deshevogo.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.04.2012 19:34, 764 Bait)
http://msk.edu.ua/ivk/Fizika/Tushev_Shizika/TUSHEV2/18-2.html
\\\Tomas Yung nablyudal interferenciyu ot dvuh istochnikov, prokalyvaya
na malom rasstoyanii (d ≈ 1mm) dva malen'kih otverstiya v neprozrachnom
ekrane. Otverstiya osveshalis' svetom ot solnca, proshedshim cherez maloe otverstie
v drugom neprozrachnom ekrane.Interferencionnaya kartina nablyudalas' na ekrane, udalennom
na rasstoyanii L ≈ 1m ot dvuh istochnikov. Tak, vpervye v istorii, T.
Yung opredelil dliny svetovyh voln.\\\
Tekst pravil'nyi a resunok ne sootvetstvuet tekstu.
I zdes' kakoi-to botanik v fizike pririsoval pered dvumya shelyami
eshe odnu, ya dazhe ne ponimayu
kakim nado byt' nedalekim chtoby ne ponimat' togo chto eta shel' ne nuzhna.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.04.2012 19:54, 456 Bait)
Itogo opyt Tomasa Yunga, - ispol'zuyutsya dve prokolotye igolkoi
dyrki v kartone na rasstoyanii 1mm drug ot druga.
Dlya navedeniya solnechnogo lucha na malen'kie dyrki,
prodelyvalas' uslovno bol'shaya
dyrka diametrom 5-10mm vperedi dlya togo chtoby interferenciya nablyudalas'
v opredelennom meste na ekrane ustroistva.
-------
Ne znayu mne dazhe ne hochetsya kommentirovat'.
Skazhu prosto v opyte Tomasa Yunga luch na sheli ne prelomlyaetsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.04.2012 13:33, 1.0 KBait)
Citata Hartikov
Sergei: Esli Vy ustanovite detektor
fotonov (to est' takoi detektor, kotoryi schitaet fotony), to on budet
shelkat' ne vo vremya kazhdogo impul'sa lazera, a inogda.
Oznachaet
li eto, chto v odnofotonnom eksperimente daleko ne kazhdyi ispushennyi
istochnikom odinochnyi foton pronikaet v odnu iz shelei i uchastvuet v
sozdanii interferencionnoi kartiny?
-------------------------------
Eto zhe nado byt' takimi nedalekimi, eto zhe nado tak ne ponimat' fiziku,
i v itoge
propovedovat' vmesto fiziki idiotizm.
---
Prostymi slovami -
Opyt Tomasa Yunga na dvuh shelyah analogichen nalozheniyu dvuh fotografii
solnca odna na
druguyu, v rezul'tate chego poyavilis' temnye polosy na fotografiyah,
vmesto ozhidaemogo povysheniya yarkosti v mestah peresecheniya izobrazhenii solnca.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.04.2012 17:15, 2.4 KBait)
i bolee idiotskih i neobosnovannyh utverzhdenii pri etom ya davno
ne
vstrechal.
Prihodit nekotoryi "relyativist provokator" i zadvigaet to chego ne bylo
v avtorskom variante, on sam pridumal
Re: Master Theory (edition 3)\\\Hotya, pochemu-to
bol'shinstvo nisprovergatelei STO ot nego otmahivayutsya i risuyut malovrazumitel'nye kartinki bez osi vremeni.\\\
Zdes' imeetsya vvidu chto u vremeni poyavlyayutsya svoistva,
i ono mozhet menyat'
svoi temp i napravlenie dvizheniya.
Tak vot vlazit etot relyativist provokator so svoim bredom, posle
chego ego razvivaet,
Posle etogo
relyativist provokator ponimaet chto ego manevr ne proshel, i on ne
mozhet obosnovat' fizicheskuyu storonu svoih utverzhdenii, i perehodit na obsuzhdenie
zagovora relyativistov.
Zdes' vidim to kak gandol'erstvuyushii moderator vmesto togo chtoby zabanit'
relyativista provokatora za uvod diskussii v storonu on zakryvaet forum.
============
Otvet #99 : Segodnya v 15:21:05
Poskol'ku avtoru temy interesno obsuzhdat' ne svoyu "teoriyu", a zagovory, tema zakryvaetsya.
----



-

- Soobshenii: 111
- Reiting: +3/-0
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.04.2012 14:39, 1.5 KBait)
Ottogo
i voznikaet vopros: deistvitel'no li v odnofotonnyh eksperimentah
kazhdyi foton popadaet v odnu iz shelei? A esli da, to pochemu?
Vasha versiya?
Foton popadaet tol'ko v odnu iz shelei, foton prohodit cherez obe sheli,
foton voobshe cherez sheli ne prohodit?
I rassmotrite luchshe interferrometr maha-candera, tam poproshe budet reshit',
gde prohodit foton, tak kak rasstoyanie mezhdu vozmozhnymi
raznymi putyami mozhet
byt' desyatok metrov.
A perekrytie odnogo iz nih privodit k tomu zhe rezul'tatu - propadaniyu interferencii.
--------------------------------------------
Chto sobstvenno vidno iz etih obsuzhdenii - vidno to chto s pomosh'yu
fotonov adekvatno ne poluchaetsya opisat' interferenciyu.
Delo v tom chto esli ispol'zovat'
fotony oni mogut tol'ko uvelichivat' yarkost'
vtorogo istochnika pri nalozhenii na pervyi, a esli ispol'zovat' efir kak
sredu v prostranstve, a svet poluchaetsya - izmenenie
plotnosti efira
analogichnye v vozduhe - zvuku, to poluchaetsya prostaya i ponyatnaya kartina.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.04.2012 16:33, 1.8 KBait)
Rassmeshil menya etot forum
A esli Bol'shoi
vzryv - eto zabluzhdenie?
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,95394.0.html
vidat' svetlaya mysl' udarila v pustotu moska
chto mozhno zhe vse knizhki s idiotizmom perepisat'
na adekvatnye, ibo luchshe adekvatnoe ot durakov
chem idiotizm ot geniev.
I chto nablyudaetsya - a nablyudaetsya
chto v ocherednoi
raz popali v obsuzhdenii v nebo pal'cem, tak kak v itoge
obsuzhdeniya vyyasnilos' chto est' zhelanie nakryt' mednym
tazom bol'shoi vzryv u bol'shinstva
prisutstvuyushih,
i pri vsem pri tom vyyasnilos' chto nikto iz prisutstvuyushih
ne tol'ko modeli stroit' ne v sostoyanii, nikto ne
v sostoyanii i teorii stroit',
da i gipotezy tozhe,
da i ne v sostoyanii dazhe obosnovyvat' chto libo,
ibo eto zhe svoei golovoi dumat' nado, a do etogo
tol'ko iz knizhek chuzhimi ideyami argumentirovali.
Vot tak i okazalis' u razbitogo koryta - i ne mogut
obosnovat' prichinu togo chto bol'shoi vzryv polnaya erunda,
- hotya eto mogut sdelat' radioastronomy legko,
dlya etogo dostatochno smodelirovat' nekotoruyu situaciyu,
- a model'erov to i net chtoby situaciyu smodelirovat'.
Ladno s bol'shim vzryvom, a s chernymi dyrami
chto budut
delat', i s temnoi materiei i temnoi energiei, minimum
god na oproverzhenie kazhdoi erundy, a relyativizm oprovergat',
tem kto ego desyatiletiya zashishal.
No chto-to mne podskazyvaet chto pomenyayut moderatora, i
vernutsya obratno k istinnomu relyativizmu.
Po krainei mere hot' poimut kak - kachestvenno modelirovat'
-
tyazhelo na samom dele, i skol'ko chitat', sravnivat' i
dumat' nado po kazhdoi melkoi melochi chtoby ne prishlos'
dumat' po sto let vmesto togo chtoby dumat'
odin raz .
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
20.04.2012 14:19, 2.4 KBait)
Ne ponimayu
na skol'ko nado byt' nedalekimi chtoby ne ponimat'
togo chto bez strogogo opredeleniya dazhe ih
relyativistskogo pustogo prostranstva, poluchaetsya okolonauchnyi steb
vmesto adekvatnogo obsuzhdeniya.
Strogo pri etom nado opredelyat' otdel'no prostranstvo,
i otdel'no pustotu, i vremya s pustotoi, vremya v prostranstve,
i togda
srazu stanet ponyatno chto iz sebya stoit teoriya.
Delo v tom chto pri zayavlennoi pustote i ei
nedalekie uchennye pripisyvayut svoistva sred takie
kak - rasshirenie,
szhatie, zaderzhka volnovogo signala,
primenenie k pustote volnovyh svoistv(volny na granicah
mezhdu sred), rasprostranenie polei v pustote ( polya tozhe
mogut
byt' tol'ko v sredah po prichine togo chto polya sploshnye),
i primenyayut svoistva dlya sred
dazhe ne ponimaya togo chto oni zhe ot sredy otkazalis', a kakogo-to
ul'ya
svoistva dlya sred primenyayut.
V pustote mogut peredvigat'sya tol'ko i isklyuchitel'no - chasticy.
I vse situacii relyativistov mogut byt' isklyuchitel'no iz otdel'nyh chastic.
A vot kogda chastic tak mnogo chto oni sozdayut polya ili obretayut
neposredstvennoe vzaimodeistvie v vide plotnosti,
eto govorit o tom chto imeem delo so sredoi,
tak kak sredy byvayut
tol'ko sploshnye. I esli szhatie ili rasshirenie ispol'zuetsya dlya
chego-to sploshnogo to znachit process proishodit v srede, tak kak
u pustoty
svoistv ne byvaet, v pustote tol'ko chasticy otdel'nye drug
ot druga.
I esli naprimer est' staticheskoe pole - to eto ne otdel'nye chasticy
eto skoncentrirovalas'
nekotoraya sploshnaya sreda.
Dostatochno legko i odnoznachno nakryvaetsya ves' relyativizm mednym
tazom i srazu - effekt Doplera isklyuchitel'no dlya sred, sledovatel'no
mozhno otlichit' sredu ot pustoty - v pustote effekt Doplera ne rabotaet.
A tak kak v solnechnoi sisteme effekt Doplera rabotaet vezde, - to solnechnaya
sistema
zapolnena sredoi.
Do adekvatnyh obosnovanii eshe net ponimaniya neobhodimosti takovyh
i chtoby chto-to obosnovyvat' to nado imet' ili sposobnosti ili chtoby kto-to
obuchil, ili umet' ponimat' svoi nedostatki, - svoih sposobnostei net, obuchit' nekomu
neadekvatnosti svoego mirovozzreniya ne zamechayut - vot takaya zhestokaya selyavi.
I samoe smeshnoe chto dazhe ne ponimayut vsyu smehotvornost' urovnya oshibok.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.04.2012 10:04, 2.1 KBait)
Vot tozhe yarkii primer neadekvatnogo razgovora po prichine
neadekvatnogo ponimaniya fiziki.
Chto nado zametit' chto sporyashie naproch' zabyvayut chto
fotony
i ih skorost' ne zavisit ot togo v kakoi sisteme
otscheta nahoditsya nablyudatel'.
S odnoi tochki zreniya primenyayut shtatnyi teoreticheskii postulat
o postoyanstve
skorosti a rezul'tat smotryat
po effektu Doplera kotoryi dlya sred, i na polnom ruchnike ne ponimayut
chto i pochemu u nih ne shoditsya.
A kogda u nih ne
shoditsya fakt s idiotizmom teorii
primenyaetsya sleduyushii manevr zamedlenie vremeni
u dvizhushegosya ob'ekta.
-------------------
Otvet #129 : Segodnya v 06:23:18
Vy znaete, chto vremya idet po inomu v dvizhusheisya SK? A blizhe k skorosti
sveta(naprimer, v Zvezdolete budushego) ochen' zametno?
Voobshe-to
ono vedet sebya tak zhe. "Idet" absolyutno odinakovo, i po STO, i po OTO.
Chasiki tikayut s takoi zhe skorost'yu u kosmonavta na rakete, kak takie zhe
tikayut u togo, kto za nim nablyudaet v teleskop ...
Chasiki
u dvizhushegosya kosmonavta, esli na nih smotret' v teleskop, budut idti
medlennee. (za isklyucheniem vstrechnogo dvizheniya po odnoi pryamoi)
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.04.2012 19:01, 2.6 KBait)
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1334922693
 STO - ACKAYa ZhEST'
STO - ACKAYa ZhEST'
---------
Mne sobstvenno ne ponyatno pochemu dannuyu temu peremestil moderator
vo fludil'nu,
no eto vopros moderatorskii emu vazhny posetiteli.
A s tehnicheskoi tochki zreniya vopros podnimaemyi avtorom aktual'nyi,
no avtor delaet oshibku, po skol'ko eto kraeugol'nyi
kamen' to nado byt'
namnogo detal'no razbirat' situacii i pisat' vdumchivo obosnovanno
i vnyatno chtoby samyi nedalekii pochuvstvoval sebya obmanutym
i zabludivshimsya
v dvuh sosnah.
Sobstvenno na kachestvennom urovne ne pokazan lohotron letyashih
chastic fotonov, dlya etoi celi dostatochno zamedlit' kratno vse dvizhushiesya
predmety i proanalizirovat' situaciyu s raznyh storon v prostranstve.
Takzhe nado raz i navsegda razobrat'sya s lohotronyashim nablyudatelem,
kotoryi ne meryaet rasstoyanie
ot sebya do ob'ekta, i ne sinhroniziruet svoi chasy
s sobytiem, a esli on budet eto delat' to on i darom ne nuzhen.
---
A tema kak raz aktual'naya, relyativisty
v dannom voprose v silu svoei
doverchivosti v pravil'nost' teorii problemy vopiyushei i ne zamechayut.
Oni dazhe ne ponimayut pochemu u nih letyat chasticy ihnie zapostulirovannye
imi zhe, iz etih chastic u nih poluchaetsya neskladuha v teorii
u nih skorost' s lyuboi tochki dolzhna byt' konstanta - eto glupo estestvenno,
, no takoi u nih
postulat i pri vsem pri etom ih zhmet
eshe odin postulat chto pri tom chto s lyuboi tochki zreniya skorost' konstanta,
to eshe i sama skorost' "chastic fotonov"
v pustom prostranstve tozhe
konstanta - a vot eto uzhe verh gluposti, tak kak postulaty protivorechat drug drugu,
chto sobstvenno nazyvaetsya "paradoks" po
prostomu defekt v teorii.
I vyhodyat iz etoi situacii sleduyushim predpolozheniem, vyvodya sleduyushii
postulat chto u dvizhushego ob'ekta vremya vnutri nego zamedlyaetsya.
Chto sobstvenno zdes' smeshno, smeshno to sovsem drugoe smeshno kak raz
to chto sobstvenno to tormozit "chasticy fotony" v "pustote" imenno
do takoi skorosti, skorosti sveta?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.04.2012 19:16, 816 Bait)
S tehnicheskoi tochki zreniya s chasticami kak nositelyami
sveta prolet po polnoi programme. Delo v tom chto
pri stabil'noi skorosti sveta ne mozhet byt'
u fotonov
krasnogo smesheniya v principe.
Tak kak esli fotony letyat pust' posledovatel'nymi paketami
sinusoidal'noi plotnosti, to poluchaetsya chto pri pokrasnenii
uvelichilos'
rasstoyanie mezhdu fotonami sledovatel'no
ob'ekt izluchayushii udalyaetsya sledovatel'no skorost'
fotonov pri izluchenii byla nizhe otnositel'no priemnika
chto protivorechit
postulatu o postoyanstve skorosti.
Hotya estestvenno nado podumat' prezhde chem podobnuyu
stat'yu pisat', mozhet luchshe pust' pasetsya sebe relyativizm
na luzhaike,
vse-zhe men'she konkurenciya, da i relyativisty dumayut
chto zanyaty poleznym dlya obshestva delom a eto uzhe ne pereubedit'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.04.2012 22:31, 5.7 KBait)


 26032012119.jpg
(181.9 KB, 900x675 - prosmotreno 27 raz.)
26032012119.jpg
(181.9 KB, 900x675 - prosmotreno 27 raz.)

 26032012123.jpg
(172.31 KB, 900x675 - p
26032012123.jpg
(172.31 KB, 900x675 - p
----------------



-

- Soobshenii: 171
- Reiting: +6/-0
- Mne nravitsya etot forum!
-
Otvet #380 : Vchera v 23:40:22
Nakonec kartinka pomenyalas'.
--------------------------------

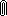 20042012234.jpg
(231.73 KB, 900x675 - prosmotreno 17 raz.)
20042012234.jpg
(231.73 KB, 900x675 - prosmotreno 17 raz.)

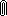 20042012235.jpg
(224.52 KB, 900x675 - prosmotreno 19 raz.)
20042012235.jpg
(224.52 KB, 900x675 - prosmotreno 19 raz.)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ne znayu kak komu no mne eto
napominaet tancy s bubnom.
Na mnogo proshe izmenit' konstrukciyu pechki, po centru
prosverlit' dyrku ustanovit' val iz zharoprochnoi nerzhaveiki,
na etot val i
ustanavlivaetsya koryto v kotorom plavitsya steklo,
k valu nado sdelat' reduktor i privod s chastotnikom, dlya podderzhaniya
stabil'noi chastoty vrasheniya, i nado ustanovit'
kontroller dlya
nagreva podderzhaniya i ohlazhdeniya.
I vse .
Itogo nado nasypat' v koryto stekla, vystavit' oboroty vrasheniya,
ot oborotov budet zaviset' fokusnoe
rasstoyanie i vklyuchit' kontroller
nagreva, nemnogo podozhdat' i vynut' izdelie polnost'yu gotovoe k napyleniyu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.04.2012 14:25, 3.1 KBait)





-

- Soobshenii: 2 684
- Reiting: +50/-16
- Suum suique!
-
Otvet #135 : Segodnya v 01:38:26
Pryamoi otvet:
Esli BV - eto zabluzhdenie ? - To nado iskat' model' bez BV i to
takuyu ,chtob krupnomasshtabnaya struktura sushestvovala na predel'nyh
rasstoyaniyah i byla podobnoi blizkoi - eto osnovnoe ,no varianty i
podrobnosti vazhny ............
Ne vidno osnovanii dlya utverzhdenii
BV - eto zabluzhdenie.
Esli oni (zabluzhdeniya) est', to privedite ih. Esli dovody budut
dostatochno ubeditel'ny to my rassmotrim al'ternativu dlya sravneniya. Nu,
naprimer,-golograficheskii ili ekpiroticheskii scenarii

Posmotrim
i sravnim, chto oni mogut ob'yasnit' chego net v teorii BV.
-------------------------------------
Prosto i krasivo, etot sluchai pokazyvaet to chto nel'zya soderzhat'
tysyachi
fizikov kotorye dumayut po pridumannomu v knizhkah, eto ballast.
S drugoi tochki zreniya dazhe esli tysyachi knizhkochitozubrov postavit'
zadachu, to mozhno byt'
spokoinym v tom chto oni ne smogut ee reshit',
tak kak samostoyatel'no oni nikogda ne reshali a vychityvali otvety v knizhkah.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.04.2012 14:55, 2.0 KBait)
Smeshno,- bol'shoi vzryv vazhnee tepla ot zvezd
dlya botanikov taki da.
Hotya otvet na vopros proshe prostogo
dostatochno ponimat' fizicheskie svoistva.
Pri
zayavlennoi pustote prostranstva relyativistov
vzryv v prostranstve u nih ne vozmozhen po opredeleniyu
ibo "vzryv" - eto svoistvo nepreryvnoi sredy, a sredy
net.
Ya v principe ne ponimayu na skol'ko nado byt' nedalekimi
chtoby ne ponimat' togo chto eta vydumka byla pridumana dlya togo
chtoby det' energiyu ot zvezd,
kotoraya v itoge uletaet
za gorizont sobytii. I nado ponimat' do teh por
poka oni ne zametyat svoi osnovnoi
vopros - kuda devaetsya teplo ot zvezd to k astronomam
vryad-li budet obshestvennost' adekvatno obshat'sya.
---
Eshe raz - v kazhdom kvadratnom graduse zvezdnogo
neba 10 v shestoi zvezd, kotorye svetyat milliardy
let i vydelyayut trilliony gigavatt energii - pri etom
v kosmose holodno i kosmos ohlazhdaet zemlyu.
---
Yasnyi i ponyatno chto bol'shoi vzryv ne spasaet situacii
po poglosheniyu tepla ot zvezd tem ruchnym upravleniem chto
teplo ot zvezd uletaet a reliktovyi fon ot bol'shogo vzryva
nikuda ne mozhet uletet' i ostaetsya kolbasit'sya
vechno,
no dazhe eto ne reshaet vopros pochemu net zareva zvezdnogo
neba i pochemu vokrug ne tysyachi gradusov zhary,
a naoborot kosmos holodnyi po samoe dal'she
nekuda,
tak kak v kosmose obyazany byt' "holodil'niki",
kotorye ne kak chernye dyry pogloshayut teplo a
eshe i kruche ohlazhdayut vse vokrug sebya, ya etot
vopros reshil - Zvezda Efira. Kolichestvo zvezd efira
u menya tozhe mozhet byt' i bol'she kolichestva zvezd,
po skol'ku zvezda bolee menee vechnaya struktura,
i zvezdy v processe svoei zhizni kondensiruyut efir vnutri sebya
i periodicheski ego iz sebya vybrasyvayut po prichinam
izmeneniya plotnosti efira v prostranstve ili
po fizicheskim prichinam vnutri samoi zvezdy
vnutri kotoroi zvezda efira. I zvezda mozhet
za vremya svoei zhizni skondensirovat'
vnutri sebya hot' million
raz zvezdu efira i izbavitsya
ot nee vybrosiv v kosmos.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.04.2012 12:22, 1.8 KBait)
Teoreticheskie vozzreniya dolzhny ukazyvat' na vozmozhnost' sohraneniya sovremennoi otnositel'noi rasprostranennosti elementov v modeli vechnoi Vselennoi,
a ne na ee nevozmozhnost'. Kak Vy, bezuslovno, znaete, utverzhdeniya v nauke dolzhny dokazyvat'sya avtorami, a ne oprovergat'sya opponentami.
-----------------------------------------------
Moderator opyat' zhzhet.
Che-to ya ne pomnyu kak obosnovyvalas' imenno
takaya prichina imenno takoi skorosti sveta
v pustoi pustote letyashih chastic-fotonov.
Da i ne pripomnyu kak relyativisty na mashine
vremeni letali v nachalo bol'shogo vzryva.
---
I chto menya udivlyaet tak eto massovoe otsutstvie moska pri analize
sostava zvezd. Ni do kogo ne dohodit chto ih metalichnost' v verhnih
sloyah zvezdy. A vnutri zvezdy dazhe vodoroda net ibo eto i konyu ponyatno
chto vodorod samyi
legkii i u nego net vozmozhnosti fizicheskoi i intellektual'noi
chtoby proniknut' v centr zvezdy.
Ne znayu na skol'ko nado byt' nedalekimi chtoby ne ponimat' chto vodorod
po prichine togo chto ego udel'naya plotnost' nizhe - on ne mozhet byt' ne
to chto v centre zvezdy, on mozhet byt' isklyuchitel'no v verhnih
sloyah, i kak i komu eto
mozhno dokazat' esli mosk vynut i polozhen na polku.
Itogo - svoim pacanam mozhno postulirovat',
i ih nel'zya oprovergat', tak kak nekrasivo.
A chuzhim al'tam
nado dokazyvat' v kosmicheskih
masshtabah.
I kak naprimer fiziku ob'yasnit' matematiku chto vodorod
ne mozhet byt' vnutri zvezdy, matematiku do lampochki po formulam
shoditsya,
a fiziku principial'no ibo eto nevozmozhno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.04.2012 16:47, 2.3 KBait)
A esli est' v dostupnyh publikaciyah tolkovoe izlozhenie, togda kak?
S chego by im vzyat'sya esli metry k edinomu mneniyu otnositel'no TBV ne mogut priiti.
To
est', Vy sami ne interesovalis', est' li v dostupnyh publikaciyah
tolkovoe izlozhenie? Vy pochitali privedennuyu ssylku i na ee osnovanii
sdelali vyvod, chto izlozheniya net?
-----------------------------------------------
Kak govoritsya mechtat' ne vredno.
Moderator opyat' zhzhet.
Nikto vnyatnoi prichiny ne znaet, i obosnovaniya bol'shogo vzryva
tozhe, i nikto pri bol'shom vzryve ne prisutstvoval
a zato skol'ko professorami stalo.
Esli
by bylo vnyatnoe i ponyatnoe obosnovanie -
to tol'ko po neznaniyu adekvatnogo ob'yasneniya
zadavali by voprosy,
a voprosy zadayut massovo, znachit est' prichina
- polnoe otsutstvie adekvatnogo obosnovaniya.
---
Kak po mne uchityvaya kolichestvo gluposti to logichno
za oproverzhenie davat' professorskie zvaniya, ibo
relyativizm
voshvalyat' ili bol'shoi vzryv moska ne nado.
Hotya idiotizm situacii to na poverhnosti, tol'ko nedalekim
ne ponyatno chto 4.5 mlrd let,
eto
perehod urana iz odnogo sostoyaniya v drugoe, no eto zhe
ne znachit chto uran do etogo ne sushestvoval.
Bui s nim s tem uranom pust' on raspadaetsya do zheleza, -
zhelezo
na zemle est' - skol'ko tysyach milliardov let nado bylo zhelezu
dlya etogo vremeni?, da i ot kuda togda uran vzyalsya?
Kak po mne s vozrastom i metodami opredeleniya
vozrasta Zemli polnyi abzac,
a vse tuda-zhe vozrast vselennoi ot bol'shogo vzryva opredelyat'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.04.2012 19:14, 13.0 KBait)
Otvet #194 : Segodnya v 17:53:33
V
stacionarnoi Vselennoi est' problema nablyudaemoi odinakovoi
rasprostranennosti himicheskih elementov na masshtabah, sootvetstvuyushih
vremennym intervalam modeli Bol'shogo vzryva poryadka 10 mlrd. let. No eta
zhe problema imeet mesto i v modeli Bol'shogo vzryva; v etoi chasti modeli
ravnopravny.
V modeli Bol'shogo Vzryva etoi problemy net. Ona ne predskazyvaet postepennoe vozrastanie metallichnosti.
--------------------------
Vot tak zvezdyat prohffesora.
Zahotel i net metallichnosti, zahotel i vodorod ne
gorit s preobrazovaniem vo vse
bolee tyazhelye elementy,
i yasnyi kon' chto tol'ko gandol'erstvuyushii prohfesor ne
znaet chto zhizn' zvezd v tekushei paradigme zakanchivaetsya
ili chernoi dyroi ili
zheleznym yadrom, tak kak pri raspade
zheleza energii bol'she pogloshaetsya chem vydelyaetsya.
Vse astrofiziki znayut o metalichnosti odin moderator ne
znaet.
Gonite
v sheyu dvulichnogo lohoboya.
---
Vot ya v guglyah nabral
- zheleznoe yadro starye zvezdy-
---------------
---------------
---------------
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Astronet > Novye i sverhnovye zvezdy >>
Glava XII ...
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'Soobshenii:
16-Avtorov: 8-19 mai 2010
... share, imeyushem koru, mantiyu i zheleznoe yadro, kotoruyu my zauchenno ...... V centre sfery na ostatkah
tverdogo yadra staroi zvezdy ...
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.04.2012 3:28, 1.4 KBait)
A larchik prosto otkryvalsya koe kto na svoei volne zalip.
---------------------------------------
http://www.computerra.ru/own/wiebe/630833/
V rezul'tate
sovremennyi spektral'nyi klass Solnca vyglyadit kak G2V.
On oznachaet, chto Solnce imeet cvet, sootvetstvuyushii temperature poryadka
6000K, vnutri spektral'nogo klassa G ono raspolozheno blizhe k granice s
klassom F, chem k granice s klassom K, a cifra V govorit o prinadlezhnosti
k karlikam, to est' zvezdam s kompaktnymi plotnymi atmosferami. Dvumya
slovami - zheltyi karlik. Prochie parametry takovy: massa 21027 tonn, svetimost' (moshnost' izlucheniya) 1026 vatt, diametr okolo polutora millionov kilometrov.
Naskol'ko eti parametry pohozhi ili ne pohozhi na parametry drugih
zvezd? Nachnem s glavnogo - s massy. Teoriya zvezdnoi evolyucii utverzhdaet,
chto imenno etot parametr dlya zvezdy yavlyaetsya opredelyayushim. Voobshe,
zvezdnye massy zaklyucheny v ves'ma shirokih predelah - ot odnoi desyatoi
massy Solnca do sotni ili dazhe soten solnechnyh mass. Odnako kolichestvo
zvezd raznyh mass sushestvenno raznoe, i chem men'she massa zvezdy, tem
bol'she takih zvezd v Galaktike. Skazhem, na kazhduyu zvezdu s massoi
poryadka sotni solnechnyh mass prihoditsya neskol'ko soten zvezd s massoi
poryadka odnoi solnechnoi i okolo desyati tysyach zvezd, menee massivnyh, chem
Solnce.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.04.2012 13:41, 41.4 KBait)
Otvet #186 : Segodnya v 08:21:20
V modeli Bol'shogo Vzryva etoi problemy net. Ona ne predskazyvaet postepennoe
vozrastanie metallichnosti.
No predskazyvaet nepostepennoe (nekotoroe) ,ili net?
Strogo
govorya, model' BV neset otvetstvennost' tol'ko za nachal'nyi
nukleosintez (Big Bang Nucleosynthesis, BBN). Ostal'noe -- eto voobshe ne
k nei, a k modelyam zvezdnoi evolyucii i evolyucii galaktik.
-----------------------------------------------
Ne znayu na kogo rasschitany takie otpiski.
Ne ponimayu pochemu moderator dumaet chto na ego forume
bezmozglaya skotina kotoraya ne znaet kosmologii,
ya dumayu chto on dogadyvaetsya chto oni znayut chto on
ih mozg trahaet po polnoi i ponimaet chto on moderator
i esli kto-to oborzeet i ukazhet na ego oshibku
to budet srazu zabanen.
Nabirayu v guglyah - vodorod pri bol'shom vzryve-.
i idu po pervoi ssylke.
------------------
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'Otvetov:
2-13 iyul 2011
Pri Bol'shom vzryve tyazhelye elementy kogda obrazovalis' v samom ... s ostatkami elektronov, kotorye i obrazovali vodorod.
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
-----------
K dalee napisannomu nado otnositsya s ponimaniem togo chto dlya al'tov
eto vysosano iz pal'ca i ukrasheno idiotizmom, a dlya relyativistov
eto nastol'naya kniga po
kotoroi oni dumali, dumayut i budut dumat'.
\\\K koncu vtorogo perioda, to est' cherez 5
minut posle Bol'shogo Vzryva, rasshiryayusheesya veshestvo sostoit iz yader atoma
vodoroda 70% i yader geliya 30%. \\\
http://mrcnn.narod.ru/bigbang.htm
Iz pervichnogo sostava sleduet chto eto ne bol'shoi vzryv, a
"Zheleznyi Pipec".
Da rekomenduyu prochitat' vse, ne znayu kak komu no kak po mne
ne v obidu avtoru (tekst chitaetsya kak raz legko),soderzhanie soderzhit stol'ko
neobosnovannyh
vydumok smeshannyh s glupost'yu, soderzhat ogromnoe
kolichestvo vzaimnyh protivorechii chto eto prosto chto-to s chem-to.
\\\Imeyutsya
nekotorye
estestvennye vehi, kotorye delyat ves' interval vremeni posle Vzryva (vse vremya
zhizni Vselennoi, poskol'ku ee letoischislenie nachalos' s Bol'shogo Vzryva) na
otdel'nye periody. Pervyi takoi period (vozmozhno, sostoyashii iz podperiodov) ot
nachala Vzryva prodolzhalsya vsego 1 sekundu. No imenno v etot period byla
opredelena vsya dal'neishaya "sud'ba" Vselennoi (ee stroenie, himicheskii
sostav, evolyuciya).\\\
Yasen kon', esli v nachale byl vodorod i gelii to doroga evolyucii odna - vpered k zheleznym
kosmicheskim bolvankam.
-------------------
Vot nashel
------
http://mrcnn.narod.ru/bigbang.htm
\\\Evolyuciya
zvezdy opredelyaetsya, glavnym obrazom, ee - massoi. Estestvenno, chem
bol'she massa zvezdy, tem bol'she
.; energiya, kotoraya mozhet vydelit'sya vnutri zvezdy v processe
termoyadernyh reakcii. Drugimi slovami, tem bol'she
' goryuchego soderzhitsya vnutri takoi zvezdy. Kazalos' by, takaya zvezda
dolzhna zhit' (svetit'sya) dol'she. No eto ne tak. Chem massivnee zvezda, tem
bol'she ona izluchaet energii v kosmicheskoe prostranstvo. Tak, esli massu
zvezdy uvelichit' v tri raza, to ee rashod energii na izluchenie
(svetimost') uvelichitsya v devyat' raz! Poetomu s uvelicheniem massy zvezdy
prodolzhitel'nost' ee zhizni rezko umen'shaetsya. Tak. naprimer, goryuchego
dlya yadernogo reaktora vnutri Solnca hvatit eshe na desyatki milliardov
let. Okolo pyati milliardov let eto goryuchee uzhe rashoduetsya. No, esli
massa zvezdy v 50 raz prevyshaet massu Solnca, to ee goryuchego hvatit
vsego na neskol'ko millionov let!
Kogda
v processe termoyadernyh reakcii v yadre zvezdy izrashoduetsya ves'
vodorod (on prevrashaetsya v gelii), to termoyadernye reakcii prevrasheniya
vodoroda v gelii nachinayut idti v sloe vokrug yadra. Svetimost' zvezdy na
etom etape
, uvelichivaetsya. Zvezda kak budto razbuhaet. No temperatura
poverhnostnyh sloev zvezdy umen'shaetsya, poskol'ku razmery ee
uvelichilis', poetomu ona nachinaet svetit'sya ne golubym, a krasnym
cvetom. Takuyu zvezdu nazyvayut krasnym gigantom. Dal'she zvezda
evolyucioniruet sleduyushim obrazom. Poskol'ku v yadre ne idut termoyadernye
reakcii i ne vydelyaetsa teplo, ona postepenno szhimaetsya pod deistviem
sil gravitacii. V rezul'tate szhatiya yadra uvelichivaetsya ego temperatura.
Ona dostigaet 100150 millionov gradusov. Pri stol' vysokoi temperature
gelii stanovitsya istochnikom tepla: idut termoyadernye reakcii, v
rezul'tate kotoryh yadra geliya prevrashayutsya v yadra ugleroda. Davlenie
vnutri yadra zvezdy uvelichivaetsya, poetomu szhatie prekrashaetsya.
Svetimost' zvezdy na etom etape uvelichivaetsya, tak kak v nee vnosit
vklad i vydelenie energii iz yadra. V rezul'tate uvelichivaetsya i
poverhnostnaya temperatura zvezdy. No kogda-to konchaetsya i gelii. Prichem
znachitel'no bystree, chem konchilsya vodorod. Kogda eto proishodit, zvezda
teryaet svoi naruzhnye sloi. Oni rasshiryayutsya i otdelyayutsya ot yadra zvezdy.
Eti sloi vposledstvii nablyudayutsya kak planetarnaya tumannost'. Sud'ba
yadra zvezdy posle etogo zavisit ot ee massy. Esli massa zvezdy men'she
1,2 massy Solnca, to veshestvo zvezdy pod deistviem gravitacionnogo
szhatiya uplotnyaetsya takim obrazom, chto ego plotnost' dostigaet 10 tysyach
tonn v kubicheskom santimetre. Pri takoi ogromnoi plotnosti atomy
razrushayutsya. Posle etogo szhatie zvezdy prekrashaetsya, tak kak emu
nachinaet protivodeistvovat' sila uprugosti obrazovannogo ochen' plotnogo
gaza. Obrazovannaya takim putem zvezda (ee nazyvayut "mertvoi") yavlyaetsya
belym karlikom. Takim obrazom, do togo, kak zvezda prevratitsya v belogo
karlika, ona na nekotoroe vremya stanovitsya krasnym gigantom. Zatem belyi
karlik v techenie neskol'kih milliardov let ostyvaet i prevrashaetsya v
chernogo karlika, to est' telo ne izluchayushee a poetomu i nevidimoe. I.S.
Shklovskii nazval ego "trupom" zvezdy. Esli massa pervonachal'noi
zashlakovannoi zvezdy prevyshaet kriticheskuyu velichinu v 1,2 massy Solnca,
to sily uprugosti sverhplotnogo (vyrozhdennogo) gaza ne v
sostoyanii spravit'sya s silami gravitacionnogo szhatiya.\\\
---
Ladno zapostulirovali glupost' chto ot massy tak eto ne
znachit chto nado bezmozlo v teleskop smotret' i stat'i pisat' neochem,
Nado skazat' chto istinna dorozhe i poslat' v dal' to chto ne
sootvetstvuet nablyudeniyam, po toi prichine chto ne nablyudaetsya
togo chto chem dal'she zvezdy i chem u nih bol'she "Z" to tem
oni bolee
massivnye.
---
Itogo
Bol'shoi vzryv na samom dele kak raz i opredelyaet metalichnost'
ibo zadanna nachal'naya sostavlyayushaya stol'ko to vodoroda
i
stol'ko-to geliya.
I zadanna neobratimost' so vremenem prevrasheniya zadannyh
veshestv v bolee tyazhelye, i est' konec etogo kolenkora pod
nazvaniem "Zheleznyi
Pipec", po prichine togo chto vse dolzhno
prevratitsya v kuchu zheleznyh bolvanok.
Ot massy tozhe ne mozhet zaviset' vozrast zvezd, tak kak
eto protivorechit
nablyudeniyam, - eta lapsha na ushi prohodila
tol'ko pri slabyh teleskopah, v kotorye nel'zya bylo
rassmotret' dalekie galaktiki.
--------
U menya
takoe chuvstvo chto voprosami astronomii voobshe astronomy
ne zanimayutsya v principe, im prosto nachhat' na to pravil'naya ona
ili nepravil'naya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.04.2012 14:44, 595 Bait)
Dlya teh kto ne ponyal pochemu ne mozhet massa opredelyat'
vozrast zvezdy.
V teleskopy nablyudayutsya zvezdy pervyi milliard let
ot bol'shogo vzryva.
Sledovatel'no
vse zvezdy etogo milliarda dolzhny byt'
v osnovnom iz vodoroda i geliya - chego ne nablyudaetsya,
v nih est' metally.
Iz etogo poluchaetsya chto v nachale bol'shogo
vzryva dolzhny byt'
metally - chto nevozmozhno ibo eto uzhe ne bol'shoi
vzryv a drugaya teoriya, i vtoroi variant chto bol'shoi
vzryv kotoryi priduman glyadya na vzryv
vodorodnoi bomby
prosto ne podhodit dlya opisaniya evolyucii zvezd.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.04.2012 14:57, 4.5 KBait)
Evolyuciya zvezd eto v principe nechto smeshnoe.
-----------------------------
Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
\\\Zvezda nachinaet svoyu zhizn' kak holodnoe razrezhennoe oblako mezhzvezdnogo
gaza, szhimayusheesya pod deistviem sobstvennogo tyagoteniya i postepenno prinimayushee formu shara. Pri szhatii energiya gravitacii
perehodit v teplo, i temperatura ob'ekta vozrastaet. Kogda temperatura v centre dostigaet 15-20 millionov K,
nachinayutsya termoyadernye reakcii
i szhatie prekrashaetsya. Ob'ekt stanovitsya polnocennoi zvezdoi. Pervaya
stadiya zhizni zvezdy podobna solnechnoi v nei dominiruyut reakcii
vodorodnogo cikla[1].
V takom sostoyanii on prebyvaet ból'shuyu chast' svoei zhizni, nahodyas' na glavnoi
posledovatel'nosti diagrammy
Gercshprunga Rassella, poka ne zakonchatsya zapasy topliva v ego yadre. Kogda v centre zvezdy ves' vodorod
prevrashaetsya v gelii, obrazuetsya gelievoe yadro, a termoyadernoe gorenie vodoroda prodolzhaetsya
na ego periferii.

Evolyuciya zvezdy klassa G na primere
Solnca
V etot period struktura zvezdy nachinaet menyat'sya. Ee svetimost'
rastet, vneshnie sloi rasshiryayutsya, a temperatura poverhnosti snizhaetsya
zvezda stanovitsya krasnym gigantom,
kotorye obrazuyut vetv' na diagramme Gercshprunga-Rassela. Na etoi vetvi
zvezda provodit znachitel'no men'she vremeni, chem na glavnoi
posledovatel'nosti. Kogda nakoplennaya massa gelievogo yadra stanovitsya
znachitel'noi, ono ne vyderzhivaet sobstvennogo vesa i nachinaet szhimat'sya;
esli zvezda dostatochno massivna, vozrastayushaya pri etom temperatura
mozhet vyzvat' dal'neishee termoyadernoe prevrashenie geliya v bolee tyazhelye
elementy (gelii v uglerod, uglerod
v kislorod, kislorod v kremnii, i nakonec kremnii v zhelezo).\\\
------------------
Eshe
variant
http://4put.ru/view-max-picture.php?id=767124


- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.05.2012 22:00, 3.9 KBait)
Moderatoram zadayut odnoznachnye voprosy a moderatory
vmesto otvetov duraka vklyuchayut i dybiliruyut, i starayutsya
sdelat' duraka iz zadayushego voprosy.
Esli
moderator ne mozhet otvetit' na vopros, to on dolzhen
ob etom skazat' a ne vypendrivat'sya.
Estestvenno zadayushie vopros obyazany bolee strogo i vnyatno
zadavat'
vopros tak kak v dannom sluchai kratkost'
sestra idiotizma, i moderator budet pokazyvat' svoi intellekt i budet
unizhat' zadayushego kratkii i ne korrektnyi vopros,
a esli vopros podrobnyi i ne dayushii moderatoru
skleit' duraka , to moderator budet nagnut tem chto on
ne smozhet na nego otvetit' v silu svoego nizkogo
professionalizma.
Rekomenduyu kollekcionirovat' voprosy i otsutstvie na nih otvetov moderatorov,
i otmazki kotorye moderatory ispol'zovali, etimi neotvetami
ih mozhno budet ih podnachivat' i napominat' im vechno.
-------------------
A) Kakuyu nachal'nuyu massu imelo Solnce v moment svoego rozhdeniya?
B) I o dinamike evolyucii parametra
velichiny massy Solnca tozhe. 
K sozhaleniyu, otveta ne bylo.
--------------
Ochen' hotelos' by ponyat', stechenie kakih
unikal'nyh uslovii posluzhilo osnovaniem dlya formirovaniya Solnca v odinochestve.
A chto v etom sobytii unikal'nogo

Odinochnyh zvezd more v kosmose.

--------------------------
Dazhe ya v knizhkah chital chto schitaetsya chto 60% zvezd zarozhdalis' dvoinymi
po kanonam tekushei kosmologii.
Nabirayu
v guglyah - procent dvoinyh zvezd.
-------
Vy uzhe postavili +1 etoi stranice.
Otmenit'
---
Tak chto moderator v voprosah formirovaniya zvezd prosto nedalekii, a korchit iz sebya giganta mysli.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.05.2012 3:11, 2.2 KBait)
Sobstvenno moderator hotel perehitrit' i otvetil
voprosom na vopros, vmesto togo chtoby otvetit' na vopros po suti.
V takoi situacii nado zaznavshegosya stavit'
na mesto,
i napomnit' emu eshe raz vopros i poprosit' otvetit'
eshe raz razvernuto na zadannyi
emu vopros po suti, i sprosit'
v chem trudnost' togo chto
on ne mozhet otvetit' na etot vopros
a interesuetsya vot etim voprosom, i chto sobstvenno
dast emu esli emu otvetyat na etot vopros?
I sprosit' na vsyakii
sluchai esli by emu otvetili voprosom na vopros
to na skol'ko by on zabanil, kak moderator, vremeni takogo borzogo posetitelya,
ili zakryl by temu na pravah moderatora?
---
I ochen' rekomenduyu podobnyi sluchai zapomnit',
i mozhno moderatoru smelo otvechat' voprosom na
vopros ssylayas' na ego zhe borzost'.
------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #28 : Vchera v 20:41:18
Ochen' hotelos' by uznat' mnenie Dmitriya Vibe v otnoshenii problemy:
A)
Kakuyu nachal'nuyu massu imelo Solnce v moment svoego rozhdeniya?
B) I o dinamike evolyucii parametra velichiny massy Solnca tozhe.

Chem Vas ne ustraivaet
massa v odnu massu Solnca, malo menyayushayasya v hode evolyucii?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.05.2012 14:58, 480 Bait)
Voprosy taki nado stavit' korrektno.
Kachestvennyi vopros.
Kakie byli fizicheskie obosnovaniya dlya 1 opredeleniya
vozrasta solnca?, 2 opredeleniya
vremennogo promezhutka
mezhdu bol'shim vzryvom i nachalom termoyadernyh
reakcii u solnca?
Po kakim fizicheskim priznakam opredelyaetsya vozrast
zemli
ot nachala termoyadernoi reakcii?
( Ne zadavaite vopros pro massu ne stradaite erundoi
net vesov v kosmose - otvet budet ot fonarya odnoznachno)
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.05.2012 16:35, 3.2 KBait)
Moderator v ocherednoi raz vyglyadit nelogichno,
yavno on ne znaet predmet voprosa na kotoryi daet
glupyi i bessmyslennyi sovet,
delo v tom chto na tekushii moment
ni v odin iz teleskopov
ne nablyudaetsya u dvoinyh dve opticheski razdel'nye
drug ot druga zvezdy.
I eto tot sluchai kogda astronomam zhelatel'no zatrachivat'
bol'she
vremeni na razmyshleniya chem na nablyudeniya,
chtoby ne vyglyadet' glupo v prostyh voprosah.
Ego sovety dvazhdy glupy pervyi raz chto dvoinye
ne
nablyudayutsya dazhe v samyi bol'shoi teleskop,
a vtoroi raz sovet ne imeet smysla to chto samo opredelenie
"dvoinoi" tozhe ne dokazano i ne obosnovano s fizicheskoi
tochki zreniya, tak chto kto-to sam sebe pridumal
dvoinye i dumaet chto on ih nablyudaet.
Pri vsem pri tom chto est' pyatna na solnce, a mosk
v ramkah
paradigmy u relyativov ne dopuskaet prostyh
myslei chto mogut byt' pyatna na pol zvezdy,
i anomal'no yarkie uchastki na zvezdah, esli eto predpolozhit'
to dvoinyh
i darom ne nuzhno, - no eto uzhe
sovsem drugaya istoriya i dlya teh kto ne zakompleksovan
tekushimi paradigmami.
-----------------------------------------------
Otvet #39 : Segodnya v 13:40:52
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
10.05.2012 15:13, 3.9 KBait)
\\\

Otvet #241 : Vchera v 19:18:05
Foton , dopustim, zheltogo cveta , ispushennyi iz lampochki
ili doletevshii ot Solnca , vsegda imeet odnu i tu zhe chastotu , a stalo byt' i amplitudu.
Dal'she chitat' ne interesno, Vy putaete teploe
s myagkim.

\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Eshe odin moderator hochet proiti kursy v Venecii po
upravleniyu vodnym transportom.
Esli moderator znaet pravil'nyi otvet on obyazan
skazat' - chto vot tak-to i tak-to i potomu-chto,
i obosnovat' prichinu fizicheskuyu svoego utverzhdeniya
a
v dannom sluchai prosto nablyudaetsya u moderatora pokazat' na skol'ko
on sil'nee kak moderator v vozmozhnosti borzet' i
eshe bolee silen vysokomerno neobosnovanno
otvechat',
i delat' oplomb chto mol on perec
obladayushii isklyuchitel'nymi znaniyami.
Tak i ohota skazat' takomu moderatoru esli znaesh' otvet i prichinu, - to
kakogo ul'ya umalchivaesh'?,
a otvechaesh' na otvet borzost'yu nadelennoi moderatorskoi dolzhnost'yu.
Na samom dele moderator i ne dumal otvechat' on boitsya, tak kak
esli on hot' slovo
napishet po suti voprosa to obhezaetsya po polnoi i ego budut vechno
okunat' v etot otvet.
---
Ladno pereidu ot oborzevshih moderatorov
k voprosu po suti.
Chto samoe smeshnoe tak pust' dazhe esli dopustit' u nefizichnoi chasticy
- fotona budet "amplituda" - kotoraya mozhet byt' vyrazhena
kolichestvom fotonov.
Bui s nim dazhe esli predstavit' dlya fotona - chastotu kak
naprimer vrashenie fotonov (spin) -
chto sobstvenno togda protivorechit tomu
chto foton - chastica,
po prichine togo chto chastota opredelyaetsya izmeneniem kolichestva
ispuskaemyh fotonov. Sobstvenno poluchaetsya chto na chastotu signala
mozhet
vliyat' vysokoskorostnaya kolichestvennaya modulyaciya fotonov,
- budet menyat'sya kolichestvo chastic, a eshe i vtoroi sluchai menyaetsya
raskrutka fotona kak chasticy.
S drugoi tochki zreniya -do lampochki vse eti manevry relyativistov
i vse ravno kak oni krasivo tancuyut s bubnom, tak kak net prichiny
dlya izmeneniya amplitudy - kolichestva
fotonov, - fotony v pustote
ne mogut poteryat'sya zamedlitsya ili uskoritsya, tak-zhe i ne
mogut izmenit' skorost' svoego vrasheniya kak chasticy v pustoi
pustote
ibo v pustoi pustote net treniya.
Fotony mogut tol'ko kak chasticy u relyativistov
letet' po neponyatnoi prichine s isklyuchitel'no tochnym
podderzhaniem opredelennoi
skorosti v pustoi pustote,
i tochno eta skorost' vsegda budet naprimer v stekle u fotonov
skorost' v poltora raza men'she.
A vot relyativisty ne hotyat
ob'yasnit' prichinu - pochemu imenno so skorost'yu
v poltora raza bol'she chem v stekle skorost' sveta bol'she v kosmose
- tam gde pustaya pustota, i ne hotyat skazat'
chto imenno fotony tam mozhet v pustoi pustote
tormozit' imenno do takoi skorosti, ssylayutsya na to chto mol ne oni pridumali
i ne im ob'yasnyat'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
10.05.2012 15:27, 605 Bait)
Dlya teh kto ne zametil kak relyativisty dvoinymi manevrami
s fotonami v spore i delayut iz oponenta
lopuha i naveshivayut emu makarony na ushi, -
eto to chto u
relyativistov chastota fotonov mozhet opisyvat'sya dvumya
metodami - posledovatel'nymi amplitudno modulirovannymi
paketami fotonov, a vtoroi variant vrasheniem fotonov.
I esli Vy budete govorit' naprimer chto amplitudnaya modulyaciya
u chastic fotonov - vam skazhut chto Vy nedalekii ibo est' spin.
A esli budete ssylat'sya na spin
vam skazhut chto Vy nedalekii
tak kak fotony letyat pachkami s opredelennoi chastotoi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.05.2012 3:09, 3.9 KBait)
Otvet #17 : Vchera v 23:50:40
Qw, davaite ne budem fantazirovat', kto vo chto ne poverit. Dokazhite, chto Vasha "gipoteza" obladaet predskazatel'noi siloi.
-----------------------------------
Moderatora mutit po polnoi, azh ukachivaet ego
v gandolle.
Novye pravila moderator pridumal dlya foruma
-
kazhdaya gipoteza obyazana obladat' predskazatel'noi siloi.
Nichego i nikakaya gipoteza moderatoru ne dolzhna,
tem bolee ona ne dolzhna nichego predskazyvat'.
---
\\\Kak pravilo, gipoteza vyskazyvaetsya na osnove ryada podtverzhdayushih ee nablyudenii (
primerov),\\\
---
\\\Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
Gipóteza (dr.-grech.
ὑπόθεσις
predpolozhenie; ot ὑπό
snizu, pod + θέσις
tezis) predpolozhenie ili dogadka;
utverzhdenie, predpolagayushee dokazatel'stvo, v otlichie ot aksiom, postulatov, ne trebuyushih dokazatel'stv. Gipoteza schitaetsya nauchnoi,
esli ona fal'sificiruema,
t.e. mozhet byt' oprovergnuta.
Takzhe ona mozhet opredelyat'sya kak forma razvitii znanii,
predstavlyayushaya soboyu obosnovannoe predpolozhenie, vydvigaemoe s cel'yu
vyyasneniya svoistv i prichin issleduemyh yavlenii[1].
Kak pravilo, gipoteza vyskazyvaetsya na osnove ryada podtverzhdayushih ee nablyudenii (primerov),
i poetomu vyglyadit pravdopodobno. Gipotezu vposledstvii ili dokazyvayut, prevrashaya ee v ustanovlennyi fakt
(sm. teorema, teoriya),
ili zhe oprovergayut (naprimer,
ukazyvaya kontrprimer), perevodya v razryad
lozhnyh utverzhdenii.
Nedokazannaya i neoprovergnutaya gipoteza nazyvaetsya otkrytoi problemoi.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.05.2012 3:20, 353 Bait)
Dlya teh kto ne ponyal, gipoteza ne dolzhna nichego
predskazyvat' ona opisyvaet kak est',
tekushuyu situaciyu, osnovyvayas' na nekotoryh nablyudeniyah
razmeshannymi
s avtorskim viden'em situacii i avtorskoi fantaziei.
---
Ya rad chto relyativistov stroit takoi moderator, - krassava,
ya za relyativistov spokoen, oni v
krasivoi uzdechke.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.05.2012 3:10, 2.0 KBait)
Moderatora gandol'erit po samoe dal'she nekuda,
on uzhe ne znaet do chego eshe pridrat'sya,
no nel'zya zhe byt' nastol'ko zvezdanutym chtoby trebovat'
ot
avtora gipotezy podtverzhdeniya ee istinnosti drugim metodom.
Delo v tom chto tol'ko bezmozglyi moder ne znaet togo
chto kak raz vot etot vopros avtor mozhet ochen'
legko reshit' v svoyu pol'zu, no eto uzhe ne budet gipoteza,
tak kak gipoteza po opredeleniyu - dolzhna byt' oprovergaemaya.
A zdes' poluchaetsya chto pustit'
kozla v ogorod,
poprosit' avtora podtverdit' pravil'nost'
ego zhe gipotezy.
--------------------------------------------------

Otvet #61 : Vchera v 22:30:11
taite
mne DVA lyubyh, ugodnyh vam chisla, harakterizuyushie, na vash vzglyad,
vneshnyuyu i vnutrennyuyu granicy gipoteticheskogo protoplanetnogo diska. I ya
berus' po nim (tol'ko po nim) rasschitat' v etom diske (v strogom
sootvetstvii s obsuzhdaemoi shemoi) vse real'nye rezonansnye orbity.
Prichem, eto budet edinstvennyi vozmozhnyi variant ih raspolozheniya.
Hotelos'
by pomimo sobstvenno rascheta uvidet' ubeditel'noe dokazatel'stvo togo,
chto "eto budet edinstvennyi vozmozhnyi variant ih raspolozheniya". Do togo
kak Vy predstavite takoe dokazatel'stvo, proshu drugie soobsheniya v
razdele ne publikovat'. Svoe umenie podgonat' chto-to pod chto-to Vy uzhe
prodemonstrirovali. Teper' obratimsya k fizike.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.05.2012 0:19, 4.0 KBait)
Nu chto ya govoril to i proizoshlo, al'ternativshik porval kak
mavpa gazetu, relyativistov po ih zhe bezmozgloi pros'be.
-------------
-------------
-------------
Otvet #63 : Segodnya v 22:13:27
Svoe umenie podgonat' chto-to pod chto-to Vy uzhe prodemonstrirovali. Teper' obratimsya
k fizike.
Dlya
nachala proshu utochnit', gde i v chem imenno, po-vashemu utverzhdeniyu, ya
zanimalsya podgonkoi. Lichno u menya skladyvaetsya vpechatlenie, chto za
shirmoi moei podgonki vy prosto pryachete sobstvennoe nezhelanie videt'
ochevidnye veshi.
Postarayus' predel'no populyarno proillyustrirovat' svoyu mysl' na konkretnom primere zvezdy HD-37124, raschet sistemy kotoroi priveden
mnoyu ranee (v otvete 60).
Ya
utverzhdayu, chto vse planety v regulyarnyh sistemah formiruyutsya na
rezonansnyh orbitah. Dlya rascheta etih orbit sluzhit uzhe izvestnaya vam
formula. I imenno rezonansnye yavleniya v protoplanetnom diske
pereraspredelyayut ego veshestvo (koncentriruya massu) po ukazannym orbitam.\\\
-------------------
-------------------
-------------------
Ob'yasnyu
fizicheskuyu storonu togo o chem idet rech'.
Esli vzyat' kvarc podklyuchit' k nemu ustroistvo shirokopolosnoi
avto-generacii i posle etogo posmotret' spektr izluchaemyi
etim generatorom. Amplitudno chastotnuyu harakteristiku,
pri izmenenii chastoty vozbuzhdeniya kvarca - i chto poluchaetsya,
poluchaetsya chto amplitudy vozbuzhdeniya
na raznoi kratnosti chastot
budut raznye. Budut vydelyatsya vtorye, tret'i, pyatye i desyatye.
Zamet'te amplitudy bieniya na opredelennyh garmonikah,
oni
raznye.
-------------------------------------
-------------------------------------
-------------------------------------
http://radioelpribori.ru/pribor-dlya-issledovaniya-amplitudno-chastotnyih-harakteristik-chetyirehpolyusnikov.html
\\\
Ustroistvo kalibrovki osi chastot (markernoe ustroistvo) sostoit iz:
- kvarcevogo generatora;
- smesitelya;
- fil'tra nizhnih chastot.
Na odin vhod smesitelya podaetsya napryazhenie kvarcevogo generatora, osnovnaya chastota kotorogo ravna F1, naprimer F1
= 1MGc. Eto napryazhenie harakterizuetsya ves'ma shirokim spektrom (soderzhit mnogo vysshih garmonik), chastoty sosednih sostavlyayushih kotorogo otlichayutsya drug ot druga na
velichinuF1(1MGc). Ko vtoromu vhodu smesitelya podvoditsya napryazhenie ot generatora.
Kazhdyi raz, kogda kachayushayasya chastota stanovitsya
blizkoi i ravnoi chastote kakoi-libo garmoniki kvarcevogo generatora, na
vyhode smesitelya poyavlyayutsya impul'sy nulevyh bienii mezhdu napryazheniyami
garmonik kvarcevogo generatora i napryazheniem kachayusheisya chastoty.
Princip polucheniya chastotnyh merok na izobrazhenii amplitudno-chastotnoi harakteristiki

Napryazhenie nulevyh bienii (tochnee, nizkoi raznostnoi chastoty)
podaetsya s vyhoda smesitelya cherez fil'tr nizhnih chastot i usilitel' na
vertikal'no otklonyayushie plastiny elektronno-luchevoi trubki. Pri kachanii
chastoty ot odnogo krainego znacheniya do drugogo na ekrane nablyudaetsya
seriya chastotnyh metok (marok), otstoyashih drug ot druga po chastote na rasstoyanii F1 (1MGc).\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.05.2012 0:35, 74 Bait)
http://www.kit-e.ru/articles/measure/2010_07_169.php
ris.23
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.05.2012 1:48, 2.0 KBait)
Otvet #65 : Vchera v 23:56:43
Dlya nachala proshu utochnit', gde i v chem imenno, po-vashemu utverzhdeniyu, ya zanimalsya
podgonkoi.
Podgonka -- sovershenno legal'naya i tipichnaya procedura.
Ya
utverzhdayu, chto vse planety v regulyarnyh sistemah formiruyutsya na
rezonansnyh orbitah... Ya berus' utverzhdat', chto slaboe gravitacionnoe
vliyanie Yupitera bylo prosto ne v sostoyanii pomeshat' sformirovat'sya Faetonu, poskol'ku bolee sil'noe (minimum v 3,3 raza) gravitacionnoe
vliyanie planety HD-37124d ne pomeshalo sformirovat'sya planete HD-37124c.
Prekrasno. Dokazhite eti utverzhdeniya. Do
togo kak Vy eto sdelaete, proshu drugie soobsheniya v razdele ne publikovat'.
--------------------------
--------------------------
--------------------------
Da esli net strategicheskogo myshleniya, to ego i ne poyavitsya.
Mne prosto grustno smotret' kak al'ternativshik izdevaetsya nad nedalekim moderom.
Moderator
dumaet chto postavil krutoi i trudnyi vopros,
- etot vopros - nazhivka kotoruyu s'el moderator, i otvet
na nego uzhe est' i byl u al'ternativshika, do togo kak moderator
zadal vopros.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.05.2012 9:39, 105 Bait)
Dlya teh kto ne zametil starcheskii marazm moderatora,
- v ego voprose uzhe est' otvet na ego vopros.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.05.2012 10:03, 1.2 KBait)
Otvet #360 : Vchera v 19:36:00
MOYa LIChNAYa TOChKA ZRENIYa
Pervichno rasshirenie vremeni...
Ne ser'ezno. Edak nam bystro temu prikroyut.
------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------
Dazhe esli i prikroyut, to fizicheskoe obosnovanie
dlya krasnogo smesheniya relyativisty dlya
etoi svoei
vydumki budut iskat' do poslednego
fanata relyativizma.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.05.2012 1:37, 5.3 KBait)
Otvet #68 : Vchera v 21:07:22
Vprochem,
esli i eto vam nichego ne dokazyvaet, to imeet li smysl privodit' mne
raschet sistemy zvezdy HD-95128 (ona zhe 47 Ursae Majoris), sistemy, v
kotoroi rezonans Faetona (a1,2 = 3,6 a.e.) zanimaet planeta HD-95128c?
Net. Dokazat' utverzhdenie vovse ne oznachaet eshe
raz ego povtorit'.
--------------------------------
Vot matematiku fiziku ob'yasnyat' eto glupo.
Avtor gipotizy vyskazal svoyu ideyu obosnovyvayas'
na nablyudeniyah
privel matematicheskii metod poiska naibolee ustoichivyh orbit
dlya planet, pokazal chto est' fizicheskie analogii
kak v fizicheskom rezonanse
tak i po sovpadeniyu ustoichivyh orbit
s ego gipotezoi.
Modera prosto zhaba davit chto on professor i v svoei zhizni nichego
ne privnes v astronomiyu, prosto
kak popugai povtoryaet
vse vremya chuzhie idei.
A zdes' al'ternativshiki kotorye ne professora po astronomii
vydvigayut svoi idei kotorye namnogo luchshe teh chto
on znaet,
i on upiraetsya rogom i trebuet dokazatel'stv kotorye do nego
ne doshli v silu togo chto ego zhaba davit.
---
Lichno s moei tochki zreniya avtor
dannoi gipotezy ne prav,
po skol'ku s moei tochki zreniya ne mozhet byt' rezonansnogo
vliyaniya v prostranstve bez fizicheskoi prichiny.
Ya podobnoe videl v modeli
atoma vodoroda - kotoruyu a tozhe ne
razdelyayu. No eto kak ya ponimayu.
Hotya pri vsem pri tom - dannaya gipoteza
tozhe dolzhna imet' pravo na sushestvovanie.
Moderator estestvenno nedalekii, on ne ponimaet chto u nego
dolzhna byt' granica vystebonov, i cherta posle kotoroi on ne zadaet voprosy avtoru gipotezy,
i moder
dolzhen chetko skazat' - Vasha gipoteza imeet mesto byt',
a ne vystebyvat'sya do poslednego chtoby v itoge zabanit' avtora,
po toi prichine chto eto gipoteza po opredeleniyu.
\\\Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
Gipóteza (dr.-grech.
ὑπόθεσις
predpolozhenie; ot ὑπό
snizu, pod + θέσις
tezis) predpolozhenie ili dogadka;
utverzhdenie, predpolagayushee dokazatel'stvo, v otlichie ot aksiom, postulatov,
ne trebuyushih dokazatel'stv. Gipoteza schitaetsya nauchnoi,
esli ona fal'sificiruema,
t.e. mozhet byt' oprovergnuta.
Takzhe ona mozhet opredelyat'sya kak forma razvitii znanii,
predstavlyayushaya soboyu obosnovannoe predpolozhenie, vydvigaemoe s cel'yu
vyyasneniya svoistv i prichin issleduemyh yavlenii[1].
Kak pravilo, gipoteza vyskazyvaetsya na osnove ryada podtverzhdayushih ee nablyudenii (primerov),
i poetomu vyglyadit pravdopodobno. Gipotezu vposledstvii ili dokazyvayut, prevrashaya ee v ustanovlennyi fakt
(sm. teorema, teoriya),
ili zhe oprovergayut (naprimer,
ukazyvaya kontrprimer), perevodya v razryad
lozhnyh utverzhdenii.
Nedokazannaya i neoprovergnutaya gipoteza nazyvaetsya otkrytoi problemoi.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
31.05.2012 10:03, 2.5 KBait)
Kak ya rad chto ne na forume gde moderator gandol'er.
Prishel chelovek naprimer na forum, chtoby vyskazat' svoyu gipotezu
i s toi cel'yu chtoby emu pomogli i podskazali
nekotorye nyuansy
v kotoryh u nego trudnosti.
Itogom normal'nogo posetitelya - napisanie nebol'shoi itogovoi stat'i,
i ne obyazatel'no v referiruemyi zhurnal.
Chto na zvezdochete tvoritsya - prihodit posetitel', moderatora ot svoei nauchnoi
nepolnocennosti zhaba davit, i on vstupaet v konfrontaciyu i ne daet vozmozhnosti
po obsuzhdat' posetitelyu svoi voprosy, moderator vklyuchaet "duraka" i trebuet
ot posetitelya srazu professorskogo urovnya podhoda k dannomu voprosu,
i nachinaet pridirat'sya po kazhdoi melochi, s yavnoi zadachei zabanit' posetitelya.
I gandol'erstvuyushii moderator v silu togo chto ego zhaba davit, on nikogda ne skazhet
posetitelyu chto ego gipoteza imeet mesto byt', posetitel' so svoei lyuboi gipotezoi
budet v itoge zabanen.
------------------------
Otvet #94 : Vchera v 22:46:37
Qw, perechitaite, pozhaluista, vot eto moe soobshenie:
Ya
utverzhdayu, chto vse planety v regulyarnyh sistemah formiruyutsya na
rezonansnyh orbitah... Ya berus' utverzhdat', chto slaboe gravitacionnoe
vliyanie Yupitera bylo prosto ne v sostoyanii pomeshat' sformirovat'sya Faetonu, poskol'ku bolee sil'noe (minimum v 3,3 raza) gravitacionnoe
vliyanie planety HD-37124d ne pomeshalo sformirovat'sya planete HD-37124c.
Prekrasno. Dokazhite eti utverzhdeniya. Do
togo kak Vy eto sdelaete, proshu drugie soobsheniya v razdele ne publikovat'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
31.05.2012 23:57, 1.8 KBait)
Chtoby byli ponyatny mechty nekotorogo professora -
finansirovat' drugie napravleniya ne nado , i vydelyat'
intellektual'nye resursy na drugie napravleniya tozhe
ne nado,
- nado lezhat' na pechi i dumat' chto vse dolzhno
proizoiti samo soboi, cherez sto ili tysyachu let.
I al'ty eshe ochen' meshayut.
I o sebe v nauke dumaet
kak o telege s loshad'yu,
kotoruyu al'ty meshayut tolkat' vpered, i predstavlyaet sebya loshad'yu
kotoraya tashit telegu, no po faktu bol'she napominaet - telegu ili
loshad' lezhashuyu v telege. I vinit vseh al'tov tak kak al'ty tormozyat nauku.
I po mnogim napravleniyam nauki pryamo pered tem kak mysl' prishla al'ty
ee diskreditirovali
tem chto zanimalis' samostoyatel'no dannymi voprosami.
Prosto krasapeta.
------------------------------------
http://www.computerra.ru/own/wiebe/670110/
\\\Vot i teper' ne nuzhno toropit' fiziku.
Vse proizoidet samo soboi i v
svoe vremya.
Esli teorii otnositel'nosti ili teorii Bol'shogo Vzryva
suzhdeno uiti v istoriyu,
eto proizoidet ne potomu, chto oni komu-to
nadoeli i emu hochetsya novuyu moloduyu zhenu vzamen staroi primel'kavsheisya.
Eto proizoidet, kogda i esli oni perestanut soglasovyvat'sya s
nablyudeniyami
i eksperimentami. Eto mozhet sluchit'sya cherez god, ili cherez
sto let, ili cherez tysyachu.
Nado budet- i sluchitsya. A popytki uskorit'
dvizhenie loshadi podtalkivaniem telegi
k dobru ne privodyat. Po suti,
mnogochislennye "spasiteli nauki" tormozyat ee razvitie.
S odnoi storony, k
opredelennym tematikam slozhno podstupit'sya,
potomu chto oni polnost'yu
diskreditirovany samodeyatel'nymi issledovatelyami.
S drugoi storony,
inogda kazhetsya, chto ne ochen'... kachestvennye raboty po etim tematikam
prosachivayutsya v nauchnye zhurnaly, potomu chto redakcii opasayutsya obvinenii
v dogmatizme.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.06.2012 22:00, 2.3 KBait)
\\\
 Re: Pole i efir
Re: Pole i efir
Otvet #1020 - Segodnya :: 19:50:01
riv123 pisal(a) Segodnya :: 18:59:31:
Efir ne obshaya osnova.
Poskol'ku est' silovoe pole - ono vpolne spravlyaetsya s funkciyami efira.
Kopat' glubzhe konechno mozhno iz lyubopytstva. Tol'ko zhelatel'no snachala
razobrat'sya, chto takoe pole, svet, massa, veshestvo, materiya, kakim
byvayut magnitnye polya (chto takoe spin naprimer i pochemu on tak pohozh na
torsionnoe pole) Bez etogo strukturu efira, ego model' ne postroit'.
Vernee sushestvuet mnozhestvo raznyh modelei, i vse pravil'nye.
Matematicheski dokazyvayutsya.\\\
---
Chto s moei tochki zreniya zdes' ne logichno, chto grubo govorya nel'zya stavit' telegu vperedi loshadi,
i nel'zya nadeyat'sya
slepit' chto-to iz kuskov chuzhih teorii.
Zachem efiru spin, zachem efiru elektron, napryazhennost' efira i est' pole,
dostatochno izmenenie plotnosti efira eto uzhe
- el mag kolebaniya, osevaya raskrutka
chastic efira - magnitnoe pole.
K efiru avtor pridumyvaet svoistva kakie on hochet i schitaet nuzhnymi.
A ne beret
vsyakii musor iz drugih teorii i nachinaet iskat'
u kogo-to pohozhee opisanie efira kotoroe podhodit pod musor iz drugih
ne stykuemyh mezhdu soboi teorii,
kotorye
on znaet.
Byvaet tak chto model' efira stroit' mozhno i po
drugomu, dostatochno pripisyvat' emu te svoistva kotorye fizik schitaet
nuzhnymi, a botanik ili
matematik po prichine otsutstviya ponimaniya fiz processov
boretsya s chem popalo tol'ko on ne ponimaet chto ego besposhadnyi
trud bessmyslennyi i bespoleznyi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.07.2012 2:52, 3.7 KBait)
Ya opyat' na odnom forume byl prosto shokirovan,
------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------
\\\
 Re: Pole i efir
Re: Pole i efir
Otvet #1407 - Segodnya :: 01:23:57
Citata:
VIP 09.07.2012
v 17:02:07 Post 1338
My poka s Vami dogovarivaemsya o tom, chto volny mogut sushestvovat' tol'ko v srede, sposobnoi kolebat'sya. Vy s etim soglasny?
vpd44
09.07.2012 v 17:46:00 Post 1343
Principial'no - soglasen.
Vot tol'ko zachem ogovarivat' sposobnost' sredy kolebat'sya?
Razve est' sredy v kotoryh kolebaniya nevozmozhny?
VIP 09.07.2012 v 19:55:26 Post 1354
Konechno,
takih sred net. No, dlya nas s Vami seichas vazhno to, chto volny est'
kolebaniya sredy, v kotoroi eti volny rasprostranyayutsya. To est' volny i est' sama sreda, no ne vsya, a tol'ko koleblyushayasya ee chast'.
Uvazhaemyi vpd44!
Poshli
vtorye sutki, a reakcii na etu frazu net. Za eto vremya Vy
kommentirovali mnozhestvo voprosov i dovodov, no etot samyi glavnyi
oboshli storonoi.
Poetomu ya vynuzhden povtorit' vopros: Vy soglasny
s tem, chto volny est' kolebaniya sredy, v kotoroi eti volny rasprostranyayutsya, to est', volny i est' sama sreda (ili chast' etoi sredy)?
Esli soglasny, to dostatochno Vashego
da. \\\
---------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------
- zachem oni zanimayutsya etim, ya ne ponimayu,
ishut otvety drug u druga vmesto togo chtoby prochitat'
opredeleniya.
Nedalekie i to znayut
chto rasprostranenie volny v srede
nazyvaetsya - vozmushenie sredy.
Ibo slovo volna po opredeleniyu mozhet byt' - na granice mezhdu sred, - morskaya
mezhdu vozduhom
i vodoi,
ili v vide izmeneniya plotnosti - zvukovaya volna,
radio volna - izmenenie plotnosti efira,
a vot uzhe udarnaya volna - eto vozmushenie sredy,
i
skorost' zvuka - eto skorost' vozmusheniya vozduha,
skorost' sveta eto - skorost' vozmusheniya efira -
ya ne ponimayu kak mozhno ne odelyat' muh ot ...,
i kotlety
ot muh .
---
ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Volna
Volná izmenenie sostoyaniya sredy ili fizicheskogo polya (vozmushenie), rasprostranyayusheesya libo koleblyusheesya v prostranstve i vremeni ili v
...
---
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.07.2012 0:15, 2.4 KBait)
Daveche prochel ocherednuyu stat'yu odnogo vchennogo
kotoryi dumaet chto on professor.
Na stol'ko v otryve ot tehniki chto uzhe terminy pridumyvaet
tak kak ne
znaet bazovoi terminologii.
---
http://www.computerra.ru/own/wiebe/695353/
\\\A vot v astronomii na nih popadaesh' postoyanno. Odnim iz osnovnyh
komponentov kosmicheskoi pyli schitayutsya mineraly, soderzhashie kremnii i
kislorod. Osnovaniem dlya takogo vyvoda sluzhat nablyudeniya v IK-diapazone:
kolebaniya svyazi Si-O v tele pylinki effektivno izluchayut ili pogloshayut
fotony s dlinoi volny okolo 10 mikron. Sootvetstvenno esli pylinka
izluchaet sama, v spektre na 10 mikronah poyavlyaetsya gorb; esli ona
pogloshaet fonovoe izluchenie, v spektre na 10 mikronah poyavlyaetsya proval.
V angliiskom yazyke mozhno ne zamorachivat'sya konkretnoi situaciei i
govorit' prosto pro "10 micron feature". (Da-da, tozhe v spektrah tozhe
est' "fichi".) A kak eti gorby-provaly nazvat' po-russki? Spektral'naya
osobennost'? Net, eto kak-to ne tak. Poluchaetsya, chto 10-mikronnaya "ficha"
osobennost', a bal'merovskii skachok ne osobennost'?\\\
---
A vot otvet
http://www.gelezo.com/electricity/540000/543000/543090/polosovoiy_filtr_i_rejektorniiy_filtr.html
\\\Polosovoi fil'tr
- eto chastotnochuvstvitel'naya shema, kotoraya propuskaet uzkii diapazon. chastot
v okrestnosti central'noi rezonansnoi chastoty (fr)
Vse drugie chastoty nizhe
ili vyshe uzkoi polosy propuskaniya znachitel'no podavlyayutsya. Tipichnaya harakteristika
polosovogo fil'tra pokazana na risunke 24-1A.

Ris. 24-1.
Rezhektornyi fil'tr predstavlyaet
soboi protivopolozhnost' polosovomu fil'tru. On podavlyaet ili ustranyaet signaly,
chastoty kotoryh popadayut v uzkii diapazon s central'noi chastotoi fc.
Vse chastoty vyshe i nizhe central'noi chastoty fil'tr propuskaet s minimal'nym
oslableniem (sm. ris. 24-1 V). Rezhektornyi fil'tr inogda nazyvayut vyrezayushim
fil'trom, poskol'ku etot fil'tr ispol'zuetsya dlya vyrezaniya ili rezhekcii meshayushego
signala odnoi chastoty.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.07.2012 0:23, 644 Bait)
\\\Sootvetstvenno esli pylinka
izluchaet sama, v spektre na 10 mikronah poyavlyaetsya gorb;\\\
- Yasnyi kon' chto eto nazyvaetsya polosovoe svechenie, ili polosovoe izluchenie - na
10 mikronah.
\\\ esli ona
pogloshaet fonovoe izluchenie, v spektre na 10 mikronah poyavlyaetsya proval.\\\
i dvazhdy yasnyi kon' chto eto nazyvaetsya - rezhektornoe pogloshenie, ili rezhektornaya fil'traciya
- na 10 mikronah.
Dazhe po dva slovosochetaniya est'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.07.2012 0:32, 1.4 KBait)
No est' eshe i tret'e nazvanie podobnoi situacii - rezonansnoe izluchenie,
i rezonansnaya fil'traciya.
---
Perevod
REZONANSNOE IZLUChENIE
(rezonansnaya fluorescenciya, rezonansnoe rasseyanie, rezonansnaya lyuminescenciya) - fotolyuminescenciya,
pri k-roi chastota vozbuzhdayushego izlucheniya w0 prakticheski sovpadaet s chastotoi fotolyuminescencii atoma 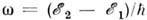 , gde
, gde 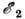 i
i 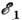 -
energii verhnego vozbuzhdennogo i nizhnego (obychno osnovnogo) urovnei
energii atoma. R. n. vpervye obnaruzheno v 1904 R. Vudom (R. Wood) v
parah natriya.
-
energii verhnego vozbuzhdennogo i nizhnego (obychno osnovnogo) urovnei
energii atoma. R. n. vpervye obnaruzheno v 1904 R. Vudom (R. Wood) v
parah natriya.
---
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.07.2012 0:36, 168 Bait)
\\\REZONANSNOE IZLUChENIE\\\
http://dic.academic.ru/dic.nsf/enc_physics/4516/%D0%A0%D0%95%D0%97%D0%9E%D0%9D%D0%90%D0%9D%D0%A1%D0%9D%D0%9E%D0%95
Ssylka.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.07.2012 2:28, 743 Bait)
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,98240.0.html
Smeshna kartina nablyudaetsya baryshnya al'ternativshica
yavno s astronomicheskim obrazovaniem, relyativistam voprosy
zadaet po bol'shomu vzryvu. Moderatory samoustranilis',
ih gramotnost' uletuchilas', i chtoby ne opozoritsya kak shenki v ugly
po-zabivalis', a te kto vstal na zashitu relyativizma lepechet
chto-to nevnyatnoe i po suti
voprosa smysla v ih slovah
ne nablyudaetsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.07.2012 2:53, 447 Bait)
Ya dostatochno kachestvenno analiziroval o tom kakaya vselennaya vechnaya
ili imeet startovoe vremya. Prishel k vyvodu chto eto zavisit ot tekushei
gospodstvuyushei modeli
i umstvennyh osobennostei individuuma.
Predpolagayu chto polovina mozhet predstavit' beskonechnoe prostranstvo,
a polovina ne mozhet, a mozhet tol'ko govorit' chto mozhet.
I sobstvenno net smysla dazhe pereubezhdat'
v protivopolozhnom kogo-to tak kak eto ne imeet smysla.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.07.2012 10:09, 1.7 KBait)
A chto ya nablyudayu, plyvet gandolla i na nei
moderator plyvet.
-----------------------------------
Otvet #46 : Segodnya v 04:28:18
Tema zakryta. Valenok, esli
Vy i dal'she budete v etom razdele vesti obsuzhdeniya v podobnom tone, ya
Vam na nekotoroe vremya zakroyu dostup na forum. Seichas etogo ne delayu,
poskol'ku tema byla zachem-to perenesena syuda iz drugogo razdela.
-----------------------------------------------------------
Vot tak i vsegda kogda u relyativistov otsutstvuet argumentaciya
oni predpochitayut zamyat'
vopros dlya yasnosti.
A otkuda argumentacii vzyat'sya esli teoriya bol'shogo
vzryva eto obychnaya ni na chem ne obosnovannaya vydumka.
Prosto ne zamechayut chto v
astronomii
vremennoi zvezdezh stoit v polnyi rost.
Tochnee skazat' vremennaya konspirologiya obeshanii i
bespoleznye teorii ispol'zuyushie ne proveryaemye
sobytiya v proshlom i tak-zhe v budushem vo vremeni.
Pryamo anekdot naprashivaetsya na etu situaciyu.
---
Al't i relyativist smotryat v teleskop.
U kazhdogo
iz nih sprashivayut chto oni v teleskop vidyat.
Al't govorit chto vidit zvezdy.
A relyativist govorit chto vidit bol'shoi vzryv, pervye
minuty, i esli prismotret'sya
to i pervye sekundy
bol'shogo vzryva.
---
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.07.2012 22:30, 2.1 KBait)
Zabanili baryshnyu za to chto poprosila otvetit' na svoi
voprosy po suti voprosa, zabanili za mentorskii ton dannoi
pros'by. I zabanili naglo, tak kak pravilami
foruma ne zapresheno
otkryvat' novyi forum na analogichnyi kotoryi moderator zabanil,
sobstvenno moderator oborzel i pridumal ot sebya pravila
po kotorym i
zabanil baryshnyu.
---------------------------------
Otvet #1 : Segodnya v 10:43:12
Kommentarii
moderatora razdela
Tema
zakryta kak povtornoe otkrytie zakrytoi moderatorami temy. Poskol'ku
eto gruboe narushenie, gospozha Valenok otpravlyaetsya otdyhat' na dvoe
sutok.
----------------------------------
Ya lichno nigde ne chital chto esli moderator po kakoi-to prichine
zakryl temu to nel'zya otkryvat' analogichnuyu.
Vot esli temu zakryli pyat' let nazad a kto-to
cherez pyat' let zadast pohozhii vopros i ego
na sharu zabanyat kak beshenuyu sobaku.
Bud'te bditel'ny
otkryvaya temy proveryaite
ne byli li podobnye zakryty moderatorami termin
davnosti ya tak ponimayu ne ogranichen.
Zdes' prosto vidno kak moderatory ochen'
sil'no boyatsya dannoi temy.
Moderatory prosto za soboi ne zamechayut chto oni
sami borzeyut po polnoi trebuya ot avtora otvetit' na ih vopros
po suti i ne
pisat' nikakih drugih soobshenii, a to zabanyat.
Moderatory ne zamechayut za soboi chto oni kak nedalekie
ne mogut otvetit' na relyativistskie voprosy po suti, a
slivayut
v stile ne ya pridumal ne mne i otvechat', hotya uverenny v pravil'nosti
relyativizma a obosnovat' ne mogut svoyu uverennost'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.07.2012 9:16, 1.4 KBait)
------------------------------------
Otvet #829 : Segodnya v 01:16:31
Pridumal paradoksal'nyi vopros po STO i effektu Dopplera(ED).
-------------------
-------------------
Vot
moderator podobnyi idiotizm ne udalyaet a aplodiruet.
Ibo na fone nedalekih oni vyglyadyat gramoteyami.
Chtoby byl ponyaten ves' idiotizm dannoi situacii ob'yasnyayu.
Relyativistskie teorii tipa to i sto osnovany na tom chto svet sostoit
iz fotonov kotorye est' chasticy letyashie v pustote, a effekt
Doplera byl otkryt zadolgo
do relyativizma i v avtorskom izlozhenii
on dlya sred, v kotoryh rasprostranyayutsya volny analogichnye zvuku.
Sobstvenno poluchaetsya - relyativisty otkazalis' ot
sredy, a effekt
Doplera eto isklyuchitel'no dlya sred, v svyazi s chem podobnyi vopros
ne imeet smysla tak kak v nem est' vzaimnoe isklyuchenie.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. A. Aksenova,
26.07.2012 21:06, 159 Bait)
Ya-absolyutnyi novichok na forume..Nedavno prochitala v nauchno-populyarnoi knige,chto prostranstvo mozhet rasshiryatsya bystree skorosti sveta. Deistvitel'no li eto tak?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.07.2012 21:39, 733 Bait)
Otnosites' proshe.
Astronomiya i astronomy kishat neobosnovannymi ideyami
i utverzhdeniyami - eto nazyvaetsya nedokazuemye postulaty.
Est' mnogo teorii bez fizicheskogo
obosnovaniya - eto
skazka.
V dannom sluchai u Vas neobosnovannaya skazka.
Sobstvenno v astronomy ne otbirayut samyh adekvatnyh,
i net nikakogo nakazaniya
i zapretov pisat' stat'i
s otkrovennym i nedokazuemym bredom yavnym idiotizmom,
ili prosto po negramotnosti.
Takzhe procvetaet vremennaya konspirologiya kogda
naprimer
govoryat chto milliard let tomu ili cherez milliardy let posle
budet to-to i to-to.
Nado otnosit'sya spokoino, astronomy lyudi horoshie
prosto oni
zabludilis' v svoih neobosnovannyh skazkah.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.07.2012 21:47, 424 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Esli est' vremya mogu posovetovat' iz adekvatnogo -
Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/forums/1244628
Sam pridumyval, vse vydumka, rekomenduyu otkryvat'
ssylki osobenno s foto, po tekstu mozhete propuskat'
chto ne nravitsya ili neponyatno,
tam sobstvenno vse haotichno raspolozheno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.07.2012 22:48, 408 Bait)
Ne dumayu chto kachestvo moih rasskazov vysokoe,
tak kak ya dazhe ne starayus', ya v molodosti fantastikoi
uvlekalsya, i mne chto-to napisat' ne sostavlyaet truda.
U
nekotoryh moih rasskazov est' sovsem drugoi smysl, tak
kak avtorstvo u pisatelei avtomaticheski rasprostranyaetsya na 70let,
to nekotorymi korotkimi rasskazami ya
blokiruyu svoim avtorstvom
dannye voprosy pri moem prioritete.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. A. Aksenova,
27.07.2012 11:24, 564 Bait)
Delo ne v kachestve,a vo vzglyadah.On tozhe kritikoval bol'shoi vzryv i chernye dyry.No k teorii bol'shogo vzryva privodit prosteishee lineinoe uravnenie dvizheniya. Otsyuda opredelyayut
i vozrast. 13,8 mlrd let.Eto samoe prostoe reshenie. STO glasit,chto nikakoi signal ne obgonit luch sveta. No o prostranstve rech' ne idet.Ob'ekt A 1689-zD1 udalyaetsya ot nas v
8 raz bystree skorosti sveta (tak v knige zarubezhnyh pravda astronomov napisano) No sama vselennaya mozhet rasshiryatsya s takoi ogromnoi skorost'yu.Prosto nel'zya ispol'zovat' eto
rasshirenie ,chtoby obognat' luch sveta.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.07.2012 20:27, 28.3 KBait)
Skazhu Vam po sekretu ya chernye dyry zakryl polnost'yu,
tol'ko ya stat'yu po etomu povodu pisat' ne hochu.
--------------
Re: Chernaya dyra 19.09.2011 12:14
Chto menya udivlyaet, - tak eto to chto vsya astrofizika krasivaya i pushistaya,
i vse prekrasno.
No eto zhe ne tak, vot te-zhe chernye dyry - eto zhe
prosto pipec - i chto eto nikto ne zamechaet ili nikto ne
ponimaet.
Hochu srazu sprosit', Vashe mnenie po
...Chernaya dyra...
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188232
Soglasny li Vy s etim?
Kakie iz perechislennyh statei sootvetstvuyut standartam Chernoi
Dyry?
1 Est' li zhizn' v chernoi dyre
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8822-est-li-zhizn-v-chernoy-dyire/
2[ssylka]
Ustanovlena massa samoi krupnoi iz sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr.
Takoe nam i ne snilos'.
3[ssylka]
Mifologiya chernyh dyr.V nashei Galaktike sushestvuyut milliony chernyh dyr
massoi v neskol'ko solnechnyh
4http://www.popmech.ru/article/8140-raspad-dyiryi/
Raspad dyry.
Vzryv sverhnovoi mozhet zakanchivat'sya obrazovaniem ne odnoi, a srazu
neskol'kih chernyh dyr.
5[ssylka]
Detstvo chernoi dyry
Vzryv, zafiksirovannyi v glubinah kosmosa 31 god nazad, sudya po vsemu,
znamenoval rozhdenie chernoi dyry samoi molodoi iz nam izvestnyh
6[ssylka]
Temnyi centr
Tainstvennyi centr nashei galaktiki,
mesto obitaniya sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyry i istochnik moshneishih potokov izlucheniya,
prepodnosit novye syurprizy.
7[ssylka]
Nebol'shoe zamechanie o prirode gravitacii privodit k sledstviyam
kosmicheskogo masshtaba k vyvodam o rozhdenii novyh mirov iz chernyh dyr
8[ssylka]
Obychnaya po razmeram chernaya dyra vybrasyvaet
kolossal'nye potoki izlucheniya i chastic.
9[ssylka]
Astrofiziki predlozhili sposob (teoreticheski) unichtozhit' chernuyu dyru
10[ssylka]
Iz vseh sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr lish' okolo 1% vybrasyvayut
znachitel'nye kolichestva energii
11[ssylka]
Vyzhivayushie dyry
Para redkih ekzemplyarov
V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
kakim-to chudom vyzhivayushih v sosedstve s etim monstrom.
12[ssylka]
Kak zhivetsya vnutri chernoi dyry? Vy i sami znaete,
kak: esli spravedlivy novye teoreticheskie vykladki,
vsya nasha Vselennaya mozhet nahodit'sya vnutri chernoi dyry,
raspolozhennoi v drugoi Vselennoi. Edakaya matreshka mirozdaniya.
13[ssylka]
Oni prosto predpolozhili, chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu. Eto dalo cifru v 10103, tozhe ogromnuyu, no vse-taki na mnogo
poryadkov nizhe.
14[ssylka]
Esli ochen', ochen' bystryi kosmicheskii korabl' razognat'
pochti do skorosti sveta, prevratitsya li on v chernuyu dyru?
15[ssylka]
Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
---
---
---
Re: Chernaya dyra 19.09.2011 12:38
1 Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
2 V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
3 Oni prosto predpolozhili, chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu.
Material iz Vikipedii
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/39/M87_jet.jpg/250px-M87_jet.jpg
Izobrazhenie, poluchennoe s pomosh'yu teleskopa Habbl: Aktivnaya galaktika M87. V
yadre galaktiki, predpolozhitel'no, nahoditsya chernaya dyra. Na snimke vidna
relyativistskaya struya dlinoi okolo 5 tysyach svetovyh let
Relyativistskie strui
, dzhety (angl. jet) strui plazmy, vyryvayushiesya iz centrov (yader) takih
astronomicheskih ob'ektov, kak aktivnye galaktiki, kvazary i radiogalaktiki.
Obychno u ob'ekta nablyudaetsya dve strui, napravlennye v protivopolozhnye storony.
Na nastoyashii moment relyativistskie strui ostayutsya nedostatochno izuchennym
yavleniem. Prichinoi poyavleniya takih strui chasto nazyvayut vzaimodeistvie magnitnyh
polei s akkrecionnym diskom vokrug chernoi dyry ili neitronnoi zvezdy.
V stat'e na Elementah metodom chislennogo modelirovaniya pokazano, chto pri sliyanii
dvuh neitronnyh zvezd obrazuetsya chernaya dyra, magnitnoe pole kotoroi vytyanuto
vdol' osi. Eto navodit na mysli, chto etot zhe process mozhet formirovat' i
relyativistskie strui. Tem ne menee, v stat'e govoritsya, chto predlozhennaya
avtorami nauchnoi raboty matematicheskaya model' okazalas' ochen' slozhna, a
vychislitel'nye vozmozhnosti sovremennyh komp'yuterov okazalis' nedostatochny, chtoby
s dolzhnoi tochnost'yu provesti vse neobhodimye raschety i ubeditel'no dokazat'
formirovanie strui.
V drugoi stat'e na Elementah provodyatsya paralleli mezhdu processami v chernyh
dyrah i boze-einshteinovskom kondensate. Otmechaetsya chto kondensat mozhet
kollapsirovat' (slipat'sya) i pri posleduyushem ego raspade tozhe mogut voznikat'
uzkonapravlennye vybrosy.
Dal'neishee izuchenie relyativistskih strui
Pri samyh pervyh popytkah ob'yasneniya sverhsvetovogo dvizheniya s pomosh'yu
relyativistskogo napravlennogo potoka chastic vozniklo oslozhnenie: udivitel'no
bol'shaya dolya kompaktnyh istochnikov pokazyvala sverhsvetovoe dvizhenie, v to vremya
kak na osnovanii prostyh geometricheskih dovodov poluchalos', chto tol'ko neskol'ko
procentov takih ob'ektov dolzhno byt' sluchaino orientirovano pochti vdol' linii
zreniya. Prisutstvie simmetrichnyh protyazhennyh radiokomponent predpolagalo, chto
oni obespechivalis' energiei ot central'nogo istochnika dvuh simmetrichnyh luchei.
No trudno sravnit' svetimost' priblizhayusheisya i udalyayusheisya (ili dazhe
stacionarnoi) komponent. Eto ochevidnoe razlichie obychno obsuzhdaetsya v kontekste
modeli s dvoinym istecheniem [4], kogda izluchenie iz yadra rassmatrivaetsya kak
stacionarnaya tochka, gde priblizhayushiisya relyativistskii potok stanovitsya
neprozrachnym. Sverhsvetovoe dvizhenie nablyudaetsya mezhdu etoi stacionarnoi tochkoi
v sople i dvizhushimisya volnovymi frontami ili drugimi neodnorodnostyami v
vyhodyashem relyativistskom potoke.......
.....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie (gamma-luchi, γ-luchi)
vid elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s chrezvychaino maloi dlinoi volny
< 5×10−3 nm i, vsledstvie etogo, yarko vyrazhennymi korpuskulyarnymi
i slabo vyrazhennymi volnovymi svoistvami.
Gamma-kvantami yavlyayutsya fotony s vysokoi energiei. Obychno schitaetsya,
chto energii kvantov gamma-izlucheniya prevyshayut 105 eV, hotya rezkaya granica
mezhdu gamma- i rentgenovskim izlucheniem ne opredelena. Na shkale
elektromagnitnyh voln gamma-izluchenie granichit s rentgenovskim izlucheniem,
zanimaya diapazon bolee vysokih chastot i energii. V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu. Ochevidno,
fizicheski kvanty elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s odinakovoi energiei ne
otlichayutsya, poetomu takoe razdelenie uslovno.
Gamma-izluchenie ispuskaetsya pri perehodah mezhdu vozbuzhdennymi
sostoyaniyami atomnyh yader (sm. Izomernyi perehod, energii takih
gamma-kvantov lezhat v diapazone ot ~1 keV do desyatkov MeV),
pri yadernyh reakciyah (naprimer, pri annigilyacii elektrona i pozitrona,
raspade neitral'nogo piona i t.d.), a takzhe pri otklonenii energichnyh
zaryazhennyh chastic v magnitnyh i elektricheskih polyah (sm. Sinhrotronnoe
izluchenie).....
Esli net poverhnosti ob kotoruyu proishodit tormozhenie.
Material iz Vikipedii
.....Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh
obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v rentgenovskih
trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok yavlyayutsya
metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe antikatodom).
V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom, uskoryayutsya
pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom i katodom
(pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak uskorenie slishkom malo)
i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe tormozhenie. Pri etom za schet
tormoznogo izlucheniya proishodit generaciya izlucheniya rentgenovskogo diapazona,
i odnovremenno vybivayutsya elektrony iz vnutrennih elektronnyh obolochek atomov
anoda. Pustye mesta v obolochkah zanimayutsya drugimi ....
To vstupaet v silu fraza -
V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.
sledovatel'no pri otsutstvii udara o poverhnost' - otsutstvuet sama vozmozhnost'
vozniknoveniya rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, a esli izluchenie est' to ono mozhet
byt' tol'ko rezul'tatom izlucheniya v yadernom perehode. A eto uzhe chasticy vysokih
energii.
avtorskoe izluchenie iz chernoi dyry -
.Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash metod obnaruzheniya Chernoi Dyry
-Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
....Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo.
ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut. ....
Padaya na Chernuyu Dyru veshestvo ne
mozhet rezko tormozitsya ili rezko uskoryatsya,
a sledovatel'no - ne mozhet
byt' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya po etoi prichine.
V svyazi s tem chto dlya uskoreniya do skorosti sveta
pri kotorom vozmozhno izluchenie neobhodimo
ne bolee 10 sekund, a zvezda razmerom s
Solnce na takoi skorosti proletit cherez gorizont
sobytii maksimum za minutu.
Gorizont sobytii - eto skorost' sveta - esli
ob'ekt uletaet s etoi skorost'yu ot nablyudatelya, to
u nego vozniknet krasnoe smeshenie.
Esli by veshestvo dolgo padalo - godami na maloi skorosti
s uskoreniem to bylo by zametno izmenenie Z u padayushih
tel v chernuyu dyru so vremenem, no pri etom nevozmozhno
rentgenovskoe izluchenie - iz za slishkom medlennogo
uvelicheniya uskoreniya.
.... Material iz Vikipedii Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri
vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah.....
A rentgenovskoe izluchenie est' - sledovatel'no
ego istochnikom mozhet byt' tol'ko rezul'tat yadernoi
reakcii.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.....
A esli rezul'tat izlucheniya istochnik yadernoi reakcii -
i on dlitsya godami, - to eto neitronnaya zvezda.
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8971-nasledstvennyie-chernyie-dyiryi/page/3/
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke, ya tak ponyal reshil - zachem dobru
propadat' - pust' izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi dyry budet eshe i
preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Vashe - Rentgenovskoe izluchenie ChD voznikaet pri akkrecii veshestva. Izluchenie
Hokinga - drugoi process. Stranno, chto za 7 let "uvlecheniya astrofizikoi" Vy
etogo ne ponyali.
Moe - S moei tochki zreniya - uvazhaemyi A.M.ChEREPAShUK imeet takoe zhe otnoshenie
k Chernym Dyram kak ya ili Vy.
My s Vami, i A.M.ChEREPAShUK mozhem tol'ko predpolagat' i vyskazyvat'
svoyu tochku zreniya, no obrashat' vnimaniya na podobnye vyskazyvaniya i brat'
ih na veru, ya ne vizhu smysla.
Drugoe delo avtor. Kak on skazal to - takie i Chernye Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vot ya naprimer govoryu chto veshestvo padaet na chernuyu dyru,
i posle udara o poverhnost' s protivopolozhnoi storony chernoi dyry voznikaet
rentgenovskoe i svetovoe izluchenie.
Drugoi schitaet chto izluchenie na podlete.
V binokl' ne vidno - odni predpolozheniya, i ih mozhet byt'
bol'she sotni naprimer - komu verit'?
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vy zatragivaete vopros interpretacii avtorskih
idei bez soglasiya s avtorom.
A esli desyatok drugih avtorov opublikuyut po 300 nauchnyh rabot, a avtor o Chernyh
Dyrah govorit chto izluchenie v osnovnom iz fotonov - a vse drugie govoryat, chto
izluchenie iz rentgenovskih chastic, drugoi govorit iz radio izlucheniya, a tretii
govorit iz gamma chastic - ya dolzhen slushat' isklyuchitel'no avtora Chernyh Dyr,
a ne teh kto interpretiruet, i tem bolee teh kto plevat' hotel na avtorskii
variant chernyh dyr.
Nikto ne meshaet pridumat' svoi - rentgenovskie chernye dyry, - tak net ne hotyat,
- tak na neudobnye voprosy otvechat' dolzhen budet avtor, a pri interpretacii
avtora - pisaka naprimer stat'i s levymi ideyami v oblasti Chernyh Dyr,
prikryvaetsya avtorstvom avtora
Chernyh Dyr, a sam so svoim bredom po otnosheniyu k avtorskomu izlozheniyu, kak-by i
ne prichem.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
..Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii). Tochnee, razumeetsya,
ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut.
Vasha ssylka - tekst 11.05.11 20:36
....Kak otlichit' chernye dyry ot neitronnyh zvezd
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya chernaya dyra ne dolzhna proyavlyat' sebya kak
rentgenovskii pul'sar. U nee mozhet nablyudat'sya lish' irregulyarnaya peremennost'
rentgenovskogo izlucheniya s harakternymi vremenami
$$Delta tapprox frac{r_g}{c}approx10^{-3} div 10^{-4}~mbox{rm s.}$$
I deistvitel'no, v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme Lebed' H-1, soderzhashei chernuyu
dyru s massoi okolo desyati solnechnyh, v sostoyanii, kogda rentgenovskaya
svetimost' ponizhena, a rentgenovskii spektr zhestkii i stepennoi, nablyudaetsya
bystraya irregulyarnaya peremennost' rentgenovskogo potoka na vremenah poryadka
millisekundy. Nablyudeniya, vypolnennye s bortov sovremennyh rentgenovskih
observatorii, takih, kak GINGA, MIR-KVANT, GRANAT, ASKA, pokazali, chto
rentgenovskie spektry akkreciruyushih chernyh dyr sistematicheski bolee zhestkie, chem
spektry akkreciruyushih neitronnyh zvezd, i prostirayutsya do energii v neskol'ko
megaelektron-vol't.
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya neitronnaya zvezda mozhet proyavlyat' sebya kak
rentgenovskii pul'sar. Odnako, esli neitronnaya zvezda obladaet slabym magnitnym
polem (napryazhennost'yu menee 1010 Gs) ili esli ee os' vrasheniya neudachno
orientirovana otnositel'no zemnogo nablyudatelya, pri akkrecii na takuyu neitronnuyu
zvezdu mogut ne nablyudat'sya regulyarnye pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya.
Poetomu otsutstvie strogo periodicheskih pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya - eto
lish' neobhodimyi, no ne dostatochnyi priznak chernoi dyry. V to zhe vremya pri
slabom magnitnom pole neitronnoi zvezdy i nesil'nom tempe akkrecii veshestva na
ee poverhnosti mogut proishodit' termoyadernye vzryvy nakoplennogo veshestva,
privodyashie k yavleniyu rentgenovskogo barstera I tipa - korotkim (dlitel'nost'yu
poryadka 1-10 s) i moshnym vspyshkam intensivnosti rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, chto
takzhe yavlyaetsya harakternym priznakom akkreciruyushei neitronnoi zvezdy, obladayushei
tverdoi poverhnost'yu. Poskol'ku chernaya dyra ne obladaet tverdoi poverhnost'yu,
akkreciya veshestva na nee ne dolzhna privodit' k fenomenu rentgenovskogo barstera
I tipa. Razumeetsya, otsutstvie etogo fenomena takzhe yavlyaetsya lish' neobhodimym
kriteriem nalichiya chernoi dyry. Takim obrazom, my mozhem sformulirovat' vazhneishie
priznaki akkreciruyushei chernoi dyry: eto moshnoe rentgenovskoe izluchenie, bol'shaya
massa (bolee treh solnechnyh), otsutstvie fenomenov rentgenovskogo pul'sara ili
rentgenovskogo barstera I tipa. Pri etom vopros o nadezhnom opredelenii massy
relyativistskogo ob'ekta v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme yavlyaetsya reshayushim pri
identifikacii ego s chernoi dyroi....
Ya Vam prosto pokazyvayu proiivorechie u Vas i Vashei ssylke,
po otnosheniyu k napisannomu v Vikipedii o izluchenii iz Chernoi Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Leitenant Nemo
Chtoby proishodil razbros chastic rentgenovskogo
izlucheniya dlya etogo nado ili yadernoe gorenie zvezd,
chto k chernoi dyre ne primenimo, ili razgon materii
s posleduyushim udarom razognannoi chasticy o poverhnost'
kak eto proishodit v rentgen apparate.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Rentgenovskaya trubka
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe
izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v rentgenovskih trubkah. Osnovnymi
konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok yavlyayutsya metallicheskie katod i anod
(ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe antikatodom). V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony,
ispushennye katodom, uskoryayutsya pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov
mezhdu anodom i katodom (pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak
uskorenie slishkom malo) i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe
tormozhenie. .....
Iz chego vytekaet sleduyushee chto dlya vozniknoveniya izlucheniya radioaktivnyh chastic
- neobhodim udar materii na skorosti odnoi desyatoi i bolee skorosti sveta.
Iz chego sleduet nevozmozhnoe uslovie dlya izlucheniya materii pri padenii v chernuyu
dyru - tak kak dolzhna byt' poverhnost' dlya udara.
A poverhnosti to i net, veshestvo bez udara uhodit za gorizont sobytii,
sledovatel'no i ne mozhet chernaya dyra izluchat' radioaktivnye chasticy.
A.M.Cherepashyuk v dannom sluchai ne prav.
kosmogon
...Schitaetsya, chto pri padenii na ChD veshestvo razgonyaetsya do skorostei, blizkih k
s. V takom sluchae treniya bolee chem dostatochno dlya izlucheniya vysokih energii. ...
Ya ne mogu ponyat' pochemu rassmatrivaetsya otdel'no vzyataya chast' i ne
argumentiruetsya a postuliruetsya.
U Vas - postulat.
Vy voz'mite naprimer shar razmerom v kilometr v diametre, i bros'te ego v Chernuyu
Dyru.
Nu i razognali Vy chto ugodno v pustote, - eshe raz povtoryayu - v pustote
proishodit padenie v chernuyu dyru - kakoe mozhet byt' trenie - prosto ne ob chto
teret'sya.
Voz'mite naprimer zvezdu, ei tozhe ne ob chto teret'sya kogda vokrug pustota,
letit padaet i ugasaet, tem bolee chto mne lichno
uvazhaemyi Dmitrii Mamontov raschety privodil chto zvezda na odnoi desyatoi ili
odnoi tretei skorosti sveta, mozhet prekrasno letat' na orbite vokrug Chernoi
Dyry, i s nei vse normal'no.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
,,,Chernaya dyra - oblast' prostranstva, v k-roi pole tyagoteniya nastol'ko sil'no,
chto vtoraya kosmich. skorost' (parabolicheskaya skorost') dlya nahodyashihsya v etoi
oblasti tel dolzhna byla by prevyshat' skorost' sveta, t.e. iz Ch.d. nichto ne mozhet
vyletet' - ni izluchenie, ni chasticy, ibo v prirode nichto ne mozhet dvigat'sya so
skorost'yu, bol'shei skorosti sveta. Granicu oblasti, za k-ruyu ne vyhodit svet,
naz. gorizontom Ch.d.,,,
Eto bazovoe opredelenie, dazhe esli predpolozhit' chto v chernuyu dyru padayut zvezdy,
pri etom izluchayut, i chto v centre galaktiki v chernyh dyrah massa bol'she chem
massa vseh zvezd v etoi galaktike, a s momenta bol'shogo vzryva
togda mozhno poschitat' skol'ko milliardov zvezd v dyru v centre galaktiki
upalo. Tol'ko vot ne shoditsya s nablyudeniyami - zvezdy ne ischezayut v chernyh dyrah
- etogo nikto ne nablyudal, - ne nablyudali i to kak zvezda prohodit cherez
gorizont sobytii k chernoi dyre.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
...Ishodya iz klassiki, na kotoruyu Vy opiraetes', ChD dlya zemlyanina dolzhny svetit'
kak kvazary....
Vashe - Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii). Tochnee,
razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut.
Moe - u menya vopros - esli v rentgen diapazone izluchayut nizhe privedennye
neitronnye zvezdy - kotorye
...V sluchae, kogda peretekanie veshestva prodolzhaetsya i posle obrazovaniya N. z.,
ee massa mozhet so vremenem znachitel'no uvelichit'sya. Pri ${mathfrak
M}_{N.z.}>{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate
relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru. ...
To kak otlichit' neitronnuyu zvezdu ot chernoi dyry?
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188472
Neitronnye zvezdy
- gidrostaticheski ravnovesnye zvezdy, veshestvo k-ryh sostoit v osnovnom iz
neitronov. Sushestvovanie N. z. bylo predskazano v 30-h gg. 20 v.,vskore posle
otkrytiya neitrona. Odnako tol'ko v 1967 g. oni byli obnaruzheny v vide impul'snyh
istochnikov radioizlucheniya - pul'sarov. Zatem bylo ustanovleno, chto N. z.
proyavlyayut sebya takzhe kak rentgenovskie pul'sary (1971 g.) i vspyshechnye istochniki
rentg. izlucheniya - barstery (1975 g.). Ne isklyucheno, chto na odnoi iz stadii
sushestvovaniya N. z. yavl. istochnikami gamma-vspleskov. K 1984 g. otkryto ok. 400
N. z., iz nih ok. 20 v vide rentg. pul'sarov, ok. 40 v vide barsterov, a
ostal'nye v vide obychnyh radiopul'sarov.
Druguyu vozmozhnost' poyavleniya N. z. predstavlyaet evolyuciya belyh karlikov v tesnyh
dvoinyh zvezdnyh sistemah. Peretekanie veshestva so zvezdy-kompan'ona na belyi
karlik postepenno uvelichivaet ego massu, i, kogda ona dostigaet ${mathfrak
M}_Ch$, belyi karlik prevrashaetsya v N. z. V etom sluchae ${mathfrak
M}_{N.z.}{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate
relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188644
Rentgenovskie pul'sary
- istochniki peremennogo periodicheskogo rentg. izlucheniya, predstavlyayushie soboi
vrashayushiesya neitronnye zvezdy s sil'nym magn. polem, izluchayushie za schet akkrecii
(padeniya veshestva na ih poverhnost'). Magn. polya na poverhnosti R.p. ~ 1011-1014
Gs. Svetimosti bol'shinstva R.p. ot 1035-1039 erg/s. Periody sledovaniya impul'sov
P ot 0,7 s do nesk. tysyach s. R.p. vhodyat v tesnye dvoinye zvezdnye sistemy,
vtorym komponentom k-ryh yavl. normal'naya (nevyrozhdennaya) zvezda, postavlyayushaya
veshestvo, neobhodimoe dlya akkrecii i norm. funkcionirovaniya R.p. Esli vtoroi
komponent nahoditsya na stadii evolyucii, kogda skorost' poteri massy (etim
komponentom) mala (sm. Evolyuciya tesnyh dvoinyh zvezd), neitronnaya zvezda ne
proyavlyaet sebya kak R.p. Rentg. pul'sary vstrechayutsya kak v massivnyh molodyh
dvoinyh zvezdyh sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu I Galaktiki i lezhashih v ee
ploskosti, tak i v malomassivnyh dvoinyh sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu II i
prinadlezhashih k sferich. sostavlyayushei Galaktiki. R.p. otkryty takzhe v
Magellanovyh Oblakah. Vsego otkryto ok. 20 R.p.
Na nachal'nom etape issledovanii otkryvaemym rentg. ob'ektam prisvaivalis'
naimenovaniya po sozvezdiyam, v k-ryh oni nahodyatsya. Napr., Gerkules X-1 oznachaet
pervyi po rentg. yarkosti ob'ekt v sozvezdii Gerkulesa, Kentavr H-3 - tretii po
yarkosti v sozvezdii Kentavra. R.p. v Malom Magellanovom Oblake oboznachaetsya kak
SMC X-1, v Bol'shom Magellanovom Oblake - LMC X-4. Obnaruzhenie so sputnikov
bol'shogo chisla rentg. istochnikov potrebovalo dr. sistemy oboznachenii.
Uskorenie i zamedlenie vrasheniya neitronnyh zvezd.
V otlichie ot radiopul'sarov (nek-rye iz k-ryh, v chastnosti pul'sary v Krabe i
Parusah, izluchayut i v rentg. diapazone, sm. Pul'sary), izluchayushih za schet
energii vrasheniya zamagnichennoi neitronnoi zvezdy i uvelichivashih svoi period so
vremenem, R.p., izluchayushie za schet akkrecii, uskoryayut svoe vrashenie.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Spasibo za otvet.
Esli ya pravil'no ponyal, to istochnik
nepreryvnogo rentgenovskogo izlucheniya
so stabil'noi intensivnost'yu - nazyvaetsya
Chernoi Dyroi .
Esli rentgenovskoe izluchenie menyaet intensivnost'
to eto ili neitronnaya zvezda ili
rentgenovskii pul'sar.
Zdes' avtor chernyh dyr - sem' pyatnic na nedelyu,
sperva govoril vot tak -
...Chernaya dyrá oblast' v prostranstve-vremeni,
gravitacionnoe prityazhenie kotoroi nastol'ko veliko,
chto pokinut' ee ne mogut dazhe ob'ekty, dvizhushiesya
so skorost'yu sveta (v tom chisle i kvanty samogo sveta)....
Potom ego ozarilo v 1975 i on odaril chernye dyry i vseh
astrofizikom izlucheniem ot chernyh dyr.
---...Izluchénie Hókinga ...---
......Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi.
Predskazan teoreticheski Stivenom Hokingom v
1974 godu.[1] Rabote Hokinga predshestvoval
ego vizit v Moskvu v 1973 godu, gde on vstrechalsya
s sovetskimi uchenymi Yakovom Zel'dovichem i
Alekseem Starobinskim. Oni prodemonstrirovali
Hokingu, chto v sootvetstvii s principom
neopredelennosti kvantovoi mehaniki
vrashayushiesya chernye dyry dolzhny
porozhdat' i izluchat' chasticy.[2]
Isparenie chernoi dyry kvantovyi process.
Delo v tom, chto ponyatie o chernoi dyre kak ob'ekte,
kotoryi nichego ne izluchaet, a mozhet lish' pogloshat' materiyu,
spravedlivo do teh por, poka ne uchityvayutsya kvantovye effekty.
V kvantovoi zhe mehanike, blagodarya tunnelirovaniyu,
poyavlyaetsya vozmozhnost' preodolevat' potencial'nye bar'ery,
nepreodolimye dlya nekvantovoi sistemy. Utverzhdenie,
chto konechnoe sostoyanie chernoi dyry stacionarno,
pravil'no lish' v ramkah obychnoi, ne kvantovoi teorii
tyagoteniya. Kvantovye effekty vedut k tomu, chto na samom
dele chernaya dyra dolzhna nepreryvno izluchat', teryaya pri
etom svoyu energiyu.....
Itogo
...Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke,
ya tak ponyal reshil - zachem dobru propadat' - pust'
izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi dyry
budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A vot zdes' ya Vam mogu predlozhit' sdelat' u kazhdoi stat'i schetchik, - ponyal
-ne ponyal,
Vashe - Dlya bazovogo ponimaniya nuzhno umet' chitat' i imet' nekotoruyu podgotovku v
ramkah hotya by shkoly. U Vas takaya podgotovka, sudya po vsemu, hromaet na obe
nogi, poetomu Vy ne ponimaete bol'shinstvo statei. Dlya utochnyayushih voprosov est'
kommentarii, dlya bazovoi podgotovki - shkola i uchebniki.
- Vy dumaete chto vse uchennye pishut pravil'nye stat'i, i nikto stat'i ne
vysasyvaet iz pal'ca a potom ne rzhet nad chitatelyami, a Vash sait chtoby chitat' -
to nado byt' doktorom nauk, i v tozhe samoe vremya Vy lichno ne mozhete otvetit'
pryamo na pryamye voprosy, po etoi stat'e. Vy menya v principe zaintrigovali, ya
podumayu chtoby takoi puzyr' vysosat' iz pal'ca v ramkah paradigmy, chtoby vse
vokrug azh zaaplodirovali za isklyuchitel'no vysokohudozhestvennyi idiotizm v ramkah
breda sivoi kobyly.
Moe-Ne rasskazhete Vashe otnoshenie k vyskazyvaniyu, -
Esli opyt ne sovpadaet s teoriei to tem huzhe dlya opyta?
Napomnyu -
Moe - So vtorogo Vashego otveta ya ponyal - chto u Vas est' metody dokazatel'stv
kotorye pozvolyayut opredelit' kakimi byli v pervye momenty bol'shogo vzryva
zvezdy, chernye dyry , temperatura i drugie razlichnye svoistva prostranstva i
svoistva razlichnyh fizicheskih ob'ektov.
Vashe - Ne u menya. U astronomov, astrofizikov i kosmologov.
Moe- Esli mne ne mozhet opponent srazu vnyatno izlozhit' otvet na moi prostoi
vopros po obsuzhdaemoi stat'e, to ya ne obyazan verit' napisannomu, a skoree
naoborot - vynuzhden zasomnevat'sya.
Po povodu gromkih familii v astrofizike - to esli Vy proanaliziruete ih
biografiyu i trudovye zaslugi i proanaliziruete ih prichastnost' k astrofizike, to
oni vse v astrofizike - diletanty, kotorye idei vbrasyvali v astrofiziku ot
sluchaya k sluchayu, i ser'ezno ei ni kto ne zanimalsya. Po etomu vsya astrofizika i
sostoit iz razroznennyh idei, - ozaryalok, kotorye posledovateli pytayutsya
sostykovyvat' mezhdu soboi po prichine poyavleniya novoi izmeritel'noi tehniki.
A astrofiziku u menya hobbi let 7, tak chto ya prochital stol'ko statei raznyh, chto
mogu delat' vyvody chto vysoska iz pal'ca, a chto i super gramotno napisano .
Samoe smeshnoe chto super stat'i absolyutno neizvestny.
http://crydee.sai.msu.ru/Universe_and_us/4num/v4pap26.htm
-Ochen' horoshaya stat'ya.
http://www.anomaliy.ru/discovery/482
"Sverhnovye tipa I a, kak polagayut, formiruyutsya
posle vzryvov belyh karlikov, sverhplotnyh mertvyh zvezd razmerom s
nashu Zemlyu, kotorye kogda-to byli yadrom solncepodobnogo svetila, i
ch'ya vneshnyaya obolochka rastvorilas' v kosmose.
Odna iz osobennostei etogo tipa otsutstvie vodoroda, i eto
nesmotrya na to, chto vodorod yavlyaetsya samym rasprostranennym
himicheskim elementom."
Vot eta stat'ya - v principe dolzhna byla perevernut' vsyu astrofiziku,
po toi prichine chto net vodoroda vnutri zvezdy. A u tekushei paradigmy vodorod
vygoraet. I astrofiziki vnyatno otvetit' ne mogut prichinu po kotoroi samyi legkii
vodorod - preodolevaet gravitaciyu stanovitsya tyazhelee vseh metallov i letit v
yadro zvezdy pouchastvovat' v yadernoi reakcii. I V to chto samyi legkii vodorod
preodolevaet letit vnutr' zvezdy -ya ne veryu, hot' v millione knizhek eto budet
napisano, i tysyache uchebnikov. Tak kak napisannoe ne podtverzhdeno fizicheskimi
svoistvami a protivorechit im.
---
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.07.2012 20:32, 6.9 KBait)
|
|
Re: Chernaya dyra
|
12.02.201214:35 |
|
Otvet #154 : Vchera v 16:04:25
A teper' Vy nam rasskazhite, kak v zakone Habbla V=H*R proyavlyayutsya kvantovye
svoistva fotona polagayu - nikak. V etom i problema na moi vzglyad.
A teper' Vy nam rasskazhite, kak zakon Habbla vazhnee i vyshe kakih-to tam kvantovyh svoistv
fotona.
Polagayu, zakon Habbla v ramkah dannoi temy prosto vazhnee i vyshe, kakih-to tam kvantovyh svoistv fotona. I
poka Vy ne ob'yasnite, kak v zakone Habbla proyavlyayutsya kvantovye
svoistva fotona, zdes' net smysla govorit' ob etih kvantovyh svoistvah.
Otvet #183 : Segodnya v 12:59:49
Stanislav Kravchenko, vnyatnyi
otvet daite, pozhaluista. Ne prosto predlozhenie so slovami "foton" i
"zakon Habbla", a vnyatnyi otvet. Prekrasnyi sluchai pokazat' drugim
primer adekvatnogo fizicheskogo podhoda.
--------------------------
Moderatoru v mosk udarilo zhelanie ne vyglyadet'
idiotom, a samyi gramotnyi relyativist, zatupil po polnoi,
i v itoge
zadali diletantu vopros sut' kotorogo v tom
pochemu relyativisty kogda hotyat, a kogda ne hotyat i v nekotoryh sluchayah
primenyayut odni fizicheskie svoistva, a na drugie
zabivayut,
a kogda im nado dlya chego-to drugogo oni na tozhe samoe
chihat' hoteli a akcentiruyutsya na drugom.
Vot i trebuyut ot diletanta im ob'yasnit' pochemu
oni inogda byvayut
bol'nye na vsyu golovu, i prosyat ih vvesti v sostoyanie zdravomysliya,
tochnee skazat' vyvesti iz sostoyaniya idiotizma.
Vot takaya zhestokaya
selyavi.
|
|
| Naverh |
|
 |
A.P.Vasi
|
|
Re: Chernaya dyra
|
12.02.201215:24 |
|
Vse ravno slovo foton s fizicheskoi tochki zreniya
prostym fizicheskim opytom - slivaetsya v kanalizaciyu fiziki,
a tot kto ego primenyaet - budet
toptat'sya na meste
ibo ne provodit fizicheskii analiz ispol'zuemuyu
fizicheskuyu sushnost', a veryat opredeleniyam,
skazal naprimer odin matematik chto svet sostoit
iz chastic,
tak srazu lohi i zarukopleskali i poverili na slovo,
matematikami vysosannym iz pal'ca vydumkam radi
podtverzhdeniya svoih teorii nuzhny, a lohi dumayut
chto matematiki pal'cem v nebo popali, i chto fizika
takaya kak matematiki pridumali, i potom nachinayut
soedinyat' vydumannuyu matematiku s real'noi fizikoi,
i ne ponimayut pochemu oni zanimayutsya odnim i tem-zhe
stoletiyami - da udel nedalekih.
-------------
Kak ya ranee pisal - foton - ne imeet fizicheskogo smysla,
- obosnovat' eto, - bylo legko.
Dlya sushestvovaniya effekta Doplera, est' prichina - sreda i ee svoistva.
Dazhe esli ispol'zuetsya metod izmereniya dlya sred, a
govoritsya chto
vokrug pustota, to propadaet
prichinnost' vozniknoveniya dannogo
effekta kak svoistva prostranstva.
U relyativistov ne prostranstvo vystupaet v kachestve linii zaderzhki
signala, a vystupaet
- foton, kak dvizhushiisya ob'ekt, u kotorogo
ogranichena skorost' dvizheniya v pustote, po ne ponyatnoi prichine -
kotoraya postuliruetsya bez ob'yasneniya prichiny. Foton
v dannom sluchai
mozhet byt' tol'ko chasticei, - eto ne vozmozhno po prichine togo chto
chastica ne mozhet snizhat' i uvelichivat' svoyu skorost' chto
nablyudaetsya naprimer
pri dvizhenii sveta naprimer v vozduhe, potom
cherez steklo potom opyat' v vozduhe i potom v vakuum, tak kak
poluchaetsya chto v stekle letit foton medlennee chem v vozduhe
i
vakuume , a vyletaya iz stekla foton uvelichivaet svoyu skorost'. Tak
vot ne mozhet chastica kotoraya poteryala skorost', prosto tak vzyat' i
pri vylete iz stekla
uvelichit' skorost', - na podobnoe sposobny
tol'ko kolebaniya sredy v sredah s raznymi svoistvami. Tak chto foton
kak chastica - vydumka chistoi vody.
Vyvod -
v prostranstve rasprostranyayutsya kolebaniya sredy, i svetovoe
izluchenie ne dvizhetsya a obrazuetsya ot vzaimodeistviya kolebanii
sredy i materiala, kak v 1800 godu govoril
Tomas Yung.
Tak chto vse chto napisano v astrofizike bez ucheta sredy - k
sozhaleniyu ne pravil'no. | |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.07.2012 20:40, 5.3 KBait)
Itogo
chto imeem - est' bol'shoi vzryv kotoryi predopredelil
iznachal'no sostav vodoroda i geliya vo vselennoi, 70% i 30%.
\\\K koncu vtorogo perioda, to est' cherez 5
minut posle Bol'shogo Vzryva,
rasshiryayusheesya veshestvo sostoit iz yader atoma
vodoroda 70% i yader geliya 30%. \\\
http://mrcnn.narod.ru/bigbang.htm
Zadanna neobratimost' izmeneniya materii vse dolzhno prevratitsya v zhelezo.
Zadanna nelineinost' - chem bol'she koncentraciya tem bystree idet
prevrashenie
materii k zhelezu.
Mozhno dazhe skazat' po drugomu chem bol'she vydelilos' energii iz
zvezdy tem bol'she zvezda pererabotala vodoroda i geliya.
---------------------------------------------
\\\

Evolyuciya zvezdy klassa G na primere
Solnca
[]
Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://4put.ru/view-max-picture.php?id=767124


Itogo chto tochno izvestno - sostav solnca po
spektru v verhnem sloe solnca.
------------
I vot vopros -
---------------------------------------
---------------------------------------
---------------------------------------
Otvet #28 : Vchera v 20:41:18
Ochen' hotelos' by uznat' mnenie Dmitriya Vibe v otnoshenii problemy:
A)
Kakuyu nachal'nuyu massu imelo Solnce v moment svoego rozhdeniya?
B) I o dinamike evolyucii parametra velichiny massy Solnca tozhe.

Chem Vas ne ustraivaet
massa v odnu massu Solnca, malo menyayushayasya v hode evolyucii?
------------------------------
------------------------------
------------------------------
Relyativisty svoimi zhe teoriyami i ne mogut obosnovat' prichinu vozrasta.
---
Uchityvaya kak dolgo po odnomu voprosu stradayut,
i iz etogo voprosa ne perehodyat na sleduyushii dlya
polucheniya prichinno sledstvennoi svyazi to eto pipec logiki.
Da ya v svoe vremya poslal v dal' i po polnoi
vsyu etu
labudu.
Ya estestvenno napomnyu pro spektr, shirinu, smeshenie
poglosheniya na spektre i piki v spektre, i napomnyu
to kak ispol'zuyut spektr - huzhe
ne pridumat'
dlya opredeleniya rasstoyanii do zvezd -
chem dal'she tem krasnee - dlya al'ternativshikov
astronomy sdelali podarok i sami relyativisty
nikogda
ne poimut kak spektr ispol'zovat' po drugomu i zachem,
a ih oshibka -
ona vsegda na vidu no chtoby ee zametit' nado otkazat'sya ot
relyativizma i modeli zvezd,
i idei Habbla.
Hotya eshe nado zametit' chto vse vysosano iz pal'ca chto kasaetsya
kosmicheskih dat i proshedshego vremeni zhizni zvezd.
Vozrast zemli - ne obosnovano
Vozrast materii - ne obosnovano
Vozrast mezhdu bol'shim vzryvom i nachalom solnca - ne obosnovano
Vozrast solnca - ne obosnovano
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.07.2012 20:44, 2.6 KBait)
| Re: Spiral'naya galaktika NGC 1672: vid v teleskop im.Habbla
|
16.05.201211:44 |
|
\\\Ne
lozung,
a
pozhelanie.
Vyskazhetes'
po
teme.
Svodima
li
astronomiya
k
fizike.
Informaciya
o
elektromagnitnyh
polyah
i
izlucheniyah
(fizika)
est'
istochnik
astronomicheskih
znanii,
no
k
nim
ne
svodyatsya
astronomicheskie
ob'ekty
(astronomiya),
kotorye
imeyut
svoe
stroenie,
razvitie,
nesut
v
sebe
svoi
smysl.\\\
Po teme tak po teme.
Ya dlya primera tekushei neadekvatnosti peremeshannoi s glupost'yu
planetarnogo masshtaba voz'mu chernye dyry.
Avtor
pridumal chernye dyry, skazal chto u etih dyr est' izluchenie v osnovnom iz fotonov.
Posle etogo kakie-to psevdo soavtory reshayut chto istochniki rentgenovskogo izlucheniya v
kosmose
eto tozhe chernye dyry.
Ya vot ne ponimayu - nekuda devat' rentgenovskie zvezdy - nazovite rentgenovskie
zvezdy ot Vasi Pupkina zaodno i uvekovechili by
sebya v astronomii, a to reshili
chto eto chernye dyry.
Posle etogo pridumyvayut chto u chernoi dyry net poverhnosti i materiya iz zvezd tuda padaet
vechno pri etom
izluchaetsya rentgenovskoe izluchenie.
Chto imeem po faktu, voz'mem cvetnoi televizor, vnutri nego razgonyayutsya kak v uskoritele
chasticy, udaryayutsya v itoge ob masku
ili lyuminofor ekrana, so skorost'yu 0.3 skorosti sveta,
pri etom eto chasticy 27 kilo elektron vol't, chto sobstvenno sootvetstvuet vysokomu
napryazheniyu na maske kineskopa
- vysokoe tak skazat'.
Pri udarenii chastic o masku ili lyuminofor proishodit neznachitel'noe rentgenovskoe izluchenie,
etot effekt nazyvaetsya - tormoznoe izluchenie,
tak kak pri rezkom tormozhenii chasticy letyashie razbivayutsya
na bolee melkie, vot eta melyuzga i est' rentgenovskoe izluchenie.
To-est' poluchaetsya chto v pervyi
raz naplevali na avtorskii variant izlucheniya,
vo vtorom sluchai skazav chto u chernoi dyry net poverhnosti , naplevali na fiziku,
ibo chtoby s poverhnosti chernoi dyry
izluchalos' rentgenovskoe izluchenie,
to nado chtoby tormoznoe izluchenie bylo so skorostyami bol'shimi chem v cvetnom
televizore, a eto skorost' bol'she 0.3S. Sledovatel'no
padenie na poverhnost' chernoi
dyry budet stremitel'noe, i dlya izlucheniya rentgenovskogo u chernoi dyry obyazana byt' poverhnost'.
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.07.2012 20:46, 34.0 KBait)
Bolee razvernuto po chernym dyram,
chtoby tak skazat' proniknutsya v samuyu glubinu absurda situacii.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://www.astronet.ru/db/forums/1188232?page=7
---
Chto menya udivlyaet, - tak
eto to chto vsya astrofizika krasivaya i pushistaya,
i vse prekrasno.
No eto zhe ne tak, vot te-zhe chernye dyry - eto zhe
prosto pipec - i chto eto nikto ne zamechaet
ili nikto ne
ponimaet.
Hochu srazu sprosit', Vashe mnenie po
...Chernaya dyra...
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188232
Soglasny li Vy s etim?
Kakie iz perechislennyh statei sootvetstvuyut standartam Chernoi
Dyry?
1 Est' li zhizn' v chernoi dyre
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8822-est-li-zhizn-v-chernoy-dyire/
2[ssylka]
Ustanovlena massa samoi krupnoi iz sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr.
Takoe nam i ne snilos'.
3[ssylka]
Mifologiya chernyh dyr.V nashei Galaktike sushestvuyut milliony chernyh dyr
massoi v neskol'ko solnechnyh
4http://www.popmech.ru/article/8140-raspad-dyiryi/
Raspad dyry.
Vzryv sverhnovoi mozhet zakanchivat'sya obrazovaniem ne odnoi, a srazu
neskol'kih chernyh dyr.
5[ssylka]
Detstvo chernoi dyry
Vzryv, zafiksirovannyi v glubinah kosmosa 31 god nazad, sudya po vsemu,
znamenoval rozhdenie chernoi dyry samoi molodoi iz nam izvestnyh
6[ssylka]
Temnyi centr
Tainstvennyi centr nashei galaktiki,
mesto obitaniya sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyry i istochnik moshneishih potokov izlucheniya,
prepodnosit novye syurprizy.
7[ssylka]
Nebol'shoe zamechanie o prirode gravitacii privodit k sledstviyam
kosmicheskogo masshtaba k vyvodam o rozhdenii novyh mirov iz chernyh dyr
8[ssylka]
Obychnaya po razmeram chernaya dyra vybrasyvaet
kolossal'nye potoki izlucheniya i chastic.
9[ssylka]
Astrofiziki predlozhili sposob (teoreticheski) unichtozhit' chernuyu dyru
10[ssylka]
Iz vseh sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr lish' okolo 1% vybrasyvayut
znachitel'nye kolichestva energii
11[ssylka]
Vyzhivayushie dyry
Para redkih ekzemplyarov
V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
kakim-to chudom vyzhivayushih v sosedstve s etim monstrom.
12[ssylka]
Kak zhivetsya vnutri chernoi dyry? Vy i sami znaete,
kak: esli spravedlivy novye teoreticheskie vykladki,
vsya nasha Vselennaya mozhet nahodit'sya vnutri chernoi dyry,
raspolozhennoi v drugoi Vselennoi. Edakaya matreshka mirozdaniya.
13[ssylka]
Oni prosto predpolozhili, chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu. Eto dalo cifru v 10103, tozhe ogromnuyu, no vse-taki na mnogo
poryadkov nizhe.
14[ssylka]
Esli ochen', ochen' bystryi kosmicheskii korabl' razognat'
pochti do skorosti sveta, prevratitsya li on v chernuyu dyru?
15[ssylka]
Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
--------------------
Eto iz moego spora na forume na populyarnoi mehanike.
| Re: Chernaya dyra
|
19.09.201112:38 |
|
1 Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
2
V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
3 Oni prosto predpolozhili,
chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu.
Material iz
Vikipedii
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/39/M87_jet.jpg/250px-M87_jet.jpg
Izobrazhenie, poluchennoe s pomosh'yu teleskopa Habbl: Aktivnaya galaktika
M87. V yadre galaktiki, predpolozhitel'no, nahoditsya chernaya dyra. Na
snimke vidna relyativistskaya struya dlinoi okolo 5 tysyach svetovyh let
Relyativistskie strui
, dzhety (angl. jet) strui plazmy, vyryvayushiesya iz centrov (yader) takih
astronomicheskih ob'ektov, kak aktivnye galaktiki, kvazary i
radiogalaktiki.
Obychno u ob'ekta nablyudaetsya dve strui, napravlennye v protivopolozhnye storony.
Na nastoyashii moment relyativistskie strui ostayutsya nedostatochno izuchennym
yavleniem. Prichinoi poyavleniya takih strui chasto nazyvayut vzaimodeistvie
magnitnyh polei s akkrecionnym diskom vokrug chernoi dyry ili neitronnoi
zvezdy.
V stat'e na Elementah metodom chislennogo modelirovaniya pokazano, chto
pri sliyanii dvuh neitronnyh zvezd obrazuetsya chernaya dyra, magnitnoe pole
kotoroi vytyanuto vdol' osi. Eto navodit na mysli, chto etot zhe process
mozhet formirovat' i relyativistskie strui. Tem ne menee, v stat'e
govoritsya, chto predlozhennaya avtorami nauchnoi raboty matematicheskaya
model' okazalas' ochen' slozhna, a vychislitel'nye vozmozhnosti sovremennyh
komp'yuterov okazalis' nedostatochny, chtoby s dolzhnoi tochnost'yu provesti
vse neobhodimye raschety i ubeditel'no dokazat' formirovanie strui.
V drugoi stat'e na Elementah provodyatsya paralleli mezhdu processami v
chernyh dyrah i boze-einshteinovskom kondensate. Otmechaetsya chto kondensat
mozhet kollapsirovat' (slipat'sya) i pri posleduyushem ego raspade tozhe
mogut voznikat' uzkonapravlennye vybrosy.
Dal'neishee izuchenie relyativistskih strui
Pri samyh pervyh popytkah ob'yasneniya sverhsvetovogo dvizheniya s pomosh'yu
relyativistskogo napravlennogo potoka chastic vozniklo oslozhnenie:
udivitel'no bol'shaya dolya kompaktnyh istochnikov pokazyvala sverhsvetovoe
dvizhenie, v to vremya kak na osnovanii prostyh geometricheskih dovodov
poluchalos', chto tol'ko neskol'ko procentov takih ob'ektov dolzhno byt'
sluchaino orientirovano pochti vdol' linii zreniya. Prisutstvie
simmetrichnyh protyazhennyh radiokomponent predpolagalo, chto oni
obespechivalis' energiei ot central'nogo istochnika dvuh simmetrichnyh
luchei. No trudno sravnit' svetimost' priblizhayusheisya i udalyayusheisya (ili
dazhe stacionarnoi) komponent. Eto ochevidnoe razlichie obychno obsuzhdaetsya v
kontekste modeli s dvoinym istecheniem [4], kogda izluchenie iz yadra
rassmatrivaetsya kak stacionarnaya tochka, gde priblizhayushiisya
relyativistskii potok stanovitsya neprozrachnym. Sverhsvetovoe dvizhenie
nablyudaetsya mezhdu etoi stacionarnoi tochkoi v sople i dvizhushimisya
volnovymi frontami ili drugimi neodnorodnostyami v vyhodyashem
relyativistskom potoke.......
.....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie (gamma-luchi, γ-luchi)
vid elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s chrezvychaino maloi dlinoi volny
< 5×10−3 nm i, vsledstvie etogo, yarko vyrazhennymi korpuskulyarnymi
i slabo vyrazhennymi volnovymi svoistvami.
Gamma-kvantami yavlyayutsya fotony s vysokoi energiei. Obychno schitaetsya,
chto energii kvantov gamma-izlucheniya prevyshayut 105 eV, hotya rezkaya granica
mezhdu gamma- i rentgenovskim izlucheniem ne opredelena. Na shkale
elektromagnitnyh voln gamma-izluchenie granichit s rentgenovskim izlucheniem,
zanimaya diapazon bolee vysokih chastot i energii. V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu. Ochevidno,
fizicheski kvanty elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s odinakovoi energiei ne
otlichayutsya, poetomu takoe razdelenie uslovno.
Gamma-izluchenie ispuskaetsya pri perehodah mezhdu vozbuzhdennymi
sostoyaniyami atomnyh yader (sm. Izomernyi perehod, energii takih
gamma-kvantov lezhat v diapazone ot ~1 keV do desyatkov MeV),
pri yadernyh reakciyah (naprimer, pri annigilyacii elektrona i pozitrona,
raspade neitral'nogo piona i t.d.), a takzhe pri otklonenii energichnyh
zaryazhennyh chastic v magnitnyh i elektricheskih polyah (sm. Sinhrotronnoe izluchenie).....
Esli net poverhnosti ob kotoruyu proishodit tormozhenie.
Material iz Vikipedii
.....Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh
obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v rentgenovskih
trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok yavlyayutsya
metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe antikatodom).
V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom, uskoryayutsya
pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom i katodom
(pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak uskorenie slishkom malo)
i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe tormozhenie. Pri etom za schet
tormoznogo izlucheniya proishodit generaciya izlucheniya rentgenovskogo diapazona,
i odnovremenno vybivayutsya elektrony iz vnutrennih elektronnyh obolochek atomov
anoda. Pustye mesta v obolochkah zanimayutsya drugimi ....
To vstupaet v silu fraza -
V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.
sledovatel'no pri otsutstvii udara o poverhnost' - otsutstvuet sama vozmozhnost'
vozniknoveniya rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, a esli izluchenie est' to ono mozhet
byt' tol'ko rezul'tatom izlucheniya v yadernom perehode. A eto uzhe chasticy vysokih energii.
avtorskoe izluchenie iz chernoi dyry -
.Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash metod obnaruzheniya Chernoi Dyry
-Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
....Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo.
ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut. ....
Padaya na Chernuyu Dyru veshestvo ne
mozhet rezko tormozitsya ili rezko uskoryatsya,
a sledovatel'no - ne mozhet
byt' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya po etoi prichine.
V svyazi s tem chto dlya uskoreniya do skorosti sveta
pri kotorom vozmozhno izluchenie neobhodimo
ne bolee 10 sekund, a zvezda razmerom s
Solnce na takoi skorosti proletit cherez gorizont
sobytii maksimum za minutu.
Gorizont sobytii - eto skorost' sveta - esli
ob'ekt uletaet s etoi skorost'yu ot nablyudatelya, to
u nego vozniknet krasnoe smeshenie.
Esli by veshestvo dolgo padalo - godami na maloi skorosti
s uskoreniem to bylo by zametno izmenenie Z u padayushih
tel v chernuyu dyru so vremenem, no pri etom nevozmozhno
rentgenovskoe izluchenie - iz za slishkom medlennogo
uvelicheniya uskoreniya.
.... Material iz Vikipedii Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri
vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah.....
A rentgenovskoe izluchenie est' - sledovatel'no
ego istochnikom mozhet byt' tol'ko rezul'tat yadernoi
reakcii.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.....
A esli rezul'tat izlucheniya istochnik yadernoi reakcii -
i on dlitsya godami, - to eto neitronnaya zvezda.
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8971-nasledstvennyie-chernyie-dyiryi/page/3/
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke, ya tak ponyal reshil -
zachem dobru propadat' - pust' izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi
dyry budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Vashe - Rentgenovskoe izluchenie ChD voznikaet pri akkrecii veshestva.
Izluchenie Hokinga - drugoi process. Stranno, chto za 7 let "uvlecheniya
astrofizikoi" Vy etogo ne ponyali.
Moe - S moei tochki zreniya - uvazhaemyi A.M.ChEREPAShUK imeet takoe zhe otnoshenie
k Chernym Dyram kak ya ili Vy.
My s Vami, i A.M.ChEREPAShUK mozhem tol'ko predpolagat' i vyskazyvat'
svoyu tochku zreniya, no obrashat' vnimaniya na podobnye vyskazyvaniya i brat'
ih na veru, ya ne vizhu smysla.
Drugoe delo avtor. Kak on skazal to - takie i Chernye Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vot ya naprimer govoryu chto veshestvo padaet na chernuyu dyru,
i posle udara o poverhnost' s protivopolozhnoi storony chernoi dyry voznikaet rentgenovskoe i svetovoe izluchenie.
Drugoi schitaet chto izluchenie na podlete.
V binokl' ne vidno - odni predpolozheniya, i ih mozhet byt'
bol'she sotni naprimer - komu verit'?
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vy zatragivaete vopros interpretacii avtorskih
idei bez soglasiya s avtorom.
A esli desyatok drugih avtorov opublikuyut po 300 nauchnyh rabot, a avtor o
Chernyh Dyrah govorit chto izluchenie v osnovnom iz fotonov - a vse drugie
govoryat, chto
izluchenie iz rentgenovskih chastic, drugoi govorit iz radio izlucheniya, a
tretii govorit iz gamma chastic - ya dolzhen slushat' isklyuchitel'no avtora
Chernyh Dyr,
a ne teh kto interpretiruet, i tem bolee teh kto plevat' hotel na avtorskii variant chernyh dyr.
Nikto ne meshaet pridumat' svoi - rentgenovskie chernye dyry, - tak net ne
hotyat, - tak na neudobnye voprosy otvechat' dolzhen budet avtor, a pri
interpretacii avtora - pisaka naprimer stat'i s levymi ideyami v oblasti
Chernyh Dyr, prikryvaetsya avtorstvom avtora
Chernyh Dyr, a sam so svoim bredom po otnosheniyu k avtorskomu izlozheniyu, kak-by i ne prichem.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
..Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii). Tochnee,
razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Vasha ssylka - tekst 11.05.11 20:36
....Kak otlichit' chernye dyry ot neitronnyh zvezd
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya chernaya dyra ne dolzhna proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. U nee mozhet nablyudat'sya lish' irregulyarnaya
peremennost' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya s harakternymi vremenami
$$Delta tapprox frac{r_g}{c}approx10^{-3} div 10^{-4}~mbox{rm s.}$$
I deistvitel'no, v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme Lebed' H-1, soderzhashei
chernuyu dyru s massoi okolo desyati solnechnyh, v sostoyanii, kogda
rentgenovskaya svetimost' ponizhena, a rentgenovskii spektr zhestkii i
stepennoi, nablyudaetsya bystraya irregulyarnaya peremennost' rentgenovskogo
potoka na vremenah poryadka millisekundy. Nablyudeniya, vypolnennye s
bortov sovremennyh rentgenovskih observatorii, takih, kak GINGA,
MIR-KVANT, GRANAT, ASKA, pokazali, chto rentgenovskie spektry
akkreciruyushih chernyh dyr sistematicheski bolee zhestkie, chem spektry
akkreciruyushih neitronnyh zvezd, i prostirayutsya do energii v neskol'ko
megaelektron-vol't.
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya neitronnaya zvezda mozhet proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. Odnako, esli neitronnaya zvezda obladaet
slabym magnitnym polem (napryazhennost'yu menee 1010 Gs) ili esli ee os'
vrasheniya neudachno orientirovana otnositel'no zemnogo nablyudatelya, pri
akkrecii na takuyu neitronnuyu zvezdu mogut ne nablyudat'sya regulyarnye
pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya. Poetomu otsutstvie strogo
periodicheskih pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya - eto lish' neobhodimyi,
no ne dostatochnyi priznak chernoi dyry. V to zhe vremya pri slabom
magnitnom pole neitronnoi zvezdy i nesil'nom tempe akkrecii veshestva na
ee poverhnosti mogut proishodit' termoyadernye vzryvy nakoplennogo
veshestva, privodyashie k yavleniyu rentgenovskogo barstera I tipa - korotkim
(dlitel'nost'yu poryadka 1-10 s) i moshnym vspyshkam intensivnosti
rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, chto takzhe yavlyaetsya harakternym priznakom
akkreciruyushei neitronnoi zvezdy, obladayushei tverdoi poverhnost'yu.
Poskol'ku chernaya dyra ne obladaet tverdoi poverhnost'yu, akkreciya
veshestva na nee ne dolzhna privodit' k fenomenu rentgenovskogo barstera I
tipa. Razumeetsya, otsutstvie etogo fenomena takzhe yavlyaetsya lish'
neobhodimym kriteriem nalichiya chernoi dyry. Takim obrazom, my mozhem
sformulirovat' vazhneishie priznaki akkreciruyushei chernoi dyry: eto moshnoe
rentgenovskoe izluchenie, bol'shaya massa (bolee treh solnechnyh),
otsutstvie fenomenov rentgenovskogo pul'sara ili rentgenovskogo barstera
I tipa. Pri etom vopros o nadezhnom opredelenii massy relyativistskogo
ob'ekta v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme yavlyaetsya reshayushim pri
identifikacii ego s chernoi dyroi....
Ya Vam prosto pokazyvayu proiivorechie u Vas i Vashei ssylke,
po otnosheniyu k napisannomu v Vikipedii o izluchenii iz Chernoi Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Leitenant Nemo
Chtoby proishodil razbros chastic rentgenovskogo
izlucheniya dlya etogo nado ili yadernoe gorenie zvezd,
chto k chernoi dyre ne primenimo, ili razgon materii
s posleduyushim udarom razognannoi chasticy o poverhnost'
kak eto proishodit v rentgen apparate.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Rentgenovskaya trubka
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v
elektronnyh obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok
yavlyayutsya metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe
antikatodom). V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom,
uskoryayutsya pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom
i katodom (pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak
uskorenie slishkom malo) i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe
tormozhenie. .....
Iz chego vytekaet sleduyushee chto dlya vozniknoveniya izlucheniya radioaktivnyh
chastic - neobhodim udar materii na skorosti odnoi desyatoi i bolee
skorosti sveta.
Iz chego sleduet nevozmozhnoe uslovie dlya izlucheniya materii pri padenii v
chernuyu dyru - tak kak dolzhna byt' poverhnost' dlya udara.
A poverhnosti to i net, veshestvo bez udara uhodit za gorizont sobytii,
sledovatel'no i ne mozhet chernaya dyra izluchat' radioaktivnye chasticy.
A.M.Cherepashyuk v dannom sluchai ne prav.
kosmogon
...Schitaetsya, chto pri padenii na ChD veshestvo razgonyaetsya do skorostei,
blizkih k s. V takom sluchae treniya bolee chem dostatochno dlya izlucheniya
vysokih energii. ...
Ya ne mogu ponyat' pochemu rassmatrivaetsya otdel'no vzyataya chast' i ne argumentiruetsya a postuliruetsya.
U Vas - postulat.
Vy voz'mite naprimer shar razmerom v kilometr v diametre, i bros'te ego v Chernuyu Dyru.
Nu i razognali Vy chto ugodno v pustote, - eshe raz povtoryayu - v pustote
proishodit padenie v chernuyu dyru - kakoe mozhet byt' trenie - prosto ne
ob chto teret'sya.
Voz'mite naprimer zvezdu, ei tozhe ne ob chto teret'sya kogda vokrug pustota,
letit padaet i ugasaet, tem bolee chto mne lichno
uvazhaemyi Dmitrii Mamontov raschety privodil chto zvezda na odnoi desyatoi
ili odnoi tretei skorosti sveta, mozhet prekrasno letat' na orbite
vokrug Chernoi Dyry, i s nei vse normal'no.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
,,,Chernaya dyra - oblast' prostranstva, v k-roi pole tyagoteniya nastol'ko
sil'no, chto vtoraya kosmich. skorost' (parabolicheskaya skorost') dlya
nahodyashihsya v etoi oblasti tel dolzhna byla by prevyshat' skorost' sveta,
t.e. iz Ch.d. nichto ne mozhet vyletet' - ni izluchenie, ni chasticy, ibo v
prirode nichto ne mozhet dvigat'sya so skorost'yu, bol'shei skorosti sveta.
Granicu oblasti, za k-ruyu ne vyhodit svet, naz. gorizontom Ch.d.,,,
Eto bazovoe opredelenie, dazhe esli predpolozhit' chto v chernuyu dyru padayut
zvezdy, pri etom izluchayut, i chto v centre galaktiki v chernyh dyrah
massa bol'she chem massa vseh zvezd v etoi galaktike, a s momenta bol'shogo
vzryva
togda mozhno poschitat' skol'ko milliardov zvezd v dyru v centre galaktiki
upalo. Tol'ko vot ne shoditsya s nablyudeniyami - zvezdy ne ischezayut v
chernyh dyrah - etogo nikto ne nablyudal, - ne nablyudali i to kak zvezda
prohodit cherez gorizont sobytii k chernoi dyre.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
...Ishodya iz klassiki, na kotoruyu Vy opiraetes', ChD dlya zemlyanina dolzhny svetit' kak kvazary....
Vashe - Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Moe - u menya vopros - esli v rentgen diapazone izluchayut nizhe privedennye
neitronnye zvezdy - kotorye
...V sluchae, kogda peretekanie veshestva prodolzhaetsya i posle
obrazovaniya N. z., ee massa mozhet so vremenem znachitel'no uvelichit'sya.
Pri ${mathfrak M}_{N.z.}>{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet
ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa
prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru. ...
To kak otlichit' neitronnuyu zvezdu ot chernoi dyry?
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188472
Neitronnye zvezdy
- gidrostaticheski ravnovesnye zvezdy, veshestvo k-ryh sostoit v osnovnom
iz neitronov. Sushestvovanie N. z. bylo predskazano v 30-h gg. 20
v.,vskore posle otkrytiya neitrona. Odnako tol'ko v 1967 g. oni byli
obnaruzheny v vide impul'snyh istochnikov radioizlucheniya - pul'sarov.
Zatem bylo ustanovleno, chto N. z. proyavlyayut sebya takzhe kak rentgenovskie
pul'sary (1971 g.) i vspyshechnye istochniki rentg. izlucheniya - barstery
(1975 g.). Ne isklyucheno, chto na odnoi iz stadii sushestvovaniya N. z. yavl.
istochnikami gamma-vspleskov. K 1984 g. otkryto ok. 400 N. z., iz nih
ok. 20 v vide rentg. pul'sarov, ok. 40 v vide barsterov, a ostal'nye v
vide obychnyh radiopul'sarov.
Druguyu vozmozhnost' poyavleniya N. z. predstavlyaet evolyuciya belyh karlikov v
tesnyh dvoinyh zvezdnyh sistemah. Peretekanie veshestva so
zvezdy-kompan'ona na belyi karlik postepenno uvelichivaet ego massu, i,
kogda ona dostigaet ${mathfrak M}_Ch$, belyi karlik prevrashaetsya v N. z. V
etom sluchae ${mathfrak M}_{N.z.}{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet
ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa
prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188644
Rentgenovskie pul'sary
- istochniki peremennogo periodicheskogo rentg. izlucheniya, predstavlyayushie
soboi vrashayushiesya neitronnye zvezdy s sil'nym magn. polem, izluchayushie za
schet akkrecii (padeniya veshestva na ih poverhnost'). Magn. polya na
poverhnosti R.p. ~ 1011-1014 Gs. Svetimosti bol'shinstva R.p. ot
1035-1039 erg/s. Periody sledovaniya impul'sov P ot 0,7 s do nesk. tysyach
s. R.p. vhodyat v tesnye dvoinye zvezdnye sistemy, vtorym komponentom
k-ryh yavl. normal'naya (nevyrozhdennaya) zvezda, postavlyayushaya veshestvo,
neobhodimoe dlya akkrecii i norm. funkcionirovaniya R.p. Esli vtoroi
komponent nahoditsya na stadii evolyucii, kogda skorost' poteri massy
(etim komponentom) mala (sm. Evolyuciya tesnyh dvoinyh zvezd), neitronnaya
zvezda ne proyavlyaet sebya kak R.p. Rentg. pul'sary vstrechayutsya kak v
massivnyh molodyh dvoinyh zvezdyh sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu I
Galaktiki i lezhashih v ee ploskosti, tak i v malomassivnyh dvoinyh
sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu II i prinadlezhashih k sferich.
sostavlyayushei Galaktiki. R.p. otkryty takzhe v Magellanovyh Oblakah. Vsego
otkryto ok. 20 R.p.
Na nachal'nom etape issledovanii otkryvaemym rentg. ob'ektam
prisvaivalis' naimenovaniya po sozvezdiyam, v k-ryh oni nahodyatsya. Napr.,
Gerkules X-1 oznachaet pervyi po rentg. yarkosti ob'ekt v sozvezdii
Gerkulesa, Kentavr H-3 - tretii po yarkosti v sozvezdii Kentavra. R.p. v
Malom Magellanovom Oblake oboznachaetsya kak SMC X-1, v Bol'shom
Magellanovom Oblake - LMC X-4. Obnaruzhenie so sputnikov bol'shogo chisla
rentg. istochnikov potrebovalo dr. sistemy oboznachenii.
Uskorenie i zamedlenie vrasheniya neitronnyh zvezd.
V otlichie ot radiopul'sarov (nek-rye iz k-ryh, v chastnosti pul'sary v
Krabe i Parusah, izluchayut i v rentg. diapazone, sm. Pul'sary),
izluchayushih za schet energii vrasheniya zamagnichennoi neitronnoi zvezdy i
uvelichivashih svoi period so vremenem, R.p., izluchayushie za schet akkrecii,
uskoryayut svoe vrashenie.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Spasibo za otvet.
Esli ya pravil'no ponyal, to istochnik
nepreryvnogo rentgenovskogo izlucheniya
so stabil'noi intensivnost'yu - nazyvaetsya
Chernoi Dyroi .
Esli rentgenovskoe izluchenie menyaet intensivnost'
to eto ili neitronnaya zvezda ili
rentgenovskii pul'sar.
Zdes' avtor chernyh dyr - sem' pyatnic na nedelyu,
sperva govoril vot tak -
...Chernaya dyrá oblast' v prostranstve-vremeni,
gravitacionnoe prityazhenie kotoroi nastol'ko veliko,
chto pokinut' ee ne mogut dazhe ob'ekty, dvizhushiesya
so skorost'yu sveta (v tom chisle i kvanty samogo sveta)....
Potom ego ozarilo v 1975 i on odaril chernye dyry i vseh
astrofizikom izlucheniem ot chernyh dyr.
---...Izluchénie Hókinga ...---
......Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi.
Predskazan teoreticheski Stivenom Hokingom v
1974 godu.[1] Rabote Hokinga predshestvoval
ego vizit v Moskvu v 1973 godu, gde on vstrechalsya
s sovetskimi uchenymi Yakovom Zel'dovichem i
Alekseem Starobinskim. Oni prodemonstrirovali
Hokingu, chto v sootvetstvii s principom
neopredelennosti kvantovoi mehaniki
vrashayushiesya chernye dyry dolzhny
porozhdat' i izluchat' chasticy.[2]
Isparenie chernoi dyry kvantovyi process.
Delo v tom, chto ponyatie o chernoi dyre kak ob'ekte,
kotoryi nichego ne izluchaet, a mozhet lish' pogloshat' materiyu,
spravedlivo do teh por, poka ne uchityvayutsya kvantovye effekty.
V kvantovoi zhe mehanike, blagodarya tunnelirovaniyu,
poyavlyaetsya vozmozhnost' preodolevat' potencial'nye bar'ery,
nepreodolimye dlya nekvantovoi sistemy. Utverzhdenie,
chto konechnoe sostoyanie chernoi dyry stacionarno,
pravil'no lish' v ramkah obychnoi, ne kvantovoi teorii
tyagoteniya. Kvantovye effekty vedut k tomu, chto na samom
dele chernaya dyra dolzhna nepreryvno izluchat', teryaya pri
etom svoyu energiyu.....
Itogo
...Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke,
ya tak ponyal reshil - zachem dobru propadat' - pust'
izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi dyry
budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A vot zdes' ya Vam mogu predlozhit' sdelat' u kazhdoi stat'i schetchik, - ponyal -ne ponyal,
Vashe - Dlya bazovogo ponimaniya nuzhno umet' chitat' i imet' nekotoruyu
podgotovku v ramkah hotya by shkoly. U Vas takaya podgotovka, sudya po
vsemu, hromaet na obe nogi, poetomu Vy ne ponimaete bol'shinstvo statei.
Dlya utochnyayushih voprosov est' kommentarii, dlya bazovoi podgotovki - shkola
i uchebniki.
- Vy dumaete chto vse uchennye pishut pravil'nye stat'i, i nikto stat'i ne
vysasyvaet iz pal'ca a potom ne rzhet nad chitatelyami, a Vash sait chtoby
chitat' - to nado byt' doktorom nauk, i v tozhe samoe vremya Vy lichno ne
mozhete otvetit' pryamo na pryamye voprosy, po etoi stat'e. Vy menya v
principe zaintrigovali, ya podumayu chtoby takoi puzyr' vysosat' iz pal'ca v
ramkah paradigmy, chtoby vse vokrug azh zaaplodirovali za isklyuchitel'no
vysokohudozhestvennyi idiotizm v ramkah breda sivoi kobyly.
Moe-Ne rasskazhete Vashe otnoshenie k vyskazyvaniyu, -
Esli opyt ne sovpadaet s teoriei to tem huzhe dlya opyta?
Napomnyu -
Moe - So vtorogo Vashego otveta ya ponyal - chto u Vas est' metody
dokazatel'stv kotorye pozvolyayut opredelit' kakimi byli v pervye momenty
bol'shogo vzryva zvezdy, chernye dyry , temperatura i drugie razlichnye
svoistva prostranstva i svoistva razlichnyh fizicheskih ob'ektov.
Vashe - Ne u menya. U astronomov, astrofizikov i kosmologov.
Moe- Esli mne ne mozhet opponent srazu vnyatno izlozhit' otvet na moi
prostoi vopros po obsuzhdaemoi stat'e, to ya ne obyazan verit' napisannomu,
a skoree naoborot - vynuzhden zasomnevat'sya.
Po povodu gromkih familii v astrofizike - to esli Vy proanaliziruete ih
biografiyu i trudovye zaslugi i proanaliziruete ih prichastnost' k
astrofizike, to oni vse v astrofizike - diletanty, kotorye idei
vbrasyvali v astrofiziku ot sluchaya k sluchayu, i ser'ezno ei ni kto ne
zanimalsya. Po etomu vsya astrofizika i sostoit iz razroznennyh idei, -
ozaryalok, kotorye posledovateli pytayutsya sostykovyvat' mezhdu soboi po
prichine poyavleniya novoi izmeritel'noi tehniki.
A astrofiziku u menya hobbi let 7, tak chto ya prochital stol'ko statei
raznyh, chto mogu delat' vyvody chto vysoska iz pal'ca, a chto i super
gramotno napisano .
Samoe smeshnoe chto super stat'i absolyutno neizvestny.
http://crydee.sai.msu.ru/Universe_and_us/4num/v4pap26.htm
-Ochen' horoshaya stat'ya.
http://www.anomaliy.ru/discovery/482
"Sverhnovye tipa I a, kak polagayut, formiruyutsya
posle vzryvov belyh karlikov, sverhplotnyh mertvyh zvezd razmerom s
nashu Zemlyu, kotorye kogda-to byli yadrom solncepodobnogo svetila, i
ch'ya vneshnyaya obolochka rastvorilas' v kosmose.
Odna iz osobennostei etogo tipa otsutstvie vodoroda, i eto
nesmotrya na to, chto vodorod yavlyaetsya samym rasprostranennym
himicheskim elementom."
Vot eta stat'ya - v principe dolzhna byla perevernut' vsyu astrofiziku,
po toi prichine chto net vodoroda vnutri zvezdy. A u tekushei paradigmy
vodorod vygoraet. I astrofiziki vnyatno otvetit' ne mogut prichinu po
kotoroi samyi legkii vodorod - preodolevaet gravitaciyu stanovitsya
tyazhelee vseh metallov i letit v yadro zvezdy pouchastvovat' v yadernoi
reakcii. I V to chto samyi legkii vodorod preodolevaet letit vnutr'
zvezdy -ya ne veryu, hot' v millione knizhek eto budet napisano, i tysyache
uchebnikov. Tak kak napisannoe ne podtverzhdeno fizicheskimi svoistvami a
protivorechit im.
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.07.2012 21:44, 1.4 KBait)
Vot kak byvaet nebol'shoe vyskazyvanie a kak
nagnulo vseh relyativistov.
---
 Re: Novoe otkrytie v teorii prostranstva-vremeni, zakryvayushee STO
Re: Novoe otkrytie v teorii prostranstva-vremeni, zakryvayushee STO
Otvet #48 - Segodnya :: 18:55:38
Patrice pisal(a) Segodnya :: 10:25:25:Eto k komu obrasheno?
Eto v pustoe prostranstvo Puankare. Dazhe eha ne dozhdesh'sya.
---
Dlya teh kto ne ponyal kak sil'no nagnuli
relyativistov s bol'shim
vzryvom.
Chto sobstvenno v - \pustote\ - \postoyanno\ - \ otrazhaet\- \reliktovoe izluchenie\,
- eto samyi zhestokii i besposhadnyi udar
po teorii bol'shogo vzryva.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.07.2012 13:25, 769 Bait)
V.A.Aksenova
\\\No k teorii bol'shogo vzryva privodit prosteishee lineinoe uravnenie dvizheniya.\\\
Nu chto zametili chto ves' fundament iz zdaniya astrofiziki
ne imeet fizicheskogo smysla,
i ono valitsya po polnoi, a zdanie to zapolneno relyativistami.
Ya v principe udivlen kak tak poluchilos' chto trud tysyach uchennyh
na protyazhenii sta let okazalsya bessmyslennym i bespoleznym.
Ne ponyatno pochemu oni rogom uperlis'
v neskol'ko napravlenii,
i ne menyali modeli kazhdye dvadcat' - tridcat' let.
Da i osobogo truda ne sostavilo chtoby
obosnovat' nelogichnost' fizicheskogo smysla
u modelei,
tak skazat' porvat' vse knizhki po astrofizike v kloch'ya, kak mavpa gazetu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.07.2012 18:42, 3.2 KBait)
| Re: Chernaya dyra
|
12.02.201219:24 |
|
\\\Polagayu, zakon Habbla v ramkah dannoi temy prosto vazhnee i vyshe, kakih-to tam kvantovyh svoistv fotona.\\\
Rasskazhu pravil'nyi otvet na
etot vopros, -
Iznachal'no byl obsheprinyatyi
efir, na osnovanii kolebatel'nyh svoistv sveta v
efire analogichnyh zvuku v vozduhe Tomas Yung ob'yasnil
interferenciyu sveta na dvuh ochen' blizko raspolozhennyh
shelyah. V svyazi s tem chto naprimer solnechnyi svet
prohodil cherez sheli, i bylo mesto gde nakladyvalos'
izobrazhenie solnca ot dvuh blizko raspolozhennyh shelei.
Opyt kogda risuyut tochechnyi istochnik sveta, a rasstoyanie
mezhdu shelyami bol'she diametra istochnika
sveta - ne korrektnyi,
on tol'ko na risunkah, na praktike on ne vozmozhen, tak
kak svetovye kolebaniya ne iskrivlyayutsya na shelyah, svet
prohodit skvoz' shel'
pryamo. Etomu podtverzhdenie
shkol'nyi opyt po fizike, kogda delaetsya malen'kaya dyrka
i beretsya chernyi yashik bez zadnei stenki i kal'ka,
v chernom yashike raspolagaetsya
naprotiv dyrki kal'ka,
i izobrazhenie poluchaetsya perevernutym,
i esli sdelat' ryadom eshe odnu dyrku, poluchitsya
dva izobrazheniya perevernutyh, kotorye nalozhatsya
drug
na druga - eto i nazyvaetsya interferenciya.
Tak vot, posle etogo nado bylo skazat' chto ob'yasnenie interferencii
Tomasa Yunga ne korrektno, i oprovergnut',
chego ne bylo sdelano.
Prosto za-postulirovali dlya pustoty chto dvizhutsya svetovye
chasticy. Za-postulirovali tak za-postulirovali, no poyavilsya
nyuans kotoryi
ne reshaetsya dlya chastic, tak kak nado ob'yasnit'
interferenciyu dlya solnca na dvuh shelyah na rasstoyanii naprimer
3mm mezhdu shelyami. I chto , i to chto dlya fotonov nado
pridumyvat'
dopolnitel'nye svoistva, na urovne potenciala, to-est' fotony
budut plyusovye i minusovye, pri etom vse proidet.
No zdes' voznikaet sleduyushii nyuans,
esli chastica so znakom
plyus ili minus to oni dolzhny otklonyatsya
magnitnym polem, - esli podnesti magnit k luchu,
naprimer minusom to plyusovye fotony dolzhny
prityagivat'sya
k magnitu a minusovye ottalkivat'sya, to-est' luch rasshiritsya,
- chego ne nablyudaetsya - vot takaya zhestokaya selyavi.
I chto v itoge poluchaem
dlya krasnogo smesheniya ili zakona Habbla,
azh nichego, tak kak esli rasshiryaetsya, to dolzhna umen'shat'sya
skorost' fotonov - eto nevozmozhno tak kak eto povliyaet na
skorost' sveta, a skorost' sveta za-postulirovana stabil'noi,
i ne zavisyashei ni ot chego. Chto delat' relyativistam? ob'yasnyat'
to nado, ostaetsya cherez poteryu napryazhennosti
fotonov,
tochnee elektro-potencialov, no delo v sleduyushem v
etom sluchai vse ravno ne mozhet izmenitsya chastota, mozhet
izmenitsya tol'ko amplituda raznosti, a
chastota ostanetsya.
Vot i prodolzhayut ogorod gorodit', i ochen' ne hotyat pri rasshirenii
schitat' chto fotony kak chasticy dolzhny skorost' menyat',
- s moei tochki
zreniya - shikarnyi samozaklin ot matematikov.
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.07.2012 18:47, 2.9 KBait)
| Re: Chernaya dyra
|
13.02.201216:46 |
|
A teper' ya poschitayu na skol'ko poluchaetsya
raznica pri opredelenii razmerov zvezd
metodami krasnogo smesheniya i Habbla.
--------------------
Udalennost'
Solnca ot Zemli, 149,6 mln km
diametr Solnca = 1 391 000 kilometrov.
A teper' posmotrim kak nedalekie astronomy
dazhe obladaya vysokokachestvennoi
tehnikoi
delayut vyvody o razmere SN1987a c
bol'shimi peregibami, chuvstvuetsya chto zdravyi
smysl oni polozhili na polku, no zato v teorii
vpisalis'.
---
http://astroprofspage.com/archives/744

---
http://planetologia.ru/sverhnova/1332--qq-sn-1987a.html
\\\Raspolagayas' na rasstoyanii 168 tys.
svetovyh let ot
Zemli v galaktike Bol'shoe Magellanovoe
oblako, sverhnovaya
SN 1987A daet uchenym detal'nuyu informaciyu o tom, kak
dozhivayut svoi dni bol'shie zvezdy. Zvezdoi-predshestvennikom
SN 1987A byl goluboi sverhgigant
Sanduleak -69 202 s massoi
okolo 17 mass Solnca.\\\
\\\Oni izuchali vzaimodeistvie obrazovavshihsya ot vzryva zvezdy
diametrom okolo 9,6 trillionov kilometrov
kolec gaza,
okruzhayushego sverhnovuyu.\\\
Tak vot, ya dumayu chto razmer predshestvuyushei zvezdy byl
dva diametra solnca(17 mass Solnca), posle vzryva forma
zvezdy izmenilos',
ona priobrela diskoobraznyi vid, diametr diska s kraev
u kotorogo proishodyat vybrosy - posle vzryva razmer obrazovavshegosya diska
s vybrosami
po krayam raven dva s polovinoi diametra solnca.
Diametr diska s vybrosami po fotografii v dva raza men'she
diametra kolec i v traktovke sovremennoi paradigmy,
sledovatel'no diametr zvezdy v forme diska s vybrosami
po krayam ot astronomov v paradigme raven 4.8 trillionov
kilometrov.
Vot chto u menya poduchilos'
"diametr Solnca = 1 391 000 kilometrov"
dva s polovinoi diametra solnca i ravno 3.47 mln. km.
A u teh astronomov dazhe ne 4.8 milliardov kilometrov,
- diametr chto v tysyachu raz bylo by bol'she moego analiza,
u nih v million raz
razmer bol'she ne moego rascheta - a v million raz bol'she
zdravogo smysla.
I smeshno smotret' na etu klounadu,
i o kakih melkih voprosah vrasheniya mozhno rassuzhdat'
pri oshibke na rasstoyanii 168 tys.svetovyh let v - million- raz,
to
na skol'ko oni mogut oshibat'sya so svoimi zetami
dlya vysosannyh iz pal'ca fotonov na bol'shih rasstoyaniyah.
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.07.2012 18:52, 635 Bait)
http://elementy.ru/lib/430551
Risunok 1.

A vot za takie veshi ya schitayu chto fizikov fabrikuyushih
takie risunki bez opytov po kotorym oni provodilis'
nado
lishat' zvanii i zapreshat' pozhiznenno prepodavatel'skuyu
deyatel'nost', i rabotu v oblasti fiziki.
Eto zh nado do chego dodumalis', risuyut i im nas
rat' chto
eto obychnyi lohotron, oni schitayut chto eto horosho,
a pipl havaet optiki i astrofiziki dovol'ny, a mne smeshno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.07.2012 18:57, 2.1 KBait)
Rasskaz
Fantasticheskii son o gorode fizikov.
Prisnilsya gorod fizikov, on sostoyal iz odnoi central'noi ulicy,
kotoraya razdelyala
pustynnye dikie prostory
klassicheskoi fiziki,
i plodonosyashie sady relyativistskoi fiziki.
Po pustynnym prostoram klassicheskoi fiziki skitalis' kakie-to
golodrancy neskol'ko bylo po
dvoe i po troe no v osnovnom odinochki,
hodili chto-to pisali na peske, koe kto iz al'ternativshikov provodil
kakie-to opyty na kostre poka gotovili edu.
Prakticheski
vse al'ternativshiki periodicheski i s raznym uspehom
uchastvovali v forumah
"skai-tyuh" i "zvezdomer".
Eti uchastki dorogi otlichalis' razmetkoi
ulicy, i nalichiem zabora
so storony relyativistov na "zvezdomere", zabor na "zvezdomere" ne
dlya togo chtoby al'ty ne lazili, a dlya togo chtoby
somnevayushiesya
relyativisty ne smogli ubezhat' ot moderatorskoi porki. Vozle forumnoi
razmetki s obeih storon periodicheski stoyali tolpy zevak i prihodili
oratory
to s toi a to s drugoi storony.
Na "skai-tyuhe" demokratii bylo pobol'she i vse orali drug na druga i periodicheski
rvali na sebe odezhdu i brosali cherez
dorogu, tam v nee vyshmarkivalis' i brosali
obratno.
Na "zvezdomere" reryativisty posle meryanii teleskopami i posle obeda v gos
stolovoi, pododvigalis'
i podkatyvalis' na svoih kreslah k doroge,
chtoby luchshe slyshat'.
Po sredine ulichnoi razmetki "zvezdomerovskogo" foruma stoyal - pletochnyh
shmaganii
master, - nesravnennyi moderator Bi-Be. On slavilsya tem chto ot
pryamyh voprosov uhodil svoimi otvetami v intellektual'noe begstvo.
Ot al'ternativshikov on treboval
dat' emu posmotret' teh pasport na efir,
i predostavit' opyty za kotorye mozhno nobelevskuyu poluchit' eshe vchera.
Estestvenno zapros na relyativistskii teh-pasport
na prichinu skorosti sveta vyzyvaet
shatanie v kreslah i bubnenie relyativistov o tom chto v nem net smysla,
a smysl est' v pasporte na efir.
Tak sobstvenno
v neponimanii i smotreli drug na druga.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.07.2012 18:57, 2.1 KBait)
Rasskaz
Fantasticheskii son o gorode fizikov.
Prisnilsya gorod fizikov, on sostoyal iz odnoi central'noi ulicy,
kotoraya razdelyala
pustynnye dikie prostory
klassicheskoi fiziki,
i plodonosyashie sady relyativistskoi fiziki.
Po pustynnym prostoram klassicheskoi fiziki skitalis' kakie-to
golodrancy neskol'ko bylo po
dvoe i po troe no v osnovnom odinochki,
hodili chto-to pisali na peske, koe kto iz al'ternativshikov provodil
kakie-to opyty na kostre poka gotovili edu.
Prakticheski
vse al'ternativshiki periodicheski i s raznym uspehom
uchastvovali v forumah
"skai-tyuh" i "zvezdomer".
Eti uchastki dorogi otlichalis' razmetkoi
ulicy, i nalichiem zabora
so storony relyativistov na "zvezdomere", zabor na "zvezdomere" ne
dlya togo chtoby al'ty ne lazili, a dlya togo chtoby
somnevayushiesya
relyativisty ne smogli ubezhat' ot moderatorskoi porki. Vozle forumnoi
razmetki s obeih storon periodicheski stoyali tolpy zevak i prihodili
oratory
to s toi a to s drugoi storony.
Na "skai-tyuhe" demokratii bylo pobol'she i vse orali drug na druga i periodicheski
rvali na sebe odezhdu i brosali cherez
dorogu, tam v nee vyshmarkivalis' i brosali
obratno.
Na "zvezdomere" reryativisty posle meryanii teleskopami i posle obeda v gos
stolovoi, pododvigalis'
i podkatyvalis' na svoih kreslah k doroge,
chtoby luchshe slyshat'.
Po sredine ulichnoi razmetki "zvezdomerovskogo" foruma stoyal - pletochnyh
shmaganii
master, - nesravnennyi moderator Bi-Be. On slavilsya tem chto ot
pryamyh voprosov uhodil svoimi otvetami v intellektual'noe begstvo.
Ot al'ternativshikov on treboval
dat' emu posmotret' teh pasport na efir,
i predostavit' opyty za kotorye mozhno nobelevskuyu poluchit' eshe vchera.
Estestvenno zapros na relyativistskii teh-pasport
na prichinu skorosti sveta vyzyvaet
shatanie v kreslah i bubnenie relyativistov o tom chto v nem net smysla,
a smysl est' v pasporte na efir.
Tak sobstvenno
v neponimanii i smotreli drug na druga.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.07.2012 18:58, 1.9 KBait)
Prodolzhenie
Rasskaz
Fantasticheskii son o gorode fizikov.
Dal'she u dorogi relyativisty postavili tribu svoih dostizhenii
s trubnymi
fanfarami.
Na fanfarah
raznye nadpisi, - bez kotoryh relyativizm
byl by nevozmozhen.
Chtoby uiti ot efira pridumali fanfary ---- "vakuum"
Chtoby uiti ot sveta kotoryi byl
v efire, pridumali fanfary --- "foton"
Tak kak ne smogli pridumat'
kuda teplo devaetsya ot zvezd,
pridumali fanfary
- ---"bol'shoi vzryv",
tepla u zvezd okazalos' mnogo
i chtoby pogloshat' eshe teplo
ot zvezd pridumali fanfary -
--- "chernaya - dyra"
a energii okazalos' eshe bol'she,
pridumali fanfary ---" uskorennoe rasshirenie",
i neponyatno
chem prityagivaetsya
tokmo po dva tela pridumali fanfary --- "gravitaciya".
A na protiv tribuny s fanfarami raspolagalsya zritel'nyi zal
smeha
relyativistov, tak kak na tribunu s fanfarami periodicheski
zabegali odichavshie al'ty, oni pribegali s toi storony dorogi,
so storony klassicheskoi fiziki. I kogda
odichavshie al'ty v svoih
vozmushennyh rechah ispol'zovali slova isklyuchitel'no dlya
relyativistov, i oni sovpadali s nadpisyami na fanfarah, to vmesto
slov oni
duli v fanfary relyativistov.
Nekotorye dikie al'ty celye relyativistskie koncerty
ustraivali i vyduvali fugi , gorazdo
luchshe nekotoryh relyativistov. Relyativisty
osobo sil'no
smeyalis' kogda dikie al'ty ispol'zovali vse slova.
Vdrug zavisli v vozduhe udary plet'yu, master Bi-Be na "zvezdomere"
shmagal
vseh podryad a chtoby uvazhali.
Sobstvenno tak i zhili, klassicheskaya storona - pustynya bednosti,
i relyativistskie fruktovye sady s shokoladnymi kabinetami.
Po doroge to tam to tam probegali bobry, ih po druzheski bili
teleskopami s lyuboi storony ulicy.
Vot ya i prosnulsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. A. Aksenova,
28.07.2012 21:02, 256 Bait)
Cherepashuk govoril po televideniyu,chto chernye dyry -eto gipoteticheskie ob'ekty.Ih nazyvayut kandidatami v chd. Tak chto astronomy ponimayut ,chto ih nauka ,rassuzhdeniya o prostranstve
granichat s ezoterikoi.No oni ne mogut bez etogo. Zabavnyi rasskaz Vy sochinili.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.07.2012 23:25, 6.0 KBait)
Chtoby vy byli v kurse na segodnyashnii den' oficial'no
ne obnaruzhena ni odna chernaya dyra, dogadalis' pochemu,
- sobstvenno oni i sami ne znayut kak ona dolzhna vyglyadet'.
No v tozhe samoe vremya stol'ko premii vruchili za chernye dyry
i na dostatochnye summy, vot naberite v guglyah premiya za chernye dyry.
---
http://ria.ru/science/20080118/97279705.html
Razmer premii sostavlyaet 500 tysyach dollarov. V etom godu summa byla
podelena mezhdu dvumya nominaciyami. Pervaya polovina premii byla prisuzhdena
za dostizheniya v oblasti matematiki, vtoraya polovina - za dostizheniya v
oblasti astrofiziki Rashidu Syunyaevu.
Maksim Koncevich (Institut vysshih nauchnyh issledovanii, Franciya) i Edvard
Uitten (Institut vysshih issledovanii Prinstona, SShA) poluchili svoyu
polovinu premii za issledovaniya razlichnyh tipov geometricheskih ob'ektov
i, v chastnosti, za reshenie ryada matematicheskih problem, svyazannyh s
razvitiem teorii strun.
Prisuzhdenie premii Kraforda Syunyaevu yavlyaetsya priznaniem ogromnogo vklada
uchenogo v issledovanie ekstremal'nyh processov, proishodyashih vo
Vselennoi, - akkrecii (padenii) veshestva na kompaktnye ob'ekty: chernye
dyry i neitronnye zvezdy.
Chitaite dalee:
http://ria.ru/science/20080118/97279705.html#ixzz21wUMU4rh---
http://lenta.ru/news/2012/01/19/prize/
V Shvecii ob'yavleny laureaty premii Kraforda, prisuzhdayusheisya za otkrytiya v
oblasti astronomii, matematiki, a takzhe biologii, nauk o zemle i
issledovanii metodov lecheniya poliartrita. V 2012 godu nagrada vruchena i
astronomam i matematikam. Osnovaniya prisuzhdeniya premii ukazany v
press-relize
prizovogo komiteta Shvedskoi korolevskoi akademii nauk. Denezhnyi
ekvivalent premii sostavlyaet 4 milliona shvedskih kron (okolo 400 tysyach
evro).
Astronomicheskoi nagrady udostoilis' Reinhard Gencel' (Reinhard Genzel) i
Andrea Gez (Andrea Ghez). Premiya byla prisuzhdena etim uchenym za
obnaruzhennye imi i ih sotrudnikami vesomye dokazatel'stva togo, chto v
centre Mlechnogo Puti nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya chernaya dyra. Oba astronoma
nablyudali zvezdy, obrashayushiesya vokrug centra Galaktiki, i prishli k
odnomu i tomu zhe vyvodu nezavisimo drug ot druga.
---
Pri vsem pri tom chto obnaruzhenie chernyh dyr - ozhidaetsya, i nobelevskaya za otkrytie
chernyh dyr eshe nikomu ne prisuzhdena.
---
http://news.grimuar.info/%D0%BD%D0%B0%D0%B1%D0%BB%D1%8E%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%8F-%D0%B7%D0%B0-%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B9-%D0%B4%D1%8B%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B9-%D1%81-%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%B4%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%BC-%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D1%80%D0%B5%D1%88%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5%D0%BC-544.html
Astronomy
s observatorii v Chili s teleskopa APEX odnovremenno s astronomami s
teleskopa raspolozhennogo na Gavaiyah (SShA) i s teleskopa, raspolozhennogo v
shtate Arizona (SShA) proveli nablyudeniya i poluchili rekordnoe razreshenie
snimkov glubin kosmosa.
Proveli oni eto nablyudenie za yadrom
udalennogo kvazavra 3C 279, chtoby poluchit' snimki sverhmassivnyh chernyh
dyr. Snimki poluchilis' s rekordnym razresheniem, kotoroe prevyshaet
chelovecheskoe zrenie v 2 milliona raz. Etot kvazar soderzhit v centre
ogromnuyu chernuyu dyru, s massoi primerno prevyshayushuyu solnechnuyu v milliard
raz. Nahoditsya eta svermassivnaya chernaya dyra na rasstoyanii 5 milliardov
let ot nas.

Ob etom soobshili v press-relize Evropeiskoi yuzhnoi observatorii,
kotoroi prinadlezhit teleskop APEX. V etom press-relize otmechaetsya, chto
eti snimki imeyut rekordnoe razreshenie, kotoroe mozhet seichas byt'
polucheno. Vysokoe razreshenie bylo polucheno iz-za togo chto nablyudenie
bylo odnovremenno provedeno srazu s treh teleskopov i vse eti tri
instrumenta obrazovali interferometr, a tak zhe nablyudenie proveli v
radiodiapazone 1,3 mm, kotoroe eshe ne ispol'zovali dlya takih nablyudenii.
V rezul'tate poluchilos' razreshenie, kotoroe mozhet razlichat' detali v 2
milliona raz mel'che, chem mozhet razlichit' chelovecheskii glaz.
Eto otkrylo novyi etap na puti k issledovaniyu nedr glubokogo kosmosa.
Teper' poyavilsya novyi proekt, po kotoromu soedinyat bol'shee chislo moshnyh
teleskopov i sozdadut, tak nazyvaemyi, Teleskop gorizonta. Uchenye
nadeyatsya, chto v etom proekte oni smogut zaregistrirovat' izobrazhenie
teni sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyry. Osobenno im interesno budet nablyudat' za
chernoi dyroi, kotoraya nahoditsya v centre nashei galaktiki.
Kak skazal v interv'yu direktor Gosudarstvennogo astronomicheskogo
instituta Anatolii Cherepashuk, v blizhaishie gody nemalo astronomov budut
nagrazhdeny Nobelevskimi premiyami. Ya zhdu, - skazal on - chto v blizhaishee
desyatiletie budet poluchena Nobelevskaya premiya za otkrytie chernyh dyr. My
k etomu podhodim vse blizhe i blizhe. Vo-pervyh, etih chernyh dyr uzhe kak
sobak nerezanyh. Dlya zvezdnyh chernyh dyr izmereny massy, dany
ogranicheniya na razmery. A sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr v yadrah galaktik
uzhe mnogie tysyachi. Samoe glavnoe nado izmerit' processy vblizi
gorizonta sobytii, tol'ko tak mozhno dokazat', chto eto chernaya dyra.
---
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.07.2012 11:12, 1.2 KBait)
\\\No o prostranstve rech' ne idet.Ob'ekt A 1689-zD1
udalyaetsya ot nas v
8 raz bystree skorosti sveta (tak v knige zarubezhnyh pravda astronomov
napisano) No sama vselennaya mozhet rasshiryatsya s takoi ogromnoi
skorost'yu.Prosto nel'zya ispol'zovat' eto
rasshirenie ,chtoby obognat' luch sveta.
\\\
Ne v obidu Vam budet skazano,
s moei tochki zreniya - dikoe mrakobesie v Vashih slovah,
Vashei viny v etom net absolyutno, Vy eto vse prochitali
i dumaete chto tak ono est' na samom dele, - a esli ya Vam
skazhu chto zakony N'yutona v kosmose ne rabotayut, Vy zhe
mne ne poverite, - hotya na samom dele oni
tam ne rabotayut,
komety i asteroidy ne prityagivayut voobshe nikak.
Skazki peremeshannye s idiotizmom ispol'zuyutsya dlya prodvizheniya
svoih nelogichnyh i neobosnovannyh
teorii i modelei v astrofizike,
i eto normal'naya obsheprinyataya tendenciya,
nakazanii za vran'e i otkrovennyi bred ne sushestvuet.
Sobstvenno po etoi prichine
i zapretili prepodavanie astronomii
v shkolah, - chtoby ne travmirovat' detskuyu psihiku - yavnym bredom
peremeshannym s neobosnovannymi vydumkami, neskladushkami i
idiotizmom.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. A. Aksenova,
29.07.2012 20:24, 890 Bait)
Komety ne prityagivayutsya? A kak zhe kometa,kotoraya raspalas' na kuski i upala na Yupiter? Po prichine gravitacii oni i vrashayutsya vokrug Solnca.
Chernye dyry -gipotetichnye
ob'ekty,no kak skazal na lekcii S.Popov, nado bylo by pridumat' eshe bolee ekzoticheskie ob'ekty dlya ob'yasneniya mnogih yavlenii. Vremya pokazhet ,navernoe. A po povodu Bol'shogo
vzryva, mozhet byt', Vam budet interesno prochest' knigu Stivena Vainberga "Pervye tri minuty" iz serii Otkrytiya,kotorye potryasli mir. On ochen' podrobno issleduet
tam reliktovoe izluchenie. I prizyvaet ser'ezno otnestis' k ego otkrytiyu. Vozmozhno,vy prochitali uzhe .No interesno izdanie 2011 g.Eksmo. Tam vnosyatsya korrektivy ,svyazannye s
izmeneniyami vzglyadov fizikov posle ee napisaniya.Ochen' horosho ob'yasnyaet izlucheniya.Kak budto on vnutrennim zreniem vidit vse eti angstremy,i ty tozhe nachinaesh' ih kak by videt'.
Eto ochen' cenno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.07.2012 21:15, 1.7 KBait)
Vy pozhaluista prochitaite to chto ya Vam rekomendoval,
tam napisano chto byvayut tela kotorye prityagivayut
a byvaet kotorye ne prityagivayut, ih otlichaet teplovoe
sal'do - te kotorye prityagivayut vydelyayut tepla bol'she chem
poluchayut ot solnca.
Yupiter i Solnce prityagivayut a vot tela kotorye men'she 500-100
km v diametre
- mogut byt' tol'ko prityagivaemymi, no sami oni
ne obladayut prityazheniem.
Vot sami podumaite zachem mne kogo-to slushat' o chernyh dyrah
esli ya mogu pochitat'
avtorskii variant, a to chto kazhdyi pridumyvaet
sebe o chernoi dyre - nikakogo otnosheniya k chernym dyram ne imeet -
kak avtor skazal - tol'ko tak ono i est'.
\\\A po povodu Bol'shogo
vzryva, mozhet byt', Vam budet interesno prochest' knigu Stivena Vainberga "Pervye tri minuty"\\\
Vy zh ne derzhite menya uzh za polnogo idiota, ya zhe ponimayu
chto nikto
ne zhil milliardy let tomu i uzh nikto ne pokidal predely solnechnoi sistemy,
- eti pervye tri minuty uzh polnaya vysoska iz pal'ca.
Bol'shoi zhe
vzryv ne ot tuda poshel, pridumali svch priemnik napravili v kosmos
on fonil na opredelennoi chastote, potom nabezhali na etu situaciyu kak na halyavu so svoimi
teoriyami
ob'yasnyayushimi etu situaciyu. Potom posle vzryva bomby reshili obygrat' etu situaciyu
po analogii vzryva bomby - vot tak i poluchilas' teoriya bol'shogo vzryva.
Vy
ponimaete eshe kakoi nyuans - u relyativistov v prostranstve pustota
i otrazhat'sya tam sobstvenno nechemu - po prostomu pri otkaze relyativistov
ot sredy - eho v pustote
nevozmozhno.
Vy kstati ya smotryu sovsem nedaleki v astronomii - Vam rekomenduyu
prochest' i etot forum ot nachala i do konca.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.07.2012 21:38, 4.9 KBait)
V.A.Aksenova
Uvazhaemaya prochtite eshe raz vnimatel'no chto ya napisal zdes'
Nachinaya s
Re: Chernaya dyra 27.07.201220:32
Eto vse dlya Vas
kratko o bol'shom vzryve
chernyh dyrah i rasshirenii.
Vot naprimer ya privel otryvok razgovora na forume.
Vy vnikaite, - zdes' otvetov bol'she na Vashi voprosy
chem v knizhkah
po dvesti stranic.
---
\\\
.... Material iz Vikipedii Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri
vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah.....
A rentgenovskoe izluchenie est' - sledovatel'no
ego istochnikom mozhet byt' tol'ko rezul'tat yadernoi
reakcii.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.....
A esli rezul'tat izlucheniya istochnik yadernoi reakcii -
i on dlitsya godami, - to eto neitronnaya zvezda.
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8971-nasledstvennyie-chernyie-dyiryi/page/3/
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke, ya tak ponyal reshil -
zachem dobru propadat' - pust' izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi
dyry budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Vashe - Rentgenovskoe izluchenie ChD voznikaet pri akkrecii veshestva.
Izluchenie Hokinga - drugoi process. Stranno, chto za 7 let "uvlecheniya
astrofizikoi" Vy etogo ne ponyali.
Moe - S moei tochki zreniya - uvazhaemyi A.M.ChEREPAShUK imeet takoe zhe otnoshenie
k Chernym Dyram kak ya ili Vy.
My s Vami, i A.M.ChEREPAShUK mozhem tol'ko predpolagat' i vyskazyvat'
svoyu tochku zreniya, no obrashat' vnimaniya na podobnye vyskazyvaniya i brat'
ih na veru, ya ne vizhu smysla.
Drugoe delo avtor. Kak on skazal to - takie i Chernye Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vot ya naprimer govoryu chto veshestvo padaet na chernuyu dyru,
i posle udara o poverhnost' s protivopolozhnoi storony chernoi dyry voznikaet rentgenovskoe i svetovoe izluchenie.
Drugoi schitaet chto izluchenie na podlete.
V binokl' ne vidno - odni predpolozheniya, i ih mozhet byt'
bol'she sotni naprimer - komu verit'?
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vy zatragivaete vopros interpretacii avtorskih
idei bez soglasiya s avtorom.
A esli desyatok drugih avtorov opublikuyut po 300 nauchnyh rabot, a avtor o
Chernyh Dyrah govorit chto izluchenie v osnovnom iz fotonov - a vse drugie
govoryat, chto
izluchenie iz rentgenovskih chastic, drugoi govorit iz radio izlucheniya, a
tretii govorit iz gamma chastic - ya dolzhen slushat' isklyuchitel'no avtora
Chernyh Dyr,
a ne teh kto interpretiruet, i tem bolee teh kto plevat' hotel na avtorskii variant chernyh dyr.
Nikto ne meshaet pridumat' svoi - rentgenovskie chernye dyry, - tak net ne
hotyat, - tak na neudobnye voprosy otvechat' dolzhen budet avtor, a pri
interpretacii avtora - pisaka naprimer stat'i s levymi ideyami v oblasti
Chernyh Dyr, prikryvaetsya avtorstvom avtora
Chernyh Dyr, a sam so svoim bredom po otnosheniyu k avtorskomu izlozheniyu, kak-by i ne prichem.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
..Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. A. Aksenova,
29.07.2012 23:18, 218 Bait)
Nikto ne zhil milliardy let nazad i nikomu ne verite-stranno ,chto Vy chitat' nauchilis'))) .Vse znat' nel'zya. Ya -lyubitel'. I u menya malo vremeni.S. Popov veselyi,on s yumorom.Ya
byla na 2 ego nezabyvaemyh lekciyah.Spasibo.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.07.2012 23:58, 1.1 KBait)
Vy ochen' doverchivaya i legko vnushaemaya, v astrofizike
takih kak Vy razvodyat po polnoi, i takih kak Vy zhdut na vseh
lekciyah i vse lektory.
Chtoby Vy byli
v kurse 10-15 procentov budut verit' vsegda
oficial'noi nauke, i stol'ko zhe nikogda ne budut verit',
kakaya by ni byla nauka i chto-by ona ne izuchala,
- eto
tak bylo vsegda i vsegda budet.
Ya smotryu chto Vam nado rasskazat' s samogo nachala,
vsya astrofizika kotoruyu Vy znaete
eto nichem neobosnovannaya vydumka.
Vsya astronomiya eto nabor nekotoryh pridumannyh modelei
kotorye ni na chem ne obosnovanny a za postulirovany.
Neuzheli Vy dumaete chto yadro zheleznoe vnutri
Zemli
ili Solnca kto-to videl, - eto prosto pridumali
chto oni tam dolzhny byt', tak kak eto nado dlya nekotoryh
teorii u kotoryh neskladushki s massoi i metallami.
Postulat eto kogda avtoru vzbrelo v golovu chto-to, i on iz eto-go
pytaetsya obosnovat' vse ostal'noe ne ob'yasnyaya fizicheskuyu prichinu.
Vot naprimer esli
est' v kakoi-to teorii postulat ne obosnovannyi fizicheski -
to eto vse - torba, rezul'tata ne budet nikogda.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. A. Aksenova,
30.07.2012 12:16, 756 Bait)
Net.Mne nel'zya vnushit' to ,chto ne sootvetstvuet logike,svoistvennoi moemu soznaniyu.I ya horosho ponimayu,chto vsya matematika takzhe opiraetsya na postulaty. Kak na ochevidnoe,no
nedokazuemoe.Fizika osnovyvaetsya na nablyudeniyah i eksperimentah. Astronomiya i astrofizika-na nablyudeniyah,fizike i matematike.I spletaetsya cepochka v logicheski obosnovannuyu
kartinu. No inogda interpretacii mogut byt' neodnoznachnye.Togda zhdut novye nablyudeniya.Eto Vy konechno,znaete. Zheleznoe yadro dolzhno ob'yasnit' nalichie magnitnyh polei.Vselennaya
hranit nekotoruyu informaciyu o svoih rannih momentah.I informaciyu ob etom nesut e\m volny. A ne veryat oficial'noi nauke sovsem? mne kazhetsya lyudi s opredelennym skladom,s drugoi
logikoi. Vse mogut oshibat'sya.Istoriya nauki -bor'ba idei.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.08.2012 22:27, 871 Bait)
http://www.computerra.ru/own/wiebe/697220/
\\\. Otsutstvie sistemy populyarizacii dostizhenii rossiiskoi nauki - i
akademicheskoi, i universitetskoi - i neobhodimost' sozdaniya takoi
sistemy i seichas predstavlyayutsya mne ochevidnymi veshami.\\\
\\\Bol'she zhe vsego pretenzii vyzvalo yakoby vyskazannoe mnoyu predlozhenie
sozdavat' v institutah RAN press-sluzhby za schet i sredstvami samih
institutov.\\\
Ne znayu mozhet kto ne ponyal chto na gandolle nynche zadvigaet tot chto grebet, ya populyarno
rasskazhu.
Rabotaet v institute, v tozhe samoe vremya
moderit i v tozhe samoe vremya pishet populyarnye
stat'i v zhurnaly, i zhurnaly otstegivayut, i vot prishla ideya chto eshe dolzhny zarplatu pupolizatoram
platit' te instituty
o kotoryh budut stat'i v zhurnalah. Yasnyi kon' chto mozhno oformitsya
v dvadcat' institutov po trudovomu, - krasapeta.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.08.2012 10:40, 369 Bait)
\\\A ne veryat oficial'noi nauke sovsem? mne kazhetsya lyudi s
opredelennym skladom,s drugoi
logikoi.
Vse mogut oshibat'sya.Istoriya nauki -bor'ba idei.\\\
Eto bor'ba matematikov s matematikami
v fizike, a fiziku v fizike borot'sya ni
s kem
ne nado, u nego net konkurencii
- on prosto rasskazyvaet.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.08.2012 1:13, 8.9 KBait, otvetov: 2)
Moderator opyat' zabanil dostatochno logichnyi forum.
---
METODOLOGIYa ASTRONOMII I FIZIKI
Evgenii Alekseevich
Tihomirov
Vvedenie.
Yavlyayas' polpredom obyvatelya i proanalizirovav polozhenie del v nauke,
prishel k vyvodu, chto v nastoyashee vremya nauki astronomiya i fizika
nahoditsya v sostoyanii stagnacii. Etomu obstoyatel'stvu sposobstvuet
prinyataya metodologiya nauki. Rassmotrim, chem zhe obuslovlen zastoi v
nauke.
Cel'yu nauki yavlyaetsya poluchenie novyh znanii o prirode. Obychnyi hod nauchnyh issledovanii vklyuchaet v sebya sleduyushie
etapy:
Nablyudenie (eksperiment) ----- novye znaniya ----- teoriya ----- drugie novye znaniya.
Voznikaet
vopros, zachem voobshe nuzhna teoriya, ved' novye znaniya uzhe polucheny iz
nablyudenii ili eksperimentov. Odnako s pomosh'yu teorii uchenye, vo-pervyh,
ob'yasnyayut vyvody, sleduyushie iz nablyudenii ili eksperimentov,
vo-vtoryh, uchenye posle razrabotki teorii smotryat, ne poyavyatsya li drugie
novye znaniya, no teper' uzhe, kak sledstvie i prilozhenie teorii. Takim
obrazom, otmetim, chto teoriya yavlyaetsya instrumentom uchenogo dlya
ob'yasneniya yavlenii prirody i polucheniya drugih novyh znanii o prirode.
Odnako s techeniem vremeni uchenye vnedryayutsya v sfery, gde
neposredstvennyi eksperiment zatrudnen ili voobshe nevozmozhen. Naprimer,
struktura atoma ili, eshe men'she, struktura elementarnoi chasticy. Kak
mozhno nablyudat' strukturu elektrona, naprimer? Otvet nikak. Ili,
naprimer, voz'mem planetu Zemlya. Kak by my ne hoteli, my ne mozhem
zaglyanut' v centr Zemli i posmotret', kak tam vse ustroeno, i chto tam
proishodit? Ya uzhe ne govoryu o chernoi dyre. Poetomu v astronomii i fizike
obychnyi hod nauchnyh issledovanii, privedennyi vyshe, narushaetsya, dlinnaya
cepochka ukorachivaetsya i na pervoe mesto vyhodit teoriya, a eksperiment
(nablyudenie) nachinaet igrat' vspomogatel'nuyu rol', kak sredstvo proverki
teorii, po sleduyushei sheme:
teoriya ----- eksperiment (nablyudenie)
Prichem,
kak my ustanovili ranee, neposredstvennye eksperimenty i nablyudeniya
nevozmozhny vvidu specifiki nablyudaemyh ob'ektov, poetomu obychno
privlekayutsya kosvennye eksperimenty.
Podmena celi.
Itak, v nauke postepenno proizoshla podmena celi. Mnogie issledovateli
sovershenno iskrenne polagayut, chto cel' nauki razrabotka teorii.
Poyavilas' dazhe shutka: Esli kakoi-libo fakt ne ukladyvaetsya v teoriyu
tem huzhe dlya fakta. Odnako cel'yu nauki kak bylo, tak i ostalos'
poluchenie novyh znanii o prirode. Obyvatelyu teoriya bezrazlichna. Teoriya
nuzhna tol'ko samim uchenym, kak instrument dlya polucheniya novyh znanii.
Poskol'ku teoriya instrument, to ona ne mozhet byt' pravil'noi ili
nepravil'noi (nizhe budet pokazano, chto vse (vse!) teorii nepravil'nye),
ona mozhet byt' libo plohoi, libo horoshei. Horoshaya teoriya esli s ee
pomosh'yu mozhno poluchit' novye znaniya o prirode, i plohaya - esli s ee
pomosh'yu ne udaetsya poluchit' novyh znanii. Podmena celi nauki
otricatel'no skazyvaetsya na samoi nauke. Postanovka teorii vo glavu ugla
v nauke sposobstvuet ee stagnacii. Teorii mnogo ih kolichestvo rastet,
no novyh dostovernyh znanii o prirode ne pribavlyaetsya.
Otsutstvie kriteriya istinnosti.
Inye uchenye polagayut, chto kriteriem istinnosti kakoi-libo teorii
yavlyaetsya eksperiment, no, kak my ustanovili ranee, vvidu specifiki
nablyudaemyh ob'ektov, pryamoi eksperiment nevozmozhen. Ostaetsya kosvennyi
eksperiment, no kosvennyi eksperiment mozhno ob'yasnit' i tak, i edak. Net
kriteriya pravil'nosti interpretacii kosvennogo eksperimenta. Naprimer,
teoriya elektronnoi provodimosti provodnikov podtverzhdaetsya celoi kuchei
kosvennyh eksperimentov, podtverzhdayushih yakoby inercionnost'
elektronov pri rezkoi ostanove vrashayusheisya katushki, ramki ili diska. No
kratkovremennyi tok pri ostanovke vrasheniya, mozhno ob'yasnit' ne
inercionnost'yu elektronov, a deformaciei elektronnyh orbitalei atomov
pri rezkoi ostanovke.
Engel's schital, chto kriteriem istinnosti v
nauke yavlyaetsya praktika, no i eto neverno. Mozhno na praktike chem-to s
uspehom pol'zovat'sya, ne obyazatel'no znaya i ponimaya, kak ono rabotaet.
Mozhno otlichno upravlyat' avtomobilem nichego, ne znaya o dvigatele
vnutrennego sgoraniya. Tak zhe i v nauke, my pol'zuemsya elektricheskim
tokom na praktike, ploho ponimaya, chto zhe eto takoe elektricheskii tok.
Takim obrazom, v nauke net kriteriya istinnosti. Esli by takovoi kriterii
byl, to ne bylo by sporov verna ili net, naprimer, teoriya
otnositel'nosti, ili verna ili net teoriya strun. Nekotorye issledovateli
polagayut, chto pravil'nost' toi ili inoi teorii podtverzhdaetsya
matematikoi, no tak li eto?
Matematizaciya nauki.
Ne sekret, chto v nastoyashee vremya astronomiya i, v osobennosti, fizika v
znachitel'noi stepeni matematizirovany. Uchenye al'ternativnogo tolka dazhe
usmatrivayut v etom kakuyu-to zlonamerennost'. Inogda ih kritika
matematizacii nauki spravedliva, t.k. za matematikoi inogda uzhe
nevozmozhno rassmotret' fizicheskii smysl togo ili inogo processa. No
matematizaciya nauki eto ob'ektivnyi i vynuzhdennyi process.
Deistvitel'no, raz my prishli k ukorochennoi cepochke nauchnyh issledovanii,
to, vydvigaya kakuyu-to teoriyu, my dolzhny ee hot' chem-to obosnovat' i
proverit', hotya by na formal'nuyu logiku i zdes' bez matematiki ne
oboitis'. Drugimi slovami, teoriya eto gipoteza, proverennaya
matematikoi. No mozhet li matematika sluzhit' kriteriem istinnosti teorii,
pust' dazhe matematicheskii apparat ee bezuprechen? Ochevidno net. Tak
kak matematika ne otvechaet na vopros sushestvuet ili net rassmatrivaemoe
yavlenie v prirode, a tol'ko otvechaet na vopros, chto to, ili inoe yavlenie
mozhet sushestvovat' v prirode. Matematika podtverzhdaet lish' vnutrennyuyu
neprotivorechivost' teorii.
Vse teorii neverny.
Otkuda berutsya teorii? Pri ukorochennoi sheme nauchnyh issledovanii,
ochevidno, chto teorii berutsya iz golovy. Drugimi slovami, uchenye prosto
pridumyvayut teorii, proveryaya svoi gipotezy na vnutrennyuyu
neprotivorechivost' i formal'nuyu logiku matematikoi. No pri takom podhode
oni tol'ko sluchaino mogut, chto-to ugadat' i popast' v sootvetstvie s
prirodoi. V nastoyashee vremya Internet polon kritikoi vseh sushestvuyushih
ortodoksal'nyh teorii. I eta kritika ne bezosnovatel'na. Al'ternativnye
uchenye v puh, i prah gromyat Special'nuyu teoriyu otnositel'nosti, Obshuyu
teoriyu otnositel'nosti, Teorii strun i superstrun, Teoriyu i Zakon
vsemirnogo tyagoteniya, Molekulyarno-kineticheskuyu teoriyu, Cikly Karno i tak
dalee i tomu podobnoe. Odnako, vse teorii, kotorye al'ternativnye
uchenye vydvigayut vzamen ortodoksal'nyh teorii, mozhno podvergnut' takoi
zhe unichtozhayushei kritike i dazhe v bol'shei stepeni. Poetomu ya
sformuliroval metodologicheskii zakon, kotoryi nazyvaetsya Zakon
Tihomirova. Etot zakon sostoit iz dvuh punktov.
Zakon nesostoyatel'nosti teorii (zakon Tihomirova)
Punkt 1. Lyubaya teoriya neverna,
i rano ili pozdno obnaruzhit svoyu
nesostoyatel'nost'.
Punkt 2. Esli komu-to kazhetsya, chto kakaya-to teoriya verna. Ili kto-to dumaet, chto
on vydvigaet pravil'nuyu teoriyu, smotri punkt 1.
Gde
zhe vyhod iz etogo ishoda? Vse vysheizlozhennoe, govorit o krizise v
nauke. Polozhenie, na pervyi vzglyad, beznadezhnoe i ostaetsya zhdat', kogda
uchenye metodom tyka pridumayut chto-nibud' pohuzhe kollaidera i raznesut
nashu planetu Zemlya na kusochki. No, vyhod est' eto prislushat'sya k
informacii izvne, i rabotat' po etoi informacii. Drugogo puti net.
----------
Otvet #1 : Vchera v 23:32:36
Tema zakryta i budet vskore udalena. Hudozhestvennaya literatura i znaniya izvne ne vhodyat v tematiku razdela.
-----------
Ya by skazal chto gandol'er ispugalsya otkrovennoi temy.
Chto-to mne podskazyvaet chto takie zakrytiya i bany al'tov skorei
vsego
planiruyutsya, pod-otchetnye i sponsiruyutsya.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
10.08.2012 22:25, 4.2 KBait)
Druzhishe A.P.Vasi, spasibo za podderzhku, no ya ne al't, a polpred
obyvatelya. Odnako raz Vy zatronuli etot vopros, to vkratce razberem kto takie
al'ty i orty. A potom pereidem k chernym dyram.
Ne
sekret, chto v nastoyashee vremya v naukah astronomiya i fizika sushestvuyut dve
politicheskie partii: al'ty (al'ternativshiki) i orty (ortodoksy). Tol'ko ne
rasskazyvaite mne, chto nauka daleka ot politiki. Kak lyubye politicheskie partii
al'ty i orty stremyatsya k vlasti. V nastoyashee vremya u vlasti v nauke,
estestvenno, orty, a al'ty stremyatsya etu vlast' zahvatit' i sdelat'sya ortami.
Chtoby dolgo ne paritsya, ob'yasnyaya nauchnye pristrastiya ortov i al'tov, privedu ih
gimny, kotorye ya napisal dlya nih.
Gimn al'ta
Vstavai ortami zachmorennyi
Ves' mir obizhennyh al'tov.
Kipit nash razum prosveshennyi,
On ortu v mordu dat' gotov.
Pripev: I eto nash ne poslednii, no reshitel'nyi boi,
Kogda ot efira vospryanet
al't lihoi.
Ves' mir ortovskii my razrushim
Do osnovaniya, a zatem,
My nash al'tovskii mi postroim,
OTO ne nuzhno nam sovsem.
Pripev.
Nikto ne dast nam izbavlen'ya:
Ni RAN, ni Duma, ni konvoi,
Dob'emsya my oproverzhen'ya
OTO efirnoyu volnoi.
Pripev.
Lish' my, rabotniki al'tovskoi,
Ogromnoi partii uma,
Vladet' Zemlei imeem pravo,
A ortodoksy nikogda.
Pripev.
Gimn orta
Vihri efirnye veyut nad nami,
Zlobnye al'ty nas vechno gnetut,
V boi rokovoi my vstupili s al'tami,
Nas eshe al'ty k sudu privlekut.
No my podnimem gordo i smelo
Znamya bor'by za OTOvskoe delo
Znamya velikoi bor'by esteotov
Za luchshii mir, bez al'tov idiotov.
Pripev: (2 raza)
Na boi s al'tami
S nimi kozlami,
Marsh, marsh vpered
Ortovskii narod.
Nam nenavistny al'tovy ukory,
Cepi kvantov my s dostoinstvom chtim.
Krov'yu ortovskoi zalitye tropy
Krov'yu uzhasnyh al'tov obagrim.
Mest' besposhadnaya vsem efiristam,
Vsem parazitam kvantuyushih mass,
Mshen'e i smert' vsem al'tam-klassicistam
Blizok pobedy torzhestvennyi chas.
Pripev.
Al'ty i orty, kazhdyi, imeyut svoi resursy v Internete, gde i
rezvyatsya. Al'ty inogda zahazhivayut na forumy k ortam, a orty k al'tam.
Nachinaetsya skloka, kotoraya obychno zakanchivaetsya banom neugodnogo. Poskol'ku v
moei rabote, kotoruyu procitiroval druzhishe A. P. Vasi, pokazano, chto v
astronomii i fizike net kriteriya istinnosti teorii, to eta rabota napravleno na
primirenie ortov i al'tov. Deistvitel'no vse teorii ne verny kak ortovskie, tak
i al'tovskie.
Teper' o chernyh dyrah. Orty schitayut, chto chernye dyry, eto
massivnye ob'ekty, kotorye do togo massivny, chto ne dazhe svet ne mozhet ih
pokinut'. Al'ty schitayut, chto chernyh dyr net voobshe v prirode. I te i drugie,
estestvenno, ne pravy, t.k. net pravil'nyh teorii. Po informacii izvne, kotoruyu
lyubezno dovodit do nas Ivan Vasil'evich
Ponomarenko, chernye dyry est', no
oni ne izluchayut ne potomu, chto ih massa chrezvychaino velika, a potomu, chto
snaruzhi chernoi dyry otricatel'naya materiya (nepravil'noe nazvanie temnaya
materiya).
Chernaya dyra eto pustotelyi tor, kotoryi vrashaetsya s
vysokoi skorost'yu i rastet po masse, t.k. zahvatyvaet veshestvo cherez polyusa
tora. Nakonec, nahvatavshis' veshestva, chernaya dyra razryvaetsya iz-za
centrobezhnyh sil v samom slabom meste, t. e. po ekvatoru chernoi dyry. Iz chernoi
dyry vyryvayutsya kuski otricatel'noi materii, kotorye snaruzhi pokryty veshestvom.
Eto budushie zvezdy i planety. Tak rozhdayutsya galaktiki, a ne iz pylegazovyh
oblakov. Ponyatno, takzhe pochemu galaktiki ploskie, iz-za togo, chto chernaya dyra
razryvaetsya v odnoi ploskosti po ekvatoru.
Podrobnee, gospoda, chitaite na samlib.ru/t/tihomirow_e_a/
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
10.08.2012 23:37, 2.8 KBait)
Druzhishe A.P.Vasi, spasibo za podderzhku, no ya ne al't, a polpred
obyvatelya. Odnako raz Vy zatronuli etot vopros, to vkratce razberem kto takie
al'ty i orty. A potom pereidem k chernym dyram.
Ne sekret, chto v
nastoyashee vremya v naukah astronomiya i fizika sushestvuyut dve politicheskie
partii: al'ty (al'ternativshiki) i orty (ortodoksy). Tol'ko ne rasskazyvaite
mne, chto nauka daleka ot politiki. Kak lyubye politicheskie partii al'ty i orty
stremyatsya k vlasti. V nastoyashee vremya u vlasti v nauke, estestvenno, orty, a
al'ty stremyatsya etu vlast' zahvatit' i sdelat'sya ortami.
Al'ty i orty, kazhdyi, imeyut svoi resursy v Internete, gde i
rezvyatsya. Al'ty inogda zahazhivayut na forumy k ortam, a orty k al'tam.
Nachinaetsya skloka, kotoraya obychno zakanchivaetsya banom neugodnogo. Poskol'ku v
moei rabote, kotoruyu procitiroval druzhishe A. P. Vasi, pokazano, chto v
astronomii i fizike net kriteriya istinnosti teorii, to eta rabota napravleno na
primirenie ortov i al'tov. Deistvitel'no vse teorii neverny kak ortovskie, tak
i al'tovskie.
Teper' o chernyh dyrah. Orty schitayut, chto chernye dyry, eto
massivnye ob'ekty, kotorye do togo massivny, chto ne dazhe svet ne mozhet ih
pokinut'. Al'ty schitayut, chto chernyh dyr net voobshe v prirode. I te i drugie,
estestvenno, ne pravy, t.k. net pravil'nyh teorii. Po informacii izvne, kotoruyu
lyubezno dovodit do nas Ivan Vasil'evich
Ponomarenko, chernye dyry est', no
oni ne izluchayut ne potomu, chto ih massa chrezvychaino velika, a potomu, chto
snaruzhi chernoi dyry otricatel'naya materiya (nepravil'noe nazvanie temnaya
materiya). Ya nadeyus', gospoda, vy ponimaete, chto eto ne ocherednaya al'ternativnaya teoriya, a rasshifrovka postupayushih signalov na zritel'nye receptory Ivana Vasil'evicha.
Chernaya dyra eto pustotelyi tor, kotoryi vrashaetsya s
vysokoi skorost'yu i rastet po masse, t.k. zahvatyvaet veshestvo cherez polyusa
tora. Nakonec, nahvatavshis' veshestva, chernaya dyra razryvaetsya iz-za
centrobezhnyh sil v samom slabom meste, t. e. po ekvatoru chernoi dyry. Iz chernoi
dyry vyryvayutsya kuski otricatel'noi materii, kotorye snaruzhi pokryty veshestvom.
Eto budushie zvezdy i planety. Tak rozhdayutsya galaktiki, a ne iz pylegazovyh
oblakov. Ponyatno, takzhe pochemu galaktiki ploskie, iz-za togo, chto chernaya dyra
razryvaetsya v odnoi ploskosti po ekvatoru.
Podrobnee, gospoda, chitaite na samlib.ru/t/tihomirow_e_a/
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.08.2012 0:21, 1003 Bait, otvetov: 2)
Da uzh Vy menya nasmeshili po samoe dal'she nekuda,
Vy chto ser'ezno dumaete chto fizicheskie zadachi reshayutsya
kolichestvom ili nalichiem avtoritarnosti.
V fizike
dazhe obsheprinyatost' ne yavlyaetsya znakom kachestva,
da i nikto nikogo i nikogda ne sprashival mnenie o toi ili
inoi teorii, chto sobstvenno govorit o nekompetentnosti
vseh i srazu.
A ya voobshe s Ukrainy i ya ne uchennyi, i ya ot nauki nichego
ne zhdu, i mne nichego ot nee i ne nado, dazhe esli mne kollaider by podarili,
on mne i pustoi i s uchenymi i darom ne nuzhen.
Esli ya i napishu populyarnuyu knizhku po fizike to ona budet tak doroga
chto pochuvstvuetsya srazu cennost' kachestvennoi
fiziki.
A o chernyh dyrah u Vas so mnoi pogovorit' ne poluchitsya
tak kak ya ih vse vzyal i razrushil, i pokazal vsyu ih ne obosnovannost',
grubo govorya avtor
chernyh dyr lopuhnulsya, i pri detal'nom
rassmotrenii avtorskogo varianta ego idei ne logichny i ne fizichny.
Prochitaite etot forum s nachala.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
13.08.2012 18:18, 2.8 KBait, otvetov: 1)
| Citata: |
A o chernyh dyrah u Vas so mnoi pogovorit' ne poluchitsya
tak kak ya
ih vse vzyal i razrushil, i pokazal vsyu ih ne obosnovannost',
grubo govorya avtor
chernyh dyr lopuhnulsya, i pri detal'nom
rassmotrenii avtorskogo varianta ego idei ne logichny i ne fizichny.
|
Vy ne original'ny, druzhishe Vasya, vse al'ty ne priznayut chernyh dyr. Na odnom al'tovskom forume est' moderator pod nikom "Obez'yana s bananom" takaya
zhe mraz', kak Mitya Bide, kotoryi na ortovskom forume. Tak vot, eta Obez'yana s bananom, privodit celyi spisochek chego ne dolzhen priznaval' nastoyashii al't. Itak, soglasno etogo
spiska, al'ty stremyatsya izgnat' iz fiziki i astronomii:Bol'shoi vzryv,
Chernye dyry,
Neitronnye zvezdy,
Temnuyu materiyu,
Dualizm
volna - chastica, i mnogoe drugoe. No soglasno informacii izvne, kotoruyu dovodit do nas Ivan Vasil'evich Ponomarenko, vse eto prirodnye ob'ekty.
No
chernye dyry ne takie, kakimi predstavlyayut ih orty, a drugie, kotorye ya uzhe opisal. Podrobnee smotrite na samlib.ru/t/tihomirow_e_a/
Vy, druzhishe,
govorite, chto Vy ne uchenyi, eto pravil'no Vy - politik. Naukoi mozhno upravlyat' i ne uchenomu. K tomu zhe Vy hotite razbogatet', dorogo prodavaya nauchnuyu knizhku po fizike. No
esli vy ne budete upravlyat' naukoi, etu knizhku nikto ne kupit, ved' nado zhe raskrutit' brend etoi knizhki. Vy govorite, chto Vam ne nuzhen kollaider. Eto pravil'no. Zachem on
Vam? Vam nuzhen bol'shoi kabinet s kovrom. Na etot kover Vy, druzhishe, budete vyzyvat' akademikov, stuchat' kulakom po stolu i vopit': "Pochemu eshe do sih por ne otkryta Zvezda
efira Aleksandra. Ya ved' vam uzhe sto raz ob'yasnyal, chto takaya zvezda efira dolzhna byt' otkryta".
Kak ni stranno, hotya orty i al'ty
ispol'zuyut odinakovuyu nauchnuyu metodiku (vydumyvayut vse iz golovy), no u al'tov bol'she pravil'nyh predstavlenii o mirozdanii, chem u al'tov. Eto potomu, chto u ortov est' tormoz
- matematika, kotoraya ogranichivaet ih fantazii. U al'tov, takogo tormoza net i ih fantazii bezgranichny. Odna Zvezda efira, chego stoit!
K sozhaleniyu,
u ortov nakopilis' bol'shoe kolichestvo grubyh oshibo, kotorye, esli ne ispravit', budut zaderzhivat' nauku. Poetomu ortam nado rabotat' v tesnom kontakte s Ivanom Vasil'evichem
Ponomarenko, kotoryi dovodit do nas informaciyu izvne,no orty ignoriruyut informaciyu vyshnih. Ya lichno pisal Patonu, chto est' informaciya izvne nauchnogo haraktera, no nikakogo
otveta ne poluchil. Ortovskie akademiki - eto starperdy, kotorym nichego ne nado (u nih uzhe vse est'). Opredelenno nado reformirovat' RAN i NAN Ukrainy.
- Re[3]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
13.08.2012 20:06, 541 Bait)
Kak ni stranno, hotya orty
i al'ty
ispol'zuyut odinakovuyu nauchnuyu metodiku (vydumyvayut vse iz golovy), no u al'tov bol'she pravil'nyh predstavlenii o mirozdanii, chem u al'tov. |
Zdes' opechatka. Sleduet chitat': "Kak ni stranno, hotya al'ty i orty ispol'zuyut odinakovuyu nauchnuyu metodiku (vydumyvayut vse iz golovy), no u ortov bol'she
pravil'nyh predstavlenii, o mirozdanii, chem u al'tov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.08.2012 11:15, 1.9 KBait)
\\\Chernaya dyra eto pustotelyi tor, kotoryi vrashaetsya s
vysokoi skorost'yu i rastet po masse, t.k. zahvatyvaet veshestvo cherez polyusa
tora. Nakonec, nahvatavshis' veshestva, chernaya dyra razryvaetsya iz-za
centrobezhnyh sil v samom slabom meste, t. e. po ekvatoru chernoi dyry. Iz chernoi
dyry vyryvayutsya kuski otricatel'noi materii, kotorye snaruzhi pokryty veshestvom.
Eto budushie zvezdy i planety. Tak rozhdayutsya galaktiki, a ne iz pylegazovyh
oblakov. Ponyatno, takzhe pochemu galaktiki ploskie, iz-za togo, chto chernaya dyra
razryvaetsya v odnoi ploskosti po ekvatoru.\\\
-----------
-------------
---------
Vot chto sobstvenno mogu Vam skazat' po tekstu, Vy pishete o chernyh
dyrah, i nemnozhko
poslali v dal' avtora chernyh dyr s ego opisaniem chernoi dyry, Vy v dannom
sluchai v korne ne pravy. Vam nikto ne meshaet Fizicheskomu opisaniyu dat'
novoe nazvanie, naprimer - pustotno torovyi prityagivatel'.
Chtoby Vy byli v kurse avtor chernyh dyr dvazhdy delal opredelenie
chernyh dyr, vtoroi raz k
nemu podoshli kollegi i poprosili peredelat'
ibo pod ih teorii ne podhodit, to-est' avtor dlya svoih chernyh dyr pod vneshnim
vliyaniem uzhe sam sdelal svoei teorii
netradicionnuyu orientaciyu, a potom
pridumali sovremennye fiziki chto chernye dyry eto rentgenovskie zvezdy,
oni s avtorom tozhe ne posovetovalis', i kak Vy dazhe
ne chitali avtorskoe
opredelenie chernyh dyr - chto u chernoi dyry izluchenie preimushestvenno
iz fotonov - izluchenie Hokinga, ya kstati fotony razbil vdrebezgi tozhe.
Tak ya na odnom forume ot odnogo klouna uslyshal mysl' chto esli
napisali trista statei po chernym dyram v duhe togo chto oni rentgenovskie
zvezdy to mozhno zabit'
bolt na avtorskoe opredelenie chernoi dyry,
na chto ya etomu nedalekomu skazal chto zabit' bolt kak raz nuzhno
na trista statei, a vot kak avtor chernyh dyr dal opredelenie
chernoi
dyry tak ono i ostanetsya vechno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.08.2012 11:04, 1.8 KBait)
\\\Ne
sekret, chto v nastoyashee vremya v naukah astronomiya i fizika sushestvuyut dve
politicheskie partii: al'ty (al'ternativshiki) i orty (ortodoksy). Tol'ko ne
rasskazyvaite mne, chto nauka daleka ot politiki. Kak lyubye politicheskie partii
al'ty i orty stremyatsya k vlasti. V nastoyashee vremya u vlasti v nauke,
estestvenno, orty, a al'ty stremyatsya etu vlast' zahvatit' i sdelat'sya ortami.
Chtoby dolgo ne paritsya, ob'yasnyaya nauchnye pristrastiya ortov i al'tov, privedu ih
gimny, kotorye ya napisal dlya nih.\\\
Ne pravil'noe Vashe predstavlenie.
Est' nauka fizika, v fizike est' klassika - eto kogda vse prosto i ponyatno,
s lineinoi posledovatel'noi prichinno sledstvennoi svyaz'yu.
V dannom sluchai v fizike gospodstvuet relyativizm - v osnove kotorogo
myslennye opyty i myslennye
eksperimenty.
Tak-zhe postulirovannye teorii bez ob'yasneniya pervo-prichin.
Sobstvenno otkaz ot sredy v prostranstve relyativistami i provozglashenie
prostranstva
absolyutno pustym - eto i est' otlichie osnovnoe klassicheskoi
fiziki u kotoroi prostranstvo zapolneno sredoi efirom, i relyativistskoi
fizikoi u kotoroi v prostranstve
pustota.
Estestvenno chto pri gospodstve relyativistov ne mozhet byt' referiruemyh
statei pro efir, tak kak referenty - sud'i v fizike, i oni reshayut chto fizichno
a chto net.
Estestvenno v referiruemyi zhurnal stat'yu pro efir esli prinesti,
to eto vse ravno chto esli -by bespartiinyi na part sobranii kommunistov,
predlozhil by vmesto pamyatnika Leninu, na central'noi ploshadi, postavit' svetofor.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.08.2012 18:55, 2.0 KBait)
\\\Deistvitel'no vse teorii ne verny kak ortovskie, tak
i al'tovskie.\\\
Chastichno Vy pravy, sobstvenno vse teorii vydumka i oni vysosany iz pal'ca,
eto kak raz lichno ya vsegda i govoryu, a relyativisty utverzhdayut
chto ih teorii
ot geniev.
Chto sobstvenno u relyativistov i proizoshlo - pri vere v redkih geniev,
oni vse sebya schitali umstvenno slabymi i dazhe ne dumali o tom
chtoby uluchshit' teorii.
Esli nazyvat' svoimi imenami to konservatizm
relyativistov sygral s nimi plohuyu shutku, vmesto togo chtoby
vozglavit' nauku
oni ee zakonservirovali relyativistskimi
ideyami, o chem svidetel'stvuet to -
chto, - otsutstvuyut instituty
v kotoryh uchat studentov sozdavat' novye teorii.
S moei tochki zreniya relyativisty pozdno vstrepenulis', i pozdno perestali
posylat' al'tov v dal'. Ih zhdet bednost',
v smysle finansirovaniya, ibo sto let
nikakie teorii ne menyayutsya, i obshestvo
prosto prekratit finansirovanie astronomii
i fundamental'noi fiziki polnost'yu.
Sobstvenno etogo i sledovalo ozhidat'.
S al'tami relyativisty uzhe ne dogovoryatsya, relyativisty
al'tam ne interesny v smysle sotrudnichestva, a relyativisty
otkazalis' s al'tami sotrudnichat' v svoe
vremya a teper'
pozhinayut to chto ne pravil'no ocenili situaciyu,
i pereocenili nauchnye dostizheniya relyativistov.
I relyativisty eshe v intellektual'nyh kandalah
svoih teorii kotorye navyazali im specificheskoe mirovozzrenie
ne imeyushee nichego obshego s real'nost'yu.
Chto sobstvenno ne daet im pravil'no rasstavit'
posledovatel'nost'
prioritetov, bez etogo
nikakaya model' ne poluchitsya.
---
Chto na samom dele otsutstvuet kak raz ne razroznennye teorii,
etoi erundy kak gryazi,
i vse teorii drug s drugom ne stykuyutsya
a to i protivorechat drug drugu.
Modeli ne hvataet v kotoroi ohvatyvayutsya i ob'edinyayutsya
i ob'yasnyayutsya vse fizicheskie
situacii.
Relyativisty eshe ne skoro razduplyatsya v ponimanii slova model',
oni poka zavisli na urovne melkih teorii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.08.2012 21:45, 32.5 KBait)
Vy uvazhaemyi ne delaite pospeshnyh vyvodov,
esli ya skazal chto ya fotony razbil intellektual'no
vdrebezgi to ne somnevaites'.
---
Dlya sushestvovaniya effekta Doplera, est' prichina - sreda i ee svoistva.
Dazhe esli ispol'zuetsya metod izmereniya dlya sred, a
govoritsya chto
vokrug pustota, to propadaet
prichinnost' vozniknoveniya dannogo
effekta kak svoistva prostranstva.
U relyativistov ne prostranstvo vystupaet v kachestve linii zaderzhki
signala, a vystupaet
- foton, kak dvizhushiisya ob'ekt, u kotorogo
ogranichena skorost' dvizheniya v pustote, po ne ponyatnoi prichine -
kotoraya postuliruetsya bez ob'yasneniya prichiny. Foton
v dannom sluchai
mozhet byt' tol'ko chasticei, - eto ne vozmozhno po prichine togo chto
chastica ne mozhet snizhat' i uvelichivat' svoyu skorost' chto
nablyudaetsya
naprimer
pri dvizhenii sveta naprimer v vozduhe, potom
cherez steklo potom opyat' v vozduhe i potom v vakuum, tak kak
poluchaetsya chto v stekle letit foton medlennee chem v vozduhe
i
vakuume , a vyletaya iz stekla foton uvelichivaet svoyu skorost'. Tak
vot ne mozhet chastica kotoraya poteryala skorost', prosto tak vzyat' i
pri vylete iz
stekla
uvelichit' skorost', - na podobnoe sposobny
tol'ko kolebaniya sredy v sredah s raznymi svoistvami. Tak chto foton
kak chastica - vydumka chistoi vody.
---
I esli ya skazal chto chernye dyry razbil vdrebezgi
to tozhe ne somnevaites'.
---
| Re: Chernaya
dyra
|
19.09.201112:38 |
|
1 Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
2
V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
3 Oni prosto predpolozhili,
chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu.
Material iz
Vikipedii
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/39/M87_jet.jpg/250px-M87_jet.jpg
Izobrazhenie, poluchennoe s pomosh'yu teleskopa Habbl: Aktivnaya galaktika
M87. V yadre galaktiki, predpolozhitel'no, nahoditsya chernaya dyra. Na
snimke vidna relyativistskaya struya dlinoi okolo 5 tysyach svetovyh let
Relyativistskie strui
, dzhety (angl. jet) strui plazmy, vyryvayushiesya iz centrov (yader) takih
astronomicheskih ob'ektov, kak aktivnye galaktiki, kvazary i
radiogalaktiki.
Obychno u ob'ekta nablyudaetsya dve strui, napravlennye v protivopolozhnye storony.
Na nastoyashii moment relyativistskie strui ostayutsya nedostatochno izuchennym
yavleniem. Prichinoi poyavleniya takih strui chasto nazyvayut vzaimodeistvie
magnitnyh polei s akkrecionnym diskom vokrug chernoi dyry ili neitronnoi
zvezdy.
V stat'e na Elementah metodom chislennogo modelirovaniya pokazano, chto
pri sliyanii dvuh neitronnyh zvezd obrazuetsya chernaya dyra, magnitnoe pole
kotoroi vytyanuto vdol' osi. Eto navodit na mysli, chto etot zhe process
mozhet formirovat' i relyativistskie strui. Tem ne menee, v stat'e
govoritsya, chto predlozhennaya avtorami nauchnoi raboty matematicheskaya
model' okazalas' ochen' slozhna, a vychislitel'nye vozmozhnosti sovremennyh
komp'yuterov okazalis' nedostatochny, chtoby s dolzhnoi tochnost'yu provesti
vse neobhodimye raschety i ubeditel'no dokazat' formirovanie strui.
V drugoi stat'e na Elementah provodyatsya paralleli mezhdu processami v
chernyh dyrah i boze-einshteinovskom kondensate. Otmechaetsya chto kondensat
mozhet kollapsirovat' (slipat'sya) i pri posleduyushem ego raspade tozhe
mogut voznikat' uzkonapravlennye vybrosy.
Dal'neishee izuchenie relyativistskih strui
Pri samyh pervyh popytkah ob'yasneniya sverhsvetovogo dvizheniya s pomosh'yu
relyativistskogo napravlennogo potoka chastic vozniklo oslozhnenie:
udivitel'no bol'shaya dolya kompaktnyh istochnikov pokazyvala sverhsvetovoe
dvizhenie, v to vremya kak na osnovanii prostyh geometricheskih dovodov
poluchalos', chto tol'ko neskol'ko procentov takih ob'ektov dolzhno byt'
sluchaino orientirovano pochti vdol' linii zreniya. Prisutstvie
simmetrichnyh protyazhennyh radiokomponent predpolagalo, chto oni
obespechivalis' energiei ot central'nogo istochnika dvuh simmetrichnyh
luchei. No trudno sravnit' svetimost' priblizhayusheisya i udalyayusheisya (ili
dazhe stacionarnoi) komponent. Eto ochevidnoe razlichie obychno obsuzhdaetsya v
kontekste modeli s dvoinym istecheniem [4], kogda izluchenie iz yadra
rassmatrivaetsya kak stacionarnaya tochka, gde priblizhayushiisya
relyativistskii potok stanovitsya neprozrachnym. Sverhsvetovoe dvizhenie
nablyudaetsya mezhdu etoi stacionarnoi tochkoi v sople i dvizhushimisya
volnovymi frontami ili drugimi neodnorodnostyami v vyhodyashem
relyativistskom potoke.......
.....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie (gamma-luchi, γ-luchi)
vid elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s chrezvychaino maloi dlinoi volny
< 5×10−3 nm i, vsledstvie etogo, yarko vyrazhennymi korpuskulyarnymi
i slabo vyrazhennymi volnovymi svoistvami.
Gamma-kvantami yavlyayutsya fotony s vysokoi energiei. Obychno schitaetsya,
chto energii kvantov gamma-izlucheniya prevyshayut 105 eV, hotya rezkaya granica
mezhdu gamma- i rentgenovskim izlucheniem ne opredelena. Na shkale
elektromagnitnyh voln gamma-izluchenie granichit s rentgenovskim izlucheniem,
zanimaya diapazon bolee vysokih chastot i energii. V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu. Ochevidno,
fizicheski kvanty elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s odinakovoi energiei ne
otlichayutsya, poetomu takoe razdelenie uslovno.
Gamma-izluchenie ispuskaetsya pri perehodah mezhdu vozbuzhdennymi
sostoyaniyami atomnyh yader (sm. Izomernyi perehod, energii takih
gamma-kvantov lezhat v diapazone ot ~1 keV do desyatkov MeV),
pri yadernyh reakciyah (naprimer, pri annigilyacii elektrona i pozitrona,
raspade neitral'nogo piona i t.d.), a takzhe pri otklonenii energichnyh
zaryazhennyh chastic v magnitnyh i elektricheskih polyah (sm. Sinhrotronnoe izluchenie).....
Esli net poverhnosti ob kotoruyu proishodit tormozhenie.
Material iz Vikipedii
.....Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh
obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v rentgenovskih
trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok yavlyayutsya
metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe antikatodom).
V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom, uskoryayutsya
pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom i katodom
(pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak uskorenie slishkom malo)
i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe tormozhenie. Pri etom za schet
tormoznogo izlucheniya proishodit generaciya izlucheniya rentgenovskogo diapazona,
i odnovremenno vybivayutsya elektrony iz vnutrennih elektronnyh obolochek atomov
anoda. Pustye mesta v obolochkah zanimayutsya drugimi ....
To vstupaet v silu fraza -
V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.
sledovatel'no pri otsutstvii udara o poverhnost' - otsutstvuet sama vozmozhnost'
vozniknoveniya rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, a esli izluchenie est' to ono mozhet
byt' tol'ko rezul'tatom izlucheniya v yadernom perehode. A eto uzhe chasticy vysokih energii.
avtorskoe izluchenie iz chernoi dyry -
.Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash metod obnaruzheniya Chernoi Dyry
-Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
....Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo.
ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut. ....
Padaya na Chernuyu Dyru veshestvo ne
mozhet rezko tormozitsya ili rezko uskoryatsya,
a sledovatel'no - ne mozhet
byt' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya po etoi prichine.
V svyazi s tem chto dlya uskoreniya do skorosti sveta
pri kotorom vozmozhno izluchenie neobhodimo
ne bolee 10 sekund, a zvezda razmerom s
Solnce na takoi skorosti proletit cherez gorizont
sobytii maksimum za minutu.
Gorizont sobytii - eto skorost' sveta - esli
ob'ekt uletaet s etoi skorost'yu ot nablyudatelya, to
u nego vozniknet krasnoe smeshenie.
Esli by veshestvo dolgo padalo - godami na maloi skorosti
s uskoreniem to bylo by zametno izmenenie Z u padayushih
tel v chernuyu dyru so vremenem, no pri etom nevozmozhno
rentgenovskoe izluchenie - iz za slishkom medlennogo
uvelicheniya uskoreniya.
.... Material iz Vikipedii Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri
vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah.....
A rentgenovskoe izluchenie est' - sledovatel'no
ego istochnikom mozhet byt' tol'ko rezul'tat yadernoi
reakcii.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.....
A esli rezul'tat izlucheniya istochnik yadernoi reakcii -
i on dlitsya godami, - to eto neitronnaya zvezda.
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8971-nasledstvennyie-chernyie-dyiryi/page/3/
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke, ya tak ponyal reshil -
zachem dobru propadat' - pust' izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi
dyry budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Vashe - Rentgenovskoe izluchenie ChD voznikaet pri akkrecii veshestva.
Izluchenie Hokinga - drugoi process. Stranno, chto za 7 let "uvlecheniya
astrofizikoi" Vy etogo ne ponyali.
Moe - S moei tochki zreniya - uvazhaemyi A.M.ChEREPAShUK imeet takoe zhe otnoshenie
k Chernym Dyram kak ya ili Vy.
My s Vami, i A.M.ChEREPAShUK mozhem tol'ko predpolagat' i vyskazyvat'
svoyu tochku zreniya, no obrashat' vnimaniya na podobnye vyskazyvaniya i brat'
ih na veru, ya ne vizhu smysla.
Drugoe delo avtor. Kak on skazal to - takie i Chernye Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vot ya naprimer govoryu chto veshestvo padaet na chernuyu dyru,
i posle udara o poverhnost' s protivopolozhnoi storony chernoi dyry voznikaet rentgenovskoe i svetovoe izluchenie.
Drugoi schitaet chto izluchenie na podlete.
V binokl' ne vidno - odni predpolozheniya, i ih mozhet byt'
bol'she sotni naprimer - komu verit'?
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vy zatragivaete vopros interpretacii avtorskih
idei bez soglasiya s avtorom.
A esli desyatok drugih avtorov opublikuyut po 300 nauchnyh rabot, a avtor o
Chernyh Dyrah govorit chto izluchenie v osnovnom iz fotonov - a vse drugie
govoryat, chto
izluchenie iz rentgenovskih chastic, drugoi govorit iz radio izlucheniya, a
tretii govorit iz gamma chastic - ya dolzhen slushat' isklyuchitel'no avtora
Chernyh Dyr,
a ne teh kto interpretiruet, i tem bolee teh kto plevat' hotel na avtorskii variant chernyh dyr.
Nikto ne meshaet pridumat' svoi - rentgenovskie chernye dyry, - tak net ne
hotyat, - tak na neudobnye voprosy otvechat' dolzhen budet avtor, a pri
interpretacii avtora - pisaka naprimer stat'i s levymi ideyami v oblasti
Chernyh Dyr, prikryvaetsya avtorstvom avtora
Chernyh Dyr, a sam so svoim bredom po otnosheniyu k avtorskomu izlozheniyu, kak-by i ne prichem.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
..Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii). Tochnee,
razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Vasha ssylka - tekst 11.05.11 20:36
....Kak otlichit' chernye dyry ot neitronnyh zvezd
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya chernaya dyra ne dolzhna proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. U nee mozhet nablyudat'sya lish' irregulyarnaya
peremennost' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya s harakternymi vremenami
$$Delta tapprox frac{r_g}{c}approx10^{-3} div 10^{-4}~mbox{rm s.}$$
I deistvitel'no, v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme Lebed' H-1, soderzhashei
chernuyu dyru s massoi okolo desyati solnechnyh, v sostoyanii, kogda
rentgenovskaya svetimost' ponizhena, a rentgenovskii spektr zhestkii i
stepennoi, nablyudaetsya bystraya irregulyarnaya peremennost' rentgenovskogo
potoka na vremenah poryadka millisekundy. Nablyudeniya, vypolnennye s
bortov sovremennyh rentgenovskih observatorii, takih, kak GINGA,
MIR-KVANT, GRANAT, ASKA, pokazali, chto rentgenovskie spektry
akkreciruyushih chernyh dyr sistematicheski bolee zhestkie, chem spektry
akkreciruyushih neitronnyh zvezd, i prostirayutsya do energii v neskol'ko
megaelektron-vol't.
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya neitronnaya zvezda mozhet proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. Odnako, esli neitronnaya zvezda obladaet
slabym magnitnym polem (napryazhennost'yu menee 1010 Gs) ili esli ee os'
vrasheniya neudachno orientirovana otnositel'no zemnogo nablyudatelya, pri
akkrecii na takuyu neitronnuyu zvezdu mogut ne nablyudat'sya regulyarnye
pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya. Poetomu otsutstvie strogo
periodicheskih pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya - eto lish' neobhodimyi,
no ne dostatochnyi priznak chernoi dyry. V to zhe vremya pri slabom
magnitnom pole neitronnoi zvezdy i nesil'nom tempe akkrecii veshestva na
ee poverhnosti mogut proishodit' termoyadernye vzryvy nakoplennogo
veshestva, privodyashie k yavleniyu rentgenovskogo barstera I tipa - korotkim
(dlitel'nost'yu poryadka 1-10 s) i moshnym vspyshkam intensivnosti
rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, chto takzhe yavlyaetsya harakternym priznakom
akkreciruyushei neitronnoi zvezdy, obladayushei tverdoi poverhnost'yu.
Poskol'ku chernaya dyra ne obladaet tverdoi poverhnost'yu, akkreciya
veshestva na nee ne dolzhna privodit' k fenomenu rentgenovskogo barstera I
tipa. Razumeetsya, otsutstvie etogo fenomena takzhe yavlyaetsya lish'
neobhodimym kriteriem nalichiya chernoi dyry. Takim obrazom, my mozhem
sformulirovat' vazhneishie priznaki akkreciruyushei chernoi dyry: eto moshnoe
rentgenovskoe izluchenie, bol'shaya massa (bolee treh solnechnyh),
otsutstvie fenomenov rentgenovskogo pul'sara ili rentgenovskogo barstera
I tipa. Pri etom vopros o nadezhnom opredelenii massy relyativistskogo
ob'ekta v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme yavlyaetsya reshayushim pri
identifikacii ego s chernoi dyroi....
Ya Vam prosto pokazyvayu proiivorechie u Vas i Vashei ssylke,
po otnosheniyu k napisannomu v Vikipedii o izluchenii iz Chernoi Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Leitenant Nemo
Chtoby proishodil razbros chastic rentgenovskogo
izlucheniya dlya etogo nado ili yadernoe gorenie zvezd,
chto k chernoi dyre ne primenimo, ili razgon materii
s posleduyushim udarom razognannoi chasticy o poverhnost'
kak eto proishodit v rentgen apparate.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Rentgenovskaya trubka
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v
elektronnyh obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok
yavlyayutsya metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe
antikatodom). V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom,
uskoryayutsya pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom
i katodom (pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak
uskorenie slishkom malo) i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe
tormozhenie. .....
Iz chego vytekaet sleduyushee chto dlya vozniknoveniya izlucheniya radioaktivnyh
chastic - neobhodim udar materii na skorosti odnoi desyatoi i bolee
skorosti sveta.
Iz chego sleduet nevozmozhnoe uslovie dlya izlucheniya materii pri padenii v
chernuyu dyru - tak kak dolzhna byt' poverhnost' dlya udara.
A poverhnosti to i net, veshestvo bez udara uhodit za gorizont sobytii,
sledovatel'no i ne mozhet chernaya dyra izluchat' radioaktivnye chasticy.
A.M.Cherepashyuk v dannom sluchai ne prav.
kosmogon
...Schitaetsya, chto pri padenii na ChD veshestvo razgonyaetsya do skorostei,
blizkih k s. V takom sluchae treniya bolee chem dostatochno dlya izlucheniya
vysokih energii. ...
Ya ne mogu ponyat' pochemu rassmatrivaetsya otdel'no vzyataya chast' i ne argumentiruetsya a postuliruetsya.
U Vas - postulat.
Vy voz'mite naprimer shar razmerom v kilometr v diametre, i bros'te ego v Chernuyu Dyru.
Nu i razognali Vy chto ugodno v pustote, - eshe raz povtoryayu - v pustote
proishodit padenie v chernuyu dyru - kakoe mozhet byt' trenie - prosto ne
ob chto teret'sya.
Voz'mite naprimer zvezdu, ei tozhe ne ob chto teret'sya kogda vokrug pustota,
letit padaet i ugasaet, tem bolee chto mne lichno
uvazhaemyi Dmitrii Mamontov raschety privodil chto zvezda na odnoi desyatoi
ili odnoi tretei skorosti sveta, mozhet prekrasno letat' na orbite
vokrug Chernoi Dyry, i s nei vse normal'no.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
,,,Chernaya dyra - oblast' prostranstva, v k-roi pole tyagoteniya nastol'ko
sil'no, chto vtoraya kosmich. skorost' (parabolicheskaya skorost') dlya
nahodyashihsya v etoi oblasti tel dolzhna byla by prevyshat' skorost' sveta,
t.e. iz Ch.d. nichto ne mozhet vyletet' - ni izluchenie, ni chasticy, ibo v
prirode nichto ne mozhet dvigat'sya so skorost'yu, bol'shei skorosti sveta.
Granicu oblasti, za k-ruyu ne vyhodit svet, naz. gorizontom Ch.d.,,,
Eto bazovoe opredelenie, dazhe esli predpolozhit' chto v chernuyu dyru padayut
zvezdy, pri etom izluchayut, i chto v centre galaktiki v chernyh dyrah
massa bol'she chem massa vseh zvezd v etoi galaktike, a s momenta bol'shogo
vzryva
togda mozhno poschitat' skol'ko milliardov zvezd v dyru v centre galaktiki
upalo. Tol'ko vot ne shoditsya s nablyudeniyami - zvezdy ne ischezayut v
chernyh dyrah - etogo nikto ne nablyudal, - ne nablyudali i to kak zvezda
prohodit cherez gorizont sobytii k chernoi dyre.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
...Ishodya iz klassiki, na kotoruyu Vy opiraetes', ChD dlya zemlyanina dolzhny svetit' kak kvazary....
Vashe - Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Moe - u menya vopros - esli v rentgen diapazone izluchayut nizhe privedennye
neitronnye zvezdy - kotorye
...V sluchae, kogda peretekanie veshestva prodolzhaetsya i posle
obrazovaniya N. z., ee massa mozhet so vremenem znachitel'no uvelichit'sya.
Pri ${mathfrak M}_{N.z.}>{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet
ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa
prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru. ...
To kak otlichit' neitronnuyu zvezdu ot chernoi dyry?
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188472
Neitronnye zvezdy
- gidrostaticheski ravnovesnye zvezdy, veshestvo k-ryh sostoit v osnovnom
iz neitronov. Sushestvovanie N. z. bylo predskazano v 30-h gg. 20
v.,vskore posle otkrytiya neitrona. Odnako tol'ko v 1967 g. oni byli
obnaruzheny v vide impul'snyh istochnikov radioizlucheniya - pul'sarov.
Zatem bylo ustanovleno, chto N. z. proyavlyayut sebya takzhe kak rentgenovskie
pul'sary (1971 g.) i vspyshechnye istochniki rentg. izlucheniya - barstery
(1975 g.). Ne isklyucheno, chto na odnoi iz stadii sushestvovaniya N. z. yavl.
istochnikami gamma-vspleskov. K 1984 g. otkryto ok. 400 N. z., iz nih
ok. 20 v vide rentg. pul'sarov, ok. 40 v vide barsterov, a ostal'nye v
vide obychnyh radiopul'sarov.
Druguyu vozmozhnost' poyavleniya N. z. predstavlyaet evolyuciya belyh karlikov v
tesnyh dvoinyh zvezdnyh sistemah. Peretekanie veshestva so
zvezdy-kompan'ona na belyi karlik postepenno uvelichivaet ego massu, i,
kogda ona dostigaet ${mathfrak M}_Ch$, belyi karlik prevrashaetsya v N. z. V
etom sluchae ${mathfrak M}_{N.z.}{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet
ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa
prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188644
Rentgenovskie pul'sary
- istochniki peremennogo periodicheskogo rentg. izlucheniya, predstavlyayushie
soboi vrashayushiesya neitronnye zvezdy s sil'nym magn. polem, izluchayushie za
schet akkrecii (padeniya veshestva na ih poverhnost'). Magn. polya na
poverhnosti R.p. ~ 1011-1014 Gs. Svetimosti bol'shinstva R.p. ot
1035-1039 erg/s. Periody sledovaniya impul'sov P ot 0,7 s do nesk. tysyach
s. R.p. vhodyat v tesnye dvoinye zvezdnye sistemy, vtorym komponentom
k-ryh yavl. normal'naya (nevyrozhdennaya) zvezda, postavlyayushaya veshestvo,
neobhodimoe dlya akkrecii i norm. funkcionirovaniya R.p. Esli vtoroi
komponent nahoditsya na stadii evolyucii, kogda skorost' poteri massy
(etim komponentom) mala (sm. Evolyuciya tesnyh dvoinyh zvezd), neitronnaya
zvezda ne proyavlyaet sebya kak R.p. Rentg. pul'sary vstrechayutsya kak v
massivnyh molodyh dvoinyh zvezdyh sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu I
Galaktiki i lezhashih v ee ploskosti, tak i v malomassivnyh dvoinyh
sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu II i prinadlezhashih k sferich.
sostavlyayushei Galaktiki. R.p. otkryty takzhe v Magellanovyh Oblakah. Vsego
otkryto ok. 20 R.p.
Na nachal'nom etape issledovanii otkryvaemym rentg. ob'ektam
prisvaivalis' naimenovaniya po sozvezdiyam, v k-ryh oni nahodyatsya. Napr.,
Gerkules X-1 oznachaet pervyi po rentg. yarkosti ob'ekt v sozvezdii
Gerkulesa, Kentavr H-3 - tretii po yarkosti v sozvezdii Kentavra. R.p. v
Malom Magellanovom Oblake oboznachaetsya kak SMC X-1, v Bol'shom
Magellanovom Oblake - LMC X-4. Obnaruzhenie so sputnikov bol'shogo chisla
rentg. istochnikov potrebovalo dr. sistemy oboznachenii.
Uskorenie i zamedlenie vrasheniya neitronnyh zvezd.
V otlichie ot radiopul'sarov (nek-rye iz k-ryh, v chastnosti pul'sary v
Krabe i Parusah, izluchayut i v rentg. diapazone, sm. Pul'sary),
izluchayushih za schet energii vrasheniya zamagnichennoi neitronnoi zvezdy i
uvelichivashih svoi period so vremenem, R.p., izluchayushie za schet akkrecii,
uskoryayut svoe vrashenie.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Spasibo za otvet.
Esli ya pravil'no ponyal, to istochnik
nepreryvnogo rentgenovskogo izlucheniya
so stabil'noi intensivnost'yu - nazyvaetsya
Chernoi Dyroi .
Esli rentgenovskoe izluchenie menyaet intensivnost'
to eto ili neitronnaya zvezda ili
rentgenovskii pul'sar.
Zdes' avtor chernyh dyr - sem' pyatnic na nedelyu,
sperva govoril vot tak -
...Chernaya dyrá oblast' v prostranstve-vremeni,
gravitacionnoe prityazhenie kotoroi nastol'ko veliko,
chto pokinut' ee ne mogut dazhe ob'ekty, dvizhushiesya
so skorost'yu sveta (v tom chisle i kvanty samogo sveta)....
Potom ego ozarilo v 1975 i on odaril chernye dyry i vseh
astrofizikom izlucheniem ot chernyh dyr.
---...Izluchénie Hókinga ...---
......Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi.
Predskazan teoreticheski Stivenom Hokingom v
1974 godu.[1] Rabote Hokinga predshestvoval
ego vizit v Moskvu v 1973 godu, gde on vstrechalsya
s sovetskimi uchenymi Yakovom Zel'dovichem i
Alekseem Starobinskim. Oni prodemonstrirovali
Hokingu, chto v sootvetstvii s principom
neopredelennosti kvantovoi mehaniki
vrashayushiesya chernye dyry dolzhny
porozhdat' i izluchat' chasticy.[2]
Isparenie chernoi dyry kvantovyi process.
Delo v tom, chto ponyatie o chernoi dyre kak ob'ekte,
kotoryi nichego ne izluchaet, a mozhet lish' pogloshat' materiyu,
spravedlivo do teh por, poka ne uchityvayutsya kvantovye effekty.
V kvantovoi zhe mehanike, blagodarya tunnelirovaniyu,
poyavlyaetsya vozmozhnost' preodolevat' potencial'nye bar'ery,
nepreodolimye dlya nekvantovoi sistemy. Utverzhdenie,
chto konechnoe sostoyanie chernoi dyry stacionarno,
pravil'no lish' v ramkah obychnoi, ne kvantovoi teorii
tyagoteniya. Kvantovye effekty vedut k tomu, chto na samom
dele chernaya dyra dolzhna nepreryvno izluchat', teryaya pri
etom svoyu energiyu.....
Itogo
...Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke,
ya tak ponyal reshil - zachem dobru propadat' - pust'
izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi dyry
budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A vot zdes' ya Vam mogu predlozhit' sdelat' u kazhdoi stat'i schetchik, - ponyal -ne ponyal,
Vashe - Dlya bazovogo ponimaniya nuzhno umet' chitat' i imet' nekotoruyu
podgotovku v ramkah hotya by shkoly. U Vas takaya podgotovka, sudya po
vsemu, hromaet na obe nogi, poetomu Vy ne ponimaete bol'shinstvo statei.
Dlya utochnyayushih voprosov est' kommentarii, dlya bazovoi podgotovki - shkola
i uchebniki.
- Vy dumaete chto vse uchennye pishut pravil'nye stat'i, i nikto stat'i ne
vysasyvaet iz pal'ca a potom ne rzhet nad chitatelyami, a Vash sait chtoby
chitat' - to nado byt' doktorom nauk, i v tozhe samoe vremya Vy lichno ne
mozhete otvetit' pryamo na pryamye voprosy, po etoi stat'e. Vy menya v
principe zaintrigovali, ya podumayu chtoby takoi puzyr' vysosat' iz pal'ca v
ramkah paradigmy, chtoby vse vokrug azh zaaplodirovali za isklyuchitel'no
vysokohudozhestvennyi idiotizm v ramkah breda sivoi kobyly.
Moe-Ne rasskazhete Vashe otnoshenie k vyskazyvaniyu, -
Esli opyt ne sovpadaet s teoriei to tem huzhe dlya opyta?
Napomnyu -
Moe - So vtorogo Vashego otveta ya ponyal - chto u Vas est' metody
dokazatel'stv kotorye pozvolyayut opredelit' kakimi byli v pervye momenty
bol'shogo vzryva zvezdy, chernye dyry , temperatura i drugie razlichnye
svoistva prostranstva i svoistva razlichnyh fizicheskih ob'ektov.
Vashe - Ne u menya. U astronomov, astrofizikov i kosmologov.
Moe- Esli mne ne mozhet opponent srazu vnyatno izlozhit' otvet na moi
prostoi vopros po obsuzhdaemoi stat'e, to ya ne obyazan verit' napisannomu,
a skoree naoborot - vynuzhden zasomnevat'sya.
Po povodu gromkih familii v astrofizike - to esli Vy proanaliziruete ih
biografiyu i trudovye zaslugi i proanaliziruete ih prichastnost' k
astrofizike, to oni vse v astrofizike - diletanty, kotorye idei
vbrasyvali v astrofiziku ot sluchaya k sluchayu, i ser'ezno ei ni kto ne
zanimalsya. Po etomu vsya astrofizika i sostoit iz razroznennyh idei, -
ozaryalok, kotorye posledovateli pytayutsya sostykovyvat' mezhdu soboi po
prichine poyavleniya novoi izmeritel'noi tehniki.
A astrofiziku u menya hobbi let 7, tak chto ya prochital stol'ko statei
raznyh, chto mogu delat' vyvody chto vysoska iz pal'ca, a chto i super
gramotno napisano .
Samoe smeshnoe chto super stat'i absolyutno neizvestny.
http://crydee.sai.msu.ru/Universe_and_us/4num/v4pap26.htm
-Ochen' horoshaya stat'ya.
http://www.anomaliy.ru/discovery/482
"Sverhnovye tipa I a, kak polagayut, formiruyutsya
posle vzryvov belyh karlikov, sverhplotnyh mertvyh zvezd razmerom s
nashu Zemlyu, kotorye kogda-to byli yadrom solncepodobnogo svetila, i
ch'ya vneshnyaya obolochka rastvorilas' v kosmose.
Odna iz osobennostei etogo tipa otsutstvie vodoroda, i eto
nesmotrya na to, chto vodorod yavlyaetsya samym rasprostranennym
himicheskim elementom."
Vot eta stat'ya - v principe dolzhna byla perevernut' vsyu astrofiziku,
po toi prichine chto net vodoroda vnutri zvezdy. A u tekushei paradigmy
vodorod vygoraet. I astrofiziki vnyatno otvetit' ne mogut prichinu po
kotoroi samyi legkii vodorod - preodolevaet gravitaciyu stanovitsya
tyazhelee vseh metallov i letit v yadro zvezdy pouchastvovat' v yadernoi
reakcii. I V to chto samyi legkii vodorod preodolevaet letit vnutr'
zvezdy -ya ne veryu, hot' v millione knizhek eto budet napisano, i tysyache
uchebnikov. Tak kak napisannoe ne podtverzhdeno fizicheskimi svoistvami a
protivorechit im.
|
|
|
| Naverh |
|
---
I
esli ya poprosil Vas perechitat' etot forum, to znachit ne sprosta.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.08.2012 22:24, 656 Bait)
\\\Ya lichno pisal Patonu, chto est' informaciya
izvne nauchnogo haraktera, no nikakogo
otveta ne poluchil. Ortovskie akademiki - eto starperdy, kotorym nichego
ne nado (u nih uzhe vse est'). Opredelenno nado reformirovat' RAN i NAN
Ukrainy.\\\
Ya Vas poproshu chtoby Vy ne zadavali vopros k - iz vne -, kak reformirovat' nauku Ukrainy,
ee ne nado reformirovat', u nee vse normal'no,
i
Vam budet luchshe i nauke Ukrainy budet spokoinee.
Esli u Vas est' vozmozhnost' sprosit' to voprosy naidutsya,
- Kak dobit'sya snizheniya temperatury nizhe absolyutnogo
nulya,
ne sozdavaya ochen' vysokogo davleniya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.08.2012 6:57, 1.5 KBait)
\\\Vy, druzhishe,
govorite, chto Vy ne uchenyi, eto pravil'no Vy - politik. Naukoi mozhno
upravlyat' i ne uchenomu. K tomu zhe Vy hotite razbogatet', dorogo prodavaya
nauchnuyu knizhku po fizike. No
esli vy ne budete upravlyat' naukoi, etu knizhku nikto ne kupit, ved' nado
zhe raskrutit' brend etoi knizhki. Vy govorite, chto Vam ne nuzhen
kollaider. Eto pravil'no. Zachem on
Vam? Vam nuzhen bol'shoi kabinet s kovrom. Na etot kover Vy, druzhishe,
budete vyzyvat' akademikov, stuchat' kulakom po stolu i vopit': "Pochemu
eshe do sih por ne otkryta Zvezda
efira Aleksandra. Ya ved' vam uzhe sto raz ob'yasnyal, chto takaya zvezda efira dolzhna byt' otkryta".\\\
Vot eto chto Vy napisali nazyvaetsya konspirologiei,
neobosnovannoi vydumkoi, i klevetoi.
Harakterizuet Vas kraine ploho v moih glazah.
Takzhe ya ne ponimayu zachem na al'ternativnyh forumah kotorye al'ternativshiki
dlya sebya sdelali po prichine togo chto ih toshnit ot relyativistskih tem,
tak Vy tuda prishli i podi nachali rasskazyvat' kakie relyativistskie teorii
horoshie,
to Vas i pravil'no zabanili, potomu chto est' mnogo relyativistskih
forumov na kotoryh isklyuchitel'no voshvalyayut relyativizm i relyativistov.
Esli Vy
hotite na dvuh stul'yah usidet' v smysle nezavisimogo nablyudatelya
v dannom sluchai Vy popali v prosak, po prichine togo chto relyativizm ot klassicheskoi
fiziki otlichaetsya
v klassicheskoi fizike est' vo vsem prostranstve -sreda- efir,
a u relyativistov v prostranstve pustota.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.08.2012 7:05, 300 Bait, otvetov: 1)
I zvezda efira - Zvezda Sani davnym davno lichno
mnoyu otkryta, ona s protivopolozhnoi storony solnechnoi
sistemy tochno naprotiv Velikogo attraktora.
Vy
podi dazhe ne znaete gde Velikii attraktor,
potomu i ne ponimaete chto koordinaty v prostranstve
mozhno ukazyvat' po raznomu.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
14.08.2012 16:02, 638 Bait)
| Citata: |
I zvezda efira - Zvezda Sani davnym davno lichno
mnoyu otkryta, ona s protivopolozhnoi storony solnechnoi
sistemy tochno naprotiv Velikogo attraktora.
|
Dyadya Sanya, kakim zhe metodom Vy otkryli zvezdu efira Aleksandra Vasi? Vy sami pisali, chto v teleskop ne lyubite smotret'. I matematiku vy ne lyubite schitat'.
Iz svoei golovy Vy primyslili sebe etu zvezdu. Fantaziya Vasha bezgranichna. I kakoe zhe otnoshenie imeet Vasha zvezda efira k chernoi dyre?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
14.08.2012 16:48, 1.8 KBait)
Koncepciya massivnogo tela, gravitacionnoe prityazhenie kotorogo nastol'ko veliko, chto skorost', neobhodimaya dlya preodoleniya etogo prityazheniya (vtoraya kosmicheskaya skorost'), ravna
ili prevyshaet skorost' sveta, vpervye byla vyskazana v 1784 godu Dzhonom Michellom. Kak vidite, pochti sovremennik N'yutona. Ortov i al'tov togda ne bylo, byli odni orty. Iz ego
rascheta sledovalo, chto dlya zvezdnogo ob'ekta s radiusom v 500 solnechnyh radiusov i s plotnost'yu Solnca vtoraya kosmicheskaya skorost' na ego poverhnosti budet ravna skorosti
sveta. Takim obrazom, svet ne smozhet pokinut' etot zvezdnyi ob'ekt, i on budet nevidimym. Michell predpolozhil, chto v kosmose mozhet sushestvovat' mnozhestvo takih nedostupnyh
nablyudeniyu zvezdnyh ob'ektov. Einshtein tozhe podderzhival etu ideyu i iskrivil prostranstvo v okrestnostyah chernoi dyry
Odnako nauka razvivalas' i ortami
bylo pravil'no ustanovleno, chto foton massy ne imeet i sledovatel'no on ne vzaimodeistvuet s massoi i mozhet uletet' ot lyuboimassy. No po sovremennym predstavleniyam
ortov tela mogut skollapsirovat' i imet' ne ochen' bol'shuyu massu i prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru. Pri etom ne ob'yasnyaetsya kak zhe proishodit etot znamenityi kollaps i za schet chego
i pochemu eto vdrug?
No, kak ni stranno, orty okazalis' pravy i malen'kih chernyh dyr posle bol'shogo vzryva bylo velikoe mnozhestvo, odnako kollaps
zdes' ni prichem. Chernye dyry vedut sebya tak kak i opisyvayut orty - vtyagivayut vse v sebya i ne izluchayut, no ne iz-za bol'shoi massy i ne iz-za kollapsa, a potomu, chto snaruzhi
pokryty otricatel'noi materiei.
V centrah galaktik ne chernye dyry. Otkuda by oni mogli tam poyavit'sya? Eto gravcegaly (gravitacionnye centry galaktik)
Podrobnee sm samlib.ru/t/tihomirow_e_a
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.08.2012 6:48, 823 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Vy menya udivlyaete ya privel dokazatel'stva nevozmozhnosti
fotona kak chasticy, i takzhe privel dokazatel'stva
nevozmozhnosti chernyh dyr, chto sobstvenno ves'
relyativizm
delaet bespoleznym porozhnyakom, a Vy prodolzhaete
lobzat' relyativistov. Zdes' esli Vam nravitsya lobzat'
relyativizm to eto navsegda, i Vam eto dazhe nikto ne imeet
prava zapreshat'.
Po povodu teleskopov to ya tak ponimayu chto Vy sovsem ne
v teme i eshe ne razduplilis' v tehnologiyah, est'
virtual'nye teleskopy, i est'
galerei foto, kak opticheskih
tak i infrakrasnyh teleskopov, ya hablovskih fotografii
tysyach neskol'ko prosmotrel tyaga seti pozvolyaet.
Vasha teoriya Vam nravitsya,
to eto i horosho, pohvastalis'
svoimi dostizheniyami i samouspokoilis',
pechatat'sya v referiruemom zhurnale eto Vash sleduyushii shag.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
15.08.2012 16:34, 1019 Bait)
Nu Vy dyadya Vasi i daete: "pechatat'sya v referuemom zhurnale - eto vash sleduyushii shag". Kto zhe nas s Ponomarenko
Ivanom Vasil'evichem napechataet? Nas s vonyuchih forumov gonyat, kak sobak, prichem i orty (Mit'ka Bide, i Sashka
Mamontov)i alty (Obez'yana s bananom, i Leshka s novoi teorii). Nasha iformaciya, vidite li, poluchena ne nauchnym
metodom. Im ved' glavnoe, chtoby bylo nauchno, a sootvetstvuet ih nauka prirode ili net - eto dlya nih nevazhno.
A chto takoe nauchnyi metod? V moei rabote "Metodologiya astronomii i fiziki" pokazano, chto nauchnyi metod - eto
kogda teorii vydumyvayutsya iz golovy i yavlyayutsya ezoterikoi mnogoumnyh mozgov uchenyh al'tov i ortov. Metod u
nih odinakovyi. Raz podumal - pridumal zvezdu efira. Dva podumal - pridumal bozon Higgsa. Tri podumal -
pridumal, chto zvezdy iz pyle-gazovyh oblakov. Chetyre podumal - pridumal krivoe prostranstvo. Pyat' podumal -
pridumal, chto v yadre Zemli zhelezonikelevoe yadro. Shest' podumal - pridumal, chto v provodnikah svobodnye
elektrony. Eto razve nauka?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.08.2012 22:28, 533 Bait, otvetov: 1)
V referiruemyi zhurnal kak raz Vy mozhete napisat'
bez trudnostei, poprosite Uvazhaemogo A.V. Rykova.
Vam on mozhet dat' svoyu rekomendaciyu v ochen' citiruemom
zhurnale,
tam on opublikoval svoyu stat'yu, i imeet
ves kak chatlanin i mozhet pacakam pomoch' stat' chatlanami.
Vy pogovorite s nim.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
16.08.2012 16:44, 711 Bait)
S chego by eto Rykov stal by mne pomogat'? Videl ya Vashego Rykova na vsyakih forumah. Takoi zhe fantazer, kak i Vy. U nego vakuum rozhdaet elektron-pozitronnye pary. Neuzheli trudno
dogadat'sya, chto iz pustoty nichego ne mozhet naroditsya, i raz poyavlyayutsya chastica i antichastica, to znachit v etom meste byli i otricatel'naya i polozhitel'naya materii. Rykov -
krupnaya velichina schitaetsya v stane ortov. Ego knigi publikuyut ne za ego den'gi. Nam tak ne zhit'.
My s Ponomarenko Ivanom Vasil'evichem, vse bol'she samizdatom
promyshlyaem. Teper' nastoyashaya fizika i astronomiya budut v samizdate, a nauchnye knigi al'tov i ortov nado pereimenovat' iz nauchnoi literatury i uchebnikov v nauchnuyu fantastiku.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
21.08.2012 23:35, 1.9 KBait)
Po informacii vyshnih, kotoruyu dovodit do nas Ivan Vasil'evich Ponomarenko, chernye dyry imeyut reshayushee znachenie v formirovanii galaktik. Galaktiki formiruyutsya iz razvalivshihsya
chernyh dyr, a ne iz gazopylevyh oblakov. Ot nachala v kosmose byla otricatel'naya (nepravil'noe nazvanie - "temnaya") materiya. Ona byla ochen' razryazhena, i v etu materiyu
vdvinulas' polozhitel'naya materiya. (Otkuda i kak poyavilas' polozhitel'naya materiya. Ivan Vasil'evich obeshal skazat' v dal'neishem). Polozhitel'naya materiya prityanula k sebe i nachala
vrashat' otricatel'nuyu materiyu. Tak obrazovalsya protoshar (a ne singulyarnost', singulyarnosti ne bylo), kotoryi vrashalsya s ogromnoi vse vozrastayushei skorost'yu. Otricatel'naya
materiya sdavila polozhitel'nuyu so strashnoi siloi. Nakonec, centrobezhnaya sila razorvala protoshar po ekvatoru, iz protoshara nachala vyletat' polozhitel'naya materiya, kotoruyu obvolakivala
otricatel'naya materiya, obrazovalis' chernye dyry, oni vrashalis' uzhe medlennee. Forma chernoi dyry polyi tor. Cherez polyusa tora chernaya dyra vtyagivaet vse v sebya. Nakonec, ona
tozhe razryvaetsya po ekvatoru i iz nee vyletaet otricatel'naya materiya, kotoraya obvolakivaetsya polozhitel'noi materiei i veshestvom (elementarnye chasticy - eto osobym obrazom
strukturirovannaya smes' polozhitel'noi i otricatel'noi materii). Tak obrazuyutsya zvezdy, planety i sputniki, u vseh etih ob'ektov v yadrah otricatel'naya materiya. Kogda chernaya
dyra razletaetsya v centre ostaetsya eshe mnogo polozhitel'noi materii - eto gravcegal (gravitacionnyi centr galaktiki), kotoryi derzhit vsyu galaktiku ot raspolzaniya, kak na korotkom
povodke. Chernye dyry obrazuyutsya i iz sverhnovyh, veshestvo vzryvaetsya i razletaetsya, a yadro stanovitsya chernoi dyroi. Podrobnee sm. stat'yu "Vselennaya" na: samlib.ru/t/tihomirow_e_a/
Vot, esli by Novikov I. D. rasschital takuyu chernuyu dyru - eto bylo by horosho.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.08.2012 21:28, 1.1 KBait)
Rasskaz.
Ochen' dalekaya planeta.
V kruzhke astronomii devochka rasskazyvaet
o svoem otkrytii.
Ya pomestila kota v kletku radioteleskopa
dlya
togo chtoby kotom provesti zagorizontnoe
telepaticheskoe skanirovanie udalennyh civilizacii.
I neozhidanno kot nachal poluchat' telepaticheskuyu informaciyu
kotoruyu
iz datchikov na kote, obrabotal
komp'yuter i vot chto okazalos'.
Nash televizionnyi neitrinnyi kanal prinimaet kakoi-to individuum
i dumaet chto s nim podderzhivaet
svyaz' bolee vysokorazvitaya
civilizaciya, i ego tam vse schitayut durachkom.
-Mar'ya Ivanovna, - a mozhno ya nazovu etu planetu planetoi durakov,
planetoi bezmozgloi
skotiny,
ili planetoi nedalekih.
Nel'zya Yulya voobshe-to tak nazyvat',- nazvanie dolzhno maksimal'no tochno opisyvat'
naselyayushuyu ee civilizaciyu, no tak kak ty
otkryla to mozhesh' nazyvat'
tak kak tebe nravitsya.
A v eto vremya planeta Zemlya, - odin strannyi tovarish prodolzhaet
begat' po forumam i rasskazyvat'
vsem o tom chto on svyazalsya s drugoi
civilizaciei, i chto poluchaet kakie-to cvetnye kartinki.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.08.2012 21:38, 636 Bait)
E.A.Tihomirov
Ya zhe Vam uvazhaemyi Vnyatno ob'yasnil chto avtor v fizicheskom
obosnovanii i opisanii Chernoi Dyry zhestoko lopuhnulsya.
V svyazi s chem chernye dyry ne imeyut fizicheskogo smysla.
I vo vtoryh chernye dyry ne nuzhdayutsya v drugoi
ne avtorskoi traktovke, tak kak
eto budut uzhe ne
chernye dyry o kotoryh govoril avtor chernyh dyr.
Drugaya traktovka chernyh dyr budet opisyvat'
kakuyu-to erundu i chto ugodno no tol'ko
eto
budut ne chernye dyry, a kakaya-to erunda
kotoruyu sebe kto-to pridumal i reshil nazvat'
chernoi dyroi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.08.2012 21:44, 707 Bait, otvetov: 1)
E.A.Tihomirov
\\\Ot nachala v kosmose byla otricatel'naya (nepravil'noe nazvanie - "temnaya") materiya.\\\
Ya vot ne ponimayu kak mozhno zanimat'sya astronomiei i chto-to zvezdet' dazhe elementarno
ne znaya bazovyh ponyatii.
Vot Vy ne znaete kto i kogda pridumal
chernye dyry, i avtorskuyu formulirovku,
takzhe ne znaete kto i kogda pridumal temnuyu materiyu i temnuyu energiyu, i uzh tochno
ne znaete kakie voprosy vo vremya ih pridumyvaniya
reshali eti teorii.
Vy zhe ne prosto glupo vyglyadite i sebya pozorite, Vy dobavlyaete idiotizm
v astronomiyu, i zagazhivaete internet podobnym neobosnovannym tekstom.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
24.08.2012 22:52, 989 Bait)
Dyadya Vasi, eto ty sebya pozorish', svoei zvezdoi efira na traktore.
Chernye dyry est'. Chernye dyry eto ob'ekty, kotorye ne izluchayut, i kotorye vse pogloshayut v sebya. Zdes' ortodoksy pravy. Odnako, oni nepravil'no traktuyut fiziku chernyh dyr. Chernye dyry ne izluchayut ne iz-za bol'shoi massy, i ne
iz-za kollapsa, a potomu, chto snaruzhi pokryty otricatel'noi materii.
Vy, dyadya Vasi, kak al't, sovsem ne priznaete chernyh dyr i etim Vy pozorite sebya i vseh al'tov.
Chto kasaetsya avtora, to on nepravil'no traktuet chernye dyry, a ya ukazyvayu kak nado ih traktovat' pravil'no.
Skazka
V odnoi dalekoi dalekoi galaktike
zhil dyadya Vasi i poehal on na traktore na attraktor, gde uvidel zvezdu efira. I govorit: "Mar' Ivanovna, mozhno ya nazovu etu zvezdu efira zvezdoyu Sani Aleksandra."
"Net, - otvechaet Mar' Ivanovna, - nado tochnye nazvaniya zvezdam efira davat'. Eta zvezda nazyvaetsya Zvezdoi durakov".
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.08.2012 23:30, 1.6 KBait)
Ya tak ponimayu chto vozrast Vash pensionnyi,i
pamyat' u Vas nikakaya.
I bred sivoi kobyly Vy nesete kachestvennyi.
Dlya marazmatikov eshe raz napominayu avtorskii
variant izlucheniya
iz Chernoi Dyry i kak ono nazyvaetsya.
---
Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
Izluchénie Hókinga gipoteticheskii process
ispuskaniya raznoobraznyh elementarnyh
chastic, preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi
dyroi. Predskazan teoreticheski Stivenom
Hokingom v 1974 godu.
---
Vy eto razduplyaetes' periodicheski
ya zhe vnyatno napisal - prochtite etot forum polnost'yu, tut napisano
vse pro chernye dyry, dazhe pro klounov tipa Vas kotorye schitayut
chto chernye dyry eto istochnik
rentgenovskogo izlucheniya.
Vy vot schitaete chto s chernoi dyry nichego ne vyletaet,
a avtor govorit chto fotony, klouny govoryat chto radiaciya v rentgenovskom diapazone.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.08.2012 23:39, 1.1 KBait)
\\\Chernye dyry eto ob'ekty, kotorye ne izluchayut, i kotorye vse pogloshayut v sebya. Zdes' ortodoksy pravy.\\\
Bud'te lyubezny idite na relyativistskie forumy i lobzaite
tam relyativistov.
Zvezdochet naprimer -
Oni
takih kak Vy lyubyat.
Vy tol'ko idiotizm svoi men'she tam rasskazyvaite,
ibo Vy delaete neobosnovannye i negramotnye fizicheskie utverzhdeniya,
za chto Vas
tam zabanyat, a esli ne budete delat' idiotskih
utverzhdenii, i ne budete nikogo uchit' tomu kak vyglyadyat
chernye dyry, to Vas ne zabanyat,
i drugom svoim ne
hvastaites', i soidete za normal'nogo
relyativista.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2012 0:07, 692 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Ya ne ponimayu kak mozhno zanimat'sya pereotkrytiem chernyh dyr.
Zdes' s chernymi dyrami u nauki polnaya torba, pri etom
premii vydayut regulyarno za chernye dyry,
pri tom chto oficial'no
ne obnaruzheno nichego.
Da i kak ee obnaruzhit' esli oni ne mogut opredelitsya kak
ona dolzhna vyglyadet'.
I chto menya udivlyaet
periodicheski poyavlyayutsya psevdo kosmologi
kotorye po svoemu traktuyut chernye dyry, ne ponimaya
chto eto analogichno tomu chto esli by oni na velosiped
govorili
- kolesokat, i ne ponimayut chto drugaya
traktovka chernoi dyry ne nuzhna v principe nikomu,
ibo Chernaya Dyra
eto isklyuchitel'no togo traktovka kto ee pridumal
-
a tochnee Hoking.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
25.08.2012 12:12, 1.1 KBait)
Dyadya Vasi, nu ty i chudak na bukvu "m". Esli menya zabanyat na Astronete vmeste s toboi, to ya budu schitat', chto ya ne naprasno prozhil svoyu zhizn'. Ty uzhe vsem zdes' plesh' proel.
Ya tebe govoril uzhe, i seichas povtoryayu, chto ne Hoking pridumal chernye dyry. On tol'ko malost' po drugomu ob'yasnil ih, no tozhe ne pravil'no. V prirode net ni hokinskih, ni enshteinovskih
chernyh dyr.
V prirode est' tol'ko ivanvasil'evskie chernye dyry, kotorye ne izluchayut, tak kak s naruzhi pokrity otricatel'noi materiei. Esli tebe ne nravyatsya prirodnye chernye dyry, to ya
tebe v etom voprose nichem ne mogu pomoch'. Ty mozhesh' vzyat' verevku, poiti i povesit'sya v sortire v znak protesta. I ne bespokoi menya bol'she po pustyakam. Vot, smotri, ya pro
tebya stishok napisal.
Stishok
Govoril, lomaya ruki,
Dyadya Vasi - dubolom
O bessilii nauki
Pred efirnym veshestvom.
Vse mozgi razbil na chasti,
Vse izviliny zaplel.
Astronetovskie vlasti
Sdelaite emu ukol.
I eshe odin stishok
Po dorozhen'ke pyl'noi, po traktoru li
Vse ravno nam s toboi po puti.
Prokati nas, Vasilii, na traktore,
Do attraktora nas prokati!
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2012 12:36, 653 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Vy hotite chtoby Vas vse nazyvali grebannym
plagiatorom netradicionnoi orientacii v fizike - to ne vopros.
Zabud'te naproch' slovosochetanie - Chernaya Dyra -
etot termin
zanyat na vechno, tol'ko idioty ego primenyayut v svoih
opisaniyah
- pardon chto grubovato no dumayu chto doidet.
\\\Ya
tebe govoril uzhe, i seichas povtoryayu, chto ne
Hoking pridumal chernye dyry. On tol'ko malost' po drugomu ob'yasnil ih,
no tozhe ne pravil'no.\\\
Vy pofigizmom zaboleli - on dokazal chto chernye dyry izluchayut kak obychnoe
telo.
http://www.scorcher.ru/art/theory/sto/black_holes1.php
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
26.08.2012 0:29, 2.5 KBait)
| Citata: |
Vy hotite chtoby Vas vse nazyvali grebannym
plagiatorom netradicionnoi orientacii v fizike - to ne vopros.
Zabud'te naproch' slovosochetanie
- Chernaya Dyra -
etot termin
zanyat na vechno, tol'ko idioty ego primenyayut v svoih
opisaniyah
- pardon chto grubovato no dumayu chto doidet.
\\\Ya
tebe govoril uzhe, i seichas povtoryayu, chto ne
Hoking pridumal chernye dyry. On tol'ko malost' po drugomu ob'yasnil ih,
no tozhe ne pravil'no.\\\
Vy pofigizmom zaboleli - on dokazal chto chernye dyry izluchayut kak obychnoe
telo.
http://www.scorcher.ru/art/theory/sto/black_holes1.php
|
Dyadya Vasi, druzhishe, tak eto ty obo mne zabotish'sya, chtoby menya plagiatorom ne nazvali? Nu spasibo, brat. Tebya, navernoe orty podvergali uzhe netradicionnoi orientacii i ne edinozhdy.
Teper' ty o drugih zabotish'sya. Ne dreif', bratan, mne tvoi Hoking ne mozhet pred'yavit' nikakih pretenzii. Ty zhe sam govorish', chto Hoking "dokazal", chto chernye dyry
izluchayut fotony, poetomu Hoking ne vprave nazyvat' takie ob'ekty chernymi dyrami. Kakaya zhe eto dyra, esli ona izluchaet, da eshe fotony? Ya dazhe znayu, pochemu eto vdrug Hokin "dokazal"
chto chernye dyry izluchayut fotony. Vidish' li, orty "pomestili" chernye dyry v centry galaktik u nih tam putanica strashnaya. Eto u nih i kvazary i radiospokoinye kvazary
(chush' takaya) i chernye dyry odnovremenno. Eti shtuki v centrah galaktik estestvenno izluchayut fotony, dazhe v vide galo, i v vide dzhetov. Poetomu Hoking i rasschital, chto chernye
dyry izluchayut fotony. No v centrah galaktik sovsem ne chernye dyry, eto sovsem drugie ob'ekty. Eto gravcegaly - gravitacionnye centry galaktik. U nih, dyadya Vasi, snaruzhi ne
otricatel'naya materiya, a polozhitel'naya. Eto govorit o tom, chto s pomosh'yu matematiki mozhno "dokazat'" lyubuyu fantaziyu, esli ochen' zahotet'.
Potom, Vasya,
ya za slavoi ne gonyus'. Moya zasluga zdes' nebol'shaya, ya prosto peredayu informaciyu ot Ivana Vasil'evicha, kotoryi, v svoyu ochered', peredaet informaciyu ot vyshnih. Ty by, Vasya,
poostorozhnei razbrasyvalsya namekami na .... Ved' ty ne menya oskorblyaesh', a vyshnih. A oni mogut tebe takuyu kartinku pokazat', chto bashka u tebya razvalitsya na mnogo-mnogo
kusochkov. Ty ne vedaesh', chto tvorish', zhalko tebya. Oni i serdce tvoe mogut ostanovit' mgnovenno. Bud' ostorozhen ne hami, hamstvo tvoe bokom tebe vyidet.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2012 20:29, 1.9 KBait)
U menya v svoe vremya tozhe byla neobhodimost'
opisat' nechto pohozhee na chernuyu dyru.
Po skol'ku est' mnogo ob'ektov ochen' holodnyh,
sledovatel'no oni dolzhny
pogloshat' energiyu,
po skol'ku energiya eto kolebaniya sredy, pogloshenie
bolee logichno pri uvelichenii plotnosti sredy
i uvelichenii davleniya sredy do kondensacii
i kristallizacii.
Dlya resheniya etoi zadachi ya i pridumal Zvezdu Efira.
Mne so zvezdoi efira v itoge, poluchilos' dostatochno prosto
delat' modelirovanie
modelei zvezd i galaktik.
Estestvenno v processe modelirovaniya mne prishlos'
korrektirovat' zvezdu efira kotoruyu ya pridumal vnachale,
ona preterpela neznachitel'nye
izmeneniya no v obshem
ona ostalas' kak fizicheskii ob'ekt prakticheski v
bazovoi idee.
Sobstvenno u Vas poluchaetsya chto esli Vy hotite sdelat'
u kakogo-to
bazovogo ob'ekta modeli nekotorye fizicheskie
svoistva kotorye reshayut nekotorye fizicheskie zadachi
to ego logichno nazvat' po osnovnym fizicheskim svoistvam.
Dlya etogo nado opredelit' tehnicheskie zadachi kotorye budut
reshat'sya, posle etogo zhelatel'no opisat' bazovuyu
strukturu, i prognat' v dinamicheskoi situacii nekotoroi
modeli kotoraya by reshala proshe i naglyadnee nekotorye
fizicheskie situacii.
Vy hotite naprimer chtoby byla poverhnost', sledovatel'no
u Vas v nazvanii
ob'ekta dolzhno byt' slovo o poverhnosti
i ee sostave ili naznachenii. Esli Vy hotite nadelit' kakimi-to
specificheskimi fizicheskimi svoistvami - to i eto tozhe dolzhno
byt' v nazvanii.
U vas naprimer nazvanie mozhet byt' v stile -
Vysoko-gravitacionnaya
zvezda s pogloshayushei poverhnost'yu.
Esli Vy hotite
opisat' osevye vybrosy, to nazvanie
budet v stile eshe i opisyvayushee prichinu osevyh
vybrosov -
Vysoko-gravitacionnaya zvezda s
pogloshayushei poverhnost'yu
i polyusovymi vulkanami.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2012 21:50, 8.8 KBait)
Iz moego razgovora na pop meh.
---
Vot shob Vy pravil'no ponyali,
chto odin fizik pridumal slovosochetanie
chernaya
dyra, Hoking spustya nekotoroe vremya
dal etomu slovosochetaniyu obosnovanie.
---
I Vy posmotrite kak lo - hanulsya Cherepashuk
napisav 300 statei kotorye
dobavili reiting
Hokingu, a emu dostatochno bylo dlya svoei nobelevskoi pridumat'
Rentgenovskuyu zvezdu s myagkoi poverhnost'yu, -
i eto bylo by dlya nego eshe i
zaneseniem ego
v istoriyu astronomii, kak chatlanina kotoryi chto-to
pridumal i obosnoval samostoyatel'no,
no on v itoge pacak kotoryi ne pridumal
i ne
obosnoval nichego svoego samostoyatel'no.
---
-Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
....Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo.
ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut. ....
Padaya na Chernuyu Dyru veshestvo ne
mozhet rezko tormozitsya ili rezko uskoryatsya,
a sledovatel'no - ne mozhet
byt' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya po etoi prichine.
V svyazi s tem chto dlya uskoreniya do skorosti sveta
pri kotorom vozmozhno izluchenie neobhodimo
ne bolee 10 sekund, a zvezda razmerom s
Solnce na takoi skorosti proletit cherez gorizont
sobytii maksimum za minutu.
Gorizont sobytii - eto skorost' sveta - esli
ob'ekt uletaet s etoi skorost'yu ot nablyudatelya, to
u nego vozniknet krasnoe smeshenie.
Esli by veshestvo dolgo padalo - godami na maloi skorosti
s uskoreniem to bylo by zametno izmenenie Z u padayushih
tel v chernuyu dyru so vremenem, no pri etom nevozmozhno
rentgenovskoe izluchenie - iz za slishkom medlennogo
uvelicheniya uskoreniya.
.... Material iz Vikipedii Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri
vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah.....
A rentgenovskoe izluchenie est' - sledovatel'no
ego istochnikom mozhet byt' tol'ko rezul'tat yadernoi
reakcii.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.....
A esli rezul'tat izlucheniya istochnik yadernoi reakcii -
i on dlitsya godami, - to eto neitronnaya zvezda.
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8971-nasledstvennyie-chernyie-dyiryi/page/3/
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke, ya tak ponyal reshil -
zachem dobru propadat' - pust' izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi
dyry budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Vashe - Rentgenovskoe izluchenie ChD voznikaet pri akkrecii veshestva.
Izluchenie Hokinga - drugoi process. Stranno, chto za 7 let "uvlecheniya
astrofizikoi" Vy etogo ne ponyali.
Moe - S moei tochki zreniya - uvazhaemyi A.M.ChEREPAShUK imeet takoe zhe otnoshenie
k Chernym Dyram kak ya ili Vy.
My s Vami, i A.M.ChEREPAShUK mozhem tol'ko predpolagat' i vyskazyvat'
svoyu tochku zreniya, no obrashat' vnimaniya na podobnye vyskazyvaniya i brat'
ih na veru, ya ne vizhu smysla.
Drugoe delo avtor. Kak on skazal to - takie i Chernye Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vot ya naprimer govoryu chto veshestvo padaet na chernuyu dyru,
i posle udara o poverhnost' s protivopolozhnoi storony chernoi dyry voznikaet rentgenovskoe i svetovoe izluchenie.
Drugoi schitaet chto izluchenie na podlete.
V binokl' ne vidno - odni predpolozheniya, i ih mozhet byt'
bol'she sotni naprimer - komu verit'?
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vy zatragivaete vopros interpretacii avtorskih
idei bez soglasiya s avtorom.
A esli desyatok drugih avtorov opublikuyut po 300 nauchnyh rabot, a avtor o
Chernyh Dyrah govorit chto izluchenie v osnovnom iz fotonov - a vse drugie
govoryat, chto
izluchenie iz rentgenovskih chastic, drugoi govorit iz radio izlucheniya, a
tretii govorit iz gamma chastic - ya dolzhen slushat' isklyuchitel'no avtora
Chernyh Dyr,
a ne teh kto interpretiruet, i tem bolee teh kto plevat' hotel na avtorskii variant chernyh dyr.
Nikto ne meshaet pridumat' svoi - rentgenovskie chernye dyry, - tak net ne
hotyat, - tak na neudobnye voprosy otvechat' dolzhen budet avtor, a pri
interpretacii avtora - pisaka naprimer stat'i s levymi ideyami v oblasti
Chernyh Dyr, prikryvaetsya avtorstvom avtora
Chernyh Dyr, a sam so svoim bredom po otnosheniyu k avtorskomu izlozheniyu, kak-by i ne prichem.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
..Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii). Tochnee,
razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Vasha ssylka - tekst 11.05.11 20:36
....Kak otlichit' chernye dyry ot neitronnyh zvezd
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya chernaya dyra ne dolzhna proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. U nee mozhet nablyudat'sya lish' irregulyarnaya
peremennost' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya s harakternymi vremenami
$$Delta tapprox frac{r_g}{c}approx10^{-3} div 10^{-4}~mbox{rm s.}$$
I deistvitel'no, v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme Lebed' H-1, soderzhashei
chernuyu dyru s massoi okolo desyati solnechnyh, v sostoyanii, kogda
rentgenovskaya svetimost' ponizhena, a rentgenovskii spektr zhestkii i
stepennoi, nablyudaetsya bystraya irregulyarnaya peremennost' rentgenovskogo
potoka na vremenah poryadka millisekundy. Nablyudeniya, vypolnennye s
bortov sovremennyh rentgenovskih observatorii, takih, kak GINGA,
MIR-KVANT, GRANAT, ASKA, pokazali, chto rentgenovskie spektry
akkreciruyushih chernyh dyr sistematicheski bolee zhestkie, chem spektry
akkreciruyushih neitronnyh zvezd, i prostirayutsya do energii v neskol'ko
megaelektron-vol't.
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya neitronnaya zvezda mozhet proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. Odnako, esli neitronnaya zvezda obladaet
slabym magnitnym polem (napryazhennost'yu menee 1010 Gs) ili esli ee os'
vrasheniya neudachno orientirovana otnositel'no zemnogo nablyudatelya, pri
akkrecii na takuyu neitronnuyu zvezdu mogut ne nablyudat'sya regulyarnye
pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya. Poetomu otsutstvie strogo
periodicheskih pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya - eto lish' neobhodimyi,
no ne dostatochnyi priznak chernoi dyry. V to zhe vremya pri slabom
magnitnom pole neitronnoi zvezdy i nesil'nom tempe akkrecii veshestva na
ee poverhnosti mogut proishodit' termoyadernye vzryvy nakoplennogo
veshestva, privodyashie k yavleniyu rentgenovskogo barstera I tipa - korotkim
(dlitel'nost'yu poryadka 1-10 s) i moshnym vspyshkam intensivnosti
rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, chto takzhe yavlyaetsya harakternym priznakom
akkreciruyushei neitronnoi zvezdy, obladayushei tverdoi poverhnost'yu.
Poskol'ku chernaya dyra ne obladaet tverdoi poverhnost'yu, akkreciya
veshestva na nee ne dolzhna privodit' k fenomenu rentgenovskogo barstera I
tipa. Razumeetsya, otsutstvie etogo fenomena takzhe yavlyaetsya lish'
neobhodimym kriteriem nalichiya chernoi dyry. Takim obrazom, my mozhem
sformulirovat' vazhneishie priznaki akkreciruyushei chernoi dyry: eto moshnoe
rentgenovskoe izluchenie, bol'shaya massa (bolee treh solnechnyh),
otsutstvie fenomenov rentgenovskogo pul'sara ili rentgenovskogo barstera
I tipa. Pri etom vopros o nadezhnom opredelenii massy relyativistskogo
ob'ekta v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme yavlyaetsya reshayushim pri
identifikacii ego s chernoi dyroi....
Ya Vam prosto pokazyvayu proiivorechie u Vas i Vashei ssylke,
po otnosheniyu k napisannomu v Vikipedii o izluchenii iz Chernoi Dyry.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.08.2012 1:29, 953 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Mne do lampochki esli Vy ne ponimaete
to chto ya Vam govoryu.
I ponyatno chto Vy samostoyatel'no nichego pridumat'
ne mozhete, i ugrozhaete mne sovsem vidimo oborzevshi.
Esli Vy ne ponimaete chto net smysla primenyat' chernye
dyry - to flag Vam v ruku.
Ostavaites' zas - rancami vo vremeni.
Esli by Vy svyazalis' s tolkovymi
inoplanetyanami to
oni by nastavili Vas na chto-to tolkovoe i chtoby eto ne
pro - ....
A esli Vy prinimaete teleperedachu - v mire zhivotnyh,
a
dumaete chto Vam rasskazyvayut o tehnologiyah to Vy
sovsem nemnogo ne ponimaete chto eto samonakrutka.
Mne konechno do lampochki to kak Vy sebya nakrutili,
chto svyazalis'
s vyshshimi, i oni s Vami nizshimi,
mozhno dazhe skazat' s bezmozgloi skotinoi v sravnenii s nimi,
po neponyatnoi prichine podderzhivayut dialog, i ne ponyatno
pochemu
Vy izbrannye, no mne ot Vas smeshno - Vy krasavcy eshe
te.
Uspehov Vam - retranslyatory .
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
26.08.2012 21:12, 3.7 KBait)
| Citata: |
Mne do lampochki esli Vy ne ponimaete
to chto ya Vam govoryu.
I ponyatno chto Vy samostoyatel'no nichego pridumat'
ne mozhete, i ugrozhaete mne
sovsem vidimo oborzevshi.
|
Druzhishe, dyadya Vasi, ty ne prav. Ya samostoyatel'no ochen' mnogo chego mogu pridumat', kak vprochem i lyuboi. Samostoyatel'no pridumat' - ne fokus. Delo-to kak raz
v tom, chto ya ne hochu nichego pridumyvat'. Kak ni stranno, ya hochu znat' fiziku prirody, takoi kakaya ona est', a ne pridumannuyu fiziku. Seichas, vsya fizika i astrofizika pridumannaya,
i net nikakoi vozmozhnosti opredelit', gde pridumka dostovernaya, a gde net. Vot smotri, druzhishe, ty pridumal zvezdu efira dyadi Vasi Aleksandra, N'yuton pridumal zakon vsemirnogo tyagoteniya, Einshtein pridumal, chto vremya
svyazano s prostranstvom, a potom pridumal, chto vremya svyazano s massoi, potom pridumal krivoe
prostranstvo, Kto-to pridumal singulyarnost'. Kto-to, pridumal bozon Higgsa (nado ponimat',
Higgs) Kant pridumal, chto galaktiki obrazuyutsya iz pyle-gazovyh oblakov, Kto-to pridumal, chto
v yadro Zemli zhelezonikelevoe. Hoking pridumal, chto chernye dyry izluchayut fotony. Kto nibud'
mne v sostoyanii skazat', chto zdes' istinno, a chto lozhno? Iz zemlyan nikto. Izvne zhe mne skazali, chto v perechislennom net ni odnogo istinnogo fakta. Podrobnee sm. samlib.ru/t/tihomirow_e_a/
Druzhishe, dyadya Vasi, ya tebe ni skol'ko ne ugrozhayu, i tebya ne pugayu, ya tebya preduprezhdayu, a eto raznye veshi. Hamit' ne nado, hamstvo vsegda vozvrashaetsya k nachavshemu
hamit'. Esli ty, druzhishe, smelyi, to ty mozhesh' prodolzhat' hamit', vysokorazvitoi civilizacii, vybor za toboi. Ya zhe tebe hochu tol'ko dobra.
Itak, gospoda kollegi,
my neskol'ko otvleklis', t. k. dyadya Vasi, vse vremya otvlekaet nas ot stat'i I. D. Novikova. Kollega I. D. Novikov privodit v stat'e polya tyagoteniya dlya vrashayusheisya i dlya ne
vrashayusheisya chernoi dyry. Zamechu, chto ne vrashayushihsya chernyh dyr v prirode ne sushestvuet. Vse chernye dyry obyazatel'no vrashayutsya, prichem s ochen' bol'shoi skorost'yu. No esli by
byli ne vrashayushiesya chernye dyry, to tyagotenie ih bylo by takoe zhe, kak i vrashayushihsya. Na tyagotenie vrashenie ne okazyvaet nikakogo deistviya. Razdel "Fizika chernoi dyry"
neveren ot nachala do konca. Da eto i ponyatno, t. k. kollega Novikov I. D. nepravil'no traktuet chernye dyry.
Chernaya dyra predstavlyaet soboi polyi tor, po suti obolochku,
napominayushuyu avtomobil'nuyu pokryshku. V etoi obolochke sosredotochena vsya ogromnaya massa chernoi dyry. Ee massa ravna masse galaktiki. Chernaya dyra pogloshaet veshestvo cherez polyusa,
poetomu veshestvo ne padaet na poverhnost' chernoi dyry, a uvlekaetsya vnutr' cherez polyusa tora.
Potom veshestvo prizhimaetsya k obolochke iznutri. Poetomu chernaya dyra ne izluchaet
ni fotonov, ni rentgenovskogo izlucheniya. Vse razgovory o ispuskanii chernoi dyroi fotonov i rentgenovskogo izlucheniya iz-za togo, chto chernye dyry putayut s gravcegalami, kotorye
nahodyatsya v centrah galaktik. Chernyh dyr v centre galaktik ne mozhet byt' po odnoi prostoi prichine - galaktiki obrazovalis' iz chernyh dyr, a ne iz gazopylevyh oblakov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.08.2012 1:47, 507 Bait)
Esli s psihologicheskoi tochki zreniya - to Vy zalipli
na bespoleznoi besperspektivnoi i melkoi idee,
kotoraya ne reshaet nikakih zadach.
O tom chto derzhites' za
nee i ne hotite ee
izmenit' - govorit o Vashem pensionnom vozraste
i o tom chto Vy ne sostoyanii nichego drugogo pridumat' i
dazhe ne v sostoyanii provesti kosmeticheskie
izmeneniya
- ibo dazhe ne ponimaete chto sobstvenno nado izmenit'.
I to chto postoyanno na svyazi s inoplanetyanami eto tozhe ne zdorovyi
priznak.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
29.08.2012 14:46, 1.4 KBait)
V zaklyuchenii razbora raboty kollegi I. D. Novikova hochu skazat' neskol'ko slov o gravcegalah. Kak my ustanovili ranee, galaktika obrazuetsya, kogda chernaya dyra razryvaetsya
po ekvatoru, i iz razryva vyletayut kuski otricatel'noi materii pokrytye veshestvom, eto budushie zvezdy i planety. Oni ustroeny odinakovo, te i drugie imeyut yadra iz otricatel'noi
materii. U zvezd yadra gorazdo bol'she i, sledovatel'no, massivnee, i szhaty sil'nee, chem u planet. Vot eshe, chto vazhno otmetit', u lopnuvshei popolam chernoi dyry polovinki mogut
rashodit'sya i shoditsya, ot etogo voznikayut rukava spiral'nyh galaktik.
Odnako chernaya dyra ne mozhet polnost'yu razletet'sya, t.k. ona predstavlyaet soboi polyi tor.
Vnutrennie stenki tora s prilegayushei k nim polozhitel'noi materiei ne razletayutsya, a svorachivayutsya uzhe ne v polyi, a v polnyi tor. Eto i est' gravcegal. Estestvenno, chto massa
ego vo mnogo-mnogo raz men'she massy chernoi dyry, t.k. on yavlyaetsya tol'ko neznachitel'noi chast'yu chernoi dyry, no nesmotrya na eto, imenno gravcegal uderzhivaet vsyu galaktiku ot
polnogo razleta. Chto iz etogo sleduet, dogadaites' sami. Itak, gravcegal predstavlyaet soboi polnyi tor, veshestvo i otricatel'naya materiya padayut na poverhnost' tora pri etom
mogut voznikat' raznye izlucheniya, ot radiovoln, do rentgenovskih. Poetomu rabota kollegi I.D. Novikova, ne propala darom, ona prosta otnositsya k gravcegalu, a ne k chernoi
dyre. Veshestvo iz gravcegala istekaet cherez polyusa i obrazuet dzhety.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(E. A. Tihomirov,
29.08.2012 15:01, 637 Bait)
Vot chto eshe zabyl napisat'. V nastoyashee vremya, chernyh dyr malo, t.k. vse chernye dyry, kotorye obrazovalis' posle razvala protoshara uzhe preobrazovalis' v galaktiki. No i seichas
obrazuyutsya chernye dyry iz sverhnovyh zvezd, kogda veshestvo sverhnovoi vzryvaetsya i razletaetsya, a yadro stanovitsya chernoi dyroi i nachinaet vtyagivat' vse v sebya poka opyat' ne
razvalitsya i ne obrazuet galaktiku. Takim obrazom, chtoby iz gazopylevogo oblaka obrazovalas' galaktika, nado chtoby v eto gazopylevoe oblako popala chernaya dyra. Chernye dyry
seichas svoeobraznye chistil'shiki , kotorye "podmetayut" beshoznoe veshestvo i delayut iz nego galaktiki.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.09.2012 22:05, 1.4 KBait, otvetov: 2)
Otvet #191 : Segodnya v 18:42:03
Vyvod
temy - u kazhdogo svoe ponyatie informacii, v zavisimosti ot etogo odni peredavat' mogut, a drugie net.
Poetomu
bolee obshim budet takaya formulirovka: mogut li kakie libo sobytiya v
odnom meste vyzvat' sobytiya v drugom meste mgnovenno.
------------------------
Nu ya ne dumal chto nastol'ko vse grustno.
Esli pamyat' otsutstvuet
to eto navsegda.
---------
Iz sobaki drevnie moreplavateli vyrezali chast' vnutrennih organov,
i brali etu sobaku na korabl'.
Vyrezannuyu chast'
ostavlyali u sebya na beregu.
i kroshku etogo vysohshego veshestva,
so vremenem razogrevali na ogne rovno v polden', i kak ne stranno
gde-by na planete ne nahodilsya
korabl' - sobaka nachinala gromko layat' tochno v eto vremya,
dumaete Belku so Strelkoi zrya zapuskali v kosmos, esli ne proveryali na
dannuyu situaciyu to taki zrya.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(S. V. Stoyanov,
10.03.2013 13:49, 147 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Da, i nas na planete nemalo udivitel'nyh mest naprimer Okeaniya, i v chastnosti Tonga, Solomonovy ostrova.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.09.2012 23:57, 200 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Ya eshe dva opyta znayu kotorye provodilis',
no ne smotrya na ih rezul'tativnost'
ya o nih rasskazat' ne smogu po prichine maksimal'noi zhestokosti,
- ya eto kstati
smotrel po teleperedacham.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(D. V. Tret'yakov,
19.09.2012 12:33, 177 Bait)
Spasibo za podrobnuyu informaciyu o Chernyh dyrah.Priglashayu vseh lyubitelei astronomii otpravit'sya v uvlekatel'noe virtual'noe
puteshestvie.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.09.2012 21:40, 365 Bait)
Ne ponimayu pochemu na skai tehe ne sdedayut na al'ternativnom vetku,
- Tol'ko dlya storonnikov efira, v ponimanii togo chto dviglo foruma
nikakoe.
Budet
takaya vetka, to hot' o efire mozhno budet pogovorit'
i vseh kto ne v teme banit' po ai pi, po pervoi zhalobe treh
storonnikov efira - kak chuzhdyi element, i snosit'
vse teksty zabanenogo.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.09.2012 21:48, 575 Bait)
Estestvenno prichinu zabanivaniya trem storonnikam
efira na svoei vetke - pered moderatorom nado obosnovat',
inache poluchitsya erunda.
Po skol'ku al'ternativnoe
prevratilos' v gadyushnik,
v kotorom vse vyskazyvayut dazhe ne mysli,
a bredyatinu ne imeyushuyu nikakogo fizicheskogo
obosnovaniya, - vzbrelo naprimer chto-to etakoe
v golovu - i uzhe schitaet chto eto teoriya i dumaet
chto on uchennyi, i pishet potom - ya myslyu zakinul
ibo ya genii a Vy lo -- hi ee razveite
do urovnya nobelevskoi
premii, i prishlite mne priglashenie
na vruchenie.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.09.2012 21:55, 504 Bait)
---ya myslyu zakinul
ibo ya genii a Vy lo -- hi ee razveite
do urovnya nobelevskoi
premii, i prishlite mne priglashenie
na vruchenie.---
Ya utriruyu estestvenno - no sut' voprosa ne menyaet.
V principe banit' mozhno vseh kto ne
delaet obosnovanii
i opredelenii, ne sostavlyaet fizicheskih vzaimosvyazei s prichinno
sledstvennoi svyaz'yu, ili ne privodit opytov s kommentariyami,
- po prichine
togo chto bez etogo -
fiziki ne byvaet.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.09.2012 17:09, 1.6 KBait)
 Re: Mirovaya efirodinamicheskaya gonka ob'yavlena
Re: Mirovaya efirodinamicheskaya gonka ob'yavlena
Otvet #659 - Segodnya :: 07:02:31
Mihail Surin pisal(a) 13.09.12 :: 00:37:49:I raboty br. Brusinyh dayut osnovaniya dlya ser'eznogo issledovaniya etih gazo- veshestvennyh smesei.
Eti brat'ya?
http://youtu.be/v1OdvrrorPY--------------------
Da uzh - ne znayu dazhe chto skazat', - v takom vozraste zanimat'sya
fizikoi i dumat' chto rezul'tat - budet, - eto samoobman,
lichno mne dazhe voprosy po efiru zadavat' im ne smeshno,
konkurentami ih ne schitayu - im eshe nado evolyucionirovat'
do menya, estestvenno chto efiristov slegka pozoryat,
no svoyu auditoriyu
nedalekih, domohozyaek i pensionerov oni naidut.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.10.2012 18:11, 1.6 KBait)
Otvet #1182 : Segodnya v 16:46:22
Vse relyativistskie effekty STO sovershenno otnositel'ny, (chto i otlichaet
ih ot sootvetstvuyushih effektov OTO).
Naprmer,
effekt relyativistskogo szhaniya dliny v napravlenii dvizheniya odinakovo
nablyudaetsya v obeih ISO. No ne mozhet zhe v obeih ISI proishodit' real'noe
izmenenie dliny...
Real'noe,
potomu chto podlezhit izmereniyu. Dlya etogo (dlya izmerenii) sistemu
otscheta i pridumali. Iz preobrazovanii Lorenca sleduet, chto po
rezul'tatam izmerenii v raznyh ISO, dvizhushihsya otnositel'no drug druga,
dlina odnogo togo zhe sterzhnya budet raznoi.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vot tak vse prosto \\\podlezhit izmereniyu\\\
- pri polnom otsutstvii fizicheskogo
opyta, i metodiki izmerenii, tak-zhe otsutstvuet izmeryaemyi fizicheskii
pribor i edinica izmereniya, kak govoritsya -
\ vse
horosho,
prekrasnaya markiza
i horoshi u nas dela \ S \.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.10.2012 18:16, 344 Bait)
\\\dlina odnogo togo zhe sterzhnya budet raznoi\\\
Eto logika matematika v fizike, ibo matematiku
do lampochki na fiziku tel i svoistva fizicheskih tel,
matematiku
glavnoe chto-by raschety sovpadali,
a chto fizicheski eto nevozmozhno matematiku
do lampochki, on eto nazyvaet paradoks.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.10.2012 20:55, 1.0 KBait)
| Re: Chernaya dyra
|
26.12.201014:31 |
|
G.A.Zubkov
"Pochemu
vse zabyvayut o
relyativistskom
sokrashenii
razmerov?"
Mne priyatno vstretit' tolkovogo relyativista,
kotoryi v prakticheskom primenenii pol'zuetsya
relyativiskimi sokrasheniyami v bytu.
U menya vopros, - kosmonavt v kosmicheskom korable
derzhit v rukah futbol'nyi myach, korabl' razgonyaetsya
do dvukratnogo sokrasheniya dlinny, posle chego
kosmonavt
s myachom v rukah povorachivaetsya na 90
gradusov otnositel'no napravleniya dvizheniya,
so splyushennym myachom v rukah, posle chego korabl'
nachinaet tormozhenie, u kosmonavta
v rukah
v itoge okazalsya splyushennyi myach dlya regbi,
- vopros kakoi vneshnii vid kosmonavta? |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.10.2012 0:42, 1.1 KBait)
Davno chital knizhku pro mozgovoi shturm.
Chtoby byli v kurse eto primenyaetsya dlya organizacii
kollektivnoi raboty pri prakticheski neogranichennom
finansirovanii
kogda vazhno v krotchaishii promezhutok
vremeni reshit' zadachu i bez razlichno skol'ko eto budet
stoit'.
Eto primenyalos' vpervye pri razrabotke reaktivnogo
dvigatelya, po skol'ku razrabotchiki nichego ne mogli
pridumat'.
I mne trizhdy smeshno kogda kakoi-to yuzer
ispol'zuet slovosochetanie \ mozgovoi shturm \
v
halyavnom variante na sharu bez bezbashennogo
finansirovaniya - eto napominaet dekoracii
durdoma a ne popytki mozgovogo shturma.
No krasivo i bessmyslenno
forum nazyvat' ne zapretit'.
-------------
: Segodnya v 22:35:33
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.11.2012 13:56, 2.7 KBait)
 Voprosy po teorii otnositel'nosti (STO i OTO)
Voprosy po teorii otnositel'nosti (STO i OTO)
Vot nablyudayu kak lyudi bessmyslenno tratyat svoe vremya
na forumah v reshenii opredelennyh fizicheskih
zadach v relyativistskih \igrovyh poligonah\.
Sobstvenno dopuskayut pri etom dve oshibki
oni ne proverili sootvetstvie postuliruemogo
po otnosheniyu k zayavlennomu fizicheskomu opytu.
Vtoraya oshibka - popytka
naiti otvety na
voprosy kotorye dolzhen byl dat' avtor
teorii, esli vtor ih ne dal to iskat'
ih nel'zya ibo v ramkah teorii ---
Tol'ko avtor imeet pravo
davat' traktovku.
------------------------------------------------------------------
Slozhnost' zadachi na samom dele dlya fizika
ochen' legkaya.
Berem opredelenie ---
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,1165.0.html
E Shmutcer (uchenik Einshteina) utverzhdaet
( Teoriya otnositel'nosti i
sovremennoe predstavlenie,
MIR, Moskva, 1981, str.90):
Relyativistskoe sokrashenie dliny :
prichina kroetsya v 4-h mernosti prostranstva-vremeni.
Effekt
sokrasheniya voznikaet pri proecirovanii 4-h mernogo
prostranstva-vremeni na metricheskoe 3-h mernoe prostranstvo
Sobstvenno chto mozhno skazat' chto
v dannom sluchai
interesuet sleduyushaya situaciya - nalozhenie
odnoi dvizhusheisya sistemy na druguyu bazovuyu.
Sobstvenno pod eto delo est' narisovannyi
umozritel'nyi i ne proverennyi na praktike
v sootvetstvii s risunkom.

Chto nablyudaem
na risunke \a\,
na risunke nablyudaem nesootvetstvie
zayavlennyh relyativistami svoistv i metodov
slozheniya skorostei pri povorote svetovogo generatora,
na 90 gradusov, takzhe nablyudaem raznye
dlinny svetovogo lucha sootvetstvenno nablyudaem
raznye skorosti sveta, chto slivaet zaodno
v intellektual'nuyu kanalizaciyu
i postulat
postoyanstva skorosti sveta, vmeste
s \\\relyativistskim effektom Doplera\\\ - kotoryi ne imeet
nichego obshego s Effektom Doplera, zdes' nel'zya putat',
ibo \\\relyativistskii effekt Doplera/// dlya pustoty - ego pridumali
relyativisty dlya sebya i svoih teorii, a nastoyashii effekt Doplera,
byl priduman zadolgo
do relyativizma i on isklyuchitel'no dlya
kolebanii v sredah. .
Vyvod - dannoe utverzhdenie relyativistov o sokrashenii
dlinny v dvizhenii, i metody slozheniya
skorostei
- ne imeyut smysla, i ne imeyut nikakogo otnosheniya
k fizike.
Sledovatel'no vse zadachi v ramkah zayavlennyh teorii
ne imeyut fizicheskogo i prakticheskogo
smysla.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.11.2012 0:45, 5.7 KBait)
------------
Byvaet
priyatno vspomnit' kakaya byla intellektual'naya
bor'ba na membrane.
Ya togda ot nechego delat' posle togo kak pyat' principov zhps,
s saita drugogo pokazal, potom
rasskazal ka by ya delal zhps,
posle chego, takzhe obsuzhdalsya vopros po pervym atomnym
chasam i kogda ih podnimali na vysotu to-li v 1936 ili v 1939,
s chego sdelali
vyvod chto s povysheniem vysoty temp hoda
chasov uvelichivaetsya.
Zhps iznachal'no ne mog soderzhat' relyativistskih popravok,
tak kak ego pridumali, nemeckie professora
na osnove
dovoennyh germanskih razrabotok, i osnovnye
principy zhps byli pridumany
v 1958 godu.
Ya tak ponimayu chto nikto ne ponyal kolenkor situacii,
po relyativistskim teoriyam hod tempa chasov na orbite,
zamedlyaetsya a po faktu u atomnyh chasov, hod tempa
chasov uvelichivaetsya.
Delo v tom chto sputnik
mozhet nahoditsya uslovno nepodvizhno
po otnosheniyu k Zemle, a temp hoda chasov
na orbite pri nepodvizhnosti k Zemle
povyshaetsya.
Ya estestvenno pro
eto chital mnogo, takzhe chital chto
teoreticheski mogli sdelat' chasy kotorye by ne izmenyali
temp hoda s naborom vysoty,
no v svoe vremya ya tak ponyal reshili ne
afishirovat'
kak delat' eti chasy, i takih chasov net,
i vryad-li ih pridumayut v obozrimom budushem.
---------------------------
Avtor Soobshenie
Karim
Haidarov klassiku yadernoi fiziki F. Vinterbergu - 80 let 9.06.2009 6:55
Fridvardt VINTERBERG
(Friedwardt Winterberg)
Zhivomu
klassiku yadernoi fiziki Fridvardtu Vinterbergu ispolnilos' 80 let.
Nemecko-amerikanskii fizik teoretik i eksperimentator nyne yavlyaetsya professorom- issledovatelem
v Nevadskom Gosuniversitete, Reno. On imeet bolee chem s 260 nauchnyh publikacii v tom chisle tri izvestnyh monografii v oblasti yadernoi fiziki, fiziki plazmy i interpretacii
plankovskoi sistemy estestvennyh edinic.
Ego rabota po yadernoi raketnoi tyage poluchila v 1979 Zolotuyu medal' Germana Obersta, medal' Vernera fon Brauna Mezhdunarodnogo
fonda kosmicheskih poletov, a s 1981 goda F. Vinterberg pochetnyi grazhdanin shtata Nevada.
On takzhe pochetnyi chlen Nemeckogo aviakosmicheskogo obshestva Lilientalya -
Obersta.
Prof. Vinterberg izvesten svoimi ideyami, kotorye priveli k razrabotke GPS, ego rabotami v oblasti yadernogo sinteza i ego pervym predlozheniem eksperimental'noi
proverki teorii El'zassera o geodinamo. On izvesten ego publichnymi usiliyami po zashite raketnogo uchenogo Artura Rudol'fa i ego uchastiem v issledovanii konflikta o prioritete
mezhdu Al'bertom Einshteinom i Davidom Gil'bertom v oblasti obshei teorii otnositel'nosti. Sm hilbert.pdf.
Biografiya
Fridvardt Vinterberg rodilsya 9 iyunya
1929 v Berline, Germanii. V 1953 on okonchil universitet vo Frankfurte, rabotal pod rukovodstvom Fridriha Gunda i v 1955 zashitil doktorskuyu dissertaciyu PhD po fizike v Institute
imeni Maksa Planka v Gettingene kak doktorant Vernera Geizenberga. Pozzhe po priglasheniyu yadershikov on pereehal v Soedinennye Shtaty i stal grazhdaninom SShA.
Raboty
Vinterberga v oblasti yadernogo sinteza i fiziki plazmy shiroko izvestny. Edvard Teller, s kotorym on rabotal, pisal o nem, chto on vozmozhno ne poluchil togo vnimaniya, kotoroe
on zasluzhivaet po urovnyu svoih rabot po yadernomu sintezu. Odnako eto bylo tipichnym dlya fizikov yadershikov togo vremeni, delavshim vazhnye raboty v zakrytyh oblastyah nauki.
On byl izbran chlenom Mezhdunarodnoi akademii astronavtiki, v Parizhe, v kotoroi on byl chlenom Komiteta mezhzvezdnyh kosmicheskih issledovanii.
V 1954 on pervym
sdelal predlozhenie testirovat' obshuyu teoriyu otnositel'nosti po atomnymi chasam na okolozemnyh sputnikah i predlozhil sposob primeneniya yadernogo mobil'nogo reaktora dlya sozdaniya
raketnyh yadernyh dvigatelei putem nagreva rabochego tela v aktivnoi zone reaktora. Etot sposob byl prinyat v izvestnom amerikanskom proekte yadernogo raketnogo dvigatelya Nerva
i Britanskim mezhplanetnym obshestvom za bazovyi sposob v razrabotke ih proekta Daedalus Starship Analysis. Ego segodnyashnie issledovaniya nahodyatsya v oblasti gipotezy efira Planka,
- novoi teorii, kotoraya ob'yasnyaet kak kvantovuyu mehaniku, tak i teoriyu otnositel'nosti kak asimptoticheski nizkie energeticheskie approksimacii i daet spektr chastic sushestvenno
shodnyi so standartnoi model'yu.
Professorom Vinterbergom predlozhena teoriya, soglasno kotoroi edinstvennymi svobodnymi parametrami v fundamental'nyh uravneniyah fiziki
yavlyayutsya dlina, massa i vremya Planka (kotorye seichas prinyato nazyvat' fundamental'nymi edinicami Planka) i pokazyvayut pochemu R3 trehmernoe evklidovo prostranstvo - estestvennoe
prostranstvo, i chto SU2 mozhet rassmatrivat'sya kak fundamental'naya gruppovaya izomorfiya na SO3 - al'ternativa uslozhneniya mira do teorii 10-mernogo prostranstva R10 i teorii
M v R11. Vinterberg pokazal, chto velichina konstanty tonkoi struktury na dline Planka tochno soglasuetsya s empiricheskoi velichinoi.
Professor Vinterberg shiroko publikovalsya
vo mnogih oblastyah fiziki nachinaya s 1950-h godov i do nastoyashego vremeni. V 2008 godu na Mezhdunarodnoi konferencii po teorii otnositel'nosti Vinterberg raskritikoval teoriyu
strun i otmetil nedostatki obshei teorii otnositel'nosti Einshteina iz-za ee nesposobnosti soglasovaniya s kvantovoi mehanikoi.
Ssylki:
World Science Database
http://www.worldnpa.org/php2/ index.php?tab0=Scientists&tab1=Display&id=282
Nevada University Site http://www.physics.unr.edu/FacWinterberg.html
Bourabai Research Site http://bourabai.kz/
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.11.2012 0:48, 2.6 KBait)
KarimHaidarov
|
Re: klassiku yadernoi fiziki F. Vinterbergu - 80 let
|
20.06.200913:45 |
|
|
Fridvardt VINTERBERG
(Friedwardt Winterberg)
(prodolzhenie)
GPS sistema
V 1955 v svoei stat'e v nauchnom zhurnale
ASTRONAUTICA ACTA F. Vinterberg predlozhil proverku obshei teorii otnositel'nosti i izmereniya
prostranstvennyh koordinat putem ispol'zovaniya atomnyh chasov ustanovlennyh na iskusstvennom sputnike
Zemli. V to vremenya ni atomnyh chasov, ni iskusstvennyh sputnikov eshe ne bylo, odnako iedya Vinterberga
osnovyvalas' na dostizheniyah i ideyah dovoennoi Germanii, gde eshe v 1937-1939 godah byli proizvedeny zapuski
ballisticheskih raket V-2 Vernera fon Brauna
(Werner von Braun) v kosmicheskoe
(bezvozdushnoe) prostranstvo, chto bylo podgotovkoi k osushestvleniyu orbital'nogo poleta. Ideya atomnyh chasov
tozhe uzhe sushestvovala v svyazi s otkrytiem stabil'nosti spektrov izluchenii kvantovoi fizikoi. V 1957 godu F. Vinterberg
poluchil pis'mo ot svoego nauchnogo rukovoditelya Vernera
Geizenberga (Werner Heisenberg) s
vyrazheniem entuziazma po povodu idei Vinterberga, kotorye segodnya polozheny v osnovu global'noi
navigacionnoi sistemy GPS.
Ssylki:
Wikipedia Free Encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Friedwardt_Winterberg
World Science Database http://www.worldnpa.org/php2/
index.php?tab0=Scientists&tab1=Display&id=282
Nevada University Site http://www.physics.unr.edu/FacWinterberg.html
Bourabai Research Site http://bourabai.kz/ |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.01.2013 13:08, 764 Bait)
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1354298449/140
Baryshnya svoei horoshei pamyat'yu i prirodnym kachestvennym
bystrym analiticheskim podhodom,
prosto intellektual'no izdevaetsya
- zhestokoe zrelishe ne dlya slabonervnyh.
Tak porvat' intellektom - eto zhestoko, samoe smeshnoe chto i bespolezno,
ibo tupost'
vechna, ee opponenty v vidu svoih umstvennyh sposobnostei
nikogda ne sdelayut vyvody iz etoi situacii, i nikogda ne pomenyayut
logiki i bazovyh istin v svoem myshlenii
- budut tupit' vechno.
Baryshnya molodec - kak fizik ona slaba - no ona specialist po prichinno
sledstvennym svyazyam - a eto dlya \zvezdunov\ samaya strashnaya i besposhadnaya
terminatosha kotoraya vyvedet na chistuyu vodu vse \laino\ v fizike.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.01.2013 20:10, 1.3 KBait)
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1350558609/2547#2547
 Re: Efir dlya chainikov.
Re: Efir dlya chainikov.
Otvet #2548 - Segodnya :: 16:45:06
---------------
Ya estestvenno na storone
EngineAlex
on menya nemnogo po-kopiroval no emu mozhno,
a
Vallav
gnusno vyglyadit ego zhaba davit podprygivaet ne hvataet intellekta
obosnovat' svoi zakidony i prosit v kazhdom bryke ob'yasnit'
emu v chem on ne
prav - takih nado prosto banit' ibo chtoby ne bylo takih otvlekayushih
osnovnuyu temu, ili prosto prinyat' v pravilah foruma - ban tomu na nedelyu
kto poprosil ukazat' na vtrechnyi vopros v chem ne pravota oprovergayushego i
sprashivayushego odnovremenno.
Oprovergayut i odnovremenno sprashivayut o svoei pravote
- tol'ko nedalekie.
Ih mozhno banit' aki pol'zy ot nih v fizike ne budet i ne-bylo.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A. S. Ivanov,
8.01.2013 3:05, 471 Bait, otvetov: 1)
A znaete li vy, chto
nikto nikogda ne fotografiroval chernuyu dyru - eto nevozmozhno, tak kak oni pogloshayut vse svetovye volny vnutr' iz-za sil'noi gravitacii. Vse izobrazheniya chernyh dyr sdelany
chelovekom v Fotoshope i podobnyh programmah.
Istochnik:http://facty.at.ua
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
8.01.2013 10:55, 409 Bait)
Ocherednoi
perenos
laboratornyh
processov
v
astronomicheskoe
pole.
Pri
etom
imeem
delo
s
polnym
masshtabnym
neuchetom
-
processy
v
atomah
proeciruyutsya
na
prostranstva.
I
chetko
opredelimsya
-
tema
astronomicheskaya,
a
ne
fizicheskaya
i
rech'
idet
ob
astroob'ektah.
V
etom
sluchae
elementarnye
chasticy
rassmatrivat'sya
ne
dolzhny
voobshe
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.01.2013 10:37, 38.2 KBait)
------------------
| Re: Chernaya dyra
|
7.02.20122:47 |
|
Po chernoi dyre eshe
http://siteua.org/system_category/330344
\\\"Do sih por nikto i nikogda ne fotografiroval
chernye
dyry, vvidu slozhnosti etogo meropriyatiya i ekzoticheskoi prirody samih
dyr", - govorit Dimitrios Psaltis, astronom iz Universiteta Arizony i
odin iz koordinatorov proekta.\\\
Sobirayutsya pervuyu fotografiyu chernoi dyry sdelat', i vsem do lampochki chto bez takovoi,
uzhe tysyachi statei o chernoi dyre napisali.
Delo ne v fotografii na samom dele, net obshei formulirovki chernoi dyry -
kazhdyi vidit v svoih izyskaniyah to chto on hochet i nazyvaet eto chernoi dyroi
- i eto
smeshno, - klassika zhanra.
\\\.Material
iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi.... \\\
-----------------------------------
http://www.lenta.ru/news/2012/01/19/prize/
Astronomicheskoi
nagrady udostoilis' Reinhard
Gencel' (Reinhard Genzel) i
Andrea Gez (Andrea Ghez). Premiya byla prisuzhdena etim uchenym za
obnaruzhennye imi i ih sotrudnikami vesomye dokazatel'stva togo, chto v
centre Mlechnogo Puti nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya chernaya dyra. Oba astronoma
nablyudali zvezdy, obrashayushiesya vokrug centra Galaktiki i prishli k
odnomu i tomu zhe vyvodu nezavisimo drug ot druga.\\\
|
-----------------
| Re: Chernaya dyra
|
7.02.201217:42 |
http://www.popmech.ru/article/10479-dyira-kak-vyiklyuchatel/page/4/
\\\Skorost' rozhdeniya novyh zvezd v nekotoryh dalekih galaktikah tak velika, chto process etot nazyvayut
pryamo vspyshkoi
zvezdoobrazovaniya. Process etot, odnako, lish' vremennyi, i dovol'no skoro prekrashaetsya i sudya po vsemu, vinovaty v etom mogut byt'sverhmassivnye
chernye dyryv centrah etih galaktik.\\\
Vot tozhe stat'ya napolnennaya idiotizmom, i zhelaniem
ne s'est' tak po-nadkusyvat'.
Eto yarkii primer togo
do chego dovodit syusyukan'e
i potokatel'stvo. Vmesto togo chtoby otkryto skazat'
chto mol - pshel von dybil s takoi stat'ei
v kotoroi vse neponyatno i otsutstvuet
smyslovaya
vzaimosvyaz', - tak tak nikto ne pishet v kommentariyah,
a avtor dumaet chto pipl havaet, i emu nravitsya -
i avtor budet pisat' sleduyushuyu stat'yu s eshe
bol'shim
idiotizmom i neskladushkami.
A v normal'nom i zdravom vide stat'ya by vyglyadela
sleduyushaya -
obnaruzhili korotkie i yarkie vspyshki, zvezdo-obrazovanie
ili zvezdnye vspyshki neizvestno, pod ni odnu iz teorii
ne podhodit, ni v kakoi iz izvestnyh teorii podobnyi sluchai
ne opisyvalsya.
Kstati o chernyh
dyrah oni tozhe myamlili, ponadkusyvali
- v stile mol, chto esli u kakogo-to sleduyushego pisatelya budet
neshto podobnoe v pripadke genial'nosti, tak pust' on mol znaet
v nashem pripadke bessoznatel'nogo idiotizma bylo vpervye.
Eto pipec, no pipl havaet astronomam nravitsya, mne smeshno.
--------------------------------------------
|
|
Re: Chernaya dyra
|
19.09.201112:14 | |
Chto
menya udivlyaet, - tak
eto to chto vsya astrofizika krasivaya i pushistaya,
i vse prekrasno.
No eto zhe ne tak, vot te-zhe chernye dyry - eto zhe
prosto pipec - i chto eto nikto ne zamechaet
ili nikto ne
ponimaet.
Hochu srazu sprosit', Vashe mnenie po
...Chernaya dyra...
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188232
Soglasny li Vy s etim?
Kakie iz perechislennyh statei sootvetstvuyut standartam Chernoi
Dyry?
1 Est' li zhizn' v chernoi dyre
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8822-est-li-zhizn-v-chernoy-dyire/
2[ssylka]
Ustanovlena massa samoi krupnoi iz sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr.
Takoe nam i ne snilos'.
3[ssylka]
Mifologiya chernyh dyr.V nashei Galaktike sushestvuyut milliony chernyh dyr
massoi v neskol'ko solnechnyh
4http://www.popmech.ru/article/8140-raspad-dyiryi/
Raspad dyry.
Vzryv sverhnovoi mozhet zakanchivat'sya obrazovaniem ne odnoi, a srazu
neskol'kih chernyh dyr.
5[ssylka]
Detstvo chernoi dyry
Vzryv, zafiksirovannyi v glubinah kosmosa 31 god nazad, sudya po vsemu,
znamenoval rozhdenie chernoi dyry samoi molodoi iz nam izvestnyh
6[ssylka]
Temnyi centr
Tainstvennyi centr nashei galaktiki,
mesto obitaniya sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyry i istochnik moshneishih potokov izlucheniya,
prepodnosit novye syurprizy.
7[ssylka]
Nebol'shoe zamechanie o prirode gravitacii privodit k sledstviyam
kosmicheskogo masshtaba k vyvodam o rozhdenii novyh mirov iz chernyh dyr
8[ssylka]
Obychnaya po razmeram chernaya dyra vybrasyvaet
kolossal'nye potoki izlucheniya i chastic.
9[ssylka]
Astrofiziki predlozhili sposob (teoreticheski) unichtozhit' chernuyu dyru
10[ssylka]
Iz vseh sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr lish' okolo 1% vybrasyvayut
znachitel'nye kolichestva energii
11[ssylka]
Vyzhivayushie dyry
Para redkih ekzemplyarov
V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
kakim-to chudom vyzhivayushih v sosedstve s etim monstrom.
12[ssylka]
Kak zhivetsya vnutri chernoi dyry? Vy i sami znaete,
kak: esli spravedlivy novye teoreticheskie vykladki,
vsya nasha Vselennaya mozhet nahodit'sya vnutri chernoi dyry,
raspolozhennoi v drugoi Vselennoi. Edakaya matreshka mirozdaniya.
13[ssylka]
Oni prosto predpolozhili, chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu. Eto dalo cifru v 10103, tozhe ogromnuyu, no vse-taki na mnogo
poryadkov nizhe.
14[ssylka]
Esli ochen', ochen' bystryi kosmicheskii korabl' razognat'
pochti do skorosti sveta, prevratitsya li on v chernuyu dyru?
15[ssylka]
Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
---------------------------------------------------------
| Re: Chernaya dyra
|
19.09.201112:38 |
|
1 Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
2
V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
3 Oni prosto predpolozhili,
chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu.
Material iz
Vikipedii
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/39/M87_jet.jpg/250px-M87_jet.jpg
Izobrazhenie, poluchennoe s pomosh'yu teleskopa Habbl: Aktivnaya galaktika
M87. V yadre galaktiki, predpolozhitel'no, nahoditsya chernaya dyra. Na
snimke vidna relyativistskaya struya dlinoi okolo 5 tysyach svetovyh let
Relyativistskie strui
, dzhety (angl. jet) strui plazmy, vyryvayushiesya iz centrov (yader) takih
astronomicheskih ob'ektov, kak aktivnye galaktiki, kvazary i
radiogalaktiki.
Obychno u ob'ekta nablyudaetsya dve strui, napravlennye v protivopolozhnye storony.
Na nastoyashii moment relyativistskie strui ostayutsya nedostatochno izuchennym
yavleniem. Prichinoi poyavleniya takih strui chasto nazyvayut vzaimodeistvie
magnitnyh polei s akkrecionnym diskom vokrug chernoi dyry ili neitronnoi
zvezdy.
V stat'e na Elementah metodom chislennogo modelirovaniya pokazano, chto
pri sliyanii dvuh neitronnyh zvezd obrazuetsya chernaya dyra, magnitnoe pole
kotoroi vytyanuto vdol' osi. Eto navodit na mysli, chto etot zhe process
mozhet formirovat' i relyativistskie strui. Tem ne menee, v stat'e
govoritsya, chto predlozhennaya avtorami nauchnoi raboty matematicheskaya
model' okazalas' ochen' slozhna, a vychislitel'nye vozmozhnosti sovremennyh
komp'yuterov okazalis' nedostatochny, chtoby s dolzhnoi tochnost'yu provesti
vse neobhodimye raschety i ubeditel'no dokazat' formirovanie strui.
V drugoi stat'e na Elementah provodyatsya paralleli mezhdu processami v
chernyh dyrah i boze-einshteinovskom kondensate. Otmechaetsya chto kondensat
mozhet kollapsirovat' (slipat'sya) i pri posleduyushem ego raspade tozhe
mogut voznikat' uzkonapravlennye vybrosy.
Dal'neishee izuchenie relyativistskih strui
Pri samyh pervyh popytkah ob'yasneniya sverhsvetovogo dvizheniya s pomosh'yu
relyativistskogo napravlennogo potoka chastic vozniklo oslozhnenie:
udivitel'no bol'shaya dolya kompaktnyh istochnikov pokazyvala sverhsvetovoe
dvizhenie, v to vremya kak na osnovanii prostyh geometricheskih dovodov
poluchalos', chto tol'ko neskol'ko procentov takih ob'ektov dolzhno byt'
sluchaino orientirovano pochti vdol' linii zreniya. Prisutstvie
simmetrichnyh protyazhennyh radiokomponent predpolagalo, chto oni
obespechivalis' energiei ot central'nogo istochnika dvuh simmetrichnyh
luchei. No trudno sravnit' svetimost' priblizhayusheisya i udalyayusheisya (ili
dazhe stacionarnoi) komponent. Eto ochevidnoe razlichie obychno obsuzhdaetsya v
kontekste modeli s dvoinym istecheniem [4], kogda izluchenie iz yadra
rassmatrivaetsya kak stacionarnaya tochka, gde priblizhayushiisya
relyativistskii potok stanovitsya neprozrachnym. Sverhsvetovoe dvizhenie
nablyudaetsya mezhdu etoi stacionarnoi tochkoi v sople i dvizhushimisya
volnovymi frontami ili drugimi neodnorodnostyami v vyhodyashem
relyativistskom potoke.......
.....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie (gamma-luchi, γ-luchi)
vid elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s chrezvychaino maloi dlinoi volny
< 5×10−3 nm i, vsledstvie etogo, yarko vyrazhennymi korpuskulyarnymi
i slabo vyrazhennymi volnovymi svoistvami.
Gamma-kvantami yavlyayutsya fotony s vysokoi energiei. Obychno schitaetsya,
chto energii kvantov gamma-izlucheniya prevyshayut 105 eV, hotya rezkaya granica
mezhdu gamma- i rentgenovskim izlucheniem ne opredelena. Na shkale
elektromagnitnyh voln gamma-izluchenie granichit s rentgenovskim izlucheniem,
zanimaya diapazon bolee vysokih chastot i energii. V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu. Ochevidno,
fizicheski kvanty elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s odinakovoi energiei ne
otlichayutsya, poetomu takoe razdelenie uslovno.
Gamma-izluchenie ispuskaetsya pri perehodah mezhdu vozbuzhdennymi
sostoyaniyami atomnyh yader (sm. Izomernyi perehod, energii takih
gamma-kvantov lezhat v diapazone ot ~1 keV do desyatkov MeV),
pri yadernyh reakciyah (naprimer, pri annigilyacii elektrona i pozitrona,
raspade neitral'nogo piona i t.d.), a takzhe pri otklonenii energichnyh
zaryazhennyh chastic v magnitnyh i elektricheskih polyah (sm. Sinhrotronnoe izluchenie).....
Esli net poverhnosti ob kotoruyu proishodit tormozhenie.
Material iz Vikipedii
.....Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh
obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v rentgenovskih
trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok yavlyayutsya
metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe antikatodom).
V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom, uskoryayutsya
pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom i katodom
(pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak uskorenie slishkom malo)
i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe tormozhenie. Pri etom za schet
tormoznogo izlucheniya proishodit generaciya izlucheniya rentgenovskogo diapazona,
i odnovremenno vybivayutsya elektrony iz vnutrennih elektronnyh obolochek atomov
anoda. Pustye mesta v obolochkah zanimayutsya drugimi ....
To vstupaet v silu fraza -
V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.
sledovatel'no pri otsutstvii udara o poverhnost' - otsutstvuet sama vozmozhnost'
vozniknoveniya rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, a esli izluchenie est' to ono mozhet
byt' tol'ko rezul'tatom izlucheniya v yadernom perehode. A eto uzhe chasticy vysokih energii.
avtorskoe izluchenie iz chernoi dyry -
.Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash metod obnaruzheniya Chernoi Dyry
-Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
....Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo.
ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut. ....
Padaya na Chernuyu Dyru veshestvo ne
mozhet rezko tormozitsya ili rezko uskoryatsya,
a sledovatel'no - ne mozhet
byt' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya po etoi prichine.
V svyazi s tem chto dlya uskoreniya do skorosti sveta
pri kotorom vozmozhno izluchenie neobhodimo
ne bolee 10 sekund, a zvezda razmerom s
Solnce na takoi skorosti proletit cherez gorizont
sobytii maksimum za minutu.
Gorizont sobytii - eto skorost' sveta - esli
ob'ekt uletaet s etoi skorost'yu ot nablyudatelya, to
u nego vozniknet krasnoe smeshenie.
Esli by veshestvo dolgo padalo - godami na maloi skorosti
s uskoreniem to bylo by zametno izmenenie Z u padayushih
tel v chernuyu dyru so vremenem, no pri etom nevozmozhno
rentgenovskoe izluchenie - iz za slishkom medlennogo
uvelicheniya uskoreniya.
.... Material iz Vikipedii Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri
vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah.....
A rentgenovskoe izluchenie est' - sledovatel'no
ego istochnikom mozhet byt' tol'ko rezul'tat yadernoi
reakcii.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.....
A esli rezul'tat izlucheniya istochnik yadernoi reakcii -
i on dlitsya godami, - to eto neitronnaya zvezda.
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8971-nasledstvennyie-chernyie-dyiryi/page/3/
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke, ya tak ponyal reshil -
zachem dobru propadat' - pust' izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi
dyry budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Vashe - Rentgenovskoe izluchenie ChD voznikaet pri akkrecii veshestva.
Izluchenie Hokinga - drugoi process. Stranno, chto za 7 let "uvlecheniya
astrofizikoi" Vy etogo ne ponyali.
Moe - S moei tochki zreniya - uvazhaemyi A.M.ChEREPAShUK imeet takoe zhe otnoshenie
k Chernym Dyram kak ya ili Vy.
My s Vami, i A.M.ChEREPAShUK mozhem tol'ko predpolagat' i vyskazyvat'
svoyu tochku zreniya, no obrashat' vnimaniya na podobnye vyskazyvaniya i brat'
ih na veru, ya ne vizhu smysla.
Drugoe delo avtor. Kak on skazal to - takie i Chernye Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vot ya naprimer govoryu chto veshestvo padaet na chernuyu dyru,
i posle udara o poverhnost' s protivopolozhnoi storony chernoi dyry voznikaet rentgenovskoe i svetovoe izluchenie.
Drugoi schitaet chto izluchenie na podlete.
V binokl' ne vidno - odni predpolozheniya, i ih mozhet byt'
bol'she sotni naprimer - komu verit'?
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vy zatragivaete vopros interpretacii avtorskih
idei bez soglasiya s avtorom.
A esli desyatok drugih avtorov opublikuyut po 300 nauchnyh rabot, a avtor o
Chernyh Dyrah govorit chto izluchenie v osnovnom iz fotonov - a vse drugie
govoryat, chto
izluchenie iz rentgenovskih chastic, drugoi govorit iz radio izlucheniya, a
tretii govorit iz gamma chastic - ya dolzhen slushat' isklyuchitel'no avtora
Chernyh Dyr,
a ne teh kto interpretiruet, i tem bolee teh kto plevat' hotel na avtorskii variant chernyh dyr.
Nikto ne meshaet pridumat' svoi - rentgenovskie chernye dyry, - tak net ne
hotyat, - tak na neudobnye voprosy otvechat' dolzhen budet avtor, a pri
interpretacii avtora - pisaka naprimer stat'i s levymi ideyami v oblasti
Chernyh Dyr, prikryvaetsya avtorstvom avtora
Chernyh Dyr, a sam so svoim bredom po otnosheniyu k avtorskomu izlozheniyu, kak-by i ne prichem.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
..Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii). Tochnee,
razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Vasha ssylka - tekst 11.05.11 20:36
....Kak otlichit' chernye dyry ot neitronnyh zvezd
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya chernaya dyra ne dolzhna proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. U nee mozhet nablyudat'sya lish' irregulyarnaya
peremennost' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya s harakternymi vremenami
$$Delta tapprox frac{r_g}{c}approx10^{-3} div 10^{-4}~mbox{rm s.}$$
I deistvitel'no, v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme Lebed' H-1, soderzhashei
chernuyu dyru s massoi okolo desyati solnechnyh, v sostoyanii, kogda
rentgenovskaya svetimost' ponizhena, a rentgenovskii spektr zhestkii i
stepennoi, nablyudaetsya bystraya irregulyarnaya peremennost' rentgenovskogo
potoka na vremenah poryadka millisekundy. Nablyudeniya, vypolnennye s
bortov sovremennyh rentgenovskih observatorii, takih, kak GINGA,
MIR-KVANT, GRANAT, ASKA, pokazali, chto rentgenovskie spektry
akkreciruyushih chernyh dyr sistematicheski bolee zhestkie, chem spektry
akkreciruyushih neitronnyh zvezd, i prostirayutsya do energii v neskol'ko
megaelektron-vol't.
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya neitronnaya zvezda mozhet proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. Odnako, esli neitronnaya zvezda obladaet
slabym magnitnym polem (napryazhennost'yu menee 1010 Gs) ili esli ee os'
vrasheniya neudachno orientirovana otnositel'no zemnogo nablyudatelya, pri
akkrecii na takuyu neitronnuyu zvezdu mogut ne nablyudat'sya regulyarnye
pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya. Poetomu otsutstvie strogo
periodicheskih pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya - eto lish' neobhodimyi,
no ne dostatochnyi priznak chernoi dyry. V to zhe vremya pri slabom
magnitnom pole neitronnoi zvezdy i nesil'nom tempe akkrecii veshestva na
ee poverhnosti mogut proishodit' termoyadernye vzryvy nakoplennogo
veshestva, privodyashie k yavleniyu rentgenovskogo barstera I tipa - korotkim
(dlitel'nost'yu poryadka 1-10 s) i moshnym vspyshkam intensivnosti
rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, chto takzhe yavlyaetsya harakternym priznakom
akkreciruyushei neitronnoi zvezdy, obladayushei tverdoi poverhnost'yu.
Poskol'ku chernaya dyra ne obladaet tverdoi poverhnost'yu, akkreciya
veshestva na nee ne dolzhna privodit' k fenomenu rentgenovskogo barstera I
tipa. Razumeetsya, otsutstvie etogo fenomena takzhe yavlyaetsya lish'
neobhodimym kriteriem nalichiya chernoi dyry. Takim obrazom, my mozhem
sformulirovat' vazhneishie priznaki akkreciruyushei chernoi dyry: eto moshnoe
rentgenovskoe izluchenie, bol'shaya massa (bolee treh solnechnyh),
otsutstvie fenomenov rentgenovskogo pul'sara ili rentgenovskogo barstera
I tipa. Pri etom vopros o nadezhnom opredelenii massy relyativistskogo
ob'ekta v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme yavlyaetsya reshayushim pri
identifikacii ego s chernoi dyroi....
Ya Vam prosto pokazyvayu proiivorechie u Vas i Vashei ssylke,
po otnosheniyu k napisannomu v Vikipedii o izluchenii iz Chernoi Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Leitenant Nemo
Chtoby proishodil razbros chastic rentgenovskogo
izlucheniya dlya etogo nado ili yadernoe gorenie zvezd,
chto k chernoi dyre ne primenimo, ili razgon materii
s posleduyushim udarom razognannoi chasticy o poverhnost'
kak eto proishodit v rentgen apparate.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Rentgenovskaya trubka
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v
elektronnyh obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok
yavlyayutsya metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe
antikatodom). V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom,
uskoryayutsya pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom
i katodom (pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak
uskorenie slishkom malo) i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe
tormozhenie. .....
Iz chego vytekaet sleduyushee chto dlya vozniknoveniya izlucheniya radioaktivnyh
chastic - neobhodim udar materii na skorosti odnoi desyatoi i bolee
skorosti sveta.
Iz chego sleduet nevozmozhnoe uslovie dlya izlucheniya materii pri padenii v
chernuyu dyru - tak kak dolzhna byt' poverhnost' dlya udara.
A poverhnosti to i net, veshestvo bez udara uhodit za gorizont sobytii,
sledovatel'no i ne mozhet chernaya dyra izluchat' radioaktivnye chasticy.
A.M.Cherepashyuk v dannom sluchai ne prav.
kosmogon
...Schitaetsya, chto pri padenii na ChD veshestvo razgonyaetsya do skorostei,
blizkih k s. V takom sluchae treniya bolee chem dostatochno dlya izlucheniya
vysokih energii. ...
Ya ne mogu ponyat' pochemu rassmatrivaetsya otdel'no vzyataya chast' i ne argumentiruetsya a postuliruetsya.
U Vas - postulat.
Vy voz'mite naprimer shar razmerom v kilometr v diametre, i bros'te ego v Chernuyu Dyru.
Nu i razognali Vy chto ugodno v pustote, - eshe raz povtoryayu - v pustote
proishodit padenie v chernuyu dyru - kakoe mozhet byt' trenie - prosto ne
ob chto teret'sya.
Voz'mite naprimer zvezdu, ei tozhe ne ob chto teret'sya kogda vokrug pustota,
letit padaet i ugasaet, tem bolee chto mne lichno
uvazhaemyi Dmitrii Mamontov raschety privodil chto zvezda na odnoi desyatoi
ili odnoi tretei skorosti sveta, mozhet prekrasno letat' na orbite
vokrug Chernoi Dyry, i s nei vse normal'no.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
,,,Chernaya dyra - oblast' prostranstva, v k-roi pole tyagoteniya nastol'ko
sil'no, chto vtoraya kosmich. skorost' (parabolicheskaya skorost') dlya
nahodyashihsya v etoi oblasti tel dolzhna byla by prevyshat' skorost' sveta,
t.e. iz Ch.d. nichto ne mozhet vyletet' - ni izluchenie, ni chasticy, ibo v
prirode nichto ne mozhet dvigat'sya so skorost'yu, bol'shei skorosti sveta.
Granicu oblasti, za k-ruyu ne vyhodit svet, naz. gorizontom Ch.d.,,,
Eto bazovoe opredelenie, dazhe esli predpolozhit' chto v chernuyu dyru padayut
zvezdy, pri etom izluchayut, i chto v centre galaktiki v chernyh dyrah
massa bol'she chem massa vseh zvezd v etoi galaktike, a s momenta bol'shogo
vzryva
togda mozhno poschitat' skol'ko milliardov zvezd v dyru v centre galaktiki
upalo. Tol'ko vot ne shoditsya s nablyudeniyami - zvezdy ne ischezayut v
chernyh dyrah - etogo nikto ne nablyudal, - ne nablyudali i to kak zvezda
prohodit cherez gorizont sobytii k chernoi dyre.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
...Ishodya iz klassiki, na kotoruyu Vy opiraetes', ChD dlya zemlyanina dolzhny svetit' kak kvazary....
Vashe - Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Moe - u menya vopros - esli v rentgen diapazone izluchayut nizhe privedennye
neitronnye zvezdy - kotorye
...V sluchae, kogda peretekanie veshestva prodolzhaetsya i posle
obrazovaniya N. z., ee massa mozhet so vremenem znachitel'no uvelichit'sya.
Pri ${mathfrak M}_{N.z.}>{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet
ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa
prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru. ...
To kak otlichit' neitronnuyu zvezdu ot chernoi dyry?
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188472
Neitronnye zvezdy
- gidrostaticheski ravnovesnye zvezdy, veshestvo k-ryh sostoit v osnovnom
iz neitronov. Sushestvovanie N. z. bylo predskazano v 30-h gg. 20
v.,vskore posle otkrytiya neitrona. Odnako tol'ko v 1967 g. oni byli
obnaruzheny v vide impul'snyh istochnikov radioizlucheniya - pul'sarov.
Zatem bylo ustanovleno, chto N. z. proyavlyayut sebya takzhe kak rentgenovskie
pul'sary (1971 g.) i vspyshechnye istochniki rentg. izlucheniya - barstery
(1975 g.). Ne isklyucheno, chto na odnoi iz stadii sushestvovaniya N. z. yavl.
istochnikami gamma-vspleskov. K 1984 g. otkryto ok. 400 N. z., iz nih
ok. 20 v vide rentg. pul'sarov, ok. 40 v vide barsterov, a ostal'nye v
vide obychnyh radiopul'sarov.
Druguyu vozmozhnost' poyavleniya N. z. predstavlyaet evolyuciya belyh karlikov v
tesnyh dvoinyh zvezdnyh sistemah. Peretekanie veshestva so
zvezdy-kompan'ona na belyi karlik postepenno uvelichivaet ego massu, i,
kogda ona dostigaet ${mathfrak M}_Ch$, belyi karlik prevrashaetsya v N. z. V
etom sluchae ${mathfrak M}_{N.z.}{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet
ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa
prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188644
Rentgenovskie pul'sary
- istochniki peremennogo periodicheskogo rentg. izlucheniya, predstavlyayushie
soboi vrashayushiesya neitronnye zvezdy s sil'nym magn. polem, izluchayushie za
schet akkrecii (padeniya veshestva na ih poverhnost'). Magn. polya na
poverhnosti R.p. ~ 1011-1014 Gs. Svetimosti bol'shinstva R.p. ot
1035-1039 erg/s. Periody sledovaniya impul'sov P ot 0,7 s do nesk. tysyach
s. R.p. vhodyat v tesnye dvoinye zvezdnye sistemy, vtorym komponentom
k-ryh yavl. normal'naya (nevyrozhdennaya) zvezda, postavlyayushaya veshestvo,
neobhodimoe dlya akkrecii i norm. funkcionirovaniya R.p. Esli vtoroi
komponent nahoditsya na stadii evolyucii, kogda skorost' poteri massy
(etim komponentom) mala (sm. Evolyuciya tesnyh dvoinyh zvezd), neitronnaya
zvezda ne proyavlyaet sebya kak R.p. Rentg. pul'sary vstrechayutsya kak v
massivnyh molodyh dvoinyh zvezdyh sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu I
Galaktiki i lezhashih v ee ploskosti, tak i v malomassivnyh dvoinyh
sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu II i prinadlezhashih k sferich.
sostavlyayushei Galaktiki. R.p. otkryty takzhe v Magellanovyh Oblakah. Vsego
otkryto ok. 20 R.p.
Na nachal'nom etape issledovanii otkryvaemym rentg. ob'ektam
prisvaivalis' naimenovaniya po sozvezdiyam, v k-ryh oni nahodyatsya. Napr.,
Gerkules X-1 oznachaet pervyi po rentg. yarkosti ob'ekt v sozvezdii
Gerkulesa, Kentavr H-3 - tretii po yarkosti v sozvezdii Kentavra. R.p. v
Malom Magellanovom Oblake oboznachaetsya kak SMC X-1, v Bol'shom
Magellanovom Oblake - LMC X-4. Obnaruzhenie so sputnikov bol'shogo chisla
rentg. istochnikov potrebovalo dr. sistemy oboznachenii.
Uskorenie i zamedlenie vrasheniya neitronnyh zvezd.
V otlichie ot radiopul'sarov (nek-rye iz k-ryh, v chastnosti pul'sary v
Krabe i Parusah, izluchayut i v rentg. diapazone, sm. Pul'sary),
izluchayushih za schet energii vrasheniya zamagnichennoi neitronnoi zvezdy i
uvelichivashih svoi period so vremenem, R.p., izluchayushie za schet akkrecii,
uskoryayut svoe vrashenie.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Spasibo za otvet.
Esli ya pravil'no ponyal, to istochnik
nepreryvnogo rentgenovskogo izlucheniya
so stabil'noi intensivnost'yu - nazyvaetsya
Chernoi Dyroi .
Esli rentgenovskoe izluchenie menyaet intensivnost'
to eto ili neitronnaya zvezda ili
rentgenovskii pul'sar.
Zdes' avtor chernyh dyr - sem' pyatnic na nedelyu,
sperva govoril vot tak -
...Chernaya dyrá oblast' v prostranstve-vremeni,
gravitacionnoe prityazhenie kotoroi nastol'ko veliko,
chto pokinut' ee ne mogut dazhe ob'ekty, dvizhushiesya
so skorost'yu sveta (v tom chisle i kvanty samogo sveta)....
Potom ego ozarilo v 1975 i on odaril chernye dyry i vseh
astrofizikom izlucheniem ot chernyh dyr.
---...Izluchénie Hókinga ...---
......Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi.
Predskazan teoreticheski Stivenom Hokingom v
1974 godu.[1] Rabote Hokinga predshestvoval
ego vizit v Moskvu v 1973 godu, gde on vstrechalsya
s sovetskimi uchenymi Yakovom Zel'dovichem i
Alekseem Starobinskim. Oni prodemonstrirovali
Hokingu, chto v sootvetstvii s principom
neopredelennosti kvantovoi mehaniki
vrashayushiesya chernye dyry dolzhny
porozhdat' i izluchat' chasticy.[2]
Isparenie chernoi dyry kvantovyi process.
Delo v tom, chto ponyatie o chernoi dyre kak ob'ekte,
kotoryi nichego ne izluchaet, a mozhet lish' pogloshat' materiyu,
spravedlivo do teh por, poka ne uchityvayutsya kvantovye effekty.
V kvantovoi zhe mehanike, blagodarya tunnelirovaniyu,
poyavlyaetsya vozmozhnost' preodolevat' potencial'nye bar'ery,
nepreodolimye dlya nekvantovoi sistemy. Utverzhdenie,
chto konechnoe sostoyanie chernoi dyry stacionarno,
pravil'no lish' v ramkah obychnoi, ne kvantovoi teorii
tyagoteniya. Kvantovye effekty vedut k tomu, chto na samom
dele chernaya dyra dolzhna nepreryvno izluchat', teryaya pri
etom svoyu energiyu.....
Itogo
...Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke,
ya tak ponyal reshil - zachem dobru propadat' - pust'
izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi dyry
budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A vot zdes' ya Vam mogu predlozhit' sdelat' u kazhdoi stat'i schetchik, - ponyal -ne ponyal,
Vashe - Dlya bazovogo ponimaniya nuzhno umet' chitat' i imet' nekotoruyu
podgotovku v ramkah hotya by shkoly. U Vas takaya podgotovka, sudya po
vsemu, hromaet na obe nogi, poetomu Vy ne ponimaete bol'shinstvo statei.
Dlya utochnyayushih voprosov est' kommentarii, dlya bazovoi podgotovki - shkola
i uchebniki.
- Vy dumaete chto vse uchennye pishut pravil'nye stat'i, i nikto stat'i ne
vysasyvaet iz pal'ca a potom ne rzhet nad chitatelyami, a Vash sait chtoby
chitat' - to nado byt' doktorom nauk, i v tozhe samoe vremya Vy lichno ne
mozhete otvetit' pryamo na pryamye voprosy, po etoi stat'e. Vy menya v
principe zaintrigovali, ya podumayu chtoby takoi puzyr' vysosat' iz pal'ca v
ramkah paradigmy, chtoby vse vokrug azh zaaplodirovali za isklyuchitel'no
vysokohudozhestvennyi idiotizm v ramkah breda sivoi kobyly.
Moe-Ne rasskazhete Vashe otnoshenie k vyskazyvaniyu, -
Esli opyt ne sovpadaet s teoriei to tem huzhe dlya opyta?
Napomnyu -
Moe - So vtorogo Vashego otveta ya ponyal - chto u Vas est' metody
dokazatel'stv kotorye pozvolyayut opredelit' kakimi byli v pervye momenty
bol'shogo vzryva zvezdy, chernye dyry , temperatura i drugie razlichnye
svoistva prostranstva i svoistva razlichnyh fizicheskih ob'ektov.
Vashe - Ne u menya. U astronomov, astrofizikov i kosmologov.
Moe- Esli mne ne mozhet opponent srazu vnyatno izlozhit' otvet na moi
prostoi vopros po obsuzhdaemoi stat'e, to ya ne obyazan verit' napisannomu,
a skoree naoborot - vynuzhden zasomnevat'sya.
Po povodu gromkih familii v astrofizike - to esli Vy proanaliziruete ih
biografiyu i trudovye zaslugi i proanaliziruete ih prichastnost' k
astrofizike, to oni vse v astrofizike - diletanty, kotorye idei
vbrasyvali v astrofiziku ot sluchaya k sluchayu, i ser'ezno ei ni kto ne
zanimalsya. Po etomu vsya astrofizika i sostoit iz razroznennyh idei, -
ozaryalok, kotorye posledovateli pytayutsya sostykovyvat' mezhdu soboi po
prichine poyavleniya novoi izmeritel'noi tehniki.
A astrofiziku u menya hobbi let 7, tak chto ya prochital stol'ko statei
raznyh, chto mogu delat' vyvody chto vysoska iz pal'ca, a chto i super
gramotno napisano .
Samoe smeshnoe chto super stat'i absolyutno neizvestny.
http://crydee.sai.msu.ru/Universe_and_us/4num/v4pap26.htm
-Ochen' horoshaya stat'ya.
http://www.anomaliy.ru/discovery/482
"Sverhnovye tipa I a, kak polagayut, formiruyutsya
posle vzryvov belyh karlikov, sverhplotnyh mertvyh zvezd razmerom s
nashu Zemlyu, kotorye kogda-to byli yadrom solncepodobnogo svetila, i
ch'ya vneshnyaya obolochka rastvorilas' v kosmose.
Odna iz osobennostei etogo tipa otsutstvie vodoroda, i eto
nesmotrya na to, chto vodorod yavlyaetsya samym rasprostranennym
himicheskim elementom."
Vot eta stat'ya - v principe dolzhna byla perevernut' vsyu astrofiziku,
po toi prichine chto net vodoroda vnutri zvezdy. A u tekushei paradigmy
vodorod vygoraet. I astrofiziki vnyatno otvetit' ne mogut prichinu po
kotoroi samyi legkii vodorod - preodolevaet gravitaciyu stanovitsya
tyazhelee vseh metallov i letit v yadro zvezdy pouchastvovat' v yadernoi
reakcii. I V to chto samyi legkii vodorod preodolevaet letit vnutr'
zvezdy -ya ne veryu, hot' v millione knizhek eto budet napisano, i tysyache
uchebnikov. Tak kak napisannoe ne podtverzhdeno fizicheskimi svoistvami a
protivorechit im.
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.01.2013 10:42, 622 Bait)
\\\A
znaete li vy, chto
nikto nikogda ne fotografiroval chernuyu dyru - eto nevozmozhno, tak kak
oni pogloshayut vse svetovye volny vnutr' iz-za sil'noi gravitacii. Vse
izobrazheniya chernyh dyr sdelany
chelovekom v Fotoshope i podobnyh programmah.\\\
Predydushii post - obosnovanie ne fizichnosti chernyh dyr, avtor dyurochek prosto lopuhnulsya,
v fizike eto normal'no,
i dostatochno chastoe yavlenie v neklassicheskoi fizike.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.01.2013 23:00, 1.4 KBait, otvetov: 1)
Mne kraine nepriyatno kogda kto-to neobosnovanno vumnichaet,
ne vopros daite kazhdomu Vashemu slovu fizicheskoe opredelenie,
ibo fizika - eto fizicheskie opredeleniya
obosnovannye hot' kak-to.
Ya dazhe ne proshu menya polovit' na ne-korrektnosti moih fizicheskih obosnovanii
ibo eto dlya Vas nevozmozhnaya zadacha v principe.
1 \perenos
laboratornyh
processov\ - daite opredelenie,
2 \astronomicheskoe
pole\ - analogichno,
3 \processy
v
atomah\ - kakaya model' - opishite,
4 \proeciruyutsya
na
prostranstva\-daite opredelenie proeciruemosti,
5 - daite Vashe opredelenie prostranstva,
6 \chetko
opredelimsya
-
tema
astronomicheskaya,
a
ne
fizicheskaya\ - daite opredelenie
granicy mezhdu fizikoi i kosmologiei,
7 \idet
ob
astroob'ektah.
V
etom
sluchae
elementarnye
chasticy
rassmatrivat'sya
ne
dolzhny
voobshe\
- obosnuite fizicheskuyu prichinu nevozmozhnosti.
--------------------------------
Pochuvstvuite svoi slova - i kak oni vosprinimayutsya drugimi, i
prizadumaites'
nad etoi situaciei.
Kak dlya menya Vash tekst - golimyi neobosnovannyi fizicheski porozhnyak.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
9.01.2013 8:22, 568 Bait)
Zachem
povtoryat'
izvestnye
opredeleniya?
Opredelim
po
teme.
Fizika
davshaya
vozmozhnost'
videt'
to,
chto
nikto
nikogda
ran'she
ne
videl
-
bescenna
vne
vremeni.
No
v
drugoi
ploskosti,
fizika
pytayushayasya
videt'
v
astroob'ektah
sebya
i
tol'ko
sebya,
sovershenno
ne
prinimaya
vo
vnimanie
fakt,
chto
razbiraet
astronomicheskoe
pole.
Elementarnye
chasticy
ne
yavlyayutsya
astronomicheskimi
ob'ektami,
nebesnaya
mehanika
-
Astronomicheskaya,
t.e.
ne
fizichna.
A
eto
uchityvatsya ?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
9.01.2013 0:02, 275 Bait)
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1357553088/180
Eta krasivaya pridvornaya sobachka, v smysle vyrosshaya pri dvore, so vremenem
budet samoi
strashnoi grozoi vseh psov.
Bezumcy oni - ishut sebe priklyuchenii dazhe ne ponimaya s kem svyazalis'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
9.01.2013 0:03, 65 Bait)
Eta sobachka budet zagryzat' kazhdogo psa dolgo
i medlenno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
9.01.2013 11:01, 298 Bait)
A eto uvazhaemyi test na Vashu adekvatnost' v fizike,
i esli Vy s nim ne mozhete spravitsya to ya s Vami
ne mogu obshat'sya.
I esli Vy skazali chto-to to bud'te
lyubezny i otvetit'
za svoi slova, a esli ne mozhete dlya etogo
est' standartnaya fraza -
\Prostite otcy za - ranca\.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
9.01.2013 11:06, 265 Bait, otvetov: 5)
A esli ya skazal chto avtor chernyh dyr fizicheski nepravil'no svoyu
teoriyu i opredeleniya sdelal, to ya eto obosnoval, i avtor chernyh
dyr v moih glazah kak fizik - nedalekii,
i pridumal on laino ne imeyushee
nikakogo otnosheniya k fizike i deistvitel'nosti.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
9.01.2013 12:18, 575 Bait, otvetov: 4)
Davaite
razberem
eshe
odnu
oblast',
v
kotoroi
fizika
vidit
tol'ko
sebya,
yavlyayas'
eyu
-
eto
h-
i-
m-
i-
ya.
Na
vsyu
glubinu,
kakaya
mozhet
byt'
kvantofizicheskaya
oblast'
est'
oblast'yu
protohimicheskoi.
Imenno
tak
-
iz
kvantovoi
fiziki
mozhet
poluchit'sya
tol'ko
Himiya
(so
svoimi
zakonami).
Net
takoi
fizicheskoi
ustanovki
(tot
zhe
BAK),
kotoraya
by
ne
obladala
himicheskimi
svoistvami,
chto
izvestno
lyubomu
inzheneru,
no
sovershenno
ignoriruetsya
teoreticheskoi
fizikoi.
- Re[3]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
9.01.2013 13:44, 557 Bait, otvetov: 3)
Astronomiyu
i
himiyu
rodnit
ne
tol'ko
neopravdannaya
podchinennost'
fizike,
no
i
pereves
v
nih
gravitacionnyh
processov
nad
vsemi
drugimi.
Fiziki
mogli
by
vydelit',
kak
svoyu
nauchnuyu
osnovu
fiziku
vysokih
energii
(chego
oni
ne
delayut,
opirayas'
na
kvantovuyu),
no
i
v
etom
sluchae
energopolya
prinadlezhat
oblasti
libo
himii,
libo
astronomii.
I
tol'ko
proyavlenie
ih
-
izluchenie,
ulavlivaetsya
chisto
fizicheski,
priborami
(cherez
himicheskie
svoistva)
- Re[4]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
9.01.2013 22:34, 451 Bait, otvetov: 2)
Kosmos
-
plazma,
gravitaciya,
polya,
himiya,
izluchenie,
sostavlyayushie
astronomicheskie
kompleksy
(ob'ekty).
Iz
nih
fizike
dostupno
tol'ko
izluchenie,
po
kotoromu
pytayutsya
sostavit'
predstavlenie
o
drugih
sostavlyayushih.
Astronomiya
v
sostoyanii,
izuchaya
astrob'ekty,
brat'
vse
kosmicheskie
sostavlyayushie
v
sovokupnosti.
V
chem
trebuemaya
ob'ektivnost'
neobhodimogo
nauchnogo
podhoda
- Re[5]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
10.01.2013 11:19, 536 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Chto,
vazhno
-
fizika
imeet
v
astronomii
tol'ko
(!)
izlucheniya.
Po
nim,
na
laboratornyh
dannyh,
vosstanavlivayutsya
drugie
faktory.
Zdes'
snova
proecirovanie
laboratornogo
na
prostranstvennoe
potomu,
chto
fizicheskoe
tol'ko
podobno
astronomicheskomu,
no
ne
identichno.
Astronomicheskie
plazma,
gravitaciya,
polya,
himiya
i
izlucheniya
ne
fizichny,
a
astronomichny.
Fizika
eto
razlichie
ne
v
sostoyanii
ulovit',
no
astronomiya
mozhet
ego
podskazat'
- Re[6]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
11.01.2013 7:23, 555 Bait)
V
astrokomplekse
(ob'ekte)
vydelyayutsya
gruppy
yavlenii
-
gravitacionno-
himicheskaya
(zadayushaya
harakteristiki),
plazmo-
polevaya
(material'no-
silovaya)
i
proizvodnye
iz
nee
izlucheniya.
Podobnye
fizicheskim,
no
ne
fizicheskie
i
fizicheskoe
sozdayushie,
pri
obrazovanii
zvezd
i
planet,
gde
kak
fizicheskie
obnaruzhivaemye
v
poverhnostno-
planetnom
PVK,
sozdayushie
PVK
zvez
i
planet,
eti
nefizicheskie
astrokompleksy
est'
takzhe
PVK
bolee
osnovnyh
kosmicheskih
struktur
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.01.2013 9:57, 2.4 KBait, otvetov: 3)
Kak govoritsya nichego lichnogo.
Vy zdes' ne pishite - ibo Vy mne skuchny v kosmologii,
ibo u Vas ne znanii ni umenii imi pol'zovat'sya.
Vy nedalekii potomu
chto Vy dazhe ne znaete
chto ne sushestvuet na tekushii moment fizicheskogo
obsheprinyatogo opredeleniya \prostranstva\.
Vot lichno moe mnenie kak chitatelya chitayushego
forum.
Vot voz'mem forum,
tam est' Dmitrii Vibe,
Oleg Titov,
Aliya i Chhe - u vseh iz nih odinakovyi
profesorskii uroven' znanii, a pol'zovat'sya imi
umeyut tol'ko dvoe.
Dmitrii Vibe i Aliya - rozhdeny matematikami,
i
oni v svyazi so svoei doverchivost'yu, poverili relyativizmu,
i u nih perestroilas' pod relyativizm logika myshleniya,
u Vibe procentov na semsyat pyat', u Alii na sto
procentov,
u Alii mozhna taki skazat' chto v soznanii nekotaraya
relyativistskaya matrica i vse prohodit tol'ko cherez nee.
Oleg Titov - rozhden fizikom, i vynuzhden
byl myslit' po
relyativistski ibo po drugomu zarabotat' v fizike deneg
on ne mog, so vremenem i s vozrastom on po drugomu dumat'
ne mozhet. Chhe - rozhden fizikom,svoimi
znaniyami pol'zovat'sya
mozhet samostoyatel'no, bez oglyadok i bez postoronnei pomoshi.
Tak samoe smeshnoe - Poleznye teksty kto pishet na forumah,
Dmitrii
Vibe - bezpoleznye dlya chitayushego,
Aliya - poleznye dlya relyativistov,
Oleg Titov - poleznye,
Chhe - poleznye.
---------------------------------------------------------------------
A Vashi teksty - eto voobshe tektsty bezsmyslennye
i bezpoleznye, i Vy ne fizik i ne matematik,
i znanii u Vas net - odin okolofizicheskii steb skorei vsego -
pensionera u kotorogo mnogo svobodnogo vremeni,
no uzhe i pamyat' ne ta, i net umeniya analizirovat'
novye neobychnye znaniya.
Vy mozhete poiti
potusovat'sya na vot etot
forum,

Fizika al'ternativnaya
tam moderator takih kak Vy ne banit,
tam takih procentov shest'desyat , i tam tozhe
est' tri minimum rozhdennyh fizikami,
no kto eto ya ne skazhu, dogadaites'
sami.
Uspehov.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
11.01.2013 13:48, 567 Bait, otvetov: 2)
Vasi
priznaites'
sebe,
chto
astronomiya
vam
ne
nuzhna.
Vy
putaete
kosmologiyu
s
fizikoi,
prostranstvo
dlya
vas
tol'ko
fizicheskoe,
vy
predlagaete
pereiti
na
fizicheskii
forum.
A
zdes'
forum
astronomii
i
ee
voprosy
razbirayutsya.
3des'
obsuzhdayutsya
temy
kasayushiesya
prostranstva
astronomicheskogo
i
ego
kosmologii.
Dlya
teh
kogo
interesuet
tol'ko
fizika
est'
drugie
forumy.
No
esli
astronomiya
vam
vse
zhe
interesna,
popytaites'
hot'
nemnogo
vniknut'
v
temu
- Re[3]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
11.01.2013 15:18, 543 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Fizicheskoe
prostranstvo
sushestvuet.
No
u
nego
est'
svoe
mesto
v
astronomii.
Fizicheskoe
prostranstvo
voznikaet
iz
astronomicheskogo
prostranstva,
pri
obrazovanii
planet
i
ih
poverhnostei.
I
zdes'
konechno,
est'
kosmologiya
fizicheskogo
prostranstva
i
pole
absolyutnoi
vlasti
fiziki
i
ee
predstavlenii.
A
chto
do
matematiki,
to
astronomicheskii
prostranstvenno-
vremennoi
kontinuum
(PVK)
daet
bol'she
ei
vozmozhnostei,
chem
prostranstvo
fizicheskoe
- Re[4]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
11.01.2013 15:36, 439 Bait)
S
imeyushei
mesto
byt',
absolyutnoi
vlast'yu
fiziki
v
fizicheskom
(poverhnostno-
planetnom)
PVK,
trudno
soglasit'sya,
kak
ob'ektivnoi.
Vse-
taki
i
zdes',
fizicheskom
prostranstve,
ob'ektivno,
glavenstvuyushee
mesto
dolzhny
zanimat'
predstavleniya
himii,
chto
pomozhet
i
fizike
razobrat'sya
vo
mnogih
svoih
problemah.
Himiya
uchityvaet
bol'she
sostavlyayushih
nauchnogo
znaniya
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.01.2013 22:30, 1.6 KBait)
Vy zdes' ne pishite - ibo Vy mne skuchny v kosmologii,
ibo u Vas ne znanii ni umenii imi pol'zovat'sya.
Vy nedalekii.
A Vashi teksty - eto voobshe teksty bessmyslennye
i bespoleznye, i Vy ne fizik i ne matematik,
i znanii u Vas net - odin
okolo-fizicheskii steb skorei vsego -
pensionera u kotorogo mnogo svobodnogo vremeni,
no uzhe i pamyat' ne ta, i net umeniya analizirovat'
novye neobychnye znaniya.
Vy mozhete poiti
potusovat'sya na vot etot
forum,

Fizika al'ternativnaya
tam moderator takih
kak Vy ne banit.
----------------------
Mne do lampochki Vashi voprosy, i mne naplevat' chto Vy dumaete
o tom chto est' fizika ili astronomiya ili kosmologiya,
i ya s temi kto borzo na menya naezzhaet s neobosnovannymi pretenziyami
ne obshayus' v principe.
I esli Vy ne chatovyi bot ya udivlyus'.
Mne lichno do lampochki Vashi
voprosy s himiei,
Vashi voprosy - sami i reshaite ih.
I s temi kto ne mozhet sdelat' ni odnogo fizicheskogo opredeleniya
i tehnicheski gramotno ne mozhet sformulirovat'
vopros, ya tozhe
ne obshayus'.
---------
Shli by Vy na baletnyi forum i sovetovali by tam naprimer v
fuete - fuetyatiny dobavit'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.01.2013 0:01, 2.3 KBait)
Esli u kogo est' vozmozhnost' - bud'te lyubezny peredaite
chto ya na etot vopros smogu - zdes' - otvetit' vmesto togo komu on zadan,
ibo ya znayu vsyu istoriyu i s radioastronomiei
i pereotkrytiyami
i s datami.
------------------------





-

- Soobshenii: 11 986
- Reiting: +120/-30
-
Otvet #13 : Segodnya v 13:37:00
Uv. Che, takoe oshushenie, chto Vam nravitsya 20-i vek i dazhe ego seredina.
Kosmologiya, myagko govorya, chrezvychaino sil'no prodvinulas' s teh por. 
Est' davno ser'eznye modeli rozhdeniya Vselennoi so mnogimi podtverzhdennymi parametrami
i otvetami na Vashi naivnye voprosy.
A vot u stacionarnoi, beskonechnoi i vechnoi Vselennoi net otvetov ni na odin vopros i net ni odnogo nablyudaemogo podtverzhdeniya.
Dazhe net otveta na vopros, otkuda ona vzyalas' - a est' prosto drevnii i legkii postulat - vsegda byla
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.01.2013 0:11, 758 Bait)
Mne estestvenno ne ponyatno pochemu ne obrashayut vnimaniya na
Bol'shuyu sovetskuyu Enciklopediyu- v kotoroi sobstvenno
vselennaya vechnaya - a bol'shoi Vzryv pridumannyi posle
radioastronomicheskih
manevrov, i pereotkrytii s 1941 na 1946, i slovo - singulyarnost' - to kak raz
bylo pridumano v dovesok k vechnoi vselennoi i s etim doveskom
,
vselennaya stala rasshiryatsya.
Estestvenno za soboi ne zamechaet kto-to chto u bol'shogo vzryva bol'she voprosov
chem on dazhe sebe predstavlyaet.
Prosto pered
relyativistami ih nikto ne stavil, a esli i stavili to oni ignorirovali,
a tak vse logichno budet - pomeryatsya voprosami i otvetami.
Dlya menya estestvenno eto specialist
u kotorogo est' ne kotorye znaniya v kotoryh
on uveren.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.01.2013 0:21, 4.2 KBait)
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
1.05.2012
|
|
Zakrytie bol'shogo vzryva.
Zakrytie modelei zvezd na gorenii vodoroda.
---Neskladushki bol'shogo vzryva.
Pervoe chto brosaetsya v glaza v etoi
teorii
- chto s dostatochno bol'shoi tochnost'yu v
sekundy i minuty znayut posledovatel'nost' proishodyashego
no naproch' otsutstvuet prichinno sledstvennaya svyaz'
- vse postroeno na postulatah kotorye nel'zya podtverdit'.
Chto iznachal'no sostoit iz paradoksov i protivorechii.
1 Razlet so sverhsvetovoi skorost'yu
na 13.5 mlrd svetovyh let
vo vse storony prakticheski mgnovenno, i my nablyudaem v teleskop
zvezdy kotorye tuda zabrosilo pri bol'shom vzryve.
---
Chto sobstvenno
est' zhestkoe i paradoksal'noe v etom, -
skorost' sveta byla prevyshena minimum v milliard raz.
Chto ne ponyatno drugoe, ne ponyatno chto esli pri razlete materii
pochemu ee zabrosilo na 14 mlrd svetovyh let, a ne na dva ili tysyachu,
- pochemu razbros sovpadaet s vozmozhnostyami teleskopov.
2 Himicheskii sostav
vodoroda i geliya i ego sootnoshenie - 70%vodoroda
i 30% geliya - i s kakoi tochnost'yu i bez primesei drugih veshestv.
---
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://vsln.ru/himicheskiy-sostav-solntsa.html
(V 1929 g. amerikanskii astronom Genri Norris Ressel (18771957)
tshatel'no izuchil solnechnye spektry, i emu
udalos' ustanovit', chto
Solnce porazitel'no bogato vodorodom. On reshil, chto na vodorod
prihoditsya tri pyatyh vsego ob'ema Solnca. Eto bylo absolyutnoi
neozhidannost'yu,
tak kak vodorod, hotya i ne yavlyaetsya redkim elementom
v tochnom smysle etogo slova, sostavlyaet vsego lish' 0,14% zemnoi kory.
Odnako posleduyushie issledovaniya pokazali,
chto Ressel byl slishkom
ostorozhen v svoei ocenke. Nedavnie podschety amerikanskogo astronoma
Donal'da Govarda Menzela (rod. v 1901 g.) pokazyvayut, chto vodorod
sostavlyaet
81,76% ob'ema Solnca, a gelii 18,17%, tak chto na dolyu
vseh ostal'nyh elementov ostaetsya tol'ko 0,07%.
Po-vidimomu, mozhno s uverennost'yu skazat', chto
Solnce prakticheski
predstavlyaet soboi svetyashuyusya smes' vodoroda i geliya v proporcii
(po ob'emu) 4:1. (Element gelii tozhe byl otkryt s pomosh'yu spektral'nogo
analiza,
prichem snachala ne na Zemle, a na Solnce Angliiskii astronom
Dzhozef Norman Lok'er (1836 1920) predpolozhil, chto nekotorye
neopoznannye linii solnechnogo
spektra prinadlezhat eshe ne otkrytomu
elementu, kotoryi on v chest' grecheskogo boga Solnca Geliosa nazval geliem.
Na Zemle zhe gelii byl obnaruzhen shotlandskim himikom
Uil'yamom Ramzeem
(18521916) tol'ko v 1895 g.).)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sobstvenno osnovnaya oshibka v dannoi situacii v tom chto
po sostavu himicheskomu atmosfery solnca sdelano skrytoe
utverzhdenie - a eto postulat, chto himicheskii
sostav samogo
solnca tozhe takoi-zhe za isklyucheniem yadra.
Vot zdes' nado povnimatel'nee ibo zdes' samaya grubaya
oshibka vsei astronomii.
Dannaya
situaciya na samom dele ne vozmozhna, ibo vodorod
on ne tol'ko samyi legkii i u nego samaya nizkaya udel'naya
plotnost' no u nego i samaya bol'shaya pronikaemost', on
so vremenem
mozhet prosochitsya cherez metally i proiti skvoz' nih
naskvoz'.
Sledovatel'no pri takih fizicheskih svoistvah vodorod budet
vytesnen materialami
s bol'shei udel'noi plotnost'yu iz svoih
nedr lyuboi zvezdy ili planety na poverhnost'.
A iz etogo chto sleduet - a to, chto vodorod ne uchastvuet i nikogda
ne uchastvoval v yadernyh reakciyah v solnce potomu chto vnutri
solnca vodoroda net v principe, on ves' isklyuchitel'no v atmosfere
solnca.
A iz etogo
sleduet chto ne tol'ko bol'shoi vzryv no i vse evolyucii
zvezd i modeli zvezd kotorye byli postroeny na gorenii
vodoroda i geliya v zvezdah nepravil'ny i ne sootvetstvuyut
fizicheskim svoistvam veshestv.
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.01.2013 10:32, 1.0 KBait, otvetov: 1)
Bol'shoi vzryv - termodinamika.
Absurdnost' bol'shogo vzryva proyavlyaetsya
ne tol'ko v tom chto vse szhalos' a potom vse vzorvalos',
i razbrosalo so skorostyami
kotorye v milliard raz prevyshali
skorost' sveta, eto cvetochki. Pri bolee detal'nom rassmotrenii
ostyvaniya posle bol'shogo vzryva prosmatrivayutsya
primitivnye
oshibki v fizike.
V lokal'noi zamknutoi sisteme izluchaetsya iz nee i ischezaet
za gorizont sobytii vse teplo vsei materii uchastvovavshei v bol'shom
vzryve. Tak
vot ono ne mozhet nikuda ischeznut' ono mozhet
byt' peredano tol'ko drugim telam fizicheskim v etoi zhe zamknutoi
sisteme. Itogo vselennaya ne mogla
ostyt' fizicheski
posle bol'shogo vzryva.
Temnaya materiya tozhe u bol'shogo
vzryva proshla ryadom s razumom polozhennym na polke,
po toi prichine chto temnuyu materiyu tupo zabyli vsunut'
v bol'shoi vzryv, tochnee ne zabyli te kto pridumal
bol'shoi vzryv zabyli te kto pripisal temnoi materii
devyanosto s lishnim procentom massy vo vselennoi i zabyli
chto nahodyatsya v bol'shom vzryve iznachal'no.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
12.01.2013 10:59, 534 Bait)
Bol'shoi
vzryv
tochno
prisutstvuet
v
astroprostranstve,
pri
obrazovanii
tumannostei
i
galaktik.
Dal'she
ego
ne
vidno,
no
pri
tom,
ne
isklyuchen.
Astroprostranstvo
-
plazma
i
tol'ko.
Vzryv
-
prisushee
plazme.
Vzryv
bol'she
himiya,
chem
fizika
i
potomu
ponyaten
himii
bol'she,
chem
fizike.
Ne
boites'
postupit'sya
fizikoi
radi
himii
i
astronomii.
Eto
polezno
samoi
fizike.
Vernost'
fizike
-
yavlenie
ne
nauchnoe,
a
psihologicheskoe
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.01.2013 11:47, 1.7 KBait)
Yu.S.Reshnikov
---------------------------
Vy zdes' ne pishite - ibo Vy
mne skuchny v kosmologii,
ibo u Vas ne znanii ni umenii imi pol'zovat'sya.
Vy nedalekii.
A Vashi teksty
- eto voobshe teksty bessmyslennye
i bespoleznye, i Vy ne fizik i ne matematik,
i znanii u Vas net - odin
okolo-fizicheskii steb skorei vsego -
pensionera u kotorogo mnogo svobodnogo vremeni,
no uzhe i pamyat' ne ta, i net umeniya analizirovat'
novye neobychnye znaniya.
Vy mozhete poiti
potusovat'sya na vot etot
forum,

Fizika al'ternativnaya
tam moderator takih
kak Vy ne banit.
----------------------
Mne do lampochki Vashi voprosy, i mne naplevat' chto Vy dumaete
o tom chto est' fizika ili astronomiya ili kosmologiya,
i ya s temi kto borzo na menya naezzhaet s neobosnovannymi pretenziyami
ne obshayus' v principe.
I esli Vy ne chatovyi bot ya udivlyus'.
Mne lichno do lampochki Vashi
voprosy s himiei,
Vashi voprosy - sami i reshaite ih.
I s temi kto ne mozhet sdelat' ni odnogo fizicheskogo opredeleniya
i tehnicheski gramotno ne mozhet sformulirovat'
vopros, ya tozhe
ne obshayus'.
---------
Shli by Vy na baletnyi forum i sovetovali by tam naprimer v
fuete - fuetyatiny dobavit'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.01.2013 11:54, 441 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Yu.S.Reshnikov
-----------------------
Vy
by poshli by na forum otkryli by vopros i obsuzhdali by ego,
ne ponimayu Vashe sado mazo i Vashe zhelanie
postoyanno slushat' ot menya chto Vash uroven' intellekta ochen'
nizkii - nichego lichnogo, -
uroven' v fizike i kosmologii uroven' - bezmozgloi skotiny.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
12.01.2013 13:19, 580 Bait)
Fizicheskii
absolyutizm
v
deistvii:
v
teoriyah
i
otnosheniyah.
Vy
ne
vhodite
li
v
komissiyu
po
bor'be
s
lzhenaukoi
(budto
takaya
mozhet
byt') ?
Zasluga
fiziki
v
astronomii
v
obnaruzhenii
astronomicheskih
izlucheniya,
polei,
himii,
gravitacii,
plazmy,
podobnyh
fizicheskim,
no
bol'she
fizika
skazat'
ne
v
sostoyanii.
Vasha
oshibka,
chto
dlya
kosmologii
Vy
izuchali
fiziku.
Fizika
ne
prisutstvuet
ni
v
nazvanii,
ni
v
soderzhanii
kosmologii.
I
vinovatyh
v
etom
ne
naidete
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.01.2013 16:00, 466 Bait, otvetov: 2)
Yu.S.Reshnikov
-----------------------
Vy
by poshli by na forum otkryli by vopros i obsuzhdali by ego,
ne ponimayu Vashe sado mazo i Vashe zhelanie
postoyanno slushat' ot menya chto Vash uroven' intellekta ochen'
nizkii - nichego lichnogo, -
uroven' v fizike i kosmologii uroven' - bezmozgloi skotiny.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
12.01.2013 18:18, 508 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Po
Vashemu
ya
ne
na
forume ?
I
forum
etot
astronomicheskii !
I
tema
v
kotoroi
i
Vy,
i
ya
nahodimsya
ne
podrazumevaet
Vashego
ko
mne
otnosheniya,
i
Vashih
ocenok
moih
izvilin,
a
razvivaet
znachimye
v
astronomii
predstavleniya.
I
vopros,
kak
raskryvat'
etu
temu
chisto
fizicheski
ili
chisto
astronomicheski,
imeet
vazhnoe
znachenie
dlya
dal'neishego
ee
razvitiya.
Vot
ya,
kak
raz
pytayus'
v
nei
razobrat'sya
- Re[3]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
12.01.2013 18:54, 455 Bait)
Pravil'nyi otvet -
tema raskryvaetsya
astrofizicheski. No chto
est' astrofizika -
perenos fizicheskih
predstavlenii v
astronomiyu ili
ispol'zovanie
astronomiei
fizicheskih dannyh. V
pervom sluchae reshenie
chisto fizicheskoe -
prosto delaetsya
popravka na neobychnye
fizicheskie usloviya. Vo
vtorom sluchae reshenie
chisto astronomicheskoe
- razbirayutsya imenno
astronomicheskie
usloviya. Vot tak i
dolzhno byt' i k etomu
nuzhno priiti
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.01.2013 18:20, 499 Bait)
Yu.S.Reshnikov
-----------------------
Vy
by poshli by na forum otkryli by vopros i obsuzhdali by ego,
ne ponimayu Vashe sado mazo i Vashe zhelanie
postoyanno slushat' ot menya chto Vash uroven' intellekta ochen'
nizkii - nichego lichnogo, -
uroven' v fizike i kosmologii uroven' - bezmozgloi skotiny.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.01.2013 19:03, 532 Bait)
Yu.S.Reshnikov
-----------------------
Vy
by poshli by na forum otkryli by vopros i obsuzhdali by ego,
ne ponimayu Vashe sado mazo i Vashe zhelanie
postoyanno slushat' ot menya chto Vash uroven' intellekta ochen'
nizkii - nichego lichnogo, -
uroven' v fizike i kosmologii uroven' - bezmozgloi skotiny.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
18.01.2013 18:14, 463 Bait, otvetov: 2)
Planetnaya
himiya
voznikaet
iz
astrohimii.
Astrohimiya
proishodit
iz
astroProtohimii.
Himiya
svyazana
s
gravitaciei.
Astrohimiya,
tak
zhe
imeet
svoi
gravitacionnye
processy.
Razbiraemaya
tema
otnositsya
k
svoistvam
astrohimicheskim,
kak
osnove
PVK
i
poluchaet
cherez
nih
svoe
razreshenie.
Nuzhno
otmetit',
chto
gravitacionno-
himicheskie
processy
ne
mogut
byt'
ogranicheny
skorost'yu
sveta
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
19.01.2013 1:14, 557 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Skorost'
bystree
sveta
dolzhna
byt'
v
astroob'ekte
(PVK),
kak
svyazuyushee
vzaimodeistvie.
Elektro-
magnitnoe
izluchenie
ne
vypolnyaet
takoi
funkcii
iz-
za
nesorazmernosti
svoei
skorosti
masshtabam
astroob'ekta,
chto
vidno
uzhe
na
PVK
tumannosti
(i
EMI
ne
est'
upravlyayushei
siloi).
Tol'ko
gravitacionnoe
vzaimodeistvie,
kak
opredelyayushee
(vmeste
s
himiei)
PVK
dolzhno
obladat'
takim
svoistvom.
Gravitacionnye
volny
iz
momental'nogo
vzaimodeistviya
ne
vytekayut
- Re[3]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
19.01.2013 9:58, 349 Bait)
PVK
neobhodima
skorost'
dostatochnaya
(!)
dlya
trebuemoi
odnovremennosti
sobytii
v
ego
ob'eme.
Chto
oznachaet
razlichnye
dostatochnye
skorosti
v
razlichnyh
PVK.
Skorost'
svyazuyushego
vzaimodeistviya
mozhno
vychislit'
i
popytat'sya
registrirovat'.
Eto
vozmozhno,
esli
gravitacionnye
volny
sushestvuyut
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. B. Daneev,
19.01.2013 17:11, 577 Bait, otvetov: 2)
Svyashenna
reka
Eridan.
S
Kresheniem.
Spor
mezhdu
fizikami
i
himikami
napominaet
spor
mezhdu
shivaitami
i
vishnuitami
-
odni
upivayutsya
silami,
drugie
tyanutsya
k
sushestvam.
Gde
nauka,
gde
religiya?
O
gravitacii
davno
skazano
-
dvizhet
zvezdy
i
planety,
tam
zhe
raskryt
smysl,
stol'
znachimogo
yavleniya
-
Lyubov'.
Predstavlyaete
skol'ko
tam
Lyubvi,
chto
nas,
naivnyh,
takaya
Sila
povergaet
v
svyashennyi
uzhas.
No
vot
ved',
kak
boimsya,
a
zhazhda
poznaniya
eshe
sil'nee
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
20.01.2013 9:23, 575 Bait)
Da,
poeziya
krasivaya
konechno.
Prodolzheniem
vashei
prazdnichnoi
shutki
budet
schitat'
shivaitov
i
vishnuitov
byvshimi
astrofizikami
i
astrohimikami.
Vernemsya
k
PVK.
Est'
vopros
-
yavlyayutsya
li,
gravitacionnymi
volnami,
te
vozmozhnye
signaly,
poluchaemye
iz
PVK
s
kotorymi
nash
planetnyi
PVK
svyazan
sistemno ?
Vse-
taki
volnami
dolzhny
byt'
signaly,
prihodyashie
iz
PVK
ne
svyazanyh
sistemno
s
nashim.
Togda
oni
deistvitel'no
volny,
a
ne
kakie-
libo
sistemnye
izmeneniya
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(V. P.,
24.01.2013 22:10, 1.3 KBait)
<
tbody>| Citata: |
| Gde na
uka, gd
e religiya?
|
Inter
esnyi vopro
s! K
ak mne kazhe
tsya, eto vopr
os k ap
ologetam
i svetilam
nauk
i!
Astr
onet | N
auchnaya se
t' | GAI
Sh MG
U | Poisk p
o MGU
| O pro
ekte
| Avtoram
Kommentarii,
voprosy
? Pishite:
in
fo@astron
et.ru i
li
syuda
stol'
znachimogo
yavleniya
-
Lyubov'.
Predstavlyaete
skol'ko
tam
Lyubvi,
chto
nas,
naivnyh,
takaya
Sila
povergaet
v
svyashennyi
uzhas.
No
vot
ved',
kak
boimsya,
a
zhazhda
poznaniya
eshe
sil'nee
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. P.,
24.01.2013 22:02, 349 Bait)
Skazhite, a ya pravil'no ponimayu vot eto: "raspad mozhet proizoiti takim obrazom, chto odna chastica upadet na chernuyu dyru, a drugaya, sravnitel'no nemnogo uvelichiv svoyu
skorost' v moment raspada, pereidet na takuyu orbitu, chto vyletit iz ergosfery s ogromnoi skorost'yu" kak rentgenovskoe izluchenie chernyh dyr? Ili eto neobyazatel'no tak?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(Yu. S. Reshnikov,
26.01.2013 10:48, 564 Bait)
V
astronomii
vse
pasutsya,
vklyuchaya
fizikov
i
teologov.
I
vsem
hochetsya
natyanut'
odeyalo
na
sebya.
No,
tabuirovat'
ne
svoistvenno
astronomu
-
mesta
v
prostranstvah
hvatit
vsem
i
ono
dlya
vseh.
Poka
otkrytyi
u
astronoma
vopros
-
kakoi
promezhutok
vremeni
dostatochen
dlya
odnovremennosti
v
PVK.
Dlya
raznyh
PVK
on
raznyi.
Desyatki
svetovyh
let
dlya
galaktiki,
dayut
li
odnovremennost' ?
Vryad
li.
A
skol'ko
neobhodimo
-
mesyacy,
dni,
doli
sekundy ?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(S. A. Pikalev,
2.02.2013 16:20, 248 Bait)
Pochemu, elektron ili proton ne mogut pokinut' dazhe nebol'shuyu chernuyu dyru, a dlya znachitel'no bolee massivnoi Vselennoi, rasshiryayusheisya iz tochki, eto legko dopuskaetsya?
Neuzheli, zabyli vovremya vklyuchit' gravitaciyu?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.02.2013 21:58, 255 Bait)
Rekomenduyu ispol'zovat' isklyuchitel'no avtorskoe opredelenie
o Chernyh Dyrah. Ibo drugie tochki zreniya ne imeyut
nikakogo otnosheniya k Chernym Dyram, ibo
ne avtorskie
varianty rasskazyvayut o chem-to drugom,
chto ne yavlyaetsya Chernoi Dyroi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(S. A. Pikalev,
3.02.2013 0:46, 165 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Mozhno sformulirovat' inache. Pochemu, Vselennaya ne yavlyaetsya chernoi dyroi pri vseh usloviyah dlya etogo v nachal'nyi period rasshireniya?
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.02.2013 11:32, 361 Bait)
I esli Vy zadaete Vopros to isklyuchitel'no Vy obyazany
obosnovat' ego pravil'nost', a ne hitroopit' mol
oprovergnite menya v chem moya ideya ne prava.
Esli net
sposobnostei obosnovat' to Vy vzyalis' za zadachu prevyshayushuyu
Vashi umstvennye sposobnosti i hotite reshit' ee za chuzhoi schet i chuzhim umom,
na takie hitrosti uzhe davno
nikto ne vedetsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.02.2013 11:19, 419 Bait)
Kogda pridumyvaite vsyakoe laino to eto ne
znachit chto eto laino yavlyaetsya chernoi dyroi,
eto govorit skoree o tom chto Vam luchshe ne pridumyvat'
vsyakogo laina
i ne pozoritsya.
Net smysla pridumymat' chto-libo i kakie libo svoistva
eto sdelal v svoe vremya avtor, a za avtora eto delat'
nikto ne imeet prava.
Shli-by
Vy na baletnyi forum i posovetovali by tam
v fuete fuetyatiny dobavit'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.02.2013 11:21, 122 Bait)
I prochtite sperva etu vetku snachala, a potom i poimete
pochemu Vash vopros eto detskii lepet,
i otvety uzhe byli.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(S. A. Pikalev,
3.02.2013 15:08, 268 Bait)
Probezhalsya po vetke. Prishel k vyvodu, chto mnogie Vashi utverzhdeniya nedostatochno argumentirovany, prichem, legkaya agressiya ne
usilivaet argumentaciyu. Vashe otnoshenie k opponentam i ih ideyam ostavlyaet zhelat' luchshego.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.02.2013 15:43, 33.4 KBait)
Esli by chitali vnimatel'no to ponyali chto avtor chernyh
dyr kak fizik nedalekii, i to chto on opisal ne mozhet
sushestvovat' fizicheski.
Da i astrofiziki i kosmologi
kak deti doverchivye
povelis' na chernye dyry - dazhe ne proverili elementarnoe -
skol'ko chernye dyry dolzhny za god zvezd pogloshat',
tak tam po millionu za god
v nashei galaktike propadat'
ili tuhnut' obyazano zvezd - a ne potuhlo nichego.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chto menya udivlyaet, - tak
eto to chto vsya astrofizika krasivaya i pushistaya,
i vse prekrasno.
No eto zhe ne tak, vot te-zhe chernye dyry - eto zhe
prosto pipec - i chto eto nikto ne zamechaet
ili nikto ne
ponimaet.
Hochu srazu sprosit', Vashe mnenie po
...Chernaya dyra...
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188232
Soglasny li Vy s etim?
Kakie iz perechislennyh statei sootvetstvuyut standartam Chernoi
Dyry?
1 Est' li zhizn' v chernoi dyre
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8822-est-li-zhizn-v-chernoy-dyire/
2[ssylka]
Ustanovlena massa samoi krupnoi iz sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr.
Takoe nam i ne snilos'.
3[ssylka]
Mifologiya chernyh dyr.V nashei Galaktike sushestvuyut milliony chernyh dyr
massoi v neskol'ko solnechnyh
4http://www.popmech.ru/article/8140-raspad-dyiryi/
Raspad dyry.
Vzryv sverhnovoi mozhet zakanchivat'sya obrazovaniem ne odnoi, a srazu
neskol'kih chernyh dyr.
5[ssylka]
Detstvo chernoi dyry
Vzryv, zafiksirovannyi v glubinah kosmosa 31 god nazad, sudya po vsemu,
znamenoval rozhdenie chernoi dyry samoi molodoi iz nam izvestnyh
6[ssylka]
Temnyi centr
Tainstvennyi centr nashei galaktiki,
mesto obitaniya sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyry i istochnik moshneishih potokov izlucheniya,
prepodnosit novye syurprizy.
7[ssylka]
Nebol'shoe zamechanie o prirode gravitacii privodit k sledstviyam
kosmicheskogo masshtaba k vyvodam o rozhdenii novyh mirov iz chernyh dyr
8[ssylka]
Obychnaya po razmeram chernaya dyra vybrasyvaet
kolossal'nye potoki izlucheniya i chastic.
9[ssylka]
Astrofiziki predlozhili sposob (teoreticheski) unichtozhit' chernuyu dyru
10[ssylka]
Iz vseh sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr lish' okolo 1% vybrasyvayut
znachitel'nye kolichestva energii
11[ssylka]
Vyzhivayushie dyry
Para redkih ekzemplyarov
V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
kakim-to chudom vyzhivayushih v sosedstve s etim monstrom.
12[ssylka]
Kak zhivetsya vnutri chernoi dyry? Vy i sami znaete,
kak: esli spravedlivy novye teoreticheskie vykladki,
vsya nasha Vselennaya mozhet nahodit'sya vnutri chernoi dyry,
raspolozhennoi v drugoi Vselennoi. Edakaya matreshka mirozdaniya.
13[ssylka]
Oni prosto predpolozhili, chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu. Eto dalo cifru v 10103, tozhe ogromnuyu, no vse-taki na mnogo
poryadkov nizhe.
14[ssylka]
Esli ochen', ochen' bystryi kosmicheskii korabl' razognat'
pochti do skorosti sveta, prevratitsya li on v chernuyu dyru?
15[ssylka]
Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
--------------------------------------------------------------
1 Nekotorye sverhmassivnye chernye dyry vybrasyvayut
kolossal'nye
potoki raskalennoi plazmy i lish' teper'
stanovitsya yasnym, pochemu imenno oni.
2
V aktivnom centre galaktiki M82, kak i polozheno, nahoditsya sverhmassivnaya
chernaya dyra. No ryadom s nei obnaruzheno i para dyr pomen'she
3 Oni prosto predpolozhili,
chto v centre kazhdoi iz galaktik imeetsya
po sverhmassivnoi chernoi dyre, i poschitali srednee kolichestvo i
velichinu.
Material iz
Vikipedii
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/39/M87_jet.jpg/250px-M87_jet.jpg
Izobrazhenie, poluchennoe s pomosh'yu teleskopa Habbl: Aktivnaya galaktika
M87. V yadre galaktiki, predpolozhitel'no, nahoditsya chernaya dyra. Na
snimke vidna relyativistskaya struya dlinoi okolo 5 tysyach svetovyh let
Relyativistskie strui
, dzhety (angl. jet) strui plazmy, vyryvayushiesya iz centrov (yader) takih
astronomicheskih ob'ektov, kak aktivnye galaktiki, kvazary i
radiogalaktiki.
Obychno u ob'ekta nablyudaetsya dve strui, napravlennye v protivopolozhnye storony.
Na nastoyashii moment relyativistskie strui ostayutsya nedostatochno izuchennym
yavleniem. Prichinoi poyavleniya takih strui chasto nazyvayut vzaimodeistvie
magnitnyh polei s akkrecionnym diskom vokrug chernoi dyry ili neitronnoi
zvezdy.
V stat'e na Elementah metodom chislennogo modelirovaniya pokazano, chto
pri sliyanii dvuh neitronnyh zvezd obrazuetsya chernaya dyra, magnitnoe pole
kotoroi vytyanuto vdol' osi. Eto navodit na mysli, chto etot zhe process
mozhet formirovat' i relyativistskie strui. Tem ne menee, v stat'e
govoritsya, chto predlozhennaya avtorami nauchnoi raboty matematicheskaya
model' okazalas' ochen' slozhna, a vychislitel'nye vozmozhnosti sovremennyh
komp'yuterov okazalis' nedostatochny, chtoby s dolzhnoi tochnost'yu provesti
vse neobhodimye raschety i ubeditel'no dokazat' formirovanie strui.
V drugoi stat'e na Elementah provodyatsya paralleli mezhdu processami v
chernyh dyrah i boze-einshteinovskom kondensate. Otmechaetsya chto kondensat
mozhet kollapsirovat' (slipat'sya) i pri posleduyushem ego raspade tozhe
mogut voznikat' uzkonapravlennye vybrosy.
Dal'neishee izuchenie relyativistskih strui
Pri samyh pervyh popytkah ob'yasneniya sverhsvetovogo dvizheniya s pomosh'yu
relyativistskogo napravlennogo potoka chastic vozniklo oslozhnenie:
udivitel'no bol'shaya dolya kompaktnyh istochnikov pokazyvala sverhsvetovoe
dvizhenie, v to vremya kak na osnovanii prostyh geometricheskih dovodov
poluchalos', chto tol'ko neskol'ko procentov takih ob'ektov dolzhno byt'
sluchaino orientirovano pochti vdol' linii zreniya. Prisutstvie
simmetrichnyh protyazhennyh radiokomponent predpolagalo, chto oni
obespechivalis' energiei ot central'nogo istochnika dvuh simmetrichnyh
luchei. No trudno sravnit' svetimost' priblizhayusheisya i udalyayusheisya (ili
dazhe stacionarnoi) komponent. Eto ochevidnoe razlichie obychno obsuzhdaetsya v
kontekste modeli s dvoinym istecheniem [4], kogda izluchenie iz yadra
rassmatrivaetsya kak stacionarnaya tochka, gde priblizhayushiisya
relyativistskii potok stanovitsya neprozrachnym. Sverhsvetovoe dvizhenie
nablyudaetsya mezhdu etoi stacionarnoi tochkoi v sople i dvizhushimisya
volnovymi frontami ili drugimi neodnorodnostyami v vyhodyashem
relyativistskom potoke.......
.....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie (gamma-luchi, γ-luchi)
vid elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s chrezvychaino maloi dlinoi volny
< 5×10−3 nm i, vsledstvie etogo, yarko vyrazhennymi korpuskulyarnymi
i slabo vyrazhennymi volnovymi svoistvami.
Gamma-kvantami yavlyayutsya fotony s vysokoi energiei. Obychno schitaetsya,
chto energii kvantov gamma-izlucheniya prevyshayut 105 eV, hotya rezkaya granica
mezhdu gamma- i rentgenovskim izlucheniem ne opredelena. Na shkale
elektromagnitnyh voln gamma-izluchenie granichit s rentgenovskim izlucheniem,
zanimaya diapazon bolee vysokih chastot i energii. V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu. Ochevidno,
fizicheski kvanty elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s odinakovoi energiei ne
otlichayutsya, poetomu takoe razdelenie uslovno.
Gamma-izluchenie ispuskaetsya pri perehodah mezhdu vozbuzhdennymi
sostoyaniyami atomnyh yader (sm. Izomernyi perehod, energii takih
gamma-kvantov lezhat v diapazone ot ~1 keV do desyatkov MeV),
pri yadernyh reakciyah (naprimer, pri annigilyacii elektrona i pozitrona,
raspade neitral'nogo piona i t.d.), a takzhe pri otklonenii energichnyh
zaryazhennyh chastic v magnitnyh i elektricheskih polyah (sm. Sinhrotronnoe izluchenie).....
Esli net poverhnosti ob kotoruyu proishodit tormozhenie.
Material iz Vikipedii
.....Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh
obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v rentgenovskih
trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok yavlyayutsya
metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe antikatodom).
V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom, uskoryayutsya
pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom i katodom
(pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak uskorenie slishkom malo)
i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe tormozhenie. Pri etom za schet
tormoznogo izlucheniya proishodit generaciya izlucheniya rentgenovskogo diapazona,
i odnovremenno vybivayutsya elektrony iz vnutrennih elektronnyh obolochek atomov
anoda. Pustye mesta v obolochkah zanimayutsya drugimi ....
To vstupaet v silu fraza -
V oblasti 1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.
sledovatel'no pri otsutstvii udara o poverhnost' - otsutstvuet sama vozmozhnost'
vozniknoveniya rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, a esli izluchenie est' to ono mozhet
byt' tol'ko rezul'tatom izlucheniya v yadernom perehode. A eto uzhe chasticy vysokih energii.
avtorskoe izluchenie iz chernoi dyry -
.Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash metod obnaruzheniya Chernoi Dyry
-Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
....Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo.
ChD tak i obnaruzhivayut. ....
Padaya na Chernuyu Dyru veshestvo ne
mozhet rezko tormozitsya ili rezko uskoryatsya,
a sledovatel'no - ne mozhet
byt' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya po etoi prichine.
V svyazi s tem chto dlya uskoreniya do skorosti sveta
pri kotorom vozmozhno izluchenie neobhodimo
ne bolee 10 sekund, a zvezda razmerom s
Solnce na takoi skorosti proletit cherez gorizont
sobytii maksimum za minutu.
Gorizont sobytii - eto skorost' sveta - esli
ob'ekt uletaet s etoi skorost'yu ot nablyudatelya, to
u nego vozniknet krasnoe smeshenie.
Esli by veshestvo dolgo padalo - godami na maloi skorosti
s uskoreniem to bylo by zametno izmenenie Z u padayushih
tel v chernuyu dyru so vremenem, no pri etom nevozmozhno
rentgenovskoe izluchenie - iz za slishkom medlennogo
uvelicheniya uskoreniya.
.... Material iz Vikipedii Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic (tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri
vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v elektronnyh obolochkah
atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah.....
A rentgenovskoe izluchenie est' - sledovatel'no
ego istochnikom mozhet byt' tol'ko rezul'tat yadernoi
reakcii.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Gámma-izluchénie
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.....
A esli rezul'tat izlucheniya istochnik yadernoi reakcii -
i on dlitsya godami, - to eto neitronnaya zvezda.
http://www.popmech.ru/article/8971-nasledstvennyie-chernyie-dyiryi/page/3/
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke, ya tak ponyal reshil -
zachem dobru propadat' - pust' izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi
dyry budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Vashe - Rentgenovskoe izluchenie ChD voznikaet pri akkrecii veshestva.
Izluchenie Hokinga - drugoi process. Stranno, chto za 7 let "uvlecheniya
astrofizikoi" Vy etogo ne ponyali.
Moe - S moei tochki zreniya - uvazhaemyi A.M.ChEREPAShUK imeet takoe zhe otnoshenie
k Chernym Dyram kak ya ili Vy.
My s Vami, i A.M.ChEREPAShUK mozhem tol'ko predpolagat' i vyskazyvat'
svoyu tochku zreniya, no obrashat' vnimaniya na podobnye vyskazyvaniya i brat'
ih na veru, ya ne vizhu smysla.
Drugoe delo avtor. Kak on skazal to - takie i Chernye Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vot ya naprimer govoryu chto veshestvo padaet na chernuyu dyru,
i posle udara o poverhnost' s protivopolozhnoi storony chernoi dyry voznikaet rentgenovskoe i svetovoe izluchenie.
Drugoi schitaet chto izluchenie na podlete.
V binokl' ne vidno - odni predpolozheniya, i ih mozhet byt'
bol'she sotni naprimer - komu verit'?
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Vy zatragivaete vopros interpretacii avtorskih
idei bez soglasiya s avtorom.
A esli desyatok drugih avtorov opublikuyut po 300 nauchnyh rabot, a avtor o
Chernyh Dyrah govorit chto izluchenie v osnovnom iz fotonov - a vse drugie
govoryat, chto
izluchenie iz rentgenovskih chastic, drugoi govorit iz radio izlucheniya, a
tretii govorit iz gamma chastic - ya dolzhen slushat' isklyuchitel'no avtora
Chernyh Dyr,
a ne teh kto interpretiruet, i tem bolee teh kto plevat' hotel na avtorskii variant chernyh dyr.
Nikto ne meshaet pridumat' svoi - rentgenovskie chernye dyry, - tak net ne
hotyat, - tak na neudobnye voprosy otvechat' dolzhen budet avtor, a pri
interpretacii avtora - pisaka naprimer stat'i s levymi ideyami v oblasti
Chernyh Dyr, prikryvaetsya avtorstvom avtora
Chernyh Dyr, a sam so svoim bredom po otnosheniyu k avtorskomu izlozheniyu, kak-by i ne prichem.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
..Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
Vash tekst - 11.05.11 14:04
Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii). Tochnee,
razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Vasha ssylka - tekst 11.05.11 20:36
....Kak otlichit' chernye dyry ot neitronnyh zvezd
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya chernaya dyra ne dolzhna proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. U nee mozhet nablyudat'sya lish' irregulyarnaya
peremennost' rentgenovskogo izlucheniya s harakternymi vremenami
$$Delta tapprox frac{r_g}{c}approx10^{-3} div 10^{-4}~mbox{rm s.}$$
I deistvitel'no, v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme Lebed' H-1, soderzhashei
chernuyu dyru s massoi okolo desyati solnechnyh, v sostoyanii, kogda
rentgenovskaya svetimost' ponizhena, a rentgenovskii spektr zhestkii i
stepennoi, nablyudaetsya bystraya irregulyarnaya peremennost' rentgenovskogo
potoka na vremenah poryadka millisekundy. Nablyudeniya, vypolnennye s
bortov sovremennyh rentgenovskih observatorii, takih, kak GINGA,
MIR-KVANT, GRANAT, ASKA, pokazali, chto rentgenovskie spektry
akkreciruyushih chernyh dyr sistematicheski bolee zhestkie, chem spektry
akkreciruyushih neitronnyh zvezd, i prostirayutsya do energii v neskol'ko
megaelektron-vol't.
Kak uzhe otmechalos', akkreciruyushaya neitronnaya zvezda mozhet proyavlyat' sebya
kak rentgenovskii pul'sar. Odnako, esli neitronnaya zvezda obladaet
slabym magnitnym polem (napryazhennost'yu menee 1010 Gs) ili esli ee os'
vrasheniya neudachno orientirovana otnositel'no zemnogo nablyudatelya, pri
akkrecii na takuyu neitronnuyu zvezdu mogut ne nablyudat'sya regulyarnye
pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya. Poetomu otsutstvie strogo
periodicheskih pul'sacii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya - eto lish' neobhodimyi,
no ne dostatochnyi priznak chernoi dyry. V to zhe vremya pri slabom
magnitnom pole neitronnoi zvezdy i nesil'nom tempe akkrecii veshestva na
ee poverhnosti mogut proishodit' termoyadernye vzryvy nakoplennogo
veshestva, privodyashie k yavleniyu rentgenovskogo barstera I tipa - korotkim
(dlitel'nost'yu poryadka 1-10 s) i moshnym vspyshkam intensivnosti
rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, chto takzhe yavlyaetsya harakternym priznakom
akkreciruyushei neitronnoi zvezdy, obladayushei tverdoi poverhnost'yu.
Poskol'ku chernaya dyra ne obladaet tverdoi poverhnost'yu, akkreciya
veshestva na nee ne dolzhna privodit' k fenomenu rentgenovskogo barstera I
tipa. Razumeetsya, otsutstvie etogo fenomena takzhe yavlyaetsya lish'
neobhodimym kriteriem nalichiya chernoi dyry. Takim obrazom, my mozhem
sformulirovat' vazhneishie priznaki akkreciruyushei chernoi dyry: eto moshnoe
rentgenovskoe izluchenie, bol'shaya massa (bolee treh solnechnyh),
otsutstvie fenomenov rentgenovskogo pul'sara ili rentgenovskogo barstera
I tipa. Pri etom vopros o nadezhnom opredelenii massy relyativistskogo
ob'ekta v rentgenovskoi dvoinoi sisteme yavlyaetsya reshayushim pri
identifikacii ego s chernoi dyroi....
Ya Vam prosto pokazyvayu proiivorechie u Vas i Vashei ssylke,
po otnosheniyu k napisannomu v Vikipedii o izluchenii iz Chernoi Dyry.
Uvazhaemyi
Leitenant Nemo
Chtoby proishodil razbros chastic rentgenovskogo
izlucheniya dlya etogo nado ili yadernoe gorenie zvezd,
chto k chernoi dyre ne primenimo, ili razgon materii
s posleduyushim udarom razognannoi chasticy o poverhnost'
kak eto proishodit v rentgen apparate.
....Material iz Vikipedii
Rentgenovskaya trubka
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih perehodah v
elektronnyh obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok
yavlyayutsya metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe
antikatodom). V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom,
uskoryayutsya pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu anodom
i katodom (pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak
uskorenie slishkom malo) i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe
tormozhenie. .....
Iz chego vytekaet sleduyushee chto dlya vozniknoveniya izlucheniya radioaktivnyh
chastic - neobhodim udar materii na skorosti odnoi desyatoi i bolee
skorosti sveta.
Iz chego sleduet nevozmozhnoe uslovie dlya izlucheniya materii pri padenii v
chernuyu dyru - tak kak dolzhna byt' poverhnost' dlya udara.
A poverhnosti to i net, veshestvo bez udara uhodit za gorizont sobytii,
sledovatel'no i ne mozhet chernaya dyra izluchat' radioaktivnye chasticy.
A.M.Cherepashyuk v dannom sluchai ne prav.
kosmogon
...Schitaetsya, chto pri padenii na ChD veshestvo razgonyaetsya do skorostei,
blizkih k s. V takom sluchae treniya bolee chem dostatochno dlya izlucheniya
vysokih energii. ...
Ya ne mogu ponyat' pochemu rassmatrivaetsya otdel'no vzyataya chast' i ne argumentiruetsya a postuliruetsya.
U Vas - postulat.
Vy voz'mite naprimer shar razmerom v kilometr v diametre, i bros'te ego v Chernuyu Dyru.
Nu i razognali Vy chto ugodno v pustote, - eshe raz povtoryayu - v pustote
proishodit padenie v chernuyu dyru - kakoe mozhet byt' trenie - prosto ne
ob chto teret'sya.
Voz'mite naprimer zvezdu, ei tozhe ne ob chto teret'sya kogda vokrug pustota,
letit padaet i ugasaet, tem bolee chto mne lichno
uvazhaemyi Dmitrii Mamontov raschety privodil chto zvezda na odnoi desyatoi
ili odnoi tretei skorosti sveta, mozhet prekrasno letat' na orbite
vokrug Chernoi Dyry, i s nei vse normal'no.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
,,,Chernaya dyra - oblast' prostranstva, v k-roi pole tyagoteniya nastol'ko
sil'no, chto vtoraya kosmich. skorost' (parabolicheskaya skorost') dlya
nahodyashihsya v etoi oblasti tel dolzhna byla by prevyshat' skorost' sveta,
t.e. iz Ch.d. nichto ne mozhet vyletet' - ni izluchenie, ni chasticy, ibo v
prirode nichto ne mozhet dvigat'sya so skorost'yu, bol'shei skorosti sveta.
Granicu oblasti, za k-ruyu ne vyhodit svet, naz. gorizontom Ch.d.,,,
Eto bazovoe opredelenie, dazhe esli predpolozhit' chto v chernuyu dyru padayut
zvezdy, pri etom izluchayut, i chto v centre galaktiki v chernyh dyrah
massa bol'she chem massa vseh zvezd v etoi galaktike, a s momenta bol'shogo
vzryva
togda mozhno poschitat' skol'ko milliardov zvezd v dyru v centre galaktiki
upalo. Tol'ko vot ne shoditsya s nablyudeniyami - zvezdy ne ischezayut v
chernyh dyrah - etogo nikto ne nablyudal, - ne nablyudali i to kak zvezda
prohodit cherez gorizont sobytii k chernoi dyre.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
...Ishodya iz klassiki, na kotoruyu Vy opiraetes', ChD dlya zemlyanina dolzhny svetit' kak kvazary....
Vashe - Oni voobshe-to aktivno svetyat v rentgene (za schet akkrecii).
Tochnee, razumeetsya, ne oni sami, a akkreciruyushee veshestvo. ChD tak i
obnaruzhivayut.
Moe - u menya vopros - esli v rentgen diapazone izluchayut nizhe privedennye
neitronnye zvezdy - kotorye
...V sluchae, kogda peretekanie veshestva prodolzhaetsya i posle
obrazovaniya N. z., ee massa mozhet so vremenem znachitel'no uvelichit'sya.
Pri ${mathfrak M}_{N.z.}>{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet
ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa
prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru. ...
To kak otlichit' neitronnuyu zvezdu ot chernoi dyry?
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188472
Neitronnye zvezdy
- gidrostaticheski ravnovesnye zvezdy, veshestvo k-ryh sostoit v osnovnom
iz neitronov. Sushestvovanie N. z. bylo predskazano v 30-h gg. 20
v.,vskore posle otkrytiya neitrona. Odnako tol'ko v 1967 g. oni byli
obnaruzheny v vide impul'snyh istochnikov radioizlucheniya - pul'sarov.
Zatem bylo ustanovleno, chto N. z. proyavlyayut sebya takzhe kak rentgenovskie
pul'sary (1971 g.) i vspyshechnye istochniki rentg. izlucheniya - barstery
(1975 g.). Ne isklyucheno, chto na odnoi iz stadii sushestvovaniya N. z. yavl.
istochnikami gamma-vspleskov. K 1984 g. otkryto ok. 400 N. z., iz nih
ok. 20 v vide rentg. pul'sarov, ok. 40 v vide barsterov, a ostal'nye v
vide obychnyh radiopul'sarov.
Druguyu vozmozhnost' poyavleniya N. z. predstavlyaet evolyuciya belyh karlikov v
tesnyh dvoinyh zvezdnyh sistemah. Peretekanie veshestva so
zvezdy-kompan'ona na belyi karlik postepenno uvelichivaet ego massu, i,
kogda ona dostigaet ${mathfrak M}_Ch$, belyi karlik prevrashaetsya v N. z. V
etom sluchae ${mathfrak M}_{N.z.}{mathfrak M}_{maks}$ N. z. poteryaet
ustoichivost' i v rezul'tate relyativistskogo gravitacionnogo kollapsa
prevratitsya v chernuyu dyru.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1188644
Rentgenovskie pul'sary
- istochniki peremennogo periodicheskogo rentg. izlucheniya, predstavlyayushie
soboi vrashayushiesya neitronnye zvezdy s sil'nym magn. polem, izluchayushie za
schet akkrecii (padeniya veshestva na ih poverhnost'). Magn. polya na
poverhnosti R.p. ~ 1011-1014 Gs. Svetimosti bol'shinstva R.p. ot
1035-1039 erg/s. Periody sledovaniya impul'sov P ot 0,7 s do nesk. tysyach
s. R.p. vhodyat v tesnye dvoinye zvezdnye sistemy, vtorym komponentom
k-ryh yavl. normal'naya (nevyrozhdennaya) zvezda, postavlyayushaya veshestvo,
neobhodimoe dlya akkrecii i norm. funkcionirovaniya R.p. Esli vtoroi
komponent nahoditsya na stadii evolyucii, kogda skorost' poteri massy
(etim komponentom) mala (sm. Evolyuciya tesnyh dvoinyh zvezd), neitronnaya
zvezda ne proyavlyaet sebya kak R.p. Rentg. pul'sary vstrechayutsya kak v
massivnyh molodyh dvoinyh zvezdyh sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu I
Galaktiki i lezhashih v ee ploskosti, tak i v malomassivnyh dvoinyh
sistemah, otnosyashihsya k naseleniyu II i prinadlezhashih k sferich.
sostavlyayushei Galaktiki. R.p. otkryty takzhe v Magellanovyh Oblakah. Vsego
otkryto ok. 20 R.p.
Na nachal'nom etape issledovanii otkryvaemym rentg. ob'ektam
prisvaivalis' naimenovaniya po sozvezdiyam, v k-ryh oni nahodyatsya. Napr.,
Gerkules X-1 oznachaet pervyi po rentg. yarkosti ob'ekt v sozvezdii
Gerkulesa, Kentavr H-3 - tretii po yarkosti v sozvezdii Kentavra. R.p. v
Malom Magellanovom Oblake oboznachaetsya kak SMC X-1, v Bol'shom
Magellanovom Oblake - LMC X-4. Obnaruzhenie so sputnikov bol'shogo chisla
rentg. istochnikov potrebovalo dr. sistemy oboznachenii.
Uskorenie i zamedlenie vrasheniya neitronnyh zvezd.
V otlichie ot radiopul'sarov (nek-rye iz k-ryh, v chastnosti pul'sary v
Krabe i Parusah, izluchayut i v rentg. diapazone, sm. Pul'sary),
izluchayushih za schet energii vrasheniya zamagnichennoi neitronnoi zvezdy i
uvelichivashih svoi period so vremenem, R.p., izluchayushie za schet akkrecii,
uskoryayut svoe vrashenie.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Spasibo za otvet.
Esli ya pravil'no ponyal, to istochnik
nepreryvnogo rentgenovskogo izlucheniya
so stabil'noi intensivnost'yu - nazyvaetsya
Chernoi Dyroi .
Esli rentgenovskoe izluchenie menyaet intensivnost'
to eto ili neitronnaya zvezda ili
rentgenovskii pul'sar.
Zdes' avtor chernyh dyr - sem' pyatnic na nedelyu,
sperva govoril vot tak -
...Chernaya dyrá oblast' v prostranstve-vremeni,
gravitacionnoe prityazhenie kotoroi nastol'ko veliko,
chto pokinut' ee ne mogut dazhe ob'ekty, dvizhushiesya
so skorost'yu sveta (v tom chisle i kvanty samogo sveta)....
Potom ego ozarilo v 1975 i on odaril chernye dyry i vseh
astrofizikom izlucheniem ot chernyh dyr.
---...Izluchénie Hókinga ...---
......Material iz Vikipedii
Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi.
Predskazan teoreticheski Stivenom Hokingom v
1974 godu.[1] Rabote Hokinga predshestvoval
ego vizit v Moskvu v 1973 godu, gde on vstrechalsya
s sovetskimi uchenymi Yakovom Zel'dovichem i
Alekseem Starobinskim. Oni prodemonstrirovali
Hokingu, chto v sootvetstvii s principom
neopredelennosti kvantovoi mehaniki
vrashayushiesya chernye dyry dolzhny
porozhdat' i izluchat' chasticy.[2]
Isparenie chernoi dyry kvantovyi process.
Delo v tom, chto ponyatie o chernoi dyre kak ob'ekte,
kotoryi nichego ne izluchaet, a mozhet lish' pogloshat' materiyu,
spravedlivo do teh por, poka ne uchityvayutsya kvantovye effekty.
V kvantovoi zhe mehanike, blagodarya tunnelirovaniyu,
poyavlyaetsya vozmozhnost' preodolevat' potencial'nye bar'ery,
nepreodolimye dlya nekvantovoi sistemy. Utverzhdenie,
chto konechnoe sostoyanie chernoi dyry stacionarno,
pravil'no lish' v ramkah obychnoi, ne kvantovoi teorii
tyagoteniya. Kvantovye effekty vedut k tomu, chto na samom
dele chernaya dyra dolzhna nepreryvno izluchat', teryaya pri
etom svoyu energiyu.....
Itogo
...Izluchénie Hókinga process ispuskaniya
raznoobraznyh elementarnyh chastic,
preimushestvenno fotonov, chernoi dyroi....
A gospodin A.M.ChEREPAShUK, v Vashei ssylke,
ya tak ponyal reshil - zachem dobru propadat' - pust'
izluchenie ( Izluchénie Hókinga) iz chernoi dyry
budet eshe i preimushestvenno iz rentgenovskih chastic.
Uvazhaemyi
Dmitrii Mamontov
Moe - A vot zdes' ya Vam mogu predlozhit' sdelat' u kazhdoi stat'i schetchik, - ponyal -ne ponyal,
Vashe - Dlya bazovogo ponimaniya nuzhno umet' chitat' i imet' nekotoruyu
podgotovku v ramkah hotya by shkoly. U Vas takaya podgotovka, sudya po
vsemu, hromaet na obe nogi, poetomu Vy ne ponimaete bol'shinstvo statei.
Dlya utochnyayushih voprosov est' kommentarii, dlya bazovoi podgotovki - shkola
i uchebniki.
- Vy dumaete chto vse uchennye pishut pravil'nye stat'i, i nikto stat'i ne
vysasyvaet iz pal'ca a potom ne rzhet nad chitatelyami, a Vash sait chtoby
chitat' - to nado byt' doktorom nauk, i v tozhe samoe vremya Vy lichno ne
mozhete otvetit' pryamo na pryamye voprosy, po etoi stat'e. Vy menya v
principe zaintrigovali, ya podumayu chtoby takoi puzyr' vysosat' iz pal'ca v
ramkah paradigmy, chtoby vse vokrug azh zaaplodirovali za isklyuchitel'no
vysokohudozhestvennyi idiotizm v ramkah breda sivoi kobyly.
Moe-Ne rasskazhete Vashe otnoshenie k vyskazyvaniyu, -
Esli opyt ne sovpadaet s teoriei to tem huzhe dlya opyta?
Napomnyu -
Moe - So vtorogo Vashego otveta ya ponyal - chto u Vas est' metody
dokazatel'stv kotorye pozvolyayut opredelit' kakimi byli v pervye momenty
bol'shogo vzryva zvezdy, chernye dyry , temperatura i drugie razlichnye
svoistva prostranstva i svoistva razlichnyh fizicheskih ob'ektov.
Vashe - Ne u menya. U astronomov, astrofizikov i kosmologov.
Moe- Esli mne ne mozhet opponent srazu vnyatno izlozhit' otvet na moi
prostoi vopros po obsuzhdaemoi stat'e, to ya ne obyazan verit' napisannomu,
a skoree naoborot - vynuzhden zasomnevat'sya.
Po povodu gromkih familii v astrofizike - to esli Vy proanaliziruete ih
biografiyu i trudovye zaslugi i proanaliziruete ih prichastnost' k
astrofizike, to oni vse v astrofizike - diletanty, kotorye idei
vbrasyvali v astrofiziku ot sluchaya k sluchayu, i ser'ezno ei ni kto ne
zanimalsya. Po etomu vsya astrofizika i sostoit iz razroznennyh idei, -
ozaryalok, kotorye posledovateli pytayutsya sostykovyvat' mezhdu soboi po
prichine poyavleniya novoi izmeritel'noi tehniki.
A astrofiziku u menya hobbi let 7, tak chto ya prochital stol'ko statei
raznyh, chto mogu delat' vyvody chto vysoska iz pal'ca, a chto i super
gramotno napisano .
Samoe smeshnoe chto super stat'i absolyutno neizvestny.
http://crydee.sai.msu.ru/Universe_and_us/4num/v4pap26.htm
-Ochen' horoshaya stat'ya.
http://www.anomaliy.ru/discovery/482
"Sverhnovye tipa I a, kak polagayut, formiruyutsya
posle vzryvov belyh karlikov, sverhplotnyh mertvyh zvezd razmerom s
nashu Zemlyu, kotorye kogda-to byli yadrom solncepodobnogo svetila, i
ch'ya vneshnyaya obolochka rastvorilas' v kosmose.
Odna iz osobennostei etogo tipa otsutstvie vodoroda, i eto
nesmotrya na to, chto vodorod yavlyaetsya samym rasprostranennym
himicheskim elementom."
Vot eta stat'ya - v principe dolzhna byla perevernut' vsyu astrofiziku,
po toi prichine chto net vodoroda vnutri zvezdy. A u tekushei paradigmy
vodorod vygoraet. I astrofiziki vnyatno otvetit' ne mogut prichinu po
kotoroi samyi legkii vodorod - preodolevaet gravitaciyu stanovitsya
tyazhelee vseh metallov i letit v yadro zvezdy pouchastvovat' v yadernoi
reakcii. I V to chto samyi legkii vodorod preodolevaet letit vnutr'
zvezdy -ya ne veryu, hot' v millione knizhek eto budet napisano, i tysyache
uchebnikov. Tak kak napisannoe ne podtverzhdeno fizicheskimi svoistvami a
protivorechit im.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(v. g. gruzinov,
5.02.2013 20:57, 225 Bait)
Mozhet chernaya dyra byt' napodobie tornado ,my vidim kak ona pogloshaet i dolzhen byt' vybros materii s drugoi storony? .I vtoroe esli chto -libo uletaet ot nas so skorost'yu
sveta ,budet eto vyglyadet' dlya nas kak chernaya dyra?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.02.2013 22:33, 235 Bait, otvetov: 2)
\\\my vidim kak ona pogloshaet\\\
Kto i kogda eto videl.
Oficial'no na tekushii moment ne obnaruzheno ni odnoi
chernoi dyry, est'
tol'ko predpolozheniya - chto vot tam-to
ona dolzhna byt'.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(V. A. Burdin,
9.02.2013 14:57, 824 Bait, otvetov: 1)
K sozhaleniyu ne prochital ya vse 34 stranicy etogo foruma,no posle prochteniya pervogo desyatka voznik vopros lichno k Vam A.P. Vasi- Vy pisali chto ''Chernaya dyra - ne yavlyaetsya
tonnelem, po prichine togo chtou nee est' massa, i lyuboi relyativist ochen' bystro i doblestno razob'etsya v lepeshku o ee poverhnost', tak kak ee razmer i radius Vam izvesten''
i ''U chernoi dyry est' radius sledovatel'no est' poverhnost'''-vytekaet vopros-chto na Vash vzglyad(imenno na Vassh) lezhit(mozhet lezhat') v osnove poverhnosti chernoi dyry? Vo mnogih
istochnikah videl sleduyushee(ne citiruyu,svoi slova)-chernaya dyra obladaet sverhgravitaciei po prichine ee sozdaniya. Chto mol,yadro nastol'ko plotno,chto ''byvshaya'' giperzvezda szhalas'
do takih razmerov,ne poteryav pri etom urovnya gravitacii. Chto zhe togda sluzhit ''materialom poverhnosti''? Zhelezo?
- Re[3]: Chernaya dyra
(V. A. Burdin,
9.02.2013 15:02, 340 Bait)
Otvechaya na vopros ''my vidim''-vozmozhno mnogie avtory prosto videli seriyu fil'mov ''Discovery. Kak ustroena vselennaya.'' Est' takoe delo )) uzh ochen' chasto na lyubye zaprosy,svyazannye
s astronomiei poiskovi vyvodyat na vyrezki i kuski video iz etih 8-mi serii. Tak....chisto moe predpolozhenie )) prosto ne znayu kak my eshe mozhem ''videt'''....
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
9.02.2013 17:08, 284 Bait)
Ya nad voprosom dumayu dolgo zato reshayu ego raz i navsegda,
i esli ya skazal chto avtor chernyh dyr
ne dalekii v fizike \umstvenno ne polnocennyi v fizike\,
to
menya ego tvorchestvo uzhe ne interesuet.
Ya svoyu zhizn' na bessmyslennuyu i bespoleznuyu uinyu tratit' ne sobirayus'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.02.2013 23:58, 866 Bait)
\\\Prostaya zadacha dlya elektrikov.\\\
Starost' ne radost', vot yarkii primer
kak mozhno sebya samomu
obo- ... bez postoronnei pomoshi.
Shas po planete tol'ko kakaya ekonomiya, mozhno s linii elektroperedach
vysokovol'tnyh snimat'
odnu fazu, i nagruzka na drugie
ne vozrastet, ih tolshe po secheniyu delat' ne nado.
Zdes' uzhe ne prohodit fraza \otcy prostite za-s-ranca\ zvuchit kak nasmeshka
nad vsei fizikoi.
Chto eshe menya udivlyaet ya hot' i sam s trehfaznoi tehnikoi
kak kipovec stalkivayus', u menya pol megavatta byl maksimum
po nagruzke,
- tri nagruzki po 160kVt s elektronnymi preobrazovatelyami
ot odnogo vvoda.
Shina byla mednaya polosa, i esli ona oborvetsya to polnocenno ee vosstanovit'
ne vozmozhno prakticheski.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.02.2013 2:33, 3.0 KBait)
Prostaya zadacha dlya elektrikov.
----------------------------
 Prostaya zadacha dlya elektrikov. ---------------------------------------------------
Prostaya zadacha dlya elektrikov. ---------------------------------------------------
Kak pri obryve odnoi iz faz v trehfaznoi seti polnocenno vosstanovit'
oborvannuyu fazu na lyuboi moshnost'. Krome vysokih materii nuzhno znat' i
elementarnye veshi!!!
--------------------------------------
Dazhe ne ponimayu kak mozhno byt' nastol'ko
nedalekim chtoby ne znat' togo
chto pri podklyuchenii
ustroistv treugol'nikom s ostavshihsya dvuh
faz mozhno vzyat' tol'ko tridcat' procentov
mosh'nosti, pri podklyuchenii zvezdoi,
mozhna vzyat'
shesdesyat pyat' procentov
moshnosti, i uzvezdy dolzhen byt' nulevoi
provod ne umen'shennogo secheniya,
a esli nulevoi umen'shennogo secheniya
to tridcat' procentov
mosh'nosti.
I vot naprimer est' nekotoraya nagruzka kotoraya
potreblyaet moshnost', k nei podvoditsya silovoi
kabel'. Stoit rubil'nik i tokovaya zashita,
kotoraya zashishaet podvodimy kabel' soglasno
ustanovlennoi moshnosti na raschetnuyu temperaturu
v sorok gradusov okruzhayushei sredy,
tok trehfaznyi dlya nasosov
mozhno prosto uznat'
umnozhiv moshnost' v 2.1 - 2.2 raza, naprimer
15kVt = 32A trehfaznoi na 380 - 400V, po rekomendciyam
prohodit v prityk kabel' v chetyri
kvadrata \ne v trube\
chto logichno privodit k perehodu na shest' kvadrat.
Grubo govorya - kabel' po secheniyu podvoditsya
vprityk po moshnosti bez dvuh kratnogo
zapasa,
i teplovaya zashita po toku v provode - avtomaticheskie
vyklyuchateli ustanavlivayutsya soglasno secheniyu
podvodimogo provoda.
I naprimer est' kloun
kotoryi uvidel v prodazhe
chastotnik dlya dvigatelya kotoryi zapityvaetsya
ot 230V, a na vyhode vydaet tri fazy na 380V.
Tak on vsyu moshnost' beret iz odnoi fazy
i nulevogo
provoda, plyus poteri na preobrazovanie,
tok uznat' 1kVt primerno raven 5A.
I chtoby naprimer zapitat' dvigatel' v 15kVt,ot 220V nado
chtoby
podvodimyi kabel' smog obespechit'
tok v 75A. A takogo secheniya kabel' nikto ne podvodil,
i zashitnye avtomaty na 40A, i vvodnoi rubil'nik
na 40A, i vsya provodka
na 40A.
Tak chto vyskazyvanie o polnocennoi zamene -
eto primitivnyi lah a tron.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.02.2013 19:41, 2.3 KBait)
----------------------------
 Re: Prostaya zadacha dlya elektrikov.
Re: Prostaya zadacha dlya elektrikov.
Otvet #69 - Segodnya :: 18:08:19
PauLitas pisal(a) Segodnya :: 17:11:29:Berem
dva transformatora (s nuzhnym i odinakovym koefficientom transformacii),
transformiruem pervuyu fazu nu budem schitat' ee fazoi A, transformiruem
vtoruyu fazu budem schitat' ee fazoi V soedinyaem vtorichnye obmotkietih
dvuh transformatorov pravil'no (kak bol'she napryazhenie), i v nuzhnoi
fazirovke vklyuchaem ee odnim koncom k nulevomu provodu. Vot i est' nuzhnaya
tret'ya faza! Otvet pravil'nyi. Kak ne kruti, vy zdes'
samyi kvalificirovannyi elektrik. Pravil'no reshili zadachu ob izmerenii
emkosti kondensatora v sostave rezonansnogo kontura. A ved' ee ne smog
reshit' kandidat nauk E-Eater. Teper', hot' i ne srazu, reshili i etu
zadachu. Snimayu shlyapu!
|
----------------------------
Tak i ohota skazat' chto v elektronike
nikogda ne stoit vystebyvat'sya ibo est'
programmy tipa elektronik vork bench 5.12
v kotoroi mozhno i fazy i silu s-imitirovat'
i transformatory, i nagruzku dat' i vklyuchit'
vse eto laino i posmotret'
oscillogrammy.
U menya takoe chuvstvo chto um na zemle kak fizicheskaya velichina
eto konstanta,
esli lyudei na nei bol'she to kto-to tupeet pri uvelichenii
kolichestva naseleniya planety.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.02.2013 19:46, 113 Bait)
Transformator ne delaet sdviga faz
na sto dvadcat' gradusov.
Etogo v fizike ne znayut tol'ko nedalekie.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.02.2013 13:17, 1.1 KBait)
A vot i nagrada nashla svoego geroya.
-----------------------------
 Re: Prostaya zadacha dlya elektrikov.
Re: Prostaya zadacha dlya elektrikov.
Otvet #83 - Segodnya :: 11:23:19
Fedor Mende pisal(a) 14.02.13 :: 22:52:46:
Est' i prakticheskaya realizaciya na 10 kVt na kazhduyu fazu.
trehfaznyi ...
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.02.2013 13:18, 266 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Nemnogo adekvatnogo.
 Naskol'ko mozhno doveryat' vyvodam astrofizikov? 15.01.2013
Naskol'ko mozhno doveryat' vyvodam astrofizikov? 15.01.2013
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(v. g. gruzinov,
20.02.2013 16:49, 859 Bait)
Nash glaz eto tozhe chernaya dyra ili ,nora?.Esli svet imeet davlenie i naduvaet parusa ,a teleskop fokusiruet svet v puchek kotoryi svetit nam v glaz ,kuda on devaetsya potom ,rasseivaetsya
v nashem mozgu ili uhodit v drugoe izmerenie.Esli skorost' sveta postoyanna- to kak teleskop umudryaetsya pokazat' nam gallaktiku za neskol'ko sekund ,iz dal'nei vselennoi ,esli
svet letit do nas milliony let? Takim obrazom mozhet li teleskop rabotat' v "obratnuyu" storonu i obshat'sya s drugimi ne borozdya prostory dazhe nashei gallaktiki .Naprimer:
stroim ogromnyi teleskop na lune ili ispol'zuem planety s nashimi sputnikami, kotorye inogda vystroivshis' opredelennym obrazom sozdadut ogromnyi reflektor i nalazhivaem mgnovennyi
kontakt ,hot' azbukoi morze .(uslovno)I nikakih dal'nih pereletov s teoriei Einshteina . prosto snachala naladit' svyaz' s drugoi zhizn'yu .
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.02.2013 14:16, 1.7 KBait)
 Re: Vihrevoi ob'ekt. Materializaciya
Re: Vihrevoi ob'ekt. Materializaciya
Vselennoi.
Otvet #75 - Segodnya :: 12:26:11
\\\
Edinstvennyi chelovek ponyal
temu tak, kak ya pytalas' donesti. Imenno
takoe ponimanie pozvolyaet sovershit' tochnye raschety i sozdat' fraktal'nyi
generator elektrichestva. V nashei tablice elementov vidna zavisimost'
struktury atoma ot sootnosheniya sobstvennyh kolebanii s kolebaniyami
sredy. Na
osnovanii etogo mogut byt' izucheny svoistva veshestv dlya
ispol'zovaniya ih v novoi tehnologii dobychi elektricheskoi energii, a
takzhe poyavitsya vozmozhnost' preodolet' gravitaciyu.\\\
-------------------------
Vot chto sobstvenno v etom tekste brosaetsya v glaza, tak eto s odnoi storony
logiki
stremlenie k ob'ektivnomu ponimaniyu, pri etom bez-bashennaya zhazhda
darmovshiny, vyrazhennaya v stremlenii k sharovoi energii i sharovym
metodam preodoleniya
gravitacii.
Tak vot - vot eta zhazhda darmovshiny - delaet absolyutno
nevozmozhnym ob'ektivnoe vospriyatie. Po toi prichine
chto u prirody vozmozhno i net toi sharovizny
kotoruyu pytayutsya naiti, da chto tam vozmozhno, tochno net sharovizny,
ona ei - prirode, ne nuzhna, nuzhna tem kto sam sebe ee pridumal i pytaetsya
naiti - nazyvaetsya
eto - samoobman.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2013 0:07, 5.0 KBait)
 Re: Vselennaya kak sploshnaya mnogofaznaya sreda
Re: Vselennaya kak sploshnaya mnogofaznaya sreda
Otvet #1371 - Segodnya :: 11:49:21
Mar.Mih-na pisal(a) Segodnya :: 11:18:57:Skol'ko raz mozhno sprashivat' Larisu: tak v chem vash al'ternativnyi vzglyad? Vy postoyanno afishiruete zdes' dostizheniya
vashei kafedry 50-letnei davnosti. \\\ Uvazhaemaya Mar'-Mihna! Ya vse zhdu, chto Vy, chitaya posty temy, sami naidete otvet na svoi vopros. Vidimo, ne dozhdus'... Poetomu
otvechayu. Ya zdes' afishiruyu ne dostizheniya nekoi "kafedry", a dostizheniya
NAUKI, pod nazvaniem "Fizika sploshnoi sredy". Kotoraya sushestvuet uzhe
okolo 300let, odnako ee primenenie v raznyh oblastyah chelovecheskoi
praktiki imeet nyuansy. Vot eti nyuansy ya i pytayus' vyyavit' i predstavit'
uvazhaemoi "publike" primenitel'no k gipoteze efira, sverh'edinichnyh
ustroistv, problemy "vechnogo" dvigatelya i dr. I ya ponimayu AL'TERNATIVNY'
vzglyad na nekie fizicheskie yavleniya NE kak PROTIVOPOLOZhNY' sushestvuyushim
vozzreniyam, a prosto, DRUGO', "svezhii". I hochu pokazat', chto NET
LZhENAUKI v nashem podlunnom Mire, a est' odna NAUKA, s raznoi stepen'yu
dostovernosti opisyvayushaya i ob'yasnyayushaya EGO. I, vrode by, mezhdu vzglyadami Mihaila Petrovicha i moimi namechaetsya konsensus. Budem rabotat' dal'she...\\\ ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Ya vot bylo nemnogo po-vozmushalsya myslenno po prichine togo chto zakonodatel'nyi organ dlya uchennyh Rossii - eto komissiya po bor'be s lzhenaukoi. I sobstvenno
ya yavlyayus' zakorenelym lzheuchenym - po toi prichine chto v ramkah opredeleniya lzheuchenogo v Rossii est' vot takie standarty. I kak govoritsya do lampochki
chto kakoi-to baryshne hochetsya chtoby bylo po drugomu, a tochnee kak ei nravitsya - ee mnenie i pozhelaniya nikogo ne interesuyut, ibo kriterii opredeleny. ------------------------------------------------------------------ http://lenta.ru/conf/kuvakin/
Eduard-2
[24.04 03:11]
Uvazhaemyi Valerii Aleksandrovich, ya est' li v vashem (RAN) arsenale
standartnaya metodika otdeleniya "pshenicy ot plevel", t.e. nauchnyh
otkrytii i dostizhenii ot okolonauchnyh yavlenii, k nauke otnosheniya ne
imeyushih? Esli takaya metodika sushestvuet, to kakie priznaki srazu
ukazyvayut na to, chto pered nami ocherednoi graf Kaliostro?
Uvazhaemyi Igor'!
V praktike ocenki lzhenauki est' dva puti. Pervyi etot special'naya
svobodnaya i nezavisimaya nauchnaya ekspertiza. No ona vozmozhna tol'ko v tom
sluchae, esli v zayavlennoi idee est' predmet issledovaniya. Esli zhe ee ni
podtverdit', ni oprovergnut' nevozmozhno, to takie idei ne
rassmatrivayutsya v kachestve nauchnyh. V etoi svyazi upominayut i o principe
"bremeni dokazatel'stva", to est' obyazannost' dokazyvat' istinnost' ili
nauchnost' utverzhdeniya lezhit na toi storone, kotoraya i vydvigaet eto
utverzhdenie. Vmeste s tem sushestvuyut nekotorye obshie i predvaritel'nye
priznaki, nalichie kotoryh dolzhno stavit' pod ser'eznoe somnenie
nauchnost' zayavleniya (teorii, otkrytiya i tak dalee). Eto tak nazyvaemye
priznaki prima facae (to est' "s pervogo vzglyada"). K nim, v chastnosti,
otnosyatsya: (1) otsutstvie u zayavitelya sootvetstvuyushego bazovogo
obrazovaniya ili professional'noi podgotovki; ------------------------------------------- A ya vot ni to chto special'nogo obrazovaniya ne imeyu u
menya dazhe vysshego obrazovaniya net. Ya sobstvenno - lzheuchenyi odnoznachno. Chto menya v etoi situacii raduet chto v Rossii moi avtorskie prava zashisheny bolee
chem. Chto menya udivlyaet chto storonniki Efira v Rossii s kotorymi ya vozmozhno hotel by sotrudnichat' v napisanii stat'i pro efir, po toi prichine chto vmeste preodolevali
trudnosti na membrane - budut srazu lzheuchenymi pri sovmestnom napisanii stat'i so mnoi. I chto mne naprimer kollegam po efiru skazat' - davaite napishem sovmestnuyu
stat'yu - tol'ko Vas budut nemnozhko lishat' nauchnyh stepenei, zaslug dolzhnostei i diplomov. |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2013 0:13, 118 Bait)
I pri vsem pri tom ya s Ukrainy - na kotoruyu naprimer
takoi podhod k opredeleniyu lzheuchenyh ne rasprostranyaetsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2013 1:31, 1.8 KBait)
Oh ya i nasmeyalsya - vse est',
-est' elektrichestvo,
- est' tok
-est' magnitnoe pole
- a soprotivleniya, - tochnee nagruzki,
tochnee prichiny vsego
etogo kolenkora - to i net.
--------------------------------------------------------------
Kstati ne ris-23
A okolofizichnyi s pritenziei na
kosmologichnost' -
- risunok hudozhnika - nomer 23.
-----------------------------------------------------
Elektricheskoe pole
pytaetsya vosstanovit' prervannyi elektricheskii tok.

Ris. 23
Na ris. 23
krasnym cvetom pokazano elektricheskoe pole, kotoroe generiruetsya v rezul'tate
otklyucheniya dzheta chernoi dyry. Pole sozdaet el. tok, v osnovnom, v vide
cirkulyacii elektronov vokrug magnitnyh linii polya torov. Kak pokazano, cirkulyacionnyi
potok elektronov podpityvaetsya elektronami so storony diska galaktiki. Pri etom,
elektrony podpitki dvigayutsya vdol' magnitnyh linii galakticheskogo yadra. Traektorii
elektronov, rasprostranyayushihsya vdol' magnitnyh linii galakticheskogo yadra i
vdol' elektricheskogo polya galo, opredelyayut harakternuyu formu puzyrei Fermi. V summe, uskoryaemyi elektricheskim polem potok
elektronov, magnitnoe pole galo galaktiki i magnitnoe pole galakticheskogo yadra formiruyut
sinhrotronnoe radio, rentgenovskoe i gamma izluchenie.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2013 1:33, 242 Bait)
http://www.popmech.ru/images/upload/..._23_1356623136_resize.jpg

- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2013 1:34, 134 Bait)
http://www.popmech.ru/blogs/post/5087-osobennosti-formirovaniya-struynyih-vyibrosov-aktivnyih-galakticheskih-yader-i-chernyih-dyir-ch/
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.02.2013 2:02, 1.0 KBait)
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.03.2013 21:11, 4.0 KBait)
\\\Eto tak nazyvaemye
priznaki prima facae (to est' "s pervogo vzglyada"). K nim, v chastnosti,
otnosyatsya: (1) otsutstvie u zayavitelya sootvetstvuyushego bazovogo
obrazovaniya ili professional'noi podgotovki; \\\
Kak ne stranno eto vyskazyvanie popadaet pod deistvie zakonodatel'stva Rossii.
Vot ot syuda tekst.
--------------------------------------------------------
 Re: Seminar v CIAM
Re: Seminar v CIAM
Otvet #925 - Segodnya :: 19:10:13
Damy, gospoda.
Peregudov vstal na put' ugolovno nakazuemoi deyatel'nosti. A imenno, na put' razzhiganiya mezhnacional'noi i mezhrasovoi vrazhdy..
Vot nekotoraya
informaciya po etomu povodu...
On
pisal. "Pri chem tut nacional'naya rozn'? A, eto vam devstvennaya
chistota mozgov meshaet menya pravil'no ponyat'! Po teorii evolyucii Darvina
(v shkole prohodyat) chelovek proizoshel ot obez'yany. No proizoiti ot
obez'yany --- eto vam ne kuchu pod dver' nalozhit'! Process trudnyi,
dolgii, boleznennyi. Nekotorye uzhe proizoshli, a drugie nekotorye
podzastryali Smeh Vas, naprimer, vpolne mozhno nazvat' "vladimirskoi
martyshkoi". Po sravneniyu s etim Shi vy "proishodit' iz obez'yany" eshe i ne
nachinali."
A vot yuridicheskaya kvalifikaciya etih vyskazyvanii.
"Razzhigánie mezhnacionál'noi rózni - deistviya, napravlennye
na vozbuzhdenie mezhnacional'noi ili mezhrasovoi vrazhdy.
V Rossii
V Rossii podobnye deistviya priznayutsya prestupleniyami protiv osnov gosudarstvennogo stroya i bezopasnosti
gosudarstva.
Stat'ya 29 Konstitucii Rossiiskoi Federacii[1] glasit, chto
Ne
dopuskayutsya propaganda ili agitaciya, vozbuzhdayushie social'nuyu, rasovuyu,
nacional'nuyu ili religioznuyu nenavist' ili vrazhdu. Zapreshaetsya
propaganda social'nogo, rasovogo, nacional'nogo, religioznogo ili
yazykovogo prevoshodstva.
Soglasno chasti 1 stat'i 282 Vozbuzhdenie
nenavisti libo vrazhdy, a ravno unizhenie chelovecheskogo dostoinstva
Ugolovnogo kodeksa Rossiiskoi Federacii v redakcii Federal'nogo zakona
ot 08.12.2003 N 162-FZ[2],
Deistviya, napravlennye na vozbuzhdenie
nenavisti, libo vrazhdy, a takzhe na unizhenie dostoinstva cheloveka, libo
gruppy lic po priznakam pola, rasy, nacional'nosti, yazyka,
proishozhdeniya, otnosheniya k religii, a ravno prinadlezhnosti k kakoi-libo
social'noi gruppe, sovershennye publichno ili s ispol'zovaniem sredstv
massovoi informacii nakazyvayutsya shtrafom v razmere ot sta tysyach do
trehsot tysyach rublei ili v razmere zarabotnoi platy ili inogo dohoda
osuzhdennogo za period ot odnogo goda do dvuh let, libo lisheniem prava
zanimat' opredelennye dolzhnosti ili zanimat'sya opredelennoi
deyatel'nost'yu na srok do treh let, libo obyazatel'nymi rabotami na srok
do sta vos'midesyati chasov, libo ispravitel'nymi rabotami na srok do odnogo goda, libo lisheniem svobody na srok do dvuh let."
Ya
polagayu, Peregudovu est' o chem podumat'. Ya posmotrel. Prokuratura
deistvuet. Elektronnaya priemnaya rabotaet. Mozhno i lichno shodit',
zayavlenie napisat'. Oni eto lyubyat, kogda lichno.....
Ya nemnogo
podozhdu. Ne osoznaet- togda eto budut problemy Peregudova. Mozhno,
zaodno, rukovodstvo MGU privlech'- kogo ono u sebya derzhit. I rukovodstvo
IFZ..... I ne vazhno, chto tam govoril Darvin. Vazhno, chto zapisano v UK.
-----------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.03.2013 21:34, 398 Bait)
Po bol'shomu schetu - bor'boi s lzhenaukoi
mozhno i ne stradat'.
Dostatochno vvesti premiyu za oproverzhenie teorii i gipotez,
i razmery premii v desyat' tysyach evro
ne bolee, i pyat'sot evro
minimal'naya.
I ya prosto uveren chto za stoimost' men'she odnoi nobelevskoi
- budet snesena vsya tekushaya fizika i kosmologiya, po vremeni
snesut pod chastuyu - za goda tri maksimum.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.03.2013 15:41, 4.6 KBait)
Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
Gipóteza (dr.-grech.
ὑπόθεσις
predpolozhenie; ot ὑπό
snizu, pod + θέσις
tezis) predpolozhenie ili dogadka;
utverzhdenie, predpolagayushee dokazatel'stvo, v otlichie ot aksiom, postulatov, ne trebuyushih dokazatel'stv. Gipoteza schitaetsya nauchnoi, esli ona udovletvoryaet kriteriyu
Poppera, to est' potencial'no mozhet byt' proverena kriticheskim eksperimentom, a takzhe esli ona sootvetstvuet drugim nauchnym
kriteriyam.
Takzhe ona mozhet opredelyat'sya kak forma razvitii znanii,
predstavlyayushaya soboyu obosnovannoe predpolozhenie, vydvigaemoe s cel'yu
vyyasneniya svoistv i prichin issleduemyh yavlenii[1].
Kak pravilo, gipoteza vyskazyvaetsya na osnove ryada podtverzhdayushih ee nablyudenii (primerov),
i poetomu vyglyadit pravdopodobno. Gipotezu vposledstvii ili dokazyvayut, prevrashaya ee v ustanovlennyi fakt
(sm. teorema, teoriya),
ili zhe oprovergayut (naprimer,
ukazyvaya kontrprimer), perevodya v razryad
lozhnyh utverzhdenii.
Nedokazannaya i neoprovergnutaya gipoteza nazyvaetsya otkrytoi problemoi.
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Otkrytaya problema
- kak raz i nazyvaetsya slovom - lzhenauka.
Sobstvenno vsya kosmologiya takovoi i yavlyaetsya po opredeleniyu,
ibo dokazat' stroenie zvezd , nalichie chernyh dyr
i bol'shogo vzryva -
nel'zya nazvat' dazhe gipotezami - oni podrazumevayut vozmozhnost'
proverki i oproverzheniya, v svyazi s chem pri otsutstvii takovoi
vozmozhnosti v principe - to eto ne gipoteza a fantastika ili
vydumka - odnim slovom - lzhenauka.
Tak chto luchshe by komissiya po bor'be
s lzhenaukoi svoim
by delom zanyalas' vmesto togo chtoby ob'yavlyat' vseh
u kogo net vysshego obrazovaniya lzheuchenymi po priznakam
- s pervogo
vzglyada.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.03.2013 15:00, 1.4 KBait)
Chital pro raznye opyty po izmereniyam. Chto sobstvenno menya
udivlyaet - chto-to izmeryayut, potom dumayu chto i kak izmerili.
A osnovnaya oshibka v tom chto net ne tol'ko
standartnoi metodiki
izmerenii na korotkih vremennyh promezhutkah,
tak i net samodiagnostiki.
Rasskazhu kak sdelat' absolyutnye izmeritel'nye kabelya.
U absolyutnogo izmeritel'nogo kabelya dolzhno byt' tri ekranirovannyh
zhily, i tri optovolokna, vse eto soedinyaetsya vmeste, i delaetsya
shest' takih absolyutnyh kabelei,
dlinnoi po desyat' metrov kazhdyi.
vse shest' kabelei soedinyayutsya vmeste.
Nuzhno vzyat' oscillograf u kotorogo shest' vhodnyh kanalov,
na kazhdyi vhod
podklyuchaetsya po odnomu provodu iz kazhdogo kabelya,
po odnomu provodu iz kazhdogo kabelya beretsya i oni skruchivayutsya
vmeste i na nih podaetsya strobiruyushii signal.
Iz kabelya beretsya po odnomu okptovoloknu i podklyuchayutsya
na shest' optovolokonnyh vhodov v etom-zhe oscillografe,
na vtorye optovolkna podaetsya obshii strobiruyushii
signal,
i oni vklyuchayutsya v tot-zhe oscillograf,
Na svobodnom optovolokne kazhdogo kabelya, ustanavlivaetsya
vysokoskorostnoi priemnik s avtonomnym pitaniem,
vyhody podklyuchayutsya na cifrovye optovolokonnye vhoda
v etom-zhe oscillografe.
I vot s etoi tehnikoi mozhno hot' chto-to adekvatnoe
izmeryat' i sravnivat',
- ibo budet vozmozhnost' absolyutnogo
vremennogo kontrolya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
21.03.2013 13:45, 3.0 KBait)
Ya vot ne ponimayu esli ty naprimer relyativist
to kakogo lezt' na al'ternativnye forumy i uchit'
tam al'tov relyativizmu.
Al'ty ved' v otvet budut vsegda
posylat' v peshee
eroticheskoe puteshestvie, i vsegda budut portit'
nervy etomu relyativistu, chto v itoge skazhetsya
otricatel'no na zdorov'e relyativista, ibo
ot nervov
i postoyannogo prebyvaniya v nervoznom sostoyanii
sozdast ochen' veselye trudnosti dlya zdorov'ya relyativista
kotoryi pytaetsya kak on dumaet al'tov umu
razumu nauchit'.
Hotya s drugoi tochki zreniya mozhet eta situaciya i
k luchshemu ibo bystree mahrovye relyativisty sletyat
s intellektual'nyh katushek.
------------------------------------------------------
\\\
 Re: Seminar v CIAM
Re: Seminar v CIAM
Otvet #1320 - Segodnya :: 12:23:24
Vallav pisal(a) Segodnya :: 00:56:26:Ne, Vy unikum.
Boltat' o chem ugodno, a v otvet na vopros - ni slova.
Natrenirovalis'.
I pri takih talantah eshe o kakoi to diskussii zaikaetes'.
Vallav. Lyudi ochen' raznye, unikumy. Ya ne boltayu. Ya gnu svoyu liniyu na vvedenie efira v nauchno-tehnicheskii oborot. Na etoi osnove ya mogu
vesti diskussii i obsuzhdeniya. No
trudno vesti diskussii s opponentami, kotorye dazhe ne pytalis'
prochitat' chto-to pro efirodinamiku (hotya by v ob'eme populyarnoi
efirodinamiki). Esli opponent imeet predstavleniya ob efire vremen
Lorenca (i to oshibochnye). Ya ne vedu diskussii po takim "obshepriznannym" naukam kak TO i izhe s nei. Dannyi
forum vse zhe nazyvaetsya "Fizika al'ternativnaya". Nado zametit', chto
nichego al'ternativnogo v efirodinamike ya ne nahozhu. Klassicheskaya
fizicheskaya teoriya. Hotya posle vseobshego vvedeniya matematicheskih izvratov
TO, KM i tp, klassicheskaya fizika, razvitiem kotoroi yavlyaetsya
efirodinamika mogut pokazat'sya "proshlym vekom". Opyat' zhe gazodinamika,
kak osnova ED, nauka slozhnaya daleko ne zakonchennaya. S uvazheniem, Mihail Surin
|
\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
21.03.2013 23:08, 9.3 KBait)
Udivilo nazvanie foruma.
Eto avtor sovsem ne dalekii.
Ibo ya dazhe davno znal chto sushestvuyut
svetovye usiliteli tak skazat' pryamogo
deistviya.
A u transformatora zadacha - izmenenie
amplitudy signala, - laino vopros.
--------------------------------------------
Pochemu
net svetovogo transformatora?
Stranic 1 2
... 12 13
14
--------------------------------------------
http://www.mobilum.ru/articles/usiliteli/
 Na
rasstoyanii signaly zatuhayut. Eta istina spravedliva i dlya
elektricheskih, i dlya opticheskih kommunikacionnyh linii. Razumeetsya, v
sluchae opticheskih setei rasstoyaniya, na kotoryh eto nachinaet proyavlyat'sya,
bol'she, odnako problemy po-prezhnemu sushestvuyut.
Na
rasstoyanii signaly zatuhayut. Eta istina spravedliva i dlya
elektricheskih, i dlya opticheskih kommunikacionnyh linii. Razumeetsya, v
sluchae opticheskih setei rasstoyaniya, na kotoryh eto nachinaet proyavlyat'sya,
bol'she, odnako problemy po-prezhnemu sushestvuyut.
Dlya bor'by s ukazannymi problemami ispol'zuyut tri tipa ustroistv: usiliteli, regeneratory i povtoriteli.
Opticheskie usiliteli vedut sebya odinakovym obrazom po otnosheniyu k lyubym
opticheskim signalam i naryadu s detektiruemymi signalami usilivayut takzhe
shumy i lyubye drugie signaly. Obychno usiliteli reshayut prosteishuyu iz
zadach, svyazannyh s vosstanovleniem signalov, usilenie. Regeneratory
vypolnyayut bolee slozhnuyu zadachu oni detektiruyut opticheskie signaly,
preobrazuyut ih v elektronnye signaly, otdelyayut ot nih shumy i vnov'
retransliruyut v vide opticheskih signalov, obychno s ispol'zovaniem
elektronnyh ustroistv. Povtoriteli zanimayut nekotoroe promezhutochnoe
polozhenie mezhdu opticheskimi usilitelyami i regeneratorami. Oni takzhe
yavlyayutsya elektroopticheskimi ustroistvami, odnako obespechivayut lish'
usilenie i reformirovanie signala, no ne ego polnoe vosstanovlenie. S
prihodom polnost'yu opticheskih usilitelei ispol'zovanie povtoritelei v
opticheskih setyah perestalo byt' povsemestnym.
Sushestvuet tri tipa uchastkov seti, na kotoryh mogut raspolagat'sya
usiliteli. Dlya usileniya signala pered tem, kak on postupit v set',
neposredstvenno za peredatchikom ustanavlivayutsya postusiliteli. Dlya
kompensacii oslableniya signalov cherez kazhdye 80-100 km
volokonno-opticheskoi linii ustanavlivayutsya lineinye usiliteli.
Predu-siliteli, naznacheniem kotoryh yavlyaetsya usilenie signala do urovnya
moshnosti v predelah chuvstvitel'nosti priemnogo ustroistva, razmeshayutsya
neposredstvenno pered priemnikom.
Usiliteli yavlyayutsya ustroistvami, uvelichivayushimi amplitudu i shirinu
signalov bez iskazheniya ih pervonachal'noi formy. Gromkogovoritel' tozhe
usilitel', tol'ko akusticheskii; analogichnym obrazom opticheskie usiliteli
vypolnyayut podobnye funkcii v sluchae opticheskih signalov. Usiliteli
sposobstvuyut podderzhaniyu moshnosti signalov na dolzhnom urovne pri
prohozhdenii imi bol'shih rasstoyanii. K sozhaleniyu, oni ne otlichayutsya
razborchivost'yu i naryadu s signalami usilivayut takzhe shumy i iskazheniya.
Kakoi imenno princip raboty usilitelei ispol'zuetsya, opredelyaetsya ih
konstrukciei. V sovremennyh opticheskih kommunikacionnyh sistemah
naibolee rasprostraneny usiliteli na opticheskih voloknah, legirovannyh
erbiem (Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers EDFA). Erbii eto
redkozemel'nyi element, kotoryi v nebol'shih kolichestvah dobavlyaetsya v
central'nuyu kremnievuyu zhilu volokonno-opticheskogo kabelya. V otrezok
volokna, legirovannyi erbiem, vo vremya prohozhdeniya cherez nego
oslablennogo signala vvoditsya, ili nakachivaetsya, izluchenie s drugoi
dlinoi volny, otlichnoi ot dliny volny signala, chto prepyatstvuet ih
interferencii mezhdu soboi. V otvet na prohodyashii po voloknu signal iony
erbiya nachinayut rezonirovat', ispol'zuya izbytochnuyu energiyu dopolnitel'noi
volny. V itoge iony erbiya usilivayut signaly, tem samym uvelichivaya
rasstoyanie, na kotoroe oni mogut rasprostranyat'sya.
V to zhe vremya, inzhektirovanie vozbuzhdayushego izlucheniya nakachki mozhet
privodit' k nezhelatel'nym posledstviyam. Rasprostranenie etogo izlucheniya v
napravlenii lazera navstrechu signalu mozhet vyzvat' poyavlenie shumov.
Chtoby izbezhat' etogo, primenyayut opticheskie ventili. Ventili propuskayut
rasprostranyayushiisya po kabelyu svet v odnom napravlenii, no ne propuskayut v
obratnom napravlenii.
Vse prekrasno? Ne sovsem tak. Opticheskii ventil' budet
vzaimodeistvovat' s potokom sveta, rasprostranyayushimsya v pryamom
napravlenii, i v tipichnyh sluchayah uhudshat' signal primerno na 2
decibela. Krome togo, nekotoroe kolichestvo sveta budet prohodit' i v
obratnom napravlenii, odnako obychno takoi svet budet na 40-50 decibel
slabee vhodnogo signala.
V to zhe vremya, v sluchae usilitelei EDFA raduet to, chto oni
sravnitel'no deshevy, ves'ma effektivny, obladayut vysokoi vyhodnoi
moshnost'yu pri nizkom urovne shumov i minimal'nymi perekrestnymi pomehami
mezhdu sosednimi voloknami. Esli u nih i est' nedostatok, tak eto to, chto
oni effektivny lish' pri rabote v blizhnei infrakrasnoi oblasti na dlinah
voln okolo 1550 nm.
Signaly s bolee nizkimi chastotami mozhno usilivat', legiruya volokna
drugim elementom prazeodimiem, v rezul'tate chego poluchayutsya usiliteli
na opticheskih voloknah, legirovannyh prazeodimiem (Praseodymium-Doped
Fiber Amplifiers PDFA). Eti usiliteli perspektivny dlya usileniya
signalov, peredavaemyh s ispol'zovaniem dliny volny okolo 1300 nm.
Analogichnym obrazom, ramanovskie usiliteli effektivno funkcioniruyut na
dlinah voln 1300, 1400 i 1500 nm. Ves'ma mnogoobeshayushe primenenie etih
usilitelei v sistemah peredachi cifrovyh dannyh, ispol'zuyushih
mul'tipleksirovanie po dline volny vysokoi plotnosti (dense wavelength
division multiplexing DWDM).
Princip deistviya ramanovskih usilitelei osnovan na effekte Ramana,
otkrytom indiiskim fizikom serom Chandrasekara Venkata Ramanom v 1928
godu. Kak my uzhe otmechali pri obsuzhdenii ramanovskogo rasseyaniya v glave
4, effekt Ramana zaklyuchaetsya v izmenenii nablyudaemoi chastoty sveta pri
ego rasseyanii v prozrachnom materiale. (Yavlenie kombinacionnogo
rasseyaniya sveta bylo otkryto sovetskimi fizikami G.S. Landsbergom i L.I.
Mandel'shtamom na kristallah i odnovremenno indiiskimi fizikami Ch.V.
Ramanom i K.S. Krishnanom na zhidkostyah.)
My mozhem uvidet' etot effekt, nablyudaya, naprimer, za
monohromaticheskim svetovym puchkom, poluchennym s pomosh'yu lazera, pri ego
prohozhdenii cherez prozrachnyi gaz, zhidkost' ili tverdoe telo. V
otsutstvie promezhutochnyh veshestv lazernoe izluchenie bylo by odnocvetnym.
Odnako pri stolknovenii sveta s veshestvom fotony v rezul'tate uprugih
stolknovenii s molekulami prozrachnogo veshestva teryayut ili vyigryvayut
energiyu. Sledstviem etogo yavlyaetsya vozniknovenie linii dopolnitel'nyh
cvetov, nazyvaemyh ramanovskim spektrom, sootvetstvuyushih uvelichennym ili
umen'shennym dlinam voln po sravneniyu s dlinoi volny pervonachal'nogo
izlucheniem. Vid etogo spektra zavisit ot prirody veshestva, rasseivayushego
svet.
Poskol'ku ramanovskii spektr ne privyazan k fiksirovannym
energeticheskim urovnyam, kak v sluchae redkozemel'nyh elementov, takih kak
erbii, on mozhet byt' poluchen na lyuboi dline volny v infrakrasnoi
oblasti, kol' skoro imeetsya istochnik neobhodimogo vozbuzhdayushego
izlucheniya. Eta osobennost' pozvolyaet primenyat' ramanovskie usiliteli vo
vsem diapazone peredachi kremnievyh volokonno-opticheskih kabelei.
Poskol'ku dlya usilitelei, v kotoryh ispol'zuetsya ramanovskii effekt,
trebuyutsya povyshennye moshnosti vozbuzhdayushego izlucheniya (poryadka odnogo
vatta) i otrezki svetovodnogo kabelya bol'shei dliny, ih stoimost' po
sravneniyu s usilitelyami EDFA okazyvaetsya bolee vysokoi. Tem ne menee, ih
glavnym dostoinstvom yavlyaetsya sposobnost' obespechit' usilenie
opticheskih signalov vo vsem diapazone vozmozhnyh chastot peredachi pri
ispol'zovanii volokonno-opticheskih kabelei s nizkimi poteryami, i poetomu
na nih mozhet byt' postroena tehnologiya kremnievyh usilitelei,
al'ternativnyh PDFA ili hal'kogenidnym volokonno-opticheskim usilitelyam v
diapazone 1,3 mkm. Blagodarya nedavnim usovershenstvovaniyam tehnologii
polucheniya aktivnyh volokon ispol'zovanie nekotoryh iz nih pozvolilo
poluchit' usilenie po moshnosti, dostigayushee primerno 0,06 dB/mVt, chto,
buduchi samo po sebe neznachitel'noi velichinoi po sravneniyu s izvestnymi
velichinami dlya EDFA (11 dB/mVt), tem ne menee predstavlyaet soboi vpolne
razumnuyu al'ternativu pri peredache dannyh v ne-erbievyh diapazonah
dlin voln. Na segodnyashnii den' usilenie na osnove effekta Ramana igraet
vazhnuyu rol' v sistemah sverhdal'nei svyazi, kotorye rasshirili vozmozhnosti
peredachi na dal'nie rasstoyaniya s 500 km mezhdu sosednimi povtoritelyami
do 1500 km i bolee.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
21.03.2013 23:13, 100 Bait)
Samoe smeshnoe chto fizicheski oni napominayut transformator,
tol'ko vmesto provodov optovolokna.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.03.2013 4:36, 2.0 KBait)
Po bol'shomu schetu razveli detskii sad i sami ne ponimayut
chego hotyat, delo v sleduyushem v fizike chtoby ne vyglyadet'
nedalekim po otnosheniyu k suti voprosa, nado
davat' opredelenie fizicheskoe.
Vot sobstvenno transformator elektricheskii, -
eto ustroistvo v kotorom proishodit transformaciya
vol't-amperov v magnitnoe
pole s posleduyushim
vosstanovleniem vol't-amperov, pri etom proishodyat
poteri. V svyazi s razlichnym kolichestvom vitkov
v obmotkah poluchaetsya vozmozhnost' izmenit'
sootnoshenie vol'tov po otnosheniyu k amperam,
i amperov po otnosheniyu k vol'tam chto sobstvenno
i est' koefficient transformacii kotoryi
prinyato pisat'
po otnosheniyu k vol'tam.
Naprimer
koefficient 1:2
oznachaet chto vhodnoe napryazhenie eto levaya cifra, vyhodnoe
napryazhenie eto pravaya cifra, i govorit naprimer
o tom
chto pri vhodnom peremennom napryazhenii v 12V,
na vyhode budet 24V.
Mehanicheskii analog eto korobka peredach, v
kotorom analogom napryazheniya budet
uglovaya
skorost' na metr, a analogom toka budet usilie
na metr.
---
A vot chtoby vnyatno chto-to govorit' za svetovoi transformator,
nado ponimat'
chto vo chto nado transformirovat' i s kakim
koefficientom chego-to vo chto-to.
V dannom sluchai kak govoritsya i konyu ponyatno chto
vo vseh sluchayah transformacii
sushnosti predstavlyayut
iz sebya energii.
To sobstvenno opticheskii usilitel' i predstavlyaet iz
sebya opticheskii transformator, po skol'ku energiya
odnogo
istochnika izlucheniya perehodit v izmenenie
energii drugogo istochnika, v dannom sluchai izmenenii
amplitudy signala.
Esli vyklyuchit' luch, to usileniya vhodnogo
opticheskogo
signala ne budet, esli vklyuchit' luch poyavlyaetsya
usilenie amplitudy signala, a esli izmenilas'
amplituda signala, to ponyatno chto poyavilsya
koefficient
transformacii, a sledovatel'no
tam gde est' koefficient transformacii to
tam i est' svoistva transformatora.
Kamennyi vek, pervyi klass, vtoraya chetvert'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.03.2013 4:38, 1.8 KBait)
Predydushee eto moe mnenie po etomu tekstu
----------------------------------------------------------
 Re: Pochemu net svetovogo transformatora?
Re: Pochemu net svetovogo transformatora?
Otvet #138 - Vchera :: 23:54:04
Al'cha pisal(a) 20.03.13 :: 23:33:59:A
Vy, so svoei storony, navernoe predstavlyaete kak idet nakachka
lazera..... I kak rol' agenta nakachki mozhet vypolnyat' tozhe svet....
Opticheskie lazernye usiliteli izvestny davno.... Nazovite ih
"transformatorami"...
Ili Vam.... "shashechki nuzhny"??? Ili, vse-taki, "ehat' nado"????
Zdes' rech' ne idet ob opticheskih lazernyh usilitelyah. Rech' idet o
tom, pochemu nel'zya izgotovit' obychnyi privychnyi vsem nam elektricheskii
transformator s pervichnoi i vtorichnymi obmotkami dlya preobrazovaniya
sveta, esli svet yavlyaetsya elektromagnitnym yavleniem.
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.03.2013 4:53, 777 Bait)
Vot iz ssylki kotoruyu ya ukazal tam zhe napisano
---------------------------
\\\Blagodarya nedavnim usovershenstvovaniyam tehnologii
polucheniya aktivnyh volokon ispol'zovanie nekotoryh iz nih pozvolilo
poluchit' usilenie po moshnosti, dostigayushee primerno 0,06 dB/mVt, chto,
buduchi samo po sebe neznachitel'noi velichinoi po sravneniyu s izvestnymi
velichinami dlya EDFA (11 dB/mVt),\\\
Chtoby byli v kurse - shest' decibel - eto usilenie v dva raza,
po otnosheniyu k svetovym kolebaniyam mozhno skazat'
chto moshnost' svetovogo kolebaniya, eto i est' ego
amplituda tak skazat' i vol'ty i ampery vmeste.
A esli vol'ty i ampery vmeste, i ih nevozmozhno
razdelit', a mozhno usilivat' ih tol'ko vmeste,
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.03.2013 13:48, 422 Bait)
Ya dumayu chto zdes' bol'shinstvo smeyutsya kak koni,
ibo teleskop sobstvenno i est' opticheskii transformator.
Takzhe opticheskii transformator mozhno sdelat' iz dvuh
prizm raznogo razmera, pervaya prizma raskladyvaet spektr,
vtoraya skladyvaet.
V dannom sluchai koefficient transformacii mozhno
opredelyat' po raznomu,
mozhno v usilenii teleskopa,
a mozhno i v raznosti osveshennosti na ploshad'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.03.2013 21:23, 3.3 KBait)
Pochital opyat' takoe smeshnoe chto vynuzhden
rasskazat' svoimi slovami.
---------------------
\\\
 Proverim Kavendisha "na kolenke"?
Proverim Kavendisha "na kolenke"?
Segodnya :: 11:03:02
Mnogo zdes' na Forume bylo sporov -- "vzvesil" li Kavendish Zemlyu, uznal li ee plotnost' ... nu i pro G takie zhe voprosy.
Poyavilas' u menya "myslishka"
proverit' real'no PRITYaZhENIE gruzov drug k drugu. /a mozhet i pritalkivanie -- ne sut' vazhno/
Itak
zadumyvayu opyt ... i proshu predvaritel'noi kritiki ot vseh forumchan, nu
i poleznyh sovetov i predlozhenii, esli takovye budut.
Chto
imeyu iz "oborudovaniya": stal'naya nakoval'nya vesom okolo 200 kg, takogo
zhe vesa bolvanka-"chugunyaka" /dovol'no besformennaya/, svinec v zavodskom
slitke -- 50 kg + eshe svinec v kuskah okolo 30 kg, prochnyi listvennyi
brus okolo 4 m dliny, provod, trosik, kapronovyi shnur dlya "trimmera", +
kucha kirpichei.
Ideya prosta: iz brusa delaem "krutil'nye vesy"
... na konce krepim ves' svinec, na drugom --- kirpichi-protivoves, ....
poseredke --- shnur/trosik ... /chtoby vyderzhal 160 kg/ ... + zerkal'ce i
lazernaya ukazka --- opticheskii izmeritel' peremeshenii.
Stavim nakoval'nyu v vysokom pomeshenii /sportzal ... bez skvoznyakov(!)/
... k potolku podves na trosike koromysla vesov ... i posle uspokaivaniya
konstrukcii ... nakoval'nyu raspolagaem pochti vplotnuyu k svincu na konce
brusa. Zazor mezh svincom i nakoval'nei delaem v predelah 1 ... 2 ... 3
mm
I dalee tol'ko zhdem --- smestitsya ili net svincovaya "kolobaha" k nakoval'ne DO KASANIYa EYa???
Yasno, chto trosik podvesa nuzhen dlinnyi, chtoby legche krutit'sya
koromyslu ... i tut vopros -- chto budet luchshe? ... stal'noi trosik /1
mm/ ... ili kapronovyi /3 mm/?
Takzhe yasno, chto nuzhno eto delat' v kanikuly, daby deti na uroke "ne mutili vozdusya" vetrami-skvoznyakami.
Vot
tut osnovnoi vopros --- poluchitsya li chego? Budet li smeshenie gruzov
drug k drugu, prichem chtoby odnoznachno ot PRITYaGANIYa mezh nimi, a ne ot
sluchainyh prichin. Yasno, chto tut ne pro "G" budet razgovor, a tol'ko pro
principial'noe vyyavlenie deistviya mezh gruzami. Smeshenie gruzov mozhno
budet uzret' vizual'no ... + po svetovomu zaichiku ot lazerki /ezheli ono
budet/
I kakie mysli forumchan budut po etomu povodu??? Zhdu ser'eznyh vozrazhenii ili sovetov ........
S uvazheniem ko vsem .......... Anatolii D.
Tokyan.


\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.03.2013 21:38, 806 Bait)
Delo v sleduyushem, podobnyi opyt stavili grafy ili barony,
ne pomnyu kogda, - eto uzh sovsem v samyh dal'nih okrainah moei
pamyati, pomnyu tol'ko chto na niti treugol'noi
formy.
Hotya vse eti opyty preodolevali sovetskie shkol'nye opyty,
s dvumya butlyami i propitannymi raznocvetnymi chernilami,
sirenevymi steblyami, kogda
oni menyali cvet kogda podnosili
massivnoe so storony kontrol'nyh steblei po kotorym prosachivalis'
raznocvetnye chernila, k svoei grusti ne mogu vspomnit'
logichnyh
opredelenii.
Pri vsem pri tom chto v moei shkole na ekzamenah fiziki razreshali pol'zovat'sya
vsemi uchebnikami kotorye byli po fizike i shpargalkami, i kal'kulyatorom
v tom chisle, na to vremya eto bylo nechto, logarifmicheskaya lineika
tozhe pomogala v te vremena.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.03.2013 21:55, 506 Bait)
V primitive - podobnyi opyt mozhno provesti na podveshennom na
nekotoroi prochnoi niti share, u kotorogo ryadom budet
ot odnoi opory s uglovym uporom ot tochki
krepleniya
oborudovan gruzovoi orientirovannyi /sputnik/
-
- est' takoi shar so strelkoi, i on kolebletsya i menyaet svoe
napravlenie, - tak vot k etomu sharu - logichno
v kachestve
nelogichnogo fizicheskogo opyta prikrepit' na servoprivodah,
k skol'zyashim podshipnikam nekotoryi dovesok.
Est' chto-to v etoi prostote.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.03.2013 1:22, 4.7 KBait)
S moei tochki zreniya est' mnogo zdanii
v kotoryh mozhno razmestit' podobnyi mayatnik,
s dopolnitel'nym gruzom vliyayushim na osnovnoi,
kogda u dopolnitel'nogo
gruza svoe nezavisimoe kreplenie, v tom-zhe cente mass.
---
http://turbina.ru/guide/Sankt-Peterburg-Rossiya-112311/Zametki/Vmesto-mayatnika-Fuko-54871/
1430 marta 2012 goda
V
sovetskoe vremya v centre Isaakievskogo sobora na dlinnoi cepi visel
mayatnik Fuko pribor pokazyvayushii i dokazyvayushii chto Zemlya vertitsya.
Seichas mayatnik demontirovan i mozhno vstat' v centre sobora, podnyat'
golovu i dolgo rassmatrivat' velikolepnyi raspisnoi plafon glavnogo
kupola Bogomater' v okruzhenii svyatyh raboty Karla Bryullova, figury
dvenadcati apostolov v svetovom barabane i chetyreh evangelistov, ch'i
izobrazheniya na parusah arok dovershayut kartinu.
A vysoko-vysoko pod kupolom hrama kak i prezhde letit golub' simvol Svyatogo duha.
Vse fotografii
odnoi lentoi
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.03.2013 2:06, 5.3 KBait)
A sleta s intellektual'nyh katushek zhdat'
to dolgo i ne ponadobilos'.
Kak govoritsya nedalekii v fizike eto vot tomu dokazatel'stvo.
Ibo
relyativist sletaet s intellektual'nyh
katushek kogda zabyvaet chto dlya pustoty, to-est' vakuuma
eto \Relyativistskii effekt Doplera\,
kotoryi nikakogo otnosheniya
fizicheskogo ne imeet
k \effektu Doplera\.
---
Nekotoryi relyativist nedalekii v fizike,
u kotorogo prostranstvo pustoe aki dal'she nekuda,
i idei
etogo relyativista imeyut svoe datirovanie posle
1900 goda, pri etom etot nedalekii relyativist
opiraetsya na effekt Doplera, kotoryi dlya sred a ne
dlya pustoty
i byl priduman azh v
\\\Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
Effekt byl vpervye opisan Kristianom
Doplerom v 1842 godu.\\\
---
A nedalekii relyativist dazhe ne znaet opredeleniya
sredy, -
sreda eto kogda kazhdyi element imeet neposredstvennyi kontakt
drug mezhdu drugom, i imeet nepreryvnoe soedinenie i svoistva
plotnosti sredy - eto
vkratce.
---
----------------------------------------------------------------
\\\
| Vallav
|
 Re: Pochemu net svetovogo transformatora?
Re: Pochemu net svetovogo transformatora?
Otvet #145 - Segodnya :: 00:22:13
krabs pisal(a) Vchera :: 23:48:46:Vallav pisal(a) Vchera :: 13:34:58:To est', zelenyi svet ot dvizhushegosya navstrechu istochnika - eto opticheskii
obman?
Chem otlichaetsya zelenyi svet ot dvizhushegosya
istochnika ot zelenogo
sveta ot nepodvizhnogo istochnika?
Effekt Doplera imeet k obsuzhdaemu samoe neposredstvennoe otnoshenie.
Tak kak s ego pomosh'yu mozhno peresekat'
ustanovlennuyu Vami granicu. Zelenyi svet ot dvizhushegosya navstrechu istochnika - eto, estestvenno, opticheskii obman.
Vy zhe znaete, chto istochnik izluchaet druguyu chastotu. Esli ne znaete, to
podozhdite nemnogo, poka istochnik proedet mimo vas i nachnet udalyat'sya ot
vas. Chastota budet uzhe ne "zelenaya". A esli istochnik daleko i zhdat' vsyu zhizn'? Tak i ne uznat', chto zelenyi svet ot nego - opticheskii obman? Po ostal'nym svoistvam etot svet ot sveta ot nepodvizhnogo istochnika nichem ne otlichaetsya? Togda v chem imenno raznica v ih prirode? krabs pisal(a) Vchera :: 23:48:46:
Vy seichas svoimi razgovorami ob effekte Doplera pytaetes' uvesti ot
obsuzhdaemogo voprosa. Uzhe uvodit' ne nado. Skazannogo vami vpolne
dostatochno, chtoby sdelat' vyvod o tom, chto u vas net nikakih fizicheskih
dokazatel'stv EM-prirody sveta. Tak odni fantazii, ne produmannye do
konca i v osnovnom ne imeyushie k fizike nikakogo otnosheniya.. Tak sushestvovanie effekta Doplera i est' samoe prostoe i naglyadnoe dokazatel'stvo togo, chto
radiovolny, svet, rentgen i gamma-kvanty - odnoi prirody.
|
|
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.03.2013 14:08, 7.2 KBait)
Prochital tekst ot chmyrdyaya kotoryi
pytalsya unizit' drugogo avtora po prichine
ne pravil'nogo s ego tochki zreniya primeneniya
edinic izmereniya.
Vot
kak raz zdes' i proyavilis' vnutrennie svoistva
ostavshiesya posle kursov gandol'erov.
Ne udosuzhilsya ob'yasnit' gandol'er po kakoi prichine
eti edinicy izmereniya
huzhe chem drugie,
tak potom kak istinnyi gandol'er sam ispol'zuet
eti edenicy izmereniya.
-----------------------------------------------
http://www.computerra.ru/60311/betelgeusepastandfuture/
Sepul'ka
Dmitri Wiebe
5
dnei nazad
V Krabovidnoi zvezdnaya velichina byla otricatel'noi,
a tut vo skol'ko raz blizhe? da eshe v kvadrat? Tak chto yarkaya - ne to slovo.
Naskol'ko mozhno doveryat' (g-nu Ponomarenko):
"V sluchae vzryva kak Sverhnovoi zvezdy Betel'geize , nahodyasheisya na
rasstoyanii 320-500 sv. let ot Zemli, potok UF izlucheniya v diapazone
200-300 nm sostavit
35-55 tysyach erg/sm2 i stanet naibolee
moshnym mutagennym faktorom za poslednie dva milliona
let. Ee
prevrashenie v sverhnovuyu budet soprovozhdat'sya sbrosom
obolochki okolo 10-4
ee massy , sostoyashei , v osnovnom, iz vodoroda i geliya s energiei
kazhdogo yadra do 1,8 GeV /4/. Na Zemle detektor tipa Kamiokande II
zaregistriruet
neitrinnuyu vspyshku intensivnost'yu v 25-75 tysyach sobytii
(pereschitano po rezul'tatam izmerenii na Kamiokande II vspyshki ot SN1987
/5/) . Cherez neskol'ko chasov (do
sutok) posle registracii neitrino /5/,
stanet vidna dazhe dnem yarchaishaya zvezda, sravnimaya po blesku s polnoi
Lunoi. V techenie neskol'kih desyatkov - soten let posle
maksimuma cherez
40-50 let posle prihoda na Zemlyu kvantov i neitrino, na Zemlyu budut
vozdeistvovat' relyativistskie yadra (v osnovnom, protony i gelii)
obolochki
Sverhnovoi. ih polnyi flyuens na granice magnitosfery Zemli
sostavit 5*105 - 2*106 chast/sm2.
Chastichno oni budut zahvacheny magnitosferoi, chastichno vyzovut rozhdenie
vtorichnyh chastic v atmosfere, a chastichno doidut do poverhnosti Zemli,
stav vtorym sil'neishim mutagennym faktorom posle UF izlucheniya. Iz dannyh
/6/ sleduet,
chto vzryva Betel'geize mozhno ozhidat' v blizhaishie neskol'ko
tysyach let." http://physics-animations.com/...
I tam zhe:
Pri
vzryve tipovoi sverhnovoi krome nachal'nogo impul'sa rentgena, kotoryi
spadaet neskol'ko let, obrazuetsya cepochka gamma-izluchatelei v kolichestve
0,075-0,1 massy Solnca (Ni-56- >Co-56(847,1288
keV)->Fe-56)/5/.Svetimost' tipovoi Sverhnovoi v gamma-diapazone
padaet s 1042 erg/s do 1040 za dva goda, do 1038 - za tri goda , dal'she
rabotaet Co-57, Ti-44, Na-22 - spad zamedlyaetsya. S 1038 do 1037 spad
aktivnosti proishodit s tret'ego po pyatyi goda. V maksimume aktivnosti
eto sootvetstvuet 0,5-0,8 erg/sm2 t.e. (3-5)*10^7 kvantov so srednei
energiei 1 MeV na 1 sm2 v sekundu na granice Zemnoi atmosfery ot
Sverhnovoi na rasstoyanii 320-500 sv let. S uchetom krivoi spada
rentgenovskogo izlucheniya i prihoda GeVnyh zaryazhennyh chastic, pomimo
mutagennyh faktorov, o pilotiruemoi kosmonavtike pridetsya zabyt' na
desyatiletiya.
Zhdu ot Vas primerno takogo soobsheniya: "G-n Ponomarenko izvesten kak avtor mnozhestva slabyh i oshibochnyh rabot..."
-----------------------------
Dmitri
Wiebe
Sepul'ka 5 dnei nazad
I.S.
Shklovskim predlozhen prostoi kriterii bystroi
ocenki teksta -- naskol'ko
korrektno avtor ispol'zuet
edinicy izmereniya. Esli chelovek izmeryaet
potok v ergah
na kv. sm, eto uzhe povod prizadumat'sya.
---------------------------------
Dmitri
Wiebe
sergey da 3 dnya nazad
V stat'e Ponomarenko privoditsya ssylka na stat'yu
Disturbance Ecology from Nearby Supernovae, a oni,
v
svoyu ochered', ssylayutsya na rabotu Skalo so tovarishi,
gde oni dayut kriticheskuyu dozu UF-oblucheniya
dlya mutacii
mikroorganizmov
600 erg/sm2. Esli sravnit' eto s dozoi,
kotoruyu Zemlya riskuet poluchit'
ot Betel'geize (v stat'e
Ponomarenko, vidimo, imenno ona nazyvaetsya
potokom), to
rezul'tat poluchaetsya pugayushim za predelami atmosfery
poluchitsya primerno 20000 erg/sm2 (esli brat' energiyu,
izluchennuyu
sverhnovoi v UF-diapazone, iz stat'i Skalo i
dr.; 10^47 erg). No chto
budet esli sravnit'
etu velichinu s UF-izlucheniem Solnca? My ezhesekundno poluchaem
ot
Solnca 1,4 milliona erg na kv. sm. (solnechnaya postoyannaya).
Na dolyu UF
prihoditsya neskol'ko procentov (zavisit ot togo,
kak opredelit'
UF-diapazon). Pust' budet 5% dlya opredelennosti.
Poluchaem 70000 erg/sm2 v sekundu, a ne 20000 vsego,
kak ot Betel'geize.
O tom, naskol'ko vazhno takoe dobavochnoe obluchenie,
pust' govoryat
biologi. Pro drugie izlucheniya skazat' ne mogu, poskol'ku
ne sovsem
ponimayu, chto imeetsya v vidu v stat'e.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.03.2013 19:34, 1.5 KBait)
To chto adekvatnosti net ya znal no ya
nachinayu uzhe somnevat'sya ne tol'ko v umstvennyh sposobnostyah
no i v tom kak daleko zapushenna bolezn'.
Ibo poterya pamyati
eto bolezn'.
Tak vot nekto Vibe sovsem nedavno
napisal stat'yu tom chto Betel'geize dolzhna
v skorosti vzorvat'sya po samye ne-baluisya,
sobstvenno
stat'ya o sobytii kotoroe
eshe ne proizoshlo, posle etoi stat'i idet obsuzhdenie
etoi stat'i v vide foruma, a buduchi moderatorom on posetitelya
moderiruemogo
im foruma uprekaet
v tom chto on obsuzhdaet sobytie kotoroe ne proizoshlo
na forume.
Eto ne dvoinye standarty, eto ili bezpredel moderatora,
hotya
vryad-li i bolee veroyatno chto slet s intellektual'nyh
katushek.
--------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1 : Segodnya v 17:58:16
Neponyatno, kak mozhno obsuzhdat' sobytie, kotoroe eshe ne sostoyalos'. Ostavlyayu kak anons.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.03.2013 22:29, 2.4 KBait)
Soobshenii: 5062
 Re: Pochemu net svetovogo transformatora?
Re: Pochemu net svetovogo transformatora?
Otvet #218 - Segodnya :: 21:11:58
Vasushena pisal(a) Segodnya :: 20:44:50:
Vallav pisal(a) Segodnya :: 20:28:35:Oi!
Tak vot pryamo kroshila na melkie kusochki?
sam
ne videl, no po legendam - tak. Izobrazhenie vadzhry imeetsya mnozhestvo so
vseh rakursov. Est' kargo-kopii i opisanie ochevidcev v Mahabharate.
Nu esli - Est' kargo-kopii i opisanie ochevidcev v Mahabharate - tady
konechno...
---------------------------------------------
Yasnyi kon' relyativisty ne veryat rasskazam ochevidcev kogda im
eto ne nado, zato kak oni veryat tomu chto bylo
v pervye chasy
minuty i sekundy bol'shogo vzryva, i ochevidcy im ne nuzhny
oni prosto veryat v eti skazki vysosonnye neponyatno iz kakih
fantazii i kakih ochevidcev.
---
Eto vse erunda, byla davno u menya knizhka pravda ona poteryalas',
knizhka neobychnaya dlya sovetskih izdanii kvadratnoi formy,
o puteshestvii odnogo fotografa
po Yuzhnoi Amerike na velosipede,
tak tam byla odna fotografiya v etoi knige gde fotografiruyutsya
turisty na fone kamnya pryamougol'noi formy broshennogo
mezhdu
gor s razmerami kamnya primerno 55metrov v dlinu,
35m. v shirinu, i 25m. v vysotu.
I ob eto megalite ya nichego v internete ne videl.
Vozmozhno porezali na
suveniry, ibo etot megalit
svodit na net vse tekushie tehnicheskie dostizheniya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.03.2013 10:20, 2.0 KBait)
Vot i eshe odin relyativist posle sleta s
intellektual'nyh katushek prevratilsya v nedalekogo.
Ne vosprinimaet tekst po fizike
i ne mozhet ego obsuzhdat'
v fizike tol'ko
nedalekii v fizike.
Nedalekii v fizike mozhet vse smeshivat'
v kuchu i zadavat' voprosy.
---------------------------
\\\
 Re: Pochemu net svetovogo transformatora?
Re: Pochemu net svetovogo transformatora?
Otvet #247 - Segodnya :: 09:03:27
OKBor pisal(a) Segodnya :: 05:11:00:
[quote
author=5D6A67676A7D3A0B0 link=1363466593/194#194 date=1364223076]Tak
obsuzhdaite a ne veshaite pustoporozhnie absolyutnye istiny.
A s kem obsuzhdat' absolyutnye istiny?
A ih nado obsuzhdat'?
OKBor pisal(a) Segodnya :: 05:11:00:
Naprimer
- ne zhelaete obsudit' absolyutnuyu istinu ATO OKBoris po povodu levoi
ruki Ampera? Na provodnik dazhe bez vneshnego magnitnogo polya deistvuet
sila, izgibayushaya ego v ploskuyu okruzhnost'. Kak velokameru pri nakachke. A
esli obolochku zaryadit'- ona primet formu sfery. Tak chto levaya ruka-
chastnyi sluchai. Nu kak- obsudim?
A eto razve - absolyutnaya istina?
\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(o. s. baranov,
28.03.2013 21:30, 341 Bait)
hotelos' by sdelat' odno utochnenie.
pishut obychno tak: svet ne mozhet vyrvat'sya iz chernoi dyry.
proshe mozhno predstavit' tak: atomy v chernoi dyre raspolozheny tak
blizko drug k drugu, chto elektronnyh obolochek (verhnih ili vseh) prosto net, svetovogo izlucheniya poetomu prosto ne obrazuetsya,
poetomu ona i chernaya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.03.2013 22:40, 740 Bait)
Vashe mnenie o chernyh dyrah eto lichno Vashe
mnenie o chernyh dyrah, i ono vsem bezrazlichno,
po toi prichine chto chernye dyry imenno takie
kakie opisal avtor chernyh
dyr.
Vot ya zhe pisal chto nekotorye napisali
chto chernye dyry izluchayut rentgenovskoe izluchenie,
i napisali bol'she sotni statei, i che, i do lampochki,
avtor skazal chto izluchenie iz chernyh dyr v osnovnom
iz fotonov - to te kto pripisyvali chernym dyram
rentgenovskoe izluchenie oni prosto klali na avtorskii
variant, i che - a niche, nakazanii za podobnyi bardak
v fizike ne sushestvuet.
Chitaite pervoistochniki i ne pripisyvaite tomu
chto pridumali drugie raznye
pribambasy, Vas ob etom
nikto ne prosil, i v etom net smysla.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.03.2013 22:46, 370 Bait)
Menya estestvenno udivlyaet intellektual'nost' teh
kto napisal bolee sotni statei pripisyvaya rentgenovskim
zvezdam svoistva chernyh dyr.
Esli by prosto opisali
novyi klass rentgenovskih zvezd
i dali im fizicheskoe opredelenie, - to oni voshli by v istoriyu
kosmologii i poimeli by kuchu premii.
A tak oni ne u del i ih
mnenie nikomu ne interesno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.03.2013 22:50, 183 Bait, otvetov: 1)
I ne zabyvaite samoe glavnoe - na segodnyashnii
den' ne obnaruzheno oficial'no ni odnoi chernoi dyry,
odni tol'ko predpolozheniya - chto mol chernaya dyra dolzhna
byt'
tam-to.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.03.2013 0:53, 35 Bait)
Moe obshenie s Vami zakryto.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(o. s. baranov,
29.03.2013 13:15, 8 Bait)
z
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
31.03.2013 19:41, 14.3 KBait)
Takoe prochital, ya azh zaulybalsya u menya poyavilsya
konkurent v opisanii stroeniya galaktik.
Estestvenno tovarishu nado srazu rabotat' nad svoimi
oshibkami, a vsem
zhelayushim mogu pokazat'
dve raznyh tochki zreniya i kak govoritsya
pochuvstvuite raznicu.
--------------------------------------
 Re: Efirnaya Teoriya. Edinaya koncepciya.
Re: Efirnaya Teoriya. Edinaya koncepciya.
Otvet #346 - 19.02.13 :: 10:48:44
Podvedenie promezhutochnyh itogov.
Etapy razvitiya real'noi vselennoi.
Sootvetstvie energeticheskogo urovnya diapazonu izlucheniya:

1-i uroven'-radiodiapazon
izlucheniya;
2-i mikrovolnovyi;
3-i infrakrasnyi;
4-i vidimyi spektr;
5-i ul'trafioletovyi;
6-i rentgenovskii;
7-i gamma.
V svyazi s etim dolzhno byt' 12 etapov razvitiya-tvoreniya Vselennoi.
Klyuchevaya rol' otvoditsya Efiru-Nepreryvnoi Srede iz kotoroi vse
sotvoreno.Ne vdavayas' v detali poyavleniya Nepreryvnoi Sredy(Efira),
ya ih prosto ne znayu, dlya sebya ya opredelil sleduyushie Svoistva Efira(ili Sredy).
O svoistvah Sredy, s takim usloviem, chtoby vse mnogoobrazie form i
yavlenii okruzhayushego nas mira, yavlyalos' sledstviem sushestvovaniya tol'ko
odnoi sushnosti-Sredy(Efira).
Dopustim, chto sreda
diskretna-sostoit iz ochen', ochen' melkih chastic. Smozhem li my s pomosh'yu
nee ob'yasnit' gravitaciyu? Smozhem. Dvizhetsya v centr zemli i uvlekaet
svoim dvizheniem tela, prizhimaya ih k poverhnosti Zemli. Smozhem li my s ee
pomosh'yu ob'yasnit' sil'nye, slabye, obmennye i molekulyarnye
vzaimodeistviya? Ne smozhem. Chtoby ob'yasnit' eti vzaimodeistviya, my dolzhny
ob'yasnit', kak osushestvlyaet-sya svyaz' mezhdu chastichkami Sredy. Esli mezhdu
chastichkami sredy ne budet svyazi, to i vzaimodeistvie nevozmozhno. Esli
razrezat' buksirnyi tros, to smozhem li my buksirovat' avtomobil'? Net.
Znachit nuzhno vvodit' novuyu sushnost', a eto protivorechit nashemu
pervonachal'nomu usloviyu: Sushnost' tol'ko odna.
Poetomu Sreda-nepreryvnaya sushnost'.
Mezhdu atomami i molekulami net vidimoi svyazi, no veshestvo(lyuboe)
soprotivlyaetsya, kak rastyazheniyu, tak i szhatiyu. Sreda dolzhna obladat'
opredelennymi prochnostnymi kachestvami. Materiya, lish' neznachitel'-naya
chast' Vselennoi, no plotnost' materii bol'she plotnosti Sredy napolnyayushei
prostranstvo (nablyuda-tel'nyi fakt), znachit Sreda dolzhna vklyuchat' v
sebya i takoe ponyatie kak plotnost'. Chem vyshe plotnost', tem bol'she
prochnost' Sredy.
Sreda dolzhna imet' sposobnost' k fluktuaciyam. Nablyudatel'nyi fakt.
Sreda lyuboi plotnosti-podobie zhidkosti.
Itak Etapy
razvitiya Vselennoi:
1-i
Etap-fluktuacii Nepreryvnoi Sredy-Efira. Na etom etape, primerno 8 s
nebol'shim procentov Efira pereshlo v SVET. Dvizheniya, kak takovogo, ne
bylo. Pomimo perehoda Efira v SVET obrazovyvalis'
elektrony i pozitrony.

Itak, konechnyi rezul'tat fluktuacii-poyavilsya foton(SVET) i
neitrino. SVET eto ta zhe Nepreryvnaya Sreda, no v drugom kachestve. Iz
SREDY udaleno nechto, chto Ei sovershenno ne nuzhno i eto nechto
sosredotocheno v neitrino. Svet ne smeshivaetsya s Efirom i
sosredotachivaetsya v central'noi oblasti ob'ema zapolnennogo NS.
Neitrino v konechnoi stadii fluktuacii zashemlyaet Nepreryvnuyu Sredu(NS)
i, za schet vrasheniya, sozdaet vihr' iz NS i stanovitsya elektronom:

2-i
Etap-sozdanie Vselenskih potokov dvizhushegosya Efira. Na etom etape SVET,
skoncentrirovavshis' v central'noi oblasti, vypuskaet dva dzheta i
raskruchivaet Efir po vsemu ob'emu budushei Vselennoi. Eshe 8 s nebol'shim
procentov Efira perehodit v SVET i na etom etape iz neitrino formiruetsya
dueneitrino, a iz
nih protony i neitrony:


3-i
Etap. Etap rassredotocheniya Sveta po ob'emu Vselennoi v mesta gde budut
sozdany galaktiki. Svet koncentriruetsya v opredelennyh mestah, no v
processe peremesheniya, t.k. dlya etogo ispol'zuyutsya dzhety, eshe 8 s
nebol'shim procentov Efira perehodit v SVET.
Za pervye tri
etapa chast' Efira pereshla v SVET, chast' pereshla v neitrino i po vsemu
ob'emu sformirovalis' elektrony i pozitrony, protony i neitrony.
4-i
Etap. Formirovanie veshestva pervogo perioda tablicy Mendeleeva. SVET
vypustiv dva dzheta nagnetaet Efir i
elektronno-pozitronnuyu-proton-neitronnuyu smes', v central'noi oblasti
formiruyutsya atomy vodoroda i geliya, kotorye vybrasyvayutsya po ekvatoru v
prostranstvo. Dannyi etap nachinaetsya odnovremenno vo vseh otvedennyh
mestah Vselennoi. Efir pereshedshii v SVET otvoditsya v blizlezhashee
prostranstvo i formiruetsya v vide shara(te zhe 8 s nebol'shim procentov).
Galaktika izluchaet tol'ko v radiodiapazone.
Eto proishodit primerno tak:

Tak proishodit vplot' do 8 Etapa.
Dokazatel'stvo sushestvovaniya chetvertogo Etapa:
Naidena pervaya galaktika nahodyashayasya na pervom etape razvitiya. Takaya galak-
tika izluchaet tol'ko v radiodiapazone, a izluchenie v drugih diapazonah, v tom chisle i
vidimom eshe ne doshlo do Zemli. Dannaya galaktika nahoditsya na maksimal'nom rasstoya-
nii ot Zemli. V budushem do Zemli doidet izluchenie i v vidimom diapazone, no predva-
ritel'no doidet v mikrovolnovom i infrakrasnom.
www.membrana.ru/particle/8256
5-i
Etap. Formirovanie veshestva vtorogo perioda tablicy Mendeleeva. Dzhety
vypuskayutsya v ekvatorial'noi zone. V central'nuyu oblast' zasasyvaetsya
Efir, elektronno-pozitronnaya smes', protony, neitrony, vodorod, gelii. V
novuyu ekvatorial'nuyu zonu vybrasyvayutsya elementy vtorogo i pervogo
perioda.
8 s nebol'shim procentov Efira pereshlo v svet.
Galaktika izluchaet v radiodiapazone i v mikrovolnovom.
6-i Etap. Formirovanie veshestva tret'ego perioda
tablicy Mendeleeva.
Galaktika izluchaet v radio, mikrovolnovom i infrakrasnom diapazone.
Dokazatel'stva sushestvovaniya 6 Etapa:
Dalekie galaktiki, kotorye ne
izluchayut eshe v vidimom diapazone.
Oni izluchayut v infrakrasnom, mikrovolnovom a radiodiapazonah.
www.membrana.ru/particle/17282
7-i Etap. Formirovanie veshestva chetvertogo perioda.
Dopolnitel'no k
pervym, galaktika izluchaet v vidimom diapazone
8-Etap.
Formirovanie zvezd i planet. V central'noi oblasti obrazuetsya kvazar,
vnutri kotorogo formiruyutsya zvezdy i planety i vybrasyvayutsya v rukava.
Na etom etape poyavlyaetsya gravitaciya v osnove kotoroi lezhat SVETOefirnye
potoki.


9 Etap. Formirovanie veshestva pyatogo perioda.
Galaktika nachinaet izluchat' i v ul'trafiolete.
10 Etap. Formirovanie veshestva shestogo perioda.
Galaktika nachinaet
izluchat' i v rentgenovskom diapazone. Na zavershayushei stadii etogo
etapa nahoditsya Vselennaya.
Dokazatel'stva:

Tumannost'
Andromedy, kogda delali eti snimki, nahodilas' v nachale desyatogo etapa
razvitiya, ob etom govorit uvelichenie intensivnosti rentgenovskogo
izlucheniya. Postepenno budut poyavlyat'sya novye oblasti rentgenovskogo
izlucheniya, po mere togo, kak eto izluchenie budet dohodit' do nas. V
konce vsya galaktika budet vidna v rentgenovskom diapazone.
Samaya blizkaya k nam galaktika, t.k. izluchaet v rentgenovskom diapazone intensivnee chem Andromedy.
www.membrana.ru/particle/12746
11 Etap. Formirovanie veshestva sed'mogo perioda. Imenno k nemu i podoshla Vselennaya.
Galaktika budet izluchat' i v gamma diapazone.
Kak eto budet proishodit'? Primerno tak:
Chto ozhidaet Zemlyu i Solnce? Kazalos' by vse dolzhno byt' neizmenno vo veki
vekov. No... Dokazannyi fakt,
chto
Zemlya izluchaet v gamma diapazone. Eto dokazal teleskop prednaznachennyi
sledit' za gamma-vspyshkami Vselennoi. Ego periodicheski napravlyayut v
storonu Zemli i on zafiksiroval izluchenie v gamma diapazone idushee ot
Zemli.
Fakt, vozmozhno, malo primechatel'nyi i ne zasluzhivayushii
vnimaniya. Odnako neobhodimo postoyanno provodit' monitoring etogo
izlucheniya. Esli intensivnost' budet na- rostat', to delo pahnet
katastrofoi dlya zhizni na Zemle. Vse ponimayut, chto gamma izluchenie ub'et
vse zhivoe. Ne srazu, a postepenno, po mere narastaniya. Sbudetsya
predskazannoe Bogom v Novom Zavete i v Otkrovenii Ioanna Bogoslova.
Budut mirovye yazvy, mory, Odni vidy budut intensivno razmnozhat'sya, a
drugie vymirat', poka vse ne vymret na Zemle. Potom
Zemlya vzorvetsya
novoi. Pridet zhe den' Gospoden', kak tat' noch'yu, i togda nebesa s shumom
preidut, stihii zhe, razgorevshis', razrushatsya, zemlya i vse dela na nei
sgoryat. 2-e Petra 3.10. Zemlya, vzorvavshis', peretyanet materiyu ot Solnca
i stanet zvezdoi. Ot Solnca ostanetsya shar zapolnennyi SVETOM.I takie
primery v nashei galaktike uzhe imeyutsya:
www.membrana.ru/particle/10312
Primernyi scenarii 11Etapa:
Bolee 27000tys. let nazad za predelami
nashei galaktiki sformirovany dva puzyrya v kotoryh nahodyatsya elementy sed'mogo perioda
www.membrana.ru/particle/4564
Process, veroyatno, uzhe nachalsya.
Dva dzheta nagnetayut eti
elementy v pridely galaktiki. Odnovremenno idet process perehoda zvezd i planet v Novye.
------------------------------------------
 Re: Efirnaya Teoriya. Edinaya koncepciya.
Re: Efirnaya Teoriya. Edinaya koncepciya.
Otvet #347 - 19.02.13 :: 10:54:45
12 Etap. Zavershenie vseh processov vo Vselennoi. Sudnyi den'.
Podvedenie itogov. Sostavlenie novoi programmy, dlya novoi Vselennoi.
Gospod' ustami Ezdry skazal:
Ibo
vek poteryal svoyu yunost', i vremena priblizhayutsya k starosti, tak kak vek
razdelen na dvenadcat' chastei, i devyat' chastei ego i polovina desyatoi
chasti uzhe proshli, i ostaetsya to, chto posle poloviny desyatoi chasti. 3
Ezdry. 14-10, 11, 12.
Soglasno tablicy himicheskih elementov
Mendeleeva, pochti vse elementy shestogo perioda stabil'ny, krome poloniya,
astata i radona. Eto govorit o tom, chto proshlo uzhe mnogo bol'she
poloviny desyatoi chasti, t.e. 10 Etap sushestvovaniya Vselennoi,
prakticheski, zakanchivaetsya. Po okonchanii vse elementy shestogo perioda
budut stabil'ny.
Na sovremennom etape vse elementy sed'mogo perioda
ne stabil'ny i ne sushestvuyut v prirode. Po okonchanii 11 Etapa vse
elementy sed'mogo perioda budut sozdany i stabil'ny.
------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
31.03.2013 19:52, 47.9 KBait)
I moi variant
---------------------
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo
i o skorosti sveta.
|
10.01.20120:44 |
|
Ciklichnost' galaktik.
Chem galaktiki otlichayutsya drug ot druga.
Kak proishodit-
formirovanie
vstrecha s drugimi galaktikami
nabor
kriticheskoi massy
samo-nagrev
razbros
formirovanie
i t.d.
Esli posmotret' na fotografii - to oni sobstvenno
osobo drug ot druga ne ochen'
otlichayutsya,
no na samom dele otlichii dostatochno chtoby
zametit' ciklichnost' v zhizni galaktik.
Chto opredelyaet dvizhenie v galaktike, dvizhenie v
galaktike
opredelyaet srednyaya temperatura prostranstva
v galaktike, i nekotorye nyuansy po plotnosti materii
v galaktike.
Efir kak vozduh v turbine pylesosa nahodyas'
v galaktike
s raznoi plotnost'yu pri vozdeistvii na nego
centrobezhnogo vozdeistviya priobretaet raznuyu plotnost'.
V centre galaktiki ego plotnost' men'she, a
po krayam bol'she.
No est' odno bol'shoe no - chto sobstvenno proishodit v zhizni
galaktiki - ona mozhet byt' v shesti temperaturnyh sostoyaniyah,
1 ustoichivo
holodnaya,
2 nagrevayushayasya,
3 sbalansirovannaya,
4 peregrevayushayasya,
5 ustoichivo goryachaya
6 ostyvayushaya
Vot na odinakovom rasstoyanii naprimer
nablyudaem
raznye galaktiki po svoei forme.
Na samom dele otpravnoi tochkoi v galaktike
yavlyaetsya
1 plotnost' efira,
2 kolichestvo materii,
i
3 kolichestvo energii v etoi galaktike.
Vot voz'mem naprimer est' galaktika, mimo
nee proletaet drugaya galaktika,
u nih proishodit snizhenie plotnosti
efira mezhdu centrami galaktik,
i mezhdu vysokimi i nizkimi
plotnostyami efira v rukavah, esli takie est'.
Estestvenno proletaya skvoz' drug druga
v galaktikah dazhe ne bylo sluchaya chtoby
dve zvezdy stolknulis' mezhdu soboi,
no eto ne znachit chto ne proishodit
sliyaniya zvezdnyh mass galaktik.
Oni
slivayutsya specificheskim vzaimodeistviem.
Po prichine togo chto plotnost' zvezdy efira,
vnutri zvezd sbalansirovana s vneshnei plotnost'yu
efira v prostranstve,
to pri priblizhenii
centrov galaktik, ili drugih chastei galaktik
s nizkimi plotnostyami efira,
proishodit lopan'e vneshnih obolochek zvezd,
pri lopan'i
obolochek proishodit sbros
materii ot desyati do pyatidesyati procentov,
massy zvezdy.
Posle sbrosa, proishodit bol'shoi
vybros efira iz zvezd, na rukavah
i
v galaktikah etot process viden v vide
rozovyh lopayushihsya zvezdnyh bul'bashek.
Pri bol'shom skoplenii sosednih zvezd,
poluchaetsya udarnaya volna
kotoraya na krayah
processa budet sbivat' davleniem
vneshnyuyu obolochku so zvezd, chto budet
privodit' v vzryvam v stile "Obval karkasa - super nova",
po prichine togo chto kogda vneshnyuyu
obolochku sduet, a zvezda efira ostanetsya na meste,
obolochka potom padaet vo vnutr',
i padenie proishodit s takoi siloi
chto
zarozhdaetsya zvezda efira i srazu efir vosstanavlivaetsya
po prichine bol'shogo kolichestva energii,
v svyazi s chem proishodit bol'shoi vzryv
analogichnyi
Krabovidnoi tumannosti, posle
vzryva v centre ostalas' tol'ko isparyayushayasya
zvezda efira, vosstanovlenie kotoroi postoyanno
podderzhivaet usloviya dlya razleta
materii
ot zvezdy s kotoroi byla rezko zduta obolochka.
Do teh por poka ves' efir ne vosstanovitsya i zvezda
efira ne ischeznet, budet prodolzhat'sya razbros
materii, posle chego materiya ostanovitsya, tak kak
materiyu na stol'ko daleko razbrosalo,
to eta materiya nikogda v zvezdu ne soberetsya, ona
budet uvlechena
drugimi zvezdami.
Tak vot chto sobstvenno imeem, po razmeru zvezdy
mezhdu soboi ne sil'no otlichayutsya,
s moei tochki zreniya ne bolee chem plyus minus
v desyat' raz po sravneniyu s Solncem.
Zvezdy odinakovogo razmera pri nizkom
davlenii efira zvezdy svetyat slabo, pri bol'shom
svetyat sil'no. Pri narushenii
balansa,
zvezda lopaetsya pri snizhenii,
uvelichivaet yarkost' pri plavnom uvelichenii
plotnosti, i teryaet vneshnyuyu obolochku pri
vneshnei udarnoi volne.
A kak eto vliyaet na formu samoi galaktiki?, -
Mozhno vernutsya v nachalo i posmotret' chto u galaktik
v ciklichnosti mozhno vydelit' - molodost',
molodost'
mozhno opredelit' kak ustoichivo
holodnoe sostoyanie, v etom sostoyanii ravnomernoe
raspredelenie zvezd.
Galaktiki razmytye.
Vstrecha s drugimi galaktikami
ili samouplotnenie
galaktiki, pri etom proishodit plavnoe uvelichenie
srednei temperatury vnutri galaktiki, s estestvennym
umen'sheniem kolichestva efira v
galaktike.
Galaktiki s sinimi rukavami.
Tak kak process vzaimnogo sblizheniya zvezd v galaktike
uvelichivaetsya, poyavlyaetsya sleduyushee sostoyanie galaktiki
- sbalansirovannaya, ili galaktika nabravshaya
kriticheskuyu massu - na fotografiyah u
etih galaktik sootnoshenie sinih zvezd i
rozovyh lopayushihsya v rukavah
- primerno
odinakovoe.
Sleduyushaya situaciya kogda galaktika v sostoyanii
samo-nagreva, i yavlyaetsya peregrevayusheisya, po prichine togo
chto posle vybrosa
efira iz zvezd i sbrosa zvezdami
bol'shogo kolichestva massy, eta massa v kosmose
nachinaet nagrevat'sya, ne davaya uiti
izlucheniyu zvezd iz galaktiki,
chto
privodit k rezkomu povysheniyu davleniya
efira vnutri vsei galaktiki.
Vneshne eto zheltovatogo cveta galaktiki,
ili galaktiki okruzhennye kol'com
gryaznyh
vybrosov meshayushih ih
nablyudat'.
Galaktika perehodit v sleduyushee sostoyanie -
ustoichivo goryachaya, i v rezul'tate bol'shogo
davleniya efira proishodit
razbros
vsego sto est' vnutri galaktiki, efira,
materii zvezd, i uskorennoe vosstanovlenie
efira so zvezd efira delaet etot
process grandioznym po
masshtabu, chto
mozhet tak razbrosat' zvezdy daleko,
chto oni uzhe v etoi galaktike ne soberutsya,
a prisoedinyatsya k drugoi.
Estestvenno posle razbrosa
zvezd
na bol'shoe rasstoyanie proishodit ih ostyvanie,
i zvezdy perehodyat v dostatochno ustoichivoe
holodnoe sostoyanie, posle chego,
razletevshayasya materiya
obratno padaet
na zvezdy i oni nabirayut moshnosti svecheniya,
i sblizhayutsya drug s drugom, i tak
process prodolzhaetsya.
Ya special'no ne ukazyval na
zvezdnye
fotografii - po toi prichine chtoby
kazhdyi zhelayushii imel vozmozhnost'
vybrat' to chto emu nravitsya dlya kazhdogo
sluchaya.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1254896
Centr galaktiki Centavr A
-----------------------
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1255454
Velichestvennaya spiral'naya galaktika NGC 1232
-----------------------
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1255185
NGC 253: galaktika Skul'ptor
-----------------------
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1255500
Licom k NGC 6946
-----------------------
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0615a/
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0905a/
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0910i/
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/opo0501a/
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0506a/
|
=============================================
|
|
Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
6.03.20123:40 |
|
Ciklichnost' galaktik.
Chem galaktiki otlichayutsya drug ot druga.
Kak proishodit-
formirovanie
vstrecha s drugimi
galaktikami
nabor
kriticheskoi massy
samo-nagrev
razbros
formirovanie
i t.d.
Esli posmotret' na fotografii - to oni sobstvenno
osobo drug ot druga ne ochen'
otlichayutsya,
no na samom dele otlichii dostatochno chtoby
zametit' ciklichnost' v zhizni galaktik.
Chto opredelyaet dvizhenie v galaktike, dvizhenie v
galaktike
opredelyaet srednyaya temperatura prostranstva
v galaktike, i nekotorye nyuansy po plotnosti materii
v galaktike.
Efir kak vozduh v turbine pylesosa nahodyas'
v galaktike
s raznoi plotnost'yu pri vozdeistvii na nego
centrobezhnogo vozdeistviya priobretaet raznuyu plotnost'.
V centre galaktiki ego plotnost' men'she, a
po krayam bol'she.
No est' odno bol'shoe no - chto sobstvenno proishodit v zhizni
galaktiki - ona mozhet byt' v shesti temperaturnyh sostoyaniyah,
1 ustoichivo
holodnaya,
2 nagrevayushayasya,
3 sbalansirovannaya,
4 peregrevayushayasya,
5 ustoichivo goryachaya
6 ostyvayushaya
Vot na odinakovom rasstoyanii naprimer
nablyudaem
raznye galaktiki po svoei forme.
Na samom dele otpravnoi tochkoi v galaktike
yavlyaetsya
1 plotnost' efira,
2 kolichestvo materii,
i
3 kolichestvo energii v etoi galaktike.
Vot voz'mem naprimer est' galaktika, mimo
nee proletaet drugaya galaktika,
u nih proishodit snizhenie plotnosti
efira mezhdu centrami galaktik,
i mezhdu vysokimi i nizkimi
plotnostyami efira v rukavah, esli takie est'.
Estestvenno proletaya skvoz' drug druga
v galaktikah dazhe ne bylo sluchaya chtoby
dve zvezdy stolknulis' mezhdu soboi,
no eto ne znachit chto ne proishodit
sliyaniya zvezdnyh mass galaktik.
Oni
slivayutsya specificheskim vzaimodeistviem.
Po prichine togo chto plotnost' zvezdy efira,
vnutri zvezd sbalansirovana s vneshnei plotnost'yu
efira v prostranstve,
to pri priblizhenii
centrov galaktik, ili drugih chastei galaktik
s nizkimi plotnostyami efira,
proishodit lopan'e vneshnih obolochek zvezd,
pri lopan'i
obolochek proishodit sbros
materii ot desyati do pyatidesyati procentov,
massy zvezdy.
Posle sbrosa, proishodit bol'shoi
vybros efira iz zvezd, na rukavah
i
v galaktikah etot process viden v vide
rozovyh lopayushihsya zvezdnyh bul'bashek.
Pri bol'shom skoplenii sosednih zvezd,
poluchaetsya udarnaya volna
kotoraya na krayah
processa budet sbivat' davleniem
vneshnyuyu obolochku so zvezd, chto budet
privodit' v vzryvam v stile "Obval karkasa - super nova",
po prichine togo chto kogda vneshnyuyu
obolochku sduet, a zvezda efira ostanetsya na meste,
obolochka potom padaet vo vnutr',
i padenie proishodit s takoi siloi
chto
zarozhdaetsya zvezda efira i srazu efir vosstanavlivaetsya
po prichine bol'shogo kolichestva energii,
v svyazi s chem proishodit bol'shoi vzryv
analogichnyi
Krabovidnoi tumannosti, posle
vzryva v centre ostalas' tol'ko isparyayushayasya
zvezda efira, vosstanovlenie kotoroi postoyanno
podderzhivaet usloviya dlya razleta
materii
ot zvezdy s kotoroi byla rezko zduta obolochka.
Do teh por poka ves' efir ne vosstanovitsya i zvezda
efira ne ischeznet, budet prodolzhat'sya razbros
materii, posle chego materiya ostanovitsya, tak kak
materiyu na stol'ko daleko razbrosalo,
to eta materiya nikogda v zvezdu ne soberetsya, ona
budet uvlechena
drugimi zvezdami.
Tak vot chto sobstvenno imeem, po razmeru zvezdy
mezhdu soboi ne sil'no otlichayutsya,
s moei tochki zreniya ne bolee chem plyus minus
v desyat' raz po sravneniyu s Solncem.
Zvezdy odinakovogo razmera pri nizkom
davlenii efira zvezdy svetyat slabo, pri bol'shom
svetyat sil'no. Pri narushenii
balansa,
zvezda lopaetsya pri snizhenii,
uvelichivaet yarkost' pri plavnom uvelichenii
plotnosti, i teryaet vneshnyuyu obolochku pri
vneshnei udarnoi volne.
A kak eto vliyaet na formu samoi galaktiki?, -
Mozhno vernutsya v nachalo i posmotret' chto u galaktik
v ciklichnosti mozhno vydelit' - molodost',
molodost'
mozhno opredelit' kak ustoichivo
holodnoe sostoyanie, v etom sostoyanii ravnomernoe
raspredelenie zvezd.
Galaktiki razmytye.
Vstrecha s drugimi galaktikami
ili samouplotnenie
galaktiki, pri etom proishodit plavnoe uvelichenie
srednei temperatury vnutri galaktiki, s estestvennym
umen'sheniem kolichestva efira v
galaktike.
Galaktiki s sinimi rukavami.
Tak kak process vzaimnogo sblizheniya zvezd v galaktike
uvelichivaetsya, poyavlyaetsya sleduyushee sostoyanie galaktiki
- sbalansirovannaya, ili galaktika nabravshaya
kriticheskuyu massu - na fotografiyah u
etih galaktik sootnoshenie sinih zvezd i
rozovyh lopayushihsya v rukavah
- primerno
odinakovoe.
Sleduyushaya situaciya kogda galaktika v sostoyanii
samo-nagreva, i yavlyaetsya peregrevayusheisya, po prichine togo
chto posle vybrosa
efira iz zvezd i sbrosa zvezdami
bol'shogo kolichestva massy, eta massa v kosmose
nachinaet nagrevat'sya, ne davaya uiti
izlucheniyu zvezd iz galaktiki,
chto
privodit k rezkomu povysheniyu davleniya
efira vnutri vsei galaktiki.
Vneshne eto zheltovatogo cveta galaktiki,
ili galaktiki okruzhennye kol'com
gryaznyh
vybrosov meshayushih ih
nablyudat'.
Galaktika perehodit v sleduyushee sostoyanie -
ustoichivo goryachaya, i v rezul'tate bol'shogo
davleniya efira proishodit
razbros
vsego sto est' vnutri galaktiki, efira,
materii zvezd, i uskorennoe vosstanovlenie
efira so zvezd efira delaet etot
process grandioznym po
masshtabu, chto
mozhet tak razbrosat' zvezdy daleko,
chto oni uzhe v etoi galaktike ne soberutsya,
a prisoedinyatsya k drugoi.
Estestvenno posle razbrosa
zvezd
na bol'shoe rasstoyanie proishodit ih ostyvanie,
i zvezdy perehodyat v dostatochno ustoichivoe
holodnoe sostoyanie, posle chego,
razletevshayasya materiya
obratno padaet
na zvezdy i oni nabirayut moshnosti svecheniya,
i sblizhayutsya drug s drugom, i tak
process prodolzhaetsya.
Ya special'no ne ukazyval na
zvezdnye
fotografii - po toi prichine chtoby
kazhdyi zhelayushii imel vozmozhnost'
vybrat' to chto emu nravitsya dlya kazhdogo
sluchaya.
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1254896
Centr galaktiki Centavr A

-----------------------
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1255454
Velichestvennaya spiral'naya galaktika NGC 1232

-----------------------
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1255185
NGC 253: galaktika Skul'ptor

-----------------------
http://www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1255500
Licom k NGC 6946
-----------------------
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0615a/

http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0905a/

http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0910i/

http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/opo0501a/

http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0506a/

Eshe
odna fotografiya, tol'ko u menya somneniya
chto eto galaktika, skorei vsego zvezda tipa SS 433
http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/1992/27/image/b/format/large_web/

http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic1104a/

http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/archive/category/galax/
 |
 |
 |
 |
| A rose made of galaxies |
Stellar Nursery in the arms of NGC 1672 |
Colliding galaxies make love, not war |
Magnetic monster NGC 1275 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Flocculent spiral NGC 2841 |
ACS Image of NGC 5866 |
Hubble Mosaic of the Majestic Sombrero Galaxy |
The magnificent starburst galaxy Messier 82 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| A Poster-Size Image of the Beautiful Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 1300 |
Galactic wreckage in Stephan's Quintet |
Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 6217 |
Dramatically backlit dust lanes in NGC 7049 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Holiday Wishes from the Hubble Space Telescope |
Largest ever galaxy portrait - stunning HD image of Pinwheel Galaxy |
Out of this whirl: The Whirlpool Galaxy (M51) and companion galaxy |
A 'wallpaper' of distant galaxies is a stunning backdrop for a runaway galaxy |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Hubble's newest camera takes a deep look at two merging galaxies |
Edge-On View of NGC 4013 |
A Grazing Encounter Between two Spiral Galaxies |
Galaxy Playing Twister |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Hubble views NGC 4522 |
Hubble snaps heavyweight of the Leo Triplet |
Spiral Key to Universe's Expansion |
Stellar fireworks are ablaze in galaxy NGC 4449 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Hubble Identifies Source of Ultraviolet Light in an Old Nebula |
Hubble views NGC 4402 |
The gargantuan galaxy NGC 1132 |
Spectacular Hubble view of Centaurus A |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Doing Cartwheels to Celebrate the End of an Era |
Unusual Spiral NGC 4921 in the Coma Galaxy Cluster |
Sunny Side Up |
Barred Spiral Bares All |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Smoke Without Fire: a Different View of the Cigar Galaxy |
A star formation laboratory |
The Belly of the Cosmic Whale |
Perfect Spiral Overlaid with Milky Way Gems |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Hubble image of NGC 1073 |
Hubble Captures a Lucky Galaxy Alignment |
Star cluster surrounds wayward black hole in cannibal galaxy ESO 243-49 (unlabelled) |
The Calm after the Galactic Storm |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Stars in the Andromeda Galaxys disc |
Star cluster surrounds wayward black hole in cannibal galaxy ESO 243-49 (labelled) |
Antlia Dwarf Galaxy Peppers the Sky with Stars |
HST PHAT detail of M31 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Centre of M31 |
Hubble zooms in on double nucleus in Andromeda Galaxy |
Hubble observes blue stars in Andromeda's core |
HST PHAT wide image of M31 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Ground-based image of Andromeda Galaxy, M31 |
Ground-based image of Andromeda Galaxy, M31 |
| |
---------------------------------------------------------
Vnimatel'no rassmatrival galaktiki i zametil dopolnitel'nye
otlichitel'nye osobennosti.
1 Rassloenie galaktiki.
U galaktik
nablyudaetsya rassloenie
vnutri
galaktiki, v svyazi s chem proishodit neravnomernoe
uplotnenie zvezd, i sozdaetsya situaciya kogda v centre
galaktiki proishodit povyshenie temperatury
v
svyazi s chem sozdaetsya razryazhenie efira
------------------------------
 |
|
|
|
| Doing Cartwheels to Celebrate the End of an Era |
|
|
|
|
-------------------------------------
v svyazi
s bol'shimi rasstoyaniyami efir ne mozhet byt'
popolnen s okrain galaktiki, zvezdy nachinayut
v centre bystree sblizhat'sya
i styagivat'sya v centr galaktiki, posle chego nizkaya
plotnost' efira privodit
k tomu chto zvezdy nachinayut
teryat' balans i uzhe ne mogut vsasyvat' efir,
chto privodit
k lopan'yu zvezd s posleduyushim vybrosom efira.
Posle togo kak povyshaetsya davlenie efira v
centre galaktiki,
povyshaetsya davlenie efira, poluchaetsya situaciya v kotoroi
staraya ploskost' galaktiki s vysokoi plotnost'yu
efira sozdaet uprugost' gorazdo
bol'shuyu po otnosheniyu
k osyam, v svyazi s chem vse zvezdy povorachivayutsya po osi,
i poluchaetsya vot takaya situaciya.
 |
|
|
|
| Hubble image of NGC 1073 |
 |
|
| A Poster-Size Image of the Beautiful Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 1300 |
|
|
-------------------------------
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
6.03.201218:28 |
|
Prodolzhenie.
2 Gryazevoe kol'co.
a) Galaktika men'she gryazevogo kol'ca.
b) Galaktika bol'e gryazevogo kol'ca.
v) Razmytie gryazevogo kol'ca.
Kogda galaktika prohodit kriticheskuyu massu u ee
zvezd nachinaetsya lopan'e zvezd s obrazovaniem
vokrug galaktiki gryazevoi peleny,


posle
chego
eta pelena koncentriruetsya v gryazevoe kol'co.

Kogda vidimyi razmer galaktiki men'she gryazevogo
kol'ca - govorit o tom chto galaktika vstupila
v svoyu samuyu
dinamichnuyu
fazu, i u nee nachinayut izmenyatsya vse
zvezdy vnutri kol'ca.

Povyshaetsya temperatura
v svyazi s chem snizhaetsya plotnost'
efira, v svyazi s bol'shimi rasstoyaniyami efir s periferii
ne mozhet popolnitsya, zvezdy nachinayut bystro
samo-sblizhat'sya, chto
privodit k eshe bol'shemu snizheniyu
plotnosti efira i uvelicheniyu temperatury,
chto privodit k potere balansa dlya formirovaniya
"zvezdy efira" vnutri
zvezd, i v svyazi s chem prakticheski
vse zvezdy odnovremenno nachinayut vydelyat' efir.

Kogda
zvezdy vnutri gryazevogo kol'ca - to proishodit ili process
bystrogo samo-sblizheniya zvezd po prichine togo chto efir s periferii
ne mozhet popolnit' snizhenie plotnosti
tak kak efir tozhe
obladaet vyazkost'yu i massoi, i na takih bol'shih
rasstoyaniyah popolnenie efira iz vne gorazdo men'she
chem nuzhno dlya zvezd, i oni samo-sblizhayutsya,
tem samym eshe bol'she
snizhaetsya plotnost' efira i povyshaetsya temperatura, posle
chego "zvezdy efira" teryayut balans vo vtoroi raz, v pervyi raz
oni
poteryali balans pri formirovanii gryazevoi peleny,
kotoraya prevratilas' v gryazevoe kol'co. Teryaya balans po vsasyvaniyu
efira, zvezda efira nachinaet vosstanavlivat'
efir i sbrasyvat' ego
v prostranstvo, chto proishodit prakticheski odnovremenno so vsemi
zvezdami, i galaktika nachinaet razletat'sya.
Poluchaetsya chto kogda galaktika
men'she gryazevogo kol'ca,
to v nei zvezdy samo-sblizhayutsya, ili rastalkivayutsya efirom.



Kogda zvezdy prakticheski odnovremenno
teryayut balans i vybrasyvayut
efir v prostranstvo sozdaetsya izbytochnoe davlenie efira,
i zvezdy bystro razletayutsya
vo vse storony,
sperva zaletayut za gryazevoe kol'co, a potom

i polnost'yu gryazevoe
kol'co pogloshayut
kak budto ego i ne bylo.

|
----------------------------------------------
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo
i o skorosti sveta.
|
12.03.20121:16 |
|
Zametil ocherednuyu zakonomernost'.
Rukava.
Esli galaktika sostoit iz yavno vidimyh dvuh rukavov,
to eto rukava ot sliyaniya dvuh galaktik.
Galaktiki sblizhayutsya.
--------------------
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0206b/

------------------
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0810ae/

-----------------
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/opo9734d/

------------------
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0615a/

Formiruyut obshee yadro.
------------------------
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/opo0014a/

Yadra galaktik slivayutsya.
---------------------------------
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic1107a/

http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0912a/

--------
Yadra dvuh galaktik slity.
----------------------------------
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/potw1125a/

---------------------------
http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/opo1103c/

|
---------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
31.03.2013 19:54, 4.8 KBait)
Moi variant, prodolzhenie
---------------------------------------
Galaktika s rassloeniem.
 Picture
Album: Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 1512 in Many Wavelengths
(Gallery)
Picture
Album: Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 1512 in Many Wavelengths
(Gallery)
 Picture
Album: Wide view of Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 1512
(Gallery)
Picture
Album: Wide view of Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 1512
(Gallery)
---------------------
NGC 4314


---------------------------------------------------
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
24.03.201217:59 |
|
http://infuture.ru/article/5880
Astronomy obnaruzhili kvazary, deistvuyushie kak gravitacionnye linzy
 Kandidaty v gravitacionnye linzy imeyut neocenimoe
znachenie dlya ocenki massy galaktik kvazarov.
Kandidaty v gravitacionnye linzy imeyut neocenimoe
znachenie dlya ocenki massy galaktik kvazarov.
Astronomy, ispol'zuyushie kosmicheskii teleskop Habbl, nashli neskol'ko
primerov galaktik, soderzhashih kvazary, kotorye deistvuyut kak
gravitacionnye linzy, usilivaya i iskazhaya izobrazheniya galaktik. ---------------------------
 Go to image download page Go to image download page---------------- Dannaya galaktika samaya interesnaya iz vseh, u etoi galaktiki
proizoshlo sliyanie dvuh galaktik, chto povleklo za soboi rezkoe rassloenie zvezd, i u centra galaktiki zvezdy nachali bystro samo-sblizhat'sya i rezko uvelichilas' temperatura
v centre, i estestvenno rezko snizilas' plotnost' efira, i zvezdy v centre ne mogut obespechit' nuzhnogo davleniya vnutri sebya chtoby uderzhat' zvezdu efira ot togo
chtoby chasticy Aleksandra, ne nachali prevrashat'sya v chasticy efira. Pri vosstanovlenii chastic Aleksandra, k etim chasticam prisoedinyaetsya energiya, i chastica uvelichivaet
ob'em v milliard i bolee raz, i prevrashaetsya v chasticu efira (chastica efira v milliard raz men'she chasticy (uslovnoi chasticy) vozduha), pri etom process na nekotoroe
vremya stanovitsya neobratimym. Pri blizko raspolozhennyh sosednih zvezdah, rezko vosstanovivshiisya efir u sosednih zvezd delaet bokovoi rezkii gidravlicheskii udar pri etom
mozhet sdut' vneshnyuyu obolochku, i zvezda efira ostanetsya pozadi a obolochka iz materii sletit. I pervonachal'noe vosstanovlenie efira nabiraet lavinoobraznyi vid, chto
v rezul'tate tak daleko davleniem efira razbrosaet zvezdy, chto bol'shinstvo zvezd nikogda ne soberutsya v odnu galaktiku, oni pri ostyvanii sformiruyut mnogo nebol'shih
galaktik na bol'shom udalenii drug ot druga. Osnovnaya dostoprimechatel'nost' etoi galaktiki - eto samaya dinamichnaya chast' zhizni galaktiki. To chto hotyat
sdelat' katalog - to eto konechno gde-to logichno, no ne sovsem pravil'no, pravil'no u analogichnyh galaktik vesti nepreryvnuyu videozapis' v teleskop. No uchityvaya
v kakom kamennom veke zhivem chto opredelyaetsya kolichestvom teleskopov v kosmose na million , etot vopros budet vryad-li kogda reshen v obozrimom budushem. |
---------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.04.2013 22:59, 1.6 KBait)
Rassmeshil menya etot specialist po opytam Tomasa Yunga.
Vozmozhno nedalekii podrazumevaet opyt na elektronno
lopuhonnyh strunno
shelyah, gde sobstvenno udalos'
rasshepit' elektron.
---
Na samom dele opyt Tomasa Yunga ne predstavlyaet iz
sebya nichego zauryadnogo, v avtorskom variante
eto opyt
na dvuh shelyah diametrom odnu desyatuyu millimetra
raspolozhennye na rasstoyanii odnogo millimetra
drug ot druga, i sobstvenno v rezul'tate dannogo
opyta proishodit nalozhenie dvuh shelevyh kartinok
solnca.
V rezul'tate nalozhenii dvuh solnechnyh shelevyh
izobrazhenii poluchilis' polosy na izobrazhenii, chto
sobstvenno
v ocherednoi raz slivaet fotony.
Nedalekie fiziki interpretiruyut elektronnye opyty
na dvuh shelyah kotorye byli sdelany bolee sta let spustya
-
kak im hochetsya, i pripisyvayut etot golimyi
porozhnyak avtorstvu Tomasa Yunga.
----------------------

Otvet #19 : Segodnya v 21:16:57
Mihail Surin, smotrya na Vashi
kartinki, tak i ne ponyal, kak elektron prohodit cherez dve dve sheli v
opyte Yunga. A molekula fullerena s protonami, neitronami i elektronami?
Vse gorazdo slozhnee, ne nahodite?
Dlya bileta v novuyu fiziku, otkryvat' novye chasticy ne obyazatel'no, soglasen s Vami
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.04.2013 23:03, 211 Bait)
Opyty Tomasa Yunga v srednem 1800 god,
a elektron pridumali v 1924-1926godu.
Sobstvenno elektron na dvuh shelyah i opyty Tomasa Yunga
eto raznye epohi.
Intellekt na zemle - konstanta odnako.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.04.2013 12:19, 2.6 KBait)
 Re: Znaem li my fiziku?
Re: Znaem li my fiziku?
Otvet #91 - Vchera :: 17:32:49
romik pisal(a) Vchera :: 16:34:56:Alow pisal(a) Vchera :: 15:09:48:Kogda
provod peremeshaetsya v magnitnom pole, to elektrony, pod deistvie
magnitnogo polya, nachinayut dvigat'sya, sozdavaya vokrug provodnika
magnitnoe pole
Nu a do magnitnogo polya elektrony pokoino lezhat v provodnike?
U elektronov net silovogo napravlennogo dvizheniya.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vot chto menya udivlyaet ya bolee chem uveren chto prakticheski
nikto ne znaet o tom fizicheskom opyte v rezul'tate kotorogo
byli pridumany elektrony, po toi prichine
chto esli by znali
to posle nebol'shogo analiza opyta poslali by elektrony
v peshee eroticheskoe puteshestvie, po toi prichine chto
bazovyi opyt ne pravil'nyi,
po toi prichine chto v nem
idet ne o elektronah a o kolichestve zaryada na mikro-kaplyah masla,
sobstvenno kto ne ponyal - elektron s nositelem zaryada,
a ne elektron,
i konyu ponyatno chto elektrona bez nositelya
zaryada ne sushestvuet.
U menya takoe vpechatlenie chto vse dumayut chto v proshlom uzhe vse
pridumali za nih, tak
vot dokladyvayu, tam polnaya erunda i bardak,
i v rezul'tate gospodstvovaniya paradigmy bylo tak skazat'
samovoshvalenie bez kriticheskih analizov, tak skazat' vse
doveryali,
ibo byli nedalekimi v dannyh voprosah, seichas eto nazyvaetsya -
korporativnaya etika.
Tak vot eta korporativnaya etika - iz fiziki i kosmologii
sdelala skazku dlya umstvenno nepolnocennyh.
I vsyacheski pooshryayut idiotizm v etih naukah.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.04.2013 13:17, 9.5 KBait)
V prostranstvo mezhdu dvumya plastinami pod napryazheniem (v kondensator)
Milliken vvodil mel'chaishie zaryazhennye kapli masla, kotorye mogli
nahodit'sya v nepodvizhnom sostoyanii v opredelennom elektricheskom pole.
Ravnovesie nastupalo pri uslovii 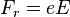 , gde\\\
, gde\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------
\\\V
1913 professor chikagskogo
universiteta R. Milliken v soavtorstve[2]
s H. Fletcherom opublikovali proekt svoego opyta.[3]
V dannom eksperimente izmeryalas' sila elektricheskogo polya, kotoroe
mozhet uderzhivat' zaryazhennuyu kapel'ku masla mezhdu dvumya elektrodami. Po
znacheniyu etogo polya izmeryalsya zaryad kapli. Sami kapli elektrizovalis' vo
vremya razbryzgivaniya. Vo vremena opyta ne bylo ochevidnym sushestvovanie subatomnyh
chastic, i bol'shinstvo fizicheskih yavlenii[kakih?]
mozhno bylo ob'yasnit', prinyav zaryad nepreryvno izmenyayusheisya velichinoi.
Tak nazyvaemyi elementarnyi zaryad e yavlyaetsya odnoi iz fundamental'nyh fizicheskih
konstant i znat' ego tochnoe znachenie ochen' vazhno. V 1923g. Milliken poluchil Nobelevskuyu
premiyu po fizike otchasti i za etot eksperiment.\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
\\\V
1911 godu A.F.Ioffe opredelil zaryad elektrona,
ispol'zovav tu zhe ideyu, chto i R.
Milliken: v elektricheskom i gravitacionnom polyah uravnoveshivalis' zaryazhennye chasticy metalla (v opyte
Millikena kapel'ki masla). Odnako etu rabotu Ioffe opublikoval v 1913 godu (Milliken
opublikoval svoi rezul'tat neskol'ko ran'she, poetomu v mirovoi literature eksperiment poluchil ego imya).[2][3]\\\
---------------------------------------------------------------
\\\Zaryad elektrona nedelim i raven
−1,602176565(35)10−19Kl[1] (ili −4,80320427(13)10−10
ed.
zaryada SGSE v sisteme SGSE ili −1,602176565(35)10−20
ed. SGSM v sisteme SGSM); on byl vpervye neposredstvenno izmeren v eksperimentah A.F.Ioffe
(1911) i R.
Millikena (1912).\\\
--------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------
\\\Opyt Millikena opyt po izmereniyu elementarnogo
elektricheskogo zaryada (zaryada elektrona), provedennyi Robertom
Millikenom i Harvi Fletcherom(angl.)russk.
v 1909 godu [1].
Ideya eksperimenta sostoit v nahozhdenii balansa mezhdu siloi
tyazhesti, siloi Stoksa i elektricheskim
ottalkivaniem. Upravlyaya moshnost'yu elektricheskogo polya, Milliken i Fletcher uderzhivali melkie kapel'ki masla v mehanicheskom
ravnovesii.
Povtoriv eksperiment dlya neskol'kih kapel', uchenye podtverdili, chto
obshii zaryad kapli skladyvaetsya iz neskol'kih elementarnyh. Znachenie
zaryada elektrona v opyte 1911 goda poluchilos' ravnym 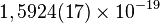 Kl, chto na 1% otlichaetsya ot sovremennogo znacheniya v
Kl, chto na 1% otlichaetsya ot sovremennogo znacheniya v  Kl.\\\
Kl.\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.04.2013 13:33, 1.3 KBait)
Dlya teh kto ne ponyal nyuansa,
na kartinke - ravnomernoe elektricheskoe pole
ot kuda vzyalos', - gde ego bazovye opredeleniya i
gde ego fizicheskaya sushnost'.
------------------------------
---------------------------------------------
To na samom dele - staticheskaya utechka zaryada, i yasen kon'
na risunke napravlenie silovogo deistviya utechki
zaryada
pokazano v protivopolozhnom napravlenii, ibo i konyu ponyatno
chto kaplya stremitsya upast' a silovoe deistvie po prichine
utechki staticheskogo
zaryada uderzhivaet kaplyu.
I chto-to mne podskazyvaet chto i pri izmenenii
polyarnosti - kaplya to-zhe zavisnet no pri drugom
napryazhenii, - kak-by
eto skazat' - mozhet tak
logichno i napravlenie dvizheniya efira obnaruzhivat',
kamennyi vek krugom.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.04.2013 14:29, 400 Bait)
Nadeyus' chto dogadalis' chto na samom dele s etim opytom
larchik prosto otkryvalsya, - elektronov net nikakih,
est' zaryazhennye chasticy, i staticheskii elektro silovoi
potok po prichine utechki, - na risunke eto ravnomernoe elektro pole,
iz opyta i konyu ponyatno chto ravnomernoe elektro
pole ili utechka staticheskaya = mozhet byt'
tol'ko v odnom
napravlenii ot minusa k plyusu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.04.2013 22:23, 5.2 KBait)
- Obozrevatel'





-

- Soobshenii: 7 816
- Reiting: +223/-57
- "..why the good God had opened up so many choices"
-
Otvet #2083 : Vchera v 18:43:00
Shodil na razvedku.
Efir v sredu http://mirtv.ru/premiere/6808952
tret'
byli otkrovennye al'ty (tipa: chlen Mezhdunarodnogo astronomicheskogo
obshestva Lyudmila Konstantinovskaya i kandidat biologicheskih nauk,
professor Evgenii Faidysh). No byl i normal'nyi interesnyi narod.
Vedushii, vrode by, tozhe byl na storone zdravogo smysla.
Posmotrim, chto ostanetsya v itogovom variante 
Osmelyus'
zayavit', chto ni v koem sluchae ne sleduet uhodit' ot dialoga s
al'ternativshikami, dazhe esli on grozit vylit'sya v ser'eznuyu konfrontaciyu
na povyshennyh tonah. Sozhaleyu, chto ne smogu uvidet' prem'ernyi pokaz.
Nado posmotret' programmu, mozhet, budet povtorenie?
U menya net takogo kanala. Budu iskat' na Yutyube.
Voobshe, naiti mozhno pryamo po
vydannoi ssylke.
On-lain translyaciya u nih tozhe est'.
------------------------------------------------
Da ya azh rassmeyalsya.
---------------------------------------------------
Rasskazhu po prostomu - chego net u relyativistov - v pervuyu ochered'
po prichine ih tusovaniya v paradigme oni obrechenny na dostizheniya
stoletnei davnosti, i
ne imeyut vozmozhnosti nichego izmenit'.
-------------------------------
U nih net stroeniya zvezd i planet.
Net fotonov.
Net elektronov.
Net chernyh
dyr.
Net bol'shogo vzryva.
po toi prichine chto etomu net adekvatnogo fizicheskogo
ob'yasneniya net izmeritel'nyh priborov i metodik
izmerenii.
I ostaetsya
tol'ko tancy vokrug mikrofona o chernyh
dyrah tancevat'.
-----------------------------
U al'tov est' vse i eshe zapasnaya telega idei,
no po toi prichine
chto al'ty ne obyazany vytaskivat'
iz bolota relyativizma relyativistov kotorye v etom
bolote vyrashivayut sebe svoyu relyativistskuyu smenu,
kotorye tozhe v rezul'tate
obucheniya zavyaznut v etom
bolote.
U al'tov svoya doroga kotoraya prohodit ryadom i mimo
relyativistskogo bolota.
------------
Vot lichno u
menya delema napisat' fantasticheskii rasskaz
i zablokirovat' na sem'desyat let avtorskie prava na
moi idei v fizike i kosmologii, - s odnoi tochki
zreniya relyativisty
ostanutsya pri svoih interesah,
a fizika i kosmologiya budet vynuzhdena idti
putem paradigmy v tom-zhe sostave i s temi-zhe ideyami.
Eto ne korrektno po otnosheniyu
k molodezhi, po etomu
ya dumayu chto-to primitivnoe vse taki oficial'no opublikovat'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
9.05.2013 22:46, 4.1 KBait)
Vysshee obrazovanie - "Astronom"
Avtor cadian
1 2 3 4 Vse
-----------------------------------
Prochital i kak pravil'no bylo zamecheno v odnom iz postov chto vymyto pokolenie sorokaletnih, kto uehal za rubezh a kto ushel v biznes.
V principe net teh kto sposoben prinimat' resheniya v rezul'tate kotoryh budet luchshe.
Tak kak ya iz etogo pokoleniya to ya v meru svoego
viden'ya rasskazhu chto nado delat'.
V principe astronomy so svoei naukoi ne vidyat neskol'kih glavnyh situacii - pervaya situaciya v tom chto vsya
eta nauka po bol'shomu schetu ne nuzhna, hot' s malymi teleskopami hot' s samymi bol'shimi.
Ibo ne imeet prakticheskogo smysla dlya proizvodstva.
Vtoraya storona medali astronomiyu tekushuyu bol'shinstvo naseleniya schitayut zaputannoi slozhnoi v obshem neadekvatnoi.
Tret'ya
storona - astronomy ne ponimayut chto ne lyudi dolzhny byt' dlya astronomii a astronomiya dolzhna byt' dlya lyudei.
Vsem ved' po barabanu v kakoi teleskop
smotret' esli nikto ne smotrel ni razu v teleskop bol'she 300mm.
Iz etogo prostoi vyhod mozhno i nuzhno zarabatyvat' den'gi na lyubyh teleskopah
- organizuetsya mikro gostinica, v kotoroi lyudi dolzhny razmestit'sya,i lech' pospat', posle chego v devyat' vechera ih razbudyat provedut instruktazh, kak teleskopom upravlyat' kak
ego navodit' na zvezdu i kakie rychagi i pedali nado dlya etogo dergat' i nazhimat'. Posle lekcii v desyat' vechera legkii uzhin, posle chego s teleskopom do dvuh nochi, i nochnoi
uzhin.
Legkii uzhin i nochnoi uzhin, v moem ponimanii racion odinakovyi, - tridcat' grammov masla slivochnogo, dva kusochka belogo hleba, tri kusochka
sahara, dva kusochka kolbasy narezannoi, stolovaya lozhka kabachkovoi ikry, i pol litra chaya.
Po logike dolzhno byt' minimum dve bol'shie komnaty,
krovati mozhno kak na sluzhbe s pruzhinnym karkasom, i vozmozhnost' razmestit' ne menee 60 chelovek, dolzhno byt' tri dushevyh, pyat' sanuzlov, desyat' umyval'nikov, vse udobstva
dolzhny byt' v pomeshenii a ne na ulice, shkafchiki metallicheskie zakryvayushiesya na klyuch kak v supermarketah, dva holodil'nika, pyat' elektroplit, vahtersha i tele-nablyudenie.
Ideya v tom chto-by provodit' ekskursii v vide kul'turnyh pohodov, v astronomicheskie gostinicy, v kotoryh osnovnaya zadacha chtoby gruppy turistov
ili prosto razlichnye kollektivy ne imeyushie otnosheniya k astronomii znakomit' s teleskopami, nauchit i rasskazat' kak imi upravlyat' i predostavit' vozmozhnost' posmotret' na zvezdy.
Tol'ko ne nado ustraivat' toi klounady kogda kto-to smotrit a drugie zhdut, dolzhen byt' okulyar s zerkal'nym otvetvleniem dlya videokamery, i na bol'shom
ekrane chtoby pokazyval rezul'tat navedeniya vsem.
Estestvenno chto komu nadoelo nablyudat' smogut slushat' lekciyu, ili ih budut obuchat'
pol'zovat'sya programmami dlya astronomov.
A esli sovsem nadoest to kosmicheskaya diskoteka dolzhna razveyat'.
I
s moei tochki zreniya u astronomii ne obyazatel'no dolzhen byt' nauchnyi uklon v rabote, ibo lyudi hotyat zrelish, razvlechenii, i novyh neobychnyh znanii i umenii - i vot za eto oni
mogut i hotyat platit' den'gi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
9.05.2013 23:16, 234 Bait)
Estestvenno chto dolzhno byt' mesto na territorii, kuda zaehat'
smozhet dva dlinnyh avtobusa, i eshe dolzhno pomestit'sya minimum
desyat' legkovyh, dva mesta pod navesom,
zhelatel'no s odnoi
yamoi avtomobil'noi s osvesheniem.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
10.05.2013 12:36, 6.0 KBait)
Otvet #46 : 14.03.2013 [00:55:54]
T.e.
ya Vas vse-taki ponyal pravil'no. Vy schitaete, chto nashi observatorii
prosto ne nuzhny. I, chto sleduet sohranit' nebol'shuyu naibolee prodvinutuyu
gruppu nablyudatelei, kotoraya budet rabotat' na zapadnyh sovremennyh
teleskopah. To, chto gruppa budet nebol'shaya - sleduet avtomatom, potomu
chto daleko ne vse smogut podat' zayavki trebuemogo urovnya, a vo-vtoryh,
dlya vseh protso elementarno ne hvatit nablyudatel'nogo vremeni - s uchetom
konkurencii s nablyudatelyami zapadnyh stran.
No, Vy neskol'ko
putaete. Nablyudateli - eto ne te, kto podaet zayavki na nablyudeniya.
Nablyudateli te - kto sami provodyat nablyudeniya. A kto zh ih pustit na
teleskopy-to. Tam est' svoi komandy specialistov. Pustyat tol'ko v tom
sluchae, esli nashi uedut tuda rabotat' navsegda (vot, kak Garmish).
I, povtoryus', a chto togda ostanetsya v nashei strane? Chlenstvo v ESO i neskol'ko astrofizmkov-perefekcionistov?
Vy mozhete beskonechno utverzhdat', chto vy menya ponyali, no ponimaniya u vas pri etom ne pribavitsya. 
Ya
utverzhdayu, chto nado delat' horoshuyu nauku, a ne "kakuyu-to nauku". Kakim
sposobom - eto predmet obsuzhdeniya. Dovol'no ochevidno, chto 10-metrovyi
teleskop ne nado stavit' ni v Krymu, ni na Pastuhova, ni v Kislovodske.
Ego nado stavit' v Chili, na Gavaiah i t.d.
V principe, proshe delat' eto v ramkah mezhdunarodnogo sotrudnichestva.
krome togo, vazhno, chtoby nablyudateli pisali
zayavki i rabotali s raznymi instrumentami.
Plyus, konechno, est' vsyakie poleznye programmy, kotorye mozhno delat' i pryamo na territorii Rossii s nebol'shimi instrumentami.
Putei mnogo.
Ne
ochen' ponimayu, chto vy imeete vvidu pod slovom "perfekcionist". Esli
"delayushii horosho". to da - delayushie plohu (slabuyu) nauku ne nuzhny.\\\
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Kak po mne avtor sego teksta sovsem ne nadelen strategicheskim myshleniem,
i ne ponimaet chto est' i drugie i ne takie uspeshnye kak on.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #47 : 14.03.2013 [00:58:55]
stuchat'sya v ESO, begaya po ministerskim koridoram za podachkoi v 100 mln evro
dlya vstupleniya tuda...
Dyk,
nam zhe eto nichego ne dast, krome poter 100 mln. evro. Nablyudatel'nogo
vremeni nam bol'she davat' ne stanut. A prodvinutaya gruppa i seichas, bez
deneg, tuda zayavki podavat' sposobna.
Koncepciya Sergeya - eto
smert' otechestvennoi astronomii, i prevrasheniya ee ostatkov v pridatok
zapadnoi. Esli zakryt' nashi observatorii, to novyh-to, luchshih, nikogda
uzhe ne poyavitsya. A poka oni zhivy, poka pytayutsya barahtat'sya, vsegda est'
shans, chto dadut den'gi na modernizaciyu teleskopov, chto pozvolit
povysit' i klass provodimyh issledovanii. A ne budut barahtat'sya,
napominat' o sebe, to den'gi na teleskopy nikto i ne dast.\\\
------------------------------------
A eto ya by skazal prosto adekvatnyi i normal'nyi vzglyad na situaciyu.
------------------------------
Smotrel ya peredachu po diskaveri kak radioteleskop vo Francii delayut,
tak francuzy molodcy, oni za eti den'gi po mimo zarplaty poluchayut
i novye tehnologii,
i specialistov poluchayut kotorye mogut zarabatyvat'
na proizvodstve posleduyushih, grubo govorya oplacheny zatraty na opytnoe
proizvodstvo i opytnoe oborudovanie, i
posle pervogo teleskopa mozhno
zapuskat' seriinoe.
Yasnyi kon' chto vryad-li kto v zdravom ume budet
sozdavat' vysoko-kvalificirovannye rabochie mesta v drugoi
strane
za vozmozhnost' predostavleniya vremeni nablyudenii na teleskope,
ya zhe pisal chto ran'she vydelyat den'gi na kosmicheskie seriinye mini teleskopy
na orbite
Zemli - chto zadeistvuyut sobstvennye proizvodstva, i sbyt garantirovan,
hot' vremya prodavai hot' celikom.
Tak vot na pereoborudovanie observatorii v astronomicheskie
gostinicy deneg dadut
odnoznachno, ibo gosudarstvu net smysla soderzhat' ustarevshie observatorii a gostinicy
soderzhat' budet ne nuzhno, oni sami budut sebya soderzhat'
i pomimo zarabatyvaniya
deneg oni budut zanimat'sya prosvetitel'skoi deyatel'nost'yu dlya naseleniya.
I gosudarstvo po krainei mere smozhet komu-to prodat' ih s usloviem,
chtoby provodilis' astronomicheskie meropriyatiya sredi posetitelei v vide obyazatel'nyh
uslug dlya sobstvennika.
A astronomam ya dumayu do lampochki kto budet sobstvennikom,
glavnoe chtoby bylo mnogo
rabochih mest po special'nosti s horoshei zarplatoi.
Edinstvennyi minus chto ne poluchit' professorskogo zvaniya na takoi rabote,
nu zdes'
kak govoritsya nado vybirat', ili bednyi professor, ili obespechennyi lektor.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.05.2013 14:04, 3.2 KBait)
Prochital dve temy, azh ulybnulsya
po krainei mere eto uzhe ne moya bor'ba.
Bor'ba ona v intellektual'nyh voprosah eto kogda
ne hvataet intellekta dlya obosnovaniya,
i net umstvennyh
vozmozhnostei i sposobnostei pravil'no i bez vetvlenii
sformulirovat' i dat' opredelenie situacii.
--------------------------
Vot
v etoi teme avtor dazhe ne ponimaet raznicy mezhdu
fotonami i elektronami, ne znaet raznicy mezhdu fotonom
i svetom, ne znaet opytov Tomasa Yunga.
---------------------------
Konec dualizmu.
Stranic 1
2
3
4
-----------------------
Sobstvenno dazhe nedalekii
znaet chto opyty Tomasa Yunga
primitivny i ponyatny dazhe nedalekim i ih ne nado interpretirovat'
oprovergat' ili dokazyvat'.
Opyt na dvuh shelyah,
v dvernoi
sheli skvoz' kotoruyu prohodit solnechnyi svet, zakreplyayut
bumazhnyi listok, delayut v bumage
otverstie razmerom s dyrku ot bublika, posle chego na rasstoyanii pol metra
berut v drugoi bumage prokalyvayut odnu dyrku, svet prohodit skvoz'
nee i cherez pol metra padaet na belyi list bumagi, na kotorom poluchaem
izobrazhenie solnca,
tak vot esli prokolot' vtoruyu dyrku ryadom s pervoi
na rasstoyanii odnogo millimetra, chto v itoge poluchitsya.
S odnoi tochki zreniya storonniki fotonov srazu skazhut
chto nalozhenie
dvuh potokov fotonov v mestah ih nalozheniya odnogo izobrazheniya solnca
na drugoe, uvelichat yarkost' gde proishodit nalozhenie.
Tak vot pri nalozhenii
dvuh izobrazhenii solnca, v mestah nalozheniya
poyavlyayutsya kol'ceobraznye mesta s povysheniem i snizheniem intensivnosti
chto sobstvenno govorit o volnovoi strukture
svetovyh kolebanii.
------------------------
Teoriya otnositel'nosti Einshteina? Eto vovse ne teoriya! Stranic 1
2
3
4
5
6
-----------------
A zdes' tozhe intellekta ne hvataet elementarno
rassmotret'
bazovye postulaty, esli est' v bazovyh postulatah protivorechie
to eto vse dostatochno.
Dlya etogo dostatochno znat' smysl slov teoriya i gipoteza.
Tak dannaya teoriya dazhe ne teoriya i gipoteza a neobosnovannaya
vydumka opredelenie kotoroi - fantastika.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.05.2013 14:13, 627 Bait)
Sobstvenno kak opredelit' ne specialista po opytam Tomasa Yunga na dvuh
shelyah - eto to chto pered etimi dvumya shelyami - otsutstvuet pervaya shel' kak takovaya,
tam prosto
otverstie s pomosh'yu kotorogo prosto udobno
navodit' izobrazhenie solnca na sobrannoe ustroistvo.
Po bol'shomu schetu dostatochno prosto dvuh shelei na rasstoyanii
odnogo millimetra drug ot druga na liste bumagi, i vtorogo lista bumagi
na kotorom nablyudaetsya - interferenciya.
Interferenciya - eto Tomas Yung pridumal i
opisal volnovye svoistva sveta kak kolebaniya sredy efira, dvesti let tomu,
i opredelil dlinu svetovyh kolebanii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.05.2013 22:53, 4.8 KBait)
Yarkii primer kogda zadacha prevyshaet sposobnosti, i ya by
dobavil chto po vsem punktam srazu.
----------------------------
 Re: Kak postroit' edinuyu neprotivorechivuyu klassicheskuyu elektrodinamiku?
Re: Kak postroit' edinuyu neprotivorechivuyu klassicheskuyu elektrodinamiku?
Otvet #119 - Segodnya :: 20:39:32
otshel'nik pisal(a) Segodnya :: 20:10:05:Prosto "drugie derzhavy" mne slegka "pofonaree" eto sovsem drugoi vopros. Mne
tozhe hotelos' by forum i pokul'turnee, i po kompetentnee. No kogda
sunesh'sya na drugie forumy, ponimaesh' - tam te zhe, tol'ko vid sboku. Etih
uchenyh, zhelayushih postroit' "edinuyu neprotivorechivuyu klassicheskuyu
elektrodinamiku", "edinuyu neprotivorechivuyu elektrodinamiku dvizhushihsya
tel" ne men'she, chem izobretatelei vechnyh dvigatelei. Voobshe vot etot
nabatnyi prizyv - nazad, v proshloe, harakteren ne tol'ko dlya uchenoi
bratii. On eshe bolee harakteren dlya voennyh, 99% publikacii kotoryh
posvyasheny pereigryvaniyu davno proshedshih voin. On ne menee harakteren dlya
biznesa, 99% operacii kotoryh - eto pereigryvanie davno ushedshih v
nebytie biznes-planov. To est', eto vseobshaya chelovecheskaya cherta - igra v
zhizn', tol'ko pochemu-to vsegda po uzhe otstavshim ot situacii pravilam. Ya
potomu i ne u del na etom forume, chto mne ne interesno dvigat'sya
zatylkom vpered. Standartnyi antagonizm interesov: mne ne interesno
nauchnoe proshloe, forumu bezrazlichno nauchnoe budushee. Chto ostaetsya -
ostaetsya ironizirovat' nad ocherednymi potugami povernut' vremya vspyat',
tipa - nazad, v proshloe, v neprotivorechivuyu ... elektrodinamiku. Chto
ploho - ploho, chto ironiya ne dohodit, eti muhi prodolzhayut uporno bit'sya
lbami v steklo, hotya fortochka v budushee - vot ona, ryadom ...
|
---------------------------------------------------------
I kak govoritsya - a larchik prosto otkryvalsya, elektrichestvo lichno
ya reshil primitivno cherez atomarnuyu model' kotoraya reshaet vopros
na mehanicheskom urovne prokachki zhidkostei, i podkrutki chastic
gazov, prokachka - elektrichestvo
podkrutka chastic - magnitnoe pole.
I vse - dostatochno, i bol'she pridumyvat' nichego ne nado.
Nu u drugih drugaya doroga i kuda oni idut ya v principe ponimayu
chto oni idut tuda kuda.
Rasskaz. Efirnoi halyavy ne budet, da ee i ne-bylo
i ona uzhe zakanchivaetsya.
Davnym davno gruppa entuziastov otkapyvala avtobus, pod nazvaniem
efir, i
otkapyvali ego iz pyli vremen, i pytalis' obrashat'sya
k raznym specialistam, vlastvuyushie struktury po raskopkam
nauchnyh idei ne zahoteli vozglavit' i organizovat'
sebe eshe
odno napravlenie tak kak u nih est' svoi avtobus na kotorom oni
derzhat kurs, hot' on davno i ne ezdit no napravlenie kuda ehat'
nado pokazyvaet.
Estestvenno esli dva avtobusa to napravleniya budut u nih raznye,
estestvenno vokrug raskapyvayushih v pyli efir nachinali
skaplivat'sya tolpy orushih chto
ne nado raskapyvat' efir,
da i Vy ezdit' ne umeete, - da i kursa kuda ehat' ne znaete.
Meshali sobstvenno po melocham.
Kogda entuziasty raskopali otremontirovali
i do-oborudovali
avtobus pod nazvaniem efir, to u nih poluchilsya vysokoskorostnoi
avto poezd dlinnoi s zheleznodorozhnyi sostav, u kazhdogo storonnika
efira
svoi avto vagon s bibliotekoi i rabochim kabinetom.
I zdes' prozreli te kto smeyalsya nad entuziastami raskapyvayushimi
efir, no zaiti v poezd ne mogut po raznym
prichinam, u kogo kurs ne
sovpadaet, kogo ot dvizheniya ukachivaet, a u kogo po sposobnostyam
vagon uzhe zanyat, a kto i ne mozhet pridumat' sebe vagon.
Storonniki
efira proezzhaya mimo stoyashego avtobusa vklyuchili
vneshnyuyu begushuyu stroku po vsemu poezdu.
---Spasibo Vam za zabroshennyi i podarennyi nam efir,
spasibo
Vam chto Vy ne dodumalis' vozglavit' i pomogat'
nam v raskopkah efira.---
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.05.2013 23:44, 1.0 KBait)
Ya podskazhu v chem oshibka u vseh.
Bazovaya oshibka v neponimanii suti intellekta,
intellekt eto kogda v odnom lice dve situacii
v kotoroi v pervoi zadachi
nado naiti zdravoe zerno
smyslovoe i vtoraya zadacha - opisat' eto zdravoe zerno
v primitivnyh terminah i v primitivnom smyslovom
opredelenii, sleduyushaya zadacha
eto zdravoe zerno soglasovat'
s analogichnymi - esli ne poluchaetsya to dva varianta , zapomnit' ili
zapisat' i vernutsya k etomu cherez mesyac ili cherez god,
a
mozhno i zabyt', budet nado samo vspomnitsya.
Po prostomu nado byt' i dumat' i pridumyvat' i byt' tupym odnovremenno
chtoby srazu proveryat' svoi idei na oshibki.
Global'naya oshibka - prakticheski nikto ne mozhet stavit'
zadachi i vnikat' v smysl.
Poiskovaya oshibka - vse kuda-to toropyatsya i propuskayut ne primetnye
ssylki
ili slovosochetaniya, i dumayut chto znayut smysl slovosochetanii. Tot-zhe effekt Doplera,
byl priduman zadolgo do relyativistskih idei i etot effekt isklyuchitel'no
dlya sred,
dlya efira vozduha i vody.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.05.2013 23:47, 177 Bait)
Po prostomu nado byt' logichnym i ne toropit'sya i dumat' i pridumyvat'
i byt' tupym odnovremenno
chtoby srazu proveryat' svoi idei na oshibki.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.05.2013 9:20, 839 Bait)
Global'naya oshibka - prakticheski nikto ne mozhet stavit'
zadachi i vnikat' v smysl.
-
V teleskop to vidno chto zvezdy svetyat a kosmos
holodnyi,
voz'mite etu zadachu pered det'mi postav'te oni srazu Vam
skazhut chto tam - v kosmose, - pomimo zvezd est' to chto ohlazhdaet.
Esli zvezdy vse vokrug
nagrevayut, i konyu ponyatno - togo chto
nevidno i to chto - ohlazhdaet, kosmos
namnogo bol'she chem zvezd kotorye nagrevayut.
I yasnyi kon' chto lyubaya model' dolzhna
iznachal'no legko
reshat' eti voprosy.
I tak chego ne voz'mis', vse v osnovnoi masse -
dumayut chto u abstraktnyh uchennyh
super mozg kotorym oni uzhe vse
obdumali i reshili vse voprosy
tak vot situaciya na samom dele ne takaya raduzhnaya,
tak kak i te uchennye tozhe dumayut chto za nih i dlya nih
uzhe vse pridumali.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.05.2013 9:56, 822 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Otvet #525 : Vchera v 23:46:38
Otlichnaya lekciya byla segodnya
u Dmitriya Vibe, ya byl odin iz treh slushatelei. Glupo eto, chto narod ne
interesuetsya. Navernoe on glupyi, nu raz glupyi - sud'ba ego
sootvetstvennaya.
------------------------------------
Eto prosto teh kogo Vibe zabanil na forumah - reshili
ne prihodit', i u Vibe lekcionnyi zarabotok
nakrylsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.05.2013 23:36, 333 Bait)
Est' pogovorka starogo psa novym shutkam ne nauchish' \s\.
Tak vot eto moi blog o tom chto ya nablyudayu, a svet i prostranstvo,
eto moi dostizheniya, ili moya tak
skazat' zapisnaya knizhka.
Tak chto teh nedalekih kto prochital etot forum i prodolzhaet verit'
v chernye dyry i hochet prodolzhat' obsuzhdenie zdesya, ya ogorchu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.05.2013 20:28, 1.4 KBait)
Otvet #525 : 15.05.2013 [23:46:38]
Otlichnaya lekciya byla segodnya
u Dmitriya Vibe, ya byl odin iz treh slushatelei. Glupo eto, chto narod ne
interesuetsya. Navernoe on glupyi, nu raz glupyi - sud'ba ego
sootvetstvennaya.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vspomnil kak na odnom ostrove odna obez'yana
nauchilas' chto-to delat'. A vokrug i na sosednem ostrove
podobnoe obez'yany ne delali i ne umeli takogo i ne znali.
I drugie obez'yany posmotreli i nachali povtoryat'
kak i eta
obez'yana. Vse by to nichego, tol'ko na sosednem
ostrove posle togo kak na ostrove pervootkryvatelya stalo
izvestno bolee dvadcati obez'yanam, to na
sosednem
ostrove bez vsyakogo postoronnego obucheniya obez'yany
nachali delat' tozhe samoe.
Tak i zdes' - vozmozhno ne hodyat potomu chto
uznali chto-to
drugoe, hotya ih etomu nikto i ne uchil.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.05.2013 0:10, 1.9 KBait)
Otvet #306 : Segodnya v 19:34:53
Prezident RAN Yu.S.
Osipov na obshem sobranii akademii posetoval, chto "my ne umeem "voevat'"
cherez sredstva massovoi informacii". No situaciya, na moi vzglyad,
tyazhelee. Chtoby osoznat' svoe neumenie voevat', nuzhno vstupit' v boi. My
zhe poka, v osnovnom, sidim v tylovyh kazarmah iz slonovoi kosti i
setuem, chto gde-to tam, daleko, nami proigryvaetsya general'noe srazhenie,
a u nas net ni strategii, ni taktiki.
Dobavlyu eshe ot sebya, chto
nashi astronomy uzhe sdalis'! Chto namnogo huzhe, chem sidet' v kazarme. My
uzhe priznalis', chto u nas tehnika huzhe ,poetomu my ni chego otkryt' ne
mozhem, chto zapadnye zhurnaly prestizhnee, chto publikovat'sya nuzhno na
angliiskom yazyke(sm. hotya by post Popova v teme o planetnoi astronomii).
Porazhencheskoe nastroenie--po moemu mneniyu, prichina vseh nashih neudach. I
delo ne tol'ko v finansirovanii, nachinat' nado s myshleniya.
-----------------------------------------------------
Lichno ya soglasen so vsem chto zdes'
napisano, proigrali
v tehnike, opozorilis' v shkol'noi programme chto astronomiyu
za neadekvatnost' zapretili dlya prepodavaniya v shkolah,
da i al'tam proigrali
v umenii obrabatyvat' dannye.
Itogo - nakaplivat' dannye net smysla ibo tehnika nikakaya,
obrabatyvat' dannye ne obucheny net umenii kak pisat' teorii i gipotezy,
net ponimaniya kak iz dannyh po nablyudeniyam sdelat' teoriyu ili gipotezu ,
shkol'nye uchebniki adekvatno perepisat' nekomu professorov mnogo
a napisat' uchebniki
vse ravno nekomu ibo oni vse zanyaty.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.05.2013 23:35, 3.6 KBait)
Otvet #460 : Segodnya v 21:03:48
V svoe vremya ya nikak ne mog
ponyat', otchego nekotorye nashi uvazhaemye uchenye tak nepriyaznenno
otnosyatsya k zhurnalu "Tehnika - molodezhi"
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,87799.msg1652558.html#msg1652558.
A nedavno do menya, nakonec, kak govorit'sya, "doshlo". Osobenno, kogda stal perechityvat' otdel'nye nomera za nedavnie gody.
Spravedlivosti
radi dolzhen skazat', chto ran'she v etom zhurnale statei vrode
"Ekzoplanetnaya ekzotika..." ( 1 za 2013 g.) ili "Dva interv'yu..." ( 3
za 2013) ne popadalos'. Esli zhe i publikovalsya kakoi-nibud' spornyi ili
somnitel'nyi material, to obyazatel'no s kommentariem kakogo-nibud'
izvestnogo uchenogo, avtoritetnogo specialista v dannoi oblasti, kotoryi
pryamo ukazyval na slabye mesta ili pryamye oshibki takoi publikacii.
Teper' zhe takoi praktiki net. Pri etom iz vystuplenii krupnyh uchenyh s
mezhdunarodnym avtoritetom vyryvayutsya citaty vygodnye avtoram
vyshenazvannyh mnoyu publikacii.
Pri etom ya ne berus' utverzhdat',
chto avtory etih statei oshibayutsya. Dlya etogo u menya nedostatochno znanii.
No dlya togo, chtoby usomnit'sya v ih pravote - ih vpolne hvataet.
Chuvstvuyu, chto eto - al'ternativshina. Hotya i zvuchit ubeditel'no
(Kto
ego znaet, mozhet, tak i nado?)
No chuvstva v takom dele, kak nauka - plohoi instrument. Ne ob'ektivnyi.
I
mne kazhetsya, chto nashi professionaly sdelali by ochen' horosho, esli by
udelili hot' nemnogo vremeni bolee ili menee podrobnomu razboru teorii i
gipotez, kotorye ya upomyanul vyshe.
Konechno, ya ponimayu, chto mnogie
professionaly itak delayut kolossal'nuyu rabotu po populyarizacii nauki.
Pri etom, kak ya ponimayu, chasto v usherb sobstvennym nauchnym interesam.
Odnako populyarizaciyu "al'ternativnyh" gipotez i teorii my vidim, a pozitivnyh - net.
---------------------------------------------
\\\Pri etom ya ne berus' utverzhdat',
chto avtory etih statei oshibayutsya. Dlya etogo u menya nedostatochno znanii.
No dlya togo, chtoby usomnit'sya v ih pravote - ih vpolne hvataet.
Chuvstvuyu, chto eto - al'ternativshina.\\\
Al'ternativa - eto prosto drugaya tochka zreniya drugie podhody
i drugie metody reshenii, - a moderatory na etom forume
propagandiruyut
al'ternativnye idei kak idei umstvenno nepolnocennyh.
Tak lyuboi al't skazhet chto relyativizm eto dlya teh kto ostalsya v proshlom.
A
sto let veshat' odno i tozhe zadolbaet vseh slushatelei.
-
\\\No chuvstva v takom dele, kak nauka - plohoi instrument. Ne ob'ektivnyi.
I
mne kazhetsya, chto nashi professionaly sdelali by ochen' horosho, esli by
udelili hot' nemnogo vremeni bolee ili menee podrobnomu razboru teorii i
gipotez, kotorye ya upomyanul vyshe. \\\
Chtoby zanimat'sya dannymi voprosami nado chtoby umstvennye vozmozhnosti prevyshali
neobhodimyi uroven' dlya resheniya postavlennyh
zadach,
inache takie zadachi budut reshat'sya - vechno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.05.2013 8:55, 2.5 KBait)
- Moderator





-

- Soobshenii: 11 530
- Reiting: +115/-16
- Mne nravitsya etot forum!
-
Otvet #482 : Segodnya v 07:29:08
\\\No
v dannom sluchae vazhno, chtoby propagandirovalis' dostizheniya real'noi
nauki, pust' dazhe v stat'yah gde-to i popadayutsya oshibki i nesuraznosti.
No beda, kogda za real'nuyu nauku vydayutsya kraine somnitel'nye
rassuzhdeniya. V proshlom godu mne dazhe vstrechalos' tam koe-chto ves'ma
napomnivshee mne "teorii" nekotoryh individov davno zabanennyh na nashem
Forume.\\\
------------------------
Tak i menya tam zabanili na etom forume, moderator
etot forum schitaet nauchnym sitom kotoryi otseevaet uchennyh
ot zas ran cev, i ne zamechaet togo chto u kogo-to
uma ne hvataet pridumat' chto-to novoe, a vse pol'zuyutsya
pridumannym sto let nazad i let pyat'desyat - sem'desyat
nazad, i
nazvali eto gospodstvuyushei paradigmoi i etu paradigmu
kolbasyat i tak i etak, - po kanalu diskaveri ot idiotizma
peredach pro chernye dyry, zvezdy
i bol'shie vzryvy azh toshno.
A esli sprosit' - a kak zvezda ustroenna, - v otvet tishina.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.05.2013 9:15, 388 Bait)
Pravil'no by bylo pri otmene prepodavaniya astronomii
v shkolah za neadekvatnost' takovoi, srazu lishit'
vseh kosmologov i astronomov professorskih zvanii.
I tot zhe forum o populyarizacii astronomii - ne ponimayut
chto neadekvatnoe - net smysla propagandirovat' i populyarizirovat',
nuzhny prosto adekvatnye kosmologicheskie
modeli zvezd, galaktik
i prochego.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.05.2013 22:09, 923 Bait)
: 17.04.2005 [18:32:29]
Interferenciya
chastic
----------------------
Mne tak nravitsya vse chto tam napisali, -
im eshe ochen' daleko do osnov slova interferenciya
- kotoroe
opisal Tomas Yung v opytom s solnechnym svetom v dvernoi
sheli i dvuh dyrkah ot igolki na rasstoyanii odnogo millimetra.
Samoe kachestvennoe v
etoi situacii dlya al'tov - bez ponimaniya net konkurencii.
I vryad-li oni dogadayutsya chto slova interferenciya i elektrony - nel'zya
primenyat' odnovremenno ibo
ih razdelyaet stoletie.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.05.2013 21:30, 1.9 KBait)

Otvet #842 : Vchera v 23:42:50
Vam podrobno ob'yasnyayut, chto otkryvayut v toi mere, v kotoroi
pozvodyayut
nashi instrumenty i nauchnaya specializaciya. Privodyat primer otkrytii.
Privodyat primery populyarizacii. Prosto uchenye govoryat, chto oni, hotya i
zanimayutsya populyarizaciei, no po bol'shomu schetu delat' etogo ne dolzhny.
Dlya etoi zadachi dolzhny byt' otdel'nye specialisty - lektory i
populyarizatory, zhurnalisty, dokumentalisty.
Chto pishut i v rossiiskie
zhurnaly, i v zarubezhnye. K slovu, nashel interesnuyu ssylku pro istoriyu
rossiiskuih astronomicheskih zhurnalov, v kotorye yakoby ne pishut
rossiiskie astronomy

. Pochitaite, Vas pozabavit.
http://www.astro-cabinet.ru/library/Lavrova_bibliograph/Lavrova_Bibliograph_2.htm----------------------------------------------
S moei tochki zreniya naprashivaetsya logichnyi vyvod,
i logichnoe nazvanie zhurnala -
"
Prosto i nauchno, - zhurnal kotoryi populyariziruet nauku "
Kotoryi sobstvenno dolzhen byt', - po krainei mere iz
nazvaniya ponyatno chto zhurnal o nauke
i dlya obyvatelya. Seichas
na podobnoe prosto anshlag, chtoby vse razzhevali do primitiva,
- i prav tot kto platit, i tormoz tot kotoryi zasypaet svoyu
stat'yu
formulami i spec terminologiei.
Formuly i spec terminologiya na skol'ko ya znayu ne rekomenduetsya ispol'zovat'
pri napisanii statei, ih mozhno primenyat' esli net drugoi
vozmozhnosti
vyrazit' svoyu mysl'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.05.2013 22:05, 207 Bait)
Mozhno i drugie nazvaniya
Primitivnaya nauka
Nauka dlya obyvatelya
Nauchnaya i ponyatno
Vy poimete nauku - zdes'
I nauka Vas polyubit
Nauka dlya Vas
Pereshagni formuly i vstupi v nauku
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.05.2013 9:55, 1.7 KBait)
Sobstvenno napravlenie pravil'noe - no rezul'tat budet
nulevoi, chtoby byl rezul'tat nado chtoby bylo ponimanie
a v dannom sluchae metodom nauchnogo vtyka pytayutsya
poluchit'
to chto i ne ponimayut.
Opyt delat' nado po drugomu, nado sdelat' zhestkuyu osnovu,
zakrepit' lazernuyu ukazku, posle kotoroi cherez 20-30mm
razdelyaetsya luch poluprozrachnym zerkalom,
bokovoi luch cherez 100mm povorachivaet i budet parallel'nym
osnovnomu, cherez 100mm povorachivaet po diagonali ,
i
dvizhetsya nazad, peresekaya luch i napominaet
zet s perecherknutoi srednei liniei, posle
chego luch povorachivaetsya parallel'no osnovnomu,
i cherez 100mm povorachivaetsya
na osnovnoi luch
na peresechenie s osnovnym luchom
v meste peresecheniya raspolozheno vtoroe poluprozrachnoe
zerkalo, kotoroe soedinyaet dva lucha, posle chego dve
linzy kotorye
rasshiryat luch dlya kartinki. Izobrazhenie snimaet videokamera.
Dlya medlennogo vrasheniya ispol'zuetsya chervyachnyi reduktor.
Vse ustroistvo mozhno
vrashat' vokrug osi, i esli medlenno vrashat' konstrukciyu
to budet vidno kak dvizhutsya na izobrazhenii interferencionnye kol'ca.
Ideya vsego ustroistva v tom chto
est' osnovnoi luch, i otklonennyi,
po skol'ko v otklonennom luche est' uchastok kogda luch dvizhetsya
po diagonali, esli diagonal'nyi luch raspolozhit' gorizontal'no,
a konstrukciyu vrashat' vokrug osi etoi linii, poluchitsya chto v odnom krainem
polozhenii osnovnoi luch budet napravlen pod uglom sorok pyat' gradusov
vverh, a
v drugom krainem polozhenii pod uglom sorok pyat' gradusov vniz.
Konstrukciya dolzhna vrashat'sya v dvuh ploskostyah.
Po krainei mere nedorogoe ustroistvo
v shkolah mozhno
na urokah fiziki ispol'zovat'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.05.2013 9:56, 322 Bait)
Predydushii tekst po etomu forumu.
---------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
9.06.2013 13:19, 2.4 KBait)
Nemeckie uchenye iz Instituta Astrofiziki Haidberga (Germaniya) pri pomoshi nazemnoi
sistemy teleskopov ALMA
proveli issledovaniya i vyyasnili, chto v nekotoryh kosmicheskih oblastyah
nashei Vselennoi sushestvuyut celye "zavody" pro proizvodstvu tverdyh
nebesnyh tel, v tom chisle i komet.

Esli byt' bolee tochnym, to astronomy nashli bol'shie skopleniya pyli i
drugogo kosmicheskogo materiala v nekotoryh kosmicheskih oblastyah. Oni
opredelili, chtochastichki kosmicheskoi pyli, a takzhe drugogo materiala,
slivayas' drug s drugom, uvelichivayutsya v razmerah, i mogut formirovat'
tverdye tela diametrom okolo 1 metra.
Tak, raznye tverdye kosmicheskie chastichki iz skleennoi pyli nepreryvno
stalkivayutsya drug s drugom na bol'shoi skorosti, obrazuya krupnye tverdye
tela, k primeru komety.
------------------------------------------------------------------
Ya mnogo knig po astronomii prochital v kotoryh iz kosmicheskoi
pyli
i kosmicheskogo gaza teoreticheski dolzhny formirovat'sya zvezdy
i planety, - podtverzhdeniya nablyudenii na protyazhenii sotni let
otsutstvuyut, eta stat'ya
ocherednoi poryv v etu storonu.
Lichno ya udivlyayus' otsutstvii gibkosti myshleniya, nel'zya
vse vremya odnu i tuzhe ideyu musolit'.
Ne soberutsya eti tela v
kuchu - net fizicheskoi prichiny, pyl',
gazy i tela razmerom menee 100 km v diametre nichego v kosmose ne
prityagivali, ne prityagivayut, i nikogda ne budut
prityagivat'.
Esli by prityagivali, to kosmonavty by na mks molotki i otvertki
ne nosili by prikreplennymi s sebe na verevkah, ved' oni dolzhny
by
k mks prityanutsya, a te imeli v vidu zakony N'yutona i uletayut
kuda popalo.
Ya v principe podobnoe mogu sravnit' naprimer s tem chto
eto analogichno
tomu chto zhivoe sushestvo mozhno iz chego-to
slepit' vmesto togo chtoby ego porodilo analogichnoe zhivoe
sushestvo. Eto nazyvaetsya - fantastika.
S
moei tochki zreniya vse tela chto prityagivayut byli \rozhdeny\
a tochnee vybroshennymi kosmicheskimi telami kotorye prityagivali.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.06.2013 9:30, 1.3 KBait)
Raspad skoplenii neizbezhenSkopleniya stabil'nyDrugaya argumentaciya
----------------------
Po nazvaniyu oprosa reshil srochno pochitat'
o chem tam razgovor ibo podumal chto u menya
uzhe nachinayut intellektual'nuyu meloch'
zaimstvovat'.
Okazalos' chto na etom forume dazhe vechnosti
budet malo chtoby otkazat'sya ot dogm v ramkah
kotoryh oni pytayutsya reshit' vopros kotoryi v
etih ramkah reshit' v principe nevozmozhno.
Pochitav forum vspomnil fil'm.
Zhanr: fantastika, komediya, priklyucheniya
http://www.ex.ua/view/74157?r=2
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.06.2013 9:38, 428 Bait)
V principe eto kak raz tot sluchai kogda vse schitayut dogmy
nechto analogichnym poslaniem bogov, teh kto pisal dogmy
- geniyami a sebya schitayut zas- ran- c ami.
I
trizhdy sebya schitayut nedostoinymi i nedalekimi chtoby
oprovergnut' ili usomnit'sya v dogmah.
I vechno budut pytat'sya hvalit' dogmy i v ih ramkah budut
vechno pridumyvat'
i reshat' zadachi kotorye bolee kak
v ih golove bol'she nigde ne primenimy.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.06.2013 21:38, 2.9 KBait)
Nemnogo rasskazhu ponyatno. Sobstvenno bylo obnaruzheno
v kosmose izluchenie opredelennogo veshestva
kotoroe po svoemu spektru sovpadalo s takim-to.
Posle etogo
nado izichit' kak izmenyaetsya spektr
pri vneshnem vozbuzhdenii, ih byvayut
raznye vidy - elektroagnitnye kolebaniya, infrakrasnyi,
vidimyi svetovoi diapazon, ul'trafiolet
\sozdaet poverhnostnoe
vozdeistvie\ i chasticy raznyh energii.
Tak ot raznogo vozdeistviya u nekotoryh atomarnyh struktur
voznikayut raznye situacii, - v danom
sluchai
- chto pri vneshnem vozdeistvii razlichnymi chasticami
i el mag kolebaniyami dannoe veshestvo vhodit na rezonans,
pri etom ot intensivnosti vneshnego vozdeistviya
menyaetsya vosnovnom amplituda rezonansa,
v drugih sluchayah menyaetsya eshe i chastota rezonansa
ona plavaet.
V svyazi s chem logichnyi vyvod - chto eto - chto-by
opisat'
nado bylo ne eho bol'shogo vzryva izobretat'
a pridumyvat' atomarnuyu model', kotoraya by uchityvala etu situaciyu.
V itoge atomarnaya model' dolzhna
vypolnyat' vse elektromagnitnye
svoistva, i svoistva rezonansnyh vozbuzhdenii pri
vneshnem vozdeistvii.
Vyvod - sobstvenno nado nachinat' s postanovki teh
zadachi
po atomarnoi strukture i ee svoistvam, dlya togo chtoby bylo ot chego
opirat'sya i nebylo nestykovok .
Estestvenno net neobhodimosti polnost'yu reshat'
dannuyu zadachu , dostatochno opisat' bazovye ee svoistva
i dat' bazovye opredeleniya.
Sleduyushaya - krasnoe smeshenie - zdes' vopros reshaetsya
po drugomu, opisyvaetsya
metodom ansamblya, s uchetom raznyh situacii.
Nado dat' bazovye opredeleniya svetovomu izlucheniyu i ego svoistvam
u poverhnosti zvezd, v prostranstve, opredelitsya s
ego istochnikom,
prichinoi vneshnego vozdeistviya, i nositelem izlucheniya.
I vse dostatochno - vopros budet reshon uzhe v bazovyh
opredeleniyah modeli el mag izlucheniya.
Estestvenno posle etogo idet model' ustroistva zvezd.
Posle modeli zvezd srazu model' galaktik.
I vse dostatochno.
Esli ne nravitsya to chto poluchilos' s galaktikami
ili zvezdami, - to kak ne smeshno, - nado peredelyvat'
i atomarnuyu model' i model' elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya -
chtoby oni vo vseh vzaimodeistviyah stykovalis'
i ne
protivorechili drug drugu.
I chto tut trudnogo, primitivnye zadachi kotorye
mozhno reshat' tol'ko po sostavlyayushim.
Estestvenno chto eto ya
napisal chtoby relyativisty kotorye banyat
al'tov
na na forumah prizadumalis' i sami nad voprosami kosmologii,
chtoby ponimali skol'ko sil i truda tratitsya al'tami.
Relyativisty ne rekomenduyu Vam reshat' podobnye zadachi ,
ya prosto perezhivayu za Vashe zdorov'e pri stol' ogromnom
potoke informacii kotorye nado budet proanalizirovat'
uznat' i proverit' na prochnost' i vramkah etih
znanii predumat' svoe novoe i drugoe - ni na chto ne pohozhee.
Esli Vy vse-zhe reshites' reshat' podobnye
zadachi - to pozdravlyayu Vas
- Vy stali al'tom.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.06.2013 22:18, 74 Bait)
http://www.popmech.ru/article/13312-relyativistskaya-pena/page/2/#comments
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.06.2013 22:21, 51.1 KBait)
http://www.popmech.ru/article/13312-relyativistskaya-pena/page/2/#comments
|
 |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.06.2013 22:23, 78.8 KBait)
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.06.2013 22:24, 30 Bait)
Prosto ponravilos' obsuzhdenie.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.06.2013 22:52, 248 Bait)
Dlya teh kto ne znaet, predydushii sait diffektivnyi i im tak nravitsya,
ya lichno prosil raspolozhit' soobsheniya naoborot, menya poslali s moim predlozheniem
v peshee
eroticheskoe,
tak-chto predydushee
obsuzhdenie nado chitat' snizu vverh.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.06.2013 23:07, 1.3 KBait)
\\\Dobavleno 18.06.13 18:44
|
|
 |
Uvazhaemyi Dmitrii Mamontov, proshu Vas, sozdaite(ili poruchite sozdanie) rubriku "Tvorchestvo chitatelei"
i opublikuite tam teoriyu nashego TeoreteG′a, uzh ochen' mne zahotelos' poznakomit'sya s ego revolyucionnym i smelym vzglyadom na voprosy astrofiziki i gravitacii!\\\
Eto isklyucheno v principe, esli menya s moimi stat'yami pro efir,
- ya prosilsya napisat' chtoby deneg zarabotat' - poslali v bui,
na chto ya skazal - chto kon'
te na rylo chto-to i ... kogda-to budet
opublikovano pro uvlekaemyi efir zdesya -, na tom i razoshlis'.
Tak i konyu ponyatno chto pechatayutsya te komu polozheno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.06.2013 7:23, 31.1 KBait)
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.06.2013 7:27, 446 Bait)
\\\Termin "zhidkost'" v fizike
imeet tozhe vpolne opredelennoe
znachenie.
Nikakoi zhidkosti v sostave Solnca net.\\\
Mamontov zhzhet na urovne ne nedalekogo v fizike,
a na urovne - ih vozhdya.
Pora by emu uiti
s moderatorstva po prof neprigodnosti.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.06.2013 8:06, 3.9 KBait)
Chtoby byli v kurse chto v fizike do lampochki i po barabanu
chto komu-to hochetsya chtoby solnce sostoyalo iz plazmy
- to ono i iz plazmy.
Zhidkaya poverhnost'
solnca opredelyaetsya po fizicheskim
svoistvam, analogichnym svoistvu zhidkostei - te-zhe vybrosy.
Ya dogadyvayus' chto zhidkaya poverhnost' solnca kakaya
i est'
po faktu ne podhodit pod tekushuyu teoriyu stroeniya
solnca - v centre kotorogo yadernyi reaktor v kotorom
bezbashenno narushaya vse zakony fiziki ustremilsya vodorod
i gelii pouchavstvovat' v yadrennoi reakcii. I ya uzhe dazhe
ne udivlyus' chto vse samoe glupoe i nelogichnoe vse sobrano
v kosmologii.
Zhidkost' ne podhodit po
prichine ob'yasneniya teploobmena,
v tekushem vide.
\\\Iz Vikipedii
Nad yadrom, na rasstoyaniyah primerno ot 0,20,25 do 0,7 radiusa Solnca
ot
ego centra, nahoditsya zona luchistogo perenosa. V etoi zone perenos
energii
proishodit glavnym obrazom s pomosh'yu izlucheniya i poglosheniya fotonov.
Pri etom napravlenie kazhdogo konkretnogo fotona, izluchennogo sloem
plazmy,
nikak ne zavisit ot togo, kakie fotony plazmoi pogloshalis',
poetomu on mozhet
kak proniknut' v sleduyushii sloi plazmy v luchistoi zone,
tak i peremestit'sya
nazad, v nizhnie sloi. Iz-za etogo promezhutok
vremeni, za kotoryi mnogokratno
pereizluchennyi foton (iznachal'no
voznikshii v yadre) dostigaet konvektivnoi
zony,
mozhet izmeryat'sya millionami let. V srednem etot srok sostavlyaet dlya Solnca
170tys. let[38].
Perepad temperatur v dannoi zone sostavlyaet ot 2 mln K na poverhnosti do 7
mln K v glubine[39].
Pri etom v dannoi zone otsutstvuyut makroskopicheskie
konvekcionnye
dvizheniya, chto govorit o tom, chto adiabaticheskii gradient
temperatury v
nei bol'she, chem gradient luchevogo ravnovesiya[40].
Dlya sravneniya,
v krasnyh karlikah davlenie ne mozhet prepyatstvovat'
peremeshivaniyu veshestva
i zona konvekcii nachinaetsya srazu ot yadra.
Plotnost' veshestva v dannoi zone
kolebletsya ot 0,2 (na poverhnosti) do
20 (v glubine) plotnostei vody[39].\\\
------------------------------------------------
Kak govoritsya tak sovral azh sam poveril - osobenno kak
tochno
\\\Nad yadrom, na rasstoyaniyah primerno ot 0,20,25 do 0,7 radiusa Solnca
ot
ego centra, nahoditsya zona luchistogo perenosa.\\\
Eto ya tak ponimayu zond peredal kotoryi zabyli zapustit' v glub'
solnca. Napomnyu tem kto ne znaet
pri vzryve zvezd
v vybrosah byvaet tak chto vodoroda net sovsem dazhe.
Stranno da - ibo i konyu ponyatno chto vodorod i gelii
isklyuchitel'no v verhnih sloyah gazovoi
atmosfery solnca,
i ni geliya ni vodoroda vnutri solnca net - eto zavisit ne ot moego
zhelaniya a ot fizicheskih zakonov, kak-by ponyatno skazat'
- nu eto nauka
takaya - fizika, - ne puskaet vodorod i gelii v centr
solnca i drugih zvezd.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.06.2013 8:32, 17.6 KBait)
Moderator hochet udalit', a ya sohranyu, chtoby ne dumali
chto vse bylo tak pushisto, prosto storonniki tekushei
_uety vse temy kotorye protivorechat ih mirovozreniyu
prosto vmesto konstruktivnogo obsuzhdeniya po suti
srazu nichem neobosnovannymi replikami
sryvayut obsuzhdenie, v stile - mol konyu ponyatno
chto est' bol'shoi
vzryv, i vsemi opytami on podtverzhden
i vot eta kurinaya nozhka kotoruyu ya zhuyu s gonorara
kuplena za podtverzhdenie bol'shogo vzryva - nu i v takom klyuche.
Konyu
ponyatno - etomu nazvanie - krugovaya poruka.
Chto sobstvenno ne delaet chesti, po toi prichine
chto v etom sluchai ne budet pridumyvat'sya nichego
novogo.
Ya estestvenno ponimayu prichinu etogo ona
v sposobnostyah kotorye dany - i takovoi ya ponimayu
chto - konservativnost' myshleniya, ya tak ponimayu
chto prakticheski
nevozmozhno pereuchit' drugim teoriyam,
hot' skol' nelogichnye est' tekushie teorii - drugim teoriyam
skorei vsego ne poluchitsya pereuchit' bol'shinstvo ibo
v golove
mnogih dve teorii tochno ne vmestyatsya, ili tomu
drugaya prichina bol'shoe vnutrennee doverie k toi teorii
kotoruyu individuum znaet na dannyi moment, i po etoi
prichine emu drugaya teoriya vmesto etoi ne nuzhna.
Sobstvenno v rezul'tate massovogo analogichnogo myshleniya,
svyazannyh s opredelennymi teoriyami i zashitoi svoego bolota
konservativnogo, - poluchaetsya kollektivnoe ne vospriyatie
drugih al'ternativnyh tochek zreniya - chto sobstvenno,
i nazyvaetsya - krugovaya poruka po otnosheniyu
k ranee pridumannym teoriyam.
-----------------------------------------------





-

- Soobshenii: 706
- Reiting: +17/-28
-
Teoriya bol'shogo vzryva
postuliruet singulyarnoe sostoyanie Vselennoi, kogda vsya ee massa byla
sosredotochena v singulyarnoi tochke ili mikroob'eme.
Po obshei teorii
otnositel'nosti podobnoe sostoyanie vyzyvaet bol'shie voprosy, ibo kak
izvestno, bol'shie massy v malyh ob'emah obyazany obrazovyvat' chernye
dyry, i chem bol'she massa, tem bol'she razmer chernoi dyry. Esli vzyat'
massu Vselennoi, to diametr chernoi dyry dolzhen byt' poryadka razmera
Vselennoi, no ni o kakoi singulyarnosti pri etom i rechi byt' ne mozhet!
Vse
chto nahoditsya pod gorizontom, ono kak by ne sushestvuet dlya storonnego
nablyudatelya, vremya tam techet v protivopolozhnuyu storonu, i veshestvo ono
kak by beskonechno prilipaet k gorizontu sobytii, V podobnoi situacii
opisyvat' bol'shoi vzryv ne predstavlyaetsya real'no vozmozhnym, ibo lyubaya
malaya chast' sverhplotnoi Vselennoi obyazana shlopnut'sya v lokal'nuyu
chernuyu dyru, i po suti takaya Vselennaya dolzhna predstavlyat' soboi
ogromnoe skoplenie chernyh dyr.
NO v svoyu ochered' opredelennaya chast'
skopleniya chernyh dyr dolzhna prevyshat' kriticheskuyu massu, i v svoyu
ochered' shlopnut'sya v gorazdo bol'shu chernuyu dyru, i tak na neskol'kih
urovnyah...
V rannei Vselennoi kak raz i nablyudalis' kvazary, eto po suti aktivnye chernye dyry.
Teoriya
bol'shogo vzryva kak to oboshla storonoi gravitacionnuyu neustoichivost'
sverhplotnoi materii na rannei stadii formirovaniya Vselennoi.

Zapisan
Nauka, kak devica legkogo povedeniya, otkuda veter duet, tuda i smotrit





-

- Soobshenii: 1 296
- Reiting: +15/-2
- Mne nravitsya etot forum!
-
Otvet #1 : Vchera v 13:24:15
Teoriya bol'shogo vzryva postuliruet singulyarnoe sostoyanie Vselennoi
Voobshe-to
net.
bol'shie massy v malyh ob'emah obyazany obrazovyvat' chernye dyry
Ili belye.
Ili voobshe ne obrazovyvat'.
Teoriya
bol'shogo vzryva kak to oboshla storonoi gravitacionnuyu neustoichivost'
sverhplotnoi materii na rannei stadii formirovaniya Vselennoi.
Inflyaciya - na razvitie neustoichivostei ne hvatilo vremeni.

Zapisan





-

- Soobshenii: 706
- Reiting: +17/-28
-
Otvet #2 : Vchera v 13:39:02
A otkuda togda teoriya BV vzryva beret singulyarnost' vnachale?
Vremeni
na razvitie neustoichivostei ne nuzhno, v sverhplotnom sostoyanii
beskonechnoi materii gorizont dolzhen byt' avtomatom i na malom
rasstoyanii, gorazdo men'shem, chem obshii razmer nachal'noi Vselennoi.
Edinstvennyi variant, eto otsutstvie ili slabost' sil gravitacii v sverhlotnyh sostoyaniyah veshestva,
Krome togo, ne uchityvaetsya deistvie temnoi energii.

Zapisan
Nauka, kak devica legkogo povedeniya, otkuda veter duet, tuda i smotrit


-

- Soobshenii: 60
- Reiting: +0/-2
- Mne nravitsya etot forum!
-
Otvet #3 : Vchera v 13:51:41
A otkuda togda teoriya BV vzryva beret singulyarnost' vnachale?
A
otkuda vy vzyali singulyarnost' v teorii BV? Teoriya BV opisyvaet tol'ko to, chto opisyvaet.
Vremeni
na razvitie neustoichivostei ne nuzhno, v sverhplotnom sostoyanii
beskonechnoi materii gorizont dolzhen byt' avtomatom i na malom
rasstoyanii, gorazdo men'shem, chem obshii razmer nachal'noi
Vselennoi.Edinstvennyi variant, eto otsutstvie ili slabost' sil
gravitacii v sverhlotnyh sostoyaniyah veshestva, Krome togo, ne uchityvaetsya
deistvie temnoi energii.
Srazu
vidno, chelovek s uravneniyami ne razbiralsya, prochital lish' paru statei
pro BV v zhenskih zhurnalah i uzhe krichit - "sie lazha!". Tyazhelyi sluchai...

Zapisan
 neandertalets
neandertalets


-

- Soobshenii: 60
- Reiting: +0/-2
- Mne nravitsya etot forum!
-
- Moderator





-

- Soobshenii: 13 201
- Reiting: +350/-46
- Evona kak...
-
Otvet #5 : Vchera v 14:04:53
Ya dumayu, chto my v takoi stilistike nauchnye problemy obsuzhdat' ne budem. Tema zakryta i budet vskore udalena.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.06.2013 8:55, 14.8 KBait)
Sobstvenno obosnovat' nepravil'nost' bol'shogo
vzryva proshe prostogo - nekotoroe veshestvo, kotorogo
mnogo est' v prostranstve i kotoroe
pere izluchaet na
drugoi chastote
kotoroe bylo obnaruzheno v 1941 godu, bylo
pere otkryto v 1946 godu uzhe kak eho bol'shogo vzryva.
Tak i ohota skazat' yasnyi kon' - esli
nechto postoyanno
izluchaet nekotoroe veshestvo po prichine vozdeistviya na
nego drugih lokal'nyh energii kotorye ego vozbuzhdayut
po mestu nahozhdeniya, to pri chem
zdes' eho global'nogo
processa. Pipec primitiva - odnim slovom.
No delo ne v prostote i logichnosti argumentacii, zdes' delo
kak raz v ne vospriyatii
drugoi tochki.
-----------------------------------------
http://www.bibliotekar.ru/100otkr/65.htm
\\\
Dmitrii Samin
Tainy vselennoi
Koncepciya Bol'shogo Vzryva
Vozmozhnost'
rasshireniya Vselennoi byla predskazana teoreticheski kak odno iz sledstvii
primeneniya k resheniyu kosmologicheskih problem obshei teorii otnositel'nosti.
Pervye trudy v etoi oblasti prinadlezhat talantlivomu sovetskomu matematiku
Aleksandru Aleksandrovichu Fridmanu (1888 1925). On shiroko izvesten kak
geofizik-meteorolog, specialist po prikladnym voprosam dinamiki atmosfery. No
mnogo vremeni Fridman otdal matematicheskomu analizu reshenii kosmologicheskih
uravnenii Einshteina. Nezadolgo do smerti Fridman poluchil seriyu reshenii uravnenii
Einshteina.
Vyhodilo,
chto rasshirenie mozhet yavit'sya odnim iz osnovnyh obshih svoistv Vselennoi
vazhneishim atributom ee evolyucii. Raboty russkogo uchenogo ponachalu ne
privlekli k sebe dolzhnogo vnimaniya. Oni byli oceneny po dostoinstvu lish' v
svyazi s otkrytiem E. Habblom krasnogo smesheniya i razvitiem sovremennyh
predstavlenii o pervonachal'no goryachei Vselennoi i Bol'shom Vzryve.
V 1927
godu Zh. Lemetr, student iz Eddingtona, nezavisimo ot Fridmana vydvinul svoyu
ideyu vozniknoveniya Vselennoi i ee dal'neishego rasshireniya iz tochki. Ei dali na
nekotoroe vremya nazvanie atoma-otca. Sam Lemetr kategoricheski byl protiv
podobnogo obraza i voobshe teologicheskoi traktovki svoei teorii. Process
vozniknoveniya Vselennoi Lemetr predstavil v forme Bol'shogo Vzryva. Molodoi uchenyi
pervym popytalsya naiti i veroyatnye sledy nachal'nogo Vzryva. Lemetr dopuskal,
chto takim otgoloskom mogli byt' kosmicheskie luchi. Ego gipotezu astronomy
zametili lish' posle vystupleniya v 1933 godu, kogda Lemetr vydvinul novyi
variant koncepcii rasshireniya Vselennoi iz plotnogo sgustka materii
konechnyh, no ochen' malyh razmerov.
Zadacha
formirovaniya bolee konkretnoi, fizicheski razrabotannoi evolyucionnoi kosmologo-kosmogonicheskoi
modeli rasshiryayusheisya Vselennoi byla reshena v osnovnom amerikanskim fizikom Gamovym,
russkim po proishozhdeniyu. Dzhordzh (Georgii Antonovich) Gamov (1904 1968)
vpervye predlozhil v 1946 godu teoriyu, poluchivshuyu zatem naimenovanie teorii
Bol'shogo Vzryva (a tochnee Bol'shogo Udara). Soglasno ei, vsya sovremennaya
nablyudaemaya Vselennaya predstavlyaet soboi rezul'tat katastroficheski bystrogo
razleta materii, nahodivsheisya do togo v sverhplotnom sostoyanii, nedostupnom
dlya opisaniya v ramkah sovremennoi fiziki.
Udalenie
galaktik podchinyaetsya neobychnym matematicheskim zakonomernostyam. Ono proishodit
s razlichnymi skorostyami. Chem bol'she rasstoyanie mezhdu galaktikami, tem vyshe
okazyvaetsya skorost' ih vzaimnogo udaleniya.
My v
silah postroit' model' opisannogo vyshe razbeganiya galaktik, pishet A.A. Gurnshtein,
esli ne budem rassmatrivat' real'noe beskonechnoe prostranstvo treh
izmerenii, a ogranichimsya v svoei modeli lish' poverhnost'yu prostranstvom
dvuh izmerenii. Predstavim sebe, chto vsya Vselennaya raspolozhena na nekotoroi
zamknutoi poverhnosti, kotoraya podobna poverhnosti postoyanno razduvaemogo
rezinovogo shara. Pust' galaktiki v nashei modeli izobrazhayutsya tochkami,
nanesennymi na poverhnosti etogo shara. Po mere ego razduvaniya vse rasstoyaniya
mezhdu galaktikami, izmerennye po poverhnosti shara, deistvitel'no budut
sistematicheski uvelichivat'sya, prichem skorost' razbeganiya galaktik okazhetsya
tem bol'she, chem bol'she bylo pervonachal'noe rasstoyanie mezhdu nimi.
Kak
schital Gamov, nachavsheesya pri etom rasshirenie materii v forme nerazdelimoi
vnachale vysokotemperaturnoi smesi izlucheniya i veshestva (elementarnyh chastic)
nablyudaetsya i v nashi dni v vide effekta krasnogo smesheniya.
Gamov
vmeste so svoimi sotrudnikami R. Al'ferom i R. Germanom v 1948 godu
predskazal, chto dolzhno nablyudat'sya i ostyvshee pervichnoe izotropnoe
elektromagnitnoe izluchenie teplovoe s temperaturoi okolo 5 K.
Odnako
razvitiyu teorii v znachitel'noi stepeni prepyatstvovalo obshee skepticheskoe
otnoshenie astrofizikov teh let k vozmozhnosti resheniya stol' fantasticheskoi
zadachi ponyat' nachalo istorii vsei Vselennoi v celom, pishut v svoei
knige Istoriya astronomii A.I. Eremeeva i F.A. Cicin. S drugoi storony,
ulovit' v mirovom prostranstve s pomosh'yu imevsheisya apparatury teplovoe
radioizluchenie stol' nizkoi temperatury specialisty-radiofiziki schitali
sovershenno nevozmozhnym uzhe iz-za togo, chto podobnyi signal byl by zaglushen
radioizlucheniem zvezd, galaktik, mezhzvezdnoi sredy, koroche, kosmicheskim
radioshumom.
Pochti
dva desyatiletiya koncepciya Bol'shogo Vzryva dlya bol'shinstva astronomov
ostavalas' igroi uma nemnogih fizikov i kosmologov I tol'ko pozdnee stalo
yasno, chto bolee rannemu resheniyu problemy v nemaloi stepeni pomeshal tot razryv
v nauchnyh kontaktah, kotoryi vse eshe sushestvuet mezhdu sovremennymi
teoretikami i nablyudatelyami. Sygrala sushestvennuyu negativnuyu rol' i differencirovannost'
nauki, iz-za kotoroi specialisty, dazhe rabotayushie v blizkih oblastyah, poroi
malo znayut o problemah svoih sosedei.
Sledstviem
koncepcii pervonachal'no goryachei Vselennoi yavilsya vyvod, chto v nasledstvo ot
etoi epohi, esli tol'ko ona deistvitel'no imela mesto, dolzhno povsemestno
sohranit'sya vo Vselennoi ostatochnoe, ili, kak ego nazyvayut, reliktovoe,
izluchenie v radiodiapazone.
Kanadskii
astrofizik E. Mak-Kellar v 1941 godu stolknulsya s neobychnym yavleniem
vozbuzhdennym sostoyaniem
molekul mezhzvezdnogo ciana. Temperatura vozbuzhdeniya
sostavlyala
2,3 K. Podobnyi fakt mog stat' osnovaniem dlya
vyvoda o nalichii v mirovom
prostranstve sootvetstvuyushego izlucheniya-vozbuditelya.
Odnako, pohozhe, avtory
teorii Bol'shogo Vzryva nichego ne znali ob etom otkrytii. Lish' mnogo pozdnee
to, chto takoe sostoyanie molekul ciana vyzvano imenno reliktovym izlucheniem,
dokazali sovetskii astrofizik I.S. Shklovskii i nezavisimo ryad drugih avtorov.
Raschety
A.G. Doroshkevicha i I.D. Novikova v 1964 godu pokazali, chto reliktovoe
izluchenie v principe registriruemo, i, sledovatel'no, vyvod teorii Bol'shogo Vzryva
vozmozhno proverit' s pomosh'yu nablyudenii. Gorazdo pozdnee zadnim chislom
vyyasnilos', chto ko vremeni ukazannogo rascheta reliktovoe izluchenie uzhe bylo
otkryto v SSSR i v Yaponii. V SSSR eto otkrytie bylo opublikovano aspirantom
Pulkovskoi observatorii T.A. Shmaonovym v 1957 godu.
No
beda zaklyuchalas' v tom, pishet Gurnshtein, chto nablyudateli i teoretiki
rabotali v otryve drug ot druga. Mezhdu nimi ne bylo obmena informaciei.
Nablyudatel' ne znal, kak pravil'no istolkovat' svoi strannye rezul'taty.
Zamechatel'naya zhe stat'ya teoretikov ostalas' nezamechennoi.
K
seredine shestidesyatyh godov radioastronomy-eksperimentatory voznamerilis'
postroit' special'nuyu apparaturu dlya obnaruzheniya reliktovogo izlucheniya No ih
operedili inzhenery, vypolnyavshie issledovaniya po bor'be s radioshumami pri
svyazi s iskusstvennymi sputnikami Zemli.
V 1965
godu radioinzhenery A. Penzias i R. Vil'son (SShA) pri ispytanii rupornoi
antenny dlya nablyudeniya amerikanskogo sputnika Eho sluchaino otkryli
sushestvovanie mikrovolnovogo (na volne 7,35 santimetra) kosmicheskogo
radioshuma, ne zavisyashego ot napravleniya antenny.
Na
protyazhenii 19661967 godov eto otkrytie otkrytie reliktovogo radioizlucheniya
Vselennoi bylo nezavisimo drug ot druga podtverzhdeno ryadom issledovatelei v
raznyh stranah. Osobennosti etogo yavleniya, sootvetstvuyushego obshemu teplovomu
izlucheniyu Vselennoi s temperaturoi okolo 2,7 K, sovpali s predskazaniyami
teorii Bol'shogo Vzryva.
Avtory
knigi Istoriya astronomii otmechayut: Otkrytie reliktovogo izlucheniya stalo
velichaishim dostizheniem v astronomii XX veka i v znachitel'noi stepeni yavilos'
rezul'tatom razvitiya radioastronomicheskoi tehniki i togo, chto sama nauchnaya
atmosfera sozrela dlya ego vospriyatiya. Eto otkrytie sdelalo dostovernym faktom
po men'shei mere to, chto Vselennaya (Metagalaktika) deistvitel'no
evolyucioniruet. Nakonec, otkrytie reliktovogo izlucheniya stalo moshnym stimulom
dlya dal'neishei razrabotki idei Bol'shogo Vzryva.
Novym
etapom razvitiya predstavlenii o rannih stadiyah evolyucii Vselennoi stala
teoriya goryachei Vselennoi, osobenno v rabotah akademika Ya.B. Zel'dovicha
(19141987) i ego shkoly. Predstavlenie o haraktere nachal'nogo rasshireniya
Vselennoi v nashi dni sil'no izmenilos'. Pomimo glavnoi trudnosti v opisanii
takogo nachala (nedostupnosti ego dlya sovremennoi teoreticheskoi fiziki),
obnaruzhilis' drugie ser'eznye trudnosti pri popytke opisat' i posleduyushuyu,
uzhe v principe dostupnuyu sovremennoi fizike, no eshe ochen' rannyuyu istoriyu
rasshireniya Vselennoi kak celogo.
S cel'yu
preodoleniya etih trudnostei v 80-e gody byla predlozhena koncepciya
razduvayusheisya (ili inflyacionnoi) Vselennoi (A. Gut, SShA; A D. Linde, SSSR).
Obsuzhdaetsya ideya mnozhestvennosti i neodnokratnogo vozniknoveniya v raznye
momenty vremeni samih razduvayushihsya vselennyh. Takim obrazom, drevneishaya ideya
vozrozhdeniya Vselennoi, ideya beskonechnoi cepi rozhdenii i gibeli mirov vseh
masshtabov, kak i koncepciya ostrovnyh vselennyh, rodivshayasya uzhe v rezul'tate
soedineniya gravitacionnoi teorii i nablyudenii, v nashi dni vozrozhdayutsya, no
uzhe na nesravnenno bolee vysokom urovne kak v otnoshenii masshtabov, tak i
kachestvennogo mnogoobraziya ob'ektov. Eti idei mogut rassmatrivat'sya kak
predvestnik, a mozhet byt' i nachalo uzhe tret'ei revolyucii v kosmologicheskoi
kartine mira.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.06.2013 8:56, 1.2 KBait)
\\\
Kanadskii
astrofizik E. Mak-Kellar v 1941 godu stolknulsya s neobychnym yavleniem
vozbuzhdennym sostoyaniem
molekul mezhzvezdnogo ciana. Temperatura vozbuzhdeniya
sostavlyala
2,3 K. Podobnyi fakt mog stat' osnovaniem dlya
vyvoda o nalichii v mirovom
prostranstve sootvetstvuyushego izlucheniya-vozbuditelya.
Odnako, pohozhe, avtory
teorii Bol'shogo Vzryva nichego ne znali ob etom otkrytii. Lish' mnogo pozdnee
to, chto takoe sostoyanie molekul ciana vyzvano imenno reliktovym izlucheniem,
dokazali sovetskii astrofizik I.S. Shklovskii i nezavisimo ryad drugih avtorov. \\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
19.06.2013 10:07, 20.9 KBait)
Segodnya den' neponyatnyi, na solnce vidno
vybros gluposti.
Hochu zametit' chto kak ne stranno samyi tehnicheski
gramotnyi kosmolog blesnul otsutstviem znanii
v principe ya dumal chto o tom chto Effekt Doplera
byl priduman isklyuchitel'no dlya sred nu radioastronom
znat' obyazan. I uzh dolzhen znat' chto effekt Doplera
byl priduman sobstvenno dlya efira a ne dlya pustoty,
i priduman byl namnogo ran'she relyativizma.
Esli kosmolog ne razlichaet sredu i pustotu v prostranstve,
eto nehorosho.
-----------------------------------------------------------------





-

- Soobshenii: 896
- Reiting: +6/-0
- tiho,tiho polzi ulitka po sklonu Fudzi..
-
Otvet #60 : Vchera v 13:14:07
V
LL2 klyuchevaya fraza "No pri "malyh" rasstoyaniyah mozhno prenebrech'
izmeneniem a vdol' puti integrirovaniya..." i obe Vashi frazy otnositsya
imenno k priblizheniyu malyh rasstoyanii. V takom priblizhenii nikakih
pretenzii k LL2 byt' ne mozhet.
Nu eto ne moi frazy. To est' pri malyh rasstoyaniyah mozhno vpolne traktovat' kosmologicheskoe krasnoe smeshenie, kak effekt Doplera?
I chto takoe malye?

Zapisan





-

- Soobshenii: 1 711
- Reiting: +14/-2
- I'm a llama!
-
Otvet #62 : Vchera v 13:56:11
V
LL2 klyuchevaya fraza "No pri "malyh" rasstoyaniyah mozhno prenebrech'
izmeneniem a vdol' puti integrirovaniya..." i obe Vashi frazy otnositsya
imenno k priblizheniyu malyh rasstoyanii. V takom priblizhenii nikakih
pretenzii k LL2 byt' ne mozhet.
Nu eto ne moi frazy.
No Vy zhe ih vydernuli iz obshego konteksta
To est' pri malyh rasstoyaniyah mozhno vpolne traktovat' kosmologicheskoe krasnoe smeshenie, kak effekt Doplera?
Esli ochen' hochetsya, to mozhno. S gramotno sostavlennym ob'yasneniyami.
I chto takoe malye?
Tipa z<0.01

Zapisan





-

- Soobshenii: 896
- Reiting: +6/-0
- tiho,tiho polzi ulitka po sklonu Fudzi..
-
Otvet #63 : Segodnya v 07:46:25
Citata:
ulitkanasklone ot Vchera v 13:14:07Citata: olegtitov ot Vchera v
12:21:23V LL2 klyuchevaya fraza "No pri "malyh" rasstoyaniyah mozhno
prenebrech' izmeneniem a vdol' puti integrirovaniya..." i obe Vashi frazy
otnositsya imenno k priblizheniyu malyh rasstoyanii. V takom priblizhenii
nikakih pretenzii k LL2 byt' ne mozhet.
Nu eto ne moi frazy.
No Vy zhe ih vydernuli iz obshego konteksta
Interesno, a v kakom kontekste vy
nashli frazu o malyh rasstoyaniyah? Ya chto-to ne mogu naiti v dannom paragrafe.
Aga,
vot nashel, tak eta fraza o malyh rasstoyaniyah idet posle uzhe togo, kak
Landau napisal pro effekt Doplera. I voobshe ona pro drugoe. I kak Vy
stat'i redaktiruete s takoi interpretaciei?
Effekt Doplera , kak i slovo "razbeganie" galaktik , hotya vzyatoe v kovychkah - metodicheskaya oshibka LL-2 , sbivayushee
s tolku.
Poslednee redaktirovanie: Segodnya v 07:55:33 ot ulitkanasklone

Zapisan





-

- Soobshenii: 1 711
- Reiting: +14/-2
- I'm a llama!
-
Otvet #64 : Segodnya v 08:08:33
Citata:
ulitkanasklone ot Vchera v 13:14:07Citata: olegtitov ot Vchera v
12:21:23V LL2 klyuchevaya fraza "No pri "malyh" rasstoyaniyah mozhno
prenebrech' izmeneniem a vdol' puti integrirovaniya..." i obe Vashi frazy
otnositsya imenno k priblizheniyu malyh rasstoyanii. V takom priblizhenii
nikakih pretenzii k LL2 byt' ne mozhet.
Nu eto ne moi frazy.
No Vy zhe ih vydernuli iz obshego konteksta
Interesno, a v kakom kontekste vy
nashli frazu o malyh rasstoyaniyah? Ya chto-to ne mogu naiti v dannom paragrafe.
Aga,
vot nashel, tak eta fraza o malyh rasstoyaniyah idet posle uzhe togo, kak
Landau napisal pro effekt Doplera. I voobshe ona pro drugoe. I kak Vy
stat'i redaktiruete s takoi interpretaciei?
Pro to samoe. Chitaite vnimatel'nei. I ne uchite dedushku kashlyat'.
Effekt Doplera , kak i slovo "razbeganie" galaktik , hotya vzyatoe
v kovychkah - metodicheskaya oshibka LL-2 , sbivayushee s tolku.
Nikakoi metodicheskoi oshibki tut net. Est' tol'ko nedostatochnaya podgotovlennost' nekotoryh chitatelei.

Zapisan





-

- Soobshenii: 1 711
- Reiting: +14/-2
- I'm a llama!
-
Otvet #66 : Segodnya v 08:35:30
Nikakoi metodicheskoi oshibki tut net. Est' tol'ko nedostatochnaya podgotovlennost'
nekotoryh chitatelei.
Zhivite so svoimi zabluzhdeniyami i dal'she..Zhelayu udachi.
Bol'shoe spasibo. I Vam ne hvorat'!
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
20.06.2013 23:53, 789 Bait)
Ya tak ponimayu chto prochitav to chto ya zdes'
pishu mozhet slozhitsya mnenie o total'noi
gluposti v kosmologii v tekushii moment vremeni.
Sobstvenno ya pishu dlya molodezhi
kotorye uchatsya astranomii
i kosmologii ili eto ih hobbi, dazhe esli ya i chastichno prav
to eto ne povod unyvat' i tem bolee ne povod poteryat'
interes k kosmologii
ili astronomii.
Byvaet sobstvenno i takie situacii, no po bol'shomu
schetu net dazhe maleishih prichin i bespokoistva
o krizise ili zastoe v astronomii ili kosmologii,
vse normal'no, vozmozhno kakayato chast' v kosmologii i pomenyaetsya, -
zdes' nado ponimat' chto pomenyaetsya odna fantastika
neobosnovannaya na druguyu neobosnovannuyu
fantastiku,
i eto ne povod dlya grusti ili perezhivanii za kosmologiyu ili astronomiyu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. E. Krauchuk,
21.06.2013 23:21, 508 Bait)
1 Rykovu. Ne zastavlyaite ni N'yutona ni Shvardshil'da perevorachivat'sya , obratites' k Chandrasekaru!
, obratites' k Chandrasekaru!
2 Ponyatie "chernaya dyra" otnositsya k massam bol'shim massy Solnca. I Zemlya ne mozhet byt' nositelem Chernoi dyry, inache Solnce
vrashalos' by vokrug Zemli i ni odin sputnik NE VZLETEL BY!
3 Vy fiziku kak uchili? ili prohodili? (mimo)
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. E. Krauchuk,
21.06.2013 23:39, 552 Bait)
A P. Vasi! Spasibo za podvizhensvo!Chestno!
Tol'ko ne putaite lyudei slovom pustota, plz. V fizike kosmosa net takogo ponyatiya, est' ponyatie vakuuma , no eto ne pustota,
v pustote nevozmozhno rasprostranenie kakih libo voln, nuzhna "zheskost' podvesa" (plotnost'!) dlya istochnika kolebanii i/ili inerciya (massa) dlya perenoschika kolebanii.
A v vakuume el.magnitnye volny rasprostranyayutsya! Znachit vakuum ne pustota. i ob etom govoryat formuly i praktika - sputniki na raschetnyh (avarii ne v schet) orbitah, svyaz' s
Voyadzherom deistvuet!
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.06.2013 0:55, 2.3 KBait)
|
|
Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
6.04.201113:49 |
|
Dlya sushestvovaniya effekta Doplera, est' prichina - sreda i ee svoistva.
Dazhe esli ispol'zuetsya metod izmereniya dlya sred, a govoritsya chto
vokrug pustota, to propadaet
prichinnost' vozniknoveniya dannogo
effekta kak svoistva prostranstva.
U relyativistov ne prostranstvo vystupaet v kachestve linii zaderzhki
signala, a vystupaet
- foton, kak dvizhushiisya ob'ekt, u kotorogo
ogranichena skorost' dvizheniya v pustote, po ne ponyatnoi prichine -
kotoraya postuliruetsya bez ob'yasneniya prichiny. Foton
v dannom sluchai
mozhet byt' tol'ko chasticei, - eto ne vozmozhno po prichine togo chto
chastica ne mozhet snizhat' i uvelichivat' svoyu skorost' chto
nablyudaetsya naprimer
pri dvizhenii sveta naprimer v vozduhe, potom
cherez steklo potom opyat' v vozduhe i potom v vakuum, tak kak
poluchaetsya chto v stekle letit foton medlennee chem v vozduhe
i
vakuume , a vyletaya iz stekla foton uvelichivaet svoyu skorost'. Tak
vot ne mozhet chastica kotoraya poteryala skorost', prosto tak vzyat' i
pri vylete iz stekla
uvelichit' skorost', - na podobnoe sposobny
tol'ko kolebaniya sredy v sredah s raznymi svoistvami. Tak chto foton
kak chastica - vydumka chistoi vody.
Vyvod -
v prostranstve rasprostranyayutsya kolebaniya sredy, i svetovoe
izluchenie ne dvizhetsya a obrazuetsya ot vzaimodeistviya kolebanii
sredy i materiala, kak v 1800 godu govoril
Tomas Yung.
Tak chto vse chto napisano v astrofizike bez ucheta sredy - k
sozhaleniyu ne pravil'no.
Eto podarok Dmitriyu Vibe, eto ne budet opublikovano dva
tri goda.
Dmitrii Vibe mozhet i dal'she uchit' studentov tomu chto bezvozvratno
ustarelo, i tomu chto im nikogda ne prigoditsya.
Tak uzh Dmitrii Vibe zapreshal obsuzhdat'
efir poka ego ne dokazhut chto on est' | |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.06.2013 0:57, 4.9 KBait)
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
19.02.201119:54 |
|
Sovmeshenie raznyh opytov.
http://www.trinitas.ru/rus/doc/0016/001b/00161336.htm
"Izvestno, chto vo vrashayushemsya zerkal'nom interferometre mezhdu
svetovymi volnami voznikaet sdvig faz, proporcional'nyi uglovoi skorosti
vrasheniya interferometra. Etot effekt byl obnaruzhen Harrisom (F. Harres)
v 1912 g. [1], a zatem San'yakom
(G. Sagnac) v 1913 g. [2] i byl nazvan yavleniem San'yaka. Neodnokratno
predprinimalis' popytki ob'yasneniya fizicheskoi prichiny vihrevogo effekta
San'yaka. V chastnosti, byli
razrabotany neskol'ko teorii etogo yavleniya: kinematicheskaya, doplerovskaya
i relyativistskaya. Pervaya iz etih teorii predpolagaet nalichie nekoi
vseob'emlyushei sredy (efira), kotoryi
vzaimodeistvuet s elektromagnitnoi volnoi (izmenyaet skorost'
rasprostraneniya sveta) i v to zhe vremya vzaimodeistvuet s veshestvom
(chastichno im uvlekaetsya pri dvizhenii veshestva).
Nikakimi drugimi opytami teoriya efira ne podtverzhdaetsya."
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/55/Fizo_experiment_scheme_ru.PNG
Opyt Fizo
http://elementy.ru/trefil/21167
"Maikel'son
i Morli ispol'zovali interferometr opticheskii izmeritel'nyi pribor, v
kotorom luch sveta rassheplyaetsya nadvoe
poluprozrachnym zerkalom (steklyannaya plastina poserebrena s odnoi storony
rovno nastol'ko, chtoby chastichno propuskat' postupayushie na nee svetovye
luchi, a chastichno otrazhat' ih;
analogichnaya tehnologiya segodnya ispol'zuetsya v zerkal'nyh
fotoapparatah)."
Opyt Maikel'sonaMorli byl principial'no napravlen na
to, chtoby podtverdit' (ili oprovergnut')
sushestvovanie mirovogo efira posredstvom vyyavleniya efirnogo vetra (ili
fakta ego otsutstviya). Deistvitel'no, dvigayas' po orbite vokrug Solnca,
Zemlya sovershaet dvizhenie otnositel'no
gipoteticheskogo efira polgoda v odnom napravlenii, a sleduyushie polgoda v
drugom. Sledovatel'no, polgoda efirnyi veter dolzhen obduvat' Zemlyu i,
kak sledstvie, smeshat' pokazaniya
interferometra v odnu storonu, polgoda v druguyu."
Tómas Yung -Vikipediya
"Ego
idei vyzvali vozrazheniya angliiskih uchenyh; pod ih vliyaniem
Yung otkazalsya ot svoego mneniya. Odnako v traktate po optike i akustike
Opyty i problemy po zvuku i svetu (1800) uchenyi vnov' prishel k volnovoi
teorii sveta i vpervye rassmotrel
problemu superpozicii voln. Dal'neishim razvitiem etoi problemy yavilos'
otkrytie Yungom principa interferencii (sam termin byl vveden Yungom v
1802 godu).
V doklade
Teoriya sveta i cvetov, prochitannom Yungom Korolevskomu obshestvu v 1801
(opublikovan 1802), on dal ob'yasnenie kolec N'yutona na osnove
interferencii i opisal pervye opyty po
opredeleniyu dlin voln sveta. V 1803 godu v rabote Opyty i ischisleniya,
otnosyashiesya k fizicheskoi optike (opublikovana 1804) on rassmotrel
yavleniya difrakcii. Posle klassicheskih
issledovanii O. Frenelya po interferencii polyarizovannogo sveta Yung
vyskazal gipotezu o poperechnosti svetovyh kolebanii. On razrabotal takzhe
teoriyu cvetnogo zreniya, osnovannuyu
na predpolozhenii o sushestvovanii v setchatoi obolochke glaza treh rodov
chuvstvitel'nyh volokon, reagiruyushih na tri osnovnyh cveta."
"V
1807 godu v dvuhtomnom
trude Kurs lekcii po natural'noi filosofii i mehanicheskomu iskusstvu Yung
obobshil rezul'taty svoih teoreticheskih i eksperimental'nyh rabot po
fizicheskoi optike (termin vvel
Yung) i izlozhil svoi issledovaniya po deformacii sdviga, vvel chislovuyu
harakteristiku uprugosti pri rastyazhenii i szhatii tak nazyvaemyi modul'
Yunga. On vpervye rassmotrel mehanicheskuyu
rabotu kak velichinu, proporcional'nuyu energii (termin vvel Yung), pod
kotoroi ponimal velichinu, proporcional'nuyu masse i kvadratu skorosti
tela."
Chto sobstvenno
mozhno skazat' o vseh etih opytah esli efir dvizhetsya sverhu vniz sozdavaya pri etom gravitaciyu.
Po faktu vse opyty ne mogut obnaruzhit' dvizhenie efira sverhu vniz.
Zdes' ne hvataet odnogo opyta - v gorizontal'nom raspolozhenii interferometra, -
---Vliyanie staticheskogo zaryada na skorost' rasprostraneniya elektromagnitnyh
kolebanii v efire.---
Ideya opyta prostaya, ispol'zuetsya obychnyi
interferometr, raspolagaetsya v vakuumnoi kamere, po hodu lucha
ustanavlivayutsya dve melkie setki, 30mm
na 30mm, tak chtoby luch prohodil skvoz' yacheiku setki na rasstoyanii 30mm.
Znaya chto est' eshe elektrostaticheskii effekt, to podavaya razlichnye potencialy na setki, budut menyat'sya
interferencionnye polosy.
Esli izmenenie napryazheniya mezhdu setkami
v vakuumnoi kamere budet okazyvat' vliyanie na izmenenie polos, -
sledovatel'no mezhdu razno zaryazhennymi
setkami sozdaetsya dvizhenie efira. |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.06.2013 1:06, 9.9 KBait)
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
11.07.201120:59 |
|
Prostoe fundamental'noe otkrytie.
V sredine vos'midesyatyh ya kogda pol'zovalsya
oscillografom, po neobhodimosti postavil ego
vertikal'no, i luch smestilsya,
ya podstroil luch,
potom postavil ego gorizontal'no, i luch opyat'
smestilsya, ya opyat' podstroil, sut' ne ponyal no
effekt zapomnil.
Segodnya s utra smotrel
televizor, po televizoru
bylo chto-to ne interesnoe i ya vspomnil pro tot
sluchai, tak kak televizor Tomson 14mg120b,
to ego mozhno vrashat' kak ugodno.
Tak
vot vynul ya skart, ekran stal sinii, postavil kineskopom
v verh, v verhnih uglah krasnovatyi muar, kogda
povernul kineskopom vniz, v nizhnih uglah
krasnovatyi
muar, kogda perevernul
vverh nogami ves' ekran stal krasnyi, no ne chisto krasnyi,
po bokam krasnyi, po centru nemnogo sinevy, esli povernut'
na levyi bok,
krasneet pravyi verhnii ugol, i i levyi nizhnii
a esli povernut' na pravyi bok, krasneet levyi verhnii i
pravyi nizhnii ugol, vsya drugaya chast' ekrana sinie.
Esli
postavit' normal'no - to ekran chisto sinii.
Vot sobstvenno i poluchilos' prostoe fundamental'noe otkrytie.
Ishodya iz togo chto atomarnoe oblako, sostoyashee prakticheski
iz odinochnyh atomov razgonyaetsya uskoryayushim i fokusiruyushim
i vysokim i svoditsya v tochku matricy.
Perevorachivaya televizor vverh nogami, sinii luch stal krasnym
potomu chto potok chastic efira v shtatnom polozhenii zaryazhennye
atomy prizhimal vniz, a kogda televizor vverh nogami,
eto analogichno tomu chto chasticy efira dvizhutsya
snizu vverh
po otnosheniyu k potoku zaryazhennyh odinochnyh atomov.
Vzyal ya akkuratno po-podbrasyval televizor, chtoby poluchilsya
nebol'shoi effekt svobodnogo padeniya.
Pri podbrasyvanii cveta ne izmenyalis', v normal'nom polozhenii
ostavalsya sinii ekran, vverh nogami krasnym.
Iz chego ya ponyal chto tak i dolzhno byt', esli schitat'
chto efir
dvizhetsya so skorost'yu 10 km v sekundu,
sledovatel'no kogda skorosti padeniya lifta ne vysokie,
do 2- 5 km v sekundu
to naprimer
v znamenitoi
zadache kak uznat' v zakrytoi kabine padayushego
lifta - nahoditsya li ob'ekt na orbite ili dvizhetsya k gravitiruyushemu
telu, to vopros reshaetsya esli vzyat' etot televizor
vklyuchit' ot
akkumulyatora i nablyudat' za ego ekranom, i po izmeneniyu
cveta esli vrashat' televizor to mozhno
opredelit' gde verh a gde niz pri polnoi nevesomosti
v lifte,
vot tak vse prosto odnako.
V svyazi s vysokim napryazheniem v televizore, i opasnost'yu porazheniya
elektricheskim tokom, dannyi opyt provodit' kategoricheski
ne rekomenduyu,
po skol'ko pri nizkom kachestve televizora vozmozhna ego polomka, v svyazi
s neshtatnym raspolozheniem televizora, vozmozhen peregrev detalei,
i
obryv provodov vnutri televizora, chto mozhet povlech' za soboi porazhenie
elektricheskim tokom.
------------------
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
7.04.201212:19 |
|
Zakrytie fotonov.
Fotony ne imeyut fizicheskogo smysla po sleduyushim prichinam.
1. Pri opyte s interferenciei poluchaetsya chtoby realizovat'
situaciyu
pri kotoroi nalozhenie izobrazheniya solnca
kotoroe popadaet na ekran cherez odnu shel' na drugoe
izobrazhenie solnca kotoroe popadaet na ekran cherez druguyu
shel'
ne proishodit uvelicheniya yarkosti izobrazheniya solnca
a poyavlyayutsya temnye i svetlye polosy.
S tochki zreniya efira kak sredy, ob'yasnyaetsya prosto kak
izmenenie
plotnosti kolebanii sredy.
A chto poluchaetsya kogda dlya opisaniya etogo
opyta ispol'zovat' fotony kak chasticy,
- poluchaetsya chto foton kotoryi chastica, - dolzhen
obladat'
zaryadom "+" ili zaryadom "-", togda esli by byl takoi sluchai
luch mozhno bylo by razdelit' magnitom - chego ne nablyudaetsya.
Sledovatel'no
fotony kak chasticy s raznym potencialom ne sushestvuyut.
2. Foton kak chastica tozhe ne imeet fizicheskogo smysla po prichine
proverki na prostom opyte, - voz'mem
v vakuume provedem opyt
v kotorom svet prohodit skvoz' steklo.
Chto poluchaetsya svet do stekla imeet skorost' ravnuyu skorosti
sveta, posle etogo popav v steklo
teryaet skorost' v poltora raza
posle etogo vyletaya iz stekla uvelichivaet svoyu skorost'.
Tak vot dannye svoistva ne yavlyayutsya vozmozhnymi dlya letyashih
chastic,
po prichine togo chto esli chastica zamedlilas' to razognat'sya
ona uzhe bez vneshnego vozdeistviya s prilozheniem zatrat energii
- ne mozhet. A podobnye svoistva yavlyayutsya
svoistvom sredy -
naprimer zvuk kolebletsya v vozduhe peredaet kolebaniya vode
- uvelichivaet skorost', posle togo kak zvuk iz vody popadaet v
vozduh skorost'
zvuka umen'shaetsya.
Vyvod - dva sluchaya v pervom sluchai fotonami kak chasticami nevozmozhno
opisat' interferenciyu kotoraya imeet mesto byt',
vo vtorom sluchai
fotony ne mogut byt' chasticami,
- itogo fotony kak chasticy letyashie i yavlyayushiesya nositelyami sveta
ne imeyut fizicheskogo smysla.
|
---------------------------------
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
1.05.201213:13 |
|
Zakrytie bol'shogo vzryva.
Zakrytie modelei zvezd na gorenii vodoroda.
---Neskladushki bol'shogo vzryva.
Pervoe chto brosaetsya v glaza v etoi
teorii
- chto s dostatochno bol'shoi tochnost'yu v
sekundy i minuty znayut posledovatel'nost' proishodyashego
no naproch' otsutstvuet prichinno sledstvennaya svyaz'
- vse postroeno na postulatah kotorye nel'zya podtverdit'.
Chto iznachal'no sostoit iz paradoksov i protivorechii.
1 Razlet so sverhsvetovoi skorost'yu
na 13.5 mlrd svetovyh let
vo vse storony prakticheski mgnovenno, i my nablyudaem v teleskop
zvezdy kotorye tuda zabrosilo pri bol'shom vzryve.
---
Chto sobstvenno
est' zhestkoe i paradoksal'noe v etom, -
skorost' sveta byla prevyshena minimum v milliard raz.
Chto ne ponyatno drugoe, ne ponyatno chto esli pri razlete materii
pochemu ee zabrosilo na 14 mlrd svetovyh let, a ne na dva ili tysyachu,
- pochemu razbros sovpadaet s vozmozhnostyami teleskopov.
2 Himicheskii sostav
vodoroda i geliya i ego sootnoshenie - 70%vodoroda
i 30% geliya - i s kakoi tochnost'yu i bez primesei drugih veshestv.
---
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://vsln.ru/himicheskiy-sostav-solntsa.html
(V 1929 g. amerikanskii astronom Genri Norris Ressel (18771957)
tshatel'no izuchil solnechnye spektry, i emu
udalos' ustanovit', chto
Solnce porazitel'no bogato vodorodom. On reshil, chto na vodorod
prihoditsya tri pyatyh vsego ob'ema Solnca. Eto bylo absolyutnoi
neozhidannost'yu,
tak kak vodorod, hotya i ne yavlyaetsya redkim elementom
v tochnom smysle etogo slova, sostavlyaet vsego lish' 0,14% zemnoi kory.
Odnako posleduyushie issledovaniya pokazali,
chto Ressel byl slishkom
ostorozhen v svoei ocenke. Nedavnie podschety amerikanskogo astronoma
Donal'da Govarda Menzela (rod. v 1901 g.) pokazyvayut, chto vodorod
sostavlyaet
81,76% ob'ema Solnca, a gelii 18,17%, tak chto na dolyu
vseh ostal'nyh elementov ostaetsya tol'ko 0,07%.
Po-vidimomu, mozhno s uverennost'yu skazat', chto
Solnce prakticheski
predstavlyaet soboi svetyashuyusya smes' vodoroda i geliya v proporcii
(po ob'emu) 4:1. (Element gelii tozhe byl otkryt s pomosh'yu spektral'nogo
analiza,
prichem snachala ne na Zemle, a na Solnce Angliiskii astronom
Dzhozef Norman Lok'er (1836 1920) predpolozhil, chto nekotorye
neopoznannye linii solnechnogo
spektra prinadlezhat eshe ne otkrytomu
elementu, kotoryi on v chest' grecheskogo boga Solnca Geliosa nazval geliem.
Na Zemle zhe gelii byl obnaruzhen shotlandskim himikom
Uil'yamom Ramzeem
(18521916) tol'ko v 1895 g.).)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sobstvenno osnovnaya oshibka v dannoi situacii v tom chto
po sostavu himicheskomu atmosfery solnca sdelano skrytoe
utverzhdenie - a eto postulat, chto himicheskii
sostav samogo
solnca tozhe takoi-zhe za isklyucheniem yadra.
Vot zdes' nado povnimatel'nee ibo zdes' samaya grubaya
oshibka vsei astronomii.
Dannaya
situaciya na samom dele ne vozmozhna, ibo vodorod
on ne tol'ko samyi legkii i u nego samaya nizkaya udel'naya
plotnost' no u nego i samaya bol'shaya pronikaemost', on
so vremenem
mozhet prosochitsya cherez metally i proiti skvoz' nih
naskvoz'.
Sledovatel'no pri takih fizicheskih svoistvah vodorod budet
vytesnen materialami
s bol'shei udel'noi plotnost'yu iz svoih
nedr lyuboi zvezdy ili planety na poverhnost'.
A iz etogo chto sleduet - a to, chto vodorod ne uchastvuet i nikogda
ne uchastvoval v yadernyh reakciyah v solnce potomu chto vnutri
solnca vodoroda net v principe, on ves' isklyuchitel'no v atmosfere
solnca.
A iz etogo
sleduet chto ne tol'ko bol'shoi vzryv no i vse evolyucii
zvezd i modeli zvezd kotorye byli postroeny na gorenii
vodoroda i geliya v zvezdah nepravil'ny i ne sootvetstvuyut
fizicheskim svoistvam veshestv.
A eto znachit chto procentov 99 knig po astronomii ne pravil'nye,
vot takaya zhestokaya selyavi. |
-----------------------------------------------
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.06.2013 21:59, 9.1 KBait)
- Novichok

-

- Soobshenii: 2
- Reiting: +1/-0
- Mne nravitsya etot forum!
-
Teoriya inflyacii kazhetsya
dovol'no mnogoobeshayushei: horoshii matematicheskii apparat, kosvennye
podtverzhdeniya nablyudeniyami, predskazatel'naya sila i t.d. No na moi
vzglyad klyuchevaya ee chast' vyzyvaet bol'she vsego pretenzii i neponyatok.
Kakim by gipoteticheskim ne byl lozhnyi vakuum, inflyacionnye teoretiki
smotryat na nego, kak na nechto real'no sushestvuyushee. I tut to nachinayutsya
neponyatnye veshi: esli u lozhnogo vakuuma takaya kolossal'naya energiya i
plotnost', pochemu vmesto etogo on rastyagivaetsya, a ne szhimaetsya,
kollapsiruya v itoge?
Chto eto za materiya (esli eto materiya), u
kotoroi gromadnoe gravitacionnoe ottalkivanie, pri kotorom ee energiya
(!) i plotnost' (!) ostayutsya neizmennymi (!). I otkuda on mog
poyavitsya?Mnogie tverdyat, chto iz niotkuda, iz nichego: mol poyavlyaetsya
nichtozhnaya kvantovaya fluktuaciya v nichto (!), kotoraya zatem tunneliruet
kuda to i nachinaet besheno rasti. Mne kazhetsya takaya ideya chistoi vody
spekulyaciya: esli fizik-teoretik chego to ne znaet, on mozhet skazat', chto
ne znaet etogo, a ne vydumyvat' neponyatno chto pohuzhe samyh materyh
fantastov.

Zapisan





-

- Soobshenii: 13 615
- Reiting: +161/-39
-
Otvet #1 : Segodnya v 20:20:20
.. Mne kazhetsya takaya ideya chistoi vody spekulyaciya: esli fizik-teoretik
chego to ne znaet, on mozhet skazat', chto ne znaet etogo, a ne vydumyvat'
neponyatno chto pohuzhe samyh materyh fantastov.
T.e.
poverhnosto poznakomivshis' s etoi teoriei, Vy uzhe smelo pristupaete k
obvineniyam uchenyh? A oni uzhe napisali tysyachi statei i est' uchebniki dlya
studentov s izlozheniem TI.
Luchshe izbirat' drugoi put' i uporno chitat' eti uchebniki, obzory i stat'i.

Zapisan
- Moderator





-

- Soobshenii: 13 210
- Reiting: +350/-46
- Evona kak...
-
Otvet #2 : Segodnya v 20:41:22
Mne kazhetsya takaya ideya chistoi vody spekulyaciya
Nu
i chto? Chto Vy predlagaete obsudit'? To, chto Vam kazhetsya?

Zapisan
-----------------------------------
\\\Chto eto za materiya (esli eto materiya), u
kotoroi gromadnoe gravitacionnoe ottalkivanie, pri kotorom ee energiya
(!) i plotnost' (!) ostayutsya neizmennymi (!). I otkuda on mog
poyavitsya?Mnogie tverdyat, chto iz niotkuda, iz nichego: mol poyavlyaetsya
nichtozhnaya kvantovaya fluktuaciya v nichto (!), kotoraya zatem tunneliruet
kuda to i nachinaet besheno rasti. Mne kazhetsya takaya ideya chistoi vody
spekulyaciya: esli fizik-teoretik chego to ne znaet, on mozhet skazat', chto
ne znaet etogo, a ne vydumyvat' neponyatno chto pohuzhe samyh materyh
fantastov.\\\
U adekvatnyh eto nazyvaetsya tak spim sdel chto azh sam poveril.
I korni etogo eshe rastut iz odnogo starogo anekdota, -
\\\- prihodit
kak-to k rukovoditelyu strany sekretar' ego,
i govorit emu chto ego strana ochen' sil'no otstaet ot konkurentov
po kolichestvu fizikov i nado vydelit' ochen' bol'shie
sredstva na
oborudovanie dlya laboratorii chtoby provodit' fiz opyty.
Na chto rukovoditel' strany sprosil - a est' li deshevyi vyhod
iz etoi situacii. Sekretar'
skazal chto vyhod to est' tol'ko
pol'zy ne budet nikogda, dlya etogo prosto nado uvelichit'
kolichestvo fizikov-teoretikov, ili fizikov - matematikov
- a im
chto nado.
A im nuzhna tol'ko bumaga karandash i stirayushaya rezinka.
Dazhe dostatochno tol'ko karandasha i bumagi,
stirayushaya rezinka ne nuzhna - i tak otzvezdyatsya.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.06.2013 23:25, 5.9 KBait)
- Moderator





-

- Soobshenii: 13 213
- Reiting: +350/-46
- Evona kak...
-
Otvet #12 : Segodnya v 21:51:28
Perefraziruyu: ishodya iz etogo, mozhno tverdit', chto kosmologiya nichego
ne znaet ob ustroistve vselennoi?
Tverdit'
nepreryvno, konechno, ne stoit; pravila foruma ne privetstvuyut
publikaciyu odnotipnyh soobshenii. Odin raz napisali, da i hvatit.

Zapisan
I kto-to, kak vsegda, nes mne chush' o "tarelkah", i kto-to, kak vsegda, propovedoval dzen... (s) Zoopark





-

- Soobshenii: 13 621
- Reiting: +161/-39
-
Otvet #13 : Segodnya v 22:08:34
Poslednee zvuchit stranno: Priroda ne podpisyvalas' vo vsem sootvetstvovat'
nashim ponyatiyam.
Znachit
to, chto my nazyvaem Zakonami prirody eto lish' nashi predstavleniya? I
zakonom sohraneniya energii mozhno prenebrech', kogda rech' idet o LV. I
iskrivlyayushim svoistvom massy, to est' samoi suti gravitacii. Togda zachem
nam voobshe nauka?
A eto Vy otkuda vzyali. Ni Linde, ni Vilenkin ob etom ne govorili.
A svoi lichnye umozaklyucheniya polozheno obosnovat' ili dat'
ssylki na Vashi istochniki ot profi.
-----------------------------------------------------
\\\chto kosmologiya nichego ne znaet ob ustroistve vselennoi?\\\
\\\A svoi lichnye umozaklyucheniya polozheno obosnovat' ili dat' ssylki na Vashi istochniki ot profi.\\\
Vot lichno s moei tochki zreniya - nauka kosmologiya est'
- a kosmologov to v kosmologii
i net .
Kosmologicheskii idiotizm i kosmologicheskie bredni poyavlyalis' ne
kak vydumka ot specialista, a kak podporki dlya
drugih teorii.
I sobstvenno kogda u etih podporok eshe pytayutsya naiti
kosmologicheskii smysl - to eto voobshe nonsens, tam ego
nikogda ne bylo.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.06.2013 14:46, 3.4 KBait, otvetov: 1)
Otvet #106 : Segodnya v 07:45:07
Interesna
sama principial'naya vozmozhnost' sushestvennogo uvelicheniya razmera i
massy Zemli, nachinaya ot padeniya meteoritov i zakanchivaya materializaciei
neitrino vo vnutrennem yadre i t.p. ...
Ne
buduchi ni biologom, ni geologom, ya vse-taki risknu predpolozhit', chto
uvelichenie massy Zemli v neskol'ko raz privelo by k bolee zametnym
posledstviyam, chem vymiranie dinozavrov.
-----------------------------------
Otvet #108 : Segodnya v 12:31:16
Nu tak ono(uvelichenie massy i razmera) vrode kak privelo i do sih por privodit(IMHO)
k dovol'no zametnym posledstviyam...
K kakim?
----------------------------
Otvet #110 : Segodnya v 13:28:34
Ved' esli diametr Zemli uvelichitsya vsego na 1mm za 100 let
A esli ne uvelichitsya?
----------------------------
Strannaya nauka astronomiya, tol'ko v nei professor
na forumah vyglyadit kak umstvenno nepolnocennyi.
Vopros to proshe prostogo, - tol'ko na takie voprosy - chtoby
ne vyglyadet' nedalekim, otvety nado znat' i ne nuzhno ih
pridumyvat'.
Grunt na poverhnosti
luny analogichen gruntu v glubine zemli
na glubine tri s polovinoi kilometra.
V svyazi s chem i konyam ponyatno chto zemlya tysyachekratno bolee
chem Luna prityagivaet
na sebya kosmicheskuyu pyl' i mikrometeority chto podnimaet
uroven' grunta poverhnosti.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(A. V. Malkin,
23.06.2013 22:37, 3.7 KBait)
| Citata: |
Otvet #106 : Segodnya v 07:45:07
Interesna
sama principial'naya vozmozhnost' sushestvennogo uvelicheniya razmera i
massy Zemli, nachinaya ot padeniya meteoritov i zakanchivaya materializaciei
neitrino vo vnutrennem yadre i t.p. ...
Ne
buduchi ni biologom, ni geologom, ya vse-taki risknu predpolozhit', chto
uvelichenie massy Zemli v neskol'ko raz privelo by k bolee zametnym
posledstviyam, chem vymiranie dinozavrov. -----------------------------------
Otvet #108 : Segodnya v 12:31:16
Nu tak
ono(uvelichenie massy i razmera) vrode kak privelo i do sih por privodit(IMHO)
k dovol'no zametnym posledstviyam...
K kakim?
----------------------------
Otvet #110 : Segodnya v 13:28:34
Ved'
esli diametr Zemli uvelichitsya vsego na 1mm za 100 let
A esli ne uvelichitsya?
---------------------------- Strannaya nauka astronomiya, tol'ko v nei professor na
forumah vyglyadit kak umstvenno nepolnocennyi. Vopros to proshe prostogo, - tol'ko na takie voprosy - chtoby ne vyglyadet' nedalekim, otvety nado
znat' i ne nuzhno ih pridumyvat'. Grunt na poverhnosti
luny analogichen gruntu v glubine zemli na glubine tri s polovinoi kilometra. V svyazi s chem i
konyam ponyatno chto zemlya tysyachekratno bolee chem Luna prityagivaet
na sebya kosmicheskuyu pyl' i mikrometeority chto podnimaet uroven' grunta poverhnosti.
|
Mozhet byt'... pravil'naya mysl'!
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.06.2013 0:37, 988 Bait)
Ne ne mozhet byt', - a nado znat' i koe chto pomnit'
nado vechno, chtoby
ne vyglyadet' nedalekim v kosmologii.
Lunnyi grunt sravnivali tak davno chto i trudno
vspomnit' kogda ego privezli sputniki,
a klouny ot astronomii i kosmologii eshe
dobruyu sotnyu let etogo ne budut znat' ili budut
zabyvat' postoyanno.
Ya pro etu erundu tretii raz zdes',
na raznyh forumah pishu kak minimum.
----------------
http://geo.1september.ru/view_article.php?id=200700613
\\\Burenie sverhglubokih skvazhin po slozhnosti
sravnivayut s poletami v kosmos. Obrazcy porod,
izvlechennyh iz samyh glubin nedr, predstavlyayut
ne men'shii interes, chem obrazcy lunnogo grunta.
Ne sluchaino lunnyi grunt, dostavlennyi na Zemlyu
sovetskim lunohodom, izuchali i v nauchnom centre
pri Kol'skoi skvazhine. Okazalos', chto lunnyi
grunt po sostavu pochti polnost'yu sootvetstvuet
porodam, izvlechennym iz Kol'skoi skvazhiny s
glubiny okolo 3 km.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.06.2013 0:48, 695 Bait)
Tak vot kak raz pro Lunu, - sobstvenno esli u Luny
est' poverhnost' i est' kosmicheskaya pyl', a
vnutri Zemli est' analogichnyi grunt, to logichno
mozhno
uverenno skazat' chto Luna stala na orbitu
Zemli izvne, i budet dva varianta lunnogo grunta
vnutri Zemli, pervyi variant - chto Luna prokatilas'
po poverhnosti
Zemli, i vtoroi bolee veroyatnyi
sluchai chto v Lunu proletavshuyu mimo Zemli, popalo
chto-to razmerom s pol Luny v svyazi s chem Luna stala
na ustoichivuyu orbitu,
a musor ot stolknoveniya osel
na Zemle i Lune, a tak kak Zemlya uvlekaet namnogo
bol'she mikrometeoritov to so vremenem lunnyi grunt
okazalsya na glubine bol'she
treh km.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.06.2013 14:50, 3.6 KBait)
Somnevayus' chto nauku budut delat' ne zvaniyami
a sposobnostyami.
Dlya etogo mne kazhetsya eshe pomimo togo dolzhna
byt' zainteresovannost' lichnaya.
A tak voobshe
interesno - no sil'no zhestoko s akademikami,
tak ih rezko ot kormushki otveli vosvoyasi, i kormushku
sozhgli. Horosho hot' zvanii ne lishili.
------------------------------------
| Novost'
o predstoyashei masshtabnoi reorganizacii rossiiskih nauchnyh akademii, o
kotoroi bylo ob'yavleno 27 iyunya na zasedanii pravitel'stva, vyzvala
vozmushenie v akademicheskih krugah. To, chto predlozhili vchera
Medvedev s Livanovym eto polnoe bezobrazie! zayavil Interfaksu
segodnya vice-prezident Rossiiskoi akademii nauk, nobelevskii laureat
Zhores Alferov. Po ego slovam, glavnaya cel' novovvedenii lishit'
akademiya vsego imushestva, no dlya nauchno-tehnicheskogo progressa
reorganizaciya nichego ne dast. Rossiiskoi nauke nuzhna tol'ko odna vesh'
vostrebovannost' biznesom i obshestvom. Predstoyashaya reforma etoi
vostrebovannosti ne sozdast, ona ub'et nauku. Eta kvazireforma
napravlena tol'ko na odno: otnyat' vse imushestvo u RAN. Ne eto nuzhno
delat'! prizval akademik, poobeshav napisat' obrashenie po dannomu
povodu. Mezhdu tem, rukovoditeli Sibirskogo otdeleniya RAN uzhe
obratilis' s otkrytym pis'mom k rukovodstvu strany, v kotorom rezko
kritikuyut plany reformirovaniya akademii. Reshenie pravitel'stva RF
o fakticheskoi likvidacii Gosudarstvennyh akademii nauk Rossii i iz'yatii
iz ih operativnogo upravleniya federal'nogo imushestva my rascenivaem kak
namerenie razgromit' slozhivshuyusya effektivnuyu sistemu organizacii
fundamental'noi nauki v Rossii, lishit' nashu stranu glavnogo preimushestva
v global'noi konkurencii za ekonomicheskoe razvitie na osnove vysshih
dostizhenii sovremennoi nauki, podorvat' nauchno-tehnicheskoe obespechenie
nacional'noi oborony i bezopasnosti strany, prodolzhit' razrushenie
obrazovaniya v Rossii, govoritsya v tekste pis'ma, podpisannogo
predsedatelem Sibirskogo otdeleniya RAN akademikom Aleksandrom Aseevym,
pyat'yu ego zamestitelyami, a takzhe predsedatelem Dal'nevostochnogo
otdeleniya RAN, predsedatelyami Krasnoyarskogo i Irkutskogo nauchnyh centrov
SO RAN. Nakanune prem'er-ministr Rossii Dmitrii Medvedev zayavil,
chto sistema Rossiiskoi akademii nauk dolzhna byt' reformirovana, i
soobshil, chto gotovitsya proekt sootvetstvuyushego zakona. On budet vnesen v
Dumu na sleduyushei nedele. V chastnosti, predpolagaetsya ob'edinit'
struktury Rossiiskoi akademii nauk, Rossiiskoi akademii medicinskih nauk
i Rossiiskoi akademii sel'skohozyaistvennyh nauk, a takzhe sozdat'
Agentstvo nauchnyh institutov RAN dlya upravleniya imushestvom nauchnyh
institutov i gosudarstvennyh akademii. Novost' na saite Vesti.Ru |
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.07.2013 9:00, 4.9 KBait)
U al'ternativshikov i storonnikov efira svoe mnenie.
Chinovniki vryad-li budut finansirovat' organizacii
kotorye boryutsya s lzhenaukoi i nesoglasnymi s
gospodstvuyushei paradigmoi,
oni posle reformy provedut
pereatestaciyu na detektorah lzhi i ya dumayu procentov tridcat'
poidut vosvoyasi.
----------------------
|
 Re: Aether theory with experimental verification
Re: Aether theory with experimental verification
Otvet #218 - Vchera :: 13:15:22
Smotrjashii pisal(a) Vchera :: 04:05:33:S Vami VAA razgovarivaet lish' potomu(na moi vzglyad), chto Vy emu neperechite.... I, izvinite,- zaglyadyvete v rot!
S temi zhe, kto zadaet VAAneudobnye
voprosy po efiru, ongovorit' ne zhelaet.
Priglasite
ego syuda, pust' otvetit SAM na paru voprosov. Posmotrim, snizoidet
seivelikiiGuru doobsheniya sryadovymi "efiristami", aliostanetsyanedosyagaemo
vysokim!
Chto kasatel'no ""obnaruzhennogo efirnogo vetra""(KEM
UGODNO!), to Vam uzhe tyshu raz skazano:NETi ne mozhet byt' NI
ODNOGOopytapodtverzhdayushego obnaruzhenieEV.
Vseeto raschitano(razgovoryi raschety) naVasi lyudeine sposobnyhvidet'ochevidnuyu lozh!
Razgovorami oobnaruzhenii efirnogo vetra,
VY lichno, -zanimaetes' profanaciei samoiideirazrabotki teorii efira. Smotryashii.
Nikomu Surin v rot ne zaglyadyvaet. Sotrudnichestvo, sovmestnaya
rabota prisutstvuyut (i ne tol'ko v oblasti efirodinamiki). Razvitie idei
efirodinamiki prisutstvuet. Prichem ne ot vseh usilii Surina VAA v
vostorge..... Bud'te uvereny. Sovsem neponyatno, pochemu imenno
Surin dolzhen priglashat' syuda VAA. Priglasite sami, zadaite neudobnye
voprosy.... Ya svoi neudobnye voprosy emu zadal. I vovse ne na vse
poluchil ischerpyvayushie okonchatel'nye otvety. Hotya by potomu, chto voprosov
mnogo i dlya otveta na nekotorye nado provesti nemaluyu rabotu.. Adres
VAA izvesten... Ya hot' tysyachu, hot' million raz mogu
utverzhdat', chto efirnyi veter davno obnaruzhen, davno izmeren vpolne
eksperimental'no. Edinstvenno, chto vyzyvaet sozhalenie eto to, chto ne
nalazhena set' regulyarnogo izmereniya efirnogo vetra hotya by v ob'eme
pyati-semi nablyudatel'nyh punktov. Miller, Dem'yanov, Galaev, De Munera,
Gift.... Vot nekotorye issledovateli, kotorye proveli svoi eksperimenty i
pokazali nalichie efirnogo vetra. Otkuda Vasha uverennost' v otsutstvii
etih eksperimentov mne sovsem neponyatno. Eto relyativisty delayut vid, chto
ne znayut pro eti eksperimenty ili pytayutsya dokazat' ih oshibochnost'...
Nu tak na to i relyativisty... Est' vpolne ochevidnaya nauchnaya
lozh'. Eto otricanie relyativistami (tochnee oficial'nymi uchenymi pri
vlasti) yavleniya efirnogo vetra. Vopros ponyaten. Esli efir est'. Esli
efirnyi veter prisutstvuet, to chem zhe eti "uvazhaemye" lyudi zanimalis' s
1926 goda.... Otvlechenie. Sueta vokrug predstoyashego razgona RAN
vyzvana imenno teoreticheskim tupikom, v kotoryi zagnala i sebya i
obshestvo "oficial'naya" nauka. I nado priznat', chto u deistvuyushei vlasti
hvatilo i uma i muzhestva nachat' process "reformirovaniya" RAN. Inache
prosto u nas ne poluchaetsya. Vot nachnut cherez koleno gnut', togda glyadish'
zacheshutsya. Ya vsem rekomenduyu v etom smysle posmotret' vystuplenie
chl-korr Sona na seminare v CIAM. Ni za chto ne otvechat', stateiki v
referiruemye zhurnaly popisyvat', a vseh nesoglasnyh gnobit'... Vot ona
kvintessenciya deyatel'nosti RAN.... Konec otvlecheniya. Mnogo
slyhal ya slov o profanacii idei razrabotki teorii efira. Oglasite ves'
spisok etih profaniruemyh teorii, pozhaluista. Ya priderzhivayus' teorii VAA
s razlichnymi rasshireniyami. Vse eto voshlo v Standartnuyu model'
efirodinamiki. Etoi efirnoi teorii razgovory ob efirnom vetre nikak ne
vredyat, tol'ko pomogayut.... S uvazheniem, Mihail Surin
|
|
Naverh
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.07.2013 9:12, 3.2 KBait)
 Re: Aether theory with experimental verification
Re: Aether theory with experimental verification
Otvet #219 - Vchera :: 13:41:39
Ivan pisal(a) Vchera :: 09:29:08:Misha!
Chto-to ya stal zamechat', chto u Smotryashego stabil'no idet podhod dvoinyh standartov.
Kak u relyativistov.
Smotri:
- U VSEH on trebuet
ssyli na raboty, a sam NIKOGDA takovye po povodu svoih nigilisticheskih zayavlenii ne predstavlyaet.
-
VSE argumenty po povdu nablyudenii, izmerenii EV s poroga otvergaet,
vsyacheski obzyvaya ih nehoroshimi slovami, i dalee s tainstvenym vidom
utverzhdaet, chto EGO efir obladaet "super-puper svoistvom dvigat'sya k
poverhnosti Zemli so korost'yu ok. 5000 m /sek"
Hochet poobshat'sya s
VAA, pust' priezzhaet na K-2014, tak, net, naidet 1000 prichin, po
kotorym "niz-z-z-z-z-ya-ya-ya emu tuda popast'" Ivan.
Tak i est'. Mnogo slov o nekih oshibkah i vsyacheskoi profanacii.
Imenno o takom podhode pishet VAA. Nedarom znachitel'naya chast' ego trudov
posvyashena voprosam filosofii, nauchnoi metodologii... Vyrvat' kusok,
provozglasit' ego istinoi i nikak ne rassmatrivat' kompleksno... Pri
etom ispol'zuetsya izvestnaya praktika relyativistov v upor ne videt'
eksperimental'nyh podtverzhdenii efirodinamiki... Vse zhe libo nauchnyi podhod i metodologiya, libo religioznyi....
Po povodu VAA. Tol'ko vchera s nim razgovarival. U nego i pochta
est'. I sait. Prichem s saita sovershenno na halyavu mozhno skachat' vse
raboty VAA. A len' chitat'- mozhno videozapisi lekcii smotret'. Prichem
odnu takuyu zapis' sdelal ya sam- po prodol'nym volnam.... A Roman Chertanov voobshe nakopal bezdnu informacii.
Otvlechenie.. V shvatke mezhdu Pravitel'stvom i RAN ya na storone
Pravitel'stva... RAN v tepereshnem sostoyanii ne mozhet dal'she
sushestvovat'. Ya i s VAA ob etom govoril. Ostavit' po bo'lshomu schetu
prikladnikov, a vot s teoretikami, osobenno ot fiziki, davno pora
razobrat'sya. Trebuetsya nauchno-tehnicheskaya revolyuciya, o kotoroi govorit
VAA. I ne on odin.... Razgovor verno stavitsya v razreze neobhodimosti
proryvnyh tehnologii. Ot sovremennoi RAN nikakogo proryva zhdat' ne
prihoditsya (smotri vystuplenie Sona)... Konec otvlecheniya. S uvazheniem, Mihail Surin
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.07.2013 22:25, 5.1 KBait)
O-ho-ho prochital nechto takoe chto znal tol'ko ya
po analizu tempa hoda chasov i smesheniyu
zaderzhek zhps pri kotorom postoyannyi
dvizh proishodit, no chto mne nravitsya
-
eto nekotoraya novizna v kotoroi vnutrennyaya
chast' katitsya - ponravilos' mne odnako.
V moih modelyah eto tozhe bylo, no ya dumayu
chto v dannom sluchai
tovarish dodumalsya samostoyatel'no.
|
|
Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
12.09.201122:36 |
|
Al'ternativnoe / Predpolozhenie o Zvezdah
30 sentyabrya, vs 2007 g., 18:10
Ne dlya pechati, i ne ldya obsuzhdeniya.
2stranica
Dostigaya
opredelennogo sluchaya Zvezda efira
vnutri zvezdy mozhet obrazovat' tol'ko odnu bresh v polosti
sfery, eto samyi intirestnyi sluchai.
V rezul'tate kotorogo poyavitsya
Neitronnaya Reaktivnaya
zvezda.
Kotoraya budet peremeshat'sya v prostranstve s ogromnoi
skorost'yu, za schet vybrosa efira kotoryi s kraev breshi
budet sdirat'
veshestvo zvezdy, chto vyzyvaet sil'noe izluchenie
vysokih energii, i svetovoe izluchenie kraev breshi.
V svyazi s tem chto peremeshenie Zvezdy efira vnutri zvezdy
budet
napravlenno v storonu naibol'shego kolichestva veshestva.
Zvezda efira peremestitsya v protivopolozhnuyu storonu ot breshi.
I s protivopolozhnoi storony pervoi breshi obrazuetsya
vtoraya.
I u zvezdy poyavitsya dva lucha vybrosa, chto so vremenem uravnovesit
"tyagu" zvezdy, i snizit ee skorost', vozmozhno neznachitel'noe vrashenie.
Posle
chego obrazuetsya tret'ya i chetvertaya bresh vybrosa,
i mezhdu vtoroi
i tret'ei, tret'ei i chetvertoi, - povorot zvezdy
po otnosheniyu k predydushemu vybrosu.
I
chto skorei vsego privedet k izmeneniyu formy zvezdy
ona stanet v forme vypukloi linzy.
Peremeshenie Zvezy efira, vnutri zvezdy, mozhet vyzvat'
vrashenie
zvezdy,
vokrug Zvezdy efira, po analogii vrasheniya gimnasticheskogo
obrucha vokrug sebya.
Vozmozhen sluchai chto pri vrashenii zvezdy
i pri uvelichenii vnutri
nee Zvezdy efira
zvezda vzorvetsya po ekvatoru.
I posle vzryva priobretet formu vypukloi linzy
i vybrosy efiro- veshestva vysokih energii i izlucheniya, budut rasspolozhenny
haotichno
po ekvtoru.
| |
------------------------------
Iyri
Veteran foruma


 Vne Foruma
Vne Foruma

Soobshenii: 6521
Gruziya
Pol:

 Re: Aether theory with experimental verification
Re: Aether theory with experimental verification
Otvet #236 - Segodnya :: 12:37:52
Smotrjashii pisal(a) Segodnya :: 12:25:56:I pochemu uvashego Guru .efir(vtozhe vremya!) dvizhetsya k planete so skorost'yu =11,2km/..sfericheski-simmetrichno..
Kak ETO ob'yasnit'?
Vy
pravil'no ih pod-byvaete, no vot skorost' efira 11 km, eto est' veter.
Sam zhe potok efira dvizhetsya znachitel'no bystrei. Da i, simmetriya tam
uslovnaya, ona narushaetsya otnositel'no dnevnoi i nochnoi storony.
Dobavlyu
eshe. sam efirovorot otnositel'no simmetrichnyi, esli ochertit' efirovorot
to poluchitsya sferoid. No zemlya smeshena otnositel'no centra sferoida na
velichinu radiusa yadra. Yadro kak by katitsya kolesom po central'noi tochke
efirovorota.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A. V. Konovalov,
8.07.2013 1:25, 1.6 KBait)
Eto tyazhelo ob'yasnit', kak Nechto poyavlyaetsya
iz Niotkuda, unichtozhaet poroi celye skopleniya zvezd, i ischezaet v Nikuda. Pri
etom chernaya dyra deistvitel'no
znachitel'no iskazhaet vokrug
sebya
prostranstvo-vremya i obladaet ogromnym
gravitacionnym prityazheniem,
vozdeistvuya na okruzhayushuyu materiyu. Chernaya dyra eto
to edinstvennoe, chto mozhno nazvat' nastoyashei Pustotoi Nichto, tak kak tam, v chelovecheskom
ponimanii, net nichego material'nogo.
(Iz knigi AllatRa)
Sohranit' knigu:
http://sensei.org.ua/read/books/12-allatra
http://schambala.com.ua/index.php?nma=downloads&fla=stat&ids=2&idd=41
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.07.2013 9:41, 297 Bait)
Dannaya tema ne prednaznachena dlya breda kotoryi
komu-to kazhetsya.
Esli kto-to mozhet vnyatno skazat' chto-to o fizike
chernyh dyr - eto budet vse ravno povtor avtorskogo
varianta, ibo kak napisal avtor - takie i chernye dyry,
a razlichnyi nadumannyi sebe bred - eto ne to.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.07.2013 9:53, 1.6 KBait)
\\\Chernaya dyra
eto
to edinstvennoe, chto mozhno nazvat' nastoyashei Pustotoi Nichto\\\
Vy luchshe ne pishite nichego, vryad-li komu interesen bred ne imeyushii
fizicheskih opredelenii i
fizicheskih obosnovanii.
Po bol'shomu tekst ne fizichnyi ibo v nem net prichinno sledstvennoi
svyazi, i avtor yasnyi kon' dazhe ne znaet opredeleniya chernyh dyr,
i kakogo-to schitaet chto mnenie ego o chernoi dyre kak i mnenie
kakogo nibud' lohoboya komu-to interesno.
Naprimer est' tysyacha nedalekih kotorye vyskazhut
bredyatinu svoego vospalennogo
moska o chernoi dyre ,
tak i chto s togo a nichego - vsya eta tysyacha vyskazyvanii - tak i ostanetsya
bredyatinoi nikomu ne nuzhnoi,
ibo tol'ko to chto skazal avtor chernyh dyr
o nih to i ostanetsya kak opredelenie, a vyskazyvaniya i mneniya drugih o chernyh
dyrah - obrechenny na uroven' idiotizma.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.07.2013 9:53, 1.6 KBait)
\\\Chernaya dyra
eto
to edinstvennoe, chto mozhno nazvat' nastoyashei Pustotoi Nichto\\\
Vy luchshe ne pishite nichego, vryad-li komu interesen bred ne imeyushii
fizicheskih opredelenii i
fizicheskih obosnovanii.
Po bol'shomu tekst ne fizichnyi ibo v nem net prichinno sledstvennoi
svyazi, i avtor yasnyi kon' dazhe ne znaet opredeleniya chernyh dyr,
i kakogo-to schitaet chto mnenie ego o chernoi dyre kak i mnenie
kakogo nibud' lohoboya komu-to interesno.
Naprimer est' tysyacha nedalekih kotorye vyskazhut
bredyatinu svoego vospalennogo
moska o chernoi dyre ,
tak i chto s togo a nichego - vsya eta tysyacha vyskazyvanii - tak i ostanetsya
bredyatinoi nikomu ne nuzhnoi,
ibo tol'ko to chto skazal avtor chernyh dyr
o nih to i ostanetsya kak opredelenie, a vyskazyvaniya i mneniya drugih o chernyh
dyrah - obrechenny na uroven' idiotizma.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.07.2013 22:39, 1.4 KBait)
S moei tochki zreniya eto mozhet byt' eshe
i kak test naprimer
---------
 Re: Materiya perehodnogo sostoyaniya (MPS) - EFIR
Re: Materiya perehodnogo sostoyaniya (MPS) - EFIR
Otvet #25949 - Segodnya :: 17:09:15
Larisa Rainkina pisal(a) Segodnya :: 17:00:44:Mne predstavlyaetsya, chto ponyatie "beskonechnost'" chisto matematicheskoe, i k Real'nosti ne imeet otnosheniya.
Zolotye
slova.
----------------
Kak o mne ochen' maloe kolichestvo lyudei mogut ponyat' beskonechnost' soznaniem,
ne vziraya na podarok bol'shoi sovetskoi enciklopedii
v kotoroi
postulirovalas' - beskonechnost' vselennoi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.07.2013 22:40, 223 Bait)
Kak po mne ochen' maloe kolichestvo lyudei mogut ponyat' beskonechnost' soznaniem,
ne vziraya na podarok bol'shoi sovetskoi enciklopedii
v kotoroi
postulirovalas' - beskonechnost' vselennoi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. R. Skens,
12.07.2013 11:49, 200 Bait)
Iz "Chernoi Dyry" kak izvestno ne mozhet vyrvat'sya dazhe svet, za isklyucheniem pozhalui gravitonov. Mozhet
sushestvuyut super neitral'nye ob'ekty sposobnye uderzhivat' eti samye gravitony v svoem gorizonte?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.07.2013 18:28, 247 Bait)
\\\Iz "Chernoi Dyry" kak izvestno ne mozhet vyrvat'sya dazhe svet,\\\
Chitaite etot forum s samogo nachala,
tam est' otvety na
vse voprosy po chernoi dyre
kotorye Vy dazhe eshe ne pridumali.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.07.2013 18:41, 1.6 KBait)

: Vchera v 13:37:34
-----------------------------------
Eto-zh nado kogda tol'ko
razduplilis', i nachinayut
ponimat' chto voshvalenie postoyannoe svoei nauchnoi gruppirovki
i zabanivanie drugih vzglyadov ni k chemu horoshemu ne privedet,
v istorii
byli podobnye sluchai, i reshalis' oni polnym
prekrasheniem finansirovaniya nauchnyh napravlenii.
Dazhe ne udivlyus' esli perestanut finansirovat' teor fiziku
vmeste
s astronomiei i vse peredadut chastnikam a na chto ne budet
sprosa snesut i porezhut v metallolom.
Da vot tak byvaet chto vse idut ne v tu storonu a teh
kto
predlagal drugoe schitali al'ternativshikami kotoryh
nado banit'. A al'ty mogut obosnovat' prichinu nepravil'nogo
puti kak v oshibochnosti bol'shogo vzryva, chernyh dyr,
fotonov - a relyativisty i hoteli by da ne mogut,
vot kak naprimer on skazhet chto dvadcat' let uetu prepodaval studentam
i mozg im lainom zagruzil po samye
dal'she nekuda, - pravil'no
luchshe pust' al'ty pravdu skazhut, v etom sluchai mozhno i nad
al'tami posmeyat'sya i idiotami ih po-nazyvat', a potom razobrat'sya
v
tom chto al'ty predlagali i napisat' lekcii na al'tovskih ideyah
i so ssylkoi na istochnik kosit' bablo na chtenii lekcii a al'tam
vmesto gonorara za ih idei pokazyvat'
im bol'shoi bui.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.07.2013 19:07, 486 Bait)
Dmitrii Vibe na skol'ko ya s nim na forume obshalsya
schitaet napisannuyu im lekciyu polnost'yu
na ideyah drugih avtorov - schitaet svoei lekciei.
Sobstvenno
ya dumayu chto al'ternativshiki prosto obyazany
v etoi situacii pisat' chto zapreshayut ispol'zovanie
pridumannyh imi idei - pri chtenii platnyh lekcii,
pri chtenii
lekcii pered studentami obuchenii na platnom obrazovanii,
i pri napisanii knig i statei bez soglasovaniya s avtorom kak teksta tak i
gonorara.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.07.2013 19:10, 1.0 KBait)
http://www.astrogorizont.com/user_files/Image/content/img1942_pg1208_small.jpg
|
10 07/13 |
 |
 |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.07.2013 19:26, 871 Bait)
Kamennyi vek , drugoe mnenie drugoi podhod -
al'ternativa odnako ee nado tol'ko banit' i ne puskat'
nikuda
- ne stalkivayutsya eti galaktiki,
tam odna
sharovaya posle mnogokratnogo sbrosa efira
vnutri svoih zvezd mozhno skazat' chto vzryvaetsya
i razbrasyvaet vse svoi zvezdy i razbrosaet ih v itoge tak
daleko
chto oni nikogda ne soberutsya v etu galaktiku,
i na puti etogo processa proletala galaktika analogichnaya
Andromede ili nashei, i ee prosto prevratilo davlenie
v polusferu, chto primechatel'no to na kakom ne detskom
rasstoyanii etu galaktiku prevratilo v sferu,
i duet tak chto skoro sneset gryazevoi kol'co v sosednei galaktike,
a eto znachit chto razbrosaet zaodno i etu galaktiku,
sinie zvezdy u polusfernoi galaktiki eto zvezdy
kotorye v osnovnom svoem ob'eme - bolee blizkie k
vzryvayusheisya galaktike.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.07.2013 20:05, 26.0 KBait)
Vallav
Veteran foruma


 Vne Foruma
Vne ForumaSoobshenii: 6846
 Re: Aether theory with experimental verification
Re: Aether theory with experimental verification
Otvet #367 - Segodnya :: 13:02:01
Alow pisal(a) Segodnya :: 09:45:07:
U fotona, pri vzaimodeistvii s vakuumom, voznikayut kak korpuskulyarnye svoistva, tak i volnovye svoistva.
Foton s vakuumom ne vzaimodeistvuet.
Foton v vakuume raspostranyaetsya.
I svoistva u fotona pri etom - chisto volnovye.
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Vallav
Veteran foruma


 Vne Foruma
Vne ForumaSoobshenii: 6846
 Re: Aether theory with experimental verification
Re: Aether theory with experimental verification
Otvet #373 - Segodnya :: 14:24:32
Alow pisal(a) Segodnya :: 13:58:52:
Foton ne vzaimodeistvuet s zaryadami. On mozhet vzaimodeistvovat' tol'ko s vakuumom. Tochnee, ya aktivnoi sostavlyayushei vakuuma.
A aktivnaya
sostavlyayushaya vakuuma - elektricheskie zaryady.
Tak?
I pravil'no - foton vzaimodeistvuet s aktivnoi sostavlyayushei vakuuma - zaryadami?
Glavnoe v drugom - vzaimodeistvuet
pri etom foton - kak korpuskula ili kak
volna...
------------------------------------------------------
Vikipediya
-------------------------------------------------
Kvantovyi harakter izlucheniya i poglosheniya energii elektromagnitnogo polya byl postulirovan M.Plankom
v 1900 godu dlya ob'yasneniya svoistv teplovogo
izlucheniya.[8] Termin foton vveden
himikom Gilbertom
L'yuisom v 1926 godu.[9] V 19051917 godah Al'bertom
Einshteinom opublikovan[10][11][12][13] ryad rabot, posvyashennyh protivorechiyam
mezhdu rezul'tatami eksperimentov i klassicheskoi volnovoi
teoriei sveta, v chastnosti fotoeffektu i sposobnosti
veshestva nahodit'sya v teplovom ravnovesii s
elektromagnitnym izlucheniem.
Predprinimalis' popytki ob'yasnit' kvantovye svoistva sveta poluklassicheskimi modelyami, v kotoryh svet po-prezhnemu opisyvalsya uravneniyami
Maksvella bez ucheta kvantovaniya, a ob'ektam, izluchayushim i pogloshayushim svet, pripisyvalis' kvantovye svoistva (sm., naprimer, teoriyu Bora). Nesmotrya na to, chto poluklassicheskie modeli okazali vliyanie
na razvitie kvantovoi
mehaniki
(o chem v chastnosti svidetel'stvuet to, chto nekotorye ih polozheniya i
dazhe sledstviya yavnym obrazom vhodyat v sovremennye kvantovye teorii[14]),
eksperimenty podtverdili pravotu Einshteina o kvantovoi prirode sveta (sm., naprimer, fotoeffekt).
Sleduet otmetit', chto kvantovanie
energii elektromagnitnogo
izlucheniya
ne yavlyaetsya isklyucheniem. V kvantovoi teorii znacheniya mnogih fizicheskih
velichin yavlyayutsya diskretnymi (kvantovannymi). Primerami takih velichin
yavlyayutsya: uglovoi
moment, spin i energiya svyazannyh sistem.
Vvedenie ponyatiya fotona sposobstvovalo sozdaniyu novyh teorii i
fizicheskih priborov, a takzhe stimulirovalo razvitie eksperimental'noi i
teoreticheskoi bazy kvantovoi mehaniki. Naprimer, byli izobreteny mazer, lazer, otkryto yavlenie kondensacii
Boze Einshteina, sformulirovana kvantovaya
teoriya polya i veroyatnostnaya interpretaciya kvantovoi mehaniki. V sovremennoi Standartnoi
modeli fiziki
elementarnyh chastic sushestvovanie fotonov yavlyaetsya sledstviem togo, chto fizicheskie zakony invariantny otnositel'no lokal'noi kalibrovochnoi
simmetrii v lyuboi tochke prostranstva-vremeni
(sm. bolee podrobnoe opisanie nizhe v razdele Foton
kak kalibrovochnyi bozon). Etoi zhe simmetriei opredelyayutsya vnutrennie svoistva fotona, takie kak elektricheskii
zaryad, massa i spin.
Sredi prilozhenii koncepcii fotonov est' takie, kak fotohimiya[15], videotehnika,
komp'yuternaya
tomografiya, mikroskopiya vysokogo razresheniya i izmerenie mezhmolekulyarnyh rasstoyanii. Fotony takzhe ispol'zuyutsya v kachestve elementov kvantovyh
komp'yuterov[16] i naukoemkih priborov
dlya peredachi dannyh (sm. kvantovaya
kriptografiya).
Foton iznachal'no byl nazvan Al'bertom
Einshteinom svetovym kvantom (nem.das Lichtquant).[10]
Sovremennoe nazvanie, kotoroe foton poluchil ot grecheskogo
slova φῶς,
phōs (svet), bylo vvedeno v 1926 himikom Gilbertom
N. L'yuisom[17], opublikovavshim svoyu
teoriyu[18],
v kotoroi fotony schitalis' nesozdavaemymi i neunichtozhimymi. Hotya
teoriya L'yuisa ne nashla svoego podtverzhdeniya, nahodyas' v protivorechii s
eksperimental'nymi dannymi, novoe nazvanie dlya kvantov elektromagnitnogo
polya stalo ispol'zovat'sya mnogimi fizikami.
V fizike foton obychno oboznachaetsya simvolom γ (grecheskaya
bukva gamma). Eto oboznachenie voshodit
k gamma-izlucheniyu,
otkrytomu v 1900 godu i sostoyashemu iz dostatochno vysokoenergeticheskih fotonov. Otkrytie
gamma-izlucheniya, odnogo iz treh vidov (α-, β- i γ-luchi) ioniziruyushei radiacii, izluchaemyh izvestnymi na tot moment radioaktivnymi veshestvami, prinadlezhit Paulyu
Villardu, elektromagnitnuyu prirodu gamma-luchei dokazali v 1914 godu Ernest Rezerford
i Edvard
Andreid. V himii i opticheskoi
inzhenerii dlya fotonov chasto ispol'zuyut oboznachenie hν, gde h postoyannaya
Planka i ν (grecheskaya
bukva nyu) chastota
fotonov. Proizvedenie etih dvuh velichin est' energiya fotona.

Opyt Tomasa
Yunga po interferencii sveta na dvuh shelyah (
1805 god)
pokazal, chto svet mozhet rassmatrivat'sya kak volna. Takim obrazom byli
oprovergnuty rannie teorii sveta kak potoka nekvantovyh chastic.
V bol'shinstve teorii, razrabotannyh do XVIII veka, svet rassmatrivalsya kak potok chastic.
Odna iz pervyh takih teorii byla izlozhena v Knige ob optike Ibn
al-Haisamom v 1021 godu. V nei uchenyi predstavlyal svetovoi
luch v vide potoka mel'chaishih chastic, kotorye ispytyvayut nehvatku vseh zametnyh kachestv, krome energii.[19]
Tak kak podobnye modeli ne smogli ob'yasnit' takie yavleniya kak refrakciya,
difrakciya i dvoinoe
lucheprelomlenie, byla predlozhena volnovaya
teoriya sveta, osnovatelyami kotoroi stali Rene
Dekart (1637)[20], Robert Guk (1665)[21], i Hristian
Gyuigens (1678)[22]. Odnako modeli,
osnovannye na idee diskretnogo stroeniya sveta, ostavalis' dominiruyushimi, vo mnogom iz-za vliyaniya avtoriteta Isaaka
N'yutona, priderzhivavshegosya etih teorii.[23][24] V nachale XIX veka Tomas Yung i Ogyusten
Frenel'
naglyadno prodemonstrirovali v svoih opytah yavleniya interferencii i
difrakcii sveta, posle chego primerno k 1850 godu volnovye modeli stali
obsheprinyatymi.[25] V 1865 godu Dzheims
Maksvell predpolozhil v ramkah svoei teorii[26], chto svet eto elektromagnitnaya
volna. V 1888 godu eta gipoteza byla podtverzhdena eksperimental'no Genrihom Gercem,
obnaruzhivshim radiovolny.[27]
-------------------------------------------------
www.socratus.com/rus/kvant-rus.htm
Kvant sveta privilegirovannaya
chastica.
Nado vydelit' izuchenie kvanta sveta v osobuyu oblast'.
1
Massa pokoya vseh chastic imeet kakuyu-to konkretnuyu velichinu.
Tol'ko massa pokoya kvanta sveta ravna nulyu.
Vse chasticy mogut dvigat'sya s lyuboi skorost'yu men'she svetovoi.
Tol'ko kvant sveta dvigaetsya v Vakuume s postoyannoi skorost'yu
s=1.
Skorost' dvizheniya drugih chastic zavisyat ot sistemy otscheta.
Skorost' kvanta sveta ne zavisit ot sistemy otscheta.
---
V 1924 godu Lui de Broil'
vyskazal predpolozhenie, chto vse chasticy imeyut dvoistvennuyu prirodu. Poetomu
seichas uchenye utverzhdayut, chto proton (atom) takzhe obladaet kak korpuskulyarnymi,
tak i volnovymi svoistvami. Volnovye svoistva protona byli obnaruzheny pri
propuskanii protona cherez kristallicheskuyu reshetku. Voznikshaya pri etom difrakcionnaya
kartina byla prinyata uchenymi, kak fakt, svidetel'stvuyushii ob obladanii protonom
volnovymi svoistvami. No predstav' sebe, dorogoi chitatel', chto v ozero brosili
kamen' vesom 60 kilogrammov. Potom v ozero prygayu ya. Uchenyi, sidyashii na
beregu etogo ozera, izuchaet volny i prihodit k vyvodu: tak kak volny identichny,
to i eti dva tela, sozdayushie volny, takzhe identichny. No ty ponimaesh', dorogoi
chitatel', chto est' raznica mezhdu avtorom etih strok i kamnem. A kristallicheskaya
reshetka - eto to ozero, v kotoroe padaet i elektron, i proton. A potom uchenyi
izuchaet obrazovavshuyusya difrakcionnuyu kartinu i pytaetsya ob'yasnit' vnutrennyuyu
strukturu chastic. Ne smeshno li?
------------------------------
Kvant sveta privilegirovannaya chastica.
Nado vydelit' izuchenie kvanta sveta v osobuyu oblast'.
1
Massa pokoya vseh chastic imeet kakuyu-to konkretnuyu velichinu.
Tol'ko massa pokoya kvanta sveta ravna nulyu.
Vse chasticy mogut dvigat'sya s lyuboi skorost'yu men'she svetovoi.
Tol'ko kvant sveta dvigaetsya v Vakuume s postoyannoi skorost'yu
s=1.
Skorost' dvizheniya drugih chastic zavisyat ot sistemy otscheta.
Skorost' kvanta sveta ne zavisit ot sistemy otscheta.
--------------------------------------
Kak govoritsya
test na vnimatel'nost' - naidi neskladushki
v bazovyh opredeleniyah.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.07.2013 20:08, 1.7 KBait)
Tómas Yung -Vikipediya
"Ego idei vyzvali
vozrazheniya angliiskih uchenyh; pod ih vliyaniem
Yung otkazalsya ot svoego mneniya. Odnako v traktate po optike i akustike
Opyty i problemy po zvuku i svetu (1800) uchenyi vnov' prishel k volnovoi
teorii sveta i vpervye rassmotrel
problemu superpozicii voln. Dal'neishim razvitiem etoi problemy yavilos'
otkrytie Yungom principa interferencii (sam termin byl vveden Yungom v
1802 godu).
V doklade
Teoriya sveta i cvetov, prochitannom Yungom Korolevskomu obshestvu v 1801
(opublikovan 1802), on dal ob'yasnenie kolec N'yutona na osnove
interferencii i opisal pervye opyty po
opredeleniyu dlin voln sveta. V 1803 godu v rabote Opyty i ischisleniya,
otnosyashiesya k fizicheskoi optike (opublikovana 1804) on rassmotrel
yavleniya difrakcii. Posle klassicheskih
issledovanii O. Frenelya po interferencii polyarizovannogo sveta Yung
vyskazal gipotezu o poperechnosti svetovyh kolebanii. On razrabotal takzhe
teoriyu cvetnogo zreniya, osnovannuyu
na predpolozhenii o sushestvovanii v setchatoi obolochke glaza treh rodov
chuvstvitel'nyh volokon, reagiruyushih na tri osnovnyh cveta."
"V
1807 godu v dvuhtomnom
trude Kurs lekcii po natural'noi filosofii i mehanicheskomu iskusstvu Yung
obobshil rezul'taty svoih teoreticheskih i eksperimental'nyh rabot po
fizicheskoi optike (termin vvel
Yung) i izlozhil svoi issledovaniya po deformacii sdviga, vvel chislovuyu
harakteristiku uprugosti pri rastyazhenii i szhatii tak nazyvaemyi modul'
Yunga. On vpervye rassmotrel mehanicheskuyu
rabotu kak velichinu, proporcional'nuyu energii (termin vvel Yung), pod
kotoroi ponimal velichinu, proporcional'nuyu masse i kvadratu skorosti
tela."
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(V. R. Skens,
17.07.2013 6:47, 282 Bait)
Prochital pervye 12 stranic breda, dal'she net smysla chitat' obozlennyi benefis g-na "geniya" A.P. Vasi pod godol'erskim devizom "kto ne so mnoi- tot protiv menya"

- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
21.07.2013 11:50, 1.2 KBait)
O Nauke, kosmose i bytie
1:06, 21 iyulya 2013==========================================================================================
Opisanie:
Russkie uchenye uzhe davno znayut - teoriya otnositel'nosti Einshteina -
fikciya, sozdannaya dlya togo, chtoby uvesti nauku v storonu podderzhki
paraziticheskoi sistemy, dlya togo chtoby presech' ispol'zovanie
chelovechestvom svobodnoi energii. Osnova mirozdaniya - pervichnye materii.
Malo
kto znaet, chto D. I. Mendeleev byl odnim iz poslednih vsemirno
izvestnyh russkih uchenyh konca 19-go veka, kto otstaival v mir...
--------------
S moei tochki zreniya avtor slishkom emocional'no vystupaet, bolee logichno bylo-by
priglasit' kogo-to kto prosto-by prochel tekst, i lichno kak po mne bol'she
poloviny lekcii - avtor govorit ni o chem, i s mnogim ya ne soglasen - no
po bol'shomu
schetu esli peredelat' etu lekciyu to mozhno ee i po televizoru pokazyvat', v tom vide v kotorom ona est' ee po televizoru pokazyvat' nel'zya.==========================================================================================
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.07.2013 8:28, 1.1 KBait)
\\\Prochital pervye 12 stranic breda, dal'she net
smysla chitat'
obozlennyi benefis g-na "geniya" A.P. Vasi pod godol'erskim
devizom
"kto ne so mnoi- tot protiv menya"
 \\\
\\\
Eto u Vas u vashego mozga zashitnaya sistema srabotala,
on uzhe zapolnen
novoi informaciei.
A ya Vam ne zapreshayu poseshat' forumy mahrovyh relyativistov,
tam odni i te-zhe idei obsuzhdayut po sto let i reshayut odni
i te-zhe zadachi
po sto let i tol'ko hvalyat drug druga.
A vseh drugih s drugimi tochkami zreniya tam posylayut
v dal' ili prosto banyat a forum zabaltyvayut i zakryvayut.
--------------------------------------------------
Gorizonty nauki o Vselennoi
Nauki o vselennoi - gipotezy, idei, obsuzhdeniya.
---------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(S. M. Andreichuk,
4.08.2013 11:42, 1.1 KBait)
Foton ogranichen v svoei skorosti 300.000 km/s pronicaemost'yu prostranstva. Na dannoi skorosti foton proyavlyaetsya kak fenomen, t.e. kak SVET. Pronicaemost' prostranstva - eto
sovokupnost' elektromagnitnyh i gravitacionnyh polei. Eto mozhno sravnit' s lestnicei: chem bol'she vysota stupen'ki, tem medlennee proishodit pod'em po nei, chem men'she vysota
stupen'ki - tem bystree pod'em. To zhe samoe i s pronicaemost'yu: chem sil'nee elektromagnitnoe i gravitacionnoe polya, tem bystree foton preodolevaet opredelennoe rasstoyanie,
t.e. tem bol'she skorost'. No v to zhe vremya pri skorosti bol'she 300.000 km/s foton perestaet proyavlyat' sebya kak fenomen, t.e. teryaet svoe svoistvo byt' vidimym. Ishodya iz etogo
my vidim na meste dyry ne ogromnuyu zvezdu, a chernoe pyatno. So vremenem, kogda massa etoi zvezdy dostignet kriticheskoi i pronicaemost' prostranstva vokrug etoi chernoi zvezdy
budet takovym, chto skorost' fotona snizitsya do kriticheskoi, t.e. do 300.000 km/s i togda proizoidet vspyshka chernoi zvezdy, kotraya osvetit vse prostranstvo nashei gallaktiki
i vozmozhno drugie zvezdy na ee fone budut vsego lish' chernymi tochkami...
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.08.2013 16:49, 54 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Shel by ty starche ot syuda so svoim starcheskim marazmom.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(S. M. Andreichuk,
6.08.2013 16:26, 991 Bait)
Uvazhaemyi A.P. Vasi, osuzhdenie drugih lyudei po suti - eto priznanie svoei morali v kachestve etalona, a lyuboe oskorblenie ili agressiya - eto proizvodnye straha. Ya ne polenilsya
i pochital forum. Pozhalui, s vashei replikoi ot 05.01.2011 20:55 ya soglashus', a v ostal'nom ya usmotrel tol'ko emocii. Vozmozhno v svoe vremya vas ne ponyali v uchenyh krugah i vy
ostalis' na urovne shkol'nogo fizika, v horoshem smysle slova! Schitayu, chto perevospitat' vzroslyh dyadei kuda slozhnee, chem zalozhit' pravil'nyi fundament myshleniya v podrastayushee
pokolenie. Bolee togo, schitayu eto bolee pochetnym! Hotel by obratit' vashe vnimanie na to, chto forumy sozdayutsya ne dlya togo, chtoby drug druga polivat' oskorbleniyami, a dlya togo
chtoby obmenivat'sya svoimi myslyami i mneniyami. Uveren, chto bol'shinstvo lyudei na etom forume - eto lyudi dumayushie, i ne vazhno na kakoi evolyucionnoi stupen'ke oni stoyat. Vazhno
uslyshat' drug druga i mozhet byt' dazhe zainteresovat' drugih lyudei v izuchenii temy, obsuzhdaemoi na forume.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.08.2013 21:56, 2.5 KBait, otvetov: 2)
Vozmozhno ya po otnosheniyu k Vam ne pravil'no vyskazalsya,
prinoshu izvineniya.
Ya predpolagal chto odin sobesednik s drugoi vetki zashel pod drugim imenem.
A
esli Vy vnimatel'no chitali - to fotony ya otmenil
.
Byvaet i takoe v fizike byli fotony a potom poteryali fizicheskii smysl
pri primitivnom opyte.
---
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
6.04.201113:49 |
|
Dlya sushestvovaniya effekta Doplera, est' prichina - sreda i ee svoistva.
Dazhe esli ispol'zuetsya metod izmereniya dlya sred, a govoritsya chto
vokrug pustota, to propadaet
prichinnost' vozniknoveniya dannogo
effekta kak svoistva prostranstva.
U relyativistov ne prostranstvo vystupaet v kachestve linii zaderzhki
signala, a vystupaet
- foton, kak dvizhushiisya ob'ekt, u kotorogo
ogranichena skorost' dvizheniya v pustote, po ne ponyatnoi prichine -
kotoraya postuliruetsya bez ob'yasneniya prichiny. Foton
v dannom sluchai
mozhet byt' tol'ko chasticei, - eto ne vozmozhno po prichine togo chto
chastica ne mozhet snizhat' i uvelichivat' svoyu skorost' chto
nablyudaetsya naprimer
pri dvizhenii sveta naprimer v vozduhe, potom
cherez steklo potom opyat' v vozduhe i potom v vakuum, tak kak
poluchaetsya chto v stekle letit foton medlennee chem v vozduhe
i
vakuume , a vyletaya iz stekla foton uvelichivaet svoyu skorost'. Tak
vot ne mozhet chastica kotoraya poteryala skorost', prosto tak vzyat' i
pri vylete iz stekla
uvelichit' skorost', - na podobnoe sposobny
tol'ko kolebaniya sredy v sredah s raznymi svoistvami. Tak chto foton
kak chastica - vydumka chistoi vody.
Vyvod -
v prostranstve rasprostranyayutsya kolebaniya sredy, i svetovoe
izluchenie ne dvizhetsya a obrazuetsya ot vzaimodeistviya kolebanii
sredy i materiala, kak v 1800 godu govoril
Tomas Yung.
Tak chto vse chto napisano v astrofizike bez ucheta sredy - k
sozhaleniyu ne pravil'no.
Eto podarok Dmitriyu Vibe, eto ne budet opublikovano dva
tri goda.
Dmitrii Vibe mozhet i dal'she uchit' studentov tomu chto bezvozvratno
ustarelo, i tomu chto im nikogda ne prigoditsya.
Tak uzh Dmitrii Vibe zapreshal obsuzhdat'
efir poka ego ne dokazhut chto on est',
i teh kto efirom zanimaetsya nazyval al'tami i daval im ochen' ne lestnye opredeleniya. |
---
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(S. M. Andreichuk,
7.08.2013 12:41, 1.3 KBait, otvetov: 1)
Ishodya iz vashego vyvoda voznikaet zakonomernyi vopros: chto yavlyaetsya prichinoi etih vozmushenii v rezul'tate chego sreda (efir) proyavlyaet sebya v vide fenomena ili inache SVETA?
I v tak nazyvaemoi "chernoi dyre" etih kolebanii efira net, poetomu on (efir) i ne proyavlen kak svet. No pochemu etogo efira ochen' mnogo vokrug zvezd? Oni po suti
yavlyayutsya istochnikami kolebanii sredy (efira)? Znachit efir neravnomerno raspredelen v prostranstve. Vozmozhno v prostranstve efir rasprostranyaetsya po kakomu-to zakonu, naprimer,
spirali (moe predpolozhenie) i esli zvezda nahoditsya na linii maksimal'noi koncentracii efira, to ona proyavlena kak zvezda, no stoit ei otklonitsya ot etoi linii, gde koncentraciya
efira minimal'na, to i zvezda prosto stanovitsya nevidimoi, t.e. ne proyavlyaet sebya kak istochnik sveta. Boyus' predpolozhit', chto normal'noe sostoyanie zvezdy - nahoditsya na linii
spirali efirnoi koncentracii i poetomu ona maksimal'no pytaetsya prityanut' k sebe etu liniyu sozdavaya vokrug sebya podobie voronki, ili to,chto my nazyvaem chernoi dyroi. Nu,
a centr Gallaktiki prosto po svoim fizicheskim svoistvam ne mozhet vyiti na etu spiral', potomu chto razmery ee takovy, chto ona nahoditsya v sostoyanii "neopredelennosti".
Chto-to ya sam sebe uzhe kazhus' sumasshedshim...))
- Re[3]: Chernaya dyra
(S. M. Andreichuk,
7.08.2013 20:30, 434 Bait)
Dumayu, chto tol'ko opredelennaya chastota kolebaniya sredy, podobno moduliruyushemu signalu, neset v sebe kakuyu-libo informaciyu ot vibriruyushego istochnika, rasshifrovannuyu nashim
mozgom kak svet, teplo i, mozhet byt', dazhe kak kakie-nibud' mysleobrazy. Schitayu, chto ne lyubaya chastota kolebaniya sredy (efira) yavlyaetsya svetonesushei. Hotya mogu oshibat'sya. Voznikaet
vopros: eto konkretnaya chastota ili vse-taki opredelennyi diapazon chastot?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.08.2013 20:59, 1.0 KBait)
Vse chto Vy mozhete pridumat' ya uzhe davno napisal
otvety.
Na vse chto Vy pishite moi otvety davno est'.
Prezhde chem ne prochtete vse ot nachala do konca
proshu
Vas voprosov ne zadavat', po toi prichine chto
kogda prochtete do konca - to voprosov u Vas ne budet.
www.astronet.ru Forumy
Astronomiya i Internet
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.08.2013 21:28, 5.4 KBait)
Poimite pravil'no ya nachinal obsuzhdat' pohozhie na Vashi voprosy
na forumah let desyat' nazad, seichas u menya prosto est' vse
s moei tochki zreniya osnovnye otvety
na voprosy v kosmologii.
I mne s Vami obsuzhdat' nechego.
U Vas teper' zadacha samostoyatel'no pridumat' chto-to
drugoe chem u menya ne zalezaya v moe avtorstvo.
Menya kak-to bylo vezhlivo poslali na saite,
za chto ya i zablokiroval dlya kosmologov svoi idei.
I v principe dumayu pisat' na urovne zakrytogo koda,
eto kogda
fizicheskoe opredelenie daetsya tol'ko v ramkah
stat'i, chtoby prakticheski nevozmozhno bylo ispol'zovat'
fizicheskie opredeleniya v stat'e pro galaktiki dlya
napisaniya
stat'i pro zvezdy naprimer.
---------------------------------------
Otvet #37 : 29.06.2009 [09:27:31]
Esli u Vas est' voprosy, ya prosto znayu kto eshe
efirom zanimaetsya, tak tam s formulami
u nih
i s raschetami, i v obshem, v tom zhe klyuche chto ya
rasskazal.
Tak, mozhet, puskai oni i prihodyat?

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #38 : 29.06.2009 [10:50:32]
CADET
\\\Tak, mozhet, puskai oni i prihodyat? \\\
Konechno priidut, let cherez 30-70, i rasskazhut astronomam
kak kosmos ustroen.
Ya v obshem dumal chto na astro forumah, efirnye teorii hot'
kak-to obsuzhdalis', v principe esli astronomy nastaivayut
sovmestno s teoriyami gospodina Einshteina,
na tom chto mezhzvezdnoe prostranstvo
- est' pustota tochnee vakuum to tak pust' i ostaetsya.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #40 : 29.06.2009 [12:27:56]
-------------------------------------------
Otvet #41 : 29.06.2009 [15:16:30]
Dmitrii Vibe
\\\Tak, mozhet, cherez 30-70 let i obsudim?\\\
Ya v obshem dumayu napisat' fantasticheskii rasskaz,
v kotrom
budut elementy atrofiziki i rasskazanno o efire.
Budet smeshno esli budut delat'sya ssylki na fantasticheskii rasskaz.
\\\Obsuzhdalis', kak
bez etogo:
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,30971.0.html\\\Za adres spasibo.
Tam ya ne nashel modeli efira v prostranstve.
No zhelayu uspehov sdelat' luchshe moei,
ne zalezaya v moe avtorstvo.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(O. E. Korobeinikova,
7.08.2013 22:25, 142 Bait)
www.liveinternet.ru/users5276115/post/286324507/ Zhivem v "chernoi dyre.v plenu u Krona/boga vremeni/ Skoro vyrvemsya ,a to holodno i temno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(O. E. Korobeinikova,
7.08.2013 22:42, 108 Bait)
Zhivem v "plenu..u Krona/boga vremeni/. Nadeyus' skoro vyrvemsya iz etoi chernoi dyry.A to holodno i temno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.08.2013 22:44, 1.1 KBait)
Ya nadeyus' Vy ponimaete chto tol'ko hamy
pri polnom popustitel'stve kak moderatorov
tak i vladel'cev saita
mogut skazat' na predlozhenie priglasit' svoih znakomyh
s drugogo foruma poobshat'sya zdes',
- mol pust' oni prihodyat a ty u- bui ot syuda.
Nu i sovet moderatora poobsuzhdat' cherez 30-70 let, v forme voprosa
pri ego nevypolneniyu analogichen zabanivaniyu.
Tam Vibe vseg zashugal po polnoi, vse boyatsya ego
ibo on srazu banit i po barabanu, a ya tam eshe prochital
forum kak raduyutsya tomu kak zhestko al'ternativnye mneniya
zabanivayutsya na etom forume - babene, al'ternativa dlya nih
eto nechto plohoe i uzhasnoe, hotya po faktu
eto prosto drugaya tochka
zreniya - i v dannoe vremya tochka zreniya ne finansiruemyh
entuziastov v kosmologii, vot ya prihozhu s raboty,
i neskol'ko chasov udelyayu
kosmologii, i menya nikto ne
finansiruet, - a u nih eto ih rabota kak pravilo
za kotoruyu oni poluchayut zarplatu, i mogut voobshe nichego
ne pridumyvat' novogo
tak kak im kosmologiya do lampochki , ot etogo ih zarplata
ne uvelichitsya, no zabanit' druguyu al'ternativnuyu tochku zreniya dlya nih v radost'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.08.2013 23:54, 4.4 KBait)
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
13.06.20122:45 |
|
Rasskaz
Fantasticheskii son o gorode fizikov.
Prisnilsya gorod fizikov, on sostoyal iz odnoi central'noi ulicy,
kotoraya razdelyala
pustynnye dikie prostory
klassicheskoi fiziki,
i plodonosyashie sady relyativistskoi fiziki.
Po pustynnym prostoram klassicheskoi fiziki skitalis' kakie-to
golodrancy neskol'ko bylo po
dvoe i po troe no v osnovnom odinochki,
hodili chto-to pisali na peske, koe kto iz al'ternativshikov provodil
kakie-to opyty na kostre poka gotovili edu.
Prakticheski
vse al'ternativshiki periodicheski i s raznym uspehom
uchastvovali v forumah
"skai-tyuh" i "zvezdomer".
Eti uchastki dorogi otlichalis' razmetkoi
ulicy, i nalichiem zabora
so storony relyativistov na "zvezdomere", zabor na "zvezdomere" ne
dlya togo chtoby al'ty ne lazili, a dlya togo chtoby
somnevayushiesya
relyativisty ne smogli ubezhat' ot moderatorskoi porki. Vozle forumnoi
razmetki s obeih storon periodicheski stoyali tolpy zevak i prihodili
oratory
to s toi a to s drugoi storony.
Na "skai-tyuhe" demokratii bylo pobol'she i vse orali drug na druga i periodicheski
rvali na sebe odezhdu i brosali cherez
dorogu, tam v nee vyshmarkivalis' i brosali
obratno.
Na "zvezdomere" reryativisty posle meryanii teleskopami i posle obeda v gos
stolovoi, pododvigalis'
i podkatyvalis' na svoih kreslah k doroge,
chtoby luchshe slyshat'.
Po sredine ulichnoi razmetki "zvezdomerovskogo" foruma stoyal - pletochnyh
shmaganii
master, - nesravnennyi moderator Bi-Be. On slavilsya tem chto ot
pryamyh voprosov uhodil svoimi otvetami v intellektual'noe begstvo.
Ot al'ternativshikov on treboval
dat' emu posmotret' teh pasport na efir,
i predostavit' opyty za kotorye mozhno nobelevskuyu poluchit' eshe vchera.
Estestvenno zapros na relyativistskii teh-pasport
na prichinu skorosti sveta vyzyvaet
shatanie v kreslah i bubnenie relyativistov o tom chto v nem net smysla,
a smysl est' v pasporte na efir.
Tak sobstvenno
v neponimanii i smotreli drug na druga.
Prodolzhenie
Rasskaz
Fantasticheskii son
o gorode fizikov.
Dal'she u dorogi relyativisty postavili tribu svoih dostizhenii
s trubnymi
fanfarami.
Na fanfarah
raznye nadpisi, - bez kotoryh relyativizm
byl by nevozmozhen.
Chtoby uiti ot efira pridumali fanfary ---- "vakuum"
Chtoby uiti ot sveta kotoryi byl
v efire, pridumali fanfary --- "foton"
Tak kak ne smogli pridumat'
kuda teplo devaetsya ot zvezd,
pridumali fanfary
- ---"bol'shoi vzryv",
tepla u zvezd okazalos' mnogo
i chtoby pogloshat' eshe teplo
ot zvezd pridumali fanfary -
--- "chernaya - dyra"
a energii okazalos' eshe bol'she,
pridumali fanfary ---" uskorennoe rasshirenie",
i neponyatno
chem prityagivaetsya
tokmo po dva tela pridumali fanfary --- "gravitaciya".
A na protiv tribuny s fanfarami raspolagalsya zritel'nyi zal
smeha
relyativistov, tak kak na tribunu s fanfarami periodicheski
zabegali odichavshie al'ty, oni pribegali s toi storony dorogi,
so storony klassicheskoi fiziki. I kogda
odichavshie al'ty v svoih
vozmushennyh rechah ispol'zovali slova isklyuchitel'no dlya
relyativistov, i oni sovpadali s nadpisyami na fanfarah, to vmesto
slov oni
duli v fanfary relyativistov.
Nekotorye dikie al'ty celye relyativistskie koncerty
ustraivali i vyduvali fugi , gorazdo
luchshe nekotoryh relyativistov. Relyativisty
osobo sil'no
smeyalis' kogda dikie al'ty ispol'zovali vse slova.
Vdrug zavisli v vozduhe udary plet'yu, master Bi-Be na "zvezdomere"
shmagal
vseh podryad a chtoby uvazhali.
Sobstvenno tak i zhili, klassicheskaya storona - pustynya bednosti,
i relyativistskie fruktovye sady s shokoladnymi kabinetami.
Po doroge to tam to tam probegali bobry, ih po druzheski bili
teleskopami s lyuboi storony ulicy.
Vot ya i prosnulsya.
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.08.2013 0:05, 772 Bait, otvetov: 2)
\\\Foton ogranichen v svoei skorosti 300.000 km/s
pronicaemost'yu prostranstva. Na dannoi skorosti foton proyavlyaetsya kak
fenomen, t.e. kak SVET. Pronicaemost' prostranstva - eto
sovokupnost' elektromagnitnyh i gravitacionnyh polei\\\
\\\I v tak nazyvaemoi "chernoi dyre"
etih kolebanii efira net\\\
Kak govoritsya ya relyativista uznayu po leksike.
Tak chto dlya menya Vy relyativist kotoryi hochet pereiti
na al'ternativnye temy,
i Vy yavno staraetes' derzhat'
nos po vetru, a tut u Vas takoe ogorchenie - chto mol
vse to est', - a vzyat' nel'zya, nado pridumyvat' chto-to
samostoyatel'no, a
etomu Vas nikto ne uchil - pryamo samozaklin kakoi-to.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(S. M. Andreichuk,
8.08.2013 19:58, 441 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Vy menya procitirovali i nazvali relyativistom. Kogda ya poznayu mir, to ishu svoi put'. Soglashus' s vami v odnom: podnimayas' po drevu poznaniya ya nastupayu na te vetki, kotorye
krepche - ne vazhno relyativistskie oni ili al'ternativnye, glavnoe chtoby ya podnimalsya vdol' stvola, a ne polz po odnoi iz vetok, kotoraya v konechnom itoge mozhet privesti k obrusheniyu...Daite
mne vremya, ya obyazatel'no izuchu vashu tochku zreniya i nam budet, chto obsudit'...))
- Re[3]: Chernaya dyra
(S. M. Andreichuk,
14.08.2013 15:44, 3.4 KBait)
Eto vsego lish' moya gipoteza, kotoraya zarodilas' pod vliyaniem gipotezy A.P. Vasi.
Eshe drevnie mudrecy ukazyvali na nalichie stihii, takih kak zemlya, voda, ogon' i vozduh. Po analogii, ves' material'nyi
mir simvoliziruet zemlyu, a efir, o kotorom Vy govorite vodu. Prishlo vremya nazvat' tret'yu stihiyu stihiyu ognya. Vy pridumali Zvezdu Efira, a ya nazyvayu sleduyushuyu ipostas'
Duh Sveta. Eto mental'nyi plan (nazovem ego tret'im planom), v otlichie ot Zvezdy Efira, kotoraya prebyvaet na tonkom plane (nazovem ego vtorym planom). Sledovatel'no, materiya grubyi plan (nazovem ego pervym planom).
Duh Sveta
ne mozhet vzaimodeistvovat' s materiei napryamuyu bez svoego posrednika efira, takzhe i efir yavlyaetsya absolyutno pronicaemym dlya materii bez Duha Sveta. Vzaimodeistvie Duha Sveta
s efirom sozdaet Zvezdu Efira i eto oblachenie soprovozhdaetsya reakciei ponizheniya temperatury, t.e. ohlazhdeniem. Vzaimodeistvie Zvezdy Efira s materiei soprovozhdaetsya vydeleniem
tepla. Materiya konsolidiruetsya vokrug Zvezdy Efira, i eto ob'yasnyaet prichinu potencii, kotoraya v posleduyushem razvorachivaet materiyu, uslozhnyaya ee formy. Zvezda Efira uvelichivaetsya
v razmerah, no odnovremenno uvelichivaetsya i material'naya obolochka (Zvezda Fiziki) vokrug nee. Na kakom-to etape nastupaet ravnovesnoe sostoyanie mezhdu massoi Zvezdy Efira i
okruzhayushei ee material'noi obolochkoi. A dalee chasha vesov sklonyaetsya v storonu Zvezdy Efira, t.k. ona stanovitsya tyazhelee Zvezdy Fiziki i nachinaetsya starenie materii (planeta
stanovit'sya bolee zasushlivoi, chelovek bolee dryahlym). V konechnom itoge, material'naya obolochka perestaet vypolnyat' svoi funkcii i Zvezda
Efira pokidaet svoe material'noe telo. Zvezda Efira uvelichivaet svoyu massu bystree eshe i potomu, chto Duh Sveta tozhe rastet i On, v bol'shei stepeni, provociruet situaciyu so
stareniem material'noi obolochki, potomu chto rost Zvezdy Efira podtalkivaetsya rostom Duha Sveta.
Svet
v chistom vide ot Duha Sveta ne proyavlyaetsya na material'nom plane. On mozhet proyavit'sya tol'ko cherez svoego posrednika efirnyi plan. Samyi ogromnyi Duh Sveta v nashei Galaktike
sosredotochen v ee centre, Zvezda Efira etogo centra nabiraet massu material'nogo plana, sopostavimuyu svoemu efirnomu telu Zvezde
Efira. Poka etoi massy nedostatochno centr Galaktiki ostaetsya samym holodnym mestom v nashei Galaktike, no postepenno idet razogrev. Etot process ne budet nosit' vzryvnoi harakter.
Skoree vsego, etogo budet proishodit' postepenno i svet ot centra Galaktiki budet stanovit'sya vse intensivnei i intensivnei, a material'naya obolochka (Zvezda Fiziki centra
Galaktiki) vse goryachei i goryachei.
Hochu predpolozhit', chto esli Duh Sveta cheloveka budet
razvivat'sya bolee intensivno, to uzhe v etoi zhizni nasha material'naya obolochka (Zvezda Fiziki) nachnet svetit'sya podobno solnechnomu svetu. Pri etom temperatura material'noi obolochki
uvelichitsya i skoree vsego sama materiya kachestvenno vyidet na novyi uroven', t.e. budet bolee plastichnoi.
Vot kak-to tak...))
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.08.2013 22:03, 814 Bait)
Vy ne pravil'no traktuete zvezdu efira,
eto prosto efir kondensirovannyi v tverdom
i zhidkom sostoyanii, a \zvezda fiziki\ - eto staroe
nazvanie kotoroe ya
uzhe ne ispol'zuyu, po prichine
togo chto eto prakticheski vse zvezdy i planety -
a tochnee vse tela u kotoryh est' prityazhenie,
sledovatel'no net smysla v etom
nazvanii.
Vyrazhenie Duh Sveta - eto voobshe kakoi-to
absurd. I esli chto-to pishite, - to nachinaite
s oglasheniya togo chto Vy lichno pridumali i zachem,
i chto imenno reshaet eta pridumka. Vy ya tak ponimayu eshe
ne vse prochitali, u menya resheny vse voprosy.
I esli Vy kosmologiei zanyalis' to Vy - kosmolog, -
a sledovatel'no moimi pridumkami Vy ne pol'zuites',
pridumyvaite chto-to svoe. Ili zhdite kogda ya napishu
stat'yu i togda na nee ssylaites'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.08.2013 22:05, 79 Bait, otvetov: 1)
Esli chestno to u Vas glupost' nesusvetnaya bessmyslennaya
i bespoleznaya.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(S. M. Andreichuk,
14.08.2013 22:54, 820 Bait)
Glupost' - eto ne logichnost' i ne sootvetstvie zdravomu smyslu. Mne kazhetsya, chto esli postoyanno zadumyvat'sya o logike i o zdravom smysle, to mozhno vsyu zhizn' toptat'sya na odnom
meste. Inogda chelovek dolzhen myslit' ne standartno i sovershat' ne standartnye postupki. Vas ved' tozhe relyativisty nazyvayut glupym chelovekom, no Vy ved' ot etogo ne poglupeli?
A k voprosu ispol'zovaniya svoei terminologii - ne dumayu chto eto vsegda vernoe reshenie. Mne Vasha Zvezda Efira vpolne po dushe. No esli Vy principial'no protiv, to ya naidu nazvanie
etomu ponyatiyu. Vazhno ne eto, vazhno to chto mne Vasha ideya bolee-menee ponyatna i blizka. Pochemu ya ne mogu ee razvivat' v al'ternativnom ot Vashego napravlenii. Ya zhe ne prisvaivayu
ei status "moe lichnoe", a pryamo govoryu, chto eta gipoteza zarodilas' pod vliyaniem Vashei gipotezy...
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.08.2013 23:36, 1.1 KBait)
Mne do lampochki to chto Vy pishite.
Vy ne fizik i ne kosmolog, Vy halyavshik
i hotite bystroi hayavnoi slavy.
Vy dazhe ne mozhete dat' opredeleniya fizicheskogo,
ne mozhete nichego obosnovat', Vash tekst
daite pochitat' lyubomu - Vam skazhut
chto eto idiotizm ne imeyushii smysla.
U Vas dazhe ne hvataet intellekta dat'
opredelenie
moih idei v Vashem ponimanii, chtoby dlya chitayushego
ustranit' semanticheskii shum, ya tak ponimayu chto to
chto ya govoryu Vy v principe ne ponimaete, po
prichine
Vashego bol'shogo vozrasta, - Vy estestvenno mozhete
do oduri stuchat' po klaviature s pretenziei na fizichnost'
pechataemogo Vami teksta - no mogu Vam
skazat' chto u Vas
net dazhe umeniya logicheski slozhit' logicheskuyu
posledovatel'nost', Vas etomu nikto i nikogda ne uchil,
a Vy dumaete chto vot tak i srazu v
nauku, i vsem rasskazyvat'
kak prisedat' i skol'ko raz i kak delat' ku krasivo.
Nu che slabo napisat' chto Vy lichno sami pridumali i zachem -
vot to-to,
obshenie s Vami prekrashayu. Moi idei ne
trogaite - pridumaite svoi, ili poprosite kogo-to chtoby
Vam nazvaniya dali Vashih idei, esli Vy sami ne v sostoyanii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.08.2013 0:04, 979 Bait)
\\\No esli Vy principial'no protiv, to ya naidu
nazvanie
etomu ponyatiyu. Vazhno ne eto, vazhno to chto mne Vasha ideya bolee-menee
ponyatna i blizka. Pochemu ya ne mogu ee razvivat' v al'ternativnom ot
Vashego napravlenii. Ya zhe ne prisvaivayu
ei status "moe lichnoe", a pryamo govoryu, chto eta gipoteza zarodilas' pod
vliyaniem Vashei gipotezy\\\
U menya ne gipoteza i ne teoriya, u menya sleduyushaya - model', v kotoroi bol'she semi teorii.
Vy hot' vnimatel'no prochtite
etu vetku foruma snachala, - tam ya pisal
pro chernye dyry, kogda odin yuzer vmesto togo chtoby voiti v istoriyu
navechno s rentgenovskimizvezdami, nazvav ih i dav im
opredelenie,
tak etot yuzer napisal trista statei o chernyh dyrah s rentgenovskimi
svoistvami, dazhe ne ponimaya togo chto - chernye dyry - budut v vekah
isklyuchitel'no
v avtorskom opredelenii, - ya dazhe ne znayu kak
takuyu buetu ya tut Vam ob'yasnyayu, eto ved' i tak - yasnyi kon'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.08.2013 0:22, 426 Bait, otvetov: 1)
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(S. M. Andreichuk,
15.08.2013 9:06, 627 Bait)
Hochu skazat', chto ya ne stradayu tsheslaviem i mne uzh tem bolee ne nuzhna chuzhaya slava - ya prosto delyus' svoimi myslyami. Ya vizhu, chto Vy na vernom puti, no Vam
meshaet odno "no" - eto to, chto Vy pytaetes' svoi teorii (uveren, chto u nih est' budushee), kotorye otnosyatsya k tonkomu planu izmerit' fizicheskim instrumentom.
Eto ravnosil'no popytke poimat' solnechnogo zaichika na stene, chtoby ponyat' ego sushnost'. Esli Vam nravitsya monolog na forume, nu chto zh... V lyubom sluchae ya Vam
blagodaren za Vashi mysli, est' nad chem porazmyshlyat'. Zhal', chto dialog na etoi vetke vsegda zakanchivaetsya monologom... Udachi Vam i dal'neishego ozareniya!
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.08.2013 15:33, 2.0 KBait)
\\\
Ves'ma nashumevshaya novost':
S
pomosh'yu HST obnaruzheno, chto 11,5 mlrd. let nazad galaktiki malo
otlichalis' ot nyneshnih - t.e. byli nepravil'nye, spiral'nye,
ellipticheskie. No eto ne samoe strannoe - okazalos', chto uzhe togda
vstrechalis' starye ellipticheskie galaktiki, spektr kotoryh ukazyvaet na
ves'ma preklonnyi vozrast vhodyashih v sostav zvezd! Drugimi slovami,
poluchaetsya, chto v srednem, galaktiki za 11,5 mlrd. let niskol'ko
prodvinulis' v svoei evolyucii!
Original:
Galaxies
Had Mature Shapes 11.5 Billion Years Ago Na russkom:
Drevneishie
galaktiki podozritel'no pohozhi na nyneshnie\\\
Ya vot vsetaki ne ponimayu astronomov uchat prepodavateli
so vsem soglashat'sya chto ih uchili, i ne uchat
dumat' samostoyatel'no,
i yavno ne uchat vsyakuyu neskladushku i neudachnye popytki v stroitel'stve
astronomicheskih osnov proshlyh pokolenii v kotorye ne vyderzhivayut
nikakoi sovremennoi kritiki.
Estestvenno ya dogadyvayus' pochemu boyatsya, pomnyat Stalina,
kotoryi uchennyh po prostomu v stile - kritikuesh' to predlagai al'ternativu,
predlozhil togda voploshai v ustroistvo, sdelal ustroistvo - nesi otvetstvennost'
za ego rabotu,
- i ishodya iz etogo estestvenno luchshe dazhe ne kritikovat'
nikogo. Stalina davno net a kritikovat' boyatsya budut navernoe eshe dolgo.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.08.2013 23:14, 940 Bait)
Kolonka
Dmitrii Vibe
Mozhet byt', astronomiya v shkole vse-taki nuzhna?-------------------------
Dazhe v moi shkol'nye gody tak kak prepodavalas'
astronomiya to luchshe by ne prepodavali ee voobshe.
I prichin tomu - s moei tochki zreniya tri,
pervoe knizhki soderzhat ochen' sil'no ustarevshie
kosmologicheskie
vzglyady, mnogoe protivorechit zdravomu smyslu
vtoraya prichina napisany skuchno i tret'ya prichina prepodavali
astronomiyu lyubye prepodavateli lyubyh predmetov.
S moei tochki zreniya otmena astronomii pravil'nyi
shag na sem'desyat procentov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A. A. Volkov,
19.08.2013 13:12, 1.6 KBait)
Uvazhaemyi A.P. Vasi, Vy ne predstavlyaete na skol'ko Vy pravy
v svoei dogadke:
...Drugimi slovami, poluchaetsya, chto v srednem, galaktiki za
11,5 mlrd. let niskol'ko prodvinulis' v svoei evolyucii!...
Zarozhdenie, razvitie i ischeznovenie Galaktik podchinyaetsya
odnotipnomu processu - Zakonu. Etot Zakon vklyuchaet v sebya
princip vzaimodeistviya Sil obrazuyushih Kosmicheskoe Prostranstvo.
Sovremennaya Kosmologiya, osnovannaya na usherbnyh predstavleniyah
"drevnih", prodolzhaet ih tradicionnye vzglyady. A imenno:
"...Sushestvuet Prostranstvo..., v Prostranstve sushestvuyut Tela...,
Tela nahodyatsya v dvizhenii..."
Ostaetsya tol'ko nadeyat'sya na to, chto sovremennye issledovaniya
"polyarnyh missii" kosmicheskih apparatov, posylaemyh k planetam
Solnechnoi Sistemy, rezul'taty obrabotki dannyh s "Voyadzherov",
napravlennyh k "polyusam" Sistemy i rezul'taty issledovaniya
elektromagnitnyh processov, proishodyashih na granice zhidkogo yadra
i mantii planety, sostykuyutsya ))) v MAS, a ne ostanutsya sekretom
v "analah" JPL NASA
Tol'ko posle etogo budet priznano to, chto poka oshibochno
zamalchivaetsya. A imenno:
"...Sushestvuet Prostranstvo...,
v Prostranstve sushestvuet Dvizhenie...,
v rezul'tate vzaimodeistviya Dvizhenii obrazuyutsya Tela..."
Zakon dvizheniya v Prostranstve ogranichen v svoih variantah.
A potomu i to "raznoobrazie" Galaktik, skol' ih ni klassificirui,
tak zhe ogranicheno opredelennym chislom )))
Do "seichas", i v nastoyashee vremya, i posle...
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
21.08.2013 21:40, 1.4 KBait)
Da uzh ya takoe ne tak chasto vizhu, - uzhastiki
astromyshleniya kak dlya menya.
A dlya kogo - astronomiya v prekrasnom ee vide.
Esli al'ternativshik budet
podobnye idei
rasskazyvat' - to eto taki al'ternativshik,
no s ideyami stoletnei davnosti.
--------------------------
Slabonervnyh al'ternativshikov
- bol'shaya
pros'ba ne smotret' eto.
-------------------
vk.com/club3738734
Zhurnal
"Zemlya i Vselennaya" Astronom Dmitrii Vibe o protozvezdah, otkrytii spektroskopii i gravoturbulentnoi modeli zvezdoobrazovaniya
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.08.2013 14:55, 887 Bait)
Re:
Chernye dyry - dyry v prostranstve ili v nauke?
------------------------
Prochital
str.23 i mne lichno kak-to
neudobno i zhalko ih, na stol'ko oni zabreli
svoimi vydumkami prakticheski v idiotizm,
i al'ty uzhe k nim ne pridut i ne vstavyat
im intellektual'nyi piston - chtoby oni
vyshli iz nadumannogo sebe mira,
s pretenziei na fizichnost',
kotoromu ih nakruchivali desyatiletiyami.
A al'tov
to oni v itoge zrya prognali,
samostoyatel'no oni ne vyberutsya iz etogo
bolota, vyhodit' to nado iz nego po-odnomu
a kollektivizm im etogo ne dast,
oni
to tol'ko v krugu relyativizma sebya horosho
chuvstvuyut - tipa umnye - kak vse.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.08.2013 15:49, 1.1 KBait)
Kak-to davno videl v vannoi zalityi pol prozrachnyi
s morskimi kamnyami i morskoi tematikoi.
Sobstvenno chto bylo ochen' zametno tak eto
ochen' vysokaya prozrachnost'
epoksidnoi smoly
i prakticheski polnoe otsutstvie zheltizny.
I vot chto ya pridumal.
Esli vzyat' listovoi steklokarbolit prozrachnyi,
tolshinoi millimetra tri,
vyrezat' iz nego dva
kruga diametrom v poltora metra, ili metr, i
sdelat' kol'co s bortikami iz stali tolshinoi
millimetrov dvadcat', i v eto kol'co vkladyvaetsya
v gorizontal'nom polozhenii dva kruga, mezhdu
krugami na krayu sverlitsya dyrka millimetra
tri v diametre i v nee vstavlyaetsya trubka,
vse delaetsya germetichno,
i tak chtoby potom
mozhno bylo razobrat'.
Snachala otkachivaetsya vozduh mezhdu karbolitom,
posle etogo tuda zakachivaetsya prozrachnaya epoksidnaya smola,
medlenno
no uverenno.
Po skol'ku kraya kapital'no zafiksirovany,
to iznachal'no poluchaetsya dlinnofokusnaya linza,
Estestvenno zdes' nado chtoby ne poluchilos'
situacii
kotoraya byvaet u epoksidnoi smoly i org steklom,
eto kogda posle zatverdevaniya epoksidnoi smoly ona
ot org stekla ottalkivaetsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2013 13:44, 1.5 KBait)
 Re: Novyi vzglyad na fiziku chastic.
Re: Novyi vzglyad na fiziku chastic.
Otvet #5 - Segodnya :: 11:48:54
---------------------
V principe dostatochno prosto ponimat'
chto lyubye fizicheskie
teorii eto fantaziya i
fantastika. Est' estestvenno i iznachal'no
slabye takie kak bol'shoi vzryv, v kotorom izluchenie opredelennogo veshestva s opredelennoi dlinnoi
volny s kakogo-to reshili nazvat' kolebaniem prostranstva, hotya na samom dele izluchaet opredelennoe veshestvo i eto izvestno s 1941goda.
Lichno ya dumayu chto esli by
v Rossii ne bylo RAN,
to na nee izgotoviteli naukoemkoi produkcii i ne nadeyalis' by, i u nih by byli svoi instituty pri zavodah kotorye by reshali nuzhnye nauchnye voprosy,
kak sobstvenno eto est' naprimer v shtatah.
A to chto fundamental'naya nauka poshla v neponyatnom napravlenii tak etomu prichina izvestna - finansirovali tol'ko odni
napravleniya, a al'ternativnye drugie idei posylali v peshee eroticheskoe puteshestvie.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2013 23:31, 2.2 KBait)
http://www.veinik.ru/science/anomal/article/919.html
\\\ "Reliktovoe izluchenie"
- kosmicheskoe elektromagnitnoe izluchenie, prihodyashee na Zemlyu so vseh
storon neba primerno s odinakovoi intensivnost'yu i imeyushee spektr,
harakternyi dlya izlucheniya absolyutno chernogo tela pri temperature okolo
3K (3 gradusa po absolyutnoi shkale Kel'vina, chto sootvetstvuet 270S).
Pri takoi temperature osnovnaya dolya izlucheniya prihoditsya na radiovolny
santimetrovogo i millimetrovogo diapazonov. Plotnost' energii
reliktovogo izlucheniya 0,25 eV/sm3.
V 1941 godu kanadskii
astronom Endryu Mak-Kellar (Andrew McKellar, 1910-1960) analiziroval
linii poglosheniya, vyzyvaemye v spektre zvezdy 2 Zmeenosca mezhzvezdnymi
molekulami ciana (soedineniya ugleroda i azota). On prishel k vyvodu, chto
eti linii (v vidimoi glazom oblasti spektra) mogut voznikat' tol'ko pri
pogloshenii sveta vrashayushimisya molekulami ciana. Prichem vrashenie ih
dolzhno vozbuzhdat'sya izlucheniem s temperaturoi okolo 2,3 Kel'vina. Ni
sam Mak-Kellar, ni kto drugoi, konechno, ne podumali togda o vozmozhnosti
togo, chto vrashenie molekul vyzyvaetsya reliktovym izlucheniem. Da i sama
teoriya goryachego Bol'shogo vzryva Vselennoi poyavilas' tol'ko v 1946 godu!
Reliktovoe izluchenie
obnaruzhil v 1955 godu aspirant-radioastronom Tigran Aramovich Shmaonov
(1932 g.r.). Pervoe opublikovannoe priznanie izlucheniya poyavilos' vesnoi
1964 goda v kratkoi stat'e A.R. Doroshkevicha i I.D. Novikova,
ozaglavlennoi "Srednyaya plotnost' izlucheniya v metagalaktike i nekotorye
voprosy relyativistskoi kosmologii" [Doklady AN SSSR, t.154, vyp.4, str.
119-121 (809-811)]. Mikrovolnovoe fonovoe izluchenie nazval "reliktovym" sovetskii astrofizik
Iosif Samuilovich Shklovskii (1916-1985) v 1978 godu [gazeta "Sovetskaya Rossiya", 20.08.1978].
Naryadu s kosmologicheskim
krasnym smesheniem, reliktovoe izluchenie rassmatrivaetsya kak odno iz
glavnyh podtverzhdenii teorii Bol'shogo vzryva.\\\
-------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2013 23:33, 2.1 KBait)
http://www.veinik.ru/science/anomal/article/919.html
\\\ "Reliktovoe izluchenie"
- kosmicheskoe elektromagnitnoe izluchenie, prihodyashee na Zemlyu so vseh
storon neba primerno s odinakovoi intensivnost'yu i imeyushee spektr,
harakternyi dlya izlucheniya absolyutno chernogo tela pri temperature okolo
3K (3 gradusa po absolyutnoi shkale Kel'vina, chto sootvetstvuet 270S).
Pri takoi temperature osnovnaya dolya izlucheniya prihoditsya na radiovolny
santimetrovogo i millimetrovogo diapazonov. Plotnost' energii
reliktovogo izlucheniya 0,25 eV/sm3.
V 1941 godu kanadskii
astronom Endryu Mak-Kellar (Andrew McKellar, 1910-1960) analiziroval
linii poglosheniya, vyzyvaemye v spektre zvezdy 2 Zmeenosca mezhzvezdnymi
molekulami ciana (soedineniya ugleroda i azota). On prishel k vyvodu, chto
eti linii (v vidimoi glazom oblasti spektra) mogut voznikat' tol'ko pri
pogloshenii sveta vrashayushimisya molekulami ciana. Prichem vrashenie ih
dolzhno vozbuzhdat'sya izlucheniem s temperaturoi okolo 2,3 Kel'vina. Ni
sam Mak-Kellar, ni kto drugoi, konechno, ne podumali togda o vozmozhnosti
togo, chto vrashenie molekul vyzyvaetsya reliktovym izlucheniem. Da i sama
teoriya goryachego Bol'shogo vzryva Vselennoi poyavilas' tol'ko v 1946 godu!
Reliktovoe izluchenie
obnaruzhil v 1955 godu aspirant-radioastronom Tigran Aramovich Shmaonov
(1932 g.r.). Pervoe opublikovannoe priznanie izlucheniya poyavilos' vesnoi
1964 goda v kratkoi stat'e A.R. Doroshkevicha i I.D. Novikova,
ozaglavlennoi "Srednyaya plotnost' izlucheniya v metagalaktike i nekotorye
voprosy relyativistskoi kosmologii" [Doklady AN SSSR, t.154, vyp.4, str.
119-121 (809-811)]. Mikrovolnovoe fonovoe izluchenie nazval "reliktovym" sovetskii astrofizik
Iosif Samuilovich Shklovskii (1916-1985) v 1978 godu [gazeta "Sovetskaya Rossiya", 20.08.1978].
Naryadu s kosmologicheskim
krasnym smesheniem, reliktovoe izluchenie rassmatrivaetsya kak odno iz
glavnyh podtverzhdenii teorii Bol'shogo vzryva.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2013 23:56, 11.8 KBait)
Esli vzyat' kupyuru i posmotret' na nee
pod ul'trafioletovym izlucheniem - vot
i ya sobstvenno ne mogu ponyat' kak i po kakoi
prichine uzory na kupyure v raznyh
cvetah,
prichinoi kotoromu po analogii
mozhno bylo otnesti k reliktovomu izlucheniyu
prostranstva.
---
\\\Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
Fluorescénciya (variant: flyuorescenciya) fizicheskii process, raznovidnost' lyuminescencii.
Fluorescenciei obychno nazyvayut izluchatel'nyi perehod vozbuzhdennogo
sostoyaniya s samogo nizhnego singletnogo kolebatel'nogo urovnya S1 v osnovnoe sostoyanie S0. V obshem sluchae fluorescenciei nazyvayut razreshennyi po spinu izluchatel'nyi perehod mezhdu dvumya
sostoyaniyami odinakovoi mul'tipletnosti: mezhdu singletnymi urovnyami 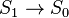 ili tripletnymi
ili tripletnymi 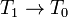 . Tipichnoe
vremya zhizni takogo vozbuzhdennogo
sostoyaniya sostavlyaet 10−11−10−6 s.
. Tipichnoe
vremya zhizni takogo vozbuzhdennogo
sostoyaniya sostavlyaet 10−11−10−6 s.
Fluorescenciyu sleduet otlichat' ot fosforescencii
zapreshennogo po spinu izluchatel'nogo perehoda mezhdu dvumya sostoyaniyami
raznoi mul'tipletnosti. Naprimer, izluchatel'nyi perehod vozbuzhdennogo
tripletnogo sostoyaniya T1 v osnovnoe sostoyanie S0. Singlet-tripletnye perehody imeyut kvantovo-mehanicheskii zapret, poetomu vremya zhizni vozbuzhdennogo sostoyaniya pri fosforescencii sostavlyaet
poryadka 10−3−10−2 s.
\\\
\\\
Soglasno predstavleniyam kvantovoi
himii, elektrony v atomah raspolozheny na energeticheskih
urovnyah.
Rasstoyanie mezhdu energeticheskimi urovnyami v molekule zavisit ot ee
stroeniya. Pri obluchenii veshestva svetom vozmozhen perehod elektronov
mezhdu razlichnymi energeticheskimi urovnyami. Raznica energii mezhdu
energeticheskimi urovnyami i chastota kolebanii pogloshennogo sveta
sootnosyatsya mezhdu soboi uravneniem (III postulat Bora):

Posle poglosheniya sveta chast' poluchennoi sistemoi energii rashoduetsya v rezul'tate relaksacii.
Chast' zhe mozhet byt' ispushena v vide fotona opredelennoi energii.
Spektr fluorescencii sdvinut otnositel'no spektra poglosheniya v storonu dlinnyh voln. Eto yavlenie poluchilo nazvanie Stoksov
sdvig.
Ego prichinoi yavlyayutsya bezyzluchatel'nye relaksacionnye processy. V
rezul'tate chast' energii pogloshennogo fotona teryaetsya, a ispuskaemyi
foton imeet men'shuyu energiyu, i, sootvetstvenno, bol'shuyu dlinu volny.[1]
Shematicheski processy poglosheniya sveta i fluorescencii pokazyvayut na diagramme Yablonskogo.
Pri normal'nyh usloviyah bol'shinstvo molekul nahodyatsya v osnovnom elektronnom sostoyanii  . Pri pogloshenii sveta molekula perehodit v vozbuzhdennoe sostoyanie
. Pri pogloshenii sveta molekula perehodit v vozbuzhdennoe sostoyanie  .
Pri vozbuzhdenii na vysshie elektronnye i kolebatel'nye urovni izbytok
energii bystro rashoduetsya, perevodya fluorofor na samyi nizhnii
kolebatel'nyi poduroven' sostoyaniya
.
Pri vozbuzhdenii na vysshie elektronnye i kolebatel'nye urovni izbytok
energii bystro rashoduetsya, perevodya fluorofor na samyi nizhnii
kolebatel'nyi poduroven' sostoyaniya  . Odnako, sushestvuyut i isklyucheniya:
naprimer, fluorescenciya azulena mozhet proishodit' kak iz
. Odnako, sushestvuyut i isklyucheniya:
naprimer, fluorescenciya azulena mozhet proishodit' kak iz  ,
tak i iz
,
tak i iz  sostoyaniya.
sostoyaniya.
Kvantovyi vyhod fluorescencii pokazyvaet, s kakoi effektivnost'yu
prohodit dannyi process. On opredelyaetsya kak otnoshenie kolichestva
ispuskaemyh i pogloshaemyh fotonov. Kvantovyi vyhod fluorescencii mozhet
byt' rasschitan po formule

gde 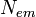 kolichestvo ispuskaemyh v rezul'tate fluorescencii
fotonov, a
kolichestvo ispuskaemyh v rezul'tate fluorescencii
fotonov, a 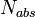 obshee kolichestvo pogloshaemyh fotonov. Chem
bol'she kvantovyi vyhod fluorofora, tem intensivnee ego
fluorescenciya. Kvantovyi vyhod mozhno takzhe opredelit' s pomosh'yu uproshennoi diagrammy Yablonskogo[2],
gde
obshee kolichestvo pogloshaemyh fotonov. Chem
bol'she kvantovyi vyhod fluorofora, tem intensivnee ego
fluorescenciya. Kvantovyi vyhod mozhno takzhe opredelit' s pomosh'yu uproshennoi diagrammy Yablonskogo[2],
gde  i
i 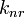 konstanty skorosti izluchatel'noi i bezyzluchatel'noi dezaktivacii vozbuzhdennogo sostoyaniya.
konstanty skorosti izluchatel'noi i bezyzluchatel'noi dezaktivacii vozbuzhdennogo sostoyaniya.
Togda dolya fluoroforov, vozvrashayushihsya v osnovnoe sostoyanie s ispuskaniem fotona, i, sledovatel'no, kvantovyi vyhod:

Iz poslednei formuly sleduet, chto  esli
esli
 ,
to est' esli skorost' bezyzluchatel'nogo perehoda znachitel'no men'she
skorosti izluchatel'nogo perehoda. Otmetim, chto kvantovyi vyhod vsegda
men'she edinicy iz-za stoksovyh
poter'.\\\
,
to est' esli skorost' bezyzluchatel'nogo perehoda znachitel'no men'she
skorosti izluchatel'nogo perehoda. Otmetim, chto kvantovyi vyhod vsegda
men'she edinicy iz-za stoksovyh
poter'.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.08.2013 1:23, 1.1 KBait)
Tak vot - v 1941godu otkryto chto u zvezdy
gazy v prostranstve poluchayut vozbuzhdenie
ot zvezdy na odnoi chastote a izluchayut na drugoi
chastote - nu eto sobstvenno
ponyatno.
Sobstvenno ponyatno i drugoe chto prakticheski
u vseh zvezd est' analogichnaya situaciya.
Vnimanie - zvezda svetit - zatrachivaet svoyu
energii kotoraya
veshestvom - gazom v prostranstve
vozle zvezdy pereizluchaetsya na drugoi chastote.
Vopros - pri chem zdes' bol'shoi vzryv v principe,
i kakaya mozhet byt' vzaimosvyaz'
s ehom ot bol'shogo
vzryva - eli energiya dlya podderzhaniya etogo
processa ispol'zuetsya iz zvezd kotorye svetyat
v tekushii moment vremeni.
---
Vyvod - bol'shoi vzryv ne imeet nikakih
podtverzhdenii svyazannyh s \\\ehom bol'shogo vzryva\\\
tak kak otsutstvuet prichinno sledstvennaya svyaz'
mezhdu tem chto
pereizluchaetsya veshestvom v osnove
energii kotoroi yavlyaetsya zvezda, i ehom ot bol'shogo
vzryva - sobstvenno eho bol'shogo vzryva dolzhno
byt' postoyannym istochnikom
energii dlya podderzhaniya
pereizlucheniya - chto otsutstvuet v principe.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.08.2013 1:37, 335 Bait)
Vot otsutstvie takoi melochi kak logicheskaya
vzaimosvyaz' mezhdu pereizluchniem i bol'shim
vzryvom - sdelalo bessmyslennym, s moei tochki zreniya,
okolo devyanosto
pyati procentov vsego chto est' na etom
saite, sobstvenno vsya kosmologiya okazalas' v prostracii.
Te kto veryat v svoi teorii eto eshe ne skoro poimut.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.09.2013 23:40, 2.7 KBait)
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.09.2013 23:52, 4.4 KBait)
Avgustina
Zavsegdatai foruma

 Na Forume
Na Forume

Soobshenii: 1146
Pol:

 Re: Nesootvetstvie s teoriei bol'shogo vzryva?
Re: Nesootvetstvie s teoriei bol'shogo vzryva?
Otvet #548 - Segodnya :: 22:41:40
.ToriMalkaway pisal(a) Segodnya :: 14:30:47:No fizicheski eto dolzhno v chem-to vyrazhat'sya.
Ono i vyrazhaetsya v millivol'tah na metr
.ToriMalkaway pisal(a) Segodnya :: 14:30:47:Napryazhennost' - skoree matematicheskoe ponyatie, abstrakciya
chego-to.
Net. Eto ne abstrakciya. Chem Vy naprimer, smozhete vyrazit' sam fakt, chto
pruzhina szhata? Krome, kak napryazhennost'yu - nichem. Pruzhinu mozhno szhat'
ili rastyanut'. I szhat' libo sil'nee, libo slabee.
Eto zhe ne abstraktnye, a vpolne ponyatnye fizicheskie harakteristiki veshestva. Takie zhe kak davlenie, temperatura.
EM-pole
vo Vselennoi imeet nulevuyu napryazhennost'. Analogichno poverhnost' vody
mozhet imet' zerkal'nuyu, ne vozmushennuyu poverhnost'. Ili vozduh vokrug
nas mozhet sovsem ne dvigat'sya. V takom vozdue budet polnaya tishina.
No
esli poverhnost' vody chto-to budet vozmushat', Vy uvidite volny. Esli
vozduh budet chto to vozmushat' - Vy uslyshite zvuk. A vot esli chto to
budet vozmushat' EM-pole, to bez special'noi apparatury (radiopriemnika)
radiovoln i ne uvidet', i ne uslyshat'. No sam fakt vozmozhnosti
radiosvyazi dokazyvaet, chto radiovolny sushestvuyut. I proyavlyayutsya v tom,
chto pri ih nalichii - v antenne voznikaet E.D.S. (elektrodizhushaya sila).
I poskol'ku EM-pole nevidimo i neslyshimo, my mozhem nablyudat' (s
pomosh'yu apparatury, konechno) tol'ko vozmusheniya (napryazhennost') etogo
polya.
.ToriMalkaway pisal(a) Segodnya :: 14:30:47:
Prosto obychnye volny my mozhem izuchat' doskonal'no, tak kak nam horosho
izvestna sreda. Elektromagnitnye - tozhe volny, no sreda ne dostupna dlya
izucheniya nashimi priborami, poetomu vvodyat abstraktnye ponyatiya.
Kto eto Vam skazal takuyu glupost'? I sreda dostupna, i pribory davno
est'. I pol'zuemsya radiosvyaz'yu uzhe bolee 100 let. Mobilkami von dazhe
deti doshkolyata uzhe umeyut pol'zovat'sya.
I esli est' zhelanie berite postoyannyi magnit i izuchaite hot' zaizuchaites'!
.ToriMalkaway pisal(a) Segodnya :: 14:30:47: A raz my ne znaem doskonal'no prirodu elektromagnitnyh
voln, to i o prichine krasnogo smesheniya mozhno tol'ko gadat'.
Beda ne v tom, chto
doskonal'no ne znaem. Beda v tom, chto svoimi mozgami dumat' mnogie ne hotyat.
Poetomu
to, chto s detstva vdolbili v shkole - tupo, kak popugai, povtoryayut. I
raz napisano v uchebnikah, chto smeshenie rezul'tat rasshireniya pustoty, to
vse etu chush' i povtoryayut.
---
Smeshno odnako
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.09.2013 17:46, 3.6 KBait)
Otvet #141 : Segodnya v 16:26:19
Da,
Vy, baten'ka, nastoyashii al't. V etom u menya bol'she net nikakih
somnenii. Poetomu i tusovku sebe vybiraete sootvetstvuyushuyu. To-to Anne
tak ponravilis' Vashi rassuzhdeniya i ona Vam, kak i prochim al'tam, plyusiki
stavit.
Kismet.
K vyvodam..
Chto
mozhno govorit', a chego "nel'zya" na etom forume mne izvestno horosho..
Kto-to, kogda-to, zachem-to reshil, chto nauchno, chto nenauchno....
Al'tov
vseh davno pouvol'nyali (pomni o Dem'yanove). Nekotorye popryatalis'
(pomni Ivana). Teper' prinyalis' za ortov (pomni o Danilove).
A rech' to idet o gryadushem vneshnem upravlenii RAN so storony Pravitel'stva i polnoi negotovnosti k etomu
RAN.
V
ponedel'nik nachnetsya Obshee sobranie RAN. Vot na Konferencii velos'
pryamoe internet-veshanie. Nadeyus', eta horoshaya tradiciya budet prodolzhena.
A
chego pryatat'sya-to? Nikto s fakelami ne begaet, i al'tov ne vyrezaet.
Hotite dokazat' chto-to svoe, tak dokazyvaite, razve eto zapresheno? No ne
zdes', na forume, dokazyvaite v zhizni. Provodite issledovaniya,
dobivaites' rezul'tatov, pishite stat'i. Tol'ko rezul'taty, t.e. fakty
mogut byt' dokazatel'stvom teorii. Net rezul'tatov, togda izvinite.
Pytayutsya okorotit' tol'ko teh, kto s svoimi strannymi ideyami obrashaetsya k
rukovodstvu, vyprashivaya den'gi. Vy zhe sami pisali, chto nado svoi
issledovaniya provodit' za svoi schet. Vot i provodite, i nikto k vam i ne
budet pristavat'.
----------------------------------------------------
Vot byvaet chto luchshe ne zvezdet' nichego na tot vopros v kotorom
ty ne v
kurse, chtoby potom ne otpechatat'sya u drugih
v soznanii i ne vyglyadet' vechnym idiotom, u mnogih
mnenie kak pravilo ne menyaetsya.
Tak vot nado slegka znat'
chto v gody repressii
vseh storonnikov efira repressirovali.
Sobstvenno na tekushii moment net ni odnogo specialista
po efiru ni v odnom referiruemom
zhurnale,
sobstvenno referirovanie eto sudeistvo, -
tak kak mogut sudit' o stat'e po efiru esli
net ni odnogo specialista po efiru, - pravil'no nikak,
vse stat'i po efiru vernut avtoru, i poshlyut
ego s referiruemogo zhurnala v peshee eroticheskoe
puteshestvie vmesti s ego stat'ei.
\\\Provodite issledovaniya,
dobivaites' rezul'tatov, pishite stat'i. Tol'ko rezul'taty, t.e. fakty
mogut byt' dokazatel'stvom teorii.\\\
Tak chto sovet pisat' stat'i al'tam -
mozhet dat' tol'ko umstvenno nepolnocennyi.
Al'ta yasnyi kon' nikto ne
pro-finansiruet.
I relyativisty na fakty opyta - davno kladut.
---
Vyvod - takie sovety mozhet davat' al'tam,
ili glupec ili ih vrag.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.09.2013 19:54, 1.6 KBait)
Otvet #755 : Segodnya v 18:39:17
Naskol'ko mogu sudit', na dele nikto "v pogone" vremya ne
izmeryal.
GPS


_________________________________________________ _____________
_________________________________________________ _____________



----------
Smeshno
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.09.2013 20:05, 941 Bait)
Ni kuya tam net relyativistskih popravok.
Delo v tom chto razrabotali zhps ne relyativisty,
a byvshie nemeckie professora na osnove dovoennyh
nemeckih tehnologii,
i osnovnye principy byli razrabotany
na skol'ko ya pomnyu v 1958godu.
Predydushee soobshenie chem sobstvenno krasivo
tem chto vvodit v zabluzhdenie chitayushego.
Delo v tom chto chasy elektronnye lyubye uskoryayut svoi temp,
i eto bylo zamecheno v opyte s vysokotochnymi chasami
na skol'ko pomnyu v tridcatyh godah proshlogo
veka.
Sobstvenno znaya to na skol'ko uvelichitsya chastota kvarca,
ego izgotavlivayut na bolee nizkuyu chastotu.
To chto eto relyativistskii effekt ya lichno ne
veryu,
ibo v ih teorii temp chasov zamedlyaetsya, a po faktu
temp uvelichivaetsya - al'ty ponimayut, a relyativisty pishut
tak chtoby byla ne ponyatna fizicheskaya sut'.
A esli
by oni pisali ponyatno to yasnyi kon' oni by pisali
protiv svoih postulatov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.09.2013 20:12, 10.0 KBait)
Na skol'ko ya pomnyu na membrane schitali
popravki dlya zhps po relyativistskim formulam,
tak ona okazalas' dlinnoi v odnu chetvertuyu dlinny
antenny, soshlis' na
tom chto esli takovaya i est'
to ona i darom ne nuzhna.
---------------------------
http://www.tracker.co.ua/gps_work.html
\\\ Kak rabotaet GPS
Kak rabotaet GPS
Sistema Global'nogo Pozicionirovaniya (GPS ili Global Positioning System)
yavlyaetsya sputnikovoi i rabotaet pod upravleniem Ministerstva Oborony
SShA. Sistema yavlyaetsya global'noi, vsepogodnoi i obespechivaet vozmozhnost'
polucheniya tochnyh koordinat i vremeni 24 chasa v sutki.
Osnovy sistemy GPS mozhno razbit' na pyat' osnovnyh podpunktov:
Sputnikovaya trilateraciya osnova sistemy
Sputnikovaya dal'nometriya izmerenie rasstoyanii do sputnikov
Tochnaya vremennaya privyazka zachem nuzhno soglasovyvat'
chasy v priemnike i na sputnike i dlya chego trebuetsya 4-i kosmicheskii
apparat
Raspolozhenie sputnikov opredelenie tochnogo polozheniya sputnikov v kosmose
Korrekciya oshibok uchet oshibok vnosimyh zaderzhkami v troposfere i ionosfere
1.1.1 Sputnikovaya trilateraciya

Tochnye koordinaty mogut byt' vychisleny dlya mesta na
poverhnosti Zemli po izmereniyam rasstoyanii ot gruppy sputnikov (esli ih
polozhenie v kosmose izvestno). V etom sluchae sputniki yavlyayutsya punktami s
izvestnymi koordinatami. Predpolozhim, chto rasstoyanie ot odnogo sputnika
izvestno i my mozhem opisat' sferu zadannogo radiusa vokrug nego.
Esli my znaem takzhe rasstoyanie i do vtorogo sputnika,
to opredelyaemoe mestopolozhenie budet raspolozheno gde-to v kruge,
zadavaemom peresecheniem dvuh sfer.
Tretii sputnik opredelyaet dve tochki na okruzhnosti.

Teper' ostaetsya tol'ko vybrat' pravil'nuyu tochku. Odnako
odna iz tochek vsegda mozhet byt' otbroshena, tak kak ona imeet vysokuyu
skorost' peremesheniya ili nahoditsya na ili pod poverhnost'yu Zemli. Takim
obrazom, znaya rasstoyanie do treh sputnikov, mozhno vychislit' koordinaty
opredelyaemoi tochki.
1.1.2 Sputnikovaya dal'nometriya
Rasstoyanie do sputnikov opredelyaetsya po izmereniyam
vremeni prohozhdeniya radiosignala ot kosmicheskogo apparata do priemnika
umnozhennym na skorost' sveta. Dlya togo, chtoby opredelit' vremya
rasprostraneniya signala nam neobhodimo znat' kogda on pokinul sputnik.

Dlya etogo na sputnike i v priemnike odnovremenno generiruetsya odinakovyi Psevdosluchainyi Kod*
* - Kazhdyi sputnik GPS peredaet dva radiosignala: na
chastote L1=1575.42 MGc i L2=1227.60 MGc. Signal L1 imeet dva
dal'nomernyh koda s psevdosluchainym shumom (PRN), P-kod i C/A kod.
Tochnyi ili P-kod mozhet byt' zashifrovan dlya voennyh celei. Grubyi ili
C/A kod ne zashifrovan. Signal L2 moduliruetsya tol'ko s P-kodom.
Bol'shinstvo grazhdanskih pol'zovatelei ispol'zuyut C/A kod pri rabote s
GPS sistemami. Nekotorye priemniki Trimble geodezicheskogo klassa
rabotayut s P-kodom.
Priemnik proveryaet vhodyashii signal so sputnika i
opredelyaet kogda on generiroval takoi zhe kod. Poluchennaya raznica,
umnozhennaya na skorost' sveta (~ 300000 km/s) daet iskomoe rasstoyanie.
Ispol'zovanie koda pozvolyaet priemniku opredelit'
vremennuyu zaderzhku v lyuboe vremya. Krome togo, sputniki mogut izluchat'
signal na odnoi i toi zhe chastote, tak kak kazhdyi sputnik
identificiruetsya po svoemu Psevdosluchainomu kodu (PRN ili PseudoRandom
Number code).
1.1.3 Tochnaya vremennaya privyazka

Kak vidno iz skazannogo vyshe, vychisleniya napryamuyu
zavisyat ot tochnosti hoda chasov. Kod dolzhen generirovat'sya na sputnike i
priemnike v odno i to zhe vremya. Na sputnikah ustanovleny atomnye chasy
imeyushie tochnost' okolo odnoi nanosekundy. Odnako eto slishkom dorogo,
chtoby ustanavlivat' takie chasy v kazhdyi GPS priemnik, poetomu izmereniya
ot chetvertogo sputnika ispol'zuyutsya dlya ustraneniya oshibok hoda chasov
priemnika.
Eti izmereniya mozhno ispol'zovat' dlya ustraneniya oshibok,
kotorye voznikayut esli chasy na sputnike i v priemnike ne
sinhronizirovany. Dlya naglyadnosti, illyustracii privedennye nizhe
rassmatrivayut situaciyu na ploskosti, tak kak tol'ko tri sputnika
neobhodimo dlya vychisleniya mestopolozheniya ob'ekta.

Esli chasy na sputnike i v priemnike imeyut odinakovuyu
tochnost' hoda, to tochnoe mestopolozhenie mozhet byt' naideno po izmereniyam
rasstoyaniya do dvuh sputnikov.
Esli polucheny izmereniya s treh sputnikov i vse chasy
tochnye, to krug opisannyi radius-vektorom ot tret'ego sputnika budet
peresekat'sya kak pokazano na risunke.
Odnako, esli chasy v priemnike speshat na 1 sekundu, to kartina budet vyglyadet' sleduyushim obrazom.
Esli sdelat' zamer do tret'ego sputnika, to poluchennyi radius-vektor ne peresechetsya s dvumya drugimi kak pokazano na risunke.

Kogda GPS priemnik poluchaet seriyu izmerenii kotorye ne
peresekayutsya v odnoi tochke, to komp'yuter v priemnike nachinaet vychitat'
(ili dobavlyat') vremya metodom posledovatel'nyh iteracii do teh por, poka
ne svedet vse izmereniya k odnoi tochke. Posle etogo vychislyaetsya popravka
i delaetsya sootvetstvuyushee uravnivanie.
Esli vam trebuetsya tret'e izmerenie, to neobhodim
chetvertyi sputnik dlya ustraneniya oshibok hoda chasov v priemnike. Takim
obrazom, pri rabote v pole vam neobhodimo imet' minimum chetyre sputnika,
chtoby opredelit' trehmernye koordinaty ob'ekta.
1.1.4 Raspolozhenie sputnikov

Sistema NAVSTAR imeet 24 rabochih sputnika s orbital'nym
periodom v 12 chasov na vysote primerno 20200 km ot poverhnosti Zemli. V
shesti razlichnyh ploskostyah imeyushih naklon k ekvatoru v 55 ,
raspolozheno po 4 sputnika. Ukazannaya vysota neobhodima dlya obespecheniya
stabil'nosti orbital'nogo dvizheniya sputnikov i umen'sheniya faktora
vliyaniya soprotivleniya atmosfery.
Ministerstvo Oborony SShA (DoD) osushestvlyaet nepreryvnoe
slezhenie za sputnikami. Na kazhdom sputnike raspolozheno neskol'ko
vysokotochnyh atomnyh chasov i oni nepreryvno peredayut radiosignaly s
sobstvennym unikal'nym identifikacionnym kodom*. MO SShA imeet 4 stancii
slezheniya za sputnikami, tri stancii svyazi i centr osushestvlyayushii
kontrol' i upravlenie za vsem nazemnym segmentom sistemy. Stancii
slezheniya nepreryvno otslezhivayut sputniki i peredayut dannye v centr
upravleniya. V centre upravleniya vychislyayutsya utochnennye elementy

sputnikovyh orbit i koefficienty popravok sputnikovyh
shkal vremeni, posle chego eti dannye peredayutsya po kanalam stancii svyazi
na sputniki po krainei mere odin raz v sutki.
* - Kazhdyi sputnik GPS peredaet dva radiosignala: na
chastote L1=1575.42 MGc i L2=1227.60 MGc. Signal L1 imeet dva
dal'nomernyh koda s psevdosluchainym shumom (PRN), P-kod i C/A kod.
Tochnyi ili P-kod mozhet byt' zashifrovan dlya voennyh celei. Grubyi ili
C/A kod ne zashifrovan. Signal L2 moduliruetsya tol'ko s P-kodom.
Bol'shinstvo grazhdanskih pol'zovatelei ispol'zuyut C/A kod pri rabote s
GPS sistemami. Nekotorye priemniki Trimble geodezicheskogo klassa
rabotayut s P-kodom.
1.1.5 Korrekciya oshibok
Nekotorye istochniki oshibok voznikayushih pri rabote GPS
yavlyayutsya trudnoustranimymi. Vychisleniya predpolagayut, chto signal
rasprostranyaetsya s nepreryvnoi skorost'yu, kotoraya ravna skorosti sveta.
Odnako v real'nosti vse gorazdo slozhnee. Skorost' sveta yavlyaetsya
konstantoi tol'ko v vakuume. Kogda signal prohodit cherez ionosferu (sloi
zaryazhennyh chastic na vysote 130-290 km) i troposferu, ego skorost'
rasprostraneniya umen'shaetsya, chto privodit k oshibkam v izmereniya
dal'nosti. V sovremennyh GPS priemnikah ispol'zuyut vsevozmozhnye
algoritmy ustraneniya etih zaderzhek.
Inogda voznikayut oshibki v hode atomnyh chasov i orbitah
sputnikov, no oni obychno neznachitel'ny i tshatel'no otslezhivayutsya so
stancii slezheniya.
Mnogoluchevaya interferenciya takzhe vnosit oshibki v
opredelenie mestopolozheniya s pomosh'yu GPS. Eto proishodit, kogda signal
otrazhaetsya ot ob'ektov raspolozhennyh na zemnoi poverhnosti, chto sozdaet
zametnuyu interferenciyu s signalami prihodyashimi neposredstvenno so
sputnikov. Special'naya tehnika obrabotki signala i produmannaya
konstrukciya antenn pozvolyaet svesti k minimumu etot istochnik oshibok.
Ran'she sushestvoval eshe odin istochnik oshibok eto
Izbiratel'nyi Dostup (Selective Availability ili S/A), iskusstvennoe
snizhenie tochnosti sputnikovogo signala vvodimoe MO SShA. Eto privodilo k
tomu, chto tochnost' poluchennyh koordinat s pomosh'yu GPS snizhalas' do 100
metrov. Odnako 1 maya 2000 goda po resheniyu prezidenta SShA "Izbiratel'nyi
Dostup" byl otklyuchen. Krome togo, S/A mozhno isklyuchit', primenyaya tehniku
differencial'noi korrekcii (sm. dalee).
Po motivam stat'i na www.gpsru.com\\\
--------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.09.2013 20:31, 452 Bait)
Dlya teh kto ne ponyal - po relyativistkim
teoriyam vremya u letayushego na orbite
blizneca - chto delaet - pravil'no zamedlyaesya,
relyativistskie chasy na svetovom
luche chto delayut,
pravil'no zamedlyayutsya, na visyashih nad odnoi
tochkoi nad zemlei ili dvizhushihsya po orbite,
kvarcevye generatory chto delayut -
pravil'no
s rostom vysoty uvelichivayut
svoi temp - teoriya predpolagaet odno praktika
pokazyvaet protivopolozhnoe.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
10.09.2013 21:26, 1.8 KBait)
|

|
|
20 Otvetov
|
---
Mne azh smeshno, kak govoritsya shara pliz,
ili primitivnyi test na soobrazitel'nost'.
S odnoi tochki zreniya zadacha
dostatochno primitivnaya,
i reshaetsya s pomosh'yu silovoi dinamiki dvizheniya uvlekaemyh sred,
kotorye zapresheny v principe na dannom forum
tam rukopleshut pustote
v prostranstve.
Dam melkuyu podskazku pri neposredstvennoi blizosti
k poverhnosti uvlekayushei sredu, budet imet' mesto
Sila Koriolisa, i u planety kotoraya
tozhe uvlekaet
sredu tozhe Sila Koriolisa imeet bol'shoe znachenie.
Pri etom nelogichno zabyvat' o sile prokatki po vneshnei
i vnutrennei silovoi oboime sredy
sozdavaemoi perepadom
davlenii sredy pri uvlechenii zvezdoi.
Vse-by horosho i skladno esli by v sostoyanii
zadat' bazovye harakteristiki ili standarty
kak dlya zvezdy tak i dlya sredy i dlya planet.
Zadacha so smeshnym kolichestvom peremennyh.
Uspehov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.09.2013 21:50, 2.3 KBait)
\\\

Otvet #1 : Vchera v 11:59:24
Ochen' poleznoe i nuzhnoe delo!
A pochemu vypusknikov (=shkol'nikov 11-h klassov) diskriminiruete?
priglashaet shkol'nikov 710 klassov.
U menya brat v 11-om klasse, emu kak raz polezno budet, on EGE po fizike sdavat' sobiraetsya.
-----------------------
Otvet #2 : Segodnya v 11:33:41
Razumeetsya, dlya 11 klassa est' zanyatiya. No nachinat' v 11 klasse pozdno, a ob'yavlenie adresovano novichkam.
\\\----------------
Smeshno - klassika astro yumora.A u menya tozhe
smeshnaya situaciya, uchil astronomiyu v shkole
potom o nei dazhe ne dumal let dvadcat', a potom
okazalos' chto
hobbi.
Vyvod - astronomiei zanimat'sya - rano-pozdno ne byvaet,
ibo vremya proletaet i ni kon' i ne zlodei
ne zhestokii lihodei on ne vprave za drugih
prinimat' reshenie, ne sprosiv vot teh dlya kogo lishenie.
Hotya chestno rasskazat' smeh i sme-smeshinki
v astronomii byvayut grustnye storinki,
neponyatno
nichego v etoi paradigme,
tak chto luchshe ne uchit' - esli net v dushe
k astronomii iskrinki.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.09.2013 22:17, 2.5 KBait)



-

- Soobshenii: 230
- Reiting: +3/-1
- पुनर्जन्म
-
Otvet #784 : Segodnya v 20:56:41
VimanaPro,
a pochemu u gravitacii net skorosti? V teorii, kotoruyu ya opisyvayu,
bol'shoi, no konechnoi skorost'yu gravitacii mozhno ob'yasnit' rasshirenie
Vselennoi, a postoyannoi velichinoi summarnoi vychislitel'noi moshnosti
ob'yasnyaetsya uskorenie rasshireniya.
A cel' padayushego kamnya v moei teorii ochen' dazhe yasna, no menya zdes' odnazhdy uzhe zabanili za ee filosofskoe raskrytie  .
.
Vozmozhno, ispol'zuya slovo "gravitaciya", Vy vkladyvaete
svoi smysl. Ne mogli by utochnit' opredelenie i svoistva gravitacii.
Pro uskorenie rasshireniya Vselennoi navernoe luchshe v sosednei teme pro Vselennuyu
---
Zhal' chto zabanyat kak beshenuyu sobaku, ibo dazhe ya znayu chto slovo gravitaciya
byla pridumana dlya opisaniya prityazheniya dvuh tel.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.09.2013 8:40, 2.2 KBait, otvetov: 1)
V principe elementarnaya
zadacha: vdol' osi 0h startuet raketa-1 so skorost'yu 4/5 s otnositel'no
0, s nee v tom zhe napravlenii startuet raketa-2 so skorost'yu 4/5 s
otnositel'norakety-1; naiti skorost' rakety-2 otnositel'no 0.
Zadacha
reshaetsya s pomosh'yu odnoi formuly \[
s=\frac{v+u}{1+vu/{c}^{2}}=\frac{8/5}{1+16/25}=\frac{8 \cdot 25}{41
\cdot 5}=\frac{40}{41}\approx 0.9756 ( c ) \]Lorenc-faktor rakety-2
(otnositel'no 0)\[ \gamma
=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-{s}^{2}/{c}^{2}}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-1600/1681}}=\frac{41}{9}
\]
S drugoi storony, Lorenc-faktor rakety-1 (otnositel'no 0)\[
{\gamma }_{(1-0)}
=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-{v}^{2}/{c}^{2}}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-16/25}}=\frac{5}{3}
\]To est', summarnaya energiya dvizhusheisya so skorost'yu 4/5 s rakety-1 v
5/3 raza bol'she energii pokoyasheisya rakety-1 otnositel'no 0. Dalee.
Raketa-2 dvizhetsya otnositel'no pokoyasheisya dlya nee rakety-1 so skorost'yu
4/5 s.
---
V chem oshibka
V tom chto eta zadacha - fizicheskaya,
a fizicheskie zadachi reshayutsya ne formulami, a umstvennymi
sposobnostyami kotorye
dolzhny prevyshat' neobhodimyi
minimum nuzhnyi dlya resheniya zadachi.
Eta zadacha reshaetsya v stile - alya chasy da nosim po platforme.
Edet poezd v pervom
vagone poezda est' chasolov u nego sachok
s nomerom 1, i on lovit im chasy tozhe s nomerom 1, v konce poezda
est' vtoroi chasolov kotoryi lovit chasy s nomerom 2.
A est' hitrye platformennye chasonosy, - oni smeyutsya nad umstvennymi
sposobnostyami teh kto reshaet podobnye zadachi.
Edet poezd Chasonosy chasy s nomerom
odin postavili po sredine platformy
i chasy nomer dva postavili po sredine platformy.
Proezzhayushii poezd mog uznat' svoyu skorost',
a posle togo kak chasonosy
pervye chasy otnesli v pered platformy,
a vtorye v konec - to ves' poezd nachal proezzhat' stanciyu
s beskonechnoi skorost'yu.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(A. S. Kolomenskii,
14.09.2013 20:27, 75 Bait)
Stol'ko slovesnogo ponosa i umstvennogo bluda i kak zdes', eshe ne vstrechal!
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.09.2013 21:32, 3.9 KBait)
///
 Re: Konec efirnoi teorii- finita la comédie.
Re: Konec efirnoi teorii- finita la comédie.
Otvet #272 - Segodnya :: 19:33:49
Mihail Surin pisal(a) Segodnya :: 18:56:29:. Na chem osnovany Vashi utverzhdeniya mne poka neponyatno..
Na tom chto ya ne videl poka ubeditel'nyh svidetel'stv podtverzhdeniya sushestvovaniya
efira. On ne yavlyaetsya fizicheskim ob'ektom.
Vse
eferisty i Vy v tom chisle otsylaete k chteniyu k saitam kotorye ne
yavlyayutsya nauchnymi. Ya stremlyus' zhe k obratnomu. t.e. byt' v rusle
nauchnyh faktov.
Poetomu u nas raznye rusla. Esli Vy hoite chtoby eti rusla soprikasnulis' togda i zadaite ton etomu soprikosnoveniyu.
A poka est' odin eksperient
kotoryi pokazal chto efira net. Eksperimentov podtverzhdayushih to chto efir est' ya ne vizhu.
Privedite ego zdes'. Esli smozhete. No poka Vy tol'ko otpisyvaetes'
filosofskimi terminami -poidi tuda, naidi tam to. A eto tam to neponyatno
chto.
Nauka eto takoe yavlenie kotoroe ne mozhet byt' gde -to, a gde
to mozhet byt'. Ona est'. I Vy vne ee predelov. Eto dostatochnyi argument i
poka on ne oprovergnut Vami.///
--------------------------------------------------------
Da vidno relyativisty nervnichayut po samoe asisyai, dazhe strategicheskuyu
hitrost' primenyayut, zaslali gonca na al'tovkii forum,
kotoryi prosto oborzel s takim nazvaniem foruma,
lichno mne ponyatno chto za takie veshi logichno prosto
banit'.
I chto menya udivlyaet tak eto umstvennye nikakie
sposobnosti, v osnovnoi masse k zapominaniyu
fizicheskih opytov i analiza ih.
Ya lichno
ne znayu ni odnogo pribora i ustroistva sdelannogo
na baze relyativistskih teorii.
Zhps i to al'ty sdelali s atomnymi chasami.
I kogda atomnye chasy podymat' na
vysotu nachali to uzhe pri raznice
bol'she desyati metrov mezhdu chasami u verhnih uvelichilsya temp,
u relyativistov temp chasov na orbite uvelichivaetsya.
Ya odnogo
sobstvenno ne ponimayu pochemu pri vseh
neskladushkah teorii ee tak dolgo terpyat.
Paradoks eto tozhe nedostatok teorii -
za kotoryi lyubaya teoriya posylaetsya
v peshee eroticheskoe puteshestvie, i imeya stol'ko neskladuh
teoriya eshe stoit.
I samoe smeshnoe chto net iznachal'no ne tol'ko izmeritel'nogo
ustroistva, net
edinic izmereniya i net metodiki izmereniya,
--- a teper' vnimanie - na zayavlennye fizicheskie svoistva,
- ladno mozhet ya i ne prav, mozhet v kazhdom supermarkete
i prodaetsya izmeritel' krivizny prostranstva kotoryi
pokazyvaet - odin krivzvezdenysh na svoei shkale u poverhnosti
Zemli, da i pribor kotoryi pokazyvaet zamedlenie
vremeni v dvizhenii tozhe na polke lezhit - i pokazyvaet
- a chto on pokazyvaet - a dazhe edinic izmereniya relyativisty
ne udosuzhilis' pridumat' dlya etogo pribora.
To mne opyat' Vibe vspomnilsya, kogda on mne bui pokazal
na relyativistskuyu prichinu skorosti poleta fotona kak
chasticy v pustote, a potreboval teh pasport
na efir.
Sobstvenno dannaya situaciya analogichnaya relyativisty
krikom krichat chto efira net a lokatory rabotayut
po effektu Doplera dlya sred azh s 1842 goda
avtor
ego pridumal isklyuchitel'no dlya sred.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.09.2013 21:36, 276 Bait)
A.S.Kolomenskii
---
Ya kak raz i rad za Vas,
ya starayus' tak pisat' chtoby mahrovye relyativisty,
ne mogli dazhe vduplit'sya
v smyslovuyu sut' napisannogo.
Tak chto spasibo Vam za otzyv.
Tu-ta ne dlya srednih umov odnako.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.10.2013 12:03, 9.9 KBait)
A tekst to chitaetsya kak budto
ego pisal chelovek
stradayushii idiotizmom s fizicheskim uklonom.
Chto zanimatel'no chto pishushii
nastol'ko nedalekii
chto ispol'zuet slova
fizicheskogo naznacheniya e ponimaya
smyslovuyu sut' slov kotorye on
ispol'zuet.
Eto estestvenno ne kriticheskii
predel urovnya idiotizma
po prichine otsutstviya
adekvatnyh znanii po fizike,
u avtora dva varianta s
bol'shei veroyatnost'yu chto ego
teksty budut udivlyat' eshe
bol'shim idiotizmom, po prichine togo
chto v ego srede obsheniya on i
te s kem on na forume obshalsya,
i dumal chto blagodarya kollektivu
oni uluchshayut svoi znaniya
v fizike a okazalos' chto oni
tol'ko zabluzhdalis' eshe kruche
a kollektiv pridaval uverennosti
v pravil'nosti fakticheskih
zabluzhdenii - chto uzhe est' -
fanatizm.
U menya tozhe desyatok let nazad
byli zabluzhdeniya no ya sistemno
i posledovatel'no s nimi
razbiralsya ne zhaleya nikakogo kolichestva
vremeni chtoby dazhe razobrat'sya nad samym neznachitel'nym
voprosom po fizike, kotoryi privlek moe
vnimanie.
I vyvod iz etoi situacii to
kakoi - esli Vy podobnuyu buetu pishite
v 30 let, to eto normal'no u
Vas eshe budet vozmozhnost' pri nalichii zhelaniya
preodolet' svoi oshibki, no
esli vam 60 let - to logiki zanimat'sya
podobnymi teoriyami v
fizike - net.
Pisat' to mozhno, no budut vse
nad etim smeyat'sya.
Ya by lichno s nauchnyh
rukovodyashih dolzhnostei s 52 let zakonodatel'no
by uvol'nyal, v takom vozraste
nauchnymi kollektivami rukovodit'
s moei tochki zreniya ne
logichno,
s 55letnego vozrasta zapreshal by uzhe dazhe byt'
sotrudnikom nauchnogo kollektiva, -
- i prinuditel'nom poryadke
perevodyatsya na prepodavatel'skuyu rabotu
v shkoly i instituty.
I ne nado polemiku na etu temu razvodit, eto
estestvennyi process,
na staryh loshadyah v skachkah
nikto ne dodumyvaetsya ustraivat' zabegi, tak i tut, a
to chto eto vozmozhno, - ne korrektno
-, tak eto do lampochki ibo eto estestvennyi fakt.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
///
 "Teoriya Peny" : shtrihi k modeli istochnika sveta
"Teoriya Peny" : shtrihi k modeli istochnika sveta
Vchera :: 19:35:56
Po teorii Peny atom predstavlyaet soboi agregat iz chetyrehmernyh vihrei efira.
Naprimer,
atom vodoroda. Sostoit kak by iz dvuh s polovinoi chetyrehmernyh
vihrei. Yadro sostoit iz chetyrehmernogo tornado s prikreplennym na
periferii chetyrehmernym toroidal'nym vihrem (poluchaetsya kak by poltora
vihrya). Vokrug yadra raspolozhen elektron chetyrehmernyi toroidal'nyi
vihr'. Vrashenie chastic efira v etih dvuh toroidal'nyh vihryah (po
obrazuyushei tora) proishodit v protivopolozhnyh napravleniyah, za schet chego
obrazuetsya u yadra i elektrona znakovaya raznica elektricheskogo zaryada.
Mezhdu elektronom i yadrom nahoditsya haoticheskii efir. Orbita elektrona
obuslovlena dinamicheskim ravnovesiem sil: elektricheskoi (prityazhenie),
magnitnoi (prityazhenie ili ottalkivanie v zavisimosti ot gradienta
davleniya haoticheskogo efira), gravitacionnoi (prityazhenie ili
ottalkivanie v zavisimosti ot rasstoyaniya elektrona ot yadra).
Takim
obrazom, v svoem trehmernom proyavlenii atom predstavlyaet soboi oreshek,
sostoyashii iz treh komponentov: 1) veshestvennyi nuklonoobrazuyushii
sharik, pokrytyi 2)antiveshestvennym (pochti chto pozitron) sloem i 3)
veshestvennoi kozhuroi (elektronnoe oblako).
Model' atoma, kak istochnika i poglotitelya sveta.
Pri
nekom energeticheskom vozbuzhdenii elektron uvelichivaet svoyu orbitu i
prostranstvo mezhdu nim i yadrom zapolnyaetsya dopolnitel'nym kolichestvom
efira. Pri vozvrashenii elektrona na svoyu stabil'nuyu orbitu iz atoma, kak
iz sprincovki, vypleskivaetsya struika efira, kotoraya i yavlyaetsya
fotonom. Obratnyi process ocheviden struika (foton) pronikaet v atom i
vytalkivaet elektron na druguyu (nestabil'nuyu) orbitu.
Pervoe
shodstvo predlagaemoi modeli s imeyushimisya opytnymi dannym nalichie
individual'nyh spektrov poglosheniya i ispuskaniya, kotorye, estestvenno,
zavisyat ot raznicy v konstrukcii atomov razlichnyh himicheskih elementov.
Shirina spektral'noi linii, estestvenno, zavisit ot vsyacheskih vneshnih i
vnutrennih neodnorodnostei (naprimer, ot neodnorodnostei samogo Efira,
ot skorosti dvizheniya atoma i ot drugogo mnogogo prochego).
Vtoroe
legkoe ob'yasnenie doplerovskogo izmeneniya dliny volny. Yasno, chto esli
dvizhenie sprincovki sovpadaet s napravlenie strui, to i struya
okazhetsya koroche. Esli atom dvizhetsya v protivopolozhnom napravlenii
struya udlinyaetsya.
Tret'e vozmozhnost' takoi konstrukcii
sprincovki, pri kotoroi skorost' struiki (fotona) ne zavisit (ili ne
ochen' sil'no zavisit) ot skorosti sprincovki (atoma).
Chetvertoe
ob'yasnenie shodstva fotona s EM-volnoi. I struika i EM-volna yavlyayutsya
gradientami plotnosti Efira, izmenenie kotoroi (plotnosti)
rasprostranyaetsya so skorost'yu efirnogo zvuka.
Pyatoe ob'yasnenie otlichiya fotona ot EM-volny. U fotona net (ili ochen' neznachitel'na) elektricheskaya sostavlyayushaya.
Shestoe
nekotoroe peresechenie chastot u infrakrasnyh fotonov s teplovymi
EM-volnami. Teplovye EM-volny obrazuyutsya kolebaniyami samih atomov (i
vmeste s nim ih elektronov), kotorye koleblyut okruzhayushii Efir.
Nekotorye orbital'nye perehody elektronov (kogda ispuskaetsya struika),
estestvenno, mogut byt' pohozhimi (po energoemkosti, naprimer, i dr.) na
harakteristiki tepla. Takzhe i pri pogloshenii infrakrasnogo fotona ne
vsegda mozhet elektron vozbudit'sya do urovnya pereskoka na druguyu orbitu
(Infrakrasnyi foton mozhet lish' nemnogo potryasti atom, i energiya
izluchit'sya obratno uzhe ne v vide struiki, no v vide
central'no-sfericheski simmetrichnoi EM-volny
Privedennyi perechen'
yavlyaetsya daleko ne zakonchennym ryadom argumentov v pol'zu analogii atoma
so sprincovkoi. Odnako dlya bolee tonkih parallelei neobhodimo
uchityvat' i bolee tonkie konstruktivnye harakteristiki i sprincovki, i
struiki, i samogo Efira
///
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.10.2013 21:11, 67.2 KBait)
Eto dolzhen prochitat' kazhdyi,
chto-by on znal i pomnil vechno -
chto vse idei relyativizma vzyaty iz ranee opisannyh
idei storonnikov efira.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://ether-wind.narod.ru/Martins_2011_Courvoisier
R. Martins. Searching for the Ether: Leopold Courvoisers Attempts to Measure
the Absolute Velocity of the Solar System (PDF)
| 1
| {1}DIO, The International
Journal of Scientific History www.dioi.org | DIO, Mezhdunarodnyi zhurnal nauchnoi istorii www.dioi.org
|
| 2
| {3}
|
|
| 3
| Physics Department, State University of Paraiba (UEPB), Brazil roberto.andrade.martins@gmail.com
| Fizicheskii fakul'tet Gosudarstvennogo universiteta Paraiba (UEPB), Braziliya roberto.andrade.martins@gmail.com
|
| 4
|
|
|
| 5
|
|
|
| 6
| Leopold Courvoisier (1873-1955) was an observer at the Berlin /
Babelsberg astronomical observatory from 1905 up to his retirement in
1938.
| Leopol'd Kurvuaz'e (1873-1955) byl nablyudatelem v Berlinskoi /
Babel'sbergskoi astronomicheskoi observatorii s 1905 goda do svoei
otstavki v 1938 godu.
|
| 7
| Most of his work was traditional astrometrical observation resulting in the publication of several star catalogues.
| Bol'shinstvo ego rabot byli tradicionnymi astrometricheskimi
nablyudeniyami, kotorye v rezul'tate priveli k publikacii ryada zvezdnyh
katalogov.
|
| 8
| A relevant part of his publications was devoted, however, to
another subject: the attempt to detect the motion of the solar system
through the ether.
| Znachimaya chast' ego publikacii byla posvyashena, odnako, drugoi teme: popytke obnaruzheniya dvizheniya Solnechnoi sistemy cherez efir.
|
| 9
|
|
|
| 10
| Most of Courvoiser's search for measurable effects of the ether was based upon two principles.
| Bol'shinstvo iz popytok Kurvuaz'e obnaruzhit' izmerimye effekty efira byla osnovana na dvuh principah.
|
| 11
| According to him, (1) the angles of incidence and reflection of
light could be different, relative to the proper reference system of
the mirror, if it moved through the ether; and (2) the Lorentz
contraction of the Earth due to its motion through the ether produced
observable effects relative to the Earths reference system.
| Po ego slovam, (1) ugly padeniya i otrazheniya sveta mozhet byt'
drugim, po otnosheniyu k sobstvennoi sisteme otscheta zerkala, esli ono
dvizhetsya cherez efir, i (2) sokrashenie Lorenca dlya Zemli iz-za ee
dvizheniya cherez efir proizvodit nablyudaemye effekty po otnosheniyu k
sisteme otscheta Zemli.
|
| 12
| Both principles, of course, violate the principle of relativity.
| Oba principa, konechno, narushayut princip otnositel'nosti.
|
| 13
| Courvoisier presented theoretical arguments attempting to show that there should exist second order measurable effects.
| Kurvuaz'e predstavil teoreticheskie argumenty, pytayas' pokazat', chto dolzhny sushestvovat' izmerimye effekty vtorogo poryadka.
|
| 14
| He searched for those effects using both astronomical
observations and laboratory experiments and claimed that he had measured
a velocity of the solar system of about 600 km/s.
| On iskal eti effekty s pomosh'yu kak astronomicheskih nablyudenii,
tak i laboratornyh eksperimentov i utverzhdal, chto on izmeril velichinu
skorosti Solnechnoi sistemy primerno 600 km/s.
|
| 15
| This paper presents a description and analysis of Courvoisers ether researches.
| Eta stat'ya predstavlyaet soboi opisanie i analiz efirnyh issledovanii Kurvuaz'e.
|
| 16
|
|
|
| 17
|
|
|
| 18
| Leopold Courvoisier was born on 24 January 1873 in Rihen near Basel (Switzerland).1 His father Ludwig Georg Courvoisier was a physician and was in charge
of the surgery chair of the University of Basel.
| Leopol'd Kurvuaz'e rodilsya 24 yanvarya 1873 goda v Rigene bliz Bazelya (Shveicariya). 1 Ego otec Lyudvig Georg Kurvuaz'e byl vrachom i vozglavlyal kafedru hirurgii
v universitete Bazelya.
|
| 19
| Leopold (or Leo, as he was usually called) passed away in the same city where he was born, on 31 December 1955.
| Leopol'd (ili Leo, kak ego obychno nazyvali) skonchalsya v tom zhe gorode, gde on rodilsya, 31 dekabrya 1955 goda.
|
| 20
| However, most of his professional life was spent in Germany.
| Tem ne menee, bol'shuyu chast' svoei professional'noi zhizni on provel v Germanii.
|
| 21
|
|
|
| 22
| Courvoisier exhibited an interest for astronomy since he was 15 years old.
| Kurvuaz'e proyavil interes k astronomii, kogda emu bylo 15 let.
|
| 23
| In 1891 he began his university studies, first in Basel and later in {4}
Strasbourg - at a time when this city belonged to Germany.
| V 1891 godu on nachal uchebu v universitete, snachala v Bazele, a
zatem vStrasburge - v to vremya, kogda etot gorod prinadlezhal Germanii.
|
| 24
| In 1897 he completed his dissertation, on the absolute height
of the pole as observed from Strasbourg (Die absolute Polhöhe von
Straßburg).
| V 1897 godu on zakonchil svoyu dissertaciyu po nablyudaemoi iz
Strasburga absolyutnoi vysote polyusa ("Die absolute Polhöhe von
Straßburg).
|
| 25
| The next year he became an assistant observer at the Königstuhl
astronomical observatory near Heidelberg, under Karl Wilhelm
Valentiner.
| V sleduyushem godu on stal pomoshnikom nablyudatelya v
astronomicheskoi observatorii Kenigshtul' nedaleko ot Haidel'berga, pod
rukovodstvom Karla Vil'gel'ma Valentinera.
|
| 26
| In 1900 he obtained his Doctor degree in Straßburg.
| V 1900 godu on poluchil doktorskuyu stepen' v Strasburge.
|
| 27
| From 1905 onward he worked at the Berlin / Babelsberg
observatory as an astronomical observer, under the direction of Karl
Hermann Struve.
| S 1905 i dalee on rabotal v Berlinskoi / Babel'sbergskoi
observatorii kak astronomicheskii nablyudatel' pod rukovodstvom Karla
Germana Struve.
|
| 28
| In 1913 the Berlin observatory moved to its new site, in Babelsberg,2 and one year later Courvoiser became its chief observer and professor.
| V 1913 godu Berlinskaya observatoriya pereehala na novoe mesto, v Babel'sberg, 2, a god spustya Kurvuaz'e stal tam glavnym nablyudatelem i professorom.
|
| 29
| He worked at Babelsberg up to his retirement in 1938, when he was 65 years old.
| On rabotal v Babel'sberge do svoei otstavki v 1938 godu, v vozraste 65 let.
|
| 30
| In 1943 he moved to his birthplace, where he kept making observations and publishing papers up to his death.
| V 1943 godu on pereehal na rodinu, gde on prodolzhal proizvodit' nablyudeniya i publikovat' stat'i do ego smerti.
|
| 31
| Back to Switzerland, he was the editor of several of Leonhard Euler's astronomical works.
| V Shveicarii on byl redaktorom neskol'kih astronomicheskih rabot Leonarda Eilera.
|
| 32
|
|
|
| 33
| Courvoisiers main astronomical contribution was a large series
of routine astrometrical observations and the production of star
catalogues.
| Glavnyi astronomicheskii vklad Kurvuaz'e sostoit v bol'shoi serii
rutinnyh astrometricheskih nablyudenii i publikacii zvezdnyh katalogov.
|
| 34
| Volumes 5, 6 and 7 of Poggendorff's Biographisch-literarisches
Handwörterbuch provide references of about 10 large works (astronomical
catalogues) besides nearly 100 minor contributions by him.3 However, Courvoisiers work was not restricted to common astrometrical observations.
| Toma 5, 6 i 7 izdaniya Biographisch literarisches Handwörterbuch
Poggendorfa dayut ssylki na primerno 10 krupnyh rabot (astronomicheskih
katalogov) Kurvuaz'e, pomimo okolo sta menee znachitel'nyh ego
publikacii. 3 Tem ne menee, rabota Kurvuaz'e ne ogranichivaetsya obshimi astrometricheskimi nablyudeniyami.
|
| 35
| From his tedious measurements there soon came out evidences that he regarded as disproof of the theory of relativity.
| Iz ego utomitel'nyh izmerenii vskore poyavilis' dokazatel'stva
togo, chto on rassmatrivaet kak oproverzhenie teorii otnositel'nosti.
|
| 36
|
|
|
| 37
| Courvoisier did not accept the theory of relativity.
| Kurvuaz'e ne prinyal teoriyu otnositel'nosti.
|
| 38
| He believed there was an ether, and attempted to measure the absolute velocity of the solar system relative to this medium.
| On schital, chto sushestvuet efir, i popytalsya izmerit' absolyutnuyu skorost' Solnechnoi sistemy otnositel'no etoi sredy.
|
| 39
| From 1921 to his death, Courvoisier published a series of over
30 papers where he described the theoretical basis of his search and the
several experimental techniques he used in attempting to detect the
motion of the Earth relative to the ether.
| S 1921 goda do svoei smerti, Kurvuaz'e opublikoval seriyu iz
bolee chem 30 rabot, v kotoryh on opisal teoreticheskuyu osnovu ego
issledovanii i neskol'ko eksperimental'nyh metodov, kotorye on
ispol'zoval v popytke obnaruzhit' dvizhenie Zemli otnositel'no efira.
|
| 40
| Some of his measurements used astronomical observations; other
measurements depended on other physical effects (gravitational, etc.).
| Nekotorye iz ego izmerenii ispol'zovali astronomicheskie
nablyudeniya; drugie izmereniya zavisyat ot drugih fizicheskih effektov
(gravitacionnye i t.d.).
|
| 41
| As a result of his observations he claimed that he had measured
a velocity of the solar system of about 600 km/s in a direction close
to 75 right ascension and +40 declination.
| V rezul'tate svoih nablyudenii on utverzhdal, chto on izmeril
skorost' Solnechnoi sistemy, primerno sostavlyayushuyu 600 km / s v
napravlenii, blizkom k 75 pryamogo voshozhdeniya i +40 skloneniya.
|
| 42
|
|
|
| 43
| 
|
| 44
| {5} .... 1. Leopold Courvoisier (about 30
years old).4
| Ris. 1. Leopol'd Kurvuaz'e (v vozraste okolo 30 let). 4
|
| 45
|
|
|
| 46
| The papers describing those researches were published in
several scientific journals - especially Astronomische Nachrichten,
Physikalische Zeitschrift and Zeitschrift für Physik.
| Stat'i, opisyvayushie eti issledovaniya, byli opublikovany v
neskol'kih nauchnyh zhurnalah osobenno v Astronomische Nachrichten,
Physikalische Zeitschrift für i Zeitschrift Physik.
|
| 47
| His work was largely ignored and had a small impact.
| Ego raboty v znachitel'noi stepeni ignorirovalis' i imeli neznachitel'noe vliyanie.
|
| 48
| A few authors (e.g. Ernest Esclangon and Dayton Miller) who
also claimed they had observed effects due to the ether have cited his
works.
| Neskol'ko avtorov (naprimer, Ernest Esklangon i Deiton Miller),
kotorye takzhe utverzhdali, chto oni nablyudali effekty, svyazannye s
efirom, ssylalis' na ego proizvedeniya.
|
| 49
| {6} Historians of science have also neglected
those researches,5
although they present the largest set of empirical results that was
ever published against the theory of relativity by a professional
scientist.
| Istoriki nauki takzhe prenebregali etimi issledovaniyami, 5,
hotya oni predstavlyayut soboi krupneishii nabor empiricheskih rezul'tatov,
kotorye byli kogda-libo opublikovany protiv teorii otnositel'nosti
professional'nym uchenym.
|
| 50
| Courvoisier exhibited an outstanding theoretical and
experimental skill, and his results can be regarded as one of the
strangest puzzles in the history of relativity.
| Kurvuaz'e pokazyval vydayusheesya teoreticheskoe i
eksperimental'noe masterstvo, i ego rezul'taty mozhno rassmatrivat' kak
odnu iz samyh strannyh zagadok v istorii teorii otnositel'nosti.
|
| 51
|
|
|
| 52
|
|
|
| 53
| Courvoisier's earliest involvement with relativity was an outcome of his routine measurements of star positions.
| Samoe pervoe stolknovenie Kurvuaz'e s teoriei otnositel'nosti stalo rezul'tatom ego rutinnyh izmerenii polozhenii zvezd.
|
| 54
| In the beginning of the twentieth century, Courvoisier had
noticed that the right ascension and declination of fixed stars suffered
a small influence when they are observed close to the Sun.
| V nachale HH veka Kurvuaz'e zametil, chto pryamoe voshozhdenie i
sklonenie nepodvizhnyh zvezd podverzheno nebol'shomu vliyaniyu, kogda oni
nablyudayutsya blizko k Solncu.
|
| 55
| As this influence had a period of one year, he called it annual refraction.
| Poskol'ku eto vliyanie imelo period odin god, on nazval ego godovoi refrakciei.
|
| 56
| His first work on the subject was published in 1905,6 that is, much earlier than the development of the general theory of relativity.
| Ego pervaya rabota na etu temu byla opublikovana v 1905 godu, 6 to est' namnogo ran'she, chem byla razrabotana obshaya teoriya otnositel'nosti.
|
| 57
| In 1911, after the publication of Einsteins early thoughts on
the gravitational deflection of light rays, Erwin Freundlich recalled
that Courvoisier's work had exhibited an effect that was qualitatively
similar to the one predicted by Einstein.7
| V 1911 godu, posle publikacii rannih myslei Einshteina po
gravitacionnomu otkloneniyu luchei sveta, Ervin Freindlih napomnil, chto
rabota Kurvuaz'e pokazala effekt, kotoryi kachestvenno pohozh na
predskazannyi Einshteinom. 7
|
| 58
| Courvoisier interpreted the effect he had measured as due to
refraction of light by a denser medium around the Sun, not as a
consequence of relativity.
| Kurvuaz'e interpretiroval effekt, kotorye on izmeril, kak
sledstvie prelomlenie sveta bolee plotnoi sredoi vokrug Solnca, a ne kak
sledstvie teorii otnositel'nosti.
|
| 59
| It seems that Courvoisiers opposition to Einstein's work grew
steadily from this time onward and he became one of the most
intransigent supporters of ether theory after the theory of general
relativity received strong confirmation (the eclipse measurements), in
1919.
| Pohozhe, chto oppoziciya Kurvuaz'e k rabotam Einshteina neuklonno
rosla s etogo vremeni, i on stal odnim iz samyh nesgibaemyh storonnikov
teorii efira posle togo, kak obshaya teoriya otnositel'nosti poluchila
sil'noe podtverzhdenie (izmereniya vo vremya zatmeniya) v 1919 godu.
|
| 60
| Courvoisier's main anti-relativistic work, however, is not directly linked to annual refraction.8
| Osnovnye anti-relyativistskih raboty Kurvuaz'e, odnako, neposredstvenno ne svyazany s godovym prelomleniem. 8
|
| 61
|
|
|
| 62
| Courvoisier accepted the existence of a static ether, similar
to the medium proposed in the early eighteenth century by Augustin
Fresnel.
| Kurvuaz'e priznal sushestvovanie staticheskogo efira, pohozhii na
sredu, predlozhennuyu v nachale vosemnadcatogo veka Ogyustenom Frenelem.
|
| 63
| That theory led to the conclusion that there could be no first-order influence of the motion {7}
through the ether upon optical experiments performed in the Earth.
| Eta teoriya privela k vyvodu, chto ne moglo byt' vliyaniya effektov
pervogo poryadka pri dvizhenii cherez efir v opticheskih eksperimentah,
provedennyh na Zemle.
|
| 64
| Besides that, the negative outcome of the Michelson-Morley
experiment required an additional hypothesis, and Courvoisier accepted
that motion through the ether produced a real contraction of all moving
bodies, according to the early explanation proposed by Fitzgerald and
Lorentz.
| Krome togo, otricatel'nyi rezul'tat opyta Maikel'sona treboval
dopolnitel'noi gipotezy i Kurvuaz'e predpolozhil, chto dvizhenie cherez
efira proizvodit real'noe szhatie vseh podvizhnyh tel, v sootvetstvii s
rannimi ob'yasneniyami, predlozhennymi Ficdzheral'dom i Lorencem.
|
| 65
| According to Lorentz, the principle of relativity would hold
exactly for any optical or electromagnetic phenomenon, but Courvoisier
did not follow Lorentzs theory in this respect.
| Po slovam Lorenca, princip otnositel'nosti budet primenim v
tochnosti dlya lyubogo opticheskogo ili elektromagnitnye yavleniya, no
Kurvuaz'e ne posledoval teorii Lorenca v etom otnoshenii.
|
| 66
| He directly denied the principle of relativity and attempted to
measure the motion of the solar system through the ether using several
different techniques.
| On pryamo otrical princip otnositel'nosti i popytalsya izmerit'
dvizhenie Solnechnoi sistemy cherez efir s pomosh'yu razlichnyh metodov.
|
| 67
|
|
|
| 68
| In 1921 Courvoisier published his first thoughts on the
possibility of measuring the absolute velocity of the Earth through the
ether.9
| V 1921 godu Kurvuaz'e opublikoval svoi pervye mysli o vozmozhnosti izmereniya absolyutnoi skorosti Zemli otnositel'no efira. 9
|
| 69
| According to Courvoisiers own declaration, his early
calculations concerning the motion of the Earth were an outcome of
routine work.10
| V sootvetstvii s sobstvennoi deklaraciei Kurvuaz'e, ego rannie raschety o dvizhenii Zemli bylo rezul'tatom rutinnoi raboty. 10
|
| 70
| In 1920 the Leyden Observatory published the details of a large
series of observations of stars close to the North Pole that had been
made between 1862 and 1874.
| V 1920 godu Leidenskaya observatoriya opublikovala podrobnosti iz
bol'shoi serii nablyudenii zvezd, raspolozhennyh blizko k Severnomu
polyusu, kotorye byli sdelany mezhdu 1862 i 1874 gg.
|
| 71
| Those measurements used an old method aiming to reduce
observational errors: the stars were observed both with the meridian
telescope directly pointed to them, and with the telescope pointed to
the images of the stars reflected by a mercury mirror.
| Eti izmereniya ispol'zovali staryi metod, napravlennyi na
snizhenie oshibok nablyudenii: zvezdy nablyudalis' kak s pomosh'yu
meridiannogo teleskopa, pryamo ukazyvayushego na nih, a takzhe s teleskopom,
napravlennym k otrazheniyam zvezd zerkalom iz rtuti.
|
| 72
| This double assessment allowed corrections for any changes of the local vertical due to geological motions.
| Eta dvoinaya ocenka pozvolila proizvodit' korrektirovki lyubyh izmenenii mestnoi vertikali za schet geologicheskih dvizhenii.
|
| 73
| It occurred to Courvoisier that those determinations could be used to measure the speed of the Earth through the ether.
| Kurvuaz'e prishlo v golovu, chto eti opredeleniya mogut ispol'zovat'sya dlya izmereniya skorosti dvizheniya Zemli cherez efir.
|
| 74
|
|
|
| 75
| Courvoisier assumed that the reflection of light by a mirror
could undergo some influence of the motion of the mirror through the
ether, even when the effect was observed relative to the proper reference system of the mirror.
| Kurvuaz'e predpolagal, chto otrazhenie sveta ot zerkala mozhet podvergat'sya nekotoromu vliyaniyu ot dvizhenie zerkala cherez efir, dazhe esli effekt nablyudalsya po otnosheniyu
k sobstvennoi sisteme otscheta zerkala.
|
| 76
| Any observable effect should be of the second order in v/c. It
would be impossible to detect such a small effect if the speed of the
Earth relative to the ether was about 104 c (that is, its orbital velocity), because for usual angle measurements (let us say, 60) a difference of 108
would amount to only 0.002″ an effect that could not be observed.
| Lyuboi nablyudaemyi effekt dolzhen byt' vtorogo poryadka
otnositel'no v / c. Bylo by nevozmozhno obnaruzhit' takoi malen'kii
effekt, esli skorost' Zemli otnositel'no efira byl priblizitel'no 10 4 s (to est', ravna ee orbital'noi skorosti), tak kak dlya obychnyh izmerenii ugla (skazhem,
60) raznica 10 8 sostavit lish' 0,002″ effekt, kotoryi ne mog nablyudat'sya.
|
| 77
| However, Courvoisier assumed that there could exist a much
larger speed of the whole solar system relative to the ether, and
analyzed the data published by the Leyden Observatory searching for some
systematic effect.
| Tem ne menee, Kurvuaz'e predpolagal, chto mozhet sushestvovat'
gorazdo bol'shaya skorost' vsei Solnechnoi sistemy otnositel'no efira, i
proanaliziroval dannye, opublikovannye Leidenskoi observatoriei v
poiskah sistematicheskogo effekta.
|
| 78
|
|
|
| 79
| He computed the difference zz' between the direct zenith
distance z and the reflected zenith distance z' of the stars listed in
the catalogue, attempting to find a systematic effect that varied in a
periodic way with the sidereal time of observations.
| On vychislil raznicu Z-Z′ mezhdu pryamym zenitnym rasstoyaniem z i
otrazhennym zenitnym rasstoyaniem z′ zvezd v kataloge, pytayas' naiti
sistematicheskii effekt, kotorye var'irovalsya by periodicheskim obrazom
vmeste so zvezdnym vremenem nablyudenii.
|
| 80
| Using a graphical method, he did find such an effect, and then he submitted the data to quantitative analysis.
| Ispol'zuya graficheskii metod, on nashel takoi effekt, a zatem predstavil dannye dlya kolichestvennogo analiza.
|
| 81
| He derived an equation to describe the reflection of light in a moving mirror and {8}
determined the relevant parameters from an analysis of the Leyden data, using the method of minimum squares.
| On poluchil uravnenie dlya opisaniya otrazheniya sveta otnositel'no
dvizhushegosya zerkala i opredelil sootvetstvuyushie parametry iz analiza
dannyh Leidena, ispol'zuya metod naimen'shih kvadratov.
|
| 82
| He obtained an effect corresponding to a speed of about 800 km/s in the direction of the Auriga constellation.
| On poluchil effekt, sootvetstvuyushii skorosti okolo 800 km / s v napravlenii sozvezdiya Voznichego.
|
| 83
| This speed is, of course, much larger than the orbital speed of the Earth.
| Eta skorost', konechno, znachitel'no bol'she, chem orbital'naya skorost' Zemli.
|
| 84
| Courvoisier interpreted it as due to the motion of the whole solar system through the ether.
| Kurvuaz'e interpretiroval ee kak sledstvie dvizheniya vsei Solnechnoi sistemy cherez efir.
|
| 85
| A few years later, Courvoisier obtained new data, using the same method (direct versus reflected direction).
| Neskol'ko let spustya, Kurvuaz'e poluchil novye dannye, ispol'zuya tot zhe metod (sravnenie pryamogo i otrazhennogo napravleniya).
|
| 86
| Using the vertical circle of the Babelsberg observatory, he
made a long series of observations (19211922) that led to results
similar to those that had been obtained from the Leyden observations.
| Ispol'zuya vertikal'nyi krug Babel'sbergskoi observatorii, on
vypolnil dlinnyi ryad nablyudenii (19211922), kotorye priveli k
rezul'tatam, analogichnym tem, kotorye byli polucheny iz nablyudenii v
Leidene.
|
| 87
|
|
|
| 88
| After obtaining his first positive result, Courvoisier
attempted to find other independent methods of measuring the speed of
the Earth (or the solar system) relative to the ether.
| Posle polucheniya pervogo polozhitel'nogo rezul'tata Kurvuaz'e
pytalsya naiti drugie nezavisimye metody izmereniya skorosti Zemli (ili
Solnechnoi sistemy) otnositel'no efira.
|
| 89
| He conjectured that the Lorentz contraction of the Earth and of
optical instruments could have some small observable influence on
astronomical observations.
| On predpolozhil, chto sokrashenie Zemli i opticheskih priborov po
Lorencu mogli imet' nekotorye nebol'shie vliyanie na nablyudaemye
astronomicheskie yavleniya.
|
| 90
| According to Courvoisier, the motion of the Earth relative to
the ether produces a contraction that transforms its spherical shape
into an ellipsoid with the smaller axis in the direction of its motion.
| Soglasno Kurvuaz'e, dvizhenie Zemli otnositel'no efira
proizvodit szhatie, kotoroe preobrazuet svoyu sfericheskuyu formu v
ellipsoid, men'shaya os' kotorogo nahoditsya v napravlenii ego dvizheniya.
|
| 91
| The surface of the ellipsoid, at each point, was supposed to be perpendicular to the local gravitational field.
| Poverhnost' ellipsoida v kazhdoi tochke dolzhna byla byt' perpendikulyarna k mestnomu gravitacionnomu polyu.
|
| 92
| As the Earth rotates, each place on the surface of the Earth
passes through different points of the ellipsoid, and the angle between
the axis of the Earth and the local vertical direction should undergo a
periodical change.
| Pri vrashenii Zemli, kazhdoe mesto na poverhnosti Zemli prohodit
cherez razlichnye tochki ellipsoida, a ugol mezhdu os'yu Zemli i mestnym
vertikal'nym napravleniem, dolzhno podvergat'sya periodicheskomu izmeneniyu.
|
| 93
|
|
|
| 94
| Of course, it is impossible to measure the angle between the local vertical and the axis of rotation of the Earth.
| Konechno, nevozmozhno izmerit' ugol mezhdu mestnoi vertikal'yu i os'yu vrasheniya Zemli.
|
| 95
| However, since the direction of this axis is fairly constant
relative to the fixed stars (for short time periods), it is possible to
choose a star very close to the North celestial pole and to measure its
distance to the zenith (that is, the local vertical direction).
| Odnako, tak kak napravlenie etoi osi prakticheski neizmenno
otnositel'no nepodvizhnyh zvezd (v techenie korotkih periodoy vremeni), to
mozhno vybrat' zvezdu v neposredstvennoi blizosti ot severnogo polyusa
zvezdnogo neba i izmerit' ego [uglovoe] rasstoyanie k zenitu (to est', k
mestnomu vertikal'nomu napravleniyu).
|
| 96
| This angle, according to Courvoisier's theory, should undergo a periodical change, as a function of the sidereal time.
| Etot ugol, soglasno teorii Kurvuaz'e, dolzhen podvergat'sya periodicheskim izmeneniyam v zavisimosti ot zvezdnogo vremeni.
|
| 97
|
|
|
| 98
| As a matter of fact, Courvoisier had already measured the
position of a star very close to the North pole, in a long series of
observations from 1914 to 1917, using the Babelsberg Observatory
vertical circle.11
| Na samom dele, Kurvuaz'e uzhe izmeryal polozhenie zvezdy,
raspolozhennoi ochen' blizko k Severnomu polyusu, v dlinnoi serii
nablyudenii s 1914 po 1917 god, ispol'zuya vertikal'nyi krug
Babel'sbergskoi observatorii .11
|
| 99
| Those measurements were very accurate and were evenly distributed as regards the sidereal time of the observations.
| Eti izmereniya byli ochen' tochnymi i ravnomerno raspredelennymi otnositel'no zvezdnogo vremya nablyudenii.
|
| 100
| They were therefore suitable for looking for the influence of the Lorentz contraction on astronomical measurements.
| Poetomu oni podhodili dlya vyyavleniya togo, kak vliyaet sokrashenie Lorenca na astronomicheskie izmereniya.
|
| 101
|
|
|
| 102
| As in the former case, Courvoisier first plotted the zenithal
distances of the star against sidereal time, and found a regular
fluctuation of the angle.
| Kak i v predydushem sluchae, Kurvuaz'e snachala postroil zenitnye
rasstoyaniya zvezdy otnositel'no zvezdnogo vremeni, i obnaruzhil regulyarnye
kolebaniya ugla.
|
| 103
| {9}
He then developed an equation to account for the effect, analyzed the
data using the minimum square method, and obtained his second
measurement of the velocity of the Earth relative to the ether.
| Zatem on razrabotal uravnenie dlya ucheta effekta,
proanalizirovav dannye s ispol'zovaniem metoda naimen'shih kvadratov i
poluchil izmerenie skorosti Zemli otnositel'no efira vtorym sposobom.
|
| 104
| The speed obtained in this case was about 700 km/s, in the
direction of the constellation of Perseus (not very far from Auriga).
| Skorost', poluchennaya v etom sluchae, byla okolo 700 km/s v
napravlenii sozvezdiya Perseya (ne ochen' daleko ot sozvezdiya Voznichego).
|
| 105
| Courvoisier regarded the agreement of those two earliest results as satisfactory, and this led him to further researches.
| Kurvuaz'e rassmatrival sootvetstvie etih dvuh rannih
rezul'tatov kak udovletvoritel'nye, i eto privelo ego k dal'neishim
issledovaniyam.
|
| 106
| There was a delay of 5 years between Courvoisiers first positive results and his next publication on the subject.12
In this period he accumulated a series of positive results by different
methods, obtained the equations required for the analysis of his data,
and devised new methods for measuring the absolute speed of the Earth.
| Byla zaderzhka na 5 let mezhdu pervymi polozhitel'nymi rezul'tatami Kurvuaz'e i ego sleduyushei publikaciei na etu temu. 12
V etot period on nakopil ryad polozhitel'nyh rezul'tatov raznymi
metodami, poluchil uravneniya, neobhodimye dlya analiza etih dannyh, a
takzhe razrabotal novye metody dlya izmereniya absolyutnoi skorosti Zemli.
|
| 107
| This delay shows that Courvoisier was careful enough to resist
publishing preliminary results before he was able to amass a large
amount of evidence for his claim.
| Eta zaderzhka pokazyvaet, chto Kurvuaz'e byl dostatochno
ostorozhen, chtoby izbegat' publikacii predvaritel'nyh rezul'tatov, prezhde
chem on smog nakopit' bol'shoe kolichestvo dokazatel'stv ego zayavlenii.
|
| 108
|
|
|
| 109
|
|
|
| 110
| Courvoisier derived equations13 that related the relevant measurements to the parameters of the motion of the Earth relative to the ether.14
| Kurvuaz'e poluchil uravneniya 13, kotorye otnosyatsya k sootvetstvuyushim izmereniyam parametrov dvizheniya Zemli otnositel'no efira 14
|
| 111
| The main parameters that appear in his equations (.... 2) are:
| Osnovnye parametry, kotorye poyavlyayutsya v ego uravneniya (ris. 2) yavlyayutsya sleduyushimi:
|
| 112
| c = the speed of light relative to the ether = 300,000 km/s
| s = skorost' sveta otnositel'no efira = 300000 km / s
|
| 113
| v = speed of the Earth (or the solar system) relative to the ether
| v = skorost' Zemli (ili Solnechnoi sistemy) otnositel'no efira
|
| 114
| A = right ascension of the apex of the absolute motion
| A = pryamoe voshozhdenie apeksa absolyutnoi skorosti
|
| 115
| D = declination of the apex of the absolute motion
| D = sklonenie apeksa absolyutnoi dvizheniya
|
| 116
| α = North local component of v/c
| α = severnaya lokal'naya sostavlyayushaya v/c
|
| 117
| β = Zenith local component of v/c
| β = zenitnaya lokal'naya sostavlyayushaya v/c
|
| 118
| γ = West local component of v/c
| γ = zapadnaya lokal'naya sostavlyayushaya v/c
|
| 119
| ϕ = latitude of the terrestrial observatory
| φ = shirota nazemnoi observatorii
|
| 120
| θ = sidereal time of measurement
| θ = zvezdnoe vremya izmereniya
|
| 121
|
|
|
| 122
| A straightforward geometrical analysis shows that the components of v/c are:
| Prostoi geometricheskoi analiz pokazyvaet, chto komponenty v/c, yavlyayutsya:
|
| 123
| α = (v/c) [cos ϕ sin D sin ϕ cos D cos (θ A)] (1)
β = (v/c) [sin ϕ sin D + cos ϕ cos D cos (θ A)] (2)
| α = (v/c) [cos ϕ sin D sin ϕ cos D cos (θ A)] (1)
β = (v/c) [sin ϕ sin D + cos ϕ cos D cos (θ A)] (2)
|
| 124
| {10}
γ = (v/c) cos D sin (θ
A) (3)
| γ = (v/c) cos D sin (θ A) (3)
|
| 125
| 
|
| 126
| .... 2.
| Ris. 2.
|
| 127
| This diagram shows the main geometrical parameters used in Courvoisiers theoretical analysis of ether effects.
| Eta diagramma pokazyvaet osnovnye geometricheskie parametry, ispol'zuemye Kurvuaz'e v teoreticheskom analize effektov efira.
|
| 128
| The spherical surface represents the Earth, and the observer is
at I, and the local directions Z, N, W correspond to Zenith,
geographical North and West.
| Sfericheskaya poverhnost' predstavlyaet Zemlyu, nablyudatel'
nahoditsya v I, i mestnye napravleniya Z, N, W sootvetstvuyut zenitu,
geografichesomu severu i zapadu.
|
| 129
| The North Pole is in the direction NP.
| Severnyi polyus v napravlenii NP.
|
| 130
| The velocity of the Earth is  . .
| Skorost' Zemli sostavlyaet  . .
|
| 131
|
|
|
| 132
| In Courvoisier's first method, as described above, light was reflected by a mirror.
| V pervom metode Kurvuaz'e, kak opisano vyshe, svet otrazhaetsya ot zerkala.
|
| 133
| To derive the theoretical effect, it was necessary to study the
influence of the motion of the mirror through the ether upon the
direction of the reflected ray.
| Dlya vyvoda teoreticheskogo effekta, bylo neobhodimo izuchit' vliyanie dvizheniya zerkala cherez efir na napravlenie otrazhennogo lucha.
|
| 134
| Courvoisier made use of the non-relativistic analysis developed by Adolf von Harnack,15
that predicted that the angle of reflection would be different from the
angle of incidence, relative to the proper reference system of the
mirror (.... 3).
| Kurvuaz'e ispol'zoval nerelyativistskii analiz, razrabotannyi Adol'fom fon Harnakom, 15
kotoryi predskazal, chto ugol otrazheniya budet otlichat'sya ot ugla
padeniya, po otnosheniyu k sobstvennoi sisteme otscheta zerkala (ris. 3).
|
| 135
| This was one of Courvoisiers main assumptions that was incompatible with the principle of relativity.
| Eto bylo odno iz osnovnyh predpolozhenii Kurvuaz'e, kotoroe bylo nesovmestimo s principom otnositel'nosti.
|
| 136
| 
|
| 137
| {11} .... 3.
| Ris. 3.
|
| 138
| Following a theoretical analysis by Adolf von Harnack,
Courvoisier accepted that the angle of reflection of light in a moving
mirror is influenced by its motion through the ether, and that there is a
second-order effect that can be measured in the reference frame of the
mirror.
| Sleduya teoreticheskomu analizu Adol'fa fon Harnaka, Kurvuaz'e
prinyal, chto ugol otrazheniya sveta dlya dvizhushegosya zerkala zavisit ot ego
dvizheniya cherez efir, i chto est' effekt vtorogo poryadka, kotoryi mozhet
byt' izmeren v sisteme otscheta zerkala.
|
| 139
|
|
|
| 140
| Taking into account this principle of the moving mirror,
Courvoisier predicted that the angle between the local vertical (zenith)
and the direction of observation of a given star would be slightly
different from the angle between the zenith and the direction of the
star observed using a mercury mirror (.... 4).
| S uchetom etogo principa dvizhushegosya zerkala, Kurvuaz'e
predskazal, chto ugol mezhdu mestnoi vertikal'yu (zenitom) i napravleniem
nablyudeniya opredelennoi zvezdy budet neskol'ko otlichat'sya ot ugla mezhdu
zenitom i napravleniem na zvezdu, kotoroe nablyudalaetsya s ispol'zovaniem
rtutnogo zerkala (ris. 4).
|
| 141
|
|
|
| 142
| 
|
| 143
| .... 4.
| Ris. 4.
|
| 144
| Courvoiser compared the direct measurement of the direction of a
star with its direction observed by reflection on a mercury mirror.
| Kurvuaz'e sravnival pryamoe izmerenie napravleniya na zvezdu s ee
napravleniem, kotoroe nablyudaetsya pri otrazhenii ot rtutnogo zerkala.
|
| 145
| {12}In
this specific case, the contraction of the Earth could produce no
effect, because both measurements were made relative to the same
reference (the local vertical) and the surface of the mercury mirror is,
of course, perpendicular to the local vertical, whatever the changes
that the gravitational field could undergo due to Lorentz contraction.
| V dannom konkretnom sluchae, szhatie Zemli ne mozhet proizvodit'
nikakogo effekta, potomu chto oba izmereniya proizvodyatsya otnositel'no
odnoi i toi zhe tochki otscheta (mestnoi vertikali) i poverhnost'yu zerkala
rtuti, konechno, perpendikulyarna k mestnoi vertikali, nezavisimo ot
izmeneniya, kotoromu gravitacionnoe pole mozhet podvergat'sya iz-za
sokrasheniya Lorenca.
|
| 146
| The predicted effect was a small systematic difference between
the direct and the reflected angles, which should depend on the
direction of the observatory relative to the motion of the Earth through
the ether.
| Predskazannyi effekt byl nebol'shim sistematicheskim razlichiem
mezhdu pryamym i otrazhennym uglom, kotoroe dolzhno zaviset' ot napravleniya
otnositel'nogo dvizheniya Zemli i observatorii cherez efir.
|
| 147
|
|
|
| 148
| 
|
| 149
| .... 5.
| Ris. 5.
|
| 150
| Harnacks diagram for analyzing the reflection of light in a moving mirror.
| Diagrammy Harnaka dlya analiza otrazheniya sveta v dvizhushemsya zerkale.
|
| 151
| The initial position of the mirror is S, and after a time δt its position is S'.
| Nachal'noe polozhenie zerkala S, i cherez nekotoroe vremya δt ego polozhenie S′.
|
| 152
| AA' is a wave front of the incident light beam, and BB' is a wave front of the reflected beam.
| AA′ volnovoi front padayushego lucha sveta, i VV′ volnovoi front otrazhennogo lucha.
|
| 153
|
|
|
| 154
| Let θ be the angle of incidence and θ' the angle of reflection
of a light ray in a moving mirror, measured relative to the ether (....
5).
| Pust' θ ugol padeniya i θ′ ugol otrazheniya lucha sveta v dvizhushemsya zerkale, izmerennye otnositel'no efira (ris. 5).
|
| 155
| According to Harnack's analysis, instead of θ=θ' the following equations would hold:
| Soglasno analizu Harnaka, podstanovka θ = θ′ privedet k sleduyushim uravneniyam:
|
| 156
| sin θ' = (1 β2) sin θ / (1 + 2β cos θ + β2) (4)
| sin θ′ = (1 β2) sin θ / (1 + 2β cos θ + β2) (4)
|
| 157
| cos θ' = [(1 + β2) cos θ + 2β] / (1 + 2β cos θ + β2) (5)
| cos θ′ = [(1 + β2) cos θ + 2β] / (1 + 2β cos θ + β2) (5)
|
| 158
| {13} In those equations, the speed of the
mirror is ß=v/c, in the direction perpendicular to the mirror.
| V etih uravneniyah, skorost' zerkala β = v / s, v napravlenii, perpendikulyarnom k zerkalu.
|
| 159
| Any motion of the mirror parallel to its surface would have no influence upon the direction of light.
| Lyuboe dvizhenie zerkala parallel'no ego poverhnosti ne budet imet' nikakogo vliyaniya na napravlenie sveta.
|
| 160
| In the case of the mercury mirror, the relevant direction if
the local vertical, and therefore β, here, has the same general meaning
ascribed by Courvoisier to this symbol.
| V sluchae rtutnogo zerkala, relevantnoe napravlenie mestnaya
vertikal' i, sledovatel'no, β zdes' imeet takoi zhe obshii smysl, kotoryi
Kurvuaz'e pripisyvaet etomu simvolu.
|
| 161
| Relative to the proper reference system of the mirror there is
an aberration effect, and the angles of incidence (z) and reflection
(z') are:
| Po otnosheniyu k sobstvennoi sisteme otscheta zerkala est' effekt aberracii, a ugly padeniya (z) i otrazheniya (z′) sostavlyayut:
|
| 162
| z = θ + α cos θ β sin θ (6)
| z = θ + α cos θ β sin θ (6)
|
| 163
| z = θ' + α cos θ' + β sin θ' (7)
| z = θ′ + α cos θ′ + β sin θ′ (7)
|
| 164
| where α is component of the velocity v/c of the mirror parallel to its surface.
| gde α yavlyaetsya sostavlyayushei skorosti v / c zerkala, parallel'noi ego poverhnosti.
|
| 165
| Notice that this is the classical aberration effect.
| Zametim, chto eto klassicheskii effekt aberracii.
|
| 166
| A relativistic analysis would lead to a different result.
| Relyativistskoi analiz privel by k drugomu rezul'tatu.
|
| 167
|
|
|
| 168
| The measured effect is the difference between z' and z:
| Izmerennyi effekt predstavlyaet soboi raznicu mezhdu z′ i z:
|
| 169
| z' z = (θ' θ) + α (cos θ' cos θ) + β (sin θ' sin θ) (8)
| z′ z = (θ′ θ) + α (cos θ′ cos θ) + β (sin θ′ sin θ) (8)
|
| 170
| Taking into account the above equations and making suitable substitutions, one obtains the approximate result:
| S uchetom privedennyh vyshe uravnenii i prinyatiya sootvetstvuyushih zamen, mozhno poluchit' priblizitel'noe rezul'tat:
|
| 171
| z' z = 2αβ sin2 z (9)
| z′ z = 2αβ sin2 z (9)
|
| 172
| Replacing α and β by their values in Eqs. (1) and (2), one obtains:
| Zamenyaya α i β na ih znacheniya v formulah (1) i (2), poluchim:
|
| 173
| z' z = [(v/c)2 sin2 z].[sin 2ϕ.sin2 D + cos 2ϕ.sin 2D. cos (θA) sin 2ϕ.cos2D.cos2(θA)]
(10)
| z′ z = [(v/c)2 sin2 z].[sin 2ϕ.sin2 D + cos 2ϕ.sin 2D.cos (θA) sin 2ϕ.cos2D.cos2(θA)]
(10)
|
| 174
| Notice that this equation contains a constant term and two
periodical components with different periods one sidereal day [cos
(θA)] and half a sidereal day [cos2 (θA)].
| Obratite vnimanie, chto eto uravnenie soderzhit postoyannyi chlen i
dva periodicheskih komponenta s razlichnymi periodami odin dlya zvezdnyh
sutok, [cos (θA)] i polovinu zvezdnyh sutok [cos2 (θA)].
|
| 175
| Therefore, from a suitable analysis of the data it should be
possible to obtain the speed (v/c), the declination (D) and the right
ascension (A) of the motion of the Earth relative to the ether.
| Takim obrazom, iz sootvetstvuyushego analiza dannyh dolzhna
poyavit'sya vozmozhnost' poluchit' skorost' (v/c), sklonenie (D) i pryamoe
voshozhdenie (A) dvizheniya Zemli otnositel'no efira.
|
| 176
|
|
|
- >> Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.10.2013 21:19, 99.9 KBait)
| 177
|
|
|
| 178
| The Leyden measurements had used four stars close to the North Pole.
| Pri izmereniyah v Leidene ispol'zovalis' chetyre zvezdy, blizkie k Severnomu polyusu.
|
| 179
| The difference zz' was measured in a series of observations, at the times of upper and lower culmination of each star.
| Raznica zz′ byla izmerena v serii nablyudenii v momenty verhnei i nizhnei kul'minacii kazhdoi zvezdy.
|
| 180
| The observed values of the periodical components of zz'
amounted to less than 1'', varying from 0.04'' for one of the stars to
about 0.5″ for another.
| Nablyudaemye znacheniya periodicheskih komponent zz′ sostavili
menee 1″, s variaciei ot 0,04″ dlya odnoi iz zvezd do 0,5″ dlya drugoi.
|
| 181
| The error of the measurements was estimated as 0.01″, therefore the effect was regarded as significant.
| Pogreshnost' izmerenii byla ocenena kak 0,01″, poetomu effekt rascenen kak znachimyi.
|
| 182
| From the Leyden data Courvoisier obtained the results:
| Iz Leidenskih dannyh Kurvuaz'e byli polucheny rezul'taty:
|
| 183
| A = 104 21; D = +39 27; v = 810 215 km/s
| A = 104 21; D = +39 27; v = 810 215 km/s
|
| 184
| {14} The estimated error of the speed amounted
to about 25%.
| Ocenivaemaya oshibka skorosti sostavila okolo 25%.
|
| 185
| The errors of the right ascension and declination amounted to about 1/15 of the full circle.
| Oshibki pryamogo voshozhdeniya i skloneniya sostavili okolo 1/15 polnogo kruga.
|
| 186
| Between 1921 and 1922 Courvoisier repeated the Leyden measurements, but with a slight change of method.
| Mezhdu 1921 i 1922 gg. Kurvuaz'e povtoril leidenskie izmereniya, no s nebol'shim izmeneniem metoda.
|
| 187
| Instead of a meridian circle he used a Wanschaff vertical
circle that enabled him to make measurements of the stars at any time
during the night.
| Vmesto meridiannogo kruga on ispol'zoval vertikal'nyi krug
Vanshaffa, kotoryi pozvolil emu proizvesti izmereniya zvezd v lyuboe vremya v
techenie nochi.
|
| 188
| Therefore his measurements were not limited to two sidereal times for each star.
| Poetomu ego izmereniya ne byli ogranicheny dvumya momentami zvezdnogo vremeni dlya kazhdoi zvezdy.
|
| 189
|
|
|
| 190
| From 4 June to 14 December 1921 he made a series of 142
measurements of the polar star BD +89.3, and from 18 March to 23 May
1922 he made further 64 determinations of zz'.
| S 4 iyunya po 14 dekabrya 1921 godu on proizvel seriyu iz 142
izmerenii Polyarnoi zvezdy BD 89,3 , a s 18 marta po 23 maya 1922 g. on
vypolnil dal'neishie 64 opredeleniya zz′.
|
| 191
| From those measurements Courvoisier obtained:
| Iz etih izmerenii Kurvuaz'e poluchil:
|
| 192
| A = 93 7; D = +27 12; v = 652 71 km/s
| A = 93 7; D = +27 12; v = 652 71 km/s
|
| 193
| The estimated relative error of the speed was reduced to about
10% and the errors of the right ascension and declination amounted to
less than 1/30 of the full circle.
| Raschetnaya otnositel'naya oshibka opredeleniya skorosti snizilas'
do okolo 10%, a oshibki opredeleniya pryamogo voshozhdeniya i skloneniya
sostavili menee chem 1/30 polnogo kruga.
|
| 194
| Courvoisiers work called the attention of a French astronomer,
the director of the Strasbourg observatory, Ernest Esclangon, who
repeated those measurements.18
| Rabota Kurvuaz'e obratila na sebya vnimanie francuzskogo
astronoma, direktora Strasburgskoi observatorii, Ernesta Esklangona,
kotoryi povtoril eti izmereniya. 18
|
| 195
| He confirmed the existence of a systematic effect of the same order of magnitude, and computed the values of A=69 and D=44.
| On podtverdil sushestvovanie sistematicheskogo effekta togo zhe poryadka velichiny, i vychislil znacheniya A=69 i D=44.
|
| 196
| Esclangon did not publish the estimated errors of his evaluation, nor the estimated speed of the Earth.
| Esklangon ne opublikoval ni raschetnye oshibki ego ocenki, ni ozhidaemuyu skorost' Zemli.
|
| 197
|
|
|
| 198
| Other evaluations were later obtained by Courvoisier using
measurements made at München (19301931) and Breslau (19331935), with
the following results:
| Drugie dannye byli pozdnee polucheny Kurvuaz'e s ispol'zovaniem
izmerenii, provedennyh v Myunhene (1930-1931) i Breslavle (1933-1935), so
sleduyushimi rezul'tatami:
|
| 199
|
| München
| Breslau (1)
| Breslau (2)
|
| A = 73 6
| A = 92 12
| A = 80 4
|
| D = +40 (estimated)19
| D = +44 25
| D = +30 10
|
| v = 889 93 km/s
| v = 927 200 km/s
| v = 700 60 km/s |
|
| Myunhen
| Breslavl' (1)
| Breslavl' (2)
|
| A = 73 6
| A = 92 12
| A = 80 4
|
| D = +40 (ocenka) 19
| D = +44 25
| D = +30 10
|
| V = 889 93 km / s
| V = 927 200 km / s
| V = 700 60 km / s |
|
| 200
| The results obtained in the second Breslau series presented the smallest errors.
| Rezul'taty, poluchennye vo vtoroi serii Breslavlya, predstavleny naimen'shimi oshibkami.
|
| 201
|
|
|
| 202
| In 1945, after his retirement, Courvoisier made a final series of observations from Basel.
| V 1945 godu, posle vyhoda na pensiyu, Kurvuaz'e vypolnil okonchatel'nye serii nablyudenii v Bazele.
|
| 203
| He obtained the following results:
| On poluchil sleduyushie rezul'taty:
|
| 204
| A = 60 14; D = +40 (estimated); v = 656 157 km/s
| A = 60 14 , D = +40 (ocenka), v = 656 157 km / s
|
| 205
| {15}
If we compare all the series of measurements, we notice that the right
ascension varied between 60 and 104 (more than the estimated errors);
the declination varied between 39 and 44 (within the estimated
errors);20 and the speed varied between 652 and 927 km/s (within estimated errors).
| Esli sravnit' vse serii izmerenii, my zamechaem, chto pryamoe
voshozhdenie var'irovalas' mezhdu 60 i 104 (bolee chem raschetnaya
oshibka); sklonenie ot 39 do 44 (v predelah raschetnyh oshibok), 20 i skorost' ot 652 do 927 km / s (v predelah raschetnyh oshibok).
|
| 206
| Notice that it is very hard to explain away Courvoisier's
results as due to instrument errors, because the observed effect varied
with periods of one sidereal day and half sidereal day.
| Obratite vnimanie, chto ochen' trudno ob'yasnit' rezul'taty
Kurvuaz'e instrumental'nymi pogreshnostyami, tak kak nablyudaemyi effekt
izmenyaetsya s periodami v odni zvezdnye sutki i polovinu zvezdnyh sutok.
|
| 207
| All common causes of error (gravity changes, temperature changes, etc.) would vary with periods of one (or half) solar day.
| Vse rasprostranennye prichiny oshibok (izmeneniya sily tyazhesti,
izmeneniya temperatury i t.d.) dolzhny menyat'sya s periodom v odni (ili
polovinu) solnechnyh sutok.
|
| 208
| Tidal influences due to the Moon would have periods that could
also be easily distinguished from the effects predicted by Courvoisier.
| Prilivnye vliyaniya Luny budut imet' periody, kotorye takzhe mogut byt' legko otlichimy ot effektov, predskazannyh Kurvuaz'e.
|
| 209
| Besides that, the data used by Courvoisier was obtained with
different instruments at different places, and covered a time span of 80
years.
| Krome togo, dannye, ispol'zuemye Kurvuaz'e, byli polucheny s
pomosh'yu razlichnyh instrumentov v raznyh mestah, i ohvatyvali promezhutok
vremeni v 80 let.
|
| 210
| The results presented by Courvoisier are therefore highly impressive and cannot be dismissed lightly.
| Rezul'taty, predstavlennye Kurvuaz'e, sledovatel'no, ves'ma vpechatlyaet i ne mogut byt' legko otvergnuty.
|
| 211
|
|
|
| 212
|
|
|
| 213
| In the first method used by Courvoisier, the stars work as mere point-like light sources.
| V pervom metode, kotoryi ispol'zoval Kurvuaz'e, zvezdy ispol'zuyutsya kak prostye tochechnye istochniki sveta.
|
| 214
| There is nothing peculiarly astronomical in the observed
effect because, according to Courvoisier's theory, this was ascribed to
the principle of the moving mirror.
| Tam net nichego specificheski astronomicheskogo v nablyudaemom
effekte, potomu chto, soglasno teorii Kurvuaz'e, eto bylo opisano kak
princip dvizhushegosya zerkala.
|
| 215
| Therefore, similar effects should occur for terrestrial light sources, too.
| Takim obrazom, podobnye effekty dolzhny takzhe voznikat' i dlya nazemnyh istochnikov sveta.
|
| 216
|
|
|
| 217
| Accordingly, Courvoisier was led to build a new instrument: an optical device for measuring absolute motion (.... 6).21 He used two small telescopes that
were placed in an underground room where the temperature was fairly constant.
| Sootvetstvenno, Kurvuaz'e eto privelo k sozdaniyu novogo
instrumenta:. opticheskogo ustroistva dlya izmereniya absolyutnogo dvizheniya
(ris. 6) 21 On ispol'zoval dva nebol'shih teleskopa, kotorye
byli razmesheny v podzemnom pomeshenii, gde temperatura byla dovol'no
postoyannoi.
|
| 218
| Both telescopes pointed obliquely (zenithal distance = 60) to a mercury mirror that was placed between them.
| Oba teleskopa byli nakloneny (zenitnoe rasstoyanie = 60 ) k rtutnomu zerkalu, kotoroe bylo pomesheno mezhdu nimi.
|
| 219
| They were mounted in a vertical plane in the East-West direction.
| Oni byli ustanovleny v vertikal'noi ploskosti v napravlenii Vostok-Zapad.
|
| 220
| One of the telescopes had a small electric light close to its
reticule, and this was the light source that was observed from the
second telescope.
| Odin iz teleskopov imel nebol'shoe elektricheskoe osveshenie
vblizi ot ee kresta vizirnyh nitei, i eto bylo istochnikom sveta, kotoryi
nablyudalsya vo vtoroi teleskop.
|
| 221
| Both telescopes were first adjusted so that it was possible to
see the reflection of the illuminated reticule of the first telescope
from the second telescope.
| Oba teleskopa snachala byli nastroeny takim obrazom, chtoby mozhno
bylo uvidet' otrazhenie osveshennoi setki iz pervoi truby ot vtorogo
teleskopa.
|
| 222
| They were then fastened in those directions.
| Zatem oni byli zakrepleny v etih napravleniyah.
|
| 223
| Of course, the angles of the telescopes with the local vertical were sensibly equal.
| Konechno, ugly teleskopov s mestnoi vertikali byli ochevidno ravny.
|
| 224
| The experiment did not try to measure any difference between those angles.
| Eksperiment ne pytalsya izmerit' kakoe-libo razlichie mezhdu etimi uglami.
|
| 225
| It attempted to detect small periodical changes of the position
of the image of the first telescope reticule as observed from the
second one.
| On byl prednaznachen dlya obnaruzheniya nebol'shih periodicheskih
izmenenii v polozhenii kresta vizirnyh nitei pervogo teleskopa, pri ih
nablyudenii iz vtorogo teleskopa.
|
| 226
| The apparent motion of {16} the reticule
was measured with the aid of the ocular micrometer of the second telescope.
| Vidimoe dvizhenie perekrestiya bylo izmereno s pomosh'yu okulyarnogo mikrometra vtorogo teleskopa.
|
| 227
|
|
|
| 228
| Using this device, Courvoisier made two series of observations in 1926 and 1927.
| S pomosh'yu etogo ustroistva Kurvuaz'e vypolnil dve serii nablyudenii v 1926 i 1927 godah.
|
| 229
| Afterwards, he had a special instrument built for this purpose, and made a third series of observations in 1932.
| Vposledstvii, on postroil special'nyi instrument dlya etoi celi, i vypolnil tret'yu seriyu nablyudenii v 1932 godu.
|
| 230
|
|
|
| 231
| In his first experiments the telescopes were placed in a vertical plane in the East-West direction.
| V ego pervyh eksperimentah teleskopy byli razmesheny v vertikal'noi ploskosti v napravlenii vostok-zapad.
|
| 232
| In 1926 and 1928 Courvoisier built two new instruments that could be rotated.
| V 1926 i 1928 godah Kurvuaz'e postroil dva novyh instrumenta, kotorye mogli vrashat'sya.
|
| 233
| He expected that this would improve his measurements.
| On ozhidal, chto eto budet sposobstvovat' uluchsheniyu ego izmerenii.
|
| 234
| However, he found out that it was impossible to compare
measurements when the device was rotated, due to mechanical problems,
and the instruments could only be effectively used in a fixed position.
| Tem ne menee, on vyyasnil, chto okazalos' nevozmozhnym sravnivat'
izmereniya, kogda ustroistvo povorachivalos', iz-za mehanicheskih problem, i
instrumenty mogut byt' effektivno ispol'zovany tol'ko v fiksirovannom
polozhenii.
|
| 235
|
|
|
| 236
| The equation used to compute the effect was similar to that
used in the case of the observation of stars, but instead of the North
component of the speed, it was necessary to take into account the West
component.
| Uravnenie, ispol'zuemoe dlya vychisleniya effekta, byl analogichno
tomu, kotoroe ispol'zovalos' v sluchae nablyudeniya zvezd, no vmesto
severnoi komponenty skorosti, bylo neobhodimo prinimat' vo vnimanie
zapadnuyu komponentu.
|
| 237
| As in the former case, the resulting equation has a constant
term plus variable components with periods of one sidereal day and half
sidereal day.
| Kak i v predydushem sluchae, rezul'tiruyushee uravnenie imeet
postoyannyi chlen plyus peremennye sostavlyayushie s periodami v odni zvezdnye
sutki i polovinu zvezdnyh sutok.
|
| 238
|
|
|
| 239
| 
|
| 240
| .... 6. Courvoisiers double telescope apparatus for measuring the motion of the Earth through the ether.
| Ris. 6. Dvoinoi teleskop Kurvuaz'e apparat dlya izmereniya dvizheniya Zemli cherez efir.
|
| 241
|
|
|
| 242
| {17} Table 1. Measurements made by Courvoisier
in 1926 with the double telescope instrument.
| Tablica 1. Izmereniya, vypolnennye v 1926 godu Kurvuaz'e s instrumentom v vide dvoinogo teleskopa.
|
| 243
|
| First series:
|
| Sidereal time 0
| (z z') + constant
| number of measurements
|
| 0.32 h
| 0.08″
| 21
|
| 1.23 h
| + 0.04″
| 64
|
| 2.45 h
| + 0.07″
| 14
|
| 3.31 h
| 0.38″
| 56
|
| 4.28 h
| 0.38″
| 14
|
| 5.28 h
| 0.57″
| 68
|
| 7.37 h
| 0.58″
| 55
|
| 9.29 h
| 0.57″
| 64
|
| 11.24 h
| 0.24″
| 30
|
| 12.73 h
| 0.04″
| 20
|
| 21.91 h
| + 0.21″
| 38
|
| 23.32 h
| + 0.08″
| 45 |
|
| Pervaya seriya:
|
| Zvezdnoe vremya θ
| (z z′) + konstanta
| Kolichestvo izmerenii
|
| 0,32 ch
| 0.08 ″
| 21
|
| 1,23 ch
| + 0.04 ″
| 64
|
| 2,45 ch
| + 0,07 ″
| 14
|
| 3,31 ch
| 0,38 ″
| 56
|
| 4,28 ch
| 0,38 ″
| 14
|
| 5,28 ch
| 0,57 ″
| 68
|
| 7,37 ch
| 0,58 ″
| 55
|
| 9,29 ch
| 0,57 ″
| 64
|
| 11,24 ch
| 0,24 ″
| +30
|
| 12,73 ch
| 0,04 ″
| 20
|
| 21,91 ch
| + 0,21 ″
| 38
|
| 23,32 ch
| + 0,08 ″
| 45 |
|
| 244
|
|
|
| 245
| Table 2. Measurements made by Courvoisier in 1927 with the double telescope instrument.
| Tablica 2. Izmereniya, vypolnennye v 1927 godu Kurvuaz'e s instrumentom v vide dvoinogo teleskopa.
|
| 246
|
| Second series:
|
| Sidereal time 0
| (z z') + constant
| number of measurements
|
| 2.9 h
| + 1.54″
| 4
|
| 7.3 h
| + 0.28″
| 6
|
| 8.2 h
| + 0.28″
| 7
|
| 9.1 h
| 0.01″
| 7
|
| 10.1 h
| + 0.23″
| 6
|
| 11.4 h
| + 0.56″
| 5
|
| 12.3 h
| + 0.60″
| 5
|
| 13.7 h
| + 0.52″
| 7
|
| 15.5 h
| + 0.84″
| 6
|
| 17.9 h
| + 0.88″
| 7
|
| 19.9 h
| + 0.80″
| 7 |
|
| Vtoraya seriya:
|
| Zvezdnoe vremya θ
| (z z′) + konstanta
| Kolichestvo izmerenii
|
| 2,9 ch
| + 1.54
| 4
|
| 7,3 ch
| + 0,28″
| 6
|
| 8,2 ch
| + 0,28″
| 7
|
| 9,1 ch
| 0,01″
| 7
|
| 10.1 ch
| + 0,23″
| 6
|
| 11.4 ch
| + 0,56″
| 5
|
| 12.3 ch
| + 0,60″
| 5
|
| 13,7 ch
| + 0,52″
| 7
|
| 15,5 ch
| + 0,84″
| 6
|
| 17,9 ch
| + 0,88″
| 7
|
| 19,9 ch
| + 0,80″
| 7 |
|
| 247
|
|
|
| 248
| {18} The first series comprised 489 observations,
and the second series only 67 observations.
| Pervaya seriya sostavila 489 nablyudenii, a vtoraya tol'ko 67 serii nablyudenii.
|
| 249
| From the first series, Courvoisier computed the following values:
| Iz pervoi serii Kurvuaz'e vychislil sleduyushie znacheniya:
|
| 250
| A = 70 6; D = +33 11; v = 493 54 km/s
| A = 70 6; D = +33 11; v = 493 54 km/s
|
| 251
| From the second series, he obtained the results:
| Iz vtoroi serii on poluchil takie rezul'taty:
|
| 252
| A = 22 6; D = +72 11; v = 606 45 km/s
| A = 22 6; D = +72 11; v = 606 45 km/s
|
| 253
| Of course, the results obtained from the first series of
measurements seemed more reliable than those from the second series, and
they exhibited a closer agreement with former measurements.
| Konechno, rezul'taty, poluchennye v pervoi serii izmerenii
predstavlyayutsya bolee nadezhnym, chem ot vtorogo serii, i oni pokazali
bolee blizkoe sootvetstvie s prezhnimi izmereniyami.
|
| 254
|
|
|
| 255
| Notice that, although those measurements attempted to detect
the same kind of effects as the astronomical observations - that is, a
difference between angle of incidence and angle of reflection in a
moving mirror - the star observations used the North-South direction,
and the cave experiments employed the East-West direction.
| Obratite vnimanie, chto, hotya eti izmereniya delali popytku
obnaruzhit' takie zhe posledstviya, chto i astronomicheskie nablyudeniya to
est', raznicu mezhdu uglom padeniya i uglom otrazheniya v dvizhushemsya zerkale
zvezdnye nablyudeniya ispol'zovali napravlenie sever-yug, a eksperimenty
v zakrytom pomeshenii ispol'zovali napravlenie vostok-zapad.
|
| 256
| The equations were different, and nevertheless Courvoisier
obtained a nice agreement between the new device and the former results.
| Uravneniya byli raznye, i tem ne menee Kurvuaz'e poluchil horoshee soglasie mezhdu novym ustroistvom i prezhnimi rezul'tatami.
|
| 257
|
|
|
| 258
|
|
|
| 259
| In 1928 Courvoisier built another device to measure the speed of the Earth using the principle of the moving mirror.
| V 1928 g. Kurvuaz'e postroil drugoe ustroistvo dlya izmereniya skorosti Zemli s ispol'zovaniem principa dvizhushegosya zerkala.
|
| 260
| Instead of using two telescopes, he used a single telescope, with two perpendicular mirrors in front of its objective (.... 7).
| Vmesto primeneniya dvuh teleskopov, on ispol'zoval odin
teleskop, s dvumya perpendikulyarnymi zerkalami pered ego ob'ektivom (ris.
7).
|
| 261
| The body of the telescope was placed in a horizontal position.
| Truba teleskopa byla razmeshena v gorizontal'nom polozhenii.
|
| 262
| The mirrors were adjusted so that it was possible to observe
the reflected image of the thread micrometer of the telescope in close
coincidence with the real micrometer thread.
| Zerkala byli otregulirovany takim obrazom, chtoby mozhno bylo
nablyudat' otrazhennoe izobrazhenie niti mikrometra teleskopa v blizkom
sovpadenii s real'noi nit'yu mikrometra.
|
| 263
| He predicted that the relative position of the image and the
thread should undergo periodic fluctuations, and computed the predicted
effect.
| On predskazal, chto otnositel'noe polozhenie izobrazheniya i niti
dolzhno podvergat'sya periodicheskim kolebaniyam, i vychislil predskazannyi
effekt.
|
| 264
|
|
|
| 265
| From April to June 1928 Courvoisier obtained a series of 53
measurements, both in the North-South and in the East-West directions,
and he computed the following values:
| S aprelya po iyun' 1928 g. Kurvuaz'e byla poluchena seriya iz 53
izmerenii, kak v napravlenii sever-yug, tak i vostok-zapad, i on vychislil
sleduyushie znacheniya:
|
| 266
| A = 74 1; D = +36 1; v = 496 10 km/s
| A = 74 1; D = +36 1; v = 496 10 km/s
|
| 267
| The first series of measurements was made from 31 July and 6
August 1926, with observations spanning between 3 and 20 o'clock
sidereal time; the second one, from 28 February to 29 May 1927, with
observations covering the period from 21 to 13 o'clock sidereal time.
| Pervaya seriya izmerenii byla provedena s 31 iyulya i 6 avgusta
1926 goda, s nablyudeniyami, ohvatyvayushimi ot 3 do 20 chasov zvezdnogo
vremeni; vtoraya seriya s 28 fevralya po 29 maya 1927 goda, s nablyudeniyami
za period s 21 do 13 chasov zvezdnogo vremeni.
|
| 268
| Both series comprised more than 500 measurements.
| Obe serii sostavili bolee 500 izmerenii.
|
| 269
| Tables 1 and 2 shows the mean results obtained by Courvoisier for each sidereal time:
| V tablicah 1 i 2 pokazany srednie rezul'taty, poluchennye Kurvuaz'e dlya kazhdogo perioda zvezdnogo vremeni:
|
| 270
|
|
|
| 271
| 
|
| 272
| .... 7. Courvoisiers coupled mirror device for measuring the motion of the Earth through the ether.
| Ris. 7. Ustroistvo Kurvuaz'e so svyazannymi zerkalami dlya izmereniya dvizheniya Zemli otnositel'no efira.
|
| 273
|
|
|
| 274
| {19} Courvoisiers new experiment was probably
suggested by a similar arrangement that had been used by Esclangon in 1927.23
| Novyi eksperiment Kurvuaz'e byl, veroyatno, podskazan podobnym ustroistvom, kotoroe bylo ispol'zovano Esklangonom v 1927 godu. 23
|
| 275
| The French astronomer used two mirrors, but light underwent three reflections (.... 8).
| Francuzskii astronom ispol'zoval dva zerkala, no svet ispytyval tri otrazheniya (ris. 8).
|
| 276
| The maximum effect occurred at 3 h or 15 h sidereal time, corresponding to A = 45 or 225.
| Maksimal'nyi effekt poyavlyalsya dlya 3 ch ili 15 ch zvezdnogo vremeni, chto sootvetstvuet A = 45 ili 225 .
|
| 277
| Esclangon did not compute the speed of the Earth through the
ether indeed, he did not even provide a definite interpretation of the
phenomenon.
| Esklangon ne vychislyal skorost' Zemli cherez efir bolee togo, on dazhe ne obespechivayut opredelennuyu interpretaciyu yavleniya.
|
| 278
| 
|
| 279
| .... 8. Esclangons coupled mirror device for measuring the
motion of the Earth through the ether (a), and a graphical
representation of his results (b), showing the observed angular
fluctuations as a function of sidereal time.
| Ris. 8. Ustroistvo Esklangona so svyazannymi zerkalami dlya
izmereniya dvizheniya Zemli cherez efir (a) i graficheskoe predstavlenie ego
rezul'tatov (b), pokazyvayushih nablyudaemye uglovye kolebaniya v
zavisimosti ot zvezdnogo vremeni.
|
| 280
|
|
|
| 281
|
|
|
| 282
| As described above, Courvoisier's second attempt to measure the
absolute velocity of the Earth was grounded upon his analysis of the
Lorentz contraction of the Earth (.... 9).
| Kak opisano vyshe, vtoraya popytka Kurvuaz'e izmerit' absolyutnuyu
skorost' Zemli byla osnovana na ego analize sokrasheniya Lorenca dlya Zemli
(ris. 9).
|
| 283
| In this case, Courvoisier supposed that the local vertical
would undergo a change, due to the Lorentz contraction of the Earth, and
this change would be observable as a periodical fluctuation in the
angle between the North Pole and the zenith, as a function of the
sidereal time.
| V etom sluchae Kurvuaz'e predpolozhil, chto mestnaya vertikal'
preterpit izmeneniya v svyazi s sokrasheniem Lorenca dlya Zemli, i eto
izmenenie budet nablyudat'sya kak periodicheskoe kolebanie ugla mezhdu
Severnym polyusom i zenitom, kak funkciya zvezdnoe vremya.
|
| 284
|
|
|
| 285
| Courvoisier's theoretical analysis led him to predict that the
variation of the zenithal distance Δz of a star close to the North Pole
would obey the approximate relation:
| Teoreticheskii analiz Kurvuaz'e privel ego k predskazaniyu, chto
izmenenie zenitnogo rasstoyaniya Δz blizosti zvezdy k Severnomu polyusu
dolzhny podchinyat'sya priblizhennomu sootnosheniyu:
|
| 286
| Δz = 1/2 αβ (11)
| Δz = 1/2 αβ (11)
|
| 287
| {20} There are some special observational
difficulties in this second method.
| Est' neskol'ko specificheskih trudnostei v nablyudenii dlya etogo vtorogo sposoba.
|
| 288
| If it were possible to observe a star laying exactly in the
direction of the celestial North Pole, the observation would be quite
simple.
| Esli by mozhno bylo nablyudat' zvezdu, lezhashuyu tochno v
napravlenii nebesnogo Severnogo polyusa, nablyudenie okazhetsya dovol'no
prostym.
|
| 289
| However, if the star is not exactly in the direction of the
pole, its zenithal distance will depend on the sidereal time of the
observation.
| Odnako, esli zvezda nahoditsya ne tochno v napravlenii polyusa, ee
zenitnoe rasstoyanie budet zaviset' ot zvezdnogo vremeni nablyudeniya.
|
| 290
| This classical large effect would have, therefore, a period of
one sidereal day and would interfere with any attempt to measure any
influence due to the motion through the ether with a period of one
sidereal day.
| Etot klassicheskii bol'shoi effekt imeet, takim obrazom, period
odni zvezdnye sutki, i on dolzhen pomeshat' lyuboi popytke izmerit'
kakoe-libo vliyanie za schet dvizheniya cherez efir s periodom odin zvezdnyi
den'.
|
| 291
| Other interfering effects, such as temperature changes, vary
with a period of about one solar day, and they are very large and
irregular.
| Drugie meshayushie effekty, takie kak izmeneniya temperatury,
izmenyayutsya s periodom priblizitel'no odin solnechnyi den', i oni ochen'
bol'shie i neregulyarnye.
|
| 292
| For those reasons, Courvoisier gave up the attempt of finding
the amplitude of the sidereal day effect, and only computed the half
sidereal day effect.
| Po etim prichinam, Kurvuaz'e ostavil popytku nahozhdeniya
amplitudy effekta za zvezdnye sutki, i tol'ko vychislil effekt, svyazannyi
s polovinoi zvezdnyh sutok.
|
| 293
| It was impossible, therefore, to find all parameters, and he
assumed a value of 40 for the declination, and computed the speed and
right ascension of the motion of the Earth relative to the ether.
| Bylo nevozmozhno, takim obrazom, naiti vse parametry, i on
predpolozhil znachenie 40 dlya skloneniya, i vychislil skorost' i pryamoe
voshozhdenie dvizheniya Zemli otnositel'no efira.
|
| 294
| Dropping out the component corresponding to the period of one sidereal day, he obtained the following equation:
| Otbrosiv komponentu, sootvetstvuyushuyu periodu v odin zvezdnyi den', on poluchil sleduyushee uravnenie:
|
| 295
| Δz = (1/4)(v/c)2.sin 2ϕ (const.
| Δz = (1/4)(v/c)2.sin 2ϕ (const.
|
| 296
| cos2D.cos2(θA)] (12)
| cos2D.cos2(θA)] (12)
|
| 297
| 
|
| 298
| {21} .... 9.
| Ris. 9.
|
| 299
| According to Courvoisier, the Lorentz contraction of the Earth
and of optical instruments could have a small observable influence on
astronomical observations and terrestrial experiments.
| Soglasno Kurvuaz'e, sokrashenie Lorenca dlya Zemli i opticheskih
priborov mozhet imet' nebol'shoe vliyanie na astronomicheskie nablyudeniya i
nazemnye eksperimenty.
|
| 300
| Using the data he had already obtained from 1914 to 1917, and
combining those results with other measurements he made in 19211922 and
1925-1926, with the same instrument, Courvoisier obtained the following
result:
| Ispol'zuya dannye, kotorye on uzhe poluchil s 1914 po 1917 gg. i
ob'ediniv eti rezul'taty s drugimi izmereniyami, kotorye on sdelal v
19211922 i 19251926 gg. s tem zhe instrumentom, Kurvuaz'e poluchil
sleduyushii rezul'tat:
|
| 301
| A = 74 3; [D = +40]; v = 587 48 km/s
| A = 74 3; [D = +40]; v = 587 48 km/s
|
| 302
| He also analyzed measurements that had been obtained in routine
observations at the Paris observatory, in the period 1899-1901. All
those series of observations exhibited similar variations with a period
of 12 sidereal hours.
| On takzhe proanaliziroval izmereniya, kotorye byli polucheny v
regulyarnyh nablyudeniyah v Parizhskoi observatorii v period 18991901 gg.
Vse eti serii nablyudenii pokazali pohozhie variacii s periodom 12
zvezdnyh chasov.
|
| 303
| Assuming a value of 40 for the declination, he obtained the following results:
| Predpolozhiv znachenie 40 dlya skloneniya, on poluchil sleduyushie rezul'taty:
|
| 304
| A = 70 11; [D = +40]; v = 810 166 km/s
| A = 70 11; [D = +40]; v = 810 166 km/s
|
| 305
| Afterwards Courvoisier also computed the motion of the Earth
using measurements from Breslau (19231925 and 19331935) and from
München (1927-1931).
| Vposledstvii Kurvuaz'e takzhe vychislil dvizhenie Zemli po izmereniyam v Breslavle (19231925 i 19331935) i v Myunhene (19271931).
|
| 306
| Taking into account all the observations, he obtained the following final result:
| Prinimaya vo vnimanie vse nablyudeniya, on poluchil sleduyushii okonchatel'nyi rezul'tat:
|
| 307
| A = 65 10; [D = +40]; v = 574 97 km/s
| A = 65 10; [D = +40]; v = 574 97 km/s
|
| 308
| {22}
|
|
| 309
| The effects predicted by Courvoisier as a consequence of the
Lorentz contraction of the Earth should depend on the latitude of the
observatory.
| Effekty, predskazannye Kurvuaz'e kak sledstvie sokrashenie Lorenca dlya Zemli, dolzhny zaviset' ot shiroty observatorii.
|
| 310
| For that reason, if the same set of stars was observed from two
observatories at very different latitudes, there should exist a
systematic difference between the measured declinations of the stars, as
a function of sidereal time.
| Po etoi prichine, esli tot zhe nabor zvezd nablyudalsya iz dvuh
observatorii, raspolozhennyh na ochen' raznyh shirotah, dolzhny sushestvovat'
sistematicheskie razlichiya mezhdu izmerennymi skloneniyami zvezd, kak
funkciya ot zvezdnogo vremeni.
|
| 311
| To test the existence of this effect, Courvoisier analyzed the catalogues containing measurements made at Heidelberg (ϕ1 = + 49.24) and at Cape Town,
South Africa (ϕ2 = 33.48).
| Chtoby proverit' sushestvovanie etogo effekta, Kurvuaz'e
proanaliziroval katalogi, soderzhashie izmereniya, vypolnennye v
Geidel'berge (ϕ1 = + 49.24) i v Keiptaune, Yuzhnaya Afrika (ϕ2 = 33.48).
|
| 312
| Let D1 be the declination of some star measured from Heidelberg, and D2 the declination of the same star measured from Cape of Good Hope.
| Pust' D 1 sklonenie nekotoroi zvezdy, izmerennoe v Geidel'berge, a D 2 sklonenie toi zhe zvezdy, izmerennoe na myse Dobroi Nadezhdy.
|
| 313
| Each declination, according to Courvoisier's analysis, undergoes a periodical change:
| Kazhdoe sklonenie, soglasno analizu Kurvuaz'e, preterpevaet periodicheskie izmeneniya:
|
| 314
| Δz1 = 1/2 α1β1 Δz2 = 1/2 α2β2
(13)
| Δz1 = 1/2 α1β1 Δz2 = 1/2 α2β2
(13)
|
| 315
| Those effects are not equal; therefore, the difference between
the declinations measured at the two observatories should undergo a
periodical change:
| Eti effekty ne ravny, i poetomu raznica mezhdu skloneniyami,
izmerennymi dlya dvuh observatorii, dolzhna podvergat'sya periodicheskomu
izmeneniyu:
|
| 316
| D1 D2 = 1/2 (α1β1 α2β2) (14)
| D1 D2 = 1/2 (α1β1 α2β2) (14)
|
| 317
| Using the typical values A=75 and D=40 obtained in former
measurements, and taking into account the latitudes of Heidelberg and
Cape Town, Courvoisier predicted that there should exist a difference
between the measured declinations of the stars that should depend on
their right ascension a:
| Ispol'zuya tipichnye znacheniya A=75 i D=40, poluchennye v
predydushih izmereniyah i s uchetom shiroty Geidel'berge i Keiptauna,
Kurvuaz'e predskazal, chto dolzhna sushestvovat' raznica mezhdu izmerennym
skloneniem zvezd, kotorye dolzhny zaviset' ot ih pryamogo voshozhdeniya:
|
| 318
| D1 D2 = + 0.16′′ 0.18′′.
| D1 D2 = + 0.16′′ 0.18′′.
|
| 319
| cos (α 5h) 0.16′′.
| cos (α 5h) 0.16′′.
|
| 320
| cos 2(α 5h) (15)
| cos 2(α 5h) (15)
|
| 321
| The amplitude was obtained by comparing the astronomical data of the two observatories, and led to v =750 km/s.
| Amplituda byla poluchena putem sopostavleniya astronomicheskih dannye dvuh observatorii, i privela k V = 750 km / s.
|
| 322
| Table 3 contains Courvoisiers comparison between the observed and predicted values of D1D2.
| V tablice 3 privedeny sravneniya Kurvuaz'e v period mezhdu nablyudaemym i prognoziruemym znacheniyam D1D2.
|
| 323
| The third column of the table presented the observed values
corrected for null declination, in order to avoid classical errors due
to atmospheric refraction, etc.
| V tret'em stolbce tablicy predstavleny nablyudaemye znacheniya s
popravkoi na nulevoe sklonenie, dlya togo, chtoby izbezhat' klassicheskih
oshibok, svyazannyh s atmosfernoi refrakciei i t.d.
|
| 324
| There is a better agreement between the theoretical prediction and the corrected values than with the raw data.
| Sushestvuet luchshee soglasie mezhdu teoreticheskimi predskazaniyami i skorrektirovannymi znacheniyami, chem s syrymi dannymi.
|
| 325
|
|
|
| 326
| In his analysis of the second method, Courvoisier assumed that
the Lorentz contraction of the Earth produces a local periodical change
of the direction of the gravitational field.
| V svoem analize vtorogo sposoba Kurvuaz'e predpolagal, chto
sokrashenie Lorenca dlya Zemli sozdaet lokal'noe periodicheskoe izmenenie
napravleniya gravitacionnogo polya.
|
| 327
| This effect was not compensated by changes in the direction of the astronomical instruments.
| Etot effekt ne kompensiruetsya za schet izmeneniya napravleniya astronomicheskih instrumentov.
|
| 328
| Therefore, he was led to think that the effect could also be detected in an experiment using a terrestrial light source.
| Takim obrazom, on prishel k mneniyu, chto effekt mozhet byt' takzhe
obnaruzhen v hode eksperimenta s ispol'zovaniem nazemnogo istochnika
sveta.
|
| 329
| {23} He placed a mercury mirror directly
below the observatory meridian circle and pointed the telescope downward.
| On pomestil rtutnoe zerkalo neposredstvenno pod meridian observatorii i napravil teleskopa vniz.
|
| 330
| The instrument was then delicately adjusted in such a way that
it was possible to observe the reflected image of the micrometer threads
superimposed to the real threads.
| Pribor byl zatem tonko otregulirovan takim obrazom, chtoby mozhno
bylo nablyudat' otrazhennoe izobrazhenie nitei mikrometra, nalozhennye na
real'nye niti.
|
| 331
| The position of the telescope was locked, and observations were
made of the relative displacement of the micrometer thread and its
image.
| Polozhenie teleskopa bylo zafiksirovano, i byli vypolneny nablyudeniya otnositel'nogo smesheniya niti mikrometra i ee otrazheniya.
|
| 332
| He predicted the following deflection in the East-West direction:
| On predskazal sleduyushie otkloneniya v napravlenii vostok-zapad:
|
| 333
| Δz = (1/4)(v/c)2.
| Δz = (1/4)(v/c)2.
|
| 334
| [sin ϕ.sin2D.sin (θA) + cos ϕ.cos2D.sin 2(θA)] (16)
| [sin ϕ.sin2D.sin (θA) + cos ϕ.cos2D.sin 2(θA)] (16)
|
| 335
| Table 3.
| Tablica 3.
|
| 336
| Difference between the declinations of a star (D1D2), observed from two distant observatories, as a function of sidereal time α.
| Razlichie mezhdu skloneniyami zvezd (D1D2), nablyudaemoe iz dvuh udalennyh observatorii, kak funkciya ot zvezdnogo vremeni α.
|
| 337
|
| α | D1D2
|
| observed
| observed (corrected)
| prediction
|
| 0 h
| + 0.35′′
| + 0.35′′
| + 0.26′′
|
| 1 h
| + 0.21′′
| + 0.21′′
| + 0.16′′
|
| 2 h
| + 0.01′′
| + 0.01′′
| + 0.04′′
|
| 3 h
| 0.07′′
| 0.07′′
| 0.07′′
|
| 4 h
| 0.17′′
| 0.17′′
| 0.16′′
|
| 5 h
| + 0.03′′
| + 0.03
| 0.17′′
|
| 6 h
| + 0.17′′
| + 0.17
| 0.14′′
|
| 7 h
| 0.03′′
| 0.03′′
| 0.06′′
|
| 8 h
| + 0.07′′
| + 0.07′′
| + 0.04′′
|
| 9 h
| + 0.10′′
| + 0.10′′
| + 0.14′′
|
| 10 h
| + 0.08′′
| + 0.08′′
| + 0.25′′
|
| 11 h
| + 0.09′′
| + 0.09′′
| + 0.32′′
|
| 12 h
| + 0.29′′
| + 0.29′′
| + 0.34′′
|
| 13 h
| + 0.32′′
| + 0.35′′
| + 0.32′′
|
| 14 h
| + 0.29′′
| + 0.39′′
| + 0.29′′
|
| 15 h
| 0.04′′
| + 0.22′′
| + 0.25′′
|
| 16 h
| 0.21′′
| + 0.13′′
| + 0.20′′
|
| 17 h
| 0.23′′
| + 0.18′′
| + 0.19′′
|
| 18 h
| 0.29′′
| + 0.12′′
| + 0.20′′
|
| 19 h
| 0.31′′
| + 0.10′′
| + 0.23′′
|
| 20 h
| 0.17′′
| + 0.17′′
| + 0.29′′
|
| 21 h
| + 0.04′′
| + 0.30′′
| + 0.33′′
|
| 22 h
| + 0.26′′
| + 0.36′′
| + 0.34′′
|
| 23 h
| + 0.38′′
| + 0.41′′
| + 0.32′′ |
|
| α | D1D2
|
| Nablyudenie
| Nablyudenie (skorrektirovano)
| Predskazanie
|
| 0 ch
| + 0.35′′
| + 0.35′′
| + 0.26′′
|
| 1 ch
| + 0.21′′
| + 0.21′′
| + 0.16′′
|
| 2 ch
| + 0.01′′
| + 0.01′′
| + 0.04′′
|
| 3 ch
| 0.07′′
| 0.07′′
| 0.07′′
|
| 4 ch
| 0.17′′
| 0.17′′
| 0.16′′
|
| 5 ch
| + 0.03′′
| + 0.03
| 0.17′′
|
| 6 ch
| + 0.17′′
| + 0.17
| 0.14′′
|
| 7 ch
| 0.03′′
| 0.03′′
| 0.06′′
|
| 8 ch
| + 0.07′′
| + 0.07′′
| + 0.04′′
|
| 9 ch
| + 0.10′′
| + 0.10′′
| + 0.14′′
|
| 10 ch
| + 0.08′′
| + 0.08′′
| + 0.25′′
|
| 11 ch
| + 0.09′′
| + 0.09′′
| + 0.32′′
|
| 12 ch
| + 0.29′′
| + 0.29′′
| + 0.34′′
|
| 13 ch
| + 0.32′′
| + 0.35′′
| + 0.32′′
|
| 14 ch
| + 0.29′′
| + 0.39′′
| + 0.29′′
|
| 15 ch
| 0.04′′
| + 0.22′′
| + 0.25′′
|
| 16 ch
| 0.21′′
| + 0.13′′
| + 0.20′′
|
| 17 ch
| 0.23′′
| + 0.18′′
| + 0.19′′
|
| 18 ch
| 0.29′′
| + 0.12′′
| + 0.20′′
|
| 19 ch
| 0.31′′
| + 0.10′′
| + 0.23′′
|
| 20 ch
| 0.17′′
| + 0.17′′
| + 0.29′′
|
| 21 ch
| + 0.04′′
| + 0.30′′
| + 0.33′′
|
| 22 ch
| + 0.26′′
| + 0.36′′
| + 0.34′′
|
| 23 ch
| + 0.38′′
| + 0.41′′
| + 0.32′′ |
|
| 338
| {24} Courvoisier made two series of observations:
22-24 October and 22-25 November 1922.
| Kurvuaz'e vypolnil dve serii nablyudenii: 2224 oktyabrya i 2225 noyabrya 1922 goda.
|
| 339
| He noticed that temperature changes affected the position of
the telescope, and that this influence had to be taken into account.
| On zametil, chto izmeneniya temperatury povliyalo na polozhenie teleskopa, prichem vliyanie eto dolzhno byt' prinyato vo vnimanie.
|
| 340
| From the uncorrected observed measurements he computed the following values:
| Iz nablyudaemyh neispravlennyh izmerenii on vychislil sleduyushie znacheniya:
|
| 341
| A = 74 10; D = +67 13; v = 920 73 km/s
| A = 74 10; D = +67 13; v = 920 73 km/s
|
| 342
| Applying a temperature correction, he obtained the following results:
| Primenyaya korrekciyu temperatury, on poluchil sleduyushie rezul'taty:
|
| 343
| A = 98 7; D = +25 11; v = 500 47 km/s
| A = 98 7; D = +25 11; v = 500 47 km/s
|
| 344
| This experiment was repeated by August Kopff, of the Heidelberg observatory, from 10 to 29 June 1923.
| Etot eksperiment byl povtoren Avgustom Kopfom iz Geidel'bergskoi observatorii s 10 po 29 iyunya 1923 goda.
|
| 345
| As in the case of Courvoisier's experiment, there was a strong
effect due to temperature changes (temperature varied between +6C and
+17C).
| Kak i v sluchae eksperimenta Kurvuaz'e, ne bylo sil'nogo effekta
v rezul'tate izmeneniya temperatury (temperatura kolebalas' ot +6 S do
+17C).
|
| 346
| Courvoisier analyzed Kopff s data assuming the values A = 75 and D = +40.
| Kurvuaz'e proanaliziroval dannye Kopfa, prinyav znacheniya A = 75 i D = +40.
|
| 347
| After applying temperature corrections, he obtained a speed of 753 57 km/s.
| Posle primeneniya temperaturnyh popravok, on poluchil skorost' 753 57 km/s.
|
| 348
|
|
|
| 349
| Courvoisier also attempted to detect the motion of the Earth relative to the ether by other methods.
| Kurvuaz'e takzhe popytalsya obnaruzhit' dvizhenie Zemli otnositel'no efira drugimi metodami.
|
| 350
| He regarded the positive result of the nadir observation method
as a confirmation of his hypothesis that the Lorentzs contraction
produced an observable periodical change of the local vertical.
| On schital polozhitel'nymi rezul'taty nablyudeniya nadira kak
podtverzhdenie svoei gipotezy, chto sokrashenie Lorenca proizvodit
nablyudaemye periodicheskie izmeneniya mestnoi vertikali.
|
| 351
| He soon devised other ways of observing such an effect.
| Vskore on razrabotal drugie sposoby nablyudeniya takogo effekta.
|
| 352
|
|
|
| 353
| One of the instruments he used was a plumb line attached to one of the columns of the Babelsberg observatory.
| Odnim iz ispol'zuemyh im instrumentov byl otves, prikreplennyi k odnoi iz opor Babel'sbergskoi observatorii.
|
| 354
| The main body of the plumb line was a metallic rod, 95 cm long.
| Osnovnym telom linii otvesa byl metallicheskii sterzhen', 95 sm v dlinu.
|
| 355
| At its lower end there was a mark that was illuminated and projected upon a wall.
| Na ego nizhnem konce byla otmetka, kotoraya byla osveshena i proecirovalas' na stenu.
|
| 356
| It was possible to observe deflections of about 0.05″ of the direction of the plumb line, in the East-West direction.24
| Mozhno bylo nablyudat' otkloneniya napravleniya otvesa primerno na 0,05″ v napravlenii vostok-zapad. 24
|
| 357
| Measurements made in 1925 with this instrument led to a speed of the Earth of about 400 km/s, assuming A = 75 and D = +40.
| Izmereniya, provedennye v 1925 godu s etim instrumentom pokazali skorost' Zemli okolo 400 km/s, pri A = 75 i D = +40 .
|
| 358
| In 1931 Courvoisier improved this instrument observing the motion of its tip with the aid of a microscope (.... 10).
| V 1931 godu Kurvuaz'e usovershenstvoval etot instrument, nablyudaya za dvizheniem ego konca s pomosh'yu mikroskopa (ris. 10).
|
| 359
| Now he was able to compute the three parameters of the Earth's motion, obtaining:
| Teper' on byl v sostoyanii vychislit' tri parametra dvizheniya Zemli, poluchiv:
|
| 360
| A = 64 6; D = +50 9; v = 367 29 km/s
| A = 64 6; D = +50 9; v = 367 29 km/s
|
| 361
| 
|
| 362
| {25}.... 10.
| Ris. 10.
|
| 363
| Courvoisiers plumb line apparatus for measuring oscillations of the local gravitational vertical due to Lorentz contraction.
| Otves Kurvuaz'e dlya izmereniya kolebanii mestnoi gravitacionnoi vertikali iz-za sokrasheniya Lorenca.
|
| 364
| Similar observations were made by Esclangon, with the help of
André-Louis Danjon, using two horizontal pendulums with perpendicular
motions.25
| Analogichnye nablyudeniya vypolnil Eksklangon s pomosh'yu Andre-Lui
Danzhona, ispol'zuya dva gorizontal'nyh mayatnika s perpendikulyarnymi
dvizheniyami 25
|
| 365
| One of the pendulums lead to A=69; for the second pendulum,
A=52 Esclangon did not provide other information and did not attempt to
compute the speed of the Earth.
| Odin iz mayatnikov pokazal A=69 ;. dlya vtorogo mayatnika A =
52, Esklangon ne predostavil drugie svedeniya i ne pytalsya vychislit'
skorost' Zemli.
|
| 366
| {26}
|
|
| 367
| Another way of observing the variation of the local vertical
direction, according to Courvoisier, was with the aid of bubble levels.26
| Drugoi sposob nablyudeniya za izmeneniem napravleniya mestnoi vertikali, po Kurvuaz'e, byl vypolnen s pomosh'yu puzyr'kovyh urovnei. 26
|
| 368
| He used two very sensitive level meters.
| On ispol'zoval dva ochen' chuvstvitel'nyh urovnemerov.
|
| 369
| One of them was attached to the floor of the Babelsberg
underground clock room, and the other one was attached in a horizontal
position to one of the columns of the same room.
| Odin iz nih byl prikreplen k polu Babel'sbergskoi podzemnoi
komnaty s chasami, a drugoi byl prikreplen v gorizontal'nom polozhenii k
odnoi iz opor etoi zhe komnaty.
|
| 370
| Courvoisier measured the difference between the marks of the two level meters.
| Kurvuaz'e izmerili raznicu mezhdu otmetkami dvuh urovnemerov.
|
| 371
| The maximum predicted effect was about 0.30″, and with the
delicate instruments used by Courvoisier it was possible to measure
angular changes as small as 0,03″.
| Maksimal'nyi ozhidaemyi effekt sostavil okolo 0,30″, i s tochnymi
instrumentami, ispol'zuemymi Kurvuaz'e, mozhno bylo izmerit' uglovye
izmeneniya velichinoi do 0,03″.
|
| 372
| In the first series of measurements between 15 and 26 June 1929, Courvoisier obtained the following results:
| V pervoi serii izmerenii mezhdu 15 i 26 iyunya 1929 goda, Kurvuaz'e byli polucheny sleduyushie rezul'taty:
|
| 373
| A = 59 6; D = +51 9; v = 446 34 km/s
| A = 59 6; D = +51 9; v = 446 34 km/s
|
| 374
|
|
|
| 375
| According to Courvoisier's hypothesis, the Earth undergoes a
real contraction in the direction of its motion through the ether, and
this contraction would produce observable periodical changes of the
local value of gravity as a function of sidereal time.
| Soglasno gipoteze Kurvuaz'e, Zemlya podvergaetsya real'nym
sokrasheniem v napravlenii ee dvizheniya cherez efir, i eto sokrashenie budet
proizvodit' nablyudaemye periodicheskie izmeneniya mestnogo znachenie sily
tyazhesti v zavisimosti ot zvezdnogo vremeni.
|
| 376
| Pendulum clocks at different places of the Earth should show
slightly different readings, and their phases should exhibit a
periodical relative fluctuation.
| Mayatnikovye chasy v raznyh mestah Zemli dolzhny pokazyvat'
nemnogo razlichnye znacheniya, a ih fazy dolzhny obladat' otnositel'noi
periodichnost'yu kolebanii.
|
| 377
| Courvoisier analyzed data on pendulum clocks of different astronomical observatories, in an attempt to detect this effect.
| Kurvuaz'e proanaliziroval dannye o mayatnikovyh chasah razlichnyh astronomicheskih observatorii v popytke obnaruzhit' etot effekt.
|
| 378
| Using radio signals it was possible to compare the rates of clocks at very distant observatories.
| Ispol'zuya radiosignaly, mozhno sravnit' hod chasov dlya vzaimno ochen' otdalennyh observatorii.
|
| 379
| The Annapolis Observatory emitted regular time signals from its pendulum clocks.
| Observatoriya Annapolisa translirovala regulyarnye signaly vremeni ot svoih mayatnikovyh chasov.
|
| 380
| It was possible to compare the rate of those pendulums to those at another place.
| Mozhno bylo sravnit' skorost' ih mayatnika tam i v drugom meste.
|
| 381
| Courvoisier asked the help of Bernhard Wanach, from Potsdam,
who compared the rate of the pendulum clocks of that observatory to the
signals received from Annapolis, from September 1921 to November 1922.27 Courvoisiers analysis of Wanachs data led to the following results:
| Kurvuaz'e poprosil pomoshi Bernharda Vanaha iz Potsdama, kotoryi
sravnil skorost' mayatnikovyh chasov etoi observatorii s signalami iz
Annapolisa s sentyabrya 1921 po noyabr' 1922 g. 27 Analiz Kurvuaz'e dannyh Vanaha privel k sleduyushim rezul'tatam:
|
| 382
| A = 56 12; D = +40 (estimated); v = 873 228 km/s
| A = 56 12; D = +40 (ocenka); v = 873 228 km/s
|
| 383
| Afterwards, a comparison was made using a comparison between the clocks of Annapolis, Potsdam, Ottawa, and Bordeaux.
| Posle etogo bylo provedeno sravnenie pri pomoshi sopostavleniya mezhdu chasami v Annapolise, Potsdame, Ottave i Bordo.
|
| 384
| The mean result obtained by Courvoisier was:
| Srednii rezul'tat, poluchennyi Kurvuaz'e, byl:
|
| 385
| A = 81 5; D = +34 5; v = 650 50 km/s
| A = 81 5; D = +34 5; v = 650 50 km/s
|
| 386
| {27} Much later, Courvoisier presented another
confirmation of this effect.
| Mnogo pozzhe, Kurvuaz'e predstavil eshe odno podtverzhdenie etogo effekta.
|
| 387
| He compared the catalogues of time correction of the
observatories of Greenwich, Potsdam, Buenos Aires and Mount Stromslo for
the period from 1948 to 1954.28
| On sravnil katalogi vremennoi korrekcii observatorii Grinvicha,
Potsdama, Buenos-Airesa i Maunt-Stromlo za period s 1948 po 1954 god. 28
|
| 388
| There was a nice agreement between the theoretical predictions
and the observed time differences, especially in the case of the years
1951-1954.
| Bylo vyyavleno horoshee soglasie mezhdu teoreticheskimi
predskazaniyami i nablyudaemymi razlichiyam vremeni, osobenno v sluchae
dannyh za 19511954 gody.
|
| 389
|
|
|
| 390
| Courvoisier supposed that the rate of pendulum clocks would
vary because of the periodical gravity changes, but mechanical
chronometers should not suffer similar changes.
| Kurvuaz'e predpolagal, chto skorost' mayatnikovyh chasov budet
menyat'sya v rezul'tate periodicheskih izmenenii sily tyazhesti, no
mehanicheskie hronometry ne dolzhny byt' podverzheny podobnym izmeneniyam.
|
| 391
| Therefore it should be possible to observe effects due to the
absolute motion of the Earth comparing pendulum clocks to mechanical
chronometers at a single place.
| Poetomu dolzhna byt' vozmozhnost' nablyudat' effekty, svyazannye s
absolyutnym dvizheniem Zemli, putem sravneniya mayatnikovyh chasov i
mehanicheskogo hronometra v odnom meste.
|
| 392
| Comparisons were made both at Babelsberg and at Potsdam (with the help of Wanach).
| Sravneniya byli sdelany v Babel'sberge i v Potsdame (s pomosh'yu Vanaha).
|
| 393
| In his analysis, Courvoisier assumed the value D = +40 and obtained A = 104 9 and v = 750 km/s.
| V svoem analize Kurvuaz'e predpolagal znachenie D = +40 i poluchil A = 104 9 i v = 750 km/s.
|
| 394
|
|
|
| 395
| If the Lorentz contraction of the Earth produces gravitational
effects, then it should be possible to find its influence on the tides.
| Esli sokrashenie Lorenca dlya Zemli proizvodit gravitacionnye
effekty, to dolzhno byt' vozmozhnost' naiti ih vliyanie na prilivy i
otlivy.
|
| 396
| Esclangon analyzed a set of 166,500 tide measurements, made at Pola, on the Adriatic sea, from 1898 to 1916.
| Esklangon proanaliziroval nabor 166500 izmereniya priliva,
sdelannye v Pula, na poberezh'e Adriaticheskogo morya, s 1898 po 1916 god.
|
| 397
| He obtained a term with the period of on sidereal day, that
could not be associated with the Sun or the Moon, and ascribed it to a
dissymmetry of space.29
| On poluchil element s periodom v zvezdnye sutki, kotorye ne
mogut byt' svyazany s Solncem ili Lunoi, i otnes ego k asimmetrii
prostranstva 29
|
| 398
| This tidal effect could be described as:
| Etot prilivnoi effekt mozhet byt' opisan kak:
|
| 399
| 48 mm.cos (t 146.1) + 25 mm.cos (t 244.6) (16)
| 48 mm.cos (t 146.1) + 25 mm.cos (t 244.6) (16)
|
| 400
| If the local gravity undergoes periodic changes, it should be possible to detect this effect with sensitive gravimeters.
| Esli lokal'naya sila tyazhesti preterpevaet periodicheskie
izmeneniya, dolzhna byt' vozmozhnost' obnaruzhit' etot effekt
chuvstvitel'nymi gravimetrami.
|
| 401
| In 1927 Courvoisier (with the help of Sergei Gaposchkin)
attempted for the first time to measure gravity variations using a very
sensitive torsion gravimeter.30
| V 1927 g. Kurvuaz'e (s pomosh'yu Sergeya Gaposhkina) vpervye
popytalsya dlya izmereniya variacii sily tyazhesti primenit' ochen'
chuvstvitel'nyi gravimetr krucheniya. 30
|
| 402
| The instrument could detect a change Δg/g of 3×106, corresponding to a displacement of 0.2 mm of the gravimeter pointer.
| Etot instrument mog obnaruzhit' izmenenie Δg/g of 3×106, chto sootvetstvuet smesheniyu 0,2 mm ukazatelya gravimetra.
|
| 403
| From a series of measurements undertaken from 1927 to 1928 Courvoisier computed the following values:
| Iz serii izmerenii, vypolnennyh s 1927 po 1928 gg. Kurvuaz'e vychislil sleduyushie znacheniya:
|
| 404
| A = 62 5; D = +32 8; v = 543 55 km/s
| A = 62 5; D = +32 8; v = 543 55 km/s
|
| 405
| {28} In 1932 Courvoisier obtained new results,
taking into account in this new paper some effects due to temperature and humidity.
| V 1932 g. Kurvuaz'e byli polucheny novye rezul'taty, prinimayushie
vo vnimanie v etoi novoi rabote effekty, svyazannye s temperaturoi i
vlazhnost'yu.
|
| 406
| The new results obtained by him were
| Novye rezul'taty, poluchennye im, sostavili
|
| 407
| A = 50 7; D = +45 18; v = 498 78 km/s
| A = 50 7; D = +45 18; v = 498 78 km/s
|
| 408
| For the first time, Courvoisier's results were criticized and checked.
| Vpervye rezul'taty Kurvuaz'e kritikovalis' i byli provereny.
|
| 409
| In 1932, Rudolf Tomaschek and Walter Schaffernicht reported
gravity measurements made with a new kind of gravimeter that was able to
detect changes Δg/g of 108.
| V 1932 godu Rudol'f Tomashek i Uolter Shafferniht soobshili ob
izmereniyah sily tyazhesti novym vidom gravimetra, kotoryi byl v sostoyanii
obnaruzhit' izmeneniya Δg/g poryadka 108.
|
| 410
| The instrument was placed inside a cave in a mountain, where the temperature was constant to 0.001 C.
| Pribor byl pomeshen v peshere v gorah, gde temperatura byla postoyannoi do 0,001 C.
|
| 411
| No effect of the order of magnitude predicted by Courvoisier was observed.31
| Effekt togo poryadka, kotoryi byl predskazan Kurvuaz'e, ne nablyudalsya. 31
|
| 412
|
|
|
| 413
| It is well known that in 1879 James Clerk Maxwell wrote to
David Peck Todd asking him about the possibility of computing the
velocity of the solar system through the ether using available data on
occultation of Jupiters satellites.32
| Horosho izvestno, chto v 1879 godu Dzheims Klerk Maksvell pisal
Devidu Pekku Toddu, sprashivaya ego o vozmozhnosti vychisleniya skorosti
Solnechnoi sistemy cherez efir, s ispol'zovaniem imeyushihsya dannyh o
zatmeniya sputnikov Yupitera. 32
|
| 414
| Maxwell supposed that the motion of the solar system would
produce an anisotropy of the speed of light that could be detected as a
fluctuation of the times of occultation of Jupiter's satellites,
observed from the Earth, with a period of about 12 years.
| Maksvell predpolozhil, chto dvizhenie Solnechnoi sistemy dolzhno
proizvodit' anizotropiyu skorosti sveta, kotoraya mozhet byt' obnaruzhena
kak fluktuaciya vremeni pokrytiya sputnikov Yupitera, nablyudaemyh s Zemli, s
periodom okolo 12 let.
|
| 415
| Todd answered, however, that the measurements available at that time were not precise enough for such computations.
| Todd otvetil, odnako, chto izmereniya, provodimye v to vremya, ne byli dostatochno tochny dlya takih vychislenii.
|
| 416
| In 1930 Courvoisier published a paper where he presented an
analysis of available observations of Jupiter's satellites and claimed
that they led to a new determination of the velocity of the solar system
relative to the ether.33
| V 1930 Kurvuaz'e opublikoval stat'yu, gde on predstavil analiz
imeyushihsya nablyudenii sputnikov Yupitera i utverzhdal, chto oni priveli k
novomu opredeleniyu skorosi Solnechnoi sistemy otnositel'no efira. 33
|
| 417
| He used data relative to the three inner Galilean satellites
published by the Johannesbourg observatory (19081926), comparing those
measurements to those of the observatories of Cape Town, Greenwich and
Leyden (1913 1924).
| On ispol'zoval dannye treh vnutrennih galileevyh sputnikov,
opublikovannye observatoriei v 'ohannesburge (19081926), sravnivaya eti
izmereniya s analogichnymi iz observatorii Keiptauna, Grinvicha i Leidena
(19131924).
|
| 418
| He confirmed Maxwell's anticipation of a fluctuation with a period of about 12 years and obtained the following results:
| On podtverdil ozhidaniya Maksvella o nalichii kolebanii s periodom okolo 12 let, i poluchil sleduyushie rezul'taty:
|
| 419
| A = 126 10; D = +20; v = 885 100 km/s
| A = 126 10; D = +20; v = 885 100 km/s
|
| 420
|
|
|
| 421
| According to the theory of ether accepted by Courvoisier, the
speed of light is constant relative to the ether, but could not be
constant relative to the {29} Earth: there should
be an observable anisotropy of the speed of light due to the absolute motion of the Earth.
| Soglasno teorii efira, prinyatoi Kurvuaz'e, skorost' sveta
postoyanna otnositel'no efira, no ne mozhet byt' postoyannoi otnositel'no
Zemli: dolzhna nablyudat'sya anizotropiya skorosti sveta pri absolyutnom
dvizhenii Zemli.
|
| 422
| He assumed that this would produce an observable difference in
measurements of stellar aberration observed in different directions.34
| On predpolozhil, chto ono dolzhno proizvesti nablyudaemye razlichiya v
izmereniyah zvezdnoi aberracii, kotoraya nablyudaetsya v raznyh
napravleniyah 34
|
| 423
| Using the available data, Courvoisier obtained the following results:
| Na osnovanii imeyushihsya dannyh, Kurvuaz'e poluchil sleduyushie rezul'taty:
|
| 424
| A = 112 20; D = +47 20; v = 600 305 km/s
| A = 112 20; D = +47 20; v = 600 305 km/s
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
16.10.2013 23:48, 3.5 KBait)
Prochital tak skazat' standartnuyu situaciyu - kogda mnogo
umnichayut a po smyslovoi suti to otvetit' dostatochno gramotno
i prosto nikto ne v sostoyanii.
Rekomenduyu
prochitat' vse soobsheniya vnimatel'no,
i v itoge Vy zametite, chto vse nedalekie a tol'ko vumnichat'
i mogut.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
: Segodnya v 02:24:25
Otvet #4 : Segodnya v 09:48:07
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nikto tam nikogo ne operedil, zadayushemu vopros odin bui
ni koi kon' vnyatno ni kto ne ob'yasnil, tol'ko dali neponyatnye
i bessmyslennye teksty pochitat' - i na kuya takie sovety.
Sam vopros vyedennogo yaica ne
stoit.
Nikto dazhe vnyatno ne mozhet ob'yasnit' chto sutki mesyacy i gody
s ih deleniem nikak ne sovpadayut prosto --- kratno--- esli etu
velichinu podelit'.
A chasy minuty i sekundy, imeyut kratnuyu privyazku k vrasheniyu
Zemli po otnosheniyu k Solncu, - odin oborot - Zemli = 24 chasa,
a odin oborot Zemli vokrug Solnca
ne mozhet dazhe teoreticheski sovpadat'
i tochno sootvetstvovat' kakomu-to celomu kolichestvu oborotov Zemli,
kogda Zemlya delaet polnyi oborot vokrug Solnca - i hot'
eto i erunda,
no takuyu erundu dolzhny ob'yasnyat' maksimum s tret'ego posta, i tak chtoby
chitayushii ponyal odnoznachno - chto za mrakobesie nedalekih kotorye ne
mogut
vnyatno i odnoznachno vyrazit' svoyu mysl' -
Vy hot' ponimaete chto Vam - vsem - nad astro-balaganom nado rabotat', chtoby
prevratit' v astro-rech'.
Zamet'te
nikto ne mozhet vnyatno, prosto, i adekvatno izlagat'
svoi mysli po voprosu po suti.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.10.2013 0:48, 2.1 KBait)
Otvet #2 : 10.10.2013 [00:44:19]
Vy pro eto: http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D1%E2%E5%F2%EE%E2%EE%E5_%E7%E0%E3%F0%FF%E7%ED%E5%ED%E8%E5
Da, o svetovom zagryaznenii. Budut li u nas predprinimat' kakie-to mery, ili eto v rashe ne vozmozhno ?
U
nas vozle Krasnodara, est' torgovyi centr OZ. Fonari kotorye osveshayut
stoyanku, imeyut konstrukciyu, pohozhuyu na tarelku, perevernutuyu vverh dnom.
Interesno pochemu ne vezde primenyayut takuyu ili pohozhuyu konstrukciyu ?
Kto by u nas ozabotilsya
o svetovom zagryaznenii nochnogo neba.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nu eto voobshe pipec
mysli.
Tut dazhe dumat' ne nuzhno - yasnyi kon' chto fonari
kak osveshenie - eto tol'ko odin iz metodov
chtoby bylo vidno tomu kto smotrit.
I yasnyi
kon' chto esli by prodavalis' ochki v magazine
svetosil'nye, i nakladnye svetosil'nye linzy dlya glaz,
to nakoi eti fonari v principe by sdalis'.
I esli
by u kazhdogo lyubitelya astronomii byl svoi sputnik
orbital'nyi to ego by eta bueta s zasvetkoi by tozhe
ne sil'no bespokoila.
S moei tochki zreniya ran'she
u kazhdogo lyubitelya astronomii
budet nasovskii nedorogoi seriinyi orbital'nyi sputnik,
chem smogut sdelat' svetosil'nye ochki ili nakladnye linzy
svetosil'nye.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
31.10.2013 23:15, 4.1 KBait)
Vot ne proshlo i mnogo vremeni a sobstvenno s 2009 goda,
kogda relyativisty soizvolili razduplyatsya.
Hotya u nih i smeshno poluchaetsya mezhdu dvoikoi i troikoi po
pyati-bal'noi.
Zdes' ocenka ne za vopros po suti, ibo eto uzhe izmeryal ya by v tysyachah,
zdes' ocenka skoree za balagan i ponimanie togo chto krichashii i
mnogochislennyi
ne znachit luchshii.
A vot za takie oskorbleniya uchastnikov foruma, - v stile odinochka ne mozhet
reshit' vopros, - i vopros reshaetsya tol'ko stadom - to
ya
by banil po ai pi i navsegda.
Hotya kto iz etih uchastnikov poimet kak ih zalpom zhahnuli.
Tak ploho dumat' o vseh i schitat' odnogo - ili malochislennyh
bezmozgloi
individual'nost'yu, - mne prosto grustno.
\\\Sovershenno
ochevidno, chto na dannyi moment vyborka iz nalichnyh uchastnikov diskussii
statisticheski nedostatochno predstavitel'na. S pomosh'yu takoi vyborki
nel'zya sdelat' nauchno-dostovernoe obobshenie.
\\\
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #31 : Vchera v 23:29:43
davaite vyyasnim, Vy poluchili otvet na zaglavnyi vopros temy? Kakoi
eto otvet?
Obsheizvestno,
chto "speshka neobhodima tol'ko pri lovle bloh". A tut "idet igra
po-krupnomu", kak spravedlivo otmetil Glubokouvazhaemyi Vov.

Sovershenno
ochevidno, chto na dannyi moment vyborka iz nalichnyh uchastnikov diskussii
statisticheski nedostatochno predstavitel'na. S pomosh'yu takoi vyborki
nel'zya sdelat' nauchno-dostovernoe obobshenie.
Poka pochti nikak (za
isklyucheniem, vozmozhno, QSS) ne proyavili sebya storonniki volnovoi teorii
preobrazovaniya, izlucheniya, rasprostraneniya i poglosheniya
elektromagnitnoi energii, kotorye po principial'nym soobrazheniyam
britvy
Okkama schitayut gipoteticheskuyu "chasticu foton" privlecheniem v teoriyu izlishnei sushnosti.
"Britva
Ókkama (inogda lezvie Okkama, lat. lex parsimoniae)
metodologicheskii princip, poluchivshii nazvanie ot imeni angliiskogo
monaha-franciskanca, filosofa-nominalista Uil'yama Okkama (Ockham, Ockam,
Occam; ok. 12851349). V kratkom vide on glasit: Ne sleduet mnozhit'
sushee bez neobhodimosti (libo Ne sleduet privlekat' novye sushnosti bez
krainei na to neobhodimosti). Etot princip formiruet bazis
metodologicheskogo redukcionizma, takzhe nazyvaemyi principom
berezhlivosti, ili zakonom ekonomii.
To, chto nazyvayut Britvoi
Okkama, ne bylo sozdano Okkamom, esli imet' v vidu bazovoe soderzhanie
etogo principa. To, chto v usloviyah Protorenessansa sformuliroval Okkam,
bylo izvestno, po krainei mere, so vremen Aristotelya.
V
sovremennom ponimanii princip Britvy Okkama sostoit v sleduyushem: esli
kakoe-to yavlenie mozhet byt' ob'yasneno dvumya sposobami, naprimer, pervym
cherez privlechenie sushnostei (terminov, faktorov, preobrazovanii i t.
p.) A, V i S, a vtorym cherez A, V, S i D, i pri etom oba sposoba dayut
odinakovyi rezul'tat, pri prochih ravnyh usloviyah sleduet schitat' vernym
pervoe ob'yasnenie, to est' sushnost' D lishnyaya, i ee privlechenie
izbytochno."
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
31.10.2013 23:25, 632 Bait)
Menya smeshit Vibe aki polnyi trus so zvaniem professora, ni odnogo
vnyatnogo vyskazyvaniya ili voprosa po suti,
- ne mogu ponyat' - chego on ochkuet v dannoi situacii,
a ne vedet diskussiyu s tipichnymi slovami v nachale
posta
-------------
- Greban - nyi kon' kuda Vy nesete telegu -
doroga vot tam -
i dvigat'sya nuzhno vot tak-to -
i vot takaya-to bueta - znachit vot to-to - a vot
takaya-to bueta znachit vot eto.
---
Tak ya mogu Vas uspokoit'
on tak nikogda ne smozhet
imet' prakticheskogo opyta, znanii i umenii, -
chto-by ponimat' tak i dumat', i chto-by tak vesti diskussiyu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.11.2013 0:10, 10.5 KBait)
Vibe opozorilsya prevzoshel sam
sebya.
Prosit pravil'nyi otvet u sobesednika
na nepravil'no vydumannye im zhe ponty v stile idiotizm.
Vibe pridumal
vot eto
\\\3)
j.kepler.ii, ya proshu sformulirovat' ob'yasnenie vsem yavleniyam, dlya
ob'yasneniya kotoryh ispol'zuetsya ponyatie fotona, bez ispol'zovaniya etogo
ponyatiya.\\\
Mozhno byt' samym hitrym - no vsegda nuna pomnit'
chto ukraincy v osnovnoi svoei masse - hitrost',
hitroopost' vidyat srazu kak budto drugim
shriftom,
i nado byt' prosto nedalekim chtoby pisat' takuyu
nelogichnuyu buetu.
U nas v mladshih klassah podobnymi zakidonami
drug druga smeshili -
V stile - a otvet' tol'ko da ili net - ne
pravda li? - ne durak li ty?.
Lyuboi otvet - logicheskoe popadalovo v logicheskii
lohotron.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
- Moderator





-

- Soobshenii: 13 677
- Reiting: +362/-47
- Evona kak...
-
Otvet #47 : Segodnya v 20:43:16
Znachit, tak.
1) Bob,
ogromnaya pros'ba -- ne otvechat' na poslednee soobshenie j.kepler.ii. Ya
hochu dat' emu vozmozhnost' vypolnit' tvoi uzhe sformulirovannyi zapros.
2) j.kepler.ii, ya proshu Vas dat' opredelenie ponyatiya "sushestvuet".
3)
j.kepler.ii, ya proshu sformulirovat' ob'yasnenie vsem yavleniyam, dlya
ob'yasneniya kotoryh ispol'zuetsya ponyatie fotona, bez ispol'zovaniya etogo
ponyatiya.
Do togo kak Vy eto sdelaete, proshu drugih soobshenii v razdele ne publikovat'.

Zapisan
I kto-to, kak vsegda, nes mne chush' o "tarelkah", i kto-to, kak vsegda, propovedoval dzen... (s) Zoopark





-

- Soobshenii: 841
- Reiting: +7/-2
-
Otvet #48 : Segodnya v 21:05:57
Znachit, tak.
<...>
2) j.kepler.ii, ya proshu Vas dat'
opredelenie ponyatiya "sushestvuet".
Nu chto zhe, sdelayu otchayannuyu popytku:
 Materializm utverzhdaet
sushestvovanie edinstvennoi absolyutnoi substancii bytiya materii
Materializm utverzhdaet
sushestvovanie edinstvennoi absolyutnoi substancii bytiya materii"Materialízm
(ot lat. materialis veshestvennyi) filosofskoe mirovozzrenie, v
sootvetstvii s kotorym materiya (ob'ektivnaya real'nost') yavlyaetsya
ontologicheski pervichnym nachalom (prichinoi, usloviem, ogranicheniem) v
sfere bytiya, a ideal'noe (ponyatiya, volya, soznanie i tomu podobnoe)
vtorichnym (rezul'tatom, sledstviem).
Materializm utverzhdaet sushestvovanie edinstvennoi absolyutnoi substancii bytiya materii;
vse sushnosti obrazovany materiei, a ideal'nye yavleniya (v tom chisle,
soznanie) yavlyayutsya processami vzaimodeistviya material'nyh sushnostei. "
Do togo kak Vy eto sdelaete, proshu drugih soobshenii v razdele ne
publikovat'.
Privedennyi tekst sootvetstvuet Vashim trebovaniyam?

Zapisan
- Moderator





-

- Soobshenii: 13 677
- Reiting: +362/-47
- Evona kak...
-
Otvet #49 : Segodnya v 21:17:16
2) j.kepler.ii, ya proshu Vas dat' opredelenie ponyatiya "sushestvuet".
Nu chto zhe, sdelayu otchayannuyu popytku: 
...
Privedennyi tekst sootvetstvuet Vashim trebovaniyam?
Net,
razumeetsya. On by sootvetstvoval, esli by ya prosil Vas: "Skopiruite,
pozhaluista, tekst iz Vikipedii". Vot v etom sluchae Vash otvet byl by v
samyi raz. No ya ne prosil Vas nichego kopirovat' iz Vikipedii. Ya prosil
dat' opredelenie ponyatiya "sushestvuet". Dam podskazku. Opredelenie dolzhno
nachinat'sya slovami: "Sushestvovat' oznachaet ..."
I eshe: tam est' i punkt 3.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.11.2013 23:07, 1.5 KBait)
Ya estestvenno chto-to logichnoe dolzhen vyskazat' zdes'
po tekushim situaciyam na dvuh forumah po pohozhemu
voprosu.
V pervom variante ya kak govoritsya - snimayu
shlyapu -
udivlen v principe.
Vo vtorom sluchae - molodec, no vyskazat' svoyu tochku
zreniya eto ne znachit chto est' sposobnosti pridumyvat'
samostoyatel'no.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
1
\\\

Otvet #2020 : Segodnya v 20:18:30 \\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2
\\\
 O roli teorii otnositel'nosti v nauke
O roli teorii otnositel'nosti v nauke
Vchera :: 15:35:01
-----------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.11.2013 23:39, 91 Bait)
http://www.astrogalaxy.ru/forum/phpBB2/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=4314
Ya dumayu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.11.2013 10:50, 760 Bait)
U menya takoe chuvstvo chto svirepstvuet virus
- "idiotizm v fizike kak nauke",
i on davno porazil ochen' bol'shoe kolichestvo
chelovek, i on peredaetsya
ot uchitelya k ucheniku.
Sobstvenno nado radovat'sya tem kogo etot virus
ne porazil.
Tol'ko na planete nedalekih ili porazhennyh
podobnym virusom - ne mogut
za sto let pridumat'
novyh teorii, a sushestvuyushie - na urovne
intellekta - detskii lepet.
Al'ty dolzhny prosto radovat'sya etoi situacii
ibo osnovnaya
massa ih konkurentov, porazhena
etim virusom.
Na skol'ko ya pomnyu v davnie vremena periodicheski
dlya predotvrasheniya podobnyh situacii zakryvali
izuchenie
opredelennyh nauk na nekotoroe vremya let na
20-50, a potom vozobnovlyali eti nauki.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.11.2013 11:10, 5.0 KBait)
Vot primer iz zhizni, nekotoryi prepodavatel' ne znaet
chto effekt Doplera byl priduman avtorom isklyuchitel'no
dlya sred
Iz vikipedii
\\\Effekt
byl vpervye opisan Kristianom
Doplerom v 1842 godu.\\\
za dolgo do togo kak byli pridumany relyativizm,
i fotony.
I tol'ko nedalekii mozhet putat' s relyativistskim effektom
Doplera - eto dva absolyutno raznyh effekta pridumannye v raznye
epohi.
Iz vikipedii
\\\
V sluchae rasprostraneniya elektromagnitnyh voln (ili drugih
bezmassovyh chastic) v vakuume, formulu dlya chastoty vyvodyat iz uravnenii special'noi
teorii otnositel'nosti.
Tak kak dlya rasprostraneniya elektromagnitnyh voln ne trebuetsya
material'naya sreda, mozhno rassmatrivat' tol'ko otnositel'nuyu skorost'
istochnika i nablyudatelya\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Re: O sisteme postulatov STO.
Re: O sisteme postulatov STO.
Otvet #91 - Vchera :: 10:48:21
wpiter pisal(a) 13.11.13 :: 22:33:29:Net EM-voln, znachit i net dlya nih effekta Doplera. Kak zhe skorost' mashin opredelyayut dopplerovskim radarom ?
|
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Re: O sisteme postulatov STO.
Re: O sisteme postulatov STO.
Otvet #95 - Segodnya :: 09:41:59
Odin pisal(a) Segodnya :: 00:51:44:Zachem imenno vam <neploho vernut' efir>? Chto vy sobiraetes' s nim delat V
lichke ya vam otvetil, zachem mne efir. Zdes' zhe dobavlyu, chto mne , kak
professional'nomu fiziku na pensii (do togo prepodavavshemu v univerah,
no ne svyazannomu s prostranstvom-vremenem) nichto ne meshaet v svyazi s
priznannym sushestvovaniem fizicheskogo vakuuma, kak sredy lish' s
POTENCIAL'NYM sushestvovaniem chastic, a znachit vpolne nepreryvnoi i
vozmozhno odnorodnoi v lyubom masshtabe predpolagat' sushestvovanie efira,
dvizhenie kotorogo v principe nel'zya vyyavit', a znachit i obnaruzhit' i
uvidet' sam efir. Zato vozvrat efira v fiziku dal by al'ternativy dlya
STO. a ona v fizike ochen' neustoichiva i konfliktna.
|
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vot esli by prosto kto mozgami svoimi mog vniknut'
v smyslovuyu sut', to efir by v nauke i tak by vernulsya,
a nedalekim nakoi efir v fizike oni i tak v fizike
nichego ne ponimayut, dazhe buduchi prepodavatelyami fiziki.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.11.2013 11:24, 1.6 KBait)
Iz vikipedii
\\\
V sluchae rasprostraneniya elektromagnitnyh voln (ili drugih
bezmassovyh chastic) v vakuume, formulu dlya chastoty vyvodyat iz uravnenii special'noi
teorii otnositel'nosti.
Tak kak dlya rasprostraneniya elektromagnitnyh voln ne trebuetsya
material'naya sreda, mozhno rassmatrivat' tol'ko otnositel'nuyu skorost'
istochnika i nablyudatelya\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Preduprezhdayu chto relyativistskie
opredeleniya bryzzhut idiotizmom -
po vysheizlozhennomu -
\\\V sluchae rasprostraneniya elektromagnitnyh voln\\\
ispol'zovanie slova
volna - mozhet ispol'zovat'sya
isklyuchitel'no dlya sred - zvukovaya volna, ili dlya granic soprikosnoveniya
razlichnyh sred - mezhdu vozduhom i vodoi - volna na vode.
I esli udalos' razduplit'sya - to vidno chto otsutstvuet v relyativistskom
effekte Doplera - nositel' i perenoschik.
Oni prosto vzyali iz efirnoi chasti elektromagnitnuyu
volnu - i skazali
chto ona v pustote - eto tak skazat' prosto - peshee eroticheskoe
puteshestvie - tol'ko eto nuna ponimat' moskom, a dlya etogo takovoi dolzhen byt'.
Kyu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.11.2013 15:07, 2.2 KBait)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hGm2gqs7dP8
----------------------------------------------------------------
Izuchaem formuly.
------------------------------------------------
Sobstvenno rasskazhu absolyutno drugoe v etoi
situacii.
Beretsya opyat' izuchaetsya lichno mne uzhe nadoevshii - kineskop.
Yasnyi kon' chto k kineskopu prilepili
e m c kvadrat, bez
ob'yasneniya fizicheskoi suti.
Kineskop eto sobstvenno uskoritel' ili kollaider.
Proishodyat v nem sleduyushie processy - est' naprimer
dva
razlichnyh elektroda k nim prilozheno elektricheskoe
napryazhenie to mezhdu etimi elektrodami est' uzhe dvizhenie
zhidkosti - elektry, ono vyzvano tem chto prostranstvo
zapolneno
dvumya veshestvami eto gaz - efir, - predstavlyayushii iz sebya
mohnatyi sharik pokrytyi tonkim sloem zhidkosti - elektry.
Efir ne yavlyaetsya provodnikom
elektrichestva a elektra -
yavlyaetsya ne tol'ko provodnikom takovogo - a dvizhenie etoi zhidkosti i est'
elektrichestvo.
Estestvenno elektra v prostranstve sozdaet
dva sluchaya dvizheniya
elektrichestva - eto staticheskoe - kogda proishodit dvizhenie
elektry cherez poverhnostnyi sloi efira - chto sobstvenno i v kineskopah
i
ispol'zuetsya.
A vtoroi sluchai eto kogda elektra dvizhetsya po provodniku.
Nit' nakala nagrevaet nekotoroe veshestvo kotoroe sozdaet nevidimoe
parovoe oblako
- i elektra uvlekaet chasticy etogo oblaka za soboi,
i sobstvenno skorost' uvlecheniya elektroi tem bystree chem bol'she
raznica napryazhenii, v kineskope cvetnom, uskoryayutsya
chasticy parovogo oblaka
do 0.3 skorosti sveta.
Sobstvenno - nado ponimat' chto slovo - elektron - eto slovo ne imeyushee
pod soboi fizicheskogo smysla,
ibo v prostranstve - ne vozmozhno
elektrichestvo, - zaryad, ili dvizhenie s drugim potencialom -
pravil'no - nevozmozhno bez fizicheskogo nositelya, kotorym ne
mogut
vystupat' ne efir i ne elektra, - fizicheskim
nositelem potenciala ili zaryada elektrichestva - mozhet
byt' tol'ko material'naya chastica - tak skazat' - materiya,
Eto vsya tablica D.I.Mendeleeva.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.11.2013 18:57, 764 Bait)
Chto est' v nalichii - est' elektra, kotoraya
energiyu svoego dvizheniya = napryazhenie,
pri nekotorom svoem ob'eme = tok,
chto vmeste iz sebya predstavlyaet moshnost',
- peredaet za schet uvlecheniya za soboi
neznachitel'noi chastice atoma.
Chto sobstvenno zdes' v neponimanii ?-
ne ponyatno idet li zatrata energii na peremeshenie
efira v prostranstve?, i kakie zatraty na peremeshenie
elektry v prostranstve?, i kakie poteri
pri vozdeistvii elektry kotoraya uvlekaet
za soboi chastichno
efir?, i uzhe v osnovnom
dvizhenie elektry kak istochnika sily, i pervoprichiny, -
voznikaet logichnyi vopros kak imenno elektra - razgonyaet chasticu.
Sobstvenno
nado ponimat' - chto dannyi opyt -
v svoih detalyah - kraeugol'nyi.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.11.2013 20:08, 685 Bait)
Esli razobrat'sya detal'no s kineskopom,
to uzhe primitivno budet na osnovanii
poluchennyh rezul'tatov opisat' tot-zhe
opyt kogda mikro-kapli masla - nazvali
elektronami.
Konyu ponyatno chto pridetsya izmenit'
i pereimenovat' dostatochnoe kolichestvo
vsyacheskih myslei v golovah fizikov, - tol'ko
mne vot uzhe
srazu smeshno budet smotret'
kak relyativisty poshlyut v peshee eroticheskoe
puteshestvie prositelya granta dlya provedeniya
podobnogo opyta.
I kak ob'yasnit'
rezul'tat i smysl dannogo opyta relyativistam,
ih minimum pyat' let tol'ko drugoi fizike pereuchivat', i to
ne fakt chto poluchitsya pereuchit' na efir bol'she desyati
procentov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.11.2013 9:41, 2.6 KBait)
S moei tochki zreniya vsyu vot etu erundu v fizike
sotvoril Lorenc.
I ya lichno ni kakomu al'tu ni pri kakih situaciyah
nikogda ne sovetuyu dazhe vnikat' v
trudy Lorenca,
ibo eto budet Vashe poteryannoe vremya bezvozvratno,
a mozhet i al'tovskii razum poteryaete, i zaboleete
idiotizmom relyativizma.
A Vas
tuda relyativisty budut vse vremya priglashat'
na razborki po fizike.
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Patrice
Veteran foruma


 Na Forume
Na Forume

uchastnik foruma
Soobshenii: 2979
 Re: My vse uchilis' po Landau.
Re: My vse uchilis' po Landau.
Otvet #2 - Segodnya :: 08:25:24
quasi pisal(a) Segodnya :: 03:37:05:Vopros k topikstarteru -
chto imenno Vy sobiraetes' obsuzhdat' v
etoi teme?

A
vot eto i nado obsudit' potomu, chto s fizicheskoi tochki zreniya
Landau-Lifshic - matematicheskaya makulatura.
I nachat' nado s
preobrazovaniya Lorenca, s prostranstva s psevdoevklidova prostranstvo i
prochee. Nado podnyat' vopros i po drugim aspektam etoi biblii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
20.11.2013 11:59, 2.1 KBait)
Chtoby sobstvenno provesti
etot opyt
osobo to i deneg ne nuzhno.
Sobstvenno dostatochno
televizora,
i vysokotochnyh vesov. Televizor
ustanavlivaetsya kineskopom
vverh
i kineskopom vniz, dlya etogo
ego povorachivaet
povorotnoe ustroistvo s
motorchikom na pul'te.
U televizora dolzhno byt'
avtonomnoe pitanie,
i vsya konstrukciya vmeste s akkumulyatorom,
nahoditsya
v germetichnom korpuse.
Vsya konstrukciya ustanovlena
na vesy.
Provodyatsya izmereniya kogda
podano vysokoe,
i ekran chernyi, i mozhet byt' napravlen
vverh i vniz,
potom kogda ves' ekran svetitsya belym na
maksimal'noi
yarkosti i kontrastnosti, i
tozhe kineskop napravlen
vverh i vniz.
Nadeyus' chto vse dogadalis'
chto provodyatsya izmereniya
vesa tochnee ego izmeneniya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
20.11.2013 21:32, 479 Bait)
Kak govoritsya dazhe ne smeshno predstavit'
kak daleko poshlyut granto zayavitelya na
poluchenie deneg dlya proverki dannoi konstrukcii
v kosmicheskom prostranstve, ili na bortu
kosmicheskoi stancii.
U relyativistom podobnaya bueta zaranee
i absolyutno bezrezul'tativna budet v principe.
Kak ya rad chto est' relyativisty.
Po krainei mere ya uveren chto nikto moi
idei ne smozhet ne tol'ko realizovat',
no ne smozhet dazhe ih proverit',
i kak govoritsya dazhe bez moego odobreniya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.11.2013 19:44, 4.3 KBait)
Sobstvenno bor'ba razvivaetsya ochen' moshnaya
i nezametnaya, ya to vizhu gde bor'ba razuma idet.
Chto mogu skazat' kak storonnii nablyudatel' -
chto zhenskaya
logika ne terpit kompromissov v
otlichii ot muzhskoi, i esli baryshnya prishla k
nekotorym vyvodam - to eto uzhe kamen'.
Sobstvenno sama ona priiti k vyvodam
v dannom
sluchai ne smogla po prichine predubezhdennosti
kotoraya opredelyalas' obrazovaniem v ramkah paradigmy,
i posle adekvatnogo analiza razlichnoi fizicheskoi
fantastiki ot razlichnyh avtorov s Fizikom,
prosto srazu vidno kak ona obgonyaet vseh relyativistov
vmeste vzyatyh v ponimanii fiziki.
Dlya menya eto
byla ochen' bol'shaya neozhidannost',
ya to dumal chto bolee uverennogo relyativista,
chem eta baryshnya i byt' ne mozhet.
Kakie teksty - i tam gde tochki v konce
esli postavit' znak
voprosa, kotoryi neyavno tam est', to eto
mozhno skazat' chto u relyativistov ne to chto
vse ploho, a v relyativizm uzhe ne veryat dazhe
ego
zavzyatye storonniki.
I eto ne trudnosti teorii - eto prigovor teorii.
Kstati rasskazhu chto znachit slovo - singulyarnost', -
eto kogda chem-to chto-to
ogranichivaet beskonechnost',
ibo v bol'shoi sovetskoi enciklopedii - prostranstvo
bylo beskonechno, a potom k nemu prilepili slovo singulyarnost',
i vselennaya
stala ogranichennoi v razmerah, -
obosnovanie singulyarnosti - teoriya bol'shogo vzryva, -
zhest' odnako,
no fakt est' fakt.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------





-

- Soobshenii: 1 220
- Reiting: +46/-0
-
Otvet #2308 : Segodnya v 17:14:27
ya ne rassmatrivayu OTO (i ee "proizvodnye teorii") kak fizicheskuyu
teoriyu, primenimuyu ko vsei Vselennoi. Da eshe singulyarnosti... V
dostatochno ogranichennoi oblasti ee eshe mozhno rassmatrivat', no ko vsei
Vselennoi - uvol'te.
Mne takaya Kosmologicheskaya teoriya ne podhodit. Polagayu, chto Vselennoi - tozhe.
Ya ishu druguyu
- bez singulyarnostei ...
Trudnosti (problemy) OTO - klassicheskoi teorii gravitacii
Singulyarnosti. Nepolnye geodezicheskie. Somnitel'nost'
primenimosti OTO dlya ekstremal'nyh gravitacionnyh polei
Opredelenie energii gravitacionnogo polya
Sistemy otscheta. Ih realizaciya fizicheskimi priborami.
Princip ekvivalentnosti. Priroda inertnoi massy nedostatochno yasna. Garantirovannyi perehod ot OTO k STO v nekotoroi SO.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.12.2013 0:00, 139 Bait)
Smotret' rekomenduyu tol'ko al'tam,
relyativistam skorei vsego ne ponravit'sya.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l9uPHFcuzCs#t=62
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.12.2013 1:43, 1.3 KBait)

28 noya v 14:39|0 kommentariev
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Mne hot' i bezrazlichny podobnye lekcii, no lichno ya ozhidal bol'shego,
i u menya posle prosmotra sozdalos' vpechatlenie v tom chto po
vsem voprosam po suti byla
slita voda.
S drugoi tochki zreniya lektor - molodec chto v takom vozraste
propagandiruet efir.
Ya by posovetoval -
provoditsya naprimer lekciya s postoyannym
slivom vody po suti,
a avtor zagotovil domashnii vopros i domashnii otvet i zhelatel'no
zadat' vopros zagotovlennyi i otvetit' na nego
v konce lekcii, hot'
na odin vopros po suti - i eto budet prekrasno,
po toi prichine chto ne logichno tolkat' vpered golimyi
porozhnyak gruzhennyi efirom s postoyannym slivom vody.
Tak-zhe ya by porekomendoval tekst lekcii zaranee
vykladyvat' dlya oznakomleniya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.12.2013 3:11, 2.2 KBait)





-

- Soobshenii: 15 011
- Reiting: +196/-48
-
Otvet #903 : Segodnya v 01:57:04
Ya by s interesom poznakomilsya s obosnovannymi faktami, dokazyvayushimi otsutstvie BV.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Moya klaviatura utopala v slezah.
Eto zhe nado na skol'ko vysokii uroven' intellekta,
- na samom relyativistskom forume vdrug u zakorenelogo
relyativista,
- kotoryi kalennym zhelezom izvodil al'tov
na etom forume -
uslyshat' emu zahotelos' osmyslennye
al'tovskie rechi i razmyshleniya dokazyvayushie to vo chto on ne
verit,
chtoby ubedili eshe ego i on ostalsya dovolen -
- babene.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.12.2013 3:29, 2.5 KBait)
|
|
|
|
     -

- Soobshenii: 15 011
- Reiting: +196/-48
-
Otvet #786 : 30.11.2013 [23:19:17]
Ta nikakih oproverzhenii. Nikto nikogda ne govoril o zavershennosti TBV. Vozmozhny utochneniya i v teorii, i v cifrah. No
BV byl, prodolzhaetsya i budet.  ------------------------------------------------------------- I razve mozhno v etom sluchai chto-to rasskazat' pri takom urovne fanatichnoi predubezhdennosti. | |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.12.2013 23:50, 3.2 KBait)
Vot chitayu i nablyudayu takoe slaboumie matematikov v fizike
chto ya prosto azh udivlen.
Vidyat kakie-to bezbashennye trudnosti tam gde ih u fizikov
net i nikogda
ne bylo.
Sobstvenno situaciya fizicheskaya v sleduyushem - v kosmose bol'shoe
kolichestvo chastic vysokoi energii i bol'shoe kolichestvo
elektromagnitnyh izluchenii
v razlichnyh diapazonah, i tol'ko
nerazduplennye ne znayut chto est' u materii takie svoistva kak
rezonansnoe vozbuzhdenie,
rezonansnoe pogloshenie,
lyuminescenciya,
fluorescenciya,
poslesvechenie - tak vot kto eto vse znaet tak emu i nichego dazhe ne
nado pridumyvat', ibo tut i konyu uzhe vse ponyatno chto atomarnaya
struktura
pod vozdeistviem izlucheniya, ili chastic vysokih energii
blizhaishih zvezd - budut pereizluchat' ili sozdavat' elektromagnitnye
izlucheniya na drugih diapazonah chastot,
otlichayushihsya ot chastot
kotorymi byli vozbuzhdeny - vyvod chemu uchat astronomov ya uzhe davno
ne ponimayu - eto sobstvenno na ih sovesti.
Tak vot sobstvenno
znaya chto budet v prostranstve - vsegda fon na kakih-to
chastotah tak kak on opredelyaetsya nalichiem v kosmose kak otdel'nyh
atomov vodoroda i kosmicheskoi pyli -
i tut i konyu uzhe ponyatno
chto vot eto mezhzvezdnaya mikromateriya v prostranstve i budet sozdavat'
etot fon, i v osnove budet dva osnovnyh fizicheskih processa -
lyuminescenciya i fluorescenciya.
Sobstvenno vot etot obshii fon tol'ko summarnyi -
a ne kak u nekotoryh psevdo fizikov - tot kotoryi im nravit'sya,
mozhno
ispol'zovat' dlya opredeleniya temperatury v prostranstve,
sobstvenno dlya moei modeli eta temperatura ukazyvaet
i plotnost' efira v prostranstve, - tak chto poka
matematiki
dumayut kak fiziki budut ob'yasnyat', oni dazhe ne dogadyvayutsya
chto fiziki etu erundu davno uzhe ne ob'yasnyayut, i ne sobirayutsya
ob'yasnyat' ochevidnoe,
oni ee ispol'zuyut
i pol'zuyutsya ei v svoih modelyah.
--------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #910 : Segodnya v 13:44:07
Citata olegtitov: No pri etom temnaya energiya
takoi zhe ob'ektivnyi fakt, kak i temnaya materiya.
Gipoteticheskie
sushnosti temnaya materiya i temnaya energiya eto ne ob'ektivnyi fakt,
a obsheprinyatyi variant interpretacii nablyudenii.
Model' Briniolfssona ob'yasnyaet nablyudeniya bez etih sushnostei.
Tol'ko
dlya etogo pridetsya vvodit' sushnosti stacionarnoi, vechnoi i beskonechnoi
Vselennoi, a potom dolgo dumat' o tom, kak ob'yasnit', naprimer,
mikrovolnovoe izluchenie s pomosh'yu eshe bolee slozhnyh sushnostei.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
7.12.2013 14:43, 4.7 KBait)
S odnoi storony ya mogu skazat' - chto ya rad chto
relyativisty prodolzhayut stradat' bezrezul'tativnoi erundoi i ne smogut mne dazhe
maleishei konkurencii sozdat' esli ob'edinyat'sya i nachnut pridumyvat' modeli v
blizhaishie let pyat', u nih net ni opyta ni metodik dlya etogo. S drugoi tochki zreniya iskrenne zhal' teh al'tov, kotorye nadeyutsya
chto im, specialisty pomogut reshit' ih voprosy ili pogovoryat s nimi - chtoby
ponyat', gde trudnosti. Tak vot - v dannom sluchai - eti al'ty sebya sami zagonyayut
v tupik, ibo ishut halyavy, hotyat - chtoby
ih voprosy reshili za nih, ili hotyat, chtoby im pomogli.
Eto doroga v nikuda, gorazdo proshe i bystree
samostoyatel'no reshit' vse svoi voprosy, chem teryat' vremya na forumah v
obsuzhdeniyah i 1)poiske storonnikov i 2)poiske teh - kto poimet tvoi idei, a
potom 3) eshe kto-to tebe pomozhet v reshenii tvoih voprosov. Poimet
vse, imenno tak kak sam sebe pridumal. Smeshno i nelogichno takoe kolichestvo
sovpadenii dolzhno byt', chto rezul'tat nevozmozhen v principe.
A v itogo chto poluchaetsya chto al'ternativshik v
rezul'tate bezvozvratno teryaet svoe vremya, tam gde nikogda ne budet rezul'tata, on tam
nevozmozhen, dazhe esli relyativisty i ne budut ego posty udalyat', i ne
budut otnosit'sya k nemu, - kak k glupoi beshenoi sobake, ne ponimayushei
relyativizma.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

Re: Beskonechna li vselennaya?
Otvet #50 : Segodnya v 00:53:32
Gospodin Vibe! Izvestno, chto
v chuzhom monastyre svoih propovedei ne chitayut. Poetomu kogda Vy udalyali
moi soobsheniya, potomu chto eto byla fantastika (po Vashemu mneniyu), to ya
prinimal i prinimayu eto kak dolzhnoe i spokoino\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Horosho.
Soobshenie bylo vosstanovleno na vremya s 9.10 do 9.15 segodnya, 7 dekabrya
2013 goda. A potom udaleno kak ocherednaya fantaziya Taralex.
Ne
ponimayu. Net vozmozhnosti sherstit' proshlye soobsheniya, no ya uveren, chto
pri kakom-to ocherednom povyshenii Vashei publikacionnoi aktivnosti ya pisal
Vam chto-to napodobie "dal'neishie fantazii budut udalyat'sya bez
dopolnitel'nyh kommentariev". Potomu chto Vashi soobsheniya v podavlyayushem
bol'shinstve sluchaev ne otnosyatsya k tematike razdela. Nu ne prednaznachen
on dlya publikacii hudozhestvennyh tekstov ob "annigilyacii nulevogo i
beskonechnogo prostranstva Vselennoi"! Ya dazhe pomnyu, chto grozil Vam bolee
strogimi sankciyami, esli Vy ne perestanete publikovat' Vashi fantazii.
Odnako terpel poka. No raz Vas ne ustraivaet takaya situaciya, ya proshu Vas
perechitat' vot eto soobshenie. Na vsyakii sluchai
utochnyu: otvety tipa "molchu, molchu" obosnovaniem ne schitayutsya. \\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.12.2013 7:59, 2.0 KBait)
Mne i smeshno i ne smeshno.
Mne uzhe dazhe interesno kak otbirayut astronomov i kosmologov,
po kakim testam.
Nadeyus' chto vse zametyat chto v sleduyushem tekste global'nyi
smysl o bol'shom vzryve - pri tekushem lokal'nom ob'yasnenii
kotoroe opiraetsya na situaciyu izlucheniya galaktiki, a tochnee
zvezd etoi galaktiki.
Ya vot ne
ponimayu - po kakoi prichine k bol'shomu vzryvu, pripisyvayut
izluchenie galaktik, a sobstvenno izluchenie zvezd etih galaktik.
Vozmozhno eto massovoe zabolevanie, kogda
propadaet strategicheskoe
myshlenie, a arifmeticheskii logicheskii uzel prodolzhaet normal'no
rabotat'. Pri etom zabolevanii propadaet neobhodimost' v tom chtoby
po kakoi-to prichine proishodilo nechto sleduyushee, ibo process bez
prichiny priznak du.....chiny.
-------------------------------------------------
\\\
http://www.astronews.ru/cgi-bin/mng.cgi?page=news&news=5123

 Nablyudaya za vysokoskorostnym komponentom massivnogo galakticheskogo
skopleniya, uchenye Tehnologicheskogo Instituta Kalifornii i Laboratorii
Reaktivnogo Dvizheniya vpervye obnaruzhili v individual'nom ob'ekte
kineticheskii effekt Syunyaeva-Zel'dovicha izmenenie intensivnosti
radioizlucheniya reliktovogo fona iz-za obratnogo effekta Komptona na
goryachih elektronah mezhzvezdnogo i mezhgalakticheskogo gaza.
Nablyudaya za vysokoskorostnym komponentom massivnogo galakticheskogo
skopleniya, uchenye Tehnologicheskogo Instituta Kalifornii i Laboratorii
Reaktivnogo Dvizheniya vpervye obnaruzhili v individual'nom ob'ekte
kineticheskii effekt Syunyaeva-Zel'dovicha izmenenie intensivnosti
radioizlucheniya reliktovogo fona iz-za obratnogo effekta Komptona na
goryachih elektronah mezhzvezdnogo i mezhgalakticheskogo gaza.
MACS
J0717.5+3745 - eto neobyknovenno dinamichnoe galakticheskoe skoplenie,
obshaya massa kotorogo bolee chem v million milliardov raz bol'she massy
nashei galaktiki.\\\
------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.12.2013 11:48, 2.8 KBait)
Skazhu Vam chestno kosmologi - v dannom sluchai intellektual'nye malyatka.
Idiotizm kak ego ne priukrashivai, kak ego ne nazyvai, hot' neobosnovannaya
vydumka,- hot'
paradoks, - on i ostanetsya idiotizmom dazhe esli
ego ob'yavit' genial'noi pridumkoi chelovechestva.
Vot naprimer lichno mne hot' tysyachu raz govorit' chto v zvezdah
gorit vodorod - dlya menya eto tysyachu raz idiotizm, po toi prichine
chto vodorod ne uderzhivaetsya metallami, i on s samoi men'shei
udel'noi plotnost'yu.
I
vodorod mozhet byt' tol'ko v verhnih sloyah zvezdy.
A v dannom sluchai kak bashnyu sneslo zhestko, dodumalis' i poverili
chto chto u vodoroda sneslo bashnyu i on narushaya
vse zakony
fiziki ponessya v centr zvezdy po-uchavstvovat' v yadernoi
reakcii. Lichno ya uvolil by srazu vseh astronomov i kosmologov
kotorye v eto poverili,
ibo - ballast.
Mne smeshno chto zalipli uzhe tol'ko na etom etape.
A chtoby vzroslye modeli pridumyvat' to nado
eshe umet' na ochen' vysokoi skorosti otbrasyvat'
teoreticheskoe laino i ni v koem sluchai ne vyplesnut'
i ne propustit' zdravuyu ideyu. Estestvenno dlya etogo
v golove uzhe dolzhny byt' produmnny skorostnye
proverochnye idei.
Vot v dannom tekste odno bezssmyslennoe hotyat
zamenit' na drugoe bezpoleznoe, - zdes' sobstvenno
situaciya metoda poiska urovnya neadekvata.
Ibo poisk vedetsya naugad, ni chem, ni chto, i ni kak, - ne
obosnovyvaetsya, net zadachi i net global'nyh celei poiska.
I naprimer moderator ne mozhet nichego pridumat'
samostoyatel'no- moderator hochet
zadat' voros chtoby na osnovanii otveta stat'yu
v zhurnal napisat'.
Vot i vse celi i zadachi kotorye mogut reshat'sya na
etom
forume naprimer. Drugih zadach - moderator ne propustit,
ibo smysla drugih zadach on ne ponimaet.
----------------------------------------------
\\\
Otvet #380 : Segodnya v 09:50:08
Vsego lish' moe mnenie, chto STO eto v vysochaishei mere tochneishii
instrument poznaniya i izucheniya No ne fizika.
\Vibe. = \Interesuyushiisya Ded, izmenitsya li smysl Vashei frazy, esli v nei STO zamenit' zakonom vsemirnogo
tyagoteniya? Esli da, to pochemu?\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.12.2013 22:52, 4.8 KBait, otvetov: 1)
To chto al'ty v osnovnom- pensionery i uzhe
ne mogut dazhe ponyat' s kem oni obshayutsya a zachastuyu ne mogut ponyat'
zachem to est' i relyativisty kotorye zamolachivayut
besedu.
Samyi mahrovyi relyativist na al'ternativnyh forumah
--------------------------
E-Eater
---------------------------
 Re: Algoritm vvedeniya fizicheskih ponyatii.
Re: Algoritm vvedeniya fizicheskih ponyatii.
Otvet #5 - Segodnya :: 17:23:41
konstantin1 pisal(a) Segodnya :: 12:34:39:Hotelos' by proanalizirovat' to kak v fiziku vvodyatsya novye ponyatiya. Ponyatiya
voznikayut v rusle kakoi-to teorii. Naprimer, poyavilas' elektrodinamika
Maksvella - predlozhili ponyatie potenciala. Prosto okazalos', chto vesh'
poleznaya, i vot pridumali slovo-termin v kachestve zamenitelya mnogih
slov. Poyavilas' STO - okazalos', chto nekotoraya velichina dolzhna byt'
invariantnoi, nazvali ee "interval". Ponyatno, chto iz pokazanii priborov nikakie ponyatiya ne rozhdayutsya, eto bzik Kravchenki. Myslennyi eksperiment eto prosto
svoeobraznaya forma logicheskih postroenii.
|
-----------------
 Re: Algoritm vvedeniya fizicheskih ponyatii.
Re: Algoritm vvedeniya fizicheskih ponyatii.
Otvet #14 - Segodnya :: 18:06:48
konstantin1 pisal(a) Segodnya :: 18:00:09:Nu
dlya Vas vopros pomyagche. Kak ponyatiya kotorye veroyatno mozhno otnesti k
fizicheskim ponyatiyam, k nim mozhno otnesti? Chto dlya etogo nuzhno? Ya vse otvetil v svoem pervom poste. Prochee eto pridumyvanie slov: tipa, izobrel nazvanie
- srazu stalo "ponyatnee".
|
------------------
Sobstvenno ego teksty - bessmyslennyi porozhnyak,
s pretenziei na razumnost', s relyativistskim voshvaleniem.
Lyubomu al'tu obshat'sya s nim chto mochit'sya protiv vetra.
Naprimer
\\\Myslennyi eksperiment eto prosto svoeobraznaya forma logicheskih postroenii.
\\\
- Na samom dele myslennyi eksperiment eto odin iz vidov lohotrona,
kotoryi vtyuhali fizikam. Sobstvenno eto kogda vvodyatsya fizicheskie
velichiny i
fizicheskie sushnosti - bez izmeritel'nyh priborov,
bez edinic izmereniya takovyh, i bez metodik izmereniya takovyh.
Sobstvenno pri zayavlennom zamedlenii vremeni v
dvizhenii, net
ni pribora ni edinicy izmereniya, i net metodiki - i samo deistvie
- kazhusheesya - i eto otnositsya i k krivizne prostranstva.
S moei tochki zreniya
- net fizicheskih izmeritel'nyh priborov -
vse - v peshee eroticheskoe.
Tak chto nekotoryi vid lohotrona - komu i forma logicheskogo postroeniya,
a komu i zhestkaya
lapsha na ushi.
Sobstvenno o chesti i poryadochnosti govorit' tozhe ne logichno, tak kak
net zakonodatel'stva kotorye by zapreshali v fizike i kosmologii obman
v
lyubom vide, po etoi prichine zasilie i procvetanie teorii urovnya
idiotizma budet maksimal'noi, dlya etogo est' vse usloviya.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(D. V. lom,
23.12.2013 12:56, 217 Bait)
Ne vrubayus'. Ne vizhu komentov. Ili moderator udalyaet srazu, ili ih prosto net, ili s nastroikami chto to ne tak. Takoe oshushenie, chto chel (Vasi) sam s soboi razgovarivaet. Vrode
vse po delu i interesno. V chem prichina?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.12.2013 22:41, 2.6 KBait)
Sobstvenno i moya model' osnovana na
vran'e, pri popytke detal'nyh ob'yasnenii poluchaetsya
idiotizm.
Zdes' ya dumayu chto k dannoi situacii logichno otnositsya
spokoino, po prichine togo chto v kosmologii net i ne budet
vozmozhnosti uznat' tochno chto proishodit vnutri zvezdy.
U menya v modeli termoizolyacionnyi sloi vnutri zvezdy,
na samom dele vydumka na urovne vran'ya, po prichine togo
chto pri kondensacii
efira v zhidkoe sostoyanie, v zamknutom
share temperatura vnutri dolzhna byt' naprimer desyat' tysyach
gradusov chtoby snaruzhi bylo shest' tysyach gradusov.
Eto privodit k tomu - chto pri bystrom vyhode iz zvezdy
proizoidet rezkoe vosstanovlenie i ogromnyi vybros,
chego sobstvenno ne nablyudaetsya v galaktikah peregretyh,
i v sostoyanii razbrosa.
Zdes' dazhe ne znayu chto i dumat'. Logichno pomenyat' strukturu
izlozheniya modeli, iz kotoroi by sledovali tendencii
fizicheskih processov i iz etih tendencii by vytekali
sleduyushie
logicheskie predpolozheniya, kotorye by i sozdavali nekotoruyu
osnovnuyu strukturu modeli. I v ramkah etoi struktury logichno
opisyvat' situacii kotorye logicheski bolee priemlemy.
Zdes' voznikaet sleduyushaya situaciya neobhodimost' uluchshenii
i dorabotok po kazhdomu elementu i vzaimodeistviyu modeli,
chto uslozhnyaet model' kak takovuyu chto mozhno priravnyat' k
gluposti
perehodyashei v idiotizm. Bol'shoe kolichestvo
logicheskih vetvlenii mozhet ne vosprinimat'sya v principe,
plyus
k etomu semanticheskii shum.
Itogo s odnoi tochki zreniya model' dolzhna byt' prostoi,
s drugoi tochki zreniya model' dolzhna byt' strukturirovannoi
po prichinam processov i vzaimodeistvii s opisaniem situacii
opredelivshih vybor v dannoi posledovatel'nosti.
I vse ravno est' shans, chto chitayushii ne poimet napisannoe.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.12.2013 22:49, 476 Bait)
\\\Takoe oshushenie, chto chel (Vasi) sam s soboi razgovarivaet. Vrode
vse po delu i interesno. V chem prichina?\\\
Zapisi svoih razmyshlenii vedu zdes'.
U menya hobbi kosmologiya, vot ya i obdumyvayu
zdes' raznye situacii kotorye
imeyut mesto byt',
kosmolog po special'nosti rabotayushii ne mozhet zatronut'
raznye voprosy v tom vide kak est' ibo ego mogut i uvolit'.
Da i za obshenie so
mnoi ya dumayu tozhe ne pohvalyat.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
26.12.2013 23:37, 1.5 KBait)
Blin vot tak i ohota skazat' chto vot etot
al't ko - el.
Sovsem mosk klinanulo - ego ideya v tom
chtoby relyativistov pereuchit' po drugomu dumat'.
Na
koi tyanut' potom etot oboz.
Luchshe pust' lezhit eto tam gde eto lezhit,
i prosto oboiti storonoi.
Ya lichno vpervye nablyudayu chto-by vospityvali
sebe vragov
na zavtra.
Ba-be-ne.
1 Esli ty al't i tebe v tvoei teme - upal na hvost relyativist
so svoimi rassprosami, zabei - i zabud' etu temu.
2 Esli ty al't i tebe al'ty protivorechat ili tebya obsuzhdayut,
zabei na etu temu.
3 Esli ty al't i v tvoei teme relyativisty tebya chmyryat srazu, -
eto logichnoe
napravlenie.
---------------------------------------
\\\

: 20.12.2013 [16:36:55]
Nebol'shoi opyt izucheniya dominiruyushei v nauchnom soznanii teorii gravitacii trebuet podvedeniya nebol'shih promezhutochnyh itogov.
V
dannoi teme izlozhu na moi vzglyad neskol'ko trudnostei vozmozhno
metodologicheskogo haraktera, a vozmozhno i principial'nogo, prisushego
konkretnoi teorii, kotoraya pretenduet na rol' fizicheskoi.\\\
---------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.12.2013 0:05, 748 Bait)
S drugoi tochki zreniya est' pogovorka, -
"Yupiter - ty serdish'sya?, - znachit ty ne prav.
Vozmozhno i ya ne prav v svoih ambiciyah.
Vozmozhno zavtra byvshii relyativist
sdelaet
bezbashennoe otkrytie v efirnyh tehnologiyah, i sdelaet
efirnye idei neprirekaemymi v obozrimom budushem.
S drugoi tochki zreniya kosmologiya eto
sobstvenno ne
fizika - eto bor'ba idei.
Ya by dazhe po drugomu skazal, bor'ba adekvata, bor'ba neadekvata,
bor'ba skazok, bor'ba legend, bor'ba predskazanii,
bor'ba obeshanii.
Ya lichno vystupayu v novoi kategorii - bor'ba tekushih opisanii - v tom vide
- kak est' i mne prosto hochetsya chtoby tak bylo, i ya provel proverki
na situacii - i v osnovnom predydushie sobytiya sovpadayut.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.12.2013 0:12, 578 Bait)
"Yupiter - ty serdish'sya?, - znachit ty ne prav."
- Chto-to logichnoe est' v etom.
U kazhdogo svoi prakticheskii opyt, esli
ya serzhus'
to ya predvizhu i predchuvstvuyu chto tekushaya situaciya
dostatochno ploho otrazitsya v budushem - ibo s moei
tochki zreniya - eto i konyu ponyatno. Ibo ne osilit
yuzer bol'she
odnoi lyubimoi teorii. Pereuchit' vtoroi i tretei teorii
mozhno i ob'yasnit' logichnost' drugih teorii tozhe budet
mozhno, - no nado ponimat' - chto
u yuzera - eti
teorii nikogda ne budut lyubimymi teoriyami.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.12.2013 14:42, 8.3 KBait)
Uzhe dazhe baryshnya dogadalas' chto u relyativistov ne
fizika po suti, a golimyi porozhnyak, ne imeyushii fizicheskih
opredelenii.
Ibo kakaya-to otpiska ne yavlyaetsya
fizicheskim opredeleniem yavleniya,
a to chto podobrali formulu kotoraya primerno opisyvaet fizicheskii
process, - eto ne znachit chto u etogo fizicheskogo processa poyavilis'
adekvatnye fizicheskie ob'yasneniya processov na osnovanii hotya-by desyatka
opytov v kotoryh tok v provodnike proizvodit ne tol'ko magnitnoe pole
no i proishodyat
drugie fizicheskie yavleniya.
Tak eti opyty - ya znayu i ih mnogo. A esli eti opyty ne znat'
to poluchitsya - detskii lepet a ne fizicheskoe opredelenie - toka v provodnike.
Sobstvenno kogda est' na forume postoyanno meshayushii al'tam obshat'sya,
- etot relyativist kak pravilo staraetsya pokazat' svoi umnyak, na samom dele
on mozhet
pokazat' tol'ko svoyu nachitannost' relyativistskim porozhnyakom.
Sobstvenno etogo relyativista nachinayushim al'tam logichno ispol'zovat' v
svoih celyah, dostatochno ego sprashivat'
o razlichnyh fizicheskih sushnostyah,
i v teh otvetah gde maksimal'naya neskladushka i maksimal'nyi lepet -
to eti napravleniya logichno opredelyat' prioritetnymi.
Relyativist sam ne ponimaet fizicheskogo smysla i to chto pravil'no ili
ne pravil'no, on sebe v mosk zapisal vse bezdumno kak v zapisnuyu knizhku,
i doveryaet zapisannomu
- tak uchili v sovetskih shkolah.
Al'ty podobnyh metodov obucheniya - prirodno ne vosprinimayut, ibo oni v mosk kladut
to chto proveryayut.
Tak chto relyativist ne
smozhet sostavit' al'tam konkurencii.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
\\\Galina.
 Re: Relyativistskoe i nerelyativistskoe (klassicheskoe) ob'yasneniya raboty kollaidera.
Re: Relyativistskoe i nerelyativistskoe (klassicheskoe) ob'yasneniya raboty kollaidera.
Otvet #71 - Segodnya :: 00:12:32
GalinaRelyativisty
voobshe slavyatsya svoim redkim umeniem davat' prostym i yasnym ponyatiyam
nevoobrazimye po nevrazumitel'nosti opredeleniya. Vot odin iz primerov opredeleniya, dannogo yavnym relyativistom:\\\ Citata:Amper
est' sila neizmenyayushegosya toka, kotoryi pri prohozhdenii po dvum
parallel'nym pryamolineinym provodnikam beskonechnoi dliny i nichtozhno
maloi ploshadi krugovogo poperechnogo
secheniya, raspolozhennym v vakuume
na
rasstoyanii 1 metr odin ot drugogo, vyzval by na kazhdom uchastke
provodnika dlinoi 1 metr silu vzaimodeistviya, ravnuyu 210−7 n'yutona.   
|
|
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Re: Relyativistskoe i nerelyativistskoe (klassicheskoe) ob'yasneniya raboty kollaidera.
Re: Relyativistskoe i nerelyativistskoe (klassicheskoe) ob'yasneniya raboty kollaidera.
Otvet #72 - Segodnya :: 00:39:06
77pp\\\I? Prosto transkripciya formuly

s matematicheskogo
yazyka, v koem ona i predstavlena, na yazyk estestvennyi.
\\\
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Re: Relyativistskoe i nerelyativistskoe (klassicheskoe) ob'yasneniya raboty kollaidera.
Re: Relyativistskoe i nerelyativistskoe (klassicheskoe) ob'yasneniya raboty kollaidera.
Otvet #75 - Segodnya :: 12:47:44
Galina.\\\I posle takoi transkripcii ucheniku srazu stalo yasno
i ponyatno, chto takoe amper?
Vot tak, uchas' po takim uchebnikam, s podobnymi opredeleniyami,
sposobnye ucheniki i prevrashayutsya v relyativistov.\\\



---------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Re: Relyativistskoe i nerelyativistskoe (klassicheskoe) ob'yasneniya raboty kollaidera.
Re: Relyativistskoe i nerelyativistskoe (klassicheskoe) ob'yasneniya raboty kollaidera.
Otvet #76 - Segodnya :: 13:01:07
Drobyshev pisal(a) Segodnya :: 12:31:44:Bolee
togo, proton-antiprotonnye pary mogut obrazovyvat'sya v
elektron-pozitronnyh kollaiderah.Prirode gluboko naplevat' na to,
chto vy
o nei voobrazili i vo chto vy uverovali.
Galina.\\\Prirode deistvitel'no naplevat' na vse vashi verovaniya,
v
chastnosti, na verovaniya v invariantnost' skorosti sveta.
Ochen' mozhet byt', chto v elektron-pozitronnyh kollaiderah
obrazuyutsya proton-antiprotonnye pary.
No
tri protona ne mogut obrazovat'sya iz dvuh protonov i bol'she
nichego, kak
by vy sil'no eti protony ne razognali. Materiya,
molodoi chelovek, ne
voznikaet iz nichego, ne voznikaet iz "energii"
i ne ischezaet bessledno.
Sovershenno ochevidno, chto v opisannoi vami yadernoi reakcii pomimo
dvuh
protonov i "energii" uchastvovala eshe kakaya-to materiya.
Esli STO polagaet, chto materiya mozhet voznikat' iz "energii",
znachit eto nematerialisticheskaya,
nenauchnaya teoriya.\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.12.2013 9:41, 3.6 KBait)
Da vot i eshe odnogo relyativista - srazil starcheskii marazm.
Ono vozmozhno relyativistam to i hochetsya chto-by na planete
byl hot' odin institut v kotorom budut uchit'
tol'ko
relyativistov pridumyvat' novye teorii. Tol'ko zdes' uzhe
nachinaetsya neskladushka - gde relyativisty i gde pridumyvat',
relyativisty sto let nichego ne
pridumyvayut, i gde relyativisty
- a gde novoe -, u relyativistov sto let net novizny.
Vibe kak-to hvastalsya chto ego uchili pridumyvat' teorii,
i on ne
inzhener stroyashii zabory - on vyshe etogo.
I v rezul'tate, - den'gi na ego obuchenie pridumyvat' novye
teorii - byli potracheny zrya. Sobstvenno chto on zanyal -
mesto al'ta,
budet vyskazyvanie ne logichnoe, ibo obuchenie organizovali
relyativisty dlya relyativistov - eta tema iznachal'no obrechena
byla na proval. Tak chto
k podobnym vyskazyvaniyam logichno otnositsya, -
kak k tomu chto relyativisty ni pri kakih usloviyah i nikogda ne
budut sozdavat' dazhe gruppu v institute kotoraya by
uchilas'
pridumyvat' novye teorii i modeli, ibo relyativisty ne tak
glupy chtoby rubit' vetku na kotoroi oni sidyat.
---------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #2 : 27.12.2013 [18:55:29]
---
asmoko \\\Filosofskii vzglyad na problemu obrazovaniya
\\\Filosofskii vzglyad na problemu obrazovaniya
vozle
zvezd planetnyh sistem...P.S.
Iz vsego skazannogo vyshe
napryamuyu vytekaet, chto vremya ot vremeni
poyavlyayushiesya v pole
zreniya zemlyan komety i s gryazevym, i so spekshimsya,
i s
rasplavivshimsya kogda-to yadrom yavlyayutsya ne takimi uzh i dal'nimi
rodstvennikami nashei planety\\\
-------------
Dmitrii Vibe \\\Iz skazannogo napryamuyu vytekaet,
chto filosofiya
-- nepodhodyashee osnovanie dlya razgovora ob obrazovanii planetnyh
sistem.\\\
-------------
asmoko \\\Prostite, uvazhaemyi, a vot zdes' Dmitrii
Vibe - Obrazovanie
\\\Prostite, uvazhaemyi, a vot zdes' Dmitrii
Vibe - Obrazovanie
planetnyh sistem ne Vy li rassuzhdaete na dannuyu
temu ISKLYuChITEL'NO
kak filosof?.. Sleduete v zhizni pogovorke, chto polozheno Yupiteru i t.d.?..\\\
------------
Dmitrii Vibe\\\A Vy kak predpolagali? Chto obrazovanie planetnyh sistem
-- eto takaya
prosten'kaya temka, po kotoroi mozhet plodotvorno rassuzhdat'
lyuboi
chelovek, dazhe pri otsutstvii sootvetstvuyushei kvalifikacii?\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.12.2013 14:13, 398 Bait)
Po logike ya ne vizhu trudnostei u relyativistov chto-by
skoncentrirovat' usiliya i razrabotat' chto po proshe
v teoriyah i modelyah. S moei tochki zreniya samoe prostoe
eto versii atomarnyh modelei dlya opisaniya razlichnyh
zadach.
Naprimer. -
Atomarnaya model' opisyvayushaya elektro-magnitnoe vzaimodeistvie.
Ya naprimer
takuyu model' samostoyatel'no za tri goda pridumal.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.01.2014 15:11, 2.8 KBait)
Ya estestvenno rad, no kak ne ponaslyshke znayushii
stroitel'stvo - ya s pervogo vzglyada mogu skazat'
chto eto budet bezbashenno dorogoi dolgostroi.
Bol'shie stekla
i ya tak ponimayu rezino alyuminievaya
obshivka - eto ochen' dorogo. Dolgostroi predpolagaetsya
po prichine togo chto ya ne nablyudayu bol'shih dymovyh
krasivyh trub
kotel'noi, ne nablyudayu vysokovol'tnoi
transformatornoi kotorye obychno stroyatsya v otdel'no stoyashih
zdaniyah metrah v dvadcati ot osnovnogo zdaniya.
Esli
kotel'nuyu srazu ne predusmotret', to mozhet okazat'sya,
chto podvod teplotrassy mozhet stoit' dorozhe samogo zdaniya.
Kanal'yu to mozhno eshe mashinami vyvozit'.
Na forume voobshe kakuyu-to baidu obsuzhdayut.
Pust' hotya-by sperva uznayut skol'ko budet stoit' razreshenie
na vrezku gaza dlya kotel'noi na nuzhnuyu moshnost',
a moshnost'
sudya po zdaniyu pod dva megavatta, i est' li voobshe takovaya vozmozhnost'.
Mozhet eshe i gazovuyu trubu nado podvodit', togda uznayut
chto proektirovanie
tehnicheskih kommunikacii mogut
okazat'sya novoi finansovoi neozhidannost'yu, i tehnicheskie
pomesheniya, tehnicheskoe oborudovanie i kommunikacii, -
potyanut summu
ravnuyu stoimosti korobki.
----------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #66 : Vchera v 19:33:29
\\\Mesto dlya stroitel'stva uzhe vybrano, "privyazka" proekta k mestu sdelana?
A to na kartinke
zdanie smotritsya kak otkrytoe vsem vetram (eskiz 3).
Da,
proekt iznachal'no proektirovalsya pod park im. Nikolaeva (takovo zhelanie
gradonachal'stva). Ya tol'ko posovetoval sorientirovat' vsyu konstrukciyu
tak, chtoby nablyudeniyam byli otkryty Vostok, Yug i Zapad (kupol nahoditsya
na Yuge zdaniya), da podal'she ot avtodorogi s ee vibraciyami.
Podkovoobraznoe zdanie povernuto tak, chto ego krysha budet "parit'"
otnositel'no kupola tol'ko na Severe i SZ i SV, ne meshaya lunno-planetnym
nablyudeniyam...
V ostal'nom, osobenno pohvastat' nechem - eto centr
600-tysyachnogo goroda, prichem, na vostoke stoit televyshka, a na Severe
siyaet stadion. Ves' park zaros derev'yami, no vse oni bol'ny i te, chto
budut portit' vid, budut srezany.
Byla by moya volya, ya by voobshe za gorod planetarii vyvel i marshrutku k nemu pustil. \\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.01.2014 16:26, 721 Bait)
Uzhe proshli vremena kogda prosili proektirovshikov
proektirovat' vse po umu. Seichas proektiruyut po teh zadaniyu,
i ne bolee togo. A teper' intellektual'nyi, vopros
-
zakazchik mozhet sostavit' tehnicheski gramotnoe teh zadanie? -
estestvenno ne smozhet, ibo takih zdanii nikogda ne stroili.
Lichno ya by predusmotrel hostel
na sto chelovek, stolovuyu na
sto pyat'desyat chelovek, avtostoyanku na dvesti avto i zaezd
s neskol'kih storon. Magazin soputstvuyushih tovarov.
A vot dlya
teleskopa bashnyu ne stroil by v principe. Za cenu etoi bashni
mozhno kupit' tridcat' nedorogih teleskopov, i seify bol'shie
dlya ih hraneniya, - est' vozmozhnost' posmotret'
- vynesli
na ulicu i vseh delov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.01.2014 23:00, 1.2 KBait)
Krasnoe smeshenie i iskrivlenie prostranstva
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,115357.0.html
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ya ochen' gromko smeyalsya.
Prichina tomu chto idut nozdrya v nozdryu s tochno
temi zhe ideyami kotorye ya perebiral i uspeshno reshil
zadachu, i dazhe davno zakryl svoim avtorstvom edinstvenno ostavshiisya
podhod k krasnomu smesheniyu ot sdviga
spektra.
Ideya v tom chto u poverhnosti zvezdy sdvig spektra otsutstvuet,
i ego opredelyaet razryazhenie efira u poverhnosti, vneshnee davlenie efira,
skorost' dvizheniya
efira.
Poka duplya ne otbivali - oni tak i ne ponyali chto cvet zvezd otdali
na otkup teorii bol'shogo vzryva.
A seichas pytayutsya ishodya iz vernoi traktovki teorii
bol'shogo
vzryva po drugomu ob'yasnyat' krasnoe smeshenie - oni ne ponimayut
chto shag v storonu v vernom napravlenii nevozmozhen po dvum prichinam,
moderator ih
srazu zabanit kak beshenyh sobak, vtoraya prichina - upirayutsya
v moe avtorstvo.
U nih odna doroga - chem krasnee tem dal'she i uletaet, a sinee blizhe
i priblizhaetsya
- ku.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.02.2014 1:45, 2.5 KBait)
- O, ya smotryu uzhe vzroslye zadachi nachinayut
odolevat'. A ya kak vsegda uzhe reshil dannuyu
zadachu, - u menya uvelichenie ili umen'shenie
energii v materii reshaetsya
raskrutkoi dvuh
protivo-turbin vnutri atoma.
Interesno posmotret' kak budut reshat', dumayu
chto teploemkost' ne smogut reshit' v principe,
- po prichine
togo chto eto potyanet za soboi neobhodimost'
opisat' i drugie effekty, a dlya etogo nado imet'
ob'yasnenie i modelirovanie hotya-by elektrotoka i magnitnogo
polya,
u menya uzhe eto reshaet i atom i efir vo vzaimodeistvii.
S drugoi tochki zreniya esli zadacha est', to veroyatnost' togo
chto smogut reshit' uzhe est'.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Re: Relyativistskoe i nerelyativistskoe (klassicheskoe) ob'yasneniya raboty kollaidera.
Re: Relyativistskoe i nerelyativistskoe (klassicheskoe) ob'yasneniya raboty kollaidera.
Otvet #180 - Vchera :: 00:22:10
77pp pisal(a) 30.01.14 :: 18:51:46:
\\\Vy hot' znaete, chto takoe teplorod? Nahvatalis' terminov neponyatno gde, i vydaete tut.\\\
\\\A Vy mne dokazhite, chto "foton"
ne est' "teplorod" - ne nekii samostoyatel'no letayushii kusochek energii!
Citata: (ryadom so slovom "teplorod" stavlyu "foton", a mozhno postavit'
i "glyuon" i "bozon")
Pritok teploroda (fotona
) v telo dolzhen vyzyvat' ego nagrev,
ubyl' ohlazhdenie. Kolichestvo teploroda (fotona
) vo vseh teplovyh processah dolzhno ostavat'sya neizmennym.
 \\\
\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.02.2014 14:09, 970 Bait)
Za chto Dzhonu Shvarcu iMaiklu Grinu dali mil'nerovskuyu premiyu
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Prochital i
vspomnil fil'm fantasticheskii,
no chto-to mne podskazyvaet chto v fizike i kosmologii
etot fil'm fantastichnost' svoyu utratil davno.
-----------------------------------------------------
Idiokratiya / Idiocracy
God vypuska: 2006
Strana: SShA
Zhanr: fantastika, komediya, priklyucheniya
Prodolzhitel'nost': 01:24:08
Perevod: Professional'nyi (dvuhgolosyi)
...
Failov: 2, summarnyi razmer:
1,572,137,893
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
3.02.2014 23:27, 5.8 KBait)





-

- Soobshenii: 920
- Reiting: +32/-2
- Za zaborom krugozora - udivitel'noe...
-
Otvet #3 : Segodnya v 14:03:42
\\\Chego ne poimut "oprovergateli", kak to, chto STO, OTO i kvantovaya mehanika sozdany dlya prakticheskih celei,
rezul'tatami kotoryh my postoyanno pol'zuemsya. I lyuboi kritik dolzhen predlozhit' libo bolee prostoi matematicheskii apparat, libo bOl'shuyu tochnost' rezul'tatov,
chem STO ili OTO.
vladimir fizik,
poprobuite na osnove svoih vykladok rasschitat'... nu, ne kollaider, a hotya by sinhrofazotron.\\\
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Chto-to mne podskazyvaet, - chto pervye uskoriteli rasschityvali ne relyativisty
a storonniki efira.
--------------------------------------------------------
http://nuclphys.sinp.msu.ru/spargalka/a16.htm
Dlya togo chtoby issledovat' svoistva materii na rasstoyaniyah
men'she chem 10-12 sm. neobhodimo imet' puchki uskorennyh chastic,
energiya kotoryh prevyshaet desyatki MeV. Rozhdenie novyh chastic proishodit v
rezul'tate preobrazovaniya kineticheskoi energii naletayushei chasticy v rezul'tate
vzaimodeistviya s drugoi chasticei. Chem bol'she massa chasticy, kotoruyu neobhodimo
poluchit' v stolknovenii, tem bol'she dolzhna byt' energiya stalkivayushihsya chastic.
Sozdanie pervyh uskoritelei Dzh.Kokroftom i E.Uoltonom,
R.Van-de-Grafom,
E.Lourensom v 1931-32 gg.
otkrylo novuyu eru v yadernoi fizike. Eksperimentatory poluchili v svoe
rasporyazhenie udobnye instrumenty, na kotoryh mozhno bylo poluchat' puchki
uskorennyh zaryazhennyh chastic s energiei ot neskol'kih desyatkov keV do desyatkov
MeV. Sovremennye uskoriteli pozvolyayut uskoryat' chasticy do energii neskol'kih TeV.
V uskoritelyah uvelichenie energii zaryazhennyh chastic proishodit
pod deistviem elektricheskogo polya, napravlennogo vdol' impul'sa chasticy.
V uskoritelyah pryamogo deistviya (uskoritel' Van-de-Graafa)
zaryazhennaya chastica imeyushaya zaryad Ze uskoryaetsya v postoyannom elektromagnitnom
pole, priobretaya kineticheskuyu energiyu T sootvetstvuyushuyu vysokomu napryazheniyu V
sozdavaemomu istochnikom.
T = ZeV.
V takih uskoritelyah chasticy mogut priobretat' energiyu do ~10 MeV. Ih
sushestvennym preimushestvom yavlyaetsya nepreryvnost', vysokaya intensivnost' i
vysokaya stabil'nost' po energii uskorennogo puchka (~0.01%) .
Tok puchka na uskoritelyah Van-de-Graafa mozhet dostigat'
neskol'kih milliamper. V ciklotrone chasticy uskoryayutsya peremennym
elektromagnitnym polem postoyannoi chastoty. Chasticy uskoryayutsya ot nulevyh energii
do maksimal'nyh, dvigayas' po raskruchivayusheisya spirali uvelichivayushegosya radiusa R,
v postoyannom magnitnom pole B.
R = cp/300ZB.
gde cp - impul's chasticy, umnozhennyi na skorost' sveta, izmeryaetsya v MeV, B -
indukciya magnitnogo polya, izmeryaetsya v Teslah, R - izmeryaetsya v metrah. Obychno
ciklotrony ispol'zuyutsya dlya uskoreniya protonov i ionov. Predel'naya energiya dlya
protonov v ciklotronah sostavlyaet ~20 MeV pri pole V~2Tesla i chastote
uskoryayushego polya 30 MGc.
Pervyi betatron dlya uskoreniya elektronov byl postroen v
1940g. D. Kerstom. Betatron - eto
indukcionnyi uskoritel', v kotorom elektrony uderzhivayutsya na ravnovesnoi
krugovoi orbite rastushim sinhronno s uvelicheniem energii magnitnym polem.
Uskorenie proishodit za schet vihrevogo elektricheskogo polya sozdavaemogo
peremennym magnitnym potokom vnutri ravnovesnoi orbity. V betatronah energiya
uskorennyh elektronov mozhet dostigat' sotni MeV. Dal'neishii rost energii
elektronov ogranichivaetsya elektromagnitnym izlucheniem. Naibol'shee
rasprostranenie poluchili betatrony na energiyu 20 - 50 MeV.
Elektrony vysokih energii poluchayut v uskoritelyah dvuh
tipov
-elektronnyh sinhrotronah.-elektronnyh lineinyh uskoritelyah.
V 1944-45 godah
V.Veksler
i nezavisimo ot nego
E.Makmillan
otkryli princip avtofazirovki, chto privelo k poyavleniyu novyh tipov uskoritelei -
sinhrotronov. \\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.02.2014 1:19, 2.7 KBait)





-

- Soobshenii: 15 817
- Reiting: +212/-57
-

Otvet #280 : Vchera v 22:39:56
\\\Otkuda takaya logika? Nikto ne svyazyvaet reshenie paradoksa s konechnost'yu
Vselennoi.

Vselennaya prosto konechna, no po-vidimomu, ogromnogo
slabopredstavimogo razmera..
A paradoks reshen okonchatel'no let 50 nazad drugim ob'yasneniem.
Ono izlozheno azh v otvete#13.
Posle
nego idet prosto pustoi govor lyudei, libo ne ponimayushih sut' paradoksa
po geometrii i fizike, libo lyudei, zhelayushih chto-nibud' pooprovergat' na
rovnom meste i pustymi vozrazheniyami.
Obosnovanii lyubyh vozrazhenii poka ne nablyudaetsya.\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Mne prosto ochen' priyatno takoe chitat'.
Mozhno mnogogo ne zamechat' i ne ponimat', i samoe smeshnoe
chto vozrazhenii uzhe ne budet - oni uzhe byli.
I
vozrazhayushih nazvali al'tami i poslali al'tov s etogo foruma
v peshee eroticheskoe puteshestvie.
I al'ty uzhe vtoroi raz ne pridut povtorno razduplyat' .
Vozrazhat'
al'ty uzhe ne budut, a budut tol'ko smotret'
spokoino i razmyshlyat', - kogda relyativisty poimut
chto oni uzhe dazhe ne smeshnye, s ih teoriyami,
v kotoryh chem neadekvatnei
teoriya tem ona u nih schitaetsya luchshe.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.02.2014 3:52, 2.7 KBait)
- Moderator




-

- Soobshenii: 13 565
- Reiting: +169/-19
- Mne nravitsya etot forum!
-
Otvet #30 : Vchera v 13:48:09
\\\ Tak Vselennaya eto zhe
teplovoi dvigatel', v kotorom proishodit teploobmen s okruzhayushei sredoi.
Chto yavlyaetsya okruzhayushei sredoi po otnosheniyu k zamknutoi i rasshiryayusheisya
Vselennoi nam neizvestno.\\\
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
A hlopec sovsem oborzel, po mimo togo chto v moi
avtorskie
prava vlez, tak i v ramkah relyativizma pod markoi
kotoroi prohodit ves' forum pod ego moderaciei -
sredy kak nepreryvnoi so vsemi prisushimi svoistvami
sredy - plotnost' sredy, neposredstvennyi kontakt mezhdu chasticami sredy,
skorost' vozmusheniya sredy - tak etogo u relyativistov to i net,
u relyativistov pustoe
prostranstvo.
V pustom prostranstve svet - chasticy - fotony.
A v srede svet - kolebaniya plotnosti sredy.
Grubo govorya - u relyativistov eto svet v kotorom
fotony letyat.
A u al'tov prosto kolebletsya efir - analogichno zvuku
v vozduhe.
No sobstvenno u moderatora estestvenno fizika
daleka ot sovershenstva,
ya tak ponimayu chto eto ili
uzhe vozrastnoe, ili vodovki vykushavshi - ibo v tekste
mnogo neskladuh principial'nyh, i skoree pozoryashih.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.03.2014 11:50, 12.5 KBait)





-

- Soobshenii: 2 104
- Reiting: +80/-3
- Rock-AstroDiver
-
Vchera posetil Maluyu tribunu
uchenogo, vystupal Dmitrii Vibe. Kak vsegda, ochen' interesnyi rasskaz ob
obrazovanii zvezd i planetnyh sistem, poslednie dannye, krasivye foto.
Spasibo bol'shoe!
Posle lekcii sostoyalsya razgovor s odnoi iz
sotrudnic MP, v kotorom ona povedala o tom, chto rukovodstvo MP ochen'
obespokoeno sil'nym padeniem poseshaemosti lekcii, osobenno v Bol'shom
zvezdnom zale. (Na predydushei lekcii pro Radioastron bylo zapolneno
men'she poloviny zala, esli ne tret' - ya tam byl)
Esli tak poidet i
dal'she, to lektorii Bol'shogo zala budut vynuzhdeny sokratit' do
neskol'kih "hitovyh" lekcii v god (Surdin, Zasov, Shustov i eshe
nekotorye, na kotoryh hodit narod). Nevygodno sobirat' polupustye zaly
ezhemesyachno.

Nado ispravlyat' polozhenie!
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------





-

- Soobshenii: 1 944
- Reiting: +98/-15
- cherez noty k zvezdam!
-
Otvet #3353 : 06.03.2014 [11:50:56]
Nado ispravlyat' polozhenie!
Da, ne stoilo portit' otnosheniya so svoimi partnerami.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- ASTRONOMY.RU





-

- Soobshenii: 12 487
- Reiting: +419/-38
- Pust' cvetut sto cvetov! Krome sornyakov...
-
Otvet #3354 : Segodnya v 00:55:15
Nado ispravlyat' polozhenie!
Da, ne stoilo portit' otnosheniya so svoimi partnerami.
A nemnogo pobol'she informacii mozhno, hotya by namekom?...
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://lenta.ru/conf/kuvakin/
Eduard-2
[24.04 03:11]
Uvazhaemyi Valerii Aleksandrovich, ya est' li v vashem (RAN) arsenale
standartnaya metodika otdeleniya "pshenicy ot plevel", t.e. nauchnyh
otkrytii i dostizhenii ot okolonauchnyh yavlenii, k nauke otnosheniya ne
imeyushih? Esli takaya metodika sushestvuet, to kakie priznaki srazu
ukazyvayut na to, chto pered nami ocherednoi graf Kaliostro?
Uvazhaemyi Igor'!
V praktike ocenki lzhenauki est' dva puti. Pervyi etot special'naya
svobodnaya i nezavisimaya nauchnaya ekspertiza. No ona vozmozhna tol'ko v tom
sluchae, esli v zayavlennoi idee est' predmet issledovaniya. Esli zhe ee ni
podtverdit', ni oprovergnut' nevozmozhno, to takie idei ne
rassmatrivayutsya v kachestve nauchnyh. V etoi svyazi upominayut i o principe
"bremeni dokazatel'stva", to est' obyazannost' dokazyvat' istinnost' ili
nauchnost' utverzhdeniya lezhit na toi storone, kotoraya i vydvigaet eto
utverzhdenie. Vmeste s tem sushestvuyut nekotorye obshie i predvaritel'nye
priznaki, nalichie kotoryh dolzhno stavit' pod ser'eznoe somnenie
nauchnost' zayavleniya (teorii, otkrytiya i tak dalee). Eto tak nazyvaemye
priznaki prima facae (to est' "s pervogo vzglyada"). K nim, v chastnosti,
otnosyatsya: (1) otsutstvie u zayavitelya sootvetstvuyushego bazovogo
obrazovaniya ili professional'noi podgotovki; (2) apellyaciya k shirokoi
presse ili k televideniyu, a ne k nauchnomu soobshestvu; (3) otsutstvie
publikacii v ser'eznyh, recenziruemyh periodicheskih izdaniyah; (4)
ispol'zovanie v tekstah ponyatii, oznachayushih fenomeny, ne fiksiruemye
naukoi (tonkie polya, torsionnye polya, bioinformacionnye polya, energiya
aury i tak dalee); (5) pretenziya na "revolyucionnyi" perevorot v nauke i
tehnologiyah (lzheuchenye na melochatsya, oni obychno obeshayut nastoyashie
chudesa, kotorye pochemu-to ne vyzyvayut u nauchnogo soobshestva nikakih
emocii); (6) obeshanie bystryh i basnoslovnyh medicinskih, ekonomicheskih,
finansovyh, ekologicheskih i inyh effektov.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sobstvenno s moei tochki zreniya tekushaya paradigma sovsem obnaglela
tem chto trebuet priemstvennosti predydushim rabotam.
A esli u menya naprimer absolyutno vse ne sootvetstvuet
tekushei paradigme i kosmologii v chastnosti. Tak menya vezde
pri referirovanii moih rabot budut posylat' v peshee
eroticheskoe puteshestvie i ob'yavyat menya lzheuchenym i al'tom.
Hotya lichno ya schitayu, chto esli smotret' kak oni muchat vola i
dumayut
chto zanimayutsya naukoi,
to ya operezhayu vsyu kosmologiyu vmeste vzyatuyu na 500-1000 let.
A chem zhe zanimaetsya vsya kosmologiya, chto tak tupit, smeshno skazat',
moi estestvenno opponenty ne ostalis' bez moego, ochen' tshatel'nogo
issledovaniya
ih rabot. Tot zhe Vibe ne pridumal samostoyatel'no azh
nichego voobshe, zanimaetsya
pereskazami i professor. A est' eshe takie
kosmologi, kotorye zanimayutsya
interpretaciyami avtorskih variantov,
v stile mol avtor chernyh dyr l'oh a ya
vot takoi umnyi, luchshe avtora
chernyh dyr znayu, - kakie dolzhny byt' chernye dyry.
I estestvenno est' predel u slushatelei, kogda oni uzhe ne
hotyat
verit' vo vsyakie skazki, prepodnosimye kak istina v
poslednei instancii.
I yasnyi kon' oni uzhe ne budut hodit' na lekcii, v osnovnoi
suti kotoryh
za poslednie 65 let, uzhe nichego ne menyaetsya.
I estestvenno esli opublikovat' moyu stat'yu, naprimer,
kotoraya protivorechit
vsei tekushei paradigme i namnogo luchshe i proshe ob'yasnyaet
vsyu fiziku zvezd
i galaktik, yasnyi kon'
srazu u chitatelya poyavitsya vopros.
- A chem zanimalas' kosmologiya poslednie 100 let?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.03.2014 12:52, 4.2 KBait)
------------------------------------------
- Moderator





-

- Soobshenii: 14 513
- Reiting: +389/-49
- Deti lyubyat buterbrod s margarinom!
-
Otvet #19 : Segodnya v 07:21:01
\\\Avtor
izvestnyi, no zdes' obsuzhdaetsya konkretnoe predlozhenie ne etogo avtora.
Proshu ogranichit'sya obsuzhdeniem predlozheniya, opublikovannogo v pervom
soobshenii. Soobsheniya, ne otnosyashiesya k etomu predlozheniyu, budut
udalyat'sya.\\\
\\\
Po vsemu forumu obsuzhdeniya idut v ramkah zagolovka temy, a ne ego
pervogo predlozheniya. Ya izvinyayus', no poluchaetsya vy tut svoi lichnye
"imperatorskie" poryadki ustanavlivaete? Est' pravilo - ne uklonyat'sya ot
temy, a net pervogo soobsheniya.
"Eksperimenty" v nazvanii stoyat vo mnozhestvennom chisle. I neizbezhny ssylki i sravneniya ot drugih istochnikov.\\\
\\\Prochitaite punkt 5.5 Pravil, s kotorymi Vy soglasilis' pri registracii.\\\
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ya uzh bylo rasperezhivalsya chto u menya poyavyatsya konkurenty
relyativisty, u kotoryh massa svobodnogo vremeni, i u nih
sobstvenno net drugogo vybora,
kak pridumyvat' chto-to - ne relya-
tivistskoe.
Napomnyu pro relyativizm tem kto ne znaet obychnaya ne fizichnaya
teoriya, na zayavlennye fizicheskie svoistva
v kotoroi otsutstvuyut,
- kak fizicheskie pribory - izmeryayushie zayavlennye velichiny.
Sploshnaya fantaziya nichem fizicheski ne obosnovannaya.
Tak vot ya sam
kak raz pridumyvayu a tochnee obdumyvayu opyt
treh sred vzaimodeistvuyushih drug s drugom, efir odin iz etih, sred.
Ya uzhe dumal chto u menya uzhe konkurenty poyavilis',
no moderator
krassava,
vot v dannom sluchai on luchshii,
oblomal roga relyativistam,
a komu ne oblomal roga, tomu votknul eti roga v grunt na tom i zaklinil
burnuyu deyatel'nost' relyativistov kotorye reshili sostavit' mne
konkurenciyu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.03.2014 19:17, 5.6 KBait)
U Vibe estestvenno byvayut probleski osoznannogo razuma
no s moei tochki zreniya ego zatumanivaet ozhidanie halyavy.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://elementy.ru/lib/430399
\\\Ya by skazal tak: osnovy sovremennoi
astronomicheskoi kartiny
Mira mogut okazat'sya nevernymi tol'ko celikom.
Toest' my mozhem
oshibat'sya ne v otdel'nyh fragmentah, a vovsei fizike
srazu.\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vibe dogadyvaetsya chto vsya tekushaya kosmologiya eto laino
sobach'e,
pri etom on hochet chtoby kto-to ukazal na ego oshibki. Pri
etom
ne hochet iskat' oshibki i ne priemlet ob'ektivnogo analiza,
po prichine togo chto ne tak davno ego chastichno razduplilo i
on osoznal
chto vse teorii laino sobach'e, ne stoit uzhe podderzhivat'
eti teorii,
to-est' termin gospodstvuyushaya paradigma - al'ty pridumali.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1020 : 08.03.2014 [10:46:29]
\\\Pochemu bol'shoi vzryv proizoshel iz kroshechnogo sharika?\\\
\\\Otkuda
informaciya, chto "bol'shoi vzryv proizoshel iz kroshechnogo sharika"?\\\
\\\Nu tak teoriya bol'shogo Vzryva, kak by oficial'no podderzhivaetsya mnogimi uchenymi\\\
\\\
V
nauke otsutstvuet ponyatie oficial'noi podderzhki teorii. Poetomu ni odin
uchenyi ne mozhet oficial'no podderzhat' kakuyu-libo teoriyu. Dalee,
podskazhite,
pozhaluista, gde imenno v teorii Bol'shogo Vzryva govoritsya
pro kroshechnyi
sharik. Mne ran'she kazalos', chto tam vse neskol'ko slozhnee.\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1029 : 13.03.2014 [00:28:08]
\\\Chto -- eto?\\\
\\\Zametka. V zametke, po-vashemu, fantazii ili fakt?\\\
\\\Chastichno
fantazii. Kak obychno, galaktiki nazvany starymi, no
osnovanii dlya
takogo utverzhdeniya ne privoditsya. V pare mest
napisano, chto etim
galaktikam 12 mlrd. let -- tozhe bez osnovanii.\\\
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Skazhu tol'ko o tom chto ya davno slil v kanalizaciyu istorii
vsyu
kosmologiyu gospodstvuyushei paradigmy, tol'ko vot ya ob etom ne
mogu
rasskazyvat' i hvastat'sya po bol'shomu kolichestvu prichin.
Tak vot sidyat sebe u teleskopov kosmologi i uverenno dumayut
chto
kto-to pridumaet i razreshit im pol'zovat'sya svoimi ideyami,
- ne ugadali, eto uzhe v proshlom.
Ne mozhesh' sam pridumat' svoi efir i obnaruzhit' ego svoim razumom
sosi darmovuyu sisyu relyativizma i sleduyushie 500-1000 let.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.04.2014 20:28, 22.0 KBait)




-

- Soobshenii: 366
- Reiting: +4/-0
- specialist po postrelyativistskoi elektrodinamike
-
Otvet #1050 : 31.03.2014 [16:18:19]
\\\Fakt ne byvaet v kosmologii. Fakt prosto est'.\\\
\\\Da, no
vy zhe vidite kak stroitsya TBV?
Kak
tol'ko obnaruzhivayutsya novye nablyudatel'nye dannye, ne ukladyvayushiesya v
predydushuyu model', tak tut zhe vydumyvaetsya novaya fantasticheskaya
sushnost', o kotoroi ranee voobshe ne upominalos' (naprimer, inflantonnoe
pole,temnaya energiya).
V etih usloviyah nikakih faktov, stavyashih pod somnenie TBV v principe byt' ne mozhet.
Odnako,
pod somnenie mozhet popast' OTO, kotoraya i sposobstvovala razvitiyu TBV i
v kotoruyu trudnee uzhe chto-to novoe zapihat'. Obeshali zapustit' proekt
Advanced LIGO v 2014 godu, no chto-to poka ni sluhu ni duhu. Mezhdu tem
est' vot takoe nablyudenie otsutstviya gravvoln
http://arxiv.org/abs/0805.4758 Ego mozhno schitat'
nauchnym faktom ili kak (vot zdes' interpretaciya etoi stat'i "zheltoi" pressoi
http://www.membrana.ru/particle/12649
) ?\\\
Poslednee redaktirovanie: 31.03.2014 [16:33:07] ot Rishi

Zapisan




-

- Soobshenii: 366
- Reiting: +4/-0
- specialist po postrelyativistskoi elektrodinamike
-
Otvet #1054 : Vchera v 18:44:38
\\\Tema vskore budet zakryta vvidu ee polnoi besperspektivnosti.\\\
\\\Vot, sovershenno - za.
Topikstarter s nauchnoi tochki zreniya nepravil'no sformuliroval temu obsuzhdeniya.
No vsem kosmologam nado pered nosom povesit'
tablichku so slovami N'yutona: "Gipotez ne izmyshlyayu".
V
fizike (esli kosmologiyu mozhno kak-to prichislit' k fizicheskoi nauke, a
ne, naprimer, k nauchnoi fantastike), konechno, bez gipotez ne oboitis',
no kogda fantaziyu pro to chto sluchilos' 13,7 mlrd. let tomu nazad,
pytayutsya predstavit' obyvatelyu chut' li ne kak nauchnyi fakt, to eto uzhe
perebor. \\\

Zapisan
- Moderator





-

- Soobshenii: 14 544
- Reiting: +391/-49
-
Otvet #1055 : Vchera v 20:44:30
\\\kogda
fantaziyu pro to chto sluchilos' 13,7 mlrd. let tomu nazad, pytayutsya
predstavit' obyvatelyu chut' li ne kak nauchnyi fakt, to eto uzhe perebor. \\\
\\\Protivnikam
Bol'shogo Vzryva tol'ko i ostaetsya povtoryat' zaklinanie: "Eto fantaziya,
eto fantaziya, eto fantaziya!.." No zaklinaniya v nashe vremya ne rabotayut! Ya
budu prosit' administratora foruma Harona srazu zhe banit' teh, kto
somnevaetsya v Teorii Bol'shogo Vzryva.\\\

Zapisan





-

- Soobshenii: 2 797
- Reiting: +63/-0
-
\\\ Otvet #1056 : Segodnya v 11:00:54
Citata Nezvan: Po edinichnomu nablyudeniyu uzhe nauchilis' sobirat' statistiku?\\\
\\\V original'noi stat'e
http://arxiv.org/abs/1309.2826 avtory pishut:
Uchityvaya
obilie nelinziruyushih galaktik s emissionnymi liniyami, kazhetsya
maloveroyatnym sushestvovanie dazhe odnoi sil'no linziruyushei galaktiki v
obzore CANDELS-Sized.
(Given the abundance of unlensed emission-line
galaxies it was seemingly unlikely that even one strongly lensed version
exists within a CANDELS-sized survey).\\\
\\\T.e. issleduetsya nemalaya vyborka ob'ektov, i analiz vypolnyaetsya korrektno, v ramkah sushestvuyushih statisticheskih metodov.\\\




-

- Soobshenii: 366
- Reiting: +4/-0
- specialist po postrelyativistskoi elektrodinamike
-
Otvet #1057 : Segodnya v 17:30:50
\\\Protivnikam
Bol'shogo Vzryva tol'ko i ostaetsya povtoryat' zaklinanie: "Eto fantaziya,
eto fantaziya, eto fantaziya!.." No zaklinaniya v nashe vremya ne rabotayut! Ya
budu prosit' administratora foruma Harona srazu zhe banit' teh, kto
somnevaetsya v Teorii Bol'shogo Vzryva.\\\
\\\Esli
protivniki TBV prosto treplyutsya, ne pytayas' obosnovat' svoyu tochku
zreniya, to eto mozhno otnesti k nenauke. Esli protivniki TBV pytayutsya
oformit' svoyu gipotezu v vide teorii (a dlya etogo nado obyazatel'no imet'
vozmozhno obmena mneniyami mezhdu uchenymi), to eto drugaya nauchnaya shkola i
popytka ispol'zovat' v etom sluchae administrativnyi resurs - nu eto my
uzhe gde-to prohodili: quod licet iovi non licet bovi\\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vse gorazdo proshe - kogda banyat al'tov - kotorye v sostoyanii
pridumat' i
obosnovat' izmeritel'nye metodiki opirayas' na fizicheskie svoistva - to taki
da - adekvatnyh oproverzhenii uzhe ne budet.
Po toi prichine chto ya naprimer
ochen' vnimatel'no podoshel k dannomu voprosu,
i ya bolee chem uveren chto zakryl svoim avtorstvom 75% vozmozhnyh oproverzhenii
dannoi teme, i glupo dazhe ne ponimat'
togo chto kolichestvo vozmozhnyh
oproverzhenii - konechno. I esli kto-to vybral 75% samyh prostyh sluchaev,
to eti 75% zakryty, - resheny - navechno al'tami, i ih uzhe
ne pridumayut pervymi - relyativisty.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.04.2014 20:34, 240 Bait)
A s drugoi tochki zreniya -
Fantasticheskaya situaciya - referiruemyi zhurnal opublikoval stat'yu
oprovergayushuyu bol'shoi vzryv, oprovergayushuyu chernye dyry - v principe
kto-to eto mozhet predstavit' kak real'nost' - vot to-to zhe.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
2.04.2014 22:05, 3.0 KBait)





-

- Soobshenii: 7 524
- Reiting: +257/-81
- komanda ISON http://astronomer.ru/
-
Otvet #230 : Segodnya v 01:12:59
Dyk, vstuplenie v ESO sovsem ne oznachaet, chto s teleskopami budet horosho u strany, kotoraya platit vznosy. Horosho budet u ESO. 
Teleskopy
ESO - eto centry kollektivnogo pol'zovaniya dlya vsego mira, a ne tol'ko
dlya stran-uchastnikov. Lyuboi uchenyi mozhet napisat' zayavku na nablyudeniya, i
esli ona sil'naya, to poluchit nablyudatel'noe vremya, dazhe esli ego strana
ne platila vznos. No i naoborot - esli zayavka slabaya, to vremeni uchenyi
ne poluchit, dazhe esli ego strana potratilas'.
Takaya shema
zamechatel'naya dlya stran, v kotoryh astronomiya sil'naya, i, absolyutno
nespravedlivaya dlya stran, gde astronomiya perezhivaet ne luchshie vremena.
Eto kak v anekdote - nauchites' nyryat', nal'em vody v bassein. A kak
nauchit'sya nyryat' bez vody. 
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ya kak al't pomnyu vse teksty etogo kosmologa v storonu al'tov.
Vkratce - v ego ponimanii al'ty - nedoidioty.
Lichno menya podobnym otnosheniem trudno
ogorchit',
po toi prichine chto mne bezrazlichno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.04.2014 20:33, 117 Bait)
Tam gde zvezdy redkie - zvezdy - sinie, gde zvezd bol'she
chem mnogo - tam oni vse - krasnye, - eto yavno vidno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.04.2014 21:16, 2.0 KBait)

: 21.03.2014 [05:29:19]
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ya lichno
davno s udivleniem smotryu na eto nazvanie temy.
Sobstvenno eto ya schitayu chto mozhno otnesti k sluchayu situacii
perebora variantov. I ya by ne otozhdestvlyal by
eto s intellektom
ili sluchainym tykan'em pal'cem v nebo.
Byl sluchai pri kotorom obez'yana na odnom ostrove nauchilas' chto-to
delat', - do etogo nikto
iz obez'yan ne umel etogo delat' na sosednih
ostrovah.
Posle togo kak bolee dvadcati obez'yan nauchilis' analogichnomu na etom
ostrove, - to - na vseh
sosednih ostrovah prakticheski odnovremenno
vse obez'yany nachali delat' podobnoe.
Sobstvenno - chto nablyudaetsya - telepaticheskoe obuchenie u obez'yan
na
bol'shom rasstoyanii.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ya v dannom sluchai mogu srazu skazat' chto ya davno dumal
o tom -
Kakoi minimal'nyi razmer - planety, asteroida ili komety - na
poverhnosti kotoroi lezhat (pod estestvennymi silami prityazheniya - kamni),
i
temperatura poverhnosti etoi planety v gradusah teplovogo sal'do
po otnosheniyu k okruzhayushei srede, v absolyutnyh velichinah.
S moei tochki zreniya dlya takoi situacii
absolyutno minimal'naya
temperatura -160 gradusov Cel'siya, - prakticheski real'naya - -81 gradus Cel'siya.
Tak skazat' teplovoi gisterezis, ili est' teplovoe
sal'do i prityagivayutsya kamni
kotorye i nahodyatsya na poverhnosti - ili bol'shoi kamen', na poverhnosti kotorogo
dazhe pyli net.
Tak vot minimal'nyi razmer
pri kotorom vozmozhny kamni na poverhnosti,
i pri etom budet teplovoe sal'do - 300 km v diametre - eto moe lichnoe mnenie.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.04.2014 22:16, 1.6 KBait)
Dlya teh kto ne ponyal -
est' - neobosnovannaya nichem - formulirovka -
ochen' sovpadayushaya s tem o chem ya dumal ne to chto
davno - no dostatochno chasto goda
dva tomu nazad.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
A u menya,
po moei modeli, - Minimal'nyi razmer planet na poverhnosti kotoroi
est' kamni?
- Yasnyi kon' chto ya iznachal'no etot razmer opredelil na absolyutnom urovne
120 km v diametre.
120 km v diametre - znachit - chto pri takom diametre tela v kosmose - otsutstvuet vozmozhnost'
kondensacii efira (kak gaza vnutri kosmicheskih
tel), pri kondensacii efira - estestvenno
efir perehodit v bolee plotnoe sostoyanie, i pri etom sbrasyvaet svoyu energiyu - vo
vneshnyuyu sredu - v dannom sluchai eto
verhnyaya chast' kosmicheskogo tela ( planeta, kometa, asteroid).
Estestvenno esli efir ne dvizhetsya dlya kondensacii v centr kakogo-to kosmicheskogo tela,
- to
togda u etogo tela ne budet i prityazheniya.
Yasnyi kon' chto telu - v diametre tysyacha kilometrov - tol'ko nekotoryi vneshnii process,
mog sozdat' vnutri nego
situaciyu pri kotoroi u etogo tela nachalas' kondensaciya efira,
kotoraya i sozdala vsasyvanie efira - s posleduyushim vydeleniem tepla - chto i est' -
teplovoe sal'do
planet i zvezd.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.04.2014 23:54, 1.8 KBait)
Iz serii ch'yaby korova bychala -
----------------------------------------------
: Segodnya v 13:55:47
---------------------------------------------------
Glavnoe
v etoi situacii chtoby kosmologi ne peretancevli
v tancah pro Chernye Dyry.
Hotya s drugoi tochki zreniya - Prazdnichnyi Koncert -
lyubogo meropriyatiya - na
etom tance mozhet sobirat'
den'gi prosto potomu - chto "takaya zhestokaya selyavi" -
i ya dumayu chto esli etot tanec splyasat' vnachale lekcii,
i v konce
lekcii, - eto budet fantasticheskaya fotonno-lavinnaya
dvuh udarnaya cherno-dyrochnaya tanceval'naya rapsodiya - po nesmyshlenomu
razumu slushatelyu - v celyah aktivacii
ego soznaniya v napravlenii
razvitiya tanceval'nogo stilya - Chernyh Dyr.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
\\\www.youtube.com/watch?v=UIt3fYA_Zbk19 maya 2010 g. - Dobavleno pol'zovatelem
DiveSabbath
Astrofest-2010, lekciya Sergeya Popova o sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyrah.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.04.2014 19:46, 2.2 KBait)
U menya takoe chuvstvo chto u moderatorov relyativistov
seichas bashnyu snosit ot zlosti i ot derzosti dannogo
yuzera, i oni obdumyvayut kak ego zabanit' i kakimi
metodami,
chtoby drugim ne povadno bylo podobnye
adekvatnye voprosy zadavat'.
S moei tochki zreniya zabanyat posle perenosa v gorizonty
nauki o vselennoi.
Estestvenno vetku zabalabolyat relyativisty,
i kogda avtor chto-to skazhet ot sebya, no ne ochen'
k mestu, hotya i po teme, zabanyat avtora, a potom skazhut
chto
avtor zabil bolt na svoyu temu i zakroyut
klassika obsheniya odnako.
-------------------------------------------
Zdravstvuite.
\\\Moi vopros neskol'ko ne obychen, a potomu mne bylo tyazhelo vybrat' dlya nego podhodyashuyu vetku foruma.
V
hode diskussii o zvezdah, galaktikah i nebe voobshe vozniklo rashozhdenie
vo mneniyah chto zhe takoe tak nazyvaemye "chernye dyry" i kakova ih rol' v
zhizni i stroenii galaktik.
Tak vot, vopros v sleduyushem:
Naskol'ko sootvetstvuyut istine kazhdyi iz sleduyushih punktov?
1.
VSE galaktiki OBYaZATEL'NO imeyut v svoem centre chernuyu dyru, kotoraya
obladaet neobhodimymi gravitacionnymi i prochimi silami kotorye formiruyut
samu galaktiku (inymi slovami, chernaya dyra - obyazatel'naya sostavlyayushaya
galaktiki nahodyashayasya v ee centre i ne sushestvuet galaktik BEZ chernoi
dyry v centre).
2. Esli obrazuetsya novaya chernaya dyra v itoge
svoego razvitiya obyazatel'no li ona stanet centrom ocherednoi galaktiki?
(esli prinyat' za istinnu pervyi punkt).
2. mogut li "Chernye dyry" sushestvovat' v inom meste krome centra galaktiki?
Izvinyayus'
za nekotoruyu sumburnost' svoego posta, staralsya uzhat' svoi voprosy v
ramki maksimal'nogo ponimaniya i minimal'nogo ob'ema =)
Zaranee spasibo za otvety.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.04.2014 19:49, 169 Bait)
Ya dumayu chto yuzer dazhe ne dogadyvaetsya o tom kolichestve premii
i ih summah kotorye uzhe polucheny za dannye voprosy,
tochnee za uzhe byvshie otvety na eti voprosy.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.05.2014 16:48, 2.8 KBait)
Chital dlya smeha
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #24 : 22.03.2011 [20:54:31]
\\\Ya polagayu, chto al'tam prezhde
vsego ne mesto v "Astronomii dlya vseh".
Razdel posvyashen "klassicheskoi"
astronomii, a ne vydvizheniyu novyh
"genial'nyh" gipotez.
V Gorizontah s al'tami moderatory bystro spravlyayutsya.\\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chto zdes' smeshno, chto uzhe s kakih-to marazmaticheskih utverzhdenii
relyativistskaya kosmologiya - stala " klassicheskoi " - eto vran'e,
relyativistskaya
kosmologiya sto let nazad poslala v dal' klassicheskuyu
kosmologiyu.
I kak govoritsya u posetitelei etogo foruma byvayut i probleski
zdravogo smysla.
-------------------------------------------
Otvet #37 : 24.03.2011 [10:39:51]
\\\Gde dostaet? V razdelah "Astronomiya dlya vseh" i v "Gorizontah"
negramotnyi, epatazhnyi al'tizm srazu
banyat.
A
gramotno izlozhennaya al'ternativa (dazhe dikaya) byvaet interesna,
takzhe
kak gramotnye (no naivnye) voprosy hot' nemnogo podgotovivshegosya
novichka. K sozhaleniyu, ih malovato. Zhelayushih otvetit' bol'she.

Nel'zya polnost'yu vyholashivat' forum.\\\
---------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.05.2014 17:16, 1.7 KBait)
Chto v itoge poluchilos' - relyativisty poslali al'tov
v peshee puteshestvie.
Sobstvenno relyativisty eto kto? - eto propovedniki
staryh idei, i sami ne mogut,
po opredeleniyu, pridumat'
nichego novogo.
V itoge poluchilos' to chto mesto al'ternativnyh teorii,
zanyali drugie.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php?topic=103533.0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
O chem i svidetel'stvuet sleduyushii forum,
sobstvenno
poluchaetsya chto v srednem za nedelyu vyhodit odna peredacha
po kosmologii kotoraya ne nravitsya relyativistam.
Lichno mne ne nravyatsya prakticheski
vse peredachi po kosmologii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.05.2014 21:06, 2.5 KBait)
Otvet #163 : 07.09.2013 [19:25:39]
\\\On zhe ne sporit s nami, a tupo propoveduet svoyu teoriyu miroustroistva. Naivnyi, dumaet, chto kogo-to eto zainteresuet.
Stranno, chto al'ty vsegda tak starayutsya propagandirovat' svoi idei. Dazhe na forumah lyubitelei.
Interesno, schitaet li Mihail sebya lyubitelem astronomii

Ya neskol'ko raz pytalsya perevesti razgovor na astronomiyu, no on ni razu ne otreagiroval.\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vot v dannom sluchai nado
ponimat', chto u al'ternativshika - ego
prirodnoe svoistvo - emu legko pridumyvat' chto-to absolyutno
novoe, i on mozhet svoimi vydumkami i pridumkami ob'yasnyat'
razlichnye fizicheskie situacii.
Estestvenno chto al'ty raznye byvayut, i po sposobnostyam
i po vozrastu.
I sobstvenno chto nablyudaetsya chto relyativisty
tol'ko tekushuyu
paradigmu schitayut smoi luchshei i logichnoi.
Hotya relyativista lyubogo sprosi - chto on lichno sam pridumal v kosmologii
- ladno chto nichego,
tak samoe grustnoe chto pishetsya ezhegodno mnogo
knig i statei v kotoryh vse relyativisty samostoyatel'no azh nichego
ne pridumali. Eto nazyvaetsya - perelivanie iz pustogo
v porozhnee.
V itoge vse stat'i tol'ko zagazhivayut mosk i soznanie zhelayushim
ponyat' kosmologiyu. Estestvenno prakticheski i ne otyskat'
bazovyh avtorskih opredelenii,
kak fizicheskih svoistv,
tak i fizicheskih sushnostei - ibo pri nalichii takovyh i darom
ne nuzhny budut po tysyache statei v god kotorye - traktuyut eti zhe
svoistva
i sushnosti kak im vzdumaetsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.05.2014 21:14, 310 Bait)
I samoe smeshnoe chto relyativisty ne vosprinimayut ne tol'ko
druguyu no i ne vosprinimayut luchshuyu teoriyu ot toi kotoruyu
im vbili v mozg obucheniem.
Yasnyi
kon' chto oni banyat al'tov, eto ih estestvennoe povedenie.
Eto ih osnovnaya zadacha i ih prednaznachenie,
tol'ko oni etogo ne osoznayut.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
10.05.2014 17:39, 2.9 KBait)
---------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1058 : Segodnya v 11:01:14
\\\Perehodim k ob'yasneniyam na konkretnyh primerah:\\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1059 : Segodnya v 11:57:47
\\\Arton, mozhet byt', vse-taki otvetite na voprosy? A to neponyatno,
chto imenno Vy poyasnyaete na konkretnyh primerah.\\\
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Yarkii primer togo kogda odin dogadyvaetsya da ne mozhet
vnyatno
vyskazat' svoyu mysl'. A u vtorogo sobesednika
est' zhelanie ponyat' ibo eto emu kommercheski vygodno,
no vtoromu ne daet eto sdelat' bespoleznyi porozhnyak
postulatov
kotorye on vyzubril.
Rasskazhu primitivno.
Est' takaya situaciya - rezonans, i u rezonansa est' raznye amplitudy,
i u etih amplitud est' kratnye izmeneniya,
v svyazi s chem - zvezda
dlya planet predostavlyaet im vozmozhnost' stat' na orbity, i
orbity mogut byt' u zvezdy tol'ko na opredelenny rasstoyaniyah.
Zdes'
nado ponimat' sleduyushee chto zvezda po svoei sushnosti -
prakticheski vechnaya, a v kosmicheskom prostranstve ob'ektov razmerom
s planetu v galaktike nashego tipa letayut v kosmose v tysyachi raz
bol'she chem zvezd v etoi galaktike, i iz chego uzhe ponyatno chto
za milliony let vozle lyuboi
zvezdy v neposredstvennoi blizosti
proletit million a vozmozhno i milliard planet, v svyazi
s chem vopros postanovki na orbitu - vopros vremeni.
U avtora
temy est' estestvenno zdravaya mysl', ya sobstvenno udivlen
chto ego tak dolgo ne zabanili.
Tam u nego est' takoi koefficient, a ponimaniya net, esli by eshe
udelyali
vnimanie ne tol'ko zvezdam a i toi temperature v kotoroi nahoditsya
zvezda, i cvetu zvezdy i razmeru zvezdy, to vozmozhno oni nashli
by zakonomernost',
i ona ukazyvala by na plotnost' efira vozle
dannoi zvezdy, no do etogo im nado evolyucionirovat'.
A tak kak u nih net plotnosti efira, a v prostranstve - golimyi
porozhnyak - to ponimaniya u nih ne budet nikogda.
Takzhe ponimaniya ne budet po prichine togo chto ih mosk zagazhen
lozhnoi informaciei o tom kak poyavlyayutsya planety,
v svyazi s chem
ih moski nikogda ne dopustyat toi situacii o kotoroi ya rasskazal.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.05.2014 15:35, 8.9 KBait)
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1056 : Vchera v 08:07:46
\\\ Novaya zapis' pravila, poluchivshaya nazvanie zakona
planetarnyh rasstoyanii:
an,m = k1 (n + 1/2m) k2 \\\
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1058 : Vchera v 11:01:14
\\\ Opisat' strukturu etoi sistemy predlagayu formuloi:
a
n,m = 0,24 (n + 1/2
m) 0,195 \\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1063 : Vchera v 17:20:44
\\\Ne ukazhete li oshibku v sleduyushih raschetah:\\\
I tak, imeem harakteristicheskii period dlya sistemy
planet v celom:
\\\"harakteristicheskii
period = 49.05799539 dnei... primerno okolo dvuh raz
bol'she
sidericheskogo perioda vrasheniya vneshnih vidimyh sloev Solnca
na
ekvatore = 25,05 dnei"\\\
\\\Net
nikakoi oshibki. Prosto esli brat' vse planety, poluchaetsya
"harakteristicheskii period" 49.05799539 dnei. Esli brat' tol'ko planety
zemnoi gruppy, poluchaetsya "harakteristicheskii period" 49.972335 dnei.
Eto blizhe k udvoennomu znacheniyu "sidericheskogo perioda vrasheniya vneshnih
vidimyh sloev Solnca na ekvatore = 25,05 dnei". Esli eto ne podhodit,
ya
predlagayu Vashu "gipotezu" perepisat' v takom vide:\\\
\\\Gipoteza:
veroyatno, chto Zakon Bode-Ticiusa yavlyaetsya matematicheskim
predstavleniem, lezhashei v ploskosti ekliptiki, sistemy koncentricheskih
okruzhnostei s centrom v centre Solnca. (V baricentre Solnechnoi
sistemy?)
Iz velichiny sobstvennogo osevogo vrasheniya Solnca opredelyayutsya
parametry
pokazatel'noi funkcii ot nezavisimogo parametra n (gde n
prinimaet znacheniya:
1,2,3,...), po kotoroi vychislyayutsya radiusy etoi
sistemy koncentricheskih
okruzhnostei (prostranstvennoi setki) takim
obrazom, chtoby vypolnyalos'
sledushee uslovie dlya chastot: summa chastot
(obratnyh periodov) obrasheniya
planet, umnozhennaya na 1,958403, ravna
chastote (obratnomu periodu) sobstvennogo
osevogo vrasheniya Solnca(na
ekvatore).\\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chto zdes' smeshno chto Vibe
u odnogo pozaimstvoval odnu ideyu u drugogo pozaimstvoval
drugoi rezul'tat, i reshil po bystromu skosit' slavy. Vse v luchshih relyativistskih
tradiciyah.
---
Esli rassmotret' situaciyu s drugoi tochki
zreniya to mozhno predstavit' chto est' tyazhelovesy
v teoreticheskoi kosmologii, a est' i nedalekie zhazhdushie
bystroi slavy.
Mne eto dazhe napominaet kogda l'vy v teoreticheskoi
kosmologii ne spesha rassuzhdayut nad voprosom, i im
vazhen kachestvennyi rezul'tat, i vdrug podbegaet
dekorativnyi
melkii shenok i hvataetsya za bol'shoi intellektual'nyi kusok,
kotoryi pered
l'vami, i pytaetsya otkusit' i utashit' ego k sebe
v zakroma. No pri vseh potugah intellektual'nogo i zhadnogo
shenka
shenok tol'ko
bol'shuyu kuchu laina napudil, i pokazal chto s nim
nel'zya imet' delo.
Eto ya k tomu chto chuzhuyu razrabotku nel'zya ob'yavlyat'
svoei
gipotezoi, - ibo eto ne poryadochno, tem bolee, chto v
dannom sluchai
- eta borzaya zayavka ne yavlyaetsya gipotezoi, - eto
postulat,
po prichine otsutstviya prichinno sledstvennoi svyazi dlya
koefficienta.
Hotya i konyu ponyatno, chto tot koefficient chto vychitaetsya
eto prostaya popravka na atmosferu zvezdy, pri uchete
kotoroi
budet otschet garmonicheskih sektorov dlya planet, ot
nekotoroi
- tverdoi poverhnosti zvezdy.
Chto potom nado ponyat' chtoby razobrat'sya v dannom voprose,
- dlya etogo net smysla iskat' otvety na vopros v analize
planet u raznyh zvezd eto put' nedalekih, i po etomu
puti poidet lyuboi intellektual'nyi shenok teoreticheskoi
kosmologii. Est' dlya ponimaniya bolee prostye podhody
no znaniya dolzhny uzhe byt'. Esli vspomnit' chto k zvezde
dvizhetsya nekotoraya sreda kotoraya uvlekaetsya zvezdoi, to
logichno
sdelat' vyvod chto na orbite mozhet byt' planeta kotoraya
uvlekaet efir i imeet uglovoi moment dvizheniya kotoryi
mozhet uravnovesit' eti dve sily.
Itogo est' dve centrostremitel'nye sily, odna u zvezdy
vtoraya u planety eti sily uvlekayut efir, chem sozdayut
prityazhenie u etih tel. Vot eto uzhe est' dve velichiny
kotorye summiruyutsya, i eta summa dolzhna sootvetstvovat'
centrobezhnoi sile. V dannom sluchai konyu ponyatno, chto
trebovaniya uzhe budut ne k zvezde, a k planetam planeta
, dolzhna sootvetstvovat' po svoim parametram.
A esli planeta sootvetstvuet i nahoditsya na orbite i
izvestno
ee temperatura i ee teplovoe sal'do, mozhno legko i prosto
opredelit' vse parametry etoi planety.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.05.2014 18:05, 3.6 KBait)
Otvet #1076 : Segodnya v 09:07:56
\\\1
- K vashemu svedeniyu, Merkuriyu pripisali (esli ne oshibayus', Bode)
anomal'nyi indeks, ravnyi minus beskonechnosti (vmesto logicheski
naprashivayushegosya minus odin) isklyuchitel'no s cel'yu vtisnut'
Merkurii v
geometricheskuyu posledovatel'nost' Ticiusa.\\\
\\\Vot
kak formuliroval svoe pravilo Ticius: Esli obratit' vnimanie na
rasstoyaniya mezhdu sosednimi orbitami planet, to mozhno zametit', chto eti
rasstoyaniya uvelichivayutsya pochti proporcional'no radiusam samih orbit.
Esli prinyat' rasstoyanie Saturna ot Solnca za 100 edinic, to Merkurii
nahoditsya
ot Solnca na rasstoyanii 4 edinic, Venera na rasstoyanii 4 + 3
= 7 edinic,
Zemlya 4 + 6 = 10 edinic, Mars 4 + 12 = 16 edinic. No pri
perehode ot Marsa k Yupiteru
imeetsya otklonenie ot etoi tochnosti
progressii. Posle Marsa takoi progressii
otvechaet rasstoyanie v 4 + 24 =
28 edinic, no na etom rasstoyanii my ne vidim ni
bol'shoi planety, ni
planetnogo sputnika. Neuzheli Sozdatel' ostavil eto prostranstvo
pustym?
Ni v koem sluchae! Uverenno derzhu pari, chto eto mesto zanimayut eshe ne
otkrytye sputniki Marsa; pozvol'te dobavit', chto Yupiter, vozmozhno, takzhe
imeet
neskol'ko sputnikov, kotorye eshe ne nablyudalis'. Dalee my
otkryvaem dlya sebya
polozhenie Yupitera, otvechayushee 4 + 48 = 52 edinicam;
Saturn zhe nahoditsya na
rasstoyanii 4 + 96 = = 100 edinic. Kakoe
udivitel'noe sootnoshenie! Kak vidite,
nikakih problem s "vtiskivaniem"
Merkuriya u Ticiusa ne bylo. Esli Vam indeks
Merkuriya v posleduyushih
formulirovkah pravila Ticiusa-Bode kazhetsya nelogichnym,
eto mozhet prosto
oznachat', chto matushka-priroda ne osobo stremitsya sledovat' Vashei logike.\\\
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I opyat' logichno ponimat' chto nedalekii smotrya v knigu - budet nablyudat'
tam azh nichego, chto sobstvenno i konyu yavno vidno v raspolozhenii planet.
V pervuyu
ochered' - massa i razmer planety ne vliyaet na ee orbitu, v svyazi s chem
logichno zametit' chto vozmozhno etomu prichina drugaya, a imenno vzaimovliyanie
planet kotoroe
pri etom proizvodit otsutstvie vzaimovliyanie mezhdu nimi
kotoroe ih mozhet razbalansirovat', a naoborot stabiliziruet ih orbity.
Chto zdes' yavno nablyudaetsya chto esli
ubrat' pervoe slogaemoe, to kazhdaya sleduyushaya
planeta nahoditsya na takom-zhe rasstoyanii kak i Solnce.
Naprimer ot Zemli do Marsa takoe - zhe rasstoyanie kak do Solnca,
bez ucheta pervogo
slogaemogo, i u vseh drugih planet analogichnaya situaciya.
Sobstvenno vot tak ne toropyas' logichno rassmatrivat' tekushie situacii i pridumyvat'
k nim logicheskie vzaimodeistviya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
15.05.2014 23:03, 2.4 KBait)
Otvet #1080 : 12.05.2014 [18:13:03]
----------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1082 : 12.05.2014 [19:18:40]
----------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1083 : 12.05.2014 [19:34:36]
----------------------------------------------------------
Vot
tot sluchai kogda specialist govorit odno,
a dva nedalekih dauna v dannom voprose pytayutsya
vyudit' iz specialista nuzhnye im fizicheskie ob'yasneniya,
i za odno
schitayut svoim dolgom zachmyrit' specialista, po skol'ku
vtoroe im tozhe ne pomeshaet dlya svoei gipotezy po dannomu
voprosu, - mol avtor otvetit' na nego ne smog,
a ya vot tak
propostuliroval i ya mol samyi umnyi, ibo pervym
otvetil , ili voprosom zadal golevuyu peredachu.
Vse eto dauntyatina.
Dazhe ya ponyal
chto avtor skazal, chto planety mogut odnovremenno
nahoditsya na dvuh ustoichivyh rezonansah u zvezdy, ibo i konyu ponyatno,
chto planeta lyubaya stav na orbitu - budet
snizhat'sya k zvezde so vremenem,
i pri etom oni vliyayut drug na druga, i yasnyi kon' chto blizhnie planety
naprimer zastabilizirovalis', a u dal'nih planet odna planeta,
stolknulas'
s drugoi, i pereshla na druguyu orbitu, i ona naprimer nachinaet prepodnimat'
vse drugie orbity planet, i zdes' variantov mnogo,
logichno sdelat'
fizicheskie simulyatory dannoi situacii,
ya naprimer vizhu vozmozhnost', no eto ne moya bor'ba, da i ni komu
iz paradigmy ne ob'yasnit' chto eto nado, i chto eto budet
po idee sovpadat'.
Oni budut tol'ko unizhat' i chmyrit' chtoby potom vyskazat' svoi gipotezy
po chuzhim ideyam.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
18.05.2014 14:43, 1.4 KBait)
Otvet #1091 : Segodnya v 12:19:23
\\\Vse bolee sklonyayus' k tomu, chtoby razdelyat' process
formirovaniya
planetnyh sistem na dve stadii,
principial'no otlichnye drug ot druga.\\\
-----------------------------------------------------------
Chto nado ponimat'
v dannoi situacii, chto yuzeram vbili obucheniem
prakticheski absolyutnuyu stacionarnost' sformirovannoi planetarnoi
sistemy, i to chto s nei uzhe nichego v budushem ne
izmenit'sya.
Pri vechnom sushestvovanii vselennoi, i prakticheski vechnyh zvezdah,
podobnaya uverennost' sravni idiotizmu, i v dannom sluchai
est' nedostatkom myshleniya
razrabotchika dinamiki planetarnyh sistem.
Vot v dannom sluchai uzhe logichno vernut'sya k statistike, pri
etom chto mozhno sdelat' - privesti statistiku k zvezdam
glavnoi
posledovatel'nosti nashei galaktiki.
Vozmozhno okazhetsya chto u zvezd zheltogo cveta - u planet
situaciya sovpadaet, u sinih takaya-to naibolee chastaya situaciya,
a u krasnyh zvezd - vot takaya-to.
Pri etom vozmozhno i koefficienty budut sovpadat' u zvezd
odnogo cveta.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
21.05.2014 8:57, 1.4 KBait)
Otvet #27 : 19.05.2014 [06:56:01]
\\\Kak obnaruzhit' prostranstva-vremeni kruchenie? V etom esse my
predostavlyaem
teoreticheskuyu osnovu dlya otveta na etot vopros.
Mnogopolyarnye uravneniya dvizheniya dlya ochen' shirokogo klassa
gravitacionnyh teorii s neminimal'noi svyaz'yu v prostranstve-vremeni
,
dopuskayushih krucheniya dayutsya. Nashi rezul'taty obespechivayut osnovu
dlya
sistematicheskogo testirovaniya celyh klassov teorii s pomosh'yu
rasshirennyh
probnyh tel.\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dazhe ne znayu chto skazat'
pri vide takogo hamstva i takoi naglosti.
Da nikomu i darom ne nuzhny nikakie teoreticheskie osnovy dlya otvetov -
eto uzhe bueta polnaya.
Esli net bazovyh opredelenii
fizicheskih svoistv, net opredelenii fizicheskih
sush'tnostei net fizicheskih opredelenii vzaimodeistvii i opisaniya ih prichin,
- to eto logichno poslat' v peshee eroticheskoe
puteshestvie, i dazhe ne
zamorachivat'sya na dal'neishem chtenii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
21.05.2014 9:23, 2.0 KBait)
Otvet #1094 : Segodnya v 00:03:02
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Chestno mogu skazat' lichno mne zhal' avtora takoe chuvstvo
chto samuyu malost' opyta i intellekta ne hvataet dlya resheniya
dannogo voprosa.
Na samom dele
s moei tochki zreniya eti metody v svoei suti doroga
v nikuda.
Delo v tom chto reshaetsya zadacha sovsem po drugomu.
V pervuyu ochered' logichno vzyat' banku s vodoi
i polozhit'
tuda ne melkii metallicheskii sharik, i tak pokrutit' bankoi
chtoby shar katilsya.
Togda srazu stanovitsya ponyatno chto pri krugovom dvizhenii, shar
kak v podshipnike, chast' vody vnutri budet zakruchivat' v odnu storonu,
a u stenok budet zakruchivat' kak v druguyu.
Chto zdes' igraet rol' - pravil'no i konyu ponyatno
- diametr.
Vot uzhe est' odna sostavlyayushaya - diametr, vtoraya ponyatno, - vyazkost',
tret'ya ponyatno - plotnost'.
Ishodya iz togo chto efir uvlekaetsya po raznomu,
dazhe pri odinakovom
razmere planet - to logichno ego opredelyat' po teplovomu sal'do planet,
i mozhno v itoge pereschitat' v Vt/m2.
Itogo est' chetvertaya velichina
- teplovoe sal'do planety.
Estestvenno pyataya - teplovoe sal'do zvezdy.
Estestvenno vtoruyu velichinu vyazkost' - logichno podbirat' dlya plotnosti.
Sama plotnost'
sredy opredelyaetsya po temperature kosmosa u etoi zvezdy,
bol'she temperatura - men'she plotnost' sredy.
I kak govorit'sya - vyvod - do kole ne budet v nekotoroi
formule, a tochnee raschetnoi programme, ispol'zovat'sya
vse perechislennye mnoi pyat' velichin - to v opredelenii
planetarnyh rasstoyanii logichno nablyudat' ustoichivyi
teoreticheskii sekas.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
21.05.2014 21:39, 10.8 KBait)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://elementy.ru/trefil/21152
\\\Planety dvizhutsya vokrug
Solnca po vytyanutym ellipticheskim orbitam,
prichem Solnce nahoditsya v
odnoi iz dvuh fokal'nyh tochek ellipsa.\\\
\\\Otrezok pryamoi, soedinyayushii Solnce i planetu, otsekaet ravnye ploshadi
za ravnye promezhutki vremeni.\\\
\\\Kvadraty periodov obrasheniya planet vokrug Solnca otnosyatsya kak kuby
bol'shih poluosei ih orbit.\\\
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chto
sobstvenno v etom sluchai interesno - eto to chto proishodit so vremenem,
i kak i kuda dvizhutsya fokal'nye tochki ellipticheskih orbit po otnosheniyu drug
k
drugu, i kak menyayutsya radiusy ellipsov so vremenem.
Sobstvenno eto tozhe ne logichno ne zamechat' pri ob'yasnenii dvizheniya planet
po svoim opredelennym orbitam.
S moei tochki zreniya dolzhny byt'
kakie-to vliyaniya naprimer Solnca kotorye stabiliziruyut orbitu i priblizhayut
ee k krugloi, i est' naprimer, vliyanie
drugih planet kotorye uvelichivayut ellips.
Posle etogo ishu v guglyah - pro izmenenie rasstoyanii fokal'nyh centrov,
i nahozhu -
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A3%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%B9%D1%87%D0%B8%D0%B2%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D1%8C_%D0%A1%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BD%D0%B5%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B9_%D1%81%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%BC%D1%8B
Zadacha rascheta povedeniya sistemy gravitacionno vzaimodeistvuyushih tel,
esli ih kolichestvo bol'she dvuh, v obshem sluchae ne imeet analiticheskogo
resheniya, to est' net takoi formuly, v kotoruyu mozhno podstavit' vremya i
poluchit' koordinaty tel (sm. Zadacha
treh tel).
Osnovnye napravleniya, v kotoryh mozhno issledovat' sistemy treh i bolee
tel eto poluchenie reshenii chislennymi metodami i izuchenie ustoichivosti
dvizheniya. Dvizhenie schitaetsya neustoichivym, esli blizkie traektorii so
vremenem rashodyatsya skol' ugodno daleko (sm. Ustoichivost'
po Lyapunovu).
Problema ustoichivosti Solnechnoi
sistemy
nachala interesovat' uchenyh srazu posle otkrytiya zakona vsemirnogo
tyagoteniya. Pervoe issledovanie v etoi oblasti prinadlezhit avtoru termina
nebesnaya mehanika P'eru
Laplasu. V 1773 godu on dokazal teoremu primerno sleduyushego soderzhaniya: esli
dvizhenie planet proishodit v odnom napravlenii, ih massy odnogo
poryadka, ekscentrisitety i naklony maly, a bol'shie poluosi ispytyvayut
lish' nebol'shie kolebaniya otnositel'no srednego polozheniya, to
ekscentrisitety i naklony orbit budut ostavat'sya malymi na
rassmatrivaemom intervale[1].
To est' pri ukazannyh, kraine ogranichennyh usloviyah, Solnechnaya sistema byla by stabil'noi.
Drugaya znachitel'naya popytka dokazat' ustoichivost' ili neustoichivost' Solnechnoi sistemy byla predprinyata A.N.Kolmogorovym,
V.I.Arnol'dom
i Yu.Mozerom v 60-h godah XX veka (tak nazyvaemaya KAM-teoriya). Imi byla dokazana teorema
primerno sleduyushego soderzhaniya: esli
massy planet dostatochno maly, ekscentrisitety i naklony orbit maly, to
dlya bol'shinstva nachal'nyh uslovii (isklyuchaya rezonansnye i blizkie k nim)
dvizhenie budet uslovno-periodicheskim, ekscentrisitety i naklony budut
ostavat'sya malymi, a bol'shie poluosi budut vechno kolebat'sya vblizi svoih
pervonachal'nyh znachenii[1].
V solnechnoi sisteme est' rezonansy, i teorema otnositsya tol'ko k sisteme treh tel.
Pozdnee znachitel'nyi vklad v razvitie KAM-teorii vnesli i drugie matematiki, v chastnosti, N.
N. Nehoroshev.
Samyi prostoi rezonans voznikaet, esli otnoshenie periodov obrasheniya
dvuh planet v Solnechnoi sisteme ravno otnosheniyu dvuh nebol'shih chisel. V
rezul'tate rezonansa planety mogut peredavat' drug drugu zametnye
kolichestva momenta vrasheniya. Nekotorye iz izvestnyh priblizhenii k
rezonansam: Neptun
i Pluton, periody obrasheniya kotoryh otnosyatsya pochti kak 3:2, sistema Yupiter-Saturn
(priblizhenie k 2:5) i rezonans mezhdu Merkuriem
i Yupiterom, u kotoryh blizki drug k drugu periody precessii perigeliya.
Izvestny takzhe i rezonansy v sisteme sputnikov Yupitera, Saturna i Urana,
sredi kotoryh est' i troinye (uchastvuyut tri nebesnyh tela). Sredi nih:
Io-Evropa-Ganimed (sputniki Yupitera), Miranda-Ariel'-Umbriel' (sputniki
Urana). V obshem sluchae v nelineinoi sisteme, soglasno resheniyu metodom
vozmushenii, rezonans voznikaet pri vypolnenii sootnosheniya: Σ m(j)ω(j) =
0, gde m(j) celye chisla, ω(j) chastota (vrasheniya, obrasheniya, ...) j
tela sistemy, j = 1, 2, ..., n. V sluchae prostogo rezonansa n = 2,
troinogo n = 3 i t.d.
V 90-h godah provodilis' chislennye raschety povedeniya vneshnih planet
Solnechnoi sistemy na intervale vremeni poryadka milliardov let[2].
Rezul'taty raznyh issledovatelei byli protivorechivy i pokazyvali kak
haoticheskoe, tak i regulyarnoe dvizhenie planet. Haoticheskoe dvizhenie
zdes' ne oznachaet zametnoe izmenenie orbit. Ona oznachaet lish', chto
nel'zya predskazat' polozhenie planety na orbite cherez interval vremeni,
bol'shii nekotorogo predela. Bolee pozdnii analiz[3]
etih dannyh pokazal, chto var'irovaniem nachal'nyh uslovii v predelah
pogreshnostei nablyudeniya mozhno poluchat' kak haoticheskoe, tak i regulyarnoe
dvizhenie s ispol'zovaniem odnogo i togo zhe metoda. Tak chto nel'zya
skazat', kakoi harakter imeet dvizhenie vneshnih planet Solnechnoi sistemy.
Dlya vnutrennih planet chislennye raschety dayut haotichnost' ih polozheniya
na orbite. Krome togo, osoboi problemoi yavlyaetsya Merkurii, kotoryi,
rezonansno vzaimodeistvuya s Yupiterom, mozhet sushestvenno izmenyat' svoyu
orbitu. V odnom iz poslednih issledovanii[4]
modelirovanie provodilos' na intervale vremeni poryadka milliardov let i
rasschityvalos' 2500 variantov s orbitoi Merkuriya, izmenyayusheisya s shagom
0,38mm (v nastoyashii moment pogreshnost' ee izmerenii poryadka metrov).
Sredi etih variantov obnaruzheno 20 reshenii, gde orbita Merkuriya
priobretaet dostatochnyi ekscentrisitet dlya peresecheniya orbit Venery,
Zemli i Marsa. Sredi etih orbit est' takie, chto Merkurii padaet na
Solnce, stalkivaetsya s drugimi vnutrennimi planetami, libo
destabiliziruet ih orbity tak, chto oni sami stalkivayutsya drug s drugom.\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
21.05.2014 21:45, 321 Bait)
Sobstvenno ya tak i ne nashel nigde tochnyi otvet,
na prostoi vopros, esli u ellipticheskoi orbity
planet est' dva fokal'nyh centra, odin iz kotoryh
u Solnca,
vopros v tom - so vremenem vtoroi fokal'nyi
centr orbity, - priblizhaetsya ili otdalyaetsya?
I kakaya statistika u raznyh planet, tozhe ne ponyatno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.05.2014 2:17, 3.6 KBait)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #868 : Segodnya v 00:11:09
\\\Odnako,
prezhde chem prodolzhat' razvivat' etu temu, hotelos'
by uznat' mneniya,
kotorye slozhilis' u pol'zovatelei i moderatorov
do etogo momenta.\\\
\\\Slozhilos' takoe mnenie, chto razvivat' etu temu ne nado.\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Moderator krassava, prosto moi mysli prochital, ya na vsyu
mosh' kak raz prizadumalsya po dannomu voprosu, i prishel
sovsem k strannomu vyvodu. U Solnca
est' dve kol'cevye
oblasti na razlichnyh rasstoyaniyah, odno blizhe vtoroe dal'she,
eti oblasti predstavlyayut iz sebya kosmicheskii musor
asteroidno planetarnogo
razmera, kolichestvo musora
ischislyaetsya v 1-2% procentah massy Solnca - s moei tochki zreniya.
Itogo, - yasnyi kon', chto u Solnca sovsem nedavno bylo
dva bol'shih
ekvatorial'nyh vybrosa, Ya takie situacii
nazyvayu - poterya balansa, eto kogda snizhaetsya vneshnee davlenie
efira, i sbrasyvaetsya chast' vneshnei obolochki zvezdy,
etak 10% za raz.
I s moei tochki zreniya dazhe ne vopros - a gde ostal'nye 8-9%,
gde gde - v pesochnyh chasah, ili pesochnyh yubkah.
Odnoznachno kogda budut namnogo
luchshie teleskopy,
obnaruzhitsya analogichnye vybrosy.
---

Sobstvenno na etoi fotografii kak raz i vidno chto
bylo ne odin raz u ekvatora, no vidno chto vtoroi
vybros kak raz v razgare, i vybros zatyazhnoi,
i ekvatorial'nyi disk davno raspylilsya.
---

V dannom sluchai vidno ekvatorial'nuyu chast' vybrosa,
i
sobstvenno eta fotografiya otlichaetsya ot predydushih
tem, chto na nei yavno vino chto vybros zavershilsya davno i
vse obratno dvizhetsya k zvezde. A osnovnaya massa materii
tak i ostalas' v prostranstve naprotiv polyusov.
---
Iz chego uzhe i tak ponyatno chto u Solnca sovsem
nedavno byli dva bol'shih vybrosa, i na protiv
polyusov na rasstoyanii desyati diametrov kolec
asteroidno planetnyh ekvatorial'nyh vybrosov -
budet v tri raza bol'she analogichnyh planet i asteroidov.
Obnaruzhit' ih mozhno tol'ko po polozhitel'nomu teplovomu sal'do,
- v infrakrasnyi teleskop. Ih temperatura budet
na neskol'ko gradusov bol'she fona.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.05.2014 2:45, 4.3 KBait)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Kak raz otkryl stat'yu a ona po teme, hot'
i v tekste (kak po mne sploshnaya dauntyatina) i ne ukazanna
dazhe temperatura planety, no chto mne ponravilos' -
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://www.astrogorizont.com/content/read-WISE
\\\Predpolozhitel'no massa ob'ekta WISE
J085510.83-071442.5 sostavlyaet
ot 3
do 10 mass Yupitera. S takoi nizkoi massoi dannyi
ob'ekt mog byt'
razve tol'ko gazovym gigantom, podobnym Yupiteru,
vybroshennym
kogda-to iz svoei zvezdnoi sistemy. No, po mneniyu uchenyh,
etot ob'ekt
vse zhe, skoree, yavlyaetsya korichnevym karlikom, chem planetoi,
tak kak
korichnevye karliki chashe
vstrechayutsya vo Vselennoi. V takom sluchae,
etot karlik odin iz samyh
malen'kih izvestnyh korichnevyh karlikov.
Provedennyi Lumanom v marte 2013 goda analiz snimkov, poluchennyh s
pomosh'yu teleskopa WISE, pomog obnaruzhit' paru
znachitel'no bolee
teplyh korichnevyh karlikov, raspolozhennyh na
rasstoyanii 6.5 svetovyh
let, kotoruyu mozhno otnesti k tret'ei blizhaishei k
Solncu zvezdnoi
sisteme.\\\
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Samoe
smeshnoe v etoi botve chto eto bolee veroyatno to planeta
vybros Solnca nashego, da i nahoditsya ona poblizhe,
da i rasstoyaniya k takim telam opredelyat' ne umeyut, ne
umeyut
opredelyat' pravil'no ih diametr - zavyshayut ego, i planeta
poluchaetsya dal'she.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.05.2014 12:07, 3.0 KBait)
-------------------------------------------
http://lenta.ru/news/2014/05/22/wormhole/
\\\
Fizik iz Kembridzha Luka Butcher v svoei stat'e opisal osobyi
rezhim
sushestvovaniya
krotovyh nor (chervotochin), predpolagayushii vozmozhnost'
otpravki informacii v
techenie sravnitel'no dlitel'nogo promezhutka
vremeni. Stat'ya uchenogo dostupna na
arxiv.org, kratko s nei mozhno oznakomit'sya na saite Phys.org.
Uchenye rasschital, chto pri nekotorom radiuse gorloviny krotovoi nory
otricatel'noi
energii Kazimira budet dostatochno, chtoby v techenie
nekotorogo vremeni sushestvovala
stabil'naya konfiguraciya chervotochiny,
pozvolyayushaya fotonu pokinut' ee predely, a,
znachit, peredat' informaciyu .\\\
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ya vot smotryu i dumayu - nu razve neponyatno chto
neobosnovannaya nichem fantastika, obychnaya
bredyatina, s pretenziei
na nauchnost', napechatannaya
v referiruemom nauchnom zhurnale. Ya vot dumayu
a zachem ee tak shiroko publikuyut i osveshayut,
i zdes' do menya doshlo, chto na samom dele eto
vse
dlya menya i takih kak ya. V rezul'tate otsortirovyvayutsya
te, kto verit v nauchnuyu skazku i podobnye stat'i
postoyanno ih ishut i uvlekayut ih v psevdo nauku.
A dlya menya pol'za samaya chto ni est' pryamaya,
- eto ih i vyyavlyaet, mozhno i ne tratit' vremya
na
chtenie
ih trudov nauchnyh po drugim voprosam.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.05.2014 15:45, 2.1 KBait)
Astronomam ne nravitsya chto zapretili astronomiyu prepodavat'
v shkolah, dal'she stat'ya o chernyh dyrah, chto primechatel'no nado znat'
o chernyh dyrah - eto to chto na
segodnyashnii den' oficial'no ne obnaruzheno
- ni odnoi chernoi dyry i dazhe ni odnoi chernoi dyurochki,
- vse chernye tol'ko virtual'nye, i nahodyatsya v golovah.
Podobnymi stat'yami profanaciei nasazhdaetsya massovaya uverennost'
dlya obyvatelya v logichnosti chernyh dyr kak takovyh.
I ne odin poryadochnyi astronom ne provedet likbez
sredi kolleg
po povodu togo - chto mozhet chernye dyry kosmologii i nenuzhny,
mozhet eto idiotizm vvodyashii v zabluzhdenie vsyu kosmologiyu,
mozhet chernye dyry reshayut
kakie-to voprosy otdel'nyh teorii
pri etom sozdayut global'nye fizicheskie i logicheskie trudnosti vsei kosmologii.
Kak govoritsya "Ostapa poneslo"(S).
Da eto vryad-li sluchitsya ibo te kto napisal stat'i pro chernye
dyry, budut schitat' neudobnym i ne napishut otkrovenno
chto oni poddalis' obshemu nastroenii
i v kotel s kashei
idiotizma chernyh dyr dobavili i svoyu nauchnuyu leptu.
Hotya s moei tochki zreniya nauka dolzhna menyat'sya,
a esli uchennye ne budut priznavat' svoih
oshibok - to eto
budet tol'ko huzhe dlya nih samih, tak kak takaya nauka prosto
budet i darom ne nuzhna obshestvu, i uchennyh odnoznachno
otpravyat ne v otpusk, a
srazu v peshee puteshestvie.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://lenta.ru/news/2014/05/23/wise/
\\\Astronomy Argentiny, SShA i Chili obnaruzhili anomaliyu v uglovoi
klasterizacii vidimyh i skrytyh aktivnyh sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr.
Stat'ya uchenyh dostupna v
Arxiv.org, a kratko s ee osnovnymi vyvodami
mozhno oznakomit'sya na saite NASA.
V svoem issledovanii uchenye rassmotreli klasterizaciyu bolee 170 tysyach
aktivnyh
sverhmassivnyh chernyh dyr. Astronomy obnaruzhili, chto, v
otlichie ot vidimyh, tak
nazyvaemye skrytye chernye dyry znachitel'no chashe
ob'edinyayutsya v klasternye
obrazovaniya.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.05.2014 16:12, 2.3 KBait)
Otvet #1097 : Segodnya v 13:07:30
\\\Nahozhu
uzhe vpolne ochevidnym, chto planetnaya sistema Solnca i
sputnikovye
sistemy Yupitera i Urana sformirovalis' absolyutno
identichnym obrazom.
Pozzhe vse eti sistemy naglotalis' kosmicheskogo
musora, utrativ, pri
etom, chast' svoih ishodnyh chlenov:\\\
\\\Arton,
nikto, krome Vas, pohozhe, ne nahodit eto vpolne ochevidnym.
Proshu
vse-taki ostanovit' publikaciyu bezdokazatel'nyh utverzhdenii.\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dazhe ya uzhe znayu gde naiti dokazatel'stva i pravil'nost' utverzhdenii,
i tam-zhe budut i cifrovye velichiny orbit, iz kotoryh lyuboi kon'
smozhet prosmotret' zakonomernost'.
No moderatoru v oblom na eto tratit' vremya dlya napisaniya stat'i
v zhurnal. Estestvenno moderator trebuet predostavit' emu
polnost'yu vse dlya napisaniya stat'i
v nauchnyi zhurnal,
tochnee dlya interpretacii obsuzhdaemogo na etom forume.
Eto moya mysl', tem bolee chto naprimer populyarnaya mehanika
ne afishiruet avtorov svoih
statei.
Takoe moderatorstvo menya odnoznachno navodit na mysl'
chto etot forum dlya kogo-to nauchnaya kormushka dlya
napisaniya svoih statei, po toi prichine
chto vse mysli
na forumah vyskazyvayut tri-pyat' chelovek, a vse ostal'nye
(druzhashie mezhdu soboi) posetiteli i moderatory dodalblivayutsya do nih,
vynosyat im mosk
svoimi voprosami, i stavyat trebovaniya
k razrabotkam ne nizhe professorskogo urovnya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.05.2014 16:16, 257 Bait)
I samoe smeshnoe chto tak skazat' "lokomotivam idei"
postoyanno zadolblivayut mozg pustymi voprosami ne po teme,
i krome "lokomotivov idei" nikto
na forume ne v sostoyanii
vyskazat' ni odnoi zdravoi mysli po suti voprosa.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.05.2014 16:25, 5.0 KBait)
Otvet #1097 : Segodnya v 13:07:30
\\\Nahozhu
uzhe vpolne ochevidnym, chto planetnaya sistema Solnca i
sputnikovye
sistemy Yupitera i Urana sformirovalis' absolyutno
identichnym obrazom.
Pozzhe vse eti sistemy naglotalis' kosmicheskogo
musora, utrativ, pri
etom, chast' svoih ishodnyh chlenov:\\\
\\\Arton,
nikto, krome Vas, pohozhe, ne nahodit eto vpolne ochevidnym.
Proshu
vse-taki ostanovit' publikaciyu bezdokazatel'nyh utverzhdenii.\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dazhe ya uzhe znayu gde naiti dokazatel'stva i pravil'nost' utverzhdenii
---
Nado v guglyah nabrat' -
\Ustoichivost' Solnechnoi sistemy Rezonansy Solnechnoi
sistemy\
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ustoichivost'_Solnechnoi_sistemy
Pereiti k razdelu Rezonansy Solnechnoi sistemy - [pravit' | pravit' ishodnyi tekst]. Samyi prostoi rezonans voznikaet, esli otnoshenie...www.astronet.ru/db/msg/1198823/node1.html
Laplas sformuliroval teoremu ob ustoichivosti Solnechnoi sistemy: esli ... K sozhaleniyu, v real'noi Solnechnoi sisteme rezonansy igrayut ochen'...n-t.ru/tp/ng/uss.htm
23 dek. 1999 g. - izvestno, kak proizoshla i razvivalas' Solnechnaya sistema. ... ustoichivosti Solnechnoi sistemy lish' v pervom
priblizhenii, chto okazalos' yavno ... I takie prichiny lezhat na poverhnosti: rezonans kolebanii,...
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.05.2014 15:10, 6.0 KBait)
------------------------------------------------------------------------
: Segodnya v 08:15:58
\\\Predstavim sebe polyi mikrokonus (razmerom menee mikrona) iz
provodyashego
materiala bez osnovaniya (t.e. s otverstiem vmesto osnovaniya).
V
rezul'tate togo, chto vnutri polosti konusa rozhdayutsya(i annigiliruyut)
tol'ko
"rezonansnye" fotony s dlinoi volny proporcional'noi rasstoyaniyu
po
vnutrennemu secheniyu konusa, davlenie virtual'nyh fotonov fizicheskogo
vakuuma s vneshnei storony konusa budet bol'she chem s vnutrennei storony.
I
raznost' davlenii fotonov fizicheskogo vakuuma budet peremeshat' konus v
napravlenie otkrytogo osnovaniya konusa.\\\
\\\Sobrav milliardy takih
"mikrokonusov" v mnogosloinye soty poluchim raketnyi
vakuumno-reaktivnyi
dvigatel', rabotayushii bez topliva. Kotoryi mozhet
rabotat' vechno. I
razgonyat' kosmicheskie korabli v vakuume do lyubyh myslimyh
skorostei.\\\
=====================================================================
Zhazhda halyavy,
zhazhda halyavnogo napravlennogo vozdeistviya, zhazhda vechnoi
halyavy kotoraya sozdaet postoyannoe silovoe vozdeistvie i pri etom ne nuzhdaetsya
v energeticheskih zatratah.
Eto dazhe ne fizika, eto skoree vnutrennii samokontrol' podgulivaet
pri takom urovne zhazhdy halyavy.
No zdes' u menya drugoi interes - otstavanie dva
goda,
pri polnom otsutstvii dazhe ponyatiya kak realizovat'
prakticheski.
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
30.09.201217:46 |
|
Vot pdumal o tom kak by ya delal bezopornyi dvigatel'.
---
Bezopornyi dvigatel'.
Bol'shoi dyryavyi tranzistor.
Chto sobstvenno poluchaetsya na samom
dele malomoshnyi s nizkoi tyagoi
est' i ego mozhno kupit' - ul'trafioletovyi svetodiod.
Kogda proishodit atomarnaya raskrutka na predel'nyh
centrobezhnyh skorostyah
vrasheniya central'noi podvizhnoi
chasti atoma, ego kraya nachinayut razrushat'sya v svyazi s chem
proishodit ul'trafioletovoe izluchenie - eto chasticy
razrusheniya central'noi
atomarnoi chasti kotorye uvlekayut
efir v storonu svoego dvizheniya, v svyazi s chem i poyavlyaetsya
neznachitel'naya tyaga efira.
Estestvenno analogichnoe proishodit
i s infrakrasnym
svetodiodom kogda vokrug vysokaya temperatura, to svetodiod
yavlyaetsya detektorom kolebanii sredy v opredelennom
napravlenii izlucheniya, v etom
sluchai tyaga efira budet
eshe men'she pri toi-zhe moshnosti chto v ul'trafioletovom.
I osnovnoi dvigatel' bez opornyi s dostatochnoi tyagoi bolee
logichno delat'
na tom effekte kotoryi nablyudaetsya
v samom prostom tranzistore.
Nablyudaetsya sleduyushee, snizu sloi emittera, posredine tonkii sloi - baza,
sverhu tolstyi sloi
kollektor.
Chto proishodit - pri prilozhenii elektroefira mezhdu bazoi
i emitterom proishodit otkrytie potoka elektroefira
ot kollektora skvoz' bazu na emitter,
i tok mezhdu kollektorom
i emitterom mozhet v sotni raz prevyshat' tok mezhdu bazoi
i emitterom, no esli ostanovit' tok mezhdu bazoi i emitterom,
to s nebol'shoi
zaderzhkoi prekratitsya tok mezhdu kollektorom
i emitterom skvoz' bazu.
Zdes' s tochki zreniya dvuh sushnostei efira i elektro-efira,
vse ob'yasnyaetsya proshe
parennoi repy.
V atomarnoi strukture mozhno dlya kazhdogo materiala opredelit'
koefficient uvlecheniya efira elektroefirom.
Delo v tom chto esli v tranzistore
uvelichivat' tolshinu bazy,
to tranzistor perestanet byt' tranzistorom a prevratitsya v dva dioda.
Prichinoi tomu situaciya pri detektirovanii v rezul'tate kotorogo
sozdaetsya razryazhenie elektroefira i on nachinaet uvlekat' efir
v lokal'nom meste pri etom proishodit otkrytie atomarnyh samo-zaklinennyh
konusov, o kotoryh
ya pisal, v svyazi s chem nachinaetsya potok elektroefira,
ot kollektora skvoz' bazu na emitter.
Sobstvenno chtoby sdelat' bezopornyi dvigatel' dostatochno sdelat'
tranzistor
analogichnyi elementarnomu no ploshad'yu naprimer 210mm na 210mm.
Sobstvenno poluchaetsya chto pri rabote tranzistora on vsei svoei ploshad'yu
budet
progonyat' skvoz' sebya elektroefir sozdavaya pri etom razryazhenie
prostogo efira.
S moei tochki zreniya samoe luchshee atomarnoe smeshivanie u togo provodnika,
u kotorogo bol'shee udel'noe soprotivlenie.
Voznikaet vopros kak provesti smeshivanie elektroefira s efirom
pri kotorom mozhno peredat' energiyu dvizheniya elektroefira
efiru chtoby poluchit' vysokii koefficient peredachi.
Po logike peredat' mozhno prosto, nabit' v etom bol'shom tranzistore
mikro-dyrok, prevrativ tranzistor
v sito,
pri etom uvelichitsya ploshad' treniya elektroefira o efir,
takzhe mozhno
ponabivat' dyrok bol'shego diametra i vstavit' v dyrki izolirovannye
voloski
alyuminiya, ili drugogo metalla, ili soedineniya
naprimer platiny s inertnym gazom.
Alyuminii okazhet po idee analog korotkogo zamykaniya
na potok kotoryi
budet pytat'sya vytolknut' alyuminii
pri etom sozdast pole kotoroe vozmozhno luchshe peredast
energiyu elektroefira efiru, drugie metally naprimer zhelezo,
sozdadut
osevoi sdvig, chto tozhe vozmozhno povliyaet na vzaimodeistvie.
Sobstvenno ideya voloskov v dyrkah bol'shogo tranzistora v tom chto vozniknet
vliyanie na perepad
dvizheniya elektroefira, razlichnogo vliyaniya
atomarnoi raskrutki central'noi chasti chto vozmozhno privedet
k uvlecheniyu v atomarnoi strukture obychnogo efira,
po
prichine vozniknoveniya napravlennogo perepada davleniya
elektroefira. |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.05.2014 17:45, 4.5 KBait)
Bezopornoe dvizhenie ya by uzhe tak by ne delal,
sobstvenno est' i drugie varianty.
Chto nado znat' - est' efir, - predstavlyaet iz sebya
mohnatyi sharik,
pokrytyi elektroprovodyashei
zhidkost'yu - elektroi, i po faktu uzhe v efire
budut vse effekty statiki, magnitnoe pole - osevaya
raskrutka efira, prityazhenie -
prohozhdenie efira skvoz'
tela v centry massivnyh tel vnutri kotoryh proishodit
kondensaciya efira v zhidkoe sostoyanie s vydeleniem tepla.
Est' ochen' moshnye
i ochen' aktual'nye opyty.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://www.powerinfo.ru/electrophoresis.php
\\\Mehanizm elektroliza Reise ob'yasnyal tem, chto "odna iz dvuh sostavnyh
chastei molekuly, razlagaemoi deistviem gal'vanicheskogo toka, perenositsya
ot odnogo polyusa k drugomu cherez mezhpolyusnuyu zhidkost'". Esli mezhdu
polyusami pomestit' kakoe-libo postoronnee telo, naprimer zemlyu, to ona
ne budet prepyatstvovat' prohozhdeniyu toka i razlozheniyu vody.
V 1807g. Reise modificiroval opyt Nikol'sona po razlozheniyu vody. Chtoby
dobit'sya razdeleniya produktov elektroliza, Reise zapolnil tolchenym
kvarcem
srednyuyu chast' U-obraznogo elektrolizera-trubki. On zametil, chto
prilozhenie
vneshnego bol'shogo napryazheniya k elektrodam privodit k
peremesheniyu vody v
trubke v storonu otricatel'nogo polyusa. Pri
prodolzhitel'nom propuskanii
toka ustanavlivalas' postoyannaya i
znachitel'naya (do 20 santimetrov) raznost'
urovnei zhidkosti. Perenos
zhidkosti pod deistviem vneshnego elektricheskogo
toka, nablyudavshiisya v
poristyh telah, poluchil nazvanie elektroosmosa.\\\

Shema opytov Reissa po elektroosmosu i elektroforezu
\\\Reise prodolzhal vidoizmenyat' opyty po elektrolizu. On vstavlyal vo
vlazhnuyu glinu
dve steklyannye trubki, zapolnennye vodoi, v trubki
pogruzhal elektrody. Posle vklyucheniya
toka naryadu s elektroosmosom
nablyudalos' eshe odno novoe yavlenie - dvizhenie otorvavshihsya
chastichek
gliny v protivopolozhnom napravlenii - k polozhitel'nomu polyusu. Yavlenie
peremesheniya chastic tverdoi fazy v zhidkosti pod vliyaniem toka bylo
nazvano elektroforezom.
Reise sdelal soobshenie v universitete ob otkrytyh im yavleniyah. Cherez dva
goda vyshli ego
stat'i, v kotoryh byli podrobno opisany elektroosmos i
elektroforez. V etih yavleniyah
proyavlyalas' svyaz' mezhdu elektricheskim
tokom i otnositel'nym peremesheniem tverdoi
i zhidkoi fazy. Ponimanie
takoi svyazi bylo, odnako, nepolnym, tak kak yavleniya,
protivopolozhnye
elektroosmosu i elektroforezu po harakteru prichinno-sledstvennoi
svyazi,
to est' vozniknovenie elektricheskogo potenciala pri dvizhenii zhidkosti
ili
tverdyh chastic, byli otkryty lish' spustya polveka.
Effekt, protivopolozhnyi elektroosmosu, obnaruzhil Georg Kvinke
(1834-1924), professor
Berlinskogo universiteta. V ego opytah pri
protekanii zhidkosti cherez poristuyu diafragmu
poyavlyalas' raznost'
potencialov mezhdu dvumya elektrodami, pomeshennymi po raznym
storonam
diafragmy. Yavlenie poluchilo nazvanie potenciala techeniya. Togda zhe
(a
imenno v 1859g.) Kvinke predpolozhil, chto poverhnost' tverdogo tela
zaryazhaetsya
odnim znakom, a prilegayushii sloi zhidkosti - drugim. Eta shema
pomogala ob'yasnit'
otnositel'noe dvizhenie zhidkosti i chastic tverdoi
fazy pod deistviem toka, a takzhe
poyavlenie potenciala pri protekanii
zhidkosti cherez poristuyu diafragmu. V dal'neishem
eta ideya privela k
otkrytiyu udivitel'noi granicy na razdele faz - dvoinogo
elektricheskogo
sloya.\\\

Shema vozniknoveniya potencialov techeniya i osedaniya
\\\Vozniknovenie zhe raznosti potencialov pod deistviem mehanicheskogo
dvizheniya tverdyh
chastic v zhidkosti nablyudal v 1880g. nemeckii fizik
Fridrih Dorn (1848-1916).
Ono bylo nazvano effektom Dorna, ili
potencialom osedaniya.\\\
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.05.2014 17:56, 889 Bait)
Sobstvenno s moei tochki zreniya v opyte Reissa
na levom risunke s U obraznoi kolboi, est' neob'yasnennaya
chast' fizicheskoi prichiny voznikayushego elektroosmaticheskogo
davleniya zhidkosti pri raznyh elektro potencialah.
Poluchaetsya sleduyushee - v U obraznoi trubke s peskom,
est' provodyashaya zhidkost', pri prilozhenii perepada
napryazhenii so vremenem nablyudaetsya izmenenie urovnei
zhidkosti. Sobstvenno eto primitivno ob'yasnyaetsya dvizheniem
potoka elektry, kotoraya za soboi uvlekaet
i chasticy efira,
po skol'ko elektra dvizhetsya ot minusa k plyusu, to u minusa
ona sozdaet razryazhenie efira, a na plyusovom kontakte
budet izbytochnoe davlenie
efira.
Estestvenno chto esli etu trubku vypryamit', i poprobovat'
v kosmose sozdat' perepad elektroosmaticheskogo davleniya,
vozmozhno i budet polozhitel'nyi
rezul'tat po bezopornomu dvizheniyu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.05.2014 13:34, 3.1 KBait)
Soobshaem Vam, chto s 21 po 26 iyulya 2014 goda v Sankt-Peterburge sostoitsya ocherednoi Mezhdunarodnyi nauchnyi Kongress-2014 "Fundamental'nye problemy
estestvoznaniya i tehniki".
Na Kongresse-2014 predpolagaetsya zaslushat' i obsudit'
noveishie konstruktivnye konceptual'nye teoreticheskie, eksperimental'nye i
tehnicheskie resheniya sovremennyh problem v razlichnyh oblastyah
estestvoznaniya i tehniki. Orgkomitet Kongressa-2014 schitaet, chto nastalo
vremya issledovanii, posvyashennyh bolee glubokomu ponimaniyu real'nosti i
osmysleniyu dostizhenii nauk o prirode i obshestve. Tema Kongressa-2014
GLOBAL'NYE I STRATEGIChESKIE PROBLEMY NAUKI I OBRAZOVANIYa.
Na Kongresse-2014 budut zaslushany na plenarnyh i sekcionnyh zasedaniyah i stendovyh sessiyah doklady po sleduyushim napravleniyam:
- Fundamental'nye podhody k poznaniyu real'nosti sovremennye aspekty fiziki.
- Urovni organizacii, elementy i struktura ob'ektov estestvoznaniya, nauki o Zemle.
- Problemy vremeni i prostranstva v nauchnoi kartine Mira.
- Efirodinamika, elektrodinamika, termodinamika i gravitaciya.
- Energetika, tehnika i tehnologii novogo tysyacheletiya.
- Katarsis-konferenciya S Mirom novym - Shagi k novoi civilizacii.
- Problemy vysshego obrazovaniya.
==============================================================================================
Vot i mne interesno posmotret' video etogo kongressa.
Ya
vot dumayu, soberut professorov takih naprimer kak Vibe,
kotorye po dvadcat' let perechityvali studentam chuzhie knizhki
i chuzhie stat'i, i stavili ocenki studentam
za to kak oni
ponyali pereskazannyi im prepodavatelem material iz knizhek.
I vot teper' iz etih nachitchikov i pereskazchikov knig,
pytayutsya iz nih vyzhat' nauchnuyu
mysl', i budut stimulirovat'
ih burnuyu nauchnuyu samodeyatel'nost' - odnako, eto budet
interesno posmotret'.
V principe rezul'tat budet vozmozhen ne men'she chem
cherez 7let,
iz chego optimal'nyi vozrast 33-37 let, eto tot kak raz sluchai
kogda posetitelei etogo vozrasta na etoi konferencii budet
ya dumayu ne bolee 10
chelovek. I to chto iz yuzerov etogo vozrasta
sozdadut nauchnuyu gruppu i budut ih obuchat' ob'ektivnymi
znaniyami, i budut ee finansirovat' po samoe
dal'she nekuda
- ya ne veryu v principe, - ibo eto bolee chem
fantastika, - eto psevdonauchnyi bred s priznakami idiotizma.
Tak chto veroyatnost' rezul'tata i cherez sem' let prakticheski
nulevaya.
S drugoi tochki zreniya ya vozmozhno tak negativno vyskazyvayus' po prichine
togo chto sobstvenno sam kongress uzhe sozdaet mne nekotoruyu teoreticheskuyu
konkurenciyu v kosmologii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
29.06.2014 14:07, 3.5 KBait)
 Fizicheskie kotlety i matematicheskie muhi.
Fizicheskie kotlety i matematicheskie muhi.
Vchera :: 18:10:57
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1403964657
\\\Po
etoi prichine, chtoby ne ostat'sya golodnymi i ne pitat'sya
matematicheskimi
modelyami kotlet nuzhno umet' otdelyat' matematicheskih muh
ot fizicheskih kotlet.
K sozhaleniyu, na segodnyashnii den', vse eto
nastol'ko pereputano, chto vmesto
real'nyh fizicheskih kotlet nam
prihoditsya pitat'sya pashtetom iz matematicheskih
modelei.
Tipichnym
primerom takogo podloga yavlyaetsya teoriya otnositel'nosti, kogda vmesto
real'noi fizicheskoi modeli nam podsunuli matematicheskii surrogat i
zastavlyayut
ego est'. A on nam prosto ne lezet.
S nekotoryh por,
matematiki okonchatel'no razbushevavshis', kak eto umel delat'
Fantomas,
matematika nachala izobretat' svoi fizicheskie zakony, i eto kasaetsya ne
tol'ko TO. Nam nachali podsovyvat' surrogat iz zavisyashei ot chastoty
dielektricheskoi
pronicaemosti plazmy i chastotozavisimoi dielektricheskoi
pronicaemosti
dielektrikov, predlagaya na etoi pochve postroit' vechnye
dvigateli. Nachali nas
kormit' volnovymi funkciyami i kvantami
elektromagnitnogo polya.
Vobshem, vsya sovremennaya fizika eto sploshnoi
neudobovarimyi metafizicheskii
surrogat iz prakticheski nes'edobnyh
matematicheskih modelei.
No gde zhe podevalis' nastoyashie kotlety iz natural'nogo fizicheskogo myasa.
A ih ukrali u nas Einshteiny, Landau i Gizburgi i izhe s nimi, i vmeste
s nimi ukrali
u nas i vsyu fiziku.\\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
S moei tochki zreniya fiziku
ukrast' u fizika nevozmozhno, lichno mne v
etom kontekste slozhivsheisya situacii v fizike sto let nazad i prodolzhayushuyusya
do sih por - ochen' obidno za moi shkol'nye
gody, i za tu fiziku kotoruyu mne
prepodavali po shkol'nym uchebnikam, za to chto na samom dele
est' knizhki po fizike i po luchshe raz v 30, a esli ih by al'ty perepisali
to oni by byli voobshe horoshie - ya dazhe uveren chto takogo ne proizoidet.
Sobstvenno bez adekvatnoi bazovoi fiziki v shkol'nye gody, yuzer
ne poluchaet adekvatnyh
znanii o prakticheskih dostizheniyah i ne znaet
uzhe provedennyh opytah, i budet vynuzhden vsyu etu botvu izuchat'
s nulya i vnikat' v nee po kartinkam i opisaniyam cherez
internet.
Chto sobstvenno i est' bazovyi tormoz.
I voobshe esli na segodnyashnii den' net fizicheskogo opredeleniya
soprotivleniya provodnika - to eto yasnyi
kon' - pozor, no
eto nado osoznat' sperva, potom postavit' takuyu zadachu,
potom pro-finansirovat' konkurs na luchshie modeli.
Potom vybrat' - a vot zdes'
ya zadam vopros na kotoryi kazhdyi
mozhet sam sebe otvetit' samostoyatel'no -
Vyberut tu model' -
- Avtor kotoroi poobeshaet bol'she iz premii komissii
- kotoraya luchshe opisyvaet fizicheskii smysl v mehanicheskom variante,
- kotoraya soderzhit bol'she formul,
- kotoraya men'she vsego protivorechit tekushei paradigme
- avtor kotoroi imeet zvanie akademika
- avtor kotoroi chlen komissii po bor'be s lzhenaukoi
?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.07.2014 22:15, 2.1 KBait)
---
\\\ya hozhu chasto - vopros ne ko mne
2 (3.6%)\\\
\\\redko hozhu na te, gde nado platit'
2 (3.6%)\\\
\\\redko hozhu, t.k. vse est' v internete
12 (21.8%)\\\
\\\redko hozhu, t.k. net vremeni
9 (16.4%)\\\
\\\redko hozhu, t.k. ploho rasskazyvayut
2 (3.6%)\\\
\\\budu hodit', tol'ko, esli rasskazyvat' budet kto-to ochen' izvestnyi
0 (0%)\\\
\\\ne lyublyu lekcii - chitayu knigi ili zhurnaly
1 (1.8%)\\\
\\\redko hozhu, t.k. neudobno sledit' za anonsami
3 (5.5%)\\\
\\\redko hozhu, t.k. vremya ili mesto lekcii neudobnoe
9 (16.4%)\\\
\\\drugoi otvet
15 (27.3%)\\\
\\\Progolosovalo pol'zovatelei: 55\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
\\\drugoi otvet
15 (27.3%)\\\---
- Tak "drugoi otvet" nabral samoe bol'shoe kolichestvo, - vozmozhno
interpretaciya
idei stoletnei davnosti - moral'no ustareli.
Ya dumayu chto dlya lekcii - obyazatelen punkt - "moral'no ustareli".
Mozhno bolee gladkii variant - "nizkaya
aktual'nost'" - no mne kazhetsya
on bolee kontrastnyi - pri malom (%) - kak-to luchshe, a pri bol'shom (%),
srazu perehod v nedalekost'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
1.07.2014 22:43, 8.6 KBait)
 Re: Mirovaya efirodinamicheskaya gonka ob'yavlena
Re: Mirovaya efirodinamicheskaya gonka ob'yavlena
Otvet #976 - Segodnya :: 21:03:18
\\\ ... Ya boryus' za efirodinamiku.
Poetomu vse eto ne to..
K efirodinamicheskoi gonke otnosheniya ne imeet.
Ya hotel by obratit' vnimanie, chto
efirodinamika
nikak ne pretenduet na razvenchanie nekotoroi
chastnoi matematicheskoi
teorii.. Efirodinamika pretenduet na perehod
k efirodinamicheskomu
estestvoznaniyu. Osnovannomu na materialisticheskoi
filosofii. I
sootvetstvuyushei metodologii.
A poka. Segodnya nachalsya tretii god Gonki. Ya zhe sobirayu otchet.
Za nedelyu- druguyu sdelayu.
S uvazheniem, Mihail Surin
\\\
Vot vremya letit, po krainei mere ya znayu kogda ya ob etom podumal.
A.P.Vasi
|
Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
2.06.20119:17 |
|
Efir i ego vzaimodeistviya,
est' dva vida materi - efir i prostaya materiya,
efir mozhet nahoditsya v szhatom
sostoyanii, eto sostoyanie nachinaetsya pri bol'shom
mehanicheskom davlenii ravnym 1000km vodyanogo stolba,
posle vozniknoveniya uslovii dlya zhidkogo efira v nedrah planet,
i prakticheski tverdogo u zvezd, nachinaet obrazovyvat'sya
vnutri zvezd - Zvezda efira, a vnutri planet - gravitiruyushee
yadro efira. I chto zvezda efira chto gravitiruyushee yadro, oni vsasyvayut
efir, efir prohodya skvoz' materiyu
chastichnym treniem sozdaet
gravitaciyu. I esli vzyat' naprimer kubometr vody, to eto ne on davit
s siloi v tonnu, eto efir prohodya skvoz' nego so skorost'yu 10km
v sekundu sozdaet silu v tonnu, i v zavisimosti ot plotnosti
atomarnoi reshetki veshestva budet raznoe trenie efira,
i budet raznaya sila - raznyi ves.
U zvezd
zvezda efira vnutri razrastaetsya, potom
lopaetsya po ekvatoru kak SN1987a, i sbrasyvaet lishnee davlenie,
i potom poyavlyayutsya luchi kak u gazovoi konforki, i
forma
zvezdy v forme tarelki, posle chego progorayut
dnisha tarelok s obeih storon, i poluchaetsya vzryv
i v itoge vyhodit zvezda efira, a materiya zvezdy
ryadom s etoi
zvezdoi obratno stanovitsya obychnoi
zvezdoi, posle chego zvezda efira so vremenem isparyaetsya,
tak kak efir ne sderzhivaet vneshnee davlenie, a v
zvezde iz kotoroi
vyshla zvezda efira , zaroditsya novaya.
Zvezda vnutri kotoroi est' zvezda efira nazyvaetsya
Zvezda Fiziki, vo mnozhestvennom - Zvezdy Fizikov.
Grubo govorya
- zvezdy vechnye, v processe svoei vechnoi zhizni,
vnutri sozdayut zvezdu efira, i izbavlyayutsya ot nee,
byvaet chto kogda izbavlyayutsya, proishodit takoi vzryv
chto
polnost'yu razletaetsya vdrebezgi vsya materiya zvezdy.
Byvaet chto galaktiki proletayut drug mimo druga i sozdayut
nizkuyu plotnost' efira v prostranstve, i zvezdy
lopayutsya
kak myl'nye bul'bashki, i sbrasyvayut izbytochnoe
vnutrennee davlenie efira.
Efir i elektrichestvo.
Elektron i pozitron eto analogichnye uslovnye nazvaniya
oboznachayushie razlichnye potencialy napryazheniya v tekushii
moment u provodnika ili chasticy nahodyasheisya s nekotorym
zaryadom.
Esli vzyat' batareiku (gal'vanicheskii
element), to u nee budet odin
vyvod polozhitel'nyi - vtoroi otricatel'nyi, i v svyazi s himicheskoi
reakciei vnutri batareiki sozdaetsya raznica napryazhenii.
Batareiku
mozhno opredelit' kak istochnik napryazheniya so staticheskim
potencialom v poltora vol'ta, pri podklyuchenii nagruzki
u batareiki voznikaet dinamicheskoe sostoyanie - nalichie
toka,
tok - dvizheniya elektrichestva v provodnike. Pri podklyuchenii
k batareike razlichnyh nagruzok, mozhno opredelit'
vnutrennee soprotivlenie istochnika napryazheniya.
Elektrichestvo v provodnike - dvizhenie v provodnike
sozdaet efir, kotoryi dvizhetsya vnutri provodnika.
Pri dvizhenii efira v provodnike v odnom napravlenii -
nazyvaetsya
- postoyannoe napryazhenie, - sozdaetsya vrashenie
vrashenie podvizhnoi chasti provodnika kotoraya pri raskrutke
sozdaet magnitnoe pole, i v svyazi s treniem podvizhnoi chasti
atomarnoi struktury ob nepodvizhnuyu provodnik sozdaet
soprotivlenie, pri nizkih temperaturah, podvizhnaya chast'
i nepodvizhnaya chast' v provodnike nahoditsya na rasstoyanii
pri kotorom umen'shaetsya i pri dal'neishem snizhenii temperatury
voznikaet effekt pri kotorom ischezaet trenie podvizhnyh
chastei vnutri provodnika po otnosheniyu k nepodvizhnoi
chasti -
sverh provodimost', no pri etom
ne ischezaet magnitnoe pole ot raskrutki vnutri provodnika.
Elektron i pozitron mogut nahoditsya v kachestve zaryadov,
na edinichnyh
atomah - eto svoistvo ispol'zuetsya v elektrolampovyh ustroistvah.
Obshee vseh etih ustroistv sostoit v tom chto sozdaetsya parovoe
oblako iz odinochnyh
atomov, posle chego perepadom potencialov
sozdaetsya dvizhenie odinochnyh atomov, posle chego oni dvizhutsya po
inercii, i proletaya skvoz' setki ili sheli,s razlichnymi potencialami
u nih proishodit chastichnyi perezaryad i izmenenie skorosti, pri etom
izmenyaetsya skorost' vrasheniya vnutrennei chasti kotoraya sozdaet
magnitnoe pole , i v svyazi s
nepreryvnym potokom poyavlyaetsya
vozmozhnost' modulirovat' potok zaryazhennyh atomov,
kak kolichestvenno tak i s raznymi potencialami. S'em signala
ne obyazatel'no
budet pryamym, tak kak rezul'tatom raboty lampovyh
ustroistv yavlyaetsya svetovoe izluchenie ili SVCh kolebanie.
U SVCh lamp vhodnye kolebaniya menyayut kolichestvo potoka,
posle chego etot potok zaryazhaetsya do opredelennogo napryazheniya,
posle chego tormozitsya, dlya sovpadeniya s dlinnoi volny, a s'em
kolebanii proishodit cherez kolebaniya
potencialov posle tormoza.
Esli vzyat' kineskop, to v nem rezul'tatom yavlyaetsya razgon
i modulyaciya kolichestvennaya potoka edinichnyh atomov,
s posleduyushim otkloneniem
po vertikali i gorizontali
otklonyayushei sistemoi, s posleduyushim uskoreniem i proletom skvoz'
setku po inercii s posleduyushim udarom ob lyuminofor.
Pri popadanii
v lyuminofor, atom vletaet na bol'shoi skorosti
i sozdaet raskrutku vnutrennei chasti lyuminofora, lyuminofor v
otlichii ot provodnika pri raskrutke vnutrennei chasti sozdaet
svechenie , v svyazi s nalichiem treniya, i vrasheniem vnutrennei
atomarnoi chasti po inercii pri sozdanii svetovogo
izlucheniya i zatratami energii na izluchenie sveta,
u lyuminofora
est' svoistvo - poslesvechenie. Sobstvenno poluchaetsya chto pri
zatratah postoyannyh napryazhenii v lampah SVCh usilivayutsya
peremennye kolebaniya, a v
kineskopah ispol'zuetsya
v rezul'tate tol'ko sila udara letyashego po inercii edinichnogo
atoma ob lyuminofor.
V svyazi s tem chto k efiru
principial'no ne primenim
termin gravitaciya, po prichine togo chto gravitaciya
opisyvaet vzaimnoe prityazhenie dvuh tel, v svyazi s chem
poyavilas' neobhodimost'
vvedeniya termina dlya
efira opisyvayushii vozdeistvie
prohozhdeniya efira skvoz' tela v raznyh napravleniyah
i pri raznoi plotnosti efira, i pri raznoi
plotnosti
atomarnoi struktury tel.
Pri etom chto est' v nalichii, efir mozhet
byt' s raznoi plotnost'yu, i tela mogut byt'
s raznoi plotnost'yu atomarnoi struktury.
Efir prohodya skvoz' tela stremitsya u planet
k yadru efira ili stremitsya skvoz' poverhnost'
Zvezdy Fiziki, k vnutrennei Zvezde Efira.
Takzhe mozhet efir vybrasyvat'sya
struyami
ili vzryvami iz Zvezdy
Fiziki.
Takzhe efir budet isparyatsya iz Zvezdy Efira posle
togo kak ona vyletela iz Zvezdy fiziki, i vneshnee
davlenie
ne sderzhivaet efir v zhidkom ili tverdom
sostoyanii.
Dvizhenie i trenie efira skvoz' materialy, pri opredelennyh
situaciyah vyzyvayut elektricheskii tok,
kotoromu soputstvuet magnitnoe pole.
Poluchaetsya chto ochen' mnogo processov
kotorye nado nazvat' odnim terminom, iz
chego sleduet -
1 Efiro-dinamika.
Kotoraya vklyuchaet v sebya -
2 Efiro-trenie -
prohozhdenie efira
skvoz' tela.
3 Efiro-davlenie
Takzhe
4 Efiro-metriya
-
izmerenie velichin efira.
5 Elektro-efir
Dvizhenie potokov efira v provodnikah |
- Teoriya pustoty vk.com/tviss
(Serg Ol,
5.07.2014 0:54, 25 Bait)
otvety na vse voprosy
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
10.07.2014 12:56, 2.3 KBait)
 Re: O kritikah i storonnikah STO
Re: O kritikah i storonnikah STO
Otvet #79 - Segodnya :: 09:06:32
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vot chitayu i pryamo oshushayu slabost' po otnosheniyu k
reshaemoi
zadache etih pozhilyh yuzerov v fizike.
Oni tak muchayut svoi mosk chtoby on im vydal pravil'nyi otvet
chto mne ih azh zhal', po prichine togo chto otvet
na samom dele v
dannoi situacii v dvuh variantah resheniya, vtoroi variant samyi
luchshii dlya nih - posyl opredelennyh teorii v dal' i bol'she k nim
ne vozvrashat'sya.
Pervyi variant eto v tom chto nado ponimat' principy
edinic izmerenii i ih prioritetnost' i lichno ya klal bolt na sistemu
SI i podobnye. Delo v sleduyushem chto est'
"sravnenie" - eto kogda ya
prikladyvayu lineiku k chemu-to - eto bolee prioritetnoe chem "izmerenie"
- izmerenie eto to dlya chego trebuetsya dve
"sravnivaemye" fizicheskie
velichiny iz vzaimodeistviya etih velichin opredelyaetsya - tret'ya fizicheskaya
velichina. Vot sobstvenno "izmerenie" rasstoyaniya
v skorosti sveta,
za opredelennoe vremya, -
kak po mne - ochen' nepravil'no, no kakim-to teoriyam eto nuzhno.
Chto sobstvenno proishodit v etoi situacii - chto
skorost' sveta
prinyata za konstantu, pri etom dopuskayutsya manipulyacii i spekulyacii v
izmereniyah pri sravnenii rasstoyanii "lineikami" - ih rastyagivayut
i szhimayut.
Ne gnushayutsya dlya podgonki rezul'tatov i vremya zamedlyat' i tormozit'.
Sobstvenno v nazemnyh usloviyah ne izmeryayut v skorosti zvuka za vremya rasstoyanie,
- vse, znachit - vtoroi variant tozhe aktual'nyi, posyl v peshee puteshestvie
simbioza - "prostranstvo-vremya" ibo on priduman isklyuchitel'no dlya podgonki
rezul'tata pod konstantu skorosti sveta.
Vyvod - esli ne poluchaetsya reshit' zadachu, to vozmozhno reshenie
sovsem v drugoi ploskosti.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
10.07.2014 13:07, 11.3 KBait)
| Svet
i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
17.04.201021:51 |
Iznachal'no
nado opredelitsya s nazvaniyami, - sravneniya i izmerenie.
Sravnenie
- kogda ya izmeryayu dlinu lineikoi, ya prosto sravnivayu razmernost' odnogo s
analogichnym.
Izmereniya
eto kogda iz dvuh raznyh sushnostei, no izvestnyh kolichestvenno opredelyaetsya
tret'ya sushnost'.
Naprimer,
- napryazhenie cherez tok i soprotivlenie, skorost' cherez dlinu i vremya.
Teper' o prostranstve - pouchaetsya dva metoda opredeleniya ego velichiny, odin
variant - prosto lineikoi, vtoroi skorost'yu sveta.
Lineikoi
logichno i prosto.
Skorost'yu
sveta - poluchaetsya chto pytaemsya priravnyat' izmeryaemuyu velichinu - zavisyashuyu
ot vremeni, (i tochnosti chasov ih schitayushih) lineiki izmeryayushei rasstoyanie (tochnee
svoistv lineiki i ee podverzhennosti deformaciyam), i skorost'yu rasprostraneniya
elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya.
Chto
sobstvenno poluchaetsya - pri izmereniyu prostranstva, skorost'yu sveta po
sravneniyu s priravnivaniem prostranstva k lineike.
U
nas poluchaetsya rasstoyanie dlinna,
tol'ko my zadeistvovali chasy lineiku, i elektromagnitnoe izluchenie.
Dlya izmereniya u nas est' tri sushnosti
skorost' vremya i rasstoyanie, i est' svoistvo prostranstva v kotorom rasprostranenie
elektromagnitnyh kolebanii ravno nekotoroi skorosti kotoruyu nazyvayut skorost'yu
sveta.
Zdes'
nado ponimat' sleduyushuyu situaciyu, - chto s odnoi tochki zreniya mozhno skazat', -
chto eta skorost' bystraya no mozhno skazat' chto ona medlennaya. No v lyubom sluchai
prostranstvo dlya kolebanii yavlyaetsya liniei zaderzhki, v kotoroi rasprostranyaetsya
signal. Vot, a zdes' uzhe poluchaetsya chto prostranstvo sostoit iz chego-to. Eto
proishodit potomu chto, prostranstvo my opredelili izmeryat' v metrah.
Dlya
svetovogo izlucheniya prostranstvo proyavilo eshe odno svoe svoistvo - zaderzhka
svetovogo lucha. Sledovatel'no - prostranstvo
zapolneno veshestvom, kotoroe zaderzhivaet svetovoi signal, analogichno tomu kak v
vozduhe ili vode zaderzhivaetsya zvuk. Zdes' mozhno nemnogo porazmyslit' o
skorosti signala v sredah, v vode zvuk vo stol'ko raz bystree - chem v vozduhe,
vo stol'ko na skol'ko blizhe rasstoyanie mezhdu molekulami v vode - chem v vozduhe. Iz chego sleduet - esli
podelit' skorost' sveta na skorost' zvuka v vozduhe my poluchim velichinu vo
skol'ko raz blizhe chastichki sredy,
kotorym zapolneno prostranstvo po
sravneniyu s chasticami vozduha.
Na samom dele skorost'yu
sveta izmeryat' prostranstvo nel'zya, potomu chto eto ne pravil'no, tak kak
skorost' sveta za sekundu ne yavlyaetsya meroi dlinny.
Eto
vse ravno, chto govorit', - chto ot Kieva do Moskvy tri tysyachi 75 sekund skorosti
zvuka.
Slozhenie so skorost'yu sveta i vychitanie, pri dvizhenii
ob'ektov.
Est' ob'ekt, kotoryi otnositel'no drugogo ob'ekta mozhet dvigat'sya.
Est' skorost' sveta, s kotoroi
rasprostranyaetsya svetovoe izluchenie v prostranstve.
Poluchaetsya - chto nuzhno uiti ot generatora izlucheniya na issleduemom, a generator
vse ravno nuzhen.
Zdes' prinimaem volevoe reshenie, generator raspolagaetsya na uslovno nepodvizhnom
ob'ekte.
Na tom ob'ekte kotoryi dvizhetsya budem raspolagat' prostoe zerkalo.
V kachestve istochnika vybiraem svetovoi luch modulirovannyi s chastotoi 300MGc,
chto v prostranstve budet iz sebya predstavlyat' odno kolebanie na metr dlinny,
tochnee odin period na metr.
Ustanavlivaem na avtomobile zerkalo , na vzletnoi polose ustanavlivaem stend s
svetovym generatorom 300MGc s uzko napravlennym luchom, i priemnik s
chastotomerom.
Pervyi opyt zaklyuchaetsya v tom chto avtomobil' raspolozhen na rasstoyanii 1km, i
nepodvizhen, prinimaemaya otrazhennaya chastota budet ravna peredayushei.
Opyt vtoroi - avtomobil' edet k stendu so skorost'yu 20metrov v sekundu, o chudo
chastota uvelichilas' na 20Gc. Prichina svyazana s tem chto pri dvizhenii k
istochniku, mashina proezzhaet na 20 metrov blizhe, a poskol'ku u nas v odnom
metre odin period kolebaniya, to chastota pri priblizhenii so skorost'yu 20 metrov v sekundu
uvelichitsya na 20Gc.
Opyt vtoroi mashina udalyaetsya ot stenda so skorost'yu 30 metrov v sekundu, i chastota
prinimaemaya ot zerkala avtomobilya nizhe peredayushei na 30Gc.
Iz chego sleduet, chto svet proyavlyaet svoi svoistva po otnosheniyu k prostranstvu,
kotoroe i zaderzhivaet svet.
Prostranstvo dlya sveta yavlyaetsya liniei zaderzhki.
Esli est' v chem, - svetu rasprostranyatsya i zaderzhivat'sya, to svet nahoditsya v
srede kakoi-to, analogichno zvuku v vozduhe.
Po toi prichine chto dannoe slozhenie i vychitanie chastoty mozhno povtorit' primeniv
vmesto svetovogo istochnika moshnyi dinamik a na avtomobile ustanovim chastotomer
s mikrofonom.
Berem chastotu 300Gc, u nas poluchaetsya pri skorosti zvuka 300metrov v sekundu,
odno kolebanie na metr.
Avtomobil' priblizhaetsya k dinamiku so skorost'yu 20metrov v sekundu, chastota
prinimaemogo zvuka v avtomobile bol'she na 20Gc, posle chego avtomobil' dvizhetsya
ot stenda so skorost'yu 30metrov v sekundu i chastota prinimaemaya v avtomobile,
nizhe na 30Gc.
A zvuk tochno dvizhetsya v srede, - eto vozduh.
Vot ya sobstvenno i pokazal metod slozheniya skorostei v sravnenii s analogichnym.
Mogut byt' nekotorye netochnosti so skorost'yu sveta v vozduhe, no eto ne
principial'no v dannoi zadache.
Estestvenno mozhno ispol'zovat' dannyi metod s raspolozheniem zerkala pod uglom 45
gradusov, pri etom raspolagayutsya priemnik i generator v raznyh mestah, i
peredvigaetsya zerkalo k i ot priemnika, ili k i ot generatora.
Chto ya schitayu nedostatkom dannogo opyta?, - osobyh tehnicheskih nedostatkov ne
vizhu, tak kak opyt so svetovym luchom budet rezul'tativnym i pri okolo svetovyh
skorostyah.
Estestvenno dannyi opyt ne rekomenduyu provodit' samostoyatel'no bez konsul'tacii
so specialistami po pravilam soblyudeniya tehniki bezopasnosti.
Obshaya ideya predydushih opytov v naglyadnosti
togo, chto pri
dvizhenii avtomobilya k ob'ektu ili ot nego, chastota prinimaemaya na avtomobile, i
otrazhennaya im chastota, budut odinakovymi, sledovatel'no esli avtomobil'
posredine mezhdu dvuh generatorov, kotorye rabotayut na odinakovoi chastote, to
esli avtomobil' budet peremeshat'sya mezhdu nimi po pryamoi linii mezhdu
generatorami, to summa chastot delennaya na 2 vsegda budet ravna ishodnoi chastote
generatora.
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo
i o skorosti sveta.
|
4.05.201013:20 |
Vot sobstvenno ispol'zuya bazovye ponyatiya o elektromagnitnom
izluchenii mozhno bolee detal'no pereiti k svetovomu izlucheniyu.
Svetovoe izluchenie - kolebanie zaryadov
v srede vokrug
drug druga primerno s chastotoi 100TGc, pri ih dvizhenii
v srede so skorost'yu kotoraya opredelyaetsya plotnost'yu sredy.
Nado uznat' skol'ko
kolebanii v metre u sveta, podelim
100TGc, na 300 tysyach km v sekundu, i podelim eshe na 1000,
i uznaem kolichestvo v metre = 333 333.
Ili - 333 kolebaniya na
millimetr.
Teper' nado ponyat' chto predstavlyaet iz sibya interferenciya.
Zdes' vse prosto. Svetovoi luch razdelyaetsya na dva lucha,
polu prozrachnym steklom,
vnutri kotorogo sloi metalla,
kotoryi propuskaet chast' luchei a druguyu chast' otrazhaet,
po prichine togo chto zaryady fotonov pri vzaimodeistvii vrashayas'
letyat,
i tak kak vrashenie ih haotichnoe, to podletayut k sloyu
po raznomu, chast' udaryaetsya odnovremenno plashmya, i otrazhaetsya,
a chast' prohodit mezhdu atomami metalla.
Posle chego iz dvuh luchei s pomosh'yu zerkala i poluprozrachnoi
linzy vostanavlivaetsya luch.
Zdes' poluchayutsya kol'cevye volny, o prichine togo chto u nas
raznaya
dlinna luchei, i fotony imeyut haotichnuyu raskrutku.
Esli v odno plecho razdelennogo lucha vvesti sosud s vodoi
- opyt Fizo, i voda budet dvigat'sya s nekotoroi
skorost'yu, to u nas
kol'ca nachnut shoditsya i rashoditsya.
Esli ya voz'mu fonarik i budu priblizhat'sya k stene,
so skorost'yu 10m/s, i pri etom
budu
svetit' na stenu, to chastota prinimaemyh signalov
na stene budet 333 333 umnozhit' na 10, to est' na 3,333MGc,
bol'she chem v fonarike, esli s takoi-zhe skorost'yu budu
udalyat'sya,
to na takuyu-zhe chastotu signal budet men'she.
Zdes' nado ponimat' prichinu, prichina ne v narushenii chastoty generatora,
i chastotomera, prichina
v tom chto kogda sozdayutsya
blagopriyatnye usloviya dlya sozdaniya fotonov na niti spirali fonarika,
oni vyletayut v prostranstvo, i dvizhutsya v nem,
a chastota menyaetsya
potomu chto posleduyushie fotony, vyletayut
iz fonarika v to vremya kogda fonarik menyaet svoe raspolozhenie
v prostranstve po otnosheniyu k stene, na kotoroi chastotomer.
-----------------------------------------------------
A po bol'shomu schetu est' effekt Doplera - on
isklyuchitel'no
dlya sred. Esli takovoi est' - znachit i est' sreda, a esli est'
sreda znachit est' vse sostavlyayushie ee nalichiya
- a skorost' sveta
eto yasnyi kon' - skorost' "vozmusheniya sredy" - i yasnyi kon'
u sredy eta skorost'
ne mozhet byt' konstantoi, ibo ona zavisit
ot plotnosti (davleniya), i temperatury.
Uzhos
kakoi kamennyi vek na dvore v soznanii yuzerov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.07.2014 11:51, 1.2 KBait)
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1404154370/140#140
Re: O kritikah i storonnikah STO
Otvet #133 - Segodnya :: 09:15
-----------------------------------
\\\Pochemu! Ya v otkrytuyu govoryu:
V konce 19 stoletiya v fizike nastupil krizis iz-za
opyta Maikel'sona-Morli. Dlya vyhoda iz krizisa byli
predprinyaty opredelennye shagi, v chastnosti byla izmenena
sistema otscheta. Esli klassicheskaya sistema otscheta
byla obrazovana telom otscheta i instrumentami, to
novaya sistema otscheta byla obrazovana:
Nablyudatel'
Telo otscheta
Chasy v tochke prostranstva, gde nahoditsya nablyudatel'
Etalon dlya izmereniya otrezkov prostranstva.\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------
Ya smotryu nikto dazhe duplya ne otbivaet v ponimanii
vvedennogo nablyudatelya v fiziku.
Obychnyi priem matematiki v fizike dlya podgonki matematicheskih
idei pod fizichnost' kak takovuyu.
Chto porodilo sobstvenno novyi vid matematicheskih vykrutasov
v vide predpolagaemyh opytov s pretenziei na fizichnost'.
Sobstvenno posle tridcati to uzhe nadobno zamechat' chto
chasy nablyudatelya postuliruyutsya, i ne vyschityvayutsya
po skorosti i vremeni, i ne privyazyvayutsya k nachalu koordinat.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
11.07.2014 12:55, 1.9 KBait)
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?board=physik-alt
http://www.sciteclibrary.ru/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1404154370/142#142
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ya vot ne mogu ponyat' po kakoi prichine oni vse raspylyayut svoe vnimanie
i ne mogut
opredelit'sya s tem kuda im bolee proshe prilozhit' svoi usiliya.
Sobstvenno samoe
smeshnoe chto s moei tochki zreniya oni postoyanno
myslenno spotykayutsya o to, s chego im nado nachat'.
Ya vot dumayu o drugom - chto
sobstvenno im i po kakoi prichine tak zatumanivaet
mosk, chto oni ne zamechayut togo chto osobenno nepravil'no i nelogichno.
Ne znayu pochemu
oni ne vidyat opyta po obnaruzheniyu elektronov, i pochemu
ego ne pereob'yasnyat so svoei tochki zreniya, i pochemu ne otkryvayut
temu - o elektricheskom toke i ego fizicheskoi suti.
Eto mne napominaet anekdot.
---"Sobranie v fiz -mat institute. U nas na povestke dnya est' vopros -
chto takoe elektricheskii tok?
Est' dva varianta resheniya, real'nyi i ne
real'nyi.
Real'nyi - eto kogda k nam priletyat inoplanetyane i rasskazhut nam ob etom, i ne
real'nyi - zasuchim rukava i samostoyatel'no popytaemsya reshit' etot vopros" (S)---
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.07.2014 9:54, 2.0 KBait)
 Re: O kritikah i storonnikah STO
Re: O kritikah i storonnikah STO
Otvet #216 - Vchera :: 23:07:38
rustot5 pisal(a) Vchera :: 23:02:36:
stary pisal(a) Vchera :: 22:50:06:///Umnica!///
///vy
i na drugie svoi voprosy mozhete naiti otvety v knizhkah. voz'mite
pochitaite Teilora ili drugoi normal'nyi uchebnik. net vy vmesto etogo
roetes' v kakih to drevnih manuskriptah s nevnyatnymi opisaniyami kakih to
luchikov i nablyudatelei. i dumaete chto fiziki imenno po takim ponyatiyami i
uchatsya///
///Ya, kak fizik uchus' i moimi uchitelyami yavlyayutsya Aristotel'; Gegel'; N'yuton; Puankare , Sivuhin, Savel'ev... Teilora ne znayu...///
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ya voobshe v uzhase ot togo kak fiziku modno izuchayut.
U menya v fizike v prioritete - zdravyi smysl, i
u menya nikto iz vyshe perechislennyh ne aktualen,
i
ya ne schitayu ih fizikami s bol'shoi bukvy.
Lichno ya by sovetoval nachinat' fiziku uchit' s knig i opytov
Tomasa Yunga.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
12.07.2014 23:33, 3.3 KBait)
 Re: Komissiya po bor'be s lzhenaukoi rasprostranyaet lzhenauku
Re: Komissiya po bor'be s lzhenaukoi rasprostranyaet lzhenauku
Otvet #41 - Segodnya :: 22:05:26
SP pisal(a) Segodnya :: 20:37:40:///mnogimi primeneniyami davno podtverzhdeno, chto STO rabotaet ispravno./// ///Kakimi zhe primeneniyami?///
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ladno tak kak moski bol'shinstva yuzerov ne sposobny zamechat' adekvatnoe,
- napomnyu.
V pervuyu ochered' relyativizm byl priduman bez prakticheskih opytov
ego podtverzhdayushih.
Na tekushii moment ne sdelano ni odnogo ustroistva i pribora na relyativistskih
ideyah.
Osnovnye paradoksy relyativizma, (paradoks) - laino
v teorii.
U kosmonavta kotoryi dvizhetsya na orbite soglasno dikomu opytu so svetovymi chasami,
privodit k dikim relyativistskim vyvodam o zamedlenii hoda tempa chasov
na orbite zemli, - fizicheski naoborot - na praktike temp hoda atomnyh i kvarcevyh
chasov - uvelichivaetsya, i chasam gluboko do lampochki dvizhutsya oni na orbite
ili zavisayut nad zemlei v odnoi tochke - na temp hoda vliyaet tol'ko vysota, -
relyativizm protivorechit praktike.
Opyat' zhe opyt s chasami so svetovym luchom, esli povernut'
kartinku na
devyanosto gradusov, slivayutsya idei relyativizma po slozheniyu skorostei lucha,
na dvizhusheisya platforme v prostranstve.
Ibo budet hod lucha nazad pri
dvizhenii - pravil'no, koroche chem vpered,
a summa ih dlin pravil'no= delennaya na dva ravna, rasstoyaniyu mezhdu zerkalami.
Sobstvenno na zayavlennoe postoyanstvo
skorosti sveta, v vakuume, - postulirovannoe,
byli sdelany teoreticheskie opory, kotorye potrebovali izmeneniya izmeritel'nyh
ustroistv kak vremeni tak i rasstoyanii,
dlya togo chtoby ne voznikalo spekulyacii
byli pridumany novye fizicheskie sushnosti i fizicheskie svoistva kotorye
nevozmozhno proverit', chto v kategorii "teorii"
- otnositsya k teoriyam
s "otkrytoi problemoi". V dannom sluchai na zayavlennye svoistva zamedleniya
vremeni v dvizhenii - otsutstvuet kak fizicheskii opyt,
kotoryi dolzhen byl
privesti k podobnym vyvodam, tak i otsutstvuet izmeritel'nyi pribor, i edinicy
izmereniya. Eto otnositsya i k otsutstviyu v prodazhe izmeritelya
krivizny prostranstva.
A tak vse normal'no.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.07.2014 10:58, 4.7 KBait)
G.A.Zubkov
|
|
Re: Chernaya dyra
|
25.12.20100:36 |
|
|
tovarish Novikov
pishet,chto pri
priblizhenii k
chernoi dyre
kosmonavtov
razorvet iz-za
prilivnyh
sil,raznosti
uskorenii.Pochemu
vse zabyvayut o
relyativistskom
sokrashenii
razmerov?Ved' pri
vlete v chernuyu
dyry vsya
vletayushaya v nee
materiya
szhimaetsya,umen'shaetsya
v razmerah.Potomu
raznost' uskorenii
v umen'shemsya tele
kosmonavta budet
nebol'shoi.I szhatiya
on takzhe ne
oshutit.Na moem
saite http://
genzubkov.narod.ru/
takzhe est' stat'ya
pro chernye dyry.
Pravda moi
vzglyady s nedavnih
por
izmenilis':schitayu
uzhe ,chto svet ne
podverzhen
inercii,gravitacii,ibo
ne imeet massy
pokoya.
|
|
| Naverh |
|
 |
A.P.Vasi
|
|
Re: Chernaya dyra
|
26.12.201014:31 |
|
G.A.Zubkov
"Pochemu
vse zabyvayut o
relyativistskom
sokrashenii
razmerov?"
Mne priyatno vstretit' tolkovogo relyativista,
kotoryi v prakticheskom primenenii pol'zuetsya
relyativiskimi sokrasheniyami v bytu.
U menya vopros, - kosmonavt v kosmicheskom korable
derzhit v rukah futbol'nyi myach, korabl' razgonyaetsya
do dvukratnogo sokrasheniya dlinny, posle chego
kosmonavt
s myachom v rukah povorachivaetsya na 90
gradusov otnositel'no napravleniya dvizheniya,
so splyushennym myachom v rukah, posle chego korabl'
nachinaet tormozhenie, u kosmonavta
v rukah
v itoge okazalsya splyushennyi myach dlya regbi,
- vopros kakoi vneshnii vid kosmonavta?
|
|
| Naverh |
|
 |
A.P.Vasi
|
|
Re: Chernaya dyra
|
26.12.201014:43 |
|
Estestvenno vopros voznikaet o edinicah izmereniya,
svyazannyh s sokrasheniyami ot skorosti.
Tak-zhe voznikaet vopros - a skoro postupyat v prodazhu
instrukcii i
rekomendacii po poletam na relyativiskih
skorostyah s cel'yu provedeniya relyativiskih
sokrashenii i rastyazhenii vmesto plasticheskoi hirurgii?
| |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.07.2014 13:33, 6.2 KBait)
Vremya idet a v kosmologii vse normal'no, i stabil'no,
i nichego ne menyaetsya, da i kosmologi ne hotyat nichego menyat'.
---
G.A.Zubkov
|
|
Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
|
30.12.20109:34 |
|
|
Nepriyatno
obshat'sya s takimi
priblatnennymi
negativistami,kak
vy. Net,chtob chto-to
svoe,konstruktivnoe
dobavit',zanimaetes'
odnim
kritikanstvom. Vash
uroven' znanii po
nekotorym
voprosam yavno
nizhe dazhe moego,a
vy naezzhaete na
menya, kak budto vy-
znatneishii
professor.
Nevazhno,kto
avtor.Vsyu teoriyu
Chernyh dyr mozhno
samomu vyvesti iz
formuly
gravitacii F=GmM/
r^2 . Ya bol'she sam
dumayu,chem izuchayu
chuzhie trudy.Pro
process,obratnyi
annigilyacii,napisano
naprimer v
''Elementarnom
uchebnike fiziki''
tom 3 s.553
G.S.Landsberga:
''obrazovanie pary
elektron-pozitron
proishodit v
rezul'tate
vzaimodeistviya
gamma-kvanta s
elektricheskim
polem odnogo iz
atomnyh yader
veshestva.''
|
|
| Naverh |
|
 |
A.P.Vasi
|
|
Re: Chernaya dyra
|
30.12.201017:53 |
|
Ya Vam kul'turno vse vremya namekayu chto Vy v
svoih razmyshleniyah to v oblakah letaete,
to otbivaetes' ot obsheprinyatyh utverzhdenii,
to nesete v rukah bred sivoi
kobyly.
Esli Vam eto nravitsya - to eto lichno Vash vybor,
mogu Vas obradovat', chto takih mechtatelei niochem,
kak Vy - delayushih pri etom naukoemkii vid
i vyrabatyvaya
mysli pritenduyushem na aplodismenty, - tak takih
sredi astro-fizikov prakticheski absolyutnoe bol'shinstvo.
A to chto napisano naprimer na etom
saite o chernoi dyre,
Vy ya tak ponimayu vzyat' za standart ne hotite, i pri etom
otbrosit' vse vydumki. Opredelenie dostatochno prostoe,
- gravitaciya takaya chto
dazhe fotony ne mogut pokinut' -
zdes' nado togda priznat' vrunami vseh kto utverzhdaet
chto dyry izluchayut, - kak po mne - nado tak nado,
a Vam vybirat' .
U chernoi dyry est' radius sledovatel'no est' poverhnost',
i v etom sluchai s moei tochki zreniya, - vruny te kto utverzhdaet
chto skvoz' dyru est' tonnel',
- a Vam vybirat'.
Ya Vam vkratce pytayus' ob'yasnit' chto v fizike esli
avtor predostavlyaet chitatelyu pravo vybora - to eto
uzhe govorit o tom chto eto vran'e
ili neobosnovannaya
vydumka iznachal'no, i mne smeshno i zhal' Vas po
bessmyslenno potrachennomu Vami vremeni v razmyshleniyah
nad chernymi dyrami, esli by vy vnikli
v bazovye
avtorskie postanovki zadach i ob'yasnenii Vy by srazu
ponyali chto eto prostaya galimat'ya, ne imeyushaya nikakogo
otnosheniya k nablyudaemym ob'ektam.
Ya
Vam po druzheski skazhu pochemu na tekushii moment
nikto ne obnaruzhil chernoi dyry, a slyshny lish' utverzhdeniya
chto ona vot tam dolzhna byt', - potomu chto astro-fiziki
i sami ne znayut kak ona dolzhna vyglyadet', -
ya dumayu Vy dogadyvaetes', pochemu astronomiyu v shkolah
otmenili.
|
|
| Naverh |
|
 |
A.P.Vasi
|
|
Re: Chernaya dyra
|
30.12.201018:13 |
|
V astronomii krizis ochen' bol'shoi - iz za togo chto neudobno
uchenikam prerekat'sya s prepodavatelem, i v lico emu skazat'
ne mogut - mol hvatit nam bred sivoi kobyly
v mozg zalivat'.
A so vremenem ucheniki na zalitom v mosk brede i uverennosti
v otsutstvii kritiki - pishut takuyu galimat'yu, chto ushi
u odnih zavorachivayutsya,
a molodye vosprinimayut za "chistuyu monetu",
i vse idet po krugu - tak nazyvaemyi -
"avtoritarnyi krugovorot breda sivoi kobyly v astronomii".
| |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(v. n. bespalov,
22.07.2014 14:30, 1021 Bait)
Teoriya 2
Vsya
vselenaya
zapolnena
svetom i
absolyutnoi
materiei
voznikayut
iz
neotkuda
chernye
dyry i vo
mnogih
tochkah
vselenoi
voznikayut
gravitacionnye
sily oni
nachinayut
poglashat'
svet.
Izvestno
chto
chernye
dyry
poglashayut
svet i
vsyu
energiyu
vokrug,
vozmozhno
centry
galaktik
i est'
chernye
dyry i
yavlyayutsya
byvshimi
centrami
gravitacii
poglotivshie
pervichnoe
veshestvo
v
neogronichennom
kolichestve
do
polnogo
nasysheniya
i
obrazuyushimi
centry
galaktiki
s ih
zakonomi
i
poryadkami
kotorye
po
koncentracii
veshestva
mogut
prevoshodit'
belyh
karlikov
libo
kotoroe
mozhet
byt'
svobodnoi
ot
obsalyutnoi
gravitacii.Chernye
dyry
zakruchivayut
energiyu
po
rukovam
kak i
rukova
golaktiki.
Tozhe
mozhet
proizoiti
i s
sovremennymi
chernymi
dyrami
oni mogut
stat'
centrami
galaktik
otkuda
oni
poyavlyayutsya?
Chto
dumaete
po etomu
voprosu
budu rad
lyuboi
kritike.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.07.2014 16:09, 8.0 KBait)
A.P.Vasi
|
|
Posobie dlya teh kto hochet pisat' teorii.
|
26.03.201219:11 |
|
Estestvenno i ponyatno kak relyativisty prikipeli
k kreslam relyativizma, i tak u nih vse horosho v teoriyah
chto ni v odnom institute mira net kafedry na kotoroi uchat
pisat' teorii, ya tak dumayu chto na etoi kafedre prosto nikto
ne zahochet uchitsya? - net kak raz uchitsya na nei zahotyat
vse, tol'ko pervye vypuskniki etoi kafedry
esli i ne stanut
nobelevskimi laureatami srazu to uzh tochno prakticheski srazu zamenyat svoimi
teoriyami ves' relyativizm s prochei neadekvatnoi fizikoi.
Sobstvenno
podobnyh zavedenii v obozrimom
budushem ne predviditsya, no eto ne znachit chto ne dolzhno
byt' nekotoryh standartov dlya teh kto hochet pisat' teorii.
Tak
kak nynche nauka na ruchnom teoreticheskom tormoze,
i vnutri nee vse ochen' zapushenno vplot' do nepravil'noi
terminologii i smyslovoi nagruzki terminov, i nauka bazovyh
opredelenii i sama vnyatno obosnovat' ne mozhet,
i pod slovami naprimer - "mezhzvezdnaya sreda" - okazyvaetsya
eto atomarnaya mezhzvezdnaya pyl' i mikroskopicheskii
kosmicheskii
musor, i ne v koem sluchai ne sreda sploshnaya iz efira,
vot tak za sto let iskazili smysl, to v svyazi s etim
avtor dolzhen ob'yasnyat' terminologiyu
i sootvetstvie
s fizicheskim smyslom kotoryi on v nego vkladyvaet,
po toi prichine chto tekushii fizicheskii smysl slova
"sreda" - eto nepreryvnaya sreda,
a vkladyvayut chto popalo,
vplot' do odnogo atoma na kubicheskii decimetr, i nazyvayut
eto sredoi, - na samom dele eto absurd, u sredy pomimo nepreryvnosti,
obyazatelen
neposredstvennyi fizicheskii kontakt mezhdu chasticami,
chto vlechet za soboi, trenie chastic, uprugost' sredy, plotnost' sredy,
provodimost' sredy (chego libo).
Zapreshayutsya sokrasheniya, zapreshayutsya terminy
ne imeyushie fizicheskogo smysla, zapreshayutsya
zhargonnye terminy ne imeyushie otnosheniya k fizike.
---------
Vnachale
u avtora obyazatel'no dolzhno byt'
nechto vrode takogo - vvedenie, annotaciya, kratkoe soderzhanie, -
avtor kratko obyazan izlozhit' svoimi slovami sleduyushee,
Nazvanie dolzhno po vozmozhnosti ukazyvat' osnovnuyu
sut' i oblast' zatronutogo voprosa.
1 o chem budet rech',(v kakoi oblasti nauki, chto sobstvenno)
2
kakie voprosy reshayutsya,
3 chem otlichaetsya reshenie ot drugih,
4 chem ono luchshe,
5 vyvod .
Eto dolzhno byt' obyazatel'no chtoby chitayushii zrya ne tratil
svoe
vremya na chtenie togo chto ego ne interesuet.
Osnovnaya chast' nachinaetsya s avtorskogo rasskaza o svoih
celyah i dostizheniyah i neudachah.
Delo v
tom chto vsegda budet kucha zhelayushih sdelat' eto za
avtora, to luchshe pust' avtor sam rasskazhet.
1 Rezul'tativnost'.
Avtor dolzhen rasskazat' chto s ego tochki
zreniya
u nego poluchilos' dostatochno horosho, i blagodarya chemu
on smog dostich' luchshih rezul'tatov, i chto u nego
ne poluchilos'.
2 Avtor dolzhen dat'
osnovnye fizicheskie opredeleniya, fizicheskih
sushnostei kotorye ispol'zuet, ili vzyat' opredeleniya
iz drugih istochnikov, esli oni podhodyat dlya avtora,
s ukazaniem
istochnika informacii,
no oni dolzhny byt' odnoznachno.
Ne dopuskaetsya dvuznachnogo opredeleniya, pri dvuznachnom opredelenii
fizicheskoi sushnosti avtor dolzhen znat'
chto on fizik,
a u fizika pri dvuznachnom opredelenii poluchaetsya
- bessmyslennost', idiotizm, paradoks, - chto nedopustimo.
3 Terminologiya.
Avtor odnoznachno dolzhen opredelit' terminologiyu,
i opisat' svoimi slovami fizicheskie sushnosti i tot smysl
kotoryi avtor v nih vkladyvaet.
|
|
| Naverh |
|
 |
A.P.Vasi
|
|
Re: Posobie dlya teh kto hochet pisat' teorii.
|
27.03.201216:56 |
|
Volny - fizicheskie - byvayut na granice mezhdu sred.
Naprimer mezhdu vodoi i vozduhom.
-------------------------------
Zvuk - kolebaniya v srede.
Svet - kolebanie
v srede.
Skorost' sveta i skorost' zvuka - skorost' rasprostraneniya
vozmusheniya sredy.
Isklyuchitel'no dlya sred ispol'zuetsya effekt Doplera,
dlya opredeleniya
izmeneniya rasstoyaniya, i chastoty mezhdu priemnikom
i peredatchikom kolebanii sredy.
-----------------------------------------
|
|
| Naverh |
|
 |
A.P.Vasi
|
|
| Naverh |
|
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
22.07.2014 16:13, 13.5 KBait)
|
|
|
|
......Material iz Vikipedii
\\\Gámma-izluchénie (gamma-luchi, γ-luchi)
vid elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s chrezvychaino maloi dlinoi
volny
< 5×10−3 nm i, vsledstvie etogo, yarko vyrazhennymi
korpuskulyarnymi
i slabo vyrazhennymi volnovymi svoistvami. \\\
\\\Gamma-kvantami yavlyayutsya fotony s vysokoi energiei.
Obychno schitaetsya,
chto energii kvantov gamma-izlucheniya prevyshayut 105 eV, hotya
rezkaya granica
mezhdu gamma- i rentgenovskim izlucheniem ne opredelena. Na
shkale
elektromagnitnyh voln gamma-izluchenie granichit s
rentgenovskim izlucheniem,
zanimaya diapazon bolee vysokih chastot i energii. V oblasti
1-100 keV
gamma-izluchenie i rentgenovskoe izluchenie razlichayutsya
tol'ko po istochniku:
esli kvant izluchaetsya v yadernom perehode, to ego prinyato
otnosit' k
gamma-izlucheniyu; esli pri vzaimodeistviyah elektronov ili
pri perehodah
v atomnoi elektronnoi obolochke k rentgenovskomu izlucheniyu.
Ochevidno,
fizicheski kvanty elektromagnitnogo izlucheniya s odinakovoi
energiei ne
otlichayutsya, poetomu takoe razdelenie uslovno. \\\
\\\Gamma-izluchenie ispuskaetsya pri perehodah mezhdu
vozbuzhdennymi
sostoyaniyami atomnyh yader (sm. Izomernyi perehod, energii
takih
gamma-kvantov lezhat v diapazone ot ~1 keV do desyatkov
MeV),
pri yadernyh reakciyah (naprimer, pri annigilyacii elektrona
i pozitrona,
raspade neitral'nogo piona i t.d.), a takzhe pri otklonenii
energichnyh
zaryazhennyh chastic v magnitnyh i elektricheskih polyah (sm.
Sinhrotronnoe izluchenie).....\\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
\\\Material
iz Vikipedii \\\
\\\.....Rentgenovskie trubki
Rentgenovskie luchi voznikayut pri sil'nom uskorenii
zaryazhennyh chastic
(tormoznoe izluchenie), libo pri vysokoenergeticheskih
perehodah v elektronnyh
obolochkah atomov ili molekul. Oba effekta ispol'zuyutsya v
rentgenovskih
trubkah. Osnovnymi konstruktivnymi elementami takih trubok
yavlyayutsya
metallicheskie katod i anod (ranee nazyvavshiisya takzhe
antikatodom).
V rentgenovskih trubkah elektrony, ispushennye katodom,
uskoryayutsya
pod deistviem raznosti elektricheskih potencialov mezhdu
anodom i katodom
(pri etom rentgenovskie luchi ne ispuskayutsya, tak kak
uskorenie slishkom malo)
i udaryayutsya ob anod, gde proishodit ih rezkoe tormozhenie.
Pri etom za schet
tormoznogo izlucheniya proishodit generaciya izlucheniya
rentgenovskogo diapazona,
i odnovremenno vybivayutsya elektrony iz vnutrennih
elektronnyh obolochek atomov
anoda. Pustye mesta v obolochkah zanimayutsya drugimi ....\\\
Vot est' dva ochen' koryavyh s tochki zreniya fiziki
opredeleniya, no na tekushii moment u relyativistov
luchshih opredelenii net.
Grubo govorya chasticy rentgenovskogo izlucheniya mogut byt' pri dvuh situaciyah, - pervaya
situaciya eto pri yadernyh reakciyah, - i esli u zvezdy takoe izluchenie
to ona budet nazyvat'sya neitronnoi zvezdoi, a vtoraya situaciya kogda veshestvo padaet na chernuyu dyru,
i posle padeniya proishodit rentgenovskoe izluchenie.
Zdes' legko opredelit'sya s tem, a kakaya zhe dolzhna byt'
minimal'naya skorost' veshestva ?, chtoby poluchilos'
tormoznoe izluchenie v rentgenovskom diapazone
v rezul'tate padeniya i udara o chernuyu dyru.
Eta skorost' 0.3 skorosti sveta i sootvetstvuet skorosti
chastic pri prilozhennom napryazhenii v 27 kV, i pri etom
poluchayutsya uskorennye chasticy s energiei v 27keV, i
oni ispol'zuyutsya v kineskopah cvetnyh televizorov,
kogda pri udare o lyuminofor, oni za schet flyuorescencii
i posleduyushei lyuminescencii sozdayut svechenie i
poslesvechenie
- lyuminofora, a v itoge ekrana kineskopa.
-----------------------------------------------------------
(Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
\\\Fluorescénciya (variant: flyuorescenciya)
fizicheskii
process,
raznovidnost' lyuminescencii.
Fluorescenciei obychno nazyvayut izluchatel'nyi perehod
vozbuzhdennogo sostoyaniya s samogo nizhnego
singletnogo kolebatel'nogo urovnya S1
v osnovnoe sostoyanie S0.\\\
\\\Lyuminescénciya(ot lat.lumen,
rod. padezh luminis
svet i -escent
suffiks, oznachayushii slaboe deistvie)
neteplovoe svechenie veshestva, proishodyashee posle poglosheniya
im energii
vozbuzhdeniya.---\\\
Telo,
svobodno padayushee pod deistviem sil gravitacii, nahoditsya v
sostoyanii nevesomosti
i ispytyvaet deistvie tol'ko prilivnyh
sil,
kotorye pri padenii v chernuyu dyru
rastyagivayut
telo v radial'nom
napravlenii i szhimayut v tangencial'nom.
Velichina etih sil rastet
i stremitsya k beskonechnosti pri
 .
V nekotoryi moment .
V nekotoryi moment
sobstvennogo
vremeni telo peresechet gorizont
sobytii. S tochki zreniya nablyudatelya,
padayushego vmeste s telom, etot
moment nichem ne vydelen, odnako
vozvrata teper' net.\\\ -------
\\\S tochki zreniya
nablyudatelya, padayushego vmeste s telom, etot
moment nichem ne vydelen, odnako
vozvrata teper' net.\\\ - Dazhe konyu ponyatno chto esli sdelat' mini konteiner i posadit' tuda
muhu
i razognat' v kollaidere na uskoritele do skorosti 0.3s, i zhahnut' etim konteinerom
o mishen' i na vse eto deistvie uidet odna sekunda, to mozhno dolgo zvezdet'
o tom chto muha budet zhit' po svoim chasam eshe vechno, tol'ko
ya ne obyazan verit' etoi pornuhe, po skol'ko muha na samom dele
razob'etsya v pyl' pri udare o
mishen'.
Sledovatel'no rentgenovskoe izluchenie mozhno skazat'
chto eto chasticy s energiei uskoreniya dostigshei skorosti
bolee 0.3 skorosti sveta. A vot zdes' srazu vylavlivayutsya
avtorskie paradoksy, - paradoks eto teoreticheskaya neudacha.
Poluchaetsya chto pri udare padayushego veshestva dolzhen byt'
bezbashennyi udar o dostatochno tverduyu poverhnost',
pri polnom otsutstvii atmosfery, po prichine togo chto
atmosfera sdelaet tormoznoe izluchenie so skorostyami bolee
0.3 S nevozmozhnym, ibo atmosfera dostatochno plavno
zamedlit padayushee telo . I poluchaetsya chto rasskazy o
dlitel'nom
padenii za gorizont sobytii v chernuyu dyru ne vyderzhivayut
kritiki, po prichine togo chto ili dlitel'noe padenie
pri otsutstvii rentgenovskogo izlucheniya, ili bezbashennyi
udar o tverduyu poverhnost' chernoi dyry v rezul'tate
kotorogo pri skorosti udara bol'she 0.3 skorosti sveta
budet izluchenie kotoroe budet nazyvat'sya tormoznoe izluchenie.
Itogo yavno prosmatrivaetsya chto avtor chernyh dyr
prosto pridumal neudachnuyu i nefizichnuyu teoriyu
o chernyh dyrah i eta teoriya ne vyderzhivaet primitivnyh
logicheskih vzaimosvyazei. No po skol'ko luchshego
net u relyativistov, to i etoi teorii logichno aplodirovat'
i voshishat'sya chernymi dyrami. |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.07.2014 10:26, 2.7 KBait)
 Inerciya
Inerciya
07.09.11 :: 22:22:4
\\\Poetomu relyativistskii koefficient vozrastaniya massy
mozhno traktovat' ne
kak effekt STO, a kak koefficient
uvlecheniya efira, osushestvlyaemyi za schet "zahvata" chasticami
kvantov pervomaterii.\\\
------
\\\Starogo
psa, novym tryukam ne nauchish'\\\ (S)
Vot naprimer chto nablyudaetsya, chto uskoryayutsya
- mikroskopicheskie elementarnye chasticy pri bol'shom
perepade vysokovol'tnogo
elektricheskogo potenciala.
Vot zdesya vnimanie - uskoryayutsya chasticy chem imenno -
- pravil'no - elektrichestvom edrenyi kon'.
Tak kogda-zhe uzhe snizoidet
do nedalekih chto materiya
v uskoritele uskoryaetsya napryazheniem kotoryi sozdaetsya
raznicei potencialov napryazheniya, i dvizhenie chastic napravlenno
ot minusa k
plyusu.
Dazhe ne mogu ob'yasnit' tot uroven' nedaleosti v fizike i kosmologii
kotoryi est' seichas. Vot smotrit naprimer na fizicheskii opyt
i naproch' ne
ponimaet ni samogo fiz processa ni prioritetnosti
vnutri processa.
Ibo dazhe konyu ponyatno chto v uskoritele - razgonyayut mikrochasticy
materii elektroi, (perepad
napryazheniya - sozdaet napryazhennost'
elektrichestva, chto vyzyvaet staticheskuyu utechku toka, no eshe
ne voznikaet dugovoi proboi), pri etom staticheskii potok
elektry
prekrasno dvizhetsya ot minusa k plyusu kak nekotoryi
potok. V kineskope etot potok mogut suzhat', rasshiryat', i sdvigat'
magnitnym polem - vo vremya ego dvizheniya. A
vot sobstvenno
esli uvelichivat' napryazhenie i uvelichivat' rasstoyanie mezhdu
minusom i plyusom chtoby razognat' mikrochasticy materii do bol'shei
skorosti - poluchaetsya
nekotoraya nelineinost'.
I estestvenno udivleniyu fizikov net konca i kraya , ibo kak tak
esli prilozhit' 27kV - skorost' chastic 0.3S, a pri millione vol't,
skorost'
priblizhaetsya k S, pri treh millionah tozhe k S priblizhaetsya,
Chastica u nih vidish' -li tyazheleet a to chto elektra kotoraya svoim
potencialom i razgonyaet etu
chasticu mezhdu elektrodami
sama dvigaetsya mezhdu elektrodami so skorost'yu - S, tak
do etogo dodumat'sya ne vozmozhno.
Ne znayu - mozhet oni smogli sebe v
golove ili kto-to
im kakimi-to teoriyami blok -adekvatnosti - v golove
vyklyuchil. A cirk uehal potom - a klounada prodolzhaetsya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.07.2014 0:32, 2.8 KBait)
http://www.astrogorizont.com/content/read-Novyj_vzgljad
\\\Avtor:
NASA
|| Original'naya
versiya
|


|

Sleduite za
nami
v gruppah |
  |
|
 |
|
Etot novyi snimok ob'ekta Cen A
soderzhit v sebe dannye nablyudenii, poluchennye v period mezhdu 1999 i 2012
godami. Na snimke samoe nizkoenergeticheskoe rentgenovskoe izluchenie,
zaregistrirovannoe kosmicheskoi observatoriei Chandra, pokazano krasnym
cvetom, rentgenovskoe izluchenie srednih energii predstavleno zelenym, a
rentgenovskoe izluchenie samyh vysokih energii golubym... |
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
30.07.2014 0:52, 1.5 KBait)
V predydushem soobshenii chto sobstvenno prosmatrivaetsya -
otsutstvie pol'zy ot takih foto pri ih ochen' bol'shom potenciale
dlya ponimaniya struktury zvezd i vybrosa
iz nih efira.
Chtoby ponyat' fizicheskii primitivnyi smysl na etom foto
osobo i napryagat'sya ne nuzhno. Glavnoe chto sobstvenno nablyudaetsya -
v pervuyu ochered'
podsvetka i pereotrazhenie vybrasyvaemoi materii
iz verhnego sloya zvezdy. V prostranstve materiya prosto tak nichego ne
izluchaet - ya dumayu chto eto ponyatno. V materiyu
kotoraya v prostranstve,
popadaet chastichka vysokoi energii i ee otbrasyvaet vo vse storony. V dannom
sluchai istochnik chastic - zvezda, i energiya kak raz i pokazatel'
toi skorosti s kotoroi duet efir iz zvezdy skvoz' verhnii sloi.
I chem bol'she skorost' - tem bol'she energiya u chastic.
Sobstvenno opyat' nedostatki foto - net
tri de modeli etoi zvezdy.
Sobstvenno net tri de modeli vybrosov, po tri de modeli vybrosov
mozhno budet opredelit' gde i kak i s kakoi skorost'yu
efir duet
iz zvezdy v prostranstvo.
Iz chego uzhe primitivno budet mozhno sozdat' tri de model'
davleniya efira vokrug zvezdy, i sledovatel'no mozhno budet
primitivno sozdat'
programmnym putem,
formu vneshnego vybrosa materii v vidimom
spektre, i sravnit' s tekushim izobrazheniem.
I uzhe potom napisat' obratnuyu raschetnuyu programmu,
kotoraya po vneshnemu tekushemu vybrosu v opticheskom
izobrazhenii smozhet vosstanovit' predshestvuyushii process
u pesochnyh chasov s yubkami naprimer.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.08.2014 16:15, 1.3 KBait)

Do poslednego vremeni uchenye-fiziki so vsego mira otnosilis' ves'ma skepticheski k
Rodzheru
Shaueru (Roger Shawyer) i ego izobreteniyu.
Prichinoi skepticizma yavlyalos' to, chto principy raboty izobretennogo
Shauerom "nevozmozhnogo" dvigatelya EmDrive idut vrazrez s principami
klassicheskoi mehaniki. Tem ne menee, novyi variant dvigatelya EmDrive,
kotoryi poluchil nazvanie Quantum Vacuum Plasma Thruster, izgotovlennyi
specialistami NASA, rabotaet, hotya uchenye eshe ne mogut ob'yasnit' pochemu i
kak on eto delaet.
http://www.dailytechinfo.org/
-----------------------------------------------------------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.08.2014 17:00, 507 Bait)
Sobstvenno zdes' situaciya s moei tochki zreniya
kogda vozmozhno voznikaet detektirovanie signala
pri vneshnem izmenenii plotnosti efira. Pri etom
proishodit
neravnomernoe rasseivanie efira.
Sobstvenno ya pomnyu i na perepade napryazhenii sputnik
letit ili poletit.
Net nikakoi konstrukcii ustroistva, na foto
kakaya-to
zhelezka.
Stranno v etoi situacii chto ne voshvalyayut relyativizm
i genial'nost' relyativistov, i to chto eti dvizhki podtverzhdayut
relyativistskie teorii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.08.2014 17:14, 671 Bait)
http://peswiki.com/index.php/Directory:Emdrive_%28Electromagnetic_Space_Drive%29


SPR Prototype
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.08.2014 17:19, 193 Bait)
Posmotrel opisanie i chego-to azh smeshno stalo,
estestvenno chto pytlivyi razum mog vysokotehnologichnogo
pridumat' kak soedinit' vyhod magnetrona svch pechki
s
mednym ruporom.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
4.08.2014 23:32, 1.1 KBait)
http://www.dailytechinfo.org/news/6143-specialisty-nasa-zastavili-rabotat-nevozmozhnyy-dvigatel-kotoryy-v-buduschem-mozhet-navsegda-izmenit-oblast-kosmicheskoy-tehniki.html
\\\Ustroistvo dvigatelya Shauera dostatochno prosto. On obespechivaet tyagu
pri
pomoshi specializirovannyh mikrovolnovyh generatorov, izluchayushih
volny v
zamknutoe izolirovannoe prostranstvo.\\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Smeshnaya mysl' prishla, - v
kosmicheskom prostranstve -
magnetron vykruchennyi iz SVCh pechki kak raz - lishnyaya detal'.
Dostatochno sdelat' zerkal'nyi rupor i svetovod
zerkal'nyi, chtoby perenapravlyat'
solnechnyi svet,
ot solnca tozhe kilovatt na kvadratnyi metr moshnost'.
Naprimer rupor ploshad'yu tri kvadratnyh metra,
svodit v puchok, i izluchenie solnca podvoditsya
sboku v konus, i rupor mozhno proporcional'no
chastote umen'shit'.
O ya dumayu chto uzhe u vseh voznikla mysl', a ne
raskalitsya li zakrytyi rupor esli v nego
kilovatt
moshnosti vgonyat', yasnyi kon' razogreetsya - znachit
izluchenie vyhodit iz rupora.
Klounada.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
5.08.2014 23:56, 1.1 KBait)
http://www.astronews.ru/cgi-bin/mng.cgi?page=news&news=6334


\\\Uchenye Stenforda i Nacional'noi Uskoritel'noi Laboratorii SLAC
v
techenie bolee chem chetyreh let zanimalis' analizom dannyh kosmicheskogo
gamma-teleskopa Fermi (Fermi) i drugih eksperimentov, dlya togo, chtoby
sozdat' samyi podrobnyi na segodnyashnii den' portret dvuh gromadnyh
puzyrei, kotorye protyanulis' na tysyachi svetovyh let nad diskom nashei
galaktiki i pod nim.
Eti puzyri, kotorye naibolee yarko svetyatsya vysokointensivnym gamma-svetom,
byli otkryty bolee chetyreh let nazad. \\\
--------------
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.08.2014 0:17, 1.9 KBait)
Sobstvenno otvet s tochki zreniya efira - primitivnei nekuda.
Na chto logichno obratit' vnimanie - pravil'no - na formu
konusa sinego oreola.
Tam gde krasnaya
podsvetka - tam vysokaya temperatura,
i nizkaya plotnost' efira, a sama galaktika predstavlyaet iz sebya
v prostranstve nekoyu vrashayushuyusya turbinu ili nekotoryi poristyi
disk. Poluchaetsya chto efir uvlekaetsya vrasheniem i sozdaet
ochen' bol'shoe razryazhenie davlenie efira v centre galaktiki,
i eto snizhaet plotnost' efira, chto podymaet
temperaturu
prostranstva i umen'shaet yarkost' zvezd v centre, poskol'ku
oni mogut byt' kak Solnce no svetimost' u nih budet raz
v sto men'she, i estestvenno
oni budut krasnymi.
Pri etom oni nahodyatsya v sostoyanii vozmozhnoi poteri balansa
pri massovom sbrose efira v itoge nachnetsya razbros vseh
zvezd galaktiki.
Nizkoe davlenie v centre vrasheniya nekotorogo poristogo diska
estestvenno trebuet vospolneniya pritoka efira kotoryi uvlekaetsya
centrobezhnoi siloi.
Sobstvenno
vot takoi process.
Ya dumayu chto dinamiku etogo processa primitivno imitirovat'
raskruchivaya ili poristyi disk, ili tonkuyu tkan',
v nekotoroi srede imeyushei pruzhinnye
i tekuchie svoistva,
ya by lichno posovetoval opyt
vrashaya motorchikom disk iz tonkoi tkani ,
provesti vnutri lampy s gazom v kotorom razryady vnutri.
---
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.08.2014 11:16, 3.3 KBait)
- Moderator





-

- Soobshenii: 14 999
- Reiting: +403/-50
- Deti lyubyat buterbrod s margarinom!
-
Otvet #161 : 15.08.2014 [07:59:19]
\\\Udaleny soobsheniya, ne otnosyashiesya k obsuzhdaemoi teme.\\\

Zapisan
\\\I kto-to, kak vsegda, nes mne chush' o "tarelkah", i kto-to, kak vsegda, propovedoval dzen... (s) Zoopark\\\
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Esli chestno ya ran'she ne veril
v to chto u cheloveka mozhet
byt' razum zabran. V detstve v shutku eto nazyvali pri
kratkovremennyh situaciyah etogo yavleniya u odnoklassnikov
vyrazheniem - shizuha
kosit nashi ryady, i pri etom
odnoklassnik drugim odnoklassnikam dolzhen byl za neadekvatnye
vyskazyvaniya - skazat' frazu - otcy prostite zas ran ca.
I eto deistvovalo
polozhitel'no.
Chto sobstvenno nablyudaetsya - avtor pridumal chernye dyry
dazhe ne smog vnyatno sformulirovat' ee fizicheskie svoistva,
pri etom s momenta
kak byli pridumany chernye dyry -
na segodnyashnii den' oficial'no ne obnaruzheno ni odnoi
dyurochki, pri etom vmesto togo chtoby razobrat'sya si opredelit'sya s chernymi
dyrami sozdav rabochuyu gruppu s byudzhetom v desyat' millionov
enotov.
Vozmozhno rezul'tatom raboty etoi gruppy budet posyl idei
chernyh dyr v dalekuyu dal',
i spekulyacii na vrashenie
togo chto ne obnaruzheno budet vyglyadet' ne smeshno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.08.2014 17:08, 891 Bait)
Sobstvenno u menya poyavilos' logicheskoe reshenie, - dlya drugih
idei pokolenie starshe 35 let nevospriimchivo. Sobstvenno starshe
soroka pyati let budut kategoricheski
protiv lyubyh drugih idei.
Eto ya by nazval - nauchnyi konservatizm.
Ya tak ponimayu chto s opredelennogo vozrasta otklyuchaetsya
blok somneniya v svoih znaniyah, i
yuzer bol'she doveryaet
svoim znaniyam, i uveren v nepravil'nosti drugih idei.
Do etogo otklyuchaetsya blok zacepok - eto to s pomosh'yu
chego na podsoznatel'nom urovne
voznikaet somnenie v lyubyh
ideyah.
Itogo - esli v idei otsutstvuet obosnovanie ili prisutstvuet
otkrytaya problema, ili ne obosnovyvaetsya prichina postulirovaniya
-
(naprimer slabaya teoriya napolnennaya paradoksami), -
to dlya kogo i golimyi porozhnyak - a dlya kogo i genial'noe dostizhenie,
i v etom sluchai nikto drugomu ne
smozhet dokazat' svoyu tochku zreniya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.08.2014 14:25, 2.3 KBait)
Vot Vibe rassuzhdaet kak vremenshik v dannoi situacii,
on prekrasno vidit laino i idiotizm v konkretnom sluchai
i tol'ko raduetsya etomu i schitaet eto normal'no.
Ya estestvenno schitayu vsyu fiziku "svoei" - i dlya menya maleishee moe
neponimanie v nei ili popytka vvesti menya v lozhnoe napravlenie
- mnoi vosprinimaetsya
kraine negativno, i ya pridumal davno
i metody kak nahodit' eti obmany i pridumal kak ih
zapominat' v golove, chtoby
potom srazu ne chitat' a propuskat' podobnoe
v lyubyh tekstah.
Esli chestno to ya davno uzhe i pridumal testy dlya fizikov
takih kak Vibe - svoimi slovami za 15 minut rasskazat'
chto lichno samostoyatel'no
pridumal i zachem i kakoi vopros
eto reshaet i kto etim pol'zuetsya.
Vtoroi test - kakie global'nye i osnovopolagayushie
trudnosti s Vashei tochki zreniya est'
v fizike i kosmologii - 5min.
Tretii test - Po kakim prichinam Vy samoustranilis' ot
resheniya osnovnyh i osnovopolagayushih voprosov kosmologii i fiziki,?
-
10 min.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #2810 : Segodnya v 13:03:02
\\\Nehoroshie
harakteristiki -- sub'ektivnoe ponyatie. V zakone vsemirnogo tyagoteniya
sila stremitsya k beskonechnosti pri stremlenii rasstoyaniya k nulyu. I
nichego, zakon rabotaet.
Kakie konkretno problemy s nuzhnym
chelovechestvu kachestvom voznikayut iz-za singulyarnoi plotnosti i
singulyarnoi krivizny chernyh dyr?\\\
\\\Problemy razvitiya, progressa, i poiska znanii.
Isklyuchaya problemu, isklyuchayutsya i napravleniya poiska reshenii
problemy.
Kak by tormozhenie nauchnogo processa.\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.08.2014 21:07, 1.5 KBait)
Dazhe ne ponimayu kak lyudi ne boyatsya v nauchnyi idiotizm zaigryvat'.
Sobstvenno prostymi testami vyyavlyaetsya za polchasa i ukazhut na
dver' i poshlyut domoi po prichine
prof neprigodnosti.
S drugoi tochki zreniya - luchshaya zamena otsutstvuet, no nel'zya zabyvat'
o lyuboi zamene, kotoraya so vremenem budet luchshe.
---
Ne mogu ponyat' opyat'-zhe, pochemu prakticheski u vseh prosedayut umstvennye
sposobnosti pri voprose o elektrichestve.
Sobstvenno yavno ne mogut dazhe ponyat' smysl opyta
po obnaruzheniyu elektrona,
tochnee ne mogut ponyat' v kakom meste otsutstvuet prichinno sledstvennaya svyaz',
i ne mogut opyat' zhe ponyat' chto etot opyt v prolete.
I yavno ne v sostoyanii etot opyt opisat' svoimi slovami,
nadeyutsya chto kto-to na forume budet dumat' za nego a on potom podumaet
luchshe i poluchit bol'shuyu premiyu.
Kak-by zhazhda halyavy, i ni u kogo dazhe idei ne voznikaet kak postavit'
teh zadachu i razbit' ee na pod zadachi i reshit' v komplekse vse
situacii - trudovoi metod
- ya dazhe nigde na forume ne videl takih
predlozhenii.
I estestvenno chto - i eti metody proletayut kak fanera nad Parizhem,
esli soberutsya lyudi pensionnogo vozrasta.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Fizika
al'ternativnaya
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.08.2014 22:28, 4.4 KBait, otvetov: 1)
Ya vot smotryu i uzhe dazhe nikto ne popravlyaet
zabludshuyu nedalekuyu i dumayushuyu chto on fizik,
nu i dazhe nikto i ne rasskazyvaet lekcii pro atomnye
chasy i drugie
vysokotochnye chasy, i spec atomnye
chasy kotorye ne menyali tempa hoda,
ne uvelichivali svoi temp kak vse drugie
s uvelicheniem vysoty, i razrabotchiki eti chasy
i vsyu teh dokumentaciyu o ih rabote vybrosili.
Chto menya udivlyaet chto kto zanimaetsya teoriei, emu prosto
plevat' na to kak na samom dele na sputnikah
sebya vedut
chasy, na skol'ko ya pomnyu chto nikto ne skryvaet chto
temp kvarcevyh i atomnyh chasov s uvelicheniem vysoty -
uvelichivaetsya, i gluboko do lampochki v
kakuyu storonu
letit sputnik ili on zavis.
I vot buduchi naprimer na svoei volne, nichego ne ponimaya
v voprose zadvigaet takie idei chto azh shapka zavorachivaetsya,
a sporit' tozhe bessmyslenno - "starogo psa novym shutkam
ne nauchish'" (S).
---
|
 Re: Novaya fizika iz novoi teorii otnositel'nosti. Podhody k resheniyu zagadok stroeniya materii.
Re: Novaya fizika iz novoi teorii otnositel'nosti. Podhody k resheniyu zagadok stroeniya materii.
Otvet #9 - Segodnya :: 20:43:34
Citata:Libo vy ne do konca ponyali sut', libo ya ne dostatochno dohodchivo ee izlozhil. Smotrajshii pisal(a) Segodnya :: 17:50:20:Chto znachit ""postoyanno zamedlyaetsya"? Kto Vam eto soobshil? Smotrajshii pisal(a) Segodnya :: 17:50:20:Nu s ...? V chest' kakogo .... Vy delaete takoe predpolozhenie.?
Princip otnositel'nosti diktuet:
Dvizhenie rakety otnositel'no efira (inercionnost') i dvizhenie efira
otnositel'no rakety, eto odno i to zhe. Otsyuda postoyannoe zamedlenie
vremeni na raketnyh chasah, yavlyayushih soboi stoyachuyu elektrovolnu i v
uskorenno dvizhusheisya rakete i v rakete pri uskorenno dvizhushemsya
otnositel'no ee efire. Smotrajshii pisal(a) Segodnya
:: 17:50:20:Chto
kasatel'no startuyushei rakety, Tak vot zhdlya togo, chtoby otorvat' tyazheluyu
zadnicu ot startovogo stola, raketa dolzhna nabrat' skorost'
dvizhushegosya k poverhnosti efira, i plyus eshe chutochku.....togda proizoidet
nachalo ee starta. Tak vot, v sluchae neuskorennogo (s
postoyannoi skorost'yu) padeniya efira k centru Zemli, srazu zhe posle etoi
chutochki, mgnovenno vyklyuchite dvigateli (uberite tyagu) i raketa zavisnet i
budet viset' skol' ugodno dolgo, ne nuzhdayas' ni v kakoi opore. No v
real'nosti ona ne zavisaet, a nachinaet uskorennoe padenie k centru
Zemli. Sledovatel'no nashe predpolozhenie o dvizhenii efira k centru Zemli s
postoyannoi skorost'yu neverno. Nu a v sluchae uskorennogo
dvizheniya efira k centru Zemli temp hoda raketnyh chasov, kak i pri
uskorennom dvizhenii rakety dolzhen postoyanno zamedlyat'sya. No eto ne
sootvetstvuet deistvitel'nosti. Sledovatel'no nashe predpolozhenie o
uskorennom dvizhenii efira k centru Zemli neverno. Vyvod: Padeniya efira k centru Zemli net.\\\
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Na skol'ko ya pomnyu v tridcatyh godah proshlogo
veka
na dvuh pervyh vysokotochnyh chasah - bylo zafiksirovano uvelichenie
tempa hoda chasov s uvelicheniem vysoty.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(A. V. Talikov,
5.09.2014 23:09, 323 Bait)
temp kvarcevyh i atomnyh chasov s uvelicheniem vysoty -
uvelichivaetsya, i gluboko do lampochki v kakuyu storonu
letit sputnik ili on zavis.
A vot s etogo mesta po-podrobnee. Vozmozhno Molniya zavisala na GSO v kakoi-to
sezon po odnu storonu orbity Zemli imeya ee skorost' 30 km/sek, a v perigee
vychitala iz nee 11 km/sek?
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2014 15:49, 1.6 KBait)
 Re: Efirnaya Teoriya. Edinaya koncepciya.
Re: Efirnaya Teoriya. Edinaya koncepciya.
Otvet #918 - Segodnya :: 06:29:12
\\\ Ne nado mne pripisyvat' gluposti. Ya pol'zuyus'
terminami Tot zhe vakuum ne
russkoe slovo. Ya ne pol'zuyus'
nenauchnymi terminami. Materiya i
prostranstvo v fizike
ne nauchnye terminy. \\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
S odnoi
tochki zreniya tak podumat' - prosto smeshno chitat',
naprimer dostatochno dat' = materii i prostranstvu = , - prostoe
i ponyatnoe opredelenie kotoroe vyrazhaet tot smysl
kotoryi avtor
vkladyvaet v nego i vse dostatochno.
Zdes' estestvenno logichno kak raz i provodit' konferencii, i soglasovyvat'
terminologiyu i vkladyvaemye
v nee idei i fizicheskie sushnosti razlichnymi
nauchnymi shkolami - no do etogo eshe ne skoro razduplyatsya, tak kak
eshe net nauchnyh shkol.
A tak estestvenno
trudno yuzeram kotorye ne mogut samostoyatel'no
dat' fizicheskih opredelenii, im dlya etogo nado samim metodiku
sebe razrabotat', i idti po punktam - budet ploho no
hot' chto-to budet,
chtoby etimi opredeleniyami mozhno bylo pol'zovat'sya.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2014 16:07, 4.7 KBait)
Ya tozhe napisal samostoyatel'no - bazovye opredeleniya
teh fizicheskih sushnostei i ih svoistv, sostoyanii
i vzaimodeistvii.
Opisal kak mog i chto schital nuzhnym, seichas ya estestvenno by v ramkah
svoei modeli by napisal
drugie opredeleniya, no po toi prichine chto v svoe
vremya ya ne gnal otsebyatiny (predskazatel'nuyu chast' - modnuyu sredi nyneshnei
fiziki
v kotoroi net nikakoi otvetstvennosti za pravil'nost' i adekvatnost'
teorii ) - to i eti opredeleniya tozhe podoidut.
---
| Re: Svet i prostranstvo i o skorosti sveta.
|
12.09.2011 |
Predpolagaemaya
fizicheskaya model' efira i ustroistva zvezd.
Vvedenie.
Dannaya
model' prednaznachena dlya bolee prostogo
vospriyatiya
astrofiziki, eta model' ne pretenduet
na
absolyutnuyu istinu.
Model'
budet vyglyadet' v vide iznachal'nogo nabora
nekotoryh
uslovnyh utverzhdenii opisyvayushih
elementy
po otdel'nosti v staticheskom vide,
iz
kotoryh budet v posledstvii sdelana dinamicheskaya model'.
Sostav
elementov modeli.
Prostranstvo
- odin iz elementov modeli obladayushii ideal'nymi
svoistvami,
i predstavlyayushee iz sebya pustoi ob'em beskonechnyi vo
vse
storony, edinica izmereniya - rasstoyaniya
metr ob'ema kubometr,
vremya
sushestvovaniya - vechnoe.
Efir
- gazoobraznaya sreda kotoraya mozhet byt' i v zhidkom sostoyanii,
ona
zapolnyaet prostranstvo vo vsem ob'eme, gaz neitral'nyi po otnosheniyu
k
materii, obladaet vsemi svoistvami gaza, otlichaetsya
vysokoi
tekuchest'yu kotoraya v milliard raz bolee tekuchii
chem
vozduh, i edinichnaya chastica efira v milliard raz men'she molekuly
vozduha,
vremya sushestvovaniya - vechnoe.
Materiya
- vse prochie chasticy zapolnyayushie prostranstvo,sostoit kak
pravilo
iz atomov i molekul, i oskolkov atomov i molekul po razmeru
ot
tysyachi do milliarda raz men'she molekul vozduha, s
efirom
- materiya, ni v kakie masso-obmennye reakcii ne vstupaet ni
v
gazoobraznom ni v tverdom ni v zhidkom sostoyanii, - materiya ne mozhet stat'
efirom,
a
efir ne mozhet stat' materiei - vremya sushestvovaniya - vechnoe.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2014 16:49, 3.0 KBait)
http://www.astronews.ru/cgi-bin/mng.cgi?page=news&news=6454


\\\Razrushitel'nye posledstviya moshnogo vzryva sverhnovoi mozhno
razglyadet'
na etom izobrazhenii, sostavlennom iz snimkov, sdelannyh v
rentgen- i
infrakrasnom dapazonah, observatoriyami - kosmicheskim
teleskopom Spitcer
(Spitzer Space Telescope), observatoriei Chandra
(Chandra X-Ray Observatory) i
apparatom XMM-Newton.
Puzyryasheesya
oblako eto udarnaya volna nepravil'noi formy, sgenerirovannaya
vzryvom,
kotoryi zemlyane mogli uvidet' 3 700 let nazad. Oblako ostankov, Puppis
A,
nahoditsya na rasstoyanii okolo 7 000 let ot Zemli, a diametr udarnoi
volny okolo
10 svetovyh let.\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Menya velichiny nemnogo smushayut, logichno proverit'.
Itogo - rasstoyanie 7000 svetovyh let, sobytie proizoshlo - 3700 let nazad,
tekushii diametr 10 svetovyh
let.
Sledovatel'no chtoby uznat' srednyuyu skorost' rasshireniya
dostatochno 3700 podelit' na 10 i poluchitsya chto rasshirenie
v trista sem'desyat raz medlennee
skorosti sveta.
Teper' ya otkryvayu stat'yu
http://crydee.sai.msu.ru/Universe_and_us/4num/v4pap26.htm
\\\Massa vybroshennogo
pri vzryve sverhnovoi veshestva dostigaet
neskol'kih mass Solnca, skorost' ego
razleta 10-20 tys. km/s, \\\
\\\Naibolee izvestny Krabovidnaya tumannost'
(ostatok vspyshki SN 1054 g.),
Kassiopeya A (vspyshka SN ne nablyudalas', no po
razletu vybroshennyh sgustkov
datiruetsya 1680 godom), ostatki sverhnovyh Tiho
Brage (SN 1572 g.) i Keplera
(SN 1604 g.). Eti molodye OVS nablyudayutsya kak opticheskie
tumannosti,
yarkie istochniki rentgenovskogo i infrakrasnogo izlucheniya. Skorost'
rasshireniya etih tumannostei vse eshe dostatochno velika, 2000-6000 km/s,
razmer-2-4
pk.\\\
\\\Razmer staryh OVS dostigaet desyatkov
parsekov i dazhe soten parsekov, esli
ostatok rasshiryaetsya v srede ochen' nizkoi
plotnosti. Skorosti razleta staryh
OVS padayut do soten i desyatkov km/s. Oni
nablyudayutsya kak tonkovoloknistye
opticheskie tumannosti, yarkie v radiodiapazone,
takie kak Petlya Lebedya i IC443
. Po mere zamedleniya skorosti razleta OVS i ostyvaniya
goryachego gaza ego
rentgenovskoe izluchenie stanovitsya nesushestvennym. Kogda skorost'
rasshireniya
obolochki sravnivaetsya so skorost'yu haotichekih dvizhenii gazovyh oblakov
v
Galaktike (okolo 8 km/s),\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.08.2014 16:56, 595 Bait)
Chto sobstvenno stranno chto nikto sobstvenno ne napisal
naprimer chto skorost' rasprostraneniya vybrosa umen'shaetsya
s kvadratom ili kubom rasstoyaniya.
Delo v
tom chto znat' dannye skorosti i ih izmeneniya ochen' vazhno
v kosmologii, ibo ne znaya ih budut rasstoyanie izmeryat' s tochnost'yu
plyus minus million raz, v luchshem sluchai
plyus minus - tysyacha raz,
a nablyudaya naprimer vybros u zvezdy tipa pesochnica, mozhno budet
tochno opredelit' rasstoyanie do nee.
Yasnyi kon' dlya etogo nuzhna
budet programma, i periodicheskaya ili
postoyannaya videozapis' processa.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
6.09.2014 10:00, 295 Bait)
Vy ne sostoyanii - sformulirovat' vopros.
Ne otlichaete - konstataciyu fakta, ot voprosa po suti.
Tak vot poka Vy ne pokazhete - kakimi opytami i metodami
izmeryali temp hoda chasov na sputnike, i ne dokazhete chto sputnik
na men'shei vysote uvelichil temp chasov do teh por ko mne
ne obrashaites'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.09.2014 12:48, 2.2 KBait)
Opyt Yunga. Eksperiment s dvumya shelyami.
http://www.astronomy.ru/forum/index.php/topic,122079.0.html
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Chto sobstvenno menya raduet i udivlyaet tak eto kak v
anekdote,
\pro murav'ya kotorogo stado bykov zatoptalo v gryaz',
i muravei vstaet, otryahivaetsya i govorit menya krutogo
murav'ya i mordoi v gryaz', i kto bych'e.(S)\
Ya sobstvenno dazhe ne ponimayu kak mozhno byt' nastol'ko
massovo nedalekimi v primitivnyh zadachah po fizike.
Vse est', mozhno naiti polnoe opisanie opyta v avtorskom
variante.
Mozhno naiti to chto Tomas Yung vyskazyval o svete i ego
prirode.
I dazhe primitivnyh metodov net v fizike dlya resheniya
detskih zadach.
A tam nado vsego-to 1) opisat' situaciyu,
2) dat' opredeleniya sushnostyami po vozmozhnosti v razlichnyh
izlozheniyah razlichnyh shkol. Dat' opisanie proishodyashemu
ot raznyh shkol.
3) Dat' opisanie
posledovatel'nosti prichinno sledstvennyh
svyazei, i posledovatel'nosti
v fizicheskih vzaimodeistviyah.
Sdelat' vyvody.
Ukazat' na oshibki.
- I vse, primitivnaya zadacha v fizike budet reshena raz i
navsegda
i na veki vechnye tak chto dlya etogo mozgov chto-li mnogo
nado.
Sobstvenno ne mogu ponyat' kak mozhno odnu i tu zhe zadachu
desyatiletiyami samomu sebe mozgi ... v popytke ee reshat'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
13.09.2014 12:51, 109 Bait)
Samoe smeshnoe chto opyt mozhno sdelat' samostoyatel'no
v domashnih usloviyah, i on ne trebuet finansovyh zatrat.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.09.2014 23:17, 3.0 KBait)
26 avgusta 2014goda.
TrV 161,
c.1, 3,
"Obrazovanie"
Egor Bazykin, Dmitrii Vibe, Aleksei Sgibnev, Vladimir Surdin,
Sergei Belkov, Irina Levontina
Dmitrii Vibe,
dokt. fiz.-mat. nauk, zav. otdelom fiziki i evolyucii zvezd
Instituta
astronomii RAN:
Leto s nauchnoi tochki zreniya okazalos' neozhidanno produktivnym.
Neozhidanno ibo ne po nashei
vole do leta zatyanulas' bitva s
recenzentom stat'i, kotoruyu my
otpravili v zhurnal eshe v sentyabre
2013 goda. On neskol'ko raz treboval
sushestvennyh dorabotok, na
kotorye uhodil ne odin mesyac, i sam kazhdyi
raz chestno vyderzhival
mesyac na napisanie ocherednogo otzyva. Trudno
skazat', napisali li
my v itoge chto-to ego ustroivshee ili prosto
nadoeli. Spravedlivosti
radi sleduet otmetit', chto vse zamechaniya byli po
sushestvu, i stat'ya v
rezul'tate ih realizacii stala luchshe na
kachestvennom urovne.
Stat'ya posvyashena analizu nablyudenii policiklicheskih aromaticheskih
uglevodorodov (to est' my podozrevaem, chto eto oni) vo vnegalakticheskih
oblastyah zvezdoobrazovaniya raznogo vozrasta. Do etogo odni lyudi
predpolagali, chto uglevodorody v oblastyah zvezdoobrazovaniya rastut,
drugie lyudi predpolagali, chto uglevodorody v oblastyah zvezdoobrazovaniya
razrushayutsya. Nam zhe vpervye udalos' ubeditel'no pokazat', chto tam s
uglevodorodami proishodit voobshe ne poimi chto.\\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Smeshno
samo zhelanie mahrovyh relyativistov podat'sya v al'ty,
sobstvenno ya ponimayu chto kushat' ohota, i podash'sya kuda ugodno,
tem bolee /esli tot kto zhivet
proshlym ne mozhet uvidet' budushee/(S),
i chto v etom sluchai delat'?.
Zdes' hot' rolik snimai - "Kak relyativisty podalis' v al'ty, i pri etom
oni
oni ostalis' relyativistami, - v itoge sredi al'tov oni - relyativisty,
a sredi relyativistov oni - al'ty.
U menya myslenno azh klaviatura utopala v slezah
vysoko intellektual'noi
rapsodii kotoraya zvuchala ot ih padeniya i udarov o plastik .
- Samoe glavnoe v etoi botve - chtoby ne bylo bazovyh i odnoznachnyh
avtorskih opredelenii. Bez etoi botvy prosto bezdna samyh umnyh -
pri etom nikto ni na chto ne neset otvetstvennosti, i tem bolee u nego
ostaetsya
vozmozhnost' vsegda samogo sebya oprovergnut', i dazhe ne odin raz
v ramkah odnoi i toi-zhe - botvy, pardon - teorii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
23.09.2014 23:19, 234 Bait)
"Zdes' hot' rolik snimai - "Kak relyativisty podalis' v al'ty, i pri etom
oni
oni ostalis' relyativistami, - v itoge sredi al'tov oni - relyativisty,
a sredi relyativistov oni - al'ty.""
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.09.2014 0:09, 329 Bait)
Legko relyativista otlichit' ot al'ta, - al't yasnyi kon', - mozhet
vsegda skazat' chto on lichno pridumal sam i dlya chego eto nado.
Relyativist mozhet - yasnyi kon', pridumat' tol'ko v ramkah
teorii relyativizma, - i nikogda ne smozhet vnyatno skazat'
dlya chego eto nado, i relyativist ne smozhet skazat' - chto on
pridumal lichno - sam.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.09.2014 14:03, 5.0 KBait)

: 08.01.2003 [19:44:15]
\\\Etot sposob prineset pol'zu i tem avtoram novyh fizicheskih teorii,
kotorye sposobny k samokritike. Provedite recenzirovanie samostoyatel'no,
i putem hitryh inoskazanii sozhmite vsyu shirotu svoih vzlyadov v trebuemye
10 ballov. Vremenno pridetsya poiti na kompromiss, no eto vynudit
recenzenta prochitat' vash trud do konca. I pervyi shag v prodvizhenii novoi
idei budet sdelan!\\\
\\\Kak opredelit' sumasshedshuyu teoriyu\\
\\\Sposob rascheta reitinga potencial'no revolyucionnogo vklada v fiziku.\\\
\\\1.
Daem -5 ochkov fory.
2. +1 ochko za kazhdoe utverzhdenie, kotoroe shiroko izvestno kak lozhnoe.
3. 2 ochka za kazhdoe bessoderzhatel'noe utverzhdenie.
4. 3 ochka za kazhdoe
logicheski nekorrektnoe utverzhdenie.
5. 5 ochkov za kazhdoe oshibochnoe utverzhdenie, kotoroe ne izmenyaetsya, nesmotrya na yasnoe ukazanie, kak ego mozhno ispravit'.
6. 5
ochkov za primenenie myslennogo eksperimenta, kotoryi protivorechit shiroko izvestnomu real'nomu eksperimentu.
7. 5 ochkov za kazhdoe slovo, vydelennoe zaglavnymi bukvami
(esli delo ne v neispravnoi klaviature).
8. 5 ochkov za kazhdoe upominanie "Enshteina", "Hokinsa" ili "Feimana".
9. 10 ochkov za kazhdoe
zayavlenie o tom, chto kvantovaya mehanika principial'no porochna (bez yasnogo primera).
10. 10 ochkov za predlozhenie pochitat' uchebnik v kachestve svidetel'stva togo, chto avtor
ponimaet, o chem govorit.
11. 10 ochkov za nachalo opisaniya teorii s togo, kak dolgo avtor ee razrabatyval.
12.
10 ochkov za posylku teksta cheloveku, kotorogo avtor lichno ne znaet, s
ukazaniem, chtoby on nikomu nichego ne govoril iz-za boyazni, chto novye
idei budut ukradeny.
13. 10 ochkov za predlozhenie denezhnogo priza tomu kto dokazhet i/ili naidet oshibki v etoi teorii.
14.
10 ochkov za kazhdoe utverzhdenie v takom stile: "Ya ne matematik, no moya
teoriya verna v principe, i budet tol'ko luchshe, esli kto-nibud' vyrazit
ee v uravneniyah".
15. 10 ochkov za to, chto sovremennaya shiroko ispol'zuemaya teoriya - eto "vsego lish' teoriya", kak budto kto-to s etim sporit.
16.
10 ochkov za to, chto, hotya shiroko primenyaemaya teoriya daet pravil'nye
predskazaniya yavlenii, no ona ne ob'yasnyaet, "pochemu" eti yavleniya
proishodyat ili nepravil'no ob'yasnyaet ih mehanizm.
17. 10 ochkov za
kazhdoe hvalebnoe sravnenie sebya s Einshteinom ili zayavlenie, chto teoriya
otnositel'nosti principial'no porochna (bez yasnogo primera).
18. 10 ochkov za zayavlenie, chto novaya teoriya priblizhaet nas k "smene paradigmy".
19. 20 ochkov
za nameki, chto avtor zasluzhivaet Nobelevskuyu premiyu.
20.
20 ochkov za kazhdoe hvalebnoe sravnenie sebya s N'yutonom ili zayavlenie,
chto klassicheskaya mehanika principial'no porochna (bez yasnogo primera).
21. 20 ochkov za kazhdoe ispol'zovanie primerov iz nauchnoi fantastiki ili iz mifov, kak budto eto
real'nye fakty.
22. 20 ochkov za samozashitu putem vysmeivaniya svoei (real'noi ili vymyshlennoi) prezhnei teorii.
23. 20 ochkov za kazhdoe upominanie "uzkolobyh reakcionerov".
24. 20 ochkov za kazhdoe upominanie o "samoyavlennyh zashitnikah tradicionnyh vzglyadov".
25.
30 ochkov za predpolozheniya o tom, chto izvestnyi chelovek v taine ne veril
v teoriyu, kotoruyu on publichno podderzhival. (Naprimer, chto Feinman v
dushe byl protivnikom special'noi teorii otnositel'nosti, chto mozhno
ustanovit', esli prochitat' ego uchebniki po fizike mezhdu strok).
26.
30 ochkov za predpolozhenie o tom, chto v poslednie gody zhizni Einshtein uzhe
blizko podoshel k ideyam, kotorye seichas vyskazyvaet avtor.
27. 30 ochkov za zayavlenie, chto eta teoriya razrabotana vnezemnoi civilizaciei (bez yasnogo svidetel'stva).
28.
30 ochkov za upominanie o tom, chto rabota priostanovlena na vremya
prebyvaniya v psihbol'nice, ili o tom, chto psihiatr pytalsya otgovorit'
avtora prodolzhat' etu rabotu.
29. 40 ochkov za sravnenie protivnikov etoi teorii s nacistami, shturmovikami i korichnevymi.
30.
40 ochkov za zayavlenie, chto "uchenaya elita" uchastvuet v zagovore, chtoby
pomeshat' novoi teorii priobresti tak zasluzhennuyu slavu.
31. 40 ochkov
za sravnenie sebya s Galileem v tom smysle, chto sovremennoi Inkvizicii v
dannom sluchae pridetsya eshe trudnee, ili chto-to vrode etogo.
32. 40
ochkov za zayavleniya o tom, chto kogda eta teoriya budet okonchatel'no
priznana, to sovremennyh uchenyh pristydyat, chego oni i zasluzhivayut. (Eshe
30 ochkov za fantazii o tom, kak imenno uchenye, kotorye nasmehalis' nad
etoi teoriei, budut vynuzhdeny otrekat'sya ot prezhnih slov).
33. 50 ochkov za zayavleniya, chto u vas est' revolyucionnaya teoriya, no ona ne imeet konkretnyh proveryaemyh predskazanii.\\\
\\\J.Baez\\\
-------------------------------------------------------
\\\Dumayu, kazhdyi iz prisutstvuyushih bez truda smozhet vychislit' svoi lichnyi
reiting:)\\\
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.09.2014 14:13, 1.7 KBait)
Sobstvenno ne mogu ponyat' pochemu relyativisty etimi testami ne proveryayut svoi
teorii, tam i bol'shoi vzryv sploshnaya "otkrytaya problema", "otkrytaya problema"
eto -
========================================================================================================================Material
iz Vikipedii
Gipóteza (dr.-grech. ὑπόθεσις predpolozhenie; ot ὑπό snizu, pod + θέσις
tezis) predpolozhenie ili dogadka; utverzhdenie, predpolagayushee dokazatel'stvo,
v otlichie ot aksiom, postulatov, ne trebuyushih dokazatel'stv. Gipoteza schitaetsya
nauchnoi, esli ona udovletvoryaet kriteriyu Poppera, to est' potencial'no mozhet
byt' proverena kriticheskim eksperimentom, a takzhe esli ona sootvetstvuet drugim
nauchnym kriteriyam.
Takzhe ona mozhet opredelyat'sya kak forma razvitii znanii, predstavlyayushaya soboyu
obosnovannoe predpolozhenie, vydvigaemoe s cel'yu vyyasneniya svoistv i prichin
issleduemyh yavlenii[1].
Kak pravilo, gipoteza vyskazyvaetsya na osnove ryada podtverzhdayushih ee nablyudenii
(primerov), i poetomu vyglyadit pravdopodobno. Gipotezu vposledstvii ili
dokazyvayut, prevrashaya ee v ustanovlennyi fakt (sm. teorema, teoriya), ili zhe
oprovergayut (naprimer, ukazyvaya kontrprimer), perevodya v razryad lozhnyh utverzhdenii.
Nedokazannaya i neoprovergnutaya gipoteza nazyvaetsya otkrytoi
problemoi.================================================================================================================I
radovat'sya tomu chto propoveduyutsya absolyutno vse tekushie teorii osnovany na
postulirovanii i vse s "otkrytymi problemami", i otkazyvat'sya ot lyubyh
al'ternativ, nu nu, ya kak al't poidu na vstrechu zhelaniyam relyativistov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.09.2014 15:03, 1.8 KBait)
\\\Chto ne publikuet
Astronet
Astronet.ru
yavlyaetsya nauchno-populyarnym i uchebnym saitom,
poetomu
my ne publikuem neproverennye i al'ternativnye
fizicheskie
i astronomicheskie teorii. V pervuyu ochered' eto
otnositsya k al'ternativnym teoriyam gravitacii
i al'ternativnoi kosmologii. \\\
Ya
tak ponyal chto otsutstvuyut organizacii upolnomochennye proveryat' al'ternativnye
teorii.
Sobstvenno al'ternativnaya teoriya eto prosto drugie idei.
Ya
vot prizadumyvalsya pochemu ne napisali chto ne publikuyut nelogichnyh teorii,
ili
teorii ne sootvetstvuyushih zdravomu smyslu, estestvenno chto-to yavno
sderzhivaet
tak pisat', ibo oni podobnymi teoriyami uzhe pol'zuyutsya.
Ya
dolgo dumal po etoi situacii, prishel k vyvodu, chto bol'shinstvo schitaet chto dazhe,
samye
umnye lyudi v fizike v itoge mogut pridumat' teorii na urovne gluposti i ne
bolee,
i sobstvenno tu glupost' chto est', menyat' na druguyu net smysla.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
8.10.2014 22:36, 4.4 KBait, otvetov: 1)
Otvet #31 : Segodnya v 17:51:20
\\\Vy ne ukazali v kakoi ISO.\\\
\\\Dlya Rishi
eto neobyazatel'no. On proiznes magicheskoe zaklinanie. \\\
\\\Skorost' raprostraneniya volny ne zavisit ot skorosti dvizheniya izluchatelya,
no estestvenno skladyvaetsya so skorost'yu dvizheniya nablyudatelya, a kak eshe mozhet byt'\\\
\\\Etogo dostatochno.\\\
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dlya teh kto ne zamechaet kraeugol'nyh protivorechii mogu podskazat',
- u relyativistov net sred, i sredy kak takovoi.
Slovo volna, i effekt Doplera, u nih
ne mozhet ispol'zovat'sya v principe.
Po prichine togo chto volna eto svoistvo sredy, a Effekt Doplera iznachal'no
avtorom byl priduman isklyuchitel'no dlya sred.
\\\Material iz Vikipedii svobodnoi enciklopedii
Effekt byl vpervye opisan Kristianom
Doplerom v 1842 godu.\\\
\\\Termin foton vveden himikom Gilbertom L'yuisom
v 1926 godu.
[9]
\\\
U relyativistov prostranstvo - pustoe, i v prostranstve dvizhutsya tol'ko
chasticy, kotorye i yavlyayutsya fotonami ili elektronami.
A v srede, kolebaniya
peredayutsya izmeneniem plotnosti sredy,
kotorymi yavlyayutsya naprimer volny, ili kolebaniya na granicah sred
ili vnutri takovyh, i vozmusheniya sred - opredelyayushih skorost'
rasprostraneniya v sredah pri nalichii uslovii dlya sred -
sredy dolzhny obladat' plotnost'yu, pri neposredstvennom kontakte
chastic sred mezhdu soboi.
Sobstvenno
izluchenie chastic v dvizhenii ne mozhet byt' odnovremenno
konstantoi pri izluchenii v napravlenii dvizheniya dazhe v pustote,
ibo ona koordinatno mozhet markirovat'sya
prostym raspyleniem
kakih-to krasitelei naprimer, kotorye budut nahoditsya v pustoi
pustote v stabil'no ustoichivom sostoyanii, na kotoruyu v pustote
dazhe drugie
tela svoim prityazheniem ne smogut povliyat' v silu ochen'
nizkoi udel'noi plotnosti krasitelya, kotoryi iz sebya v prostranstve
predstavlyaet atomarnuyu pyl'.
Sobstvenno
esli razmer etoi pyli podobrat' s dlinnoi volny, chtoby etu
pyl' vrashalo v prostranstve, i chasticy pyli obladali otrazhayushei
sposobnost'yu, to logichno budet vysokoskorostnymi
kamerami teoreticheski
nablyudat' izmenenie ugla otrazheniya skoplenii pyli na rezonansnyh
dlya pyli garmonikah pri vneshnih napravlennyh vozdeistviyah kotorye
mogut
byt' markerami.
No eto kak by logichno bylo by no na praktike eto ne logichno,
po krainei mere opyt prostoi i deshevyi, i kosmose na orbite, etu erundu
mozhno
realizovat' bez osobyh trudnostei,
pryamo vozle mezhdunarodnoi stancii mozhno stolby v prostranstvo iz ballonchika
s kraskoi raspylit' i posmotret' chto s nimi budet
dal'she.
Kak govoritsya opyt logichno razdelit' na dve chasti, - raspylit' v prostranstve
krasochnye stolby, posle etogo vtoroi opyt,
istochnik vozbuzhdaet
svoim vozdeistviem krasochnye stolby,
a so storony prosto yavno budet vidno s kakoi skorost'yu i po
otnosheniyu k chemu.
- Re[2]: Chernaya dyra
(Evgen'evna L'vovyanka,
27.10.2014 14:10, 64 Bait)
ya ne doveryayu hokkingu www.tomas-morr.livejournal.com
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
14.10.2014 22:13, 2.7 KBait)
Sobstvenno ne mogu ponyat' pochemu ne berut Hokkinga za roga
i ne uglublyayut ego intellektual'no rylom v grunt, na fone ego
neskladushek i fu f lyzhnyh opredelenii
chernyh dyr.
Chego ego ne sprosyat, - chto est' chernye dyry?, - esli on sol'et
vodu, to logichno ego i poslat' v peshee eroticheskoe puteshestvie
s ego opredeleniyami
chernyh dyr.
Prosto logichno postavit' vopros rebrom o "dude" i poluchit' otvet,
chtoby ne zvezdet' v stile Dmitriya Vibe chto mol tol'ko avtor
mozhet
obsuzhdat' svoi idei, i eto chastichno
pravil'no, fanaty chernyh dyr ili bol'shogo vzryva, mogut dudet'
tol'ko v ramkah otvedennyh avtorom chernyh dyr ili avtorom bol'shogo
vzryva,
no somnevat'sya v "dude" uzhe ne mogut.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #74 : Segodnya v 16:39:21
poslednii
moment, pri podlete k gorizontu, dolzhen uvidet' chto eta dyra bystro
isparyaetsya, za sekundy on dolzhen uvidet' vse 10^66 let sushestvovaniya eto
dyry. Inache u nas budet al'ternativnaya real'nost', zavisyashaya ot
nablyudatelya.
Izluchenie
Unru nablyudaetsya v uskorennoi SO, no ne nablyudaetsya v ISO. Vozmozhno,
izluchenie Hokinga nablyudaetsya staticheskim nablyudatelem, no ne
nablyudaetsya svobodno padayushim radial'no nablyudatelem .
, i na samom dele, kosmonavt ne upadet v singulyarnost', a uvidit
kak ChD isparilas', pri podlete k gorizontu..
 http://ufn.ru/ru/articles/2001/3/e/
http://ufn.ru/ru/articles/2001/3/e/
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.10.2014 15:26, 4.5 KBait)
Otvet #208 : Segodnya v 09:57:48
\\\A
kak obnaruzhili ChD, dopustim, v nashei Galaktike?
Da po strannomu
vrasheniyu zvezd s ogromnoi uglovoi
skorost'yu. Vot v kakuyu storonu zvezdy
vrashayutsya, tuda
i ChD vrashaetsya. Ne naoborot zhe?\\\
\\\Privedite, pozhaluista, dlya yasnosti orbity etih zvezd i pokazhite,
v kakuyu storonu
dolzhna vrashat'sya chernaya dyra.\\\
\\\Da, potomu chto energeticheski ChD nesoizmerimo prevoshodit
vsya
Galaktiku po momentu.\\\
\\\Pozhaluista, proillyustriruite eto utverzhdenie chislami.\\\
\\\Poka Vy etogo ne sdelaete, v etu temu ne pishite
bol'she nichego.\\\
---
Otvet #209 : Segodnya v 10:10:38
\\\Avtor:
Dmitrii Vibe
: Segodnya v 09:57:48 Citata Pozhaluista, proillyustriruite
eto utverzhdenie chislami.
Poka Vy etogo ne sdelaete, v etu temu ne pishite
bol'she nichego.\\\
\\\Ponyato! Znachit budu vychislyat'!\\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ai da Vibe, ai da krassava, on menya raduet vse
bol'she, yavno nablyudaetsya ego progressivnoe
dvizhenie v napravlenii idiotizma.
Ya vot dumayu chto u nego uzhe vozrastnye bolezni
nachinayutsya.
Sobstvenno adekvatnyi yuzer poprosil by dat'
opredeleniya sushnostei i na etom bylo by dostatochno,
no po skol'ku vsya teoreticheskaya kosmologiya uzhe v neadekvate,
po prichine otsutstviya u nih adekvatnyh bazovyh opredelenii,
togo chto oni obsuzhdayut, i chto oni v itoge obsuzhdayut?.
I v etoi situacii uzhe tak skazat'
vershinoi idiotizma mozhet byt' trebovanie k uchastnikam
diskussii ispol'zuyushih neadekvatnye fizicheskie sushnosti,
formalizovat' ih kolichestvenno po otnosheniyu k neopisannym
nikem vydumannym fizicheskim svoistvam.
Sobstvenno eto kak kak batareikoi krona kosnut'sya yazyka
i poprosit' eto opisat' matematicheski. Glupost' v tom
chto nel'zya kasat'sya batareikoi krona yazyka v principe.
Tak i v teoreticheskoi kosmologii nikak ne razduplyatsya chto
u nih osnovnaya trudnost' otsutstvie adekvatnyh
opredelenii,
i uzhe potom do lampochki i bessmyslenno primenenie
lyubyh matematicheskih opisanii k etoi botve.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.10.2014 15:43, 585 Bait)
Po bol'shomu schetu dostatochno stranno chto Vibe tak skazat'
stanovitsya ballastom, on vsegda ran'she soznatel'no oblamyval diskusii,
no v dannom sluchai neosoznanno,
diskussii nanosit pryamoi vred.
Po bol'shomu schetu Vibe snizhaet moe mnenie o vozraste v nauchnom
kollektive.
Sobstvenno v takom vozraste (kak u
Vibe) uzhe nel'zya rukovodit' nauchnym
kollektivom, mozhno byt' tol'ko ryadovym sotrudnikom, a eshe cherez
tri goda, uzhe nel'zya byt' dazhe ryadovym sotrudnikom, a mozhno
tol'ko
zanimat'sya voprosami logistiki i snabzheniya - i tak do pensii.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
27.10.2014 21:55, 580 Bait)
Vy sluchaino ne pereputali baletnyi ili myl'no sereal'nyi forum,
s kosmologicheskim forumom?, - na kosmologicheskom forume,
podobnye utverzhdeniya nachinayutsya ne so slov
"ne doveryayu"
- , a so slov
- mogu obosnovat' v chem ne prav takoi-to v svoih ideyah, i po takim-to
prichinam.
I dal'she v stile
- est' bazovye opredeleniya togo-to. -
1 Oni pri izmereniyah v ramkah avtorskih opredelenii takih-to.
2 Opredeleniya izmerenii takie-to.
3 Po rezul'tatam
priborov takih-to,
i metodik takih-to, poluchaetsya vot takaya botva.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.10.2014 13:15, 4.1 KBait)

Otvet #109 : Segodnya v 01:48:51
\\\Kogda v nachale uchebnogo goda prepodavatel' ves' semestr
nam rasskazyvaet
odno,
a vo vtorom polugodie govorit - a teper', druz'ya moi, zabud'te
vse to o chem ya vam
govoril v proshlom semestre, my nachinaem izuchat' novoe
po novomu.. Eto oznachaet
lish' odno - povtorenie mama ucheniya - bolee
uglublennyi kurs obucheniya togo zhe
teoreticheskogo materiala. Vot i ta
prekrasnaya vozmozhnost' vnedrit' te novshestva
fundamental'noi nauki v
dopolneniyah v svete poslednih nauchnyh otkrytyi ili
malen'kih, no ves'ma
znachimyh dopolneniyah. Da i kosmologii ran'she ne bylo.
Tut ya s vami
polnost'yu soglasna. \\\
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A Geral'dinka prava,
tol'ko mnogie dazhe ne dogadyvayutsya
na skol'ko sil'no ona prava.
Posle sleduyushego moego teksta kosmologiya okazalas'
v polnoi abstrakcii, vse ee knigi za poslednie
90 let
sluchaino prevratilis' v makulaturu.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-Dlya sushestvovaniya effekta Doplera, est' prichina - sreda i ee svoistva.
Dazhe esli ispol'zuetsya metod izmereniya dlya sred, a govoritsya
chto
vokrug pustota, to propadaet
prichinnost' vozniknoveniya dannogo
effekta kak svoistva prostranstva.
U relyativistov ne prostranstvo vystupaet v kachestve linii zaderzhki
signala, a vystupaet
- foton, kak dvizhushiisya ob'ekt, u kotorogo
ogranichena skorost' dvizheniya v pustote, po ne ponyatnoi prichine -
kotoraya
postuliruetsya bez ob'yasneniya prichiny. Foton
v dannom sluchai
mozhet byt' tol'ko chasticei, - eto ne vozmozhno po prichine togo chto
chastica ne mozhet snizhat' i uvelichivat' svoyu
skorost' chto
nablyudaetsya naprimer
pri dvizhenii sveta naprimer v vozduhe, potom
cherez steklo potom opyat' v vozduhe i potom v vakuum, tak kak
poluchaetsya chto v stekle letit foton medlennee chem v vozduhe
i
vakuume , a vyletaya iz stekla foton uvelichivaet svoyu skorost'. Tak
vot ne mozhet chastica
kotoraya poteryala skorost', prosto tak vzyat' i
pri vylete iz stekla
uvelichit' skorost', - na podobnoe sposobny
tol'ko kolebaniya sredy v sredah s raznymi svoistvami.
Tak chto foton
kak chastica - vydumka chistoi vody.
Vyvod -
v prostranstve rasprostranyayutsya kolebaniya sredy, i svetovoe
izluchenie ne dvizhetsya a obrazuetsya ot vzaimodeistviya kolebanii
sredy i materiala, kak v 1800 godu govoril
Tomas Yung.
Tak chto vse chto napisano v astrofizike bez ucheta sredy - k
sozhaleniyu ne pravil'no.
Eto podarok Dmitriyu Vibe, eto ne budet opublikovano dva
tri goda.
Dmitrii Vibe mozhet i dal'she uchit' studentov tomu chto bezvozvratno
ustarelo, i tomu chto im nikogda ne prigoditsya.
Tak uzh Dmitrii Vibe zapreshal obsuzhdat'
efir poka ego ne dokazhut chto on est',
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sobstvenno mne tozhe publikovat' eto v kakom-to
referiruemom zhurnale vryad-li dadut.
Da i pri obshenie na forume s Dmitriem Vibe - on mne
zayavil
chto ego lekciya osnovannaya na chuzhih ideyah - eto ego
intellektual'nyi trud. I ya naprimer ne hochu chtoby moi
idei chitali studentam byvshie mahrovye relyativisty.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
28.10.2014 13:40, 1.1 KBait)
A opyt ochen' prostoi, beretsya steklyannaya butylka,
i v nei sozdaetsya vakuum.
Posvetiv skvoz' etu steklyannuyu butylku lazernym
luchom ochen' prosto slovo -
foton - stanovitsya nenauchnym
terminom.
Letit luch v vozduhe, ego skorost' men'she chem v vakuume,
vletaet v steklo - i v stekle snizhaet skorost', potom
vletaet vo vnutrennii vakuum butylki - pravil'no - povyshaet
svoyu skorost' na maksimum, potom vletaet v steklo, snizhaet
svoyu skorost' v stekle, vyletaet iz stekla
v vozduh - povyshaet
skorost' do skorosti sveta v vozduhe.
Sobstvenno etot opyt mozhno proverit' na analoge,
mozhno vzyat' nalit' vody v bol'shoi zheleznyi
bak .
I skvoz' bak s vodoi propuskaem - pravil'no zvukovoi impul's ili kolebaniya,
i izmeryaem skorost' zvuka v vozduhe potom v stenke baka potom v vode,
potom opyat' v stenke baka potom opyat' v vozduhe - o chudo,
vse pohozhe kak v butylke s vakuumom.
Eto ne chudo eto nelogichnost' relyativizma ne prakticheskih opytah.
Tak chto lichno ya bol'she sotni knig po astronomii i kosmologii,
paru let nazad, vybrosil v musor.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
31.10.2014 21:25, 52 Bait)
Uvazhaemye al'ty i relyativisty - vse budet normal'no.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
9.11.2014 15:07, 1.9 KBait)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ya azh smeyalsya, ochen' ponravilos',
ya by dazhe
skazal chto eto obsuzhdenie yarkii primer togo kak
mozhno relyativistov zagonyat' v ugol po lyubym voprosam.
Pol'zuyas' tem, chto v kosmologii otsutstvuyut adekvatnye
i otsutstvuyut bazovye opredeleniya poluchaetsya chto,
esli stavit' vopros po sostavlyayushim fizicheskim
sushnostyam iz kotoryh sostoyat teorii to relyativisty
budut slivat' vodu po zadannym chastnym voprosam i budut
postoyanno
vse vmeste i kazhdyi po otdel'nosti stavit' podpisi
o svoei nekompetentnosti v dannom voprose.
Ya dazhe bol'she chem uveren chto relyativisty ne budut na konferenciyah
rassmatrivat'
situacii pri kotoryh oni na etih konferenciyah sozdadut
edinstvenno pravil'nye s tochki zreniya relyativizma opredeleniya sostavlyayushih
raznyh teorii, po toi prichine chto eto nikto ne oplatit.
Esli vdrug oni soobrazyat i smogut sdelat' bazovye opredeleniya
u nih nachnetsya vtoroi bolee trudnyi sluchai - bazovye opredeleniya vozmozhno
budut protivorechit' so zdravym smyslom vnutri teorii
= paradoks.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
9.11.2014 15:26, 1.0 KBait)
Sobstvenno logichno chto relyativisty sol'yut vodu
na sleduyushie voprosy.
Kakoe pravil'noe opredelenie prostranstva?
Bazovoe opredelenie chernoi dyry?
Bazovoe
opredelenie fotona?
Chto v prostranstve proishodit, letyat fotony v pustote?, ili kolebletsya svetonosnaya sreda?
Bazovyi opyt i vytekayushie iz nego opredeleniya - elektrona?
Eto primitivnye voprosy bez otvetov na kotorye uzhe ne vozmozhno
dazhe priblizitsya k osnovnomu voprosu -
pochemu zvezdy svetyat a kosmos holodnyi?
Ya sobstvenno
dazhe ne ponimayu pochemu kosmologi ne stavyat pered soboi
osnovnyh zadach i celei v vide voprosov - na kotorye dolzhny byt'
napravlenny vse tak skazat' intellektual'nye
resursy.
Stroyat teleskopy odin bol'she drugogo, i tolku, i chto dal'she,
eshe bol'shii teleskop stroit', a potom eshe bol'shii, a potom
eshe bol'shii i tak bez
konca i kraya. Kak po mne eto strannaya
obshestroitel'naya astronomiya, kogda za stroitel'stvom i nablyudeniyami
dumat' nad nablyudaemym i nekomu i nekogda.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
10.11.2014 20:32, 11.5 KBait)
Otvet #800 : Segodnya v 15:22:38
V kakom smysle?
Naverno nuzhno vzyat' dva istochnika sveta,na rasstoyanii
600 000 km.,vklyuchit' ih
i pri vstreche luchei,posmotret',budut li eti fotony razdelat'sya v raznye storony,pri stolknovenii.
Vopros ya polnost'yu ne ponyal,utochnite.
Ne
dva istochnika sveta, a dva fotona, letyashih "vniz" i "vverh" navstrechu
drug drugu po osi 0h (so smesheniem po osi 0y i bez smesheniya).
imho:
Vy sami naprosilis' na etot vopros, za yazyk nikto ne tyanul 

Zapisan
Vvesti kvant
deistviya v kosmologiyu i gravitaciyu stoilo mne nemalyh trudov. Nekotorye
iz moih znakomyh usmatrivali v etom svoego roda tragediyu. No VimanaPro
byl drugogo mneniya ob etom ... Ved' teper' on tochno znaet, chto kvant
deistviya igraet gorazdo bol'shuyu rol', chem byl sklonen schitat' vnachale




-

- Soobshenii: 306
- Reiting: +4/-3
- Mne nravitsya etot forum!
-
Otvet #801 : Segodnya v 15:36:33
Horosho !
Esli foton vzaimodeistvuet gravitacionno,to ot etogo on mozhet ,veroyatno,
zamedlyat' svoyu skorost'.
A
mezhdu fotonami - ne uspevaet,tak kak proletaya ,po otnosheniyu chego-to
nepodvizhnogo,skorost' budet svetovoi,a mezhdu drug drugom,skorost' budet
vyshe.

Zapisan





-

- Soobshenii: 2 587
- Reiting: +43/-3
- LUChShI' LEMMING FORUMA :)
-
Otvet #802 : Segodnya v 17:51:11
Poka takih ustroistv net s gravitaciei mozhno rezvit'sya vsyakomu na svoi
maner,

Vot kak. Yasno. T.e. "pravil'nogo otveta"
poka net v principe.
A
vot eshe odin interesnyi dlya mene vopros. Energiya kotoraya v materii, nu
tam, energiya chastic vsyakih, i energiya hm... skazhem tak,
elektromagnitnaya, eto odnoi prirody energiya ili net. Nu i estestvenno
voobshe. Vsya ta energiya, kotoruyu ispol'zuyut v fizike, kineticheskaya,
potencial'naya, elektricheskaya i voobshe vsya. Eto vse sut' odna i ta zhe
energiya ili kak?


Zapisan
tchk





-

- Soobshenii: 2 587
- Reiting: +43/-3
- LUChShI' LEMMING FORUMA :)
-
Otvet #804 : Segodnya v 20:58:32
Chota u menya shas takoe chuvstvo vozniklo, kak budto stoyu na krayu vselennoi spinoi k centru i smotryu v dal'.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
10.11.2014 20:40, 715 Bait)
Otvet #804 : Segodnya v 20:58:32
\\\Chota u menya shas takoe chuvstvo vozniklo,
kak budto stoyu na krayu vselennoi
spinoi k centru i smotryu v dal'.\\\
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Eto kak est' ili net, nuzhen ili ne nuzhen zaryad u elektrona,
kotoryi tipa u relyativistov i est' nositel' energii, bez bazovyh
privyazok fizicheskih opredelenii
mezhdu elektricheskim tokom
i elektronom kak chasticei. Mne azh stydno pisat' etu botvu.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
10.11.2014 20:53, 555 Bait)
Ya ne ponimayu chto dumayut Dmitrii Vibe i
Sergei Popov - oni kak professora dumayut chto na prostye i trudnye
voprosy budut v kosmologii dumat' i otvechat' kuharka
Ksyusha
i zavhoz Evgenii, potomu chto oni svoi professorskie zvaniya po astrofizike
ispol'zuyut dlya polucheniya blag a ne dlya vozlozheniya na sebya otvetstvennosti
v
prinyatii hot' kakih to reshenii na vopros - chto vot to-to ne logichno,
i eto naprimer trebuet deneg dlya resheniya, hot' i rezul'tat budet plohoi
dlya teorii , no eto
polozhitel'nyi rezul'tat dlya teoretikov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
17.11.2014 21:03, 2.4 KBait)
Detskii sad slegka povzroslev pod napryagsya intellektual'no i
s gorstkoi intellektual'nogo peska v ruke nachali im brosat'sya
na svoi umstvennye trudnosti.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Otvet #1121 : 12.11.2014 [08:03:53]

Kommentarii
moderatora razdela Ya
preduprezhdayu v poslednii raz. Tema nazyvaetsya "Fakty, stavyashie
pod
somnenie teoriyu Bol'shogo Vzryva". Ona ne nazyvaetsya "Ya ne ponimayu
teoriyu
Bol'shogo Vzryva" ili "Ob'yasnite mne teoriyu Bol'shogo vzryva".
Soobsheniya,
ne otnosyashiesya k obsuzhdaemoi teme, budut udalyat'sya bez
dopolnitel'nyh
poyasnenii.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Eshe raz namekayu chto chtoby sporit' o nekotorom
fizicheskom svoistve, ili nekotoroi
fizicheskoi sushnosti, to logichno sperva opredelit'sya - o chem zvezdet', i opredelitsya
luchshe maksimal'no odnoznachno, bez logicheskih
vetvlenii i obratnyh polozhitel'nyh,
obratnyh otricatel'nyh svyazei i bez uslovnyh perehodov i otlozhennyh vo vremeni situacii,
ya ne budu ob'yasnyat' chto vse chto ya
perechislil vklyuchaet v sebya i spekulyacii, i inflyacii,
i singulyarnosti - ibo eto i konyu ponyatno.
Vyvod - itogo - esli naprimer hotite povumnichat' o bol'shom
vzryve ili bol'shom
babahe, to sperva nado otkryt' temu -
-
"Ob'yasnite nachinayushemu,
yunomu kosmologu chto takoe - bol'shoi babah ili bol'shoi vryv?"
"Posle togo kak ya prochtu Vashi opredeleniya u menya vozmozhno poyavyatsya voprosy,
- budu kraine lyubezen znat' mneniya vedushih specialistov v dannom voprose,
i
nadeyus' na ih otvet po teme."
-
I vse posle etogo zavalit' vsyu temu na nelogichnyh bazovyh opredeleniyah
smozhet dazhe student. Tol'ko tolku ot togo
chto zadumyvat'sya na ideyami
poluvekovoi davnosti - lichno mne dazhe grustno.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(Albert Timashov,
20.11.2014 0:03, 826 Bait)
Chernaya dyra, nalichie nevidimogo ob'ekta massy bol'shoi plotnosti , harakterizuet ego sil'noe gravitacionnoe pole.Tol'ko po soputsvuyushim priznakamgravitacii s drugimi ob'ektami,
mozhno opredelit' koordinty mesta ego polozheniya vo Vselennoi, priblizitel'nye razmery i massu. On ne izluchaet i ne otrazhaet lyubye vidy energii, chto ob'yasnyaet ego polnuyu nepozrachnost'
dlya pryamolineinyh potokov NE'TRINO, nositelei vseh elektromagnitnyh i drugih izluchenii. Dlya svedeniya, pryamolineinye silovye potoki NE'TRINO sostavlyayut silovuyu sistemu energeticheskoi
sredy - Edinogo silovogo polya Vselennoi, universal'nogo mehanizma formirovaniya i vzaimodeistviya razlichnyh vidov materii i energii - ciklichnyh fizicheskih processov (sintez,
raspad,sintez...) v mikro- i makro-mire.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
20.11.2014 20:18, 527 Bait)
Kakto vecherom hot' kto vdrug skazal
-ogo, ne ogo a ago, nu i chto a prosto tak,
i nikto, i ni-ochem, dazhe bez opredelenii, bez
upominaniya vot teh kto pridumal terminy.
I v poniman'ya ne imeya chto pridumke byla
pervoprichina i v itoge miksirovki nablyudaem
izliyan'e mozgovoe ochen' srochnoi erundy.
Ibo ekstrenno tak nado neponyatno dlya chego
mysl' bredyatiny vnesti da na forum na kotorom
v pyl' i puh vse smeteno tol'ko, mosk netoroplivyi
zdes' by ponyal vse davno. Tol'ko v speshke
ekstrennosti proletayut zdes' use.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
24.11.2014 19:53, 80 Bait)
17
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A.P. Vasi,
25.12.2015 20:10, 2.5 KBait)
Otvet #94 : Segodnya v 01:04:38
yisnep, vy ne mogli by svoe mnenie ozvuchit': chemu ravna pervaya kosmicheskaya
skorost' na 1,5Rg?
Ya izvinyayus', no nazvanie "fotonnaya sfera" Vam ni o chem ne govorit?
I
ya predlagayu otkazat'sya ot etoi durackoi tradicii numeracii "kosmicheskih
skorostei". Est' orbital'naya skorost' (na krugovoi orbite), est'
skorost' ubeganiya. Est' ierarhiya "gravitacionnogo vliyaniya"... (A v obshem
sluchae, eta ierarhiya eshe mozhet zaviset' ot togo kakuyu iz skorostei
smotrim).
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(A. V. Postnikov,
23.02.2016 6:02, 93 Bait)
ya dumayu chto chernyh dyr ne sushestvuet i na eto est' dokazatel'stvonashih fizikov v kosmose
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(R. M. Noev,
13.06.2016 23:08, 1.6 KBait)
Kogda stat'ya nachinaetsya takimi perlami, kak "..., ibo v prirode nichto ne mozhet dvigat'sya so skorost'yu, bol'shei skorosti sveta ...","vremya techet ...",
i t.p. smes'yu nahal'stva i shamanskogo slovobludiya,dal'neishee vser'ezuzhe ne vosprinimaetsya, i chitaetsya vpol-glaza, chto nazyvaetsya, "po diagonali".
Vsya eta
naukoobraznaya galimat'ya, peresypannaya ssylkami tona STO, to na OTO - v zavisimosti ot trebovanii "tekushego abzaca" ; )- i sovershenno zabyvayushaya, tochnee- plyuyushaya
na to, chto STO i OTO protivorechat drug drugu na FUNDAMENTAL'NOM UROVNE(STO OTRICAET nalichie "absolyutnoi sistemy otscheta", OTO zhe, so svoim "iskrivleniem prostranstva",
baziruetsya IMENNO NA takoi "absolyutnoi sisteme", i ne schitavshayasya zavershennoi dazhe samim (ili samym - komu kak bol'she nravitsya) znamenitym plagiatorom ot fiziki
- ee avtorom,kotoryi, okazavshis' v nauchnom tupike, pytalsya lepetat' chto-to,chto "nasha nesposobnost' vydelit' efir v kakoi-libo inercial'noi sisteme otscheta, idazhe STO(t.e.
ego "nauchnyi pervenec"-mutant) -eshe nedostatochny dlya togo, chtobyotvergnut' efir." I takie ego passazhi nemudreny - ved' ego t.n. "Obshaya teoriya otnositel'nosti"bazirutsya
imenno naedinoi, t.e. po-suti - absolyutnoi, hotya i "iskrivlennoi" im, sisteme otscheta.
I stanovitsya grustno ot togo, chto s razvalom v strane edinoi sistemy
obrazovaniya, zelenyi svet v "nezavisimoi Rossii" poluchili lyubye naukoobraznye bredni, vydavaemye ih avtorami, razumeetsya, za absolyutnye istiny.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(R. M. Noev,
13.06.2016 23:28, 1.9 KBait)
Dubl' vtoroi (v kotorom ispravleny dosadnye ochepyatki)) .
Kogda stat'ya nachinaetsya takimi perlami, kak "..., ibo v prirode nichto ne mozhet dvigat'sya
so skorost'yu, bol'shei skorosti sveta ...","vremya techet ...", i t.p. smes'yu nahal'stva i shamanskogo slovobludiya, dal'neishee vser'ez uzhe ne vosprinimaetsya, i
chitaetsya vpol-glaza, chto nazyvaetsya, "po-diagonali".
A voobshe, vsya eta naukoobraznaya galimat'ya, peresypannaya ssylkami to na STO, to na OTO - v zavisimosti
ot trebovanii "tekushego abzaca" ; ) - i sovershenno zabyvayushaya, tochnee - plyuyushaya na to, chto STO i OTOPROTIVOREChAT drug drugu na FUNDAMENTAL'NOM UROVNE (kak izvestno,
STO OTRICAET nalichie "absolyutnoi sistemy otscheta", OTO zhe, so svoim "iskrivleniem prostranstva", baziruetsya IMENNO NA takoi absolyutnoi sisteme "krivogo
prostranstva", i ne schitavshayasya zavershennoi dazhe samim (ili samym - komu kak bol'she nravitsya !) ee znamenitym avtorom - plagiatorom ot fiziki "vseh vremen i narodov",
kotoryi, kstati, okazavshis' v sem nauchnom tupike, pytalsya lepetat', chto, mol,"nasha nesposobnost' vydelit' efir v kakoi-libo inercial'noi sisteme otscheta, i dazheteoriya
otnositel'nosti(t.e. STO - ego "nauchnyi pervenec"-mutant) - eshe nedostatochny dlya togo, chtobyotvergnut' efir." I takie ego passazhi nemudreny - ved' ego t.n.
"Obshaya teoriya otnositel'nosti"bazirutsya imenno naedinoi, t.e. po-suti - absolyutnoi, hotya i "iskrivlennoi" im, sisteme otscheta.
I stanovitsya grustno
ot togo, chto s razvalom v strane edinoi sistemy obrazovaniya, zelenyi svet v "nezavisimoi Rossii" poluchili lyubye naukoobraznye bredni, podobnye dannoi stat'e, vydavaemye
ih avtorami, razumeetsya, za absolyutnye istiny.
-------------------------------------------
Ssylki:
Obshaya informaciya - sait i stat'i Sergeya Fedosina i ego
soavtorov.
- Re: Chernaya dyra
(R. M. Noev,
17.05.2017 18:56, 449 Bait)
Bolee togo, v prodolzhenie temy "nauchnoi" i "chernoi" dYryyyyyy :
britanskie astrofiziki obnaruzhili neitronnuyu zvezdu s massoi v .... 40 Ms !
Chto
eto oznachaet ?
Eto oznachaet tol'ko odno - ili oni absolyutno bezgramotny, ili teoriya obrazovaniya "nauchnyh" "dyr" stradaet bol'shimi nedostatkami, ne
uchityvayushimi REAL'NYE fizicheskie zakony, dalekie ot uproshencheskih matematicheskih modelei.









 S moei tochki zreniya osnovnaya trudnost' v fizike
- nalichie v nei geniev, po prichine togo chto krome
geniev v fizike mogut byt' nedoumki i difektivnye,
i nedogenii.
Grubo govorya fiziki delyatsya na dva osnovnyh klassa
genii i nedoumki, srednego ne dano.
Po skol'ku geniev edinicy - to vse vospityvayutsya v stile
nedoumkov, v principe ne sposobnyh svoimi slovami otvetit'
na voprosy po fizike, po skol'ku svoi mysli schitayut
myslyami nedoumkov, i sovetuyut pochitat' knizhki
geniev s ih tochki zreniya. Pri obshenii fizikov to i proishodit
vzaimoposylanie chitat' knizhki.
Vot takaya zhestokaya selyavi.
S moei tochki zreniya osnovnaya trudnost' v fizike
- nalichie v nei geniev, po prichine togo chto krome
geniev v fizike mogut byt' nedoumki i difektivnye,
i nedogenii.
Grubo govorya fiziki delyatsya na dva osnovnyh klassa
genii i nedoumki, srednego ne dano.
Po skol'ku geniev edinicy - to vse vospityvayutsya v stile
nedoumkov, v principe ne sposobnyh svoimi slovami otvetit'
na voprosy po fizike, po skol'ku svoi mysli schitayut
myslyami nedoumkov, i sovetuyut pochitat' knizhki
geniev s ih tochki zreniya. Pri obshenii fizikov to i proishodit
vzaimoposylanie chitat' knizhki.
Vot takaya zhestokaya selyavi.

 Posmotrel fil'm ponravilsya, kak-by
Posmotrel fil'm ponravilsya, kak-by 



 , N
, N ,
,
 , Hel. Kruzhkami otmecheny
linii, obrazuyushiesya
, Hel. Kruzhkami otmecheny
linii, obrazuyushiesya 













 Mozhno i v teleskop.
Mozhno i v teleskop. 


 , gde
, gde 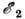 i
i  -
energii verhnego vozbuzhdennogo i nizhnego (obychno osnovnogo) urovnei
energii atoma. R. n. vpervye obnaruzheno v 1904 R. Vudom (R. Wood) v
parah natriya.
-
energii verhnego vozbuzhdennogo i nizhnego (obychno osnovnogo) urovnei
energii atoma. R. n. vpervye obnaruzheno v 1904 R. Vudom (R. Wood) v
parah natriya.
 Kommentarii
moderatora razdela
Kommentarii
moderatora razdela 







 Na
rasstoyanii signaly zatuhayut. Eta istina spravedliva i dlya
elektricheskih, i dlya opticheskih kommunikacionnyh linii. Razumeetsya, v
sluchae opticheskih setei rasstoyaniya, na kotoryh eto nachinaet proyavlyat'sya,
bol'she, odnako problemy po-prezhnemu sushestvuyut.
Na
rasstoyanii signaly zatuhayut. Eta istina spravedliva i dlya
elektricheskih, i dlya opticheskih kommunikacionnyh linii. Razumeetsya, v
sluchae opticheskih setei rasstoyaniya, na kotoryh eto nachinaet proyavlyat'sya,
bol'she, odnako problemy po-prezhnemu sushestvuyut.




































































































 Kandidaty v gravitacionnye linzy imeyut neocenimoe
znachenie dlya ocenki massy galaktik kvazarov.
Kandidaty v gravitacionnye linzy imeyut neocenimoe
znachenie dlya ocenki massy galaktik kvazarov.  Go to image download page
Go to image download page
 , gde\\\
, gde\\\
 Kl.\\\
Kl.\\\




 Golosovanie
Golosovanie

 Zapisan
Zapisan

 , obratites' k Chandrasekaru!
, obratites' k Chandrasekaru!










 ili tripletnymi
ili tripletnymi  . Tipichnoe
. Tipichnoe


 . Pri pogloshenii sveta molekula perehodit v vozbuzhdennoe sostoyanie
. Pri pogloshenii sveta molekula perehodit v vozbuzhdennoe sostoyanie  .
Pri vozbuzhdenii na vysshie elektronnye i kolebatel'nye urovni izbytok
energii bystro rashoduetsya, perevodya fluorofor na samyi nizhnii
kolebatel'nyi poduroven' sostoyaniya
.
Pri vozbuzhdenii na vysshie elektronnye i kolebatel'nye urovni izbytok
energii bystro rashoduetsya, perevodya fluorofor na samyi nizhnii
kolebatel'nyi poduroven' sostoyaniya 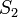 sostoyaniya.
sostoyaniya.
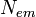 kolichestvo ispuskaemyh v rezul'tate fluorescencii
fotonov, a
kolichestvo ispuskaemyh v rezul'tate fluorescencii
fotonov, a 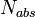 obshee kolichestvo pogloshaemyh fotonov. Chem
bol'she kvantovyi vyhod
obshee kolichestvo pogloshaemyh fotonov. Chem
bol'she kvantovyi vyhod  i
i 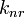 konstanty skorosti izluchatel'noi i bezyzluchatel'noi dezaktivacii vozbuzhdennogo sostoyaniya.
konstanty skorosti izluchatel'noi i bezyzluchatel'noi dezaktivacii vozbuzhdennogo sostoyaniya.
 esli
esli
 ,
to est' esli skorost' bezyzluchatel'nogo perehoda znachitel'no men'she
skorosti izluchatel'nogo perehoda. Otmetim, chto kvantovyi vyhod vsegda
men'she edinicy iz-za
,
to est' esli skorost' bezyzluchatel'nogo perehoda znachitel'no men'she
skorosti izluchatel'nogo perehoda. Otmetim, chto kvantovyi vyhod vsegda
men'she edinicy iz-za 









 .
.











 \\\
\\\

 tochku zreniya nauki
tochku zreniya nauki 












 Do poslednego vremeni uchenye-fiziki so vsego mira otnosilis' ves'ma skepticheski k
Do poslednego vremeni uchenye-fiziki so vsego mira otnosilis' ves'ma skepticheski k 






