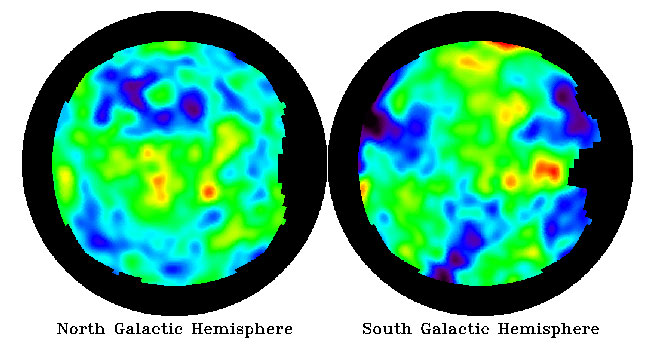
Explanation: These spots are the oldest, most distant structures known. They are seen on the above two images of the microwave sky, north and south of our galaxy's equator, based on four-year's worth of data from NASA's COsmic Background Explorer (COBE) satellite (1989-1993). The spots represent temperature variations in the early universe. As our universe expanded and cooled, conglomerations of mass formed. These COBE images confirmed that only a million years after the big-bang - which occurred roughly 15 billion years ago - parts of the universe were visibly hotter than other parts. By studying the size and distribution of the spots found on the microwave background, astronomers hope to learn what matter and processes caused the spots to form - and hence determine the composition, density, and future of our Universe. Results from recent measurements of the cosmic microwave background are consistent with a universe stranger than previously thought, possibly filled with unexpected forms of dark matter and dark energy. A more detailed analysis might result after NASA's Microwave Anisotropy Probe is launched in 2001.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
COBE - hotspots - cosmic microwave background radiation
Publikacii so slovami: COBE - hotspots - cosmic microwave background radiation | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |