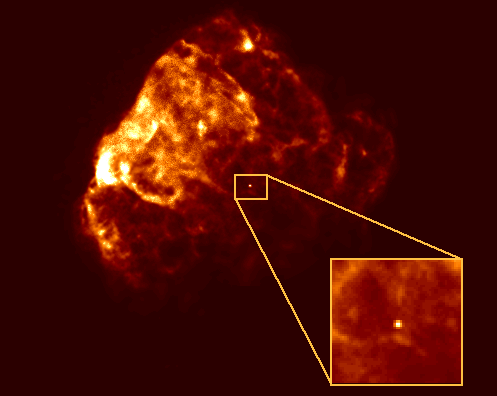
Explanation: A massive star ends life as a supernova, blasting its outer layers back to interstellar space. The spectacular death explosion is initiated by the collapse of what has become an impossibly dense stellar core. However, this core is not necessarily destroyed. Instead, it may be transformed into an exotic object with the density of an atomic nucleus but more total mass than the sun - a neutron star. Directly viewing a neutron star is difficult because it is small (roughly 10 miles in diameter) and therefore dim, but newly formed in this violent crucible it is intensely hot, glowing in X-rays. Images from the ROSAT X-ray observatory above may offer a premier view of such a recently formed neutron stars' X-ray glow. Pictured is the supernova remnant Puppis A, one of the brightest sources in the X-ray sky, with shocked gas clouds still expanding and radiating X-rays. In the inset close-up view, a faint pinpoint source of X-rays is visible which is most likely the young neutron star, kicked out by the asymmetric explosion and moving away from the site of the original supernova at about 600 miles per second.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
Sverhnovye - ostatok Sverhnovoi - neitronnye zvezdy - Evolyuciya zvezd - rentgenovskie luchi
Publikacii so slovami: Sverhnovye - ostatok Sverhnovoi - neitronnye zvezdy - Evolyuciya zvezd - rentgenovskie luchi | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |