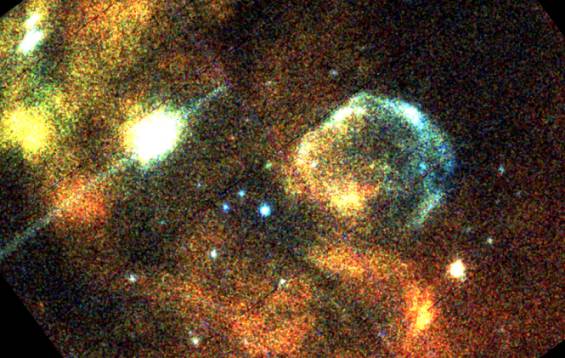Credit & Copyright: XMM Project,
ESA
Explanation:
Recently the European Space Agency released this and other
spectacular "first light" pictures from its new
orbiting x-ray observatory, christened
XMM-Newton.
A churning region of star birth and death
in our small neighboring galaxy, the
Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC),
this field was one of several
chosen to test out XMM-Newton's
x-ray imaging capabilities.
The picture is a false-colour one in which low energy x-rays
are translated to red, medium energy to green, and high energy
to blue.
Image colours therefore
represent the relative million degree
temperatures of the x-ray emitting regions, red being the coolest
and blue the hottest.
Remains of the star that exploded as
Supernova 1987a appear here
as the white x-ray source at the lower right, while another
supernova remnant,
cataloged as N157D is the brightest
source at the upper left.
The bluish arc (near center) also appears to be a
supernova remnant whose
expanding debris cloud is interacting with
the LMC's local interstellar gas.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
LMC - XMM-Newton - rentgenovskie nablyudeniya - Rentgenovskii teleskop - rentgenovskoe izluchenie - Bol'shoe Magellanovo Oblako - kosmicheskie observatorii
Publikacii so slovami: LMC - XMM-Newton - rentgenovskie nablyudeniya - Rentgenovskii teleskop - rentgenovskoe izluchenie - Bol'shoe Magellanovo Oblako - kosmicheskie observatorii | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |