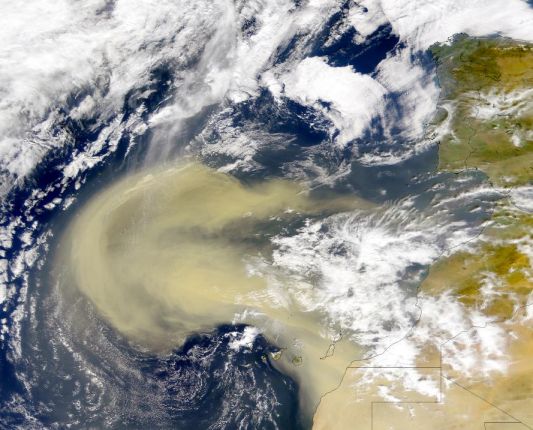
Explanation: From low Earth orbit, NASA's SeaWIFS instrument records ocean color, tracking changes in our water world's climate and biosphere. But even an ocean planet can have dust storms. On February 26th, SeaWIFS returned this dramatic close-up view of a vast, developing cloud of Saharan desert dust blowing from northwest Africa (lower right) a thousand miles or more out over the Atlantic Ocean. While there are indications that the planet-spanning effects of the Saharan dust events include the decline of the ecologies of coral reefs in the Caribbean and an increased frequency of Atlantic hurricanes, there is also evidence that the dust provides nutrients to the Amazonian rain forests. From space-based vantage points, other satellite images have also revealed storms which transport massive quantities of fine sand and dust across Earth's oceans.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
Earth - dust - storm - ocean - seawifs - dust storm - meteorologiya - meteorologicheskii sputnik - ekologiya
Publikacii so slovami: Earth - dust - storm - ocean - seawifs - dust storm - meteorologiya - meteorologicheskii sputnik - ekologiya | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |