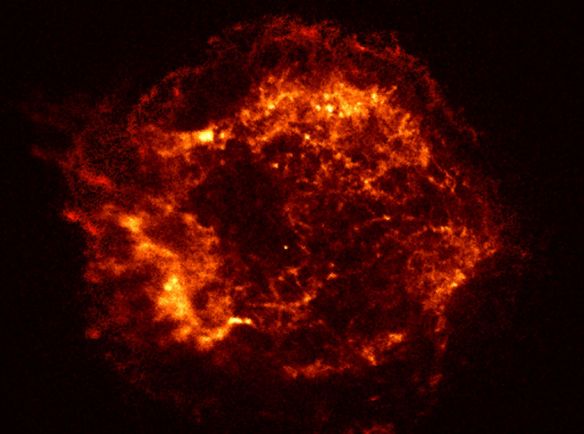
Explanation: Cosmic wreckage from the detonation of a massive star is the subject of this official first image from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. The supernova remnant, known as Cassiopeia A, was produced when a star exploded around 300 years ago in this northern sky constellation. It is revealed here in unprecedented detail in the light of X-rays - photons with thousands of times the energy of visible light. Shock waves expanding at 10 million miles-per-hour are seen to have heated this 10 light-year diameter bubble of stellar debris to X-ray emitting temperatures of 50 million kelvins. The tantalizing bright speck near the bubble's center could well be the dense, hot remnant of the stellar core collapsed to form a newborn neutron star. With this and other first light images, the Chandra Observatory is still undergoing check out operations in preparation for its much anticipated exploration of the X-ray sky. Chandra was launched aboard the space shuttle Columbia in July.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
Chandra - Cas A - supernova remnant - Rentgenovskii teleskop - rentgenovskoe izluchenie - ostatok Sverhnovoi - kosmicheskaya rentgenovskaya observatoriya - kosmicheskie observatorii
Publikacii so slovami: Chandra - Cas A - supernova remnant - Rentgenovskii teleskop - rentgenovskoe izluchenie - ostatok Sverhnovoi - kosmicheskaya rentgenovskaya observatoriya - kosmicheskie observatorii | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |