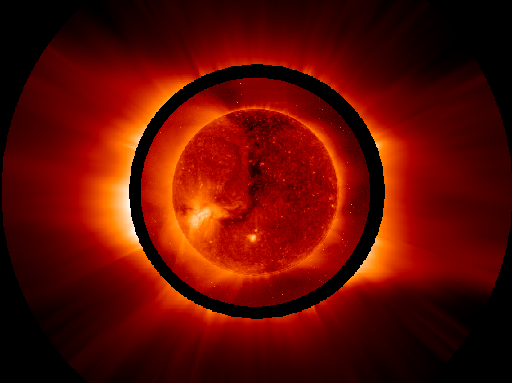
Explanation: A wind from the Sun blows through our Solar System. The behaviour of comet tails as they flapped and waved in this interplanetary breeze gave astronomers the first hint of its existence. Streaming outward at 250-400 miles/second, electrons and ions boiling off the Sun's incredibly hot but tenuous corona account for the Solar Wind - now known to affect the Earth and other planets along with voyaging spacecraft. Rooted in the Solar Magnetic Field, the structure of the corona is visible in this composite image from the EIT and UVCS instruments onboard the SOHO spacecraft, extending a million miles above the Sun's surface. The dark areas, known as coronal holes, represent the regions where the highest speed Solar Wind originates.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
Sun - wind - Solnechnyi veter - magnitnoe pole Solnca - Solnechnaya korona
Publikacii so slovami: Sun - wind - Solnechnyi veter - magnitnoe pole Solnca - Solnechnaya korona | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |