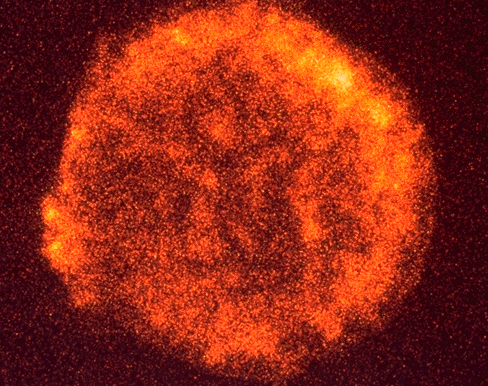
Explanation: How often do stars explode? By looking at external galaxies, astronomers can guess that these events, known as a supernovae, should occur about once every 30 years in a typical spiral galaxy like our MilkyWay. However, the obscuring gas and dust in the disk of our galaxy probably prevents us from seeing many galactic supernovae -- making observations of these events in our own galaxy relatively rare. In fact, in 1572, the revered Danish astronomer, Tycho Brahe, witnessed one of the last to be seen. The remnant of this explosion is still visible today as the shockwave it generated continues to expand into the gas and dust between the stars.Above is an image of the X-rays emitted by this shockwave made by a telescope onboard the ROSAT spacecraft. The nebula is known as Tycho's Supernova Remnant.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
nebula - molecular cloud - supernova remnant - supernova - tumannost' - Sverhnovye
Publikacii so slovami: nebula - molecular cloud - supernova remnant - supernova - tumannost' - Sverhnovye | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |