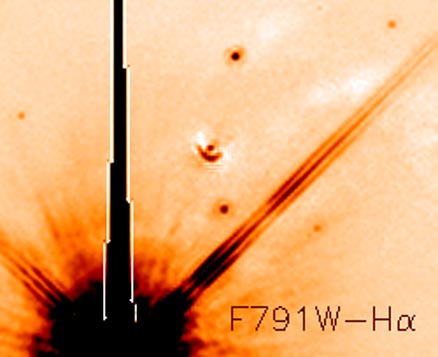
Explanation: Unusual appendages around bright stars are commonplace, but never seem to be mentioned. What are they? First, a telescope brings starlight falling over a large area to a small area. To get at this small area, however, one must go inside a reflecting telescope, and this can only be done with support rods, which are right in the view of the telescope. The wave nature of light causes it to deflect when passing near these rods. Light scatters away from the original destination point ending up elsewhere and appearing as "diffraction spikes." These annoying spikes steal precious light from the central image and hide light from fainter, more interesting stars. Above, astronomers are more interested in the half-circled point near the image center, than the cool-looking diffraction spikes from the bright star at the bottom. Apparently, that half-circle is a new stellar system forming in the Lagoon Nebula.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
star - telescope - difrakcionnye luchi - Teleskopy opticheskie
Publikacii so slovami: star - telescope - difrakcionnye luchi - Teleskopy opticheskie | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |