Credit & Copyright: ESA/ISO,
ISOCAM Team and P. Cox et al.
Explanation:
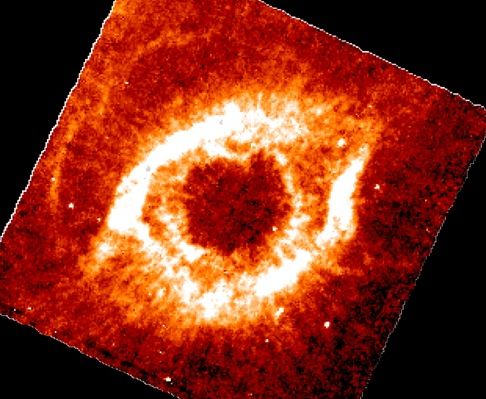
Five hundred light years from Earth, in
the constellation Aquarius,
a sun-like star is dying.
Its last few thousand years have produced
the Helix, a
well studied and nearby
example of a Planetary Nebula - typical
of this
final phase of stellar evolution.
The emission in this
Infrared Space Observatory image of the Helix nebula
comes mostly from the expanding shells of molecular hydrogen gas.
Dust, normally expected in such nebulae, should also radiate strongly
at infrared wavelengths but
mysteriously seems to be absent here.
The culprit may
may well be the Helix's central star, a contracting
white dwarf.
This small but extremely hot star radiates most of its
energy at
short Ultraviolet wavelengths and
is invisible in this infrared mage.
Astronomers suspect that over time,
this intense Ultraviolet radiation may have destroyed
the dust.
The Sun is expected to go through
its own Planetary Nebula phase ...
in another 5 billion years.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
infrared - Tumannost' Ulitka - Planetarnaya tumannost' - belyi karlik - infrakrasnoe izluchenie
Publikacii so slovami: infrared - Tumannost' Ulitka - Planetarnaya tumannost' - belyi karlik - infrakrasnoe izluchenie | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |