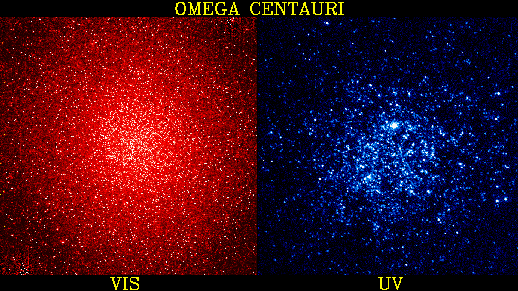
Explanation: Does an old, red globular cluster have any hot, blue stars? The rightmost picture, taken by the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope in ultraviolet light, shows that indeed it does. Pictured, Omega Centauri is the largest known globular cluster in our Galaxy, containing well over a million stars. Many of these stars are evident in the visible light photograph on the left. When photographed in ultraviolet light, however, different and less numerous stars emerge, as evident on the photograph on the right. Most of these stars are thought to have evolved past the current stage of our Sun. These stars no longer fuse hydrogen to helium in their core but rather fuse helium into carbon. These stars will soon shed their outer envelopes and end up as smoldering carbon embers known as white dwarf stars.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
Sharovoe skoplenie - Omega Centavra - Ul'trafioletovoe izluchenie
Publikacii so slovami: Sharovoe skoplenie - Omega Centavra - Ul'trafioletovoe izluchenie | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |