Credit & Copyright: M. Weber &
P. Sturrock
(Stanford),
J. Scargle
(NASA /
ARC),
SOHO / MDI, GALLEX / GNO
Explanation:
Neutrinos
are subatomic particles generated by the nuclear
reactions which power stars like our Sun.
Flying outward from the Sun's core, they easily pass through
the Sun (and almost
anything else!) unimpeded and should
be detectable by earth-based neutrino "telescopes".
Still, to the long-standing
consternation
of astrophysicists, the
observed flux of solar neutrinos is less than expected.
In a new twist to this solar neutrino saga,
an
analysis of data from the
GALLEX /
GNO
neutrino
detector finds a solar neutrino flux
that
varies over about 27 days ...
approximately matching the Sun's rotation period.
In fact, since
different parts
of the Sun rotate at different rates,
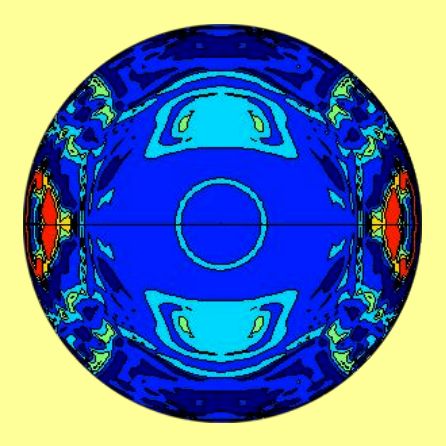
the neutrino flux variations match most exactly the rotation rates
of the areas shown in red on this colorful cross-sectional map of the
solar
interior rotation.
So how could solar rotation affect the neutrino flux?
Some theoretical models say that neutrinos can change quantum
properties when they interact
with tangled solar magnetic fields and become particles that the
neutrino experiments were not designed to detect.
Then, as the Sun rotates,
the neutrinos sometimes come to us unaffected
and sometimes come through magnetic fields, diminishing
the flux that can be measured.
SOHO / MDI, GALLEX / GNO
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
solar neutrinos - solar rotation - neitrino - solnechnoe vrashenie - neutrino
Publikacii so slovami: solar neutrinos - solar rotation - neitrino - solnechnoe vrashenie - neutrino | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |