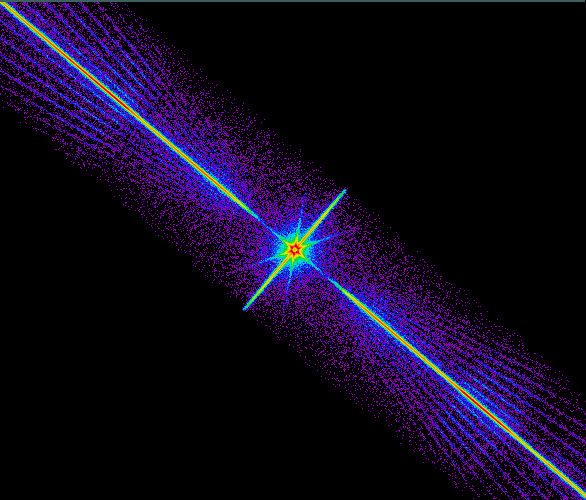
Explanation: A drop of water or prism of glass can spread out visible sunlight into a rainbow of colors. In order of increasing energy, the well known spectrum of colors in a rainbow runs red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet. X-ray light too can be spread out into a spectrum ordered by energy ... but not by drops of water or glass. Instead, the orbiting Chandra X-ray Observatory uses a set of 540 finely ruled, gold gratings to spread out the x-rays, recording the results with digital detectors. The resulting x-ray spectrum reveals much about the compositions, temperatures, and motions within cosmic x-ray sources. This false color Chandra image shows the x-ray spectrum of a star system in Ursa Major cataloged as XTE J1118+480 and thought to consist of a sun-like star orbiting a black hole. Unlike the familiar appearance of a prism's visible light rainbow, the energies here are ordered along radial lines with the highest energy x-rays near the center and lowest energies near the upper left and lower right edges of the image. The central spiky region itself is created by x-rays from the source which are not spread out by the array of gratings.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
XTE J1118+480 - raduga - Spektr - rentgenovskoe izluchenie - spectrum - light - rainbow
Publikacii so slovami: XTE J1118+480 - raduga - Spektr - rentgenovskoe izluchenie - spectrum - light - rainbow | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |