Credit & Copyright: Voyager
Project, JPL,
NASA
Explanation:
When NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft flew by
distant Neptune in August of 1989,
astronomers
were shocked.
Since Neptune receives only 3 percent
the sunlight Jupiter does, they
expected to find a dormant, dark, frigid planet.
Instead, the Voyager images revealed
evidence of a dynamic and turbulent world.
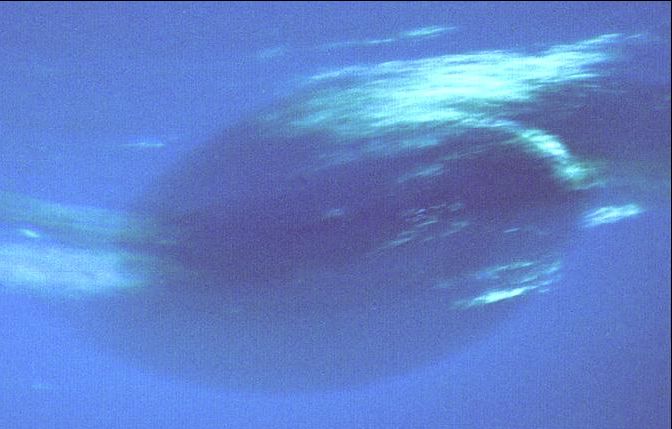
One of the most spectacular discoveries was of the Great Dark Spot, shown here in close-up.
Surprisingly, it was
comparable in size and at the same relative southern latitude as Jupiter's
Great Red Spot, appearing to be a
similar rotating storm system.
Winds near the spot were measured up to
1500 miles per hour, the strongest recorded on any planet.
The Voyager data also revealed that the Great
Dark Spot varied significantly in size during the brief flyby.
When the Hubble
Space Telescope viewed the planet in 1994, the spot had
vanished -- only to be replaced by another dark
spot in the planet's northern hemisphere!
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
Great Dark Spot - Voyager project - Voyadzher - Bol'shoe Temnoe Pyatno - Neptun - Neptune - Voyager 2
Publikacii so slovami: Great Dark Spot - Voyager project - Voyadzher - Bol'shoe Temnoe Pyatno - Neptun - Neptune - Voyager 2 | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |