Credit & Copyright: Visualization:
Ralf Kaehler
(ZIB) &
Tom Abel
(Penn. State)
Simulation: Tom Abel (Penn. State), Greg Bryan (Oxford) & Mike Norman (UCSD)
Explanation:
What became of the first stars?
No known stars
appear to be composed of truly
primordial gas -- all of the stars around us have too many heavy elements.
Our own Sun
is thought to be a third generation star, with many second-generation
stars seen in globular clusters.
This year, however, significant progress is being made on solving
this perennial astronomical mystery.
Analyses of recent WMAP satellite images
of the cosmic microwave background indicate that this
primordial light was ionized by a first generation of stars that
came and went only 200 million years after the
Big Bang.
Additionally computer codes are now more-accurately tracking the
likely creation and evolution of
first stars in the early universe.
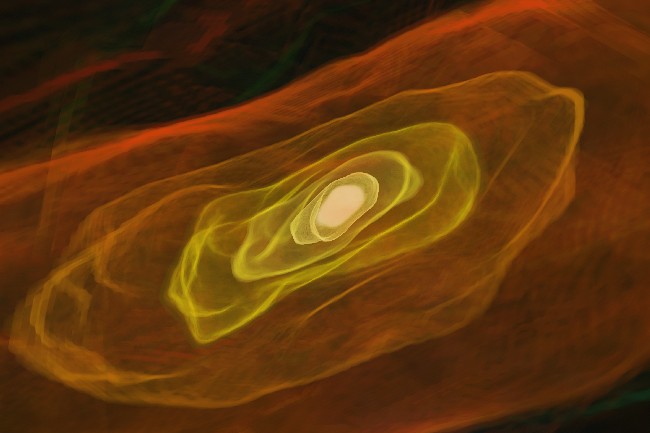
Pictured above at a scale of one
light-month, a computer-generated model resolves the scale of the first stars,
indicating clean cocoons that condensed into stars always
over 30 times the mass of our Sun.
Stars like this
quickly fused pristine gas into heavier elements and then exploded,
seeding the universe with
elements that would become part of
the stars we know and, ultimately,
ourselves.
Simulation: Tom Abel (Penn. State), Greg Bryan (Oxford) & Mike Norman (UCSD)
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
stars - Population III - zvezdy - zvezdoobrazovanie - naseleniya zvezdnye
Publikacii so slovami: stars - Population III - zvezdy - zvezdoobrazovanie - naseleniya zvezdnye | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |