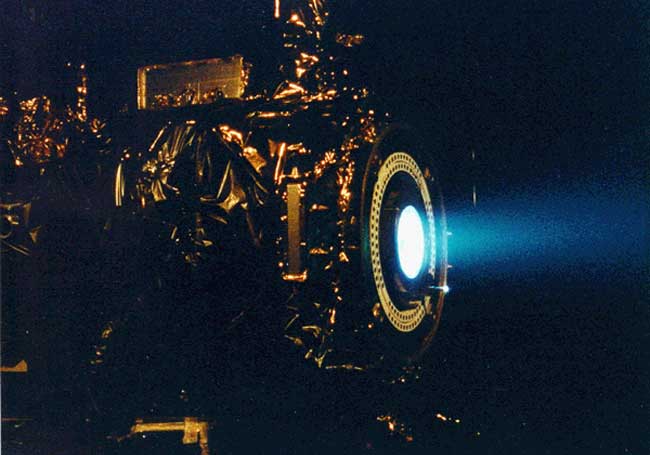
Explanation: Space travel entered the age of the ion drive in 1998 with the launch of Deep Space 1, a NASA mission designed primarily to test new technologies. Although the ion drive on Deep Space 1 provided acceleration much smaller than we feel toward Earth, it gradually gave the spacecraft the speed it needed to travel across our Solar System. The propulsion drive worked by ionizing xenon atoms with power provided by large panels that collect sunlight. As these ions were expelled by a strong electric field out the back, the spacecraft slowly gained speed. Pictured above, hot blue ions emerge from a prototype drive that was successfully tested at JPL in 1997. Deep Space 1 successfully zoomed past asteroid 9969 Braille in July 1999 and then Comet Borrelly in September 2001, then obtaining the most detailed photograph ever taken of a comet nucleus. The spacecraft was retired in December 2001
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
Deep Space 1 - ion drive - kosmicheskie korabli - ionnyi dvigatel' - Dip Speis-1
Publikacii so slovami: Deep Space 1 - ion drive - kosmicheskie korabli - ionnyi dvigatel' - Dip Speis-1 | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |