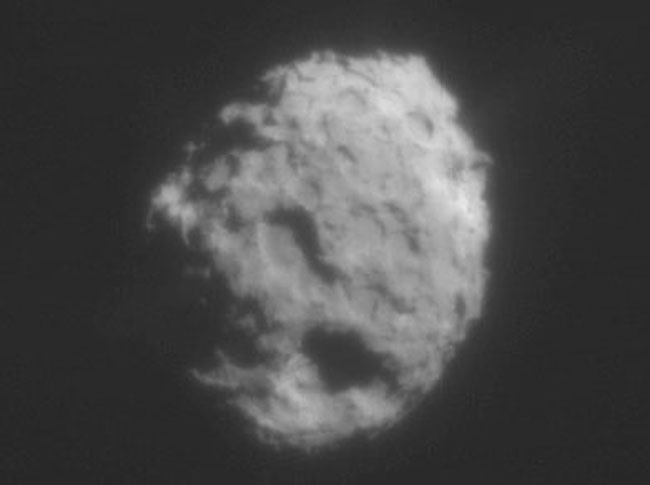
Explanation: What does a comet nucleus look like? Yesterday the robot spacecraft Stardust answered this question by returning the most detailed images yet of the center of a comet. The icy centers of comets are usually hidden from Earth-bound telescopes by opaque dust and gas that boils off during approach to the Sun. Twice before, however, in the cases of Comet Halley and Comet Borrelly, spacecraft dove through the debris cloud of a comet's coma to image the nucleus. Pictured above is the nucleus of Comet Wild 2 taken by Stardust when passing within 500 kilometers. Clearly visible are numerous craters and hilly terrain. The Stardust mission is yet more ambitious -- it has captured particles from the coma and will jettison them to Earth in 2006. Analyses of the images and returned particles will likely give fresh information about our Solar System back near its beginning, when Comet Wild 2 formed.
News on the NASA Mars Landings
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
Comet Wild 2 - Stardust project - komety - kometa Vild-2
Publikacii so slovami: Comet Wild 2 - Stardust project - komety - kometa Vild-2 | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |