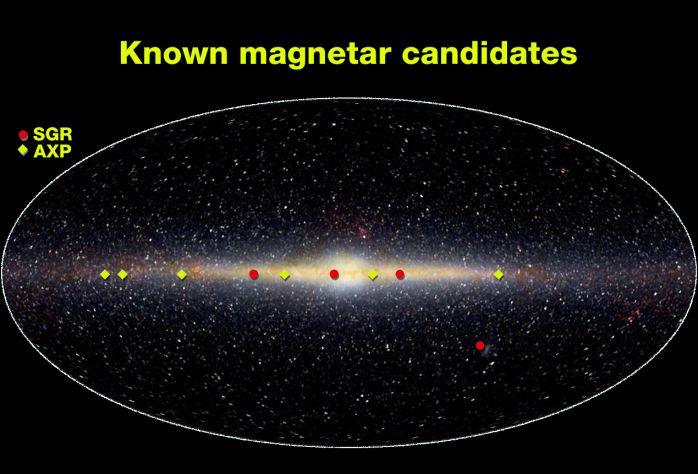
Explanation: Indicated on this infrared image of the galactic center region are positions of candidate magnetars -- believed to be the strongest magnets in the galaxy. Classified by observers as Soft Gamma Repeaters (SGRs) and Anomalous X-ray Pulsars (AXPs), these cosmic powerhouses are likely city-sized, spinning, highly-magnetized neutron stars. How strong is a magnetar's magnetic field? The Earth's magnetic field which deflects compass needles is measured to be about 1 Gauss, while the strongest fields sustainable in earthbound laboratories are about 100,000 Gauss. A magnetar's monster magnetic field is estimated to be as high as 1,000,000,000,000,000 Gauss. A magnet this strong, located at about half the distance to the Moon would easily erase your credit cards and suck pens out of your pocket. In 1998, from a distance of about 20,000 light-years, one magnetar, SGR 1900+14 generated a powerful flash of gamma-rays detected by many spacecraft. That blast of high-energy radiation is now known to have had a measurable effect on Earth's ionosphere. At the surface of the magnetar, its powerful magnetic field is thought to buckle and shift the neutron star crust generating the intense high-energy flares
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
magnetar - magnetic field - pulsar - neutron star - Magnitary - magnitnoe pole - neitronnye zvezdy - Pul'sar
Publikacii so slovami: magnetar - magnetic field - pulsar - neutron star - Magnitary - magnitnoe pole - neitronnye zvezdy - Pul'sar | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |