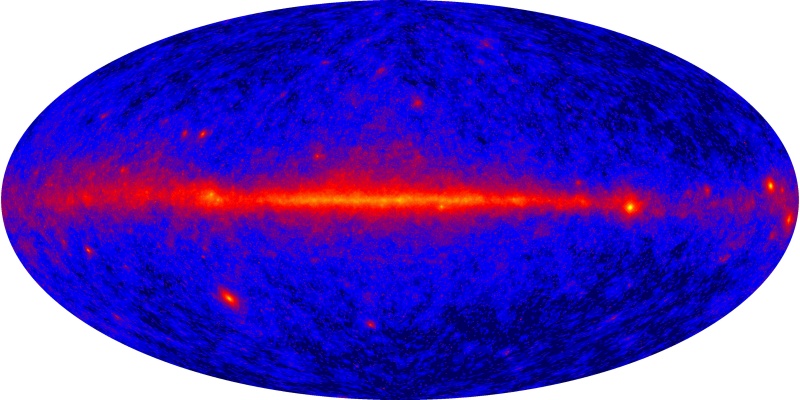
Explanation: Launched on June 11 to explore the universe at extreme energies, the Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope has been officially renamed the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, in honor of Nobel Laureate Enrico Fermi (1901-1954), pioneer in high-energy physics. After testing, Fermi's two instruments, the Gamma-ray Burst Monitor (GBM) and the Large Area Telescope (LAT), are now regularly returning data. Fermi's first map of the gamma-ray sky from the LAT is shown in this false-color image, an all-sky view that looks toward the center of our Milky Way Galaxy with the galactic plane projected across the middle. What shines in the gamma-ray sky? Along the galactic plane, energetic cosmic rays collide with gas and dust to produce the diffuse gamma-ray glow. Strong emission from spinning neutron stars or pulsars, and distant active galaxies known as blazars, can be identified by placing your cursor over the map. A prelude to future discoveries, the remarkable result combines only 4 days of observations, equivalent to a year of observations with the Compton Gamma-ray Observatory mission of the 1990s. In addition to the ability to monitor gamma-ray bursts, the greatly improved sensitivity will allow Fermi to look deeper into the high-energy Universe.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
gamma ray - gamma observations - gamma-izluchenie - gamma-astronomiya
Publikacii so slovami: gamma ray - gamma observations - gamma-izluchenie - gamma-astronomiya | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |