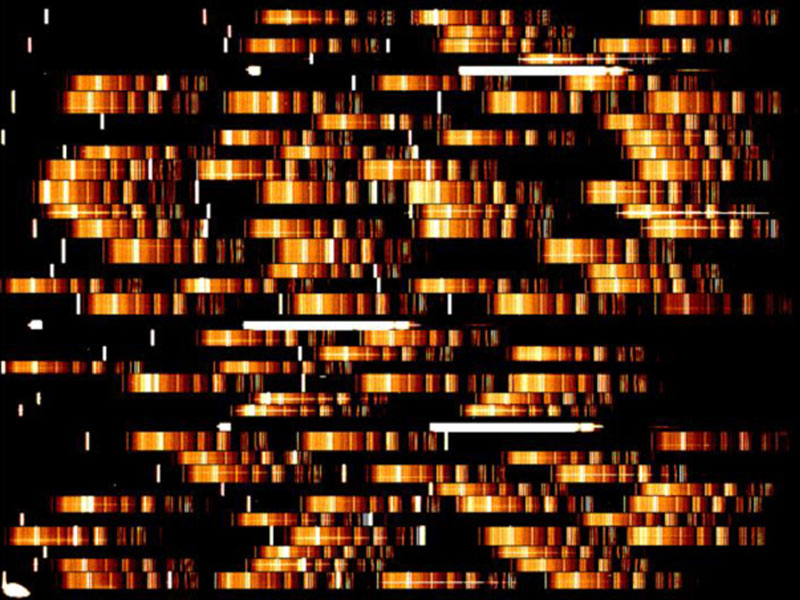
Explanation: In the distant universe, time appears to run slow. Since time-dilated light appears shifted toward the red end of the spectrum (redshifted), astronomers are able to use cosmological time-slowing to help measure vast distances in the universe. Above, the light from distant galaxies has been broken up into its constituent colors (spectra), allowing astronomers to measure the redshift of known spectral lines. The novelty of the above image is that the distance to hundreds of galaxies can now be measured on a single frame using the Visible MultiObject Spectrograph operating at the Very Large Telescope array in Chile. Analyzing the space distribution of distant objects will allow insight into when and how stars, galaxies, and quasars formed, clustered, and evolved in the early universe.
digg_url = 'http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap090104.html'; digg_skin = 'compact';
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
spectrum - redshift - cosmology - Spektr - galaktika - Kosmologiya - krasnoe smeshenie
Publikacii so slovami: spectrum - redshift - cosmology - Spektr - galaktika - Kosmologiya - krasnoe smeshenie | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |