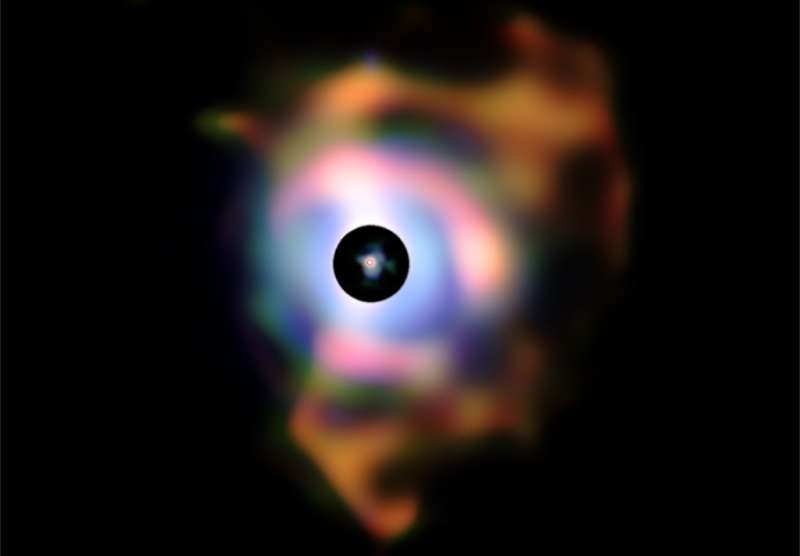
Explanation: An expansive nebula of dust is seen to surround red supergiant star Betegeuse in this remarkable high resolution composite, an infrared VLT image from the European Southern Observatory. Betelgeuse itself is outlined by the small, central red circle. If found in our own solar system its diameter would almost encompass the orbit of Jupiter. But the larger envelope of circumstellar dust extends some 60 billion kilometers into space, equivalent to about 400 times the Earth-Sun distance. The dust is likely formed as the swollen atmosphere of the supergiant sheds material into space, a final phase in the evolution of a massive star. Mixing with the interstellar medium, the dust could ultimately form rocky terrestrial planets like Earth. The central bright portion of the outer image has been masked to reveal fainter extended structures. The field of view is 5.63 arcseconds across.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
Betelgeuse - red supergiant - massive stars - dust cloud - Betel'geize - krasnyi sverhgigant - massivnye zvezdy - pylevoe oblako
Publikacii so slovami: Betelgeuse - red supergiant - massive stars - dust cloud - Betel'geize - krasnyi sverhgigant - massivnye zvezdy - pylevoe oblako | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |