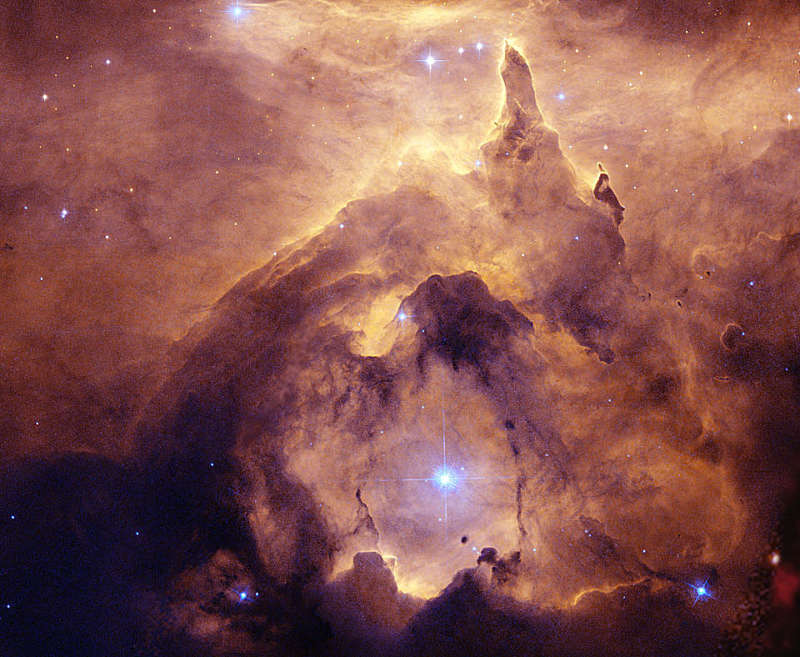
Explanation: For reasons unknown, NGC 6357 is forming some of the most massive stars ever discovered. One such massive star, near the center of NGC 6357, is framed above carving out its own interstellar castle with its energetic light from surrounding gas and dust. In the greater nebula, the intricate patterns are caused by complex interactions between interstellar winds, radiation pressures, magnetic fields, and gravity. The overall glow of the nebula results from the emission of light from ionized hydrogen gas. Near the more obvious Cat's Paw nebula, NGC 6357 houses the open star cluster Pismis 24, home to many of these tremendously bright and blue stars. The central part of NGC 6357 shown spans about 10 light years and lies about 8,000 light years away toward the constellation of the Scorpion.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
stellar wind - emissionnaya tumannost' - zvezdoobrazovanie - zvezdnyi veter
Publikacii so slovami: stellar wind - emissionnaya tumannost' - zvezdoobrazovanie - zvezdnyi veter | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |