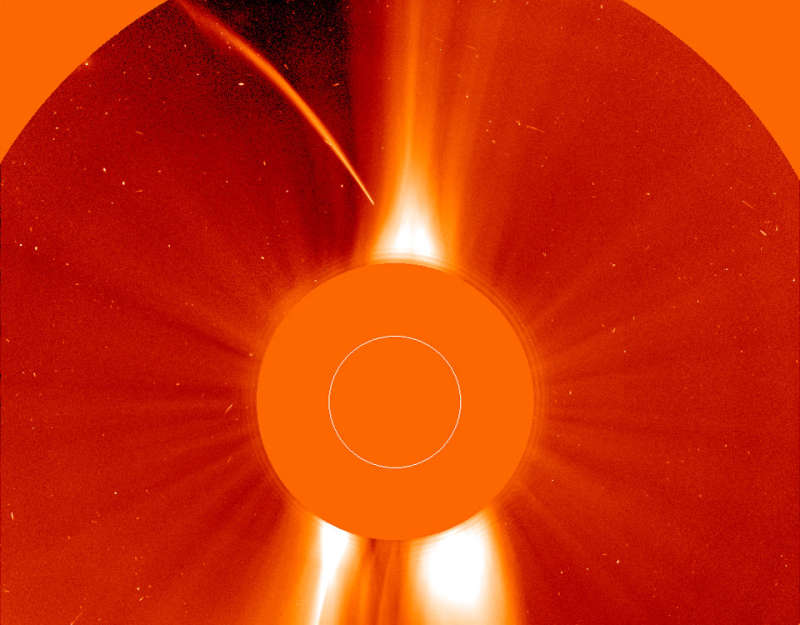
Explanation: Arcing toward a fiery fate, this Sungrazer comet was recorded by the SOHO spacecraft's Large Angle Spectrometric COronagraph(LASCO) on December 23, 1996. LASCO uses an occulting disk, partially visible at the lower right, to block out the otherwise overwhelming solar disk allowing it to image the inner 8 million kilometers of the relatively faint corona. The comet is seen as its coma enters the bright equatorial solar wind region (oriented vertically). Positioned in space to continuously observe the Sun, SOHO has now been used to discover over 1,500 comets, including numerous sungrazers. Based on their orbits, the vast majority of sungrazers are believed to belong to the Kreutz family of sungrazing comets created by successive break ups from a single large parent comet that passed very near the Sun in the twelfth century. The Great Comet of 1965, Ikeya-Seki, was also a member of the Kreutz family, coming within about 650,000 kilometers of the Sun's surface. Passing so close to the Sun, Sungrazers are subjected to destructive tidal forces along with intense solar heat. This small comet, known as the Christmas Comet SOHO 6, did not survive. Later this year, Comet ISON, potentially the brightest sungrazer in recorded history but not a Kreutz sungrazer, is expected to survive.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
comet - sungrazer - Sun - komety - Solnce
Publikacii so slovami: comet - sungrazer - Sun - komety - Solnce | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |