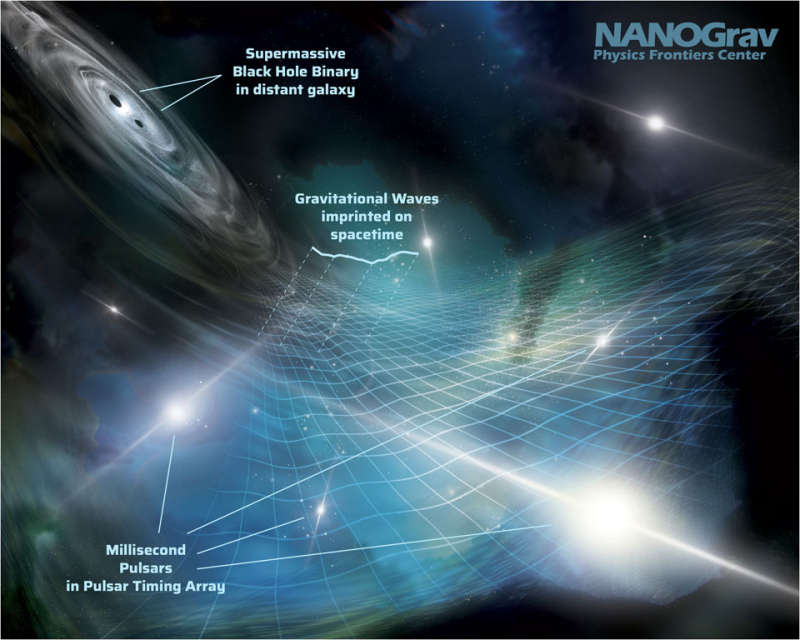
Explanation: Monitoring 68 pulsars with very large radio telescopes, the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves (NANOGrav) has uncovered evidence for the gravitational wave (GW) background by carefully measuring slight shifts in the arrival times of pulses. These shifts are correlated between different pulsars in a way that indicates that they are caused by GWs. This GW background is likely due to hundreds of thousands or even millions of supermassive black hole binaries. Teams in Europe, Asia and Australia have also independently reported their results today. Previously, the LIGO and Virgo detectors have detected higher-frequency GWs from the merging of individual pairs of massive orbiting objects, such as stellar-mass black holes. The featured illustration highlights this spacetime-shaking result by depicting two orbiting supermassive black holes and several of the pulsars that would appear to have slight timing shifts. The imprint these GWs make on spacetime itself is illustrated by a distorted grid.
Open Science:
Browse 3,000+ codes in the Astrophysics Source Code Library
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 |
Yanvar' Fevral' Mart Aprel' Mai Iyun' Iyul' Avgust Sentyabr' Oktyabr' Noyabr' Dekabr' |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Publikacii s klyuchevymi slovami:
universe - gravitational radiation - Vselennaya - gravitacionnye volny
Publikacii so slovami: universe - gravitational radiation - Vselennaya - gravitacionnye volny | |
Sm. takzhe:
Vse publikacii na tu zhe temu >> | |