|
Peremennye Zvezdy (Variable Stars) 28, No. 6, 2008 Received 28 March; accepted 25 April. |
Article in PDF |
SN 2005kd: Another Very Luminous, Slowly Declining Type IIn Supernova
Sternberg Astronomical Institute, University Ave. 13, 119992 Moscow, Russia; e-mail: tsvetkov@sai.msu.su
|
CCD |
SN 2005kd was discovered by T.Puckett and A.Pelloni with an 0.35-m
automated supernova patrol telescope on 2005 November 12.22 UT at
magnitude 17.0, while on November 9 the object was not detected
(fainter than 20![]() ). It is located at
). It is located at
![]() (2000.0),
which is
(2000.0),
which is
![]() west and
west and
![]() north from the center of the
Sc galaxy PGC 14370 (Puckett and Pelloni, 2005).
north from the center of the
Sc galaxy PGC 14370 (Puckett and Pelloni, 2005).
SN 2005kd was found by an Ohio State University group (Prieto, 2005) to be a young type IIn supernova from a 390-730 nm spectrogram taken on November 13.3 UT with the MDM 2.4-m telescope; the spectrum shows a blue continuum and strong hydrogen Balmer and He I lines in emission.
We started our photometric observations of SN 2005kd immediately after its discovery, on 2005 November 13, and continued till 2007 April 16. Observations were carried out with the following telescopes and CCD cameras: the 60-cm reflector of the Crimean Observatory of Sternberg Astronomical Institute (C60) equipped with an Apogee AP-47p camera; the 50/70-cm meniscus telescope of the Crimean Observatory (C50) with a Meade Pictor 416XT camera; the 70-cm reflector in Moscow (M70) with Apogee AP-47p (a) or AP-7p (b) cameras.
The color terms for C60 and M70 were reported by Tsvetkov et al.
(2006). The observations with C50 were carried out only using a
![]() filter close to the standard system, so no correction was
applied.
filter close to the standard system, so no correction was
applied.
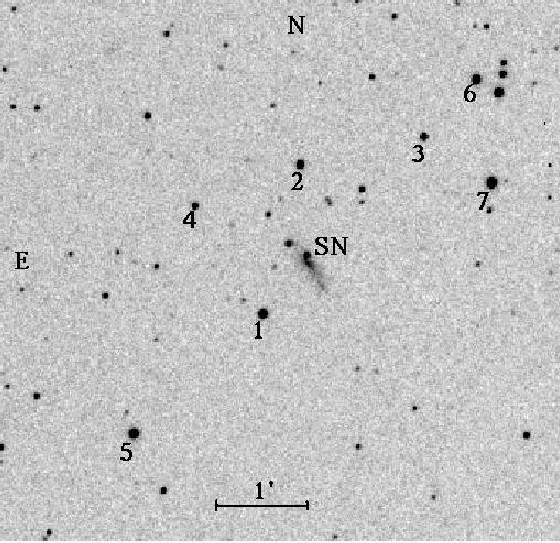
All image reductions and photometry were made using IRAF1. The position of SN 2005kd is quite close to the center of the host galaxy, and the subtraction of galaxy background is necessary for reliable photometry. The template images were constructed from frames obtained on 2007 August 8 and 2007 September 25, when the SN was no longer visible. After template subtraction, the magnitudes of the SN were derived by PSF fitting relative to a sequence of local standard stars. The image of SN 2005kd with local standard stars is shown in Fig. 1, and the magnitudes of these stars are reported in Table 1.
| Star | ||||||||||
| 1 | 15.50 | 0.08 | 15.21 | 0.02 | 14.51 | 0.03 | 14.09 | 0.02 | 13.68 | 0.02 |
| 2 | 16.15 | 0.03 | 15.09 | 0.02 | 14.45 | 0.02 | 13.92 | 0.02 | ||
| 3 | 16.50 | 0.05 | 15.90 | 0.04 | 15.41 | 0.03 | 15.01 | 0.02 | ||
| 4 | 16.80 | 0.04 | 16.13 | 0.04 | 15.62 | 0.03 | 15.24 | 0.02 | ||
| 5 | 15.76 | 0.10 | 15.10 | 0.03 | 14.13 | 0.02 | 13.62 | 0.01 | 13.10 | 0.02 |
| 6 | 15.36 | 0.14 | 15.18 | 0.05 | 14.42 | 0.04 | 13.98 | 0.02 | 13.56 | 0.02 |
| 7 | 15.33 | 0.16 | 14.80 | 0.05 | 13.82 | 0.04 | 13.32 | 0.05 | 12.81 | 0.03 |
The observations of SN 2005kd are presented in Table 2, and the
light curves are shown in Fig. 2. Some unfiltered CCD magnitudes
were reported in IAU Circulars and at SNWeb2,
they are also plotted in Fig. 2. The data show that SN 2005kd was
discovered immediately after its explosion, and our first two
observations were on the rising branch of the light curve. The
rate of brightness increase was about 0![]() 3-0
3-0![]() 4 per day in
all bands. Most likely, the outburst occurred on 2005 November 10
or 11, and we accept JD 2453685 as the explosion date.
Unfortunately, we missed the most interesting part of the light
curve and cannot reliably establish the shape of the light curve
peak and the maximum luminosity. Our next observation was only on
2006 January 3, and on this date, the SN was the brightest of all
our data set. The magnitudes from SNWeb allow to suggest quite a
flat maximum, but they also have a large gap. After a small drop
from the maximum, the SN entered a plateau stage, which lasted for
at least 192 days, from day 119 till day 311 past explosion.
Another gap in observations does not allow to determine the length
of the plateau more definitely. Since 2005 September 17 (day 341)
and till the end of our observations on day 522, the SN was
gradually fading, but at different rates. To day 405, the decline
was slow, with rates of 0
4 per day in
all bands. Most likely, the outburst occurred on 2005 November 10
or 11, and we accept JD 2453685 as the explosion date.
Unfortunately, we missed the most interesting part of the light
curve and cannot reliably establish the shape of the light curve
peak and the maximum luminosity. Our next observation was only on
2006 January 3, and on this date, the SN was the brightest of all
our data set. The magnitudes from SNWeb allow to suggest quite a
flat maximum, but they also have a large gap. After a small drop
from the maximum, the SN entered a plateau stage, which lasted for
at least 192 days, from day 119 till day 311 past explosion.
Another gap in observations does not allow to determine the length
of the plateau more definitely. Since 2005 September 17 (day 341)
and till the end of our observations on day 522, the SN was
gradually fading, but at different rates. To day 405, the decline
was slow, with rates of 0![]() 0077 per day in the
0077 per day in the ![]() and
and ![]() bands, 0
bands, 0![]() 0087 per day in
0087 per day in ![]() , and 0
, and 0![]() 013 per day in
013 per day in ![]() . The
late decline was about twice faster: 0
. The
late decline was about twice faster: 0![]() 017 mag per day in the
017 mag per day in the
![]() and
and ![]() bands, 0
bands, 0![]() 025 per day in
025 per day in ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
| JD 2450000+ | Tel. | ||||||||||
| 3688.47 | 15.38 | 0.12 | 16.06 | 0.03 | 16.06 | 0.03 | 15.77 | 0.03 | 15.77 | 0.06 | C60 |
| 3689.52 | 15.15 | 0.09 | 15.72 | 0.03 | 15.68 | 0.02 | 15.48 | 0.02 | 15.41 | 0.03 | C60 |
| 3739.47 | 15.67 | 0.03 | 15.10 | 0.03 | 14.59 | 0.02 | 14.17 | 0.03 | M70b | ||
| 3804.36 | 16.12 | 0.03 | 15.54 | 0.03 | 14.91 | 0.02 | 14.47 | 0.02 | M70a | ||
| 3822.30 | 16.06 | 0.03 | 15.60 | 0.04 | 14.94 | 0.02 | 14.51 | 0.03 | M70a | ||
| 3831.27 | 16.07 | 0.04 | 15.59 | 0.03 | 14.94 | 0.02 | 14.49 | 0.02 | M70a | ||
| 3852.28 | 16.02 | 0.03 | 15.66 | 0.03 | 14.88 | 0.02 | 14.50 | 0.02 | M70a | ||
| 3872.34 | 16.03 | 0.03 | 15.59 | 0.02 | 14.86 | 0.02 | 14.44 | 0.03 | M70a | ||
| 3996.42 | 16.42 | 0.07 | 16.61 | 0.04 | 15.53 | 0.02 | 15.20 | 0.03 | M70b | ||
| 4026.44 | 16.93 | 0.14 | 17.00 | 0.04 | 16.86 | 0.03 | 15.74 | 0.03 | 15.35 | 0.07 | M70b |
| 4044.61 | 16.93 | 0.07 | 16.08 | 0.04 | C60 | ||||||
| 4056.49 | 17.07 | 0.08 | C50 | ||||||||
| 4059.38 | 17.26 | 0.04 | C50 | ||||||||
| 4059.53 | 17.57 | 0.03 | 17.38 | 0.04 | 15.97 | 0.06 | 15.70 | 0.08 | C60 | ||
| 4062.38 | 17.26 | 0.03 | C50 | ||||||||
| 4090.48 | 17.69 | 0.04 | 17.21 | 0.06 | 16.07 | 0.04 | 15.81 | 0.03 | M70b | ||
| 4118.30 | 18.50 | 0.04 | 18.17 | 0.07 | 16.85 | 0.03 | 16.36 | 0.04 | M70b | ||
| 4127.25 | 17.04 | 0.08 | M70b | ||||||||
| 4131.27 | 18.99 | 0.12 | 17.06 | 0.05 | 16.81 | 0.09 | M70b | ||||
| 4143.23 | 18.94 | 0.10 | 19.07 | 0.20 | 17.35 | 0.06 | 16.83 | 0.08 | M70b | ||
| 4158.26 | 17.70 | 0.05 | 17.21 | 0.12 | M70b | ||||||
| 4180.30 | 17.99 | 0.06 | 17.40 | 0.06 | M70b | ||||||
| 4183.28 | 19.78 | 0.13 | 19.44 | 0.28 | 17.70 | 0.09 | 17.29 | 0.08 | M70b | ||
| 4187.27 | 17.80 | 0.04 | 17.30 | 0.04 | M70b | ||||||
| 4201.27 | 18.21 | 0.10 | 17.58 | 0.08 | M70b | ||||||
| 4207.27 | 18.11 | 0.04 | 17.80 | 0.10 | M70b |
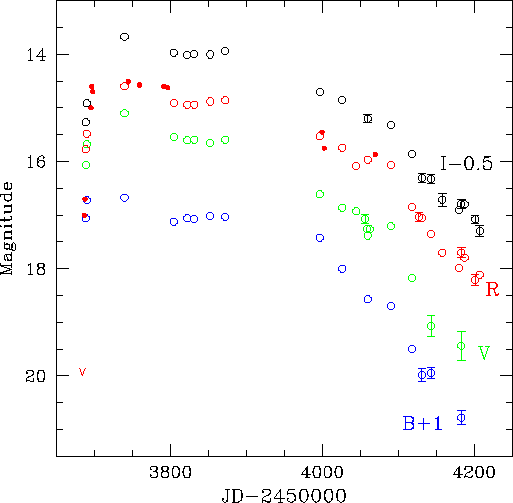 |
Fig. 2.
|
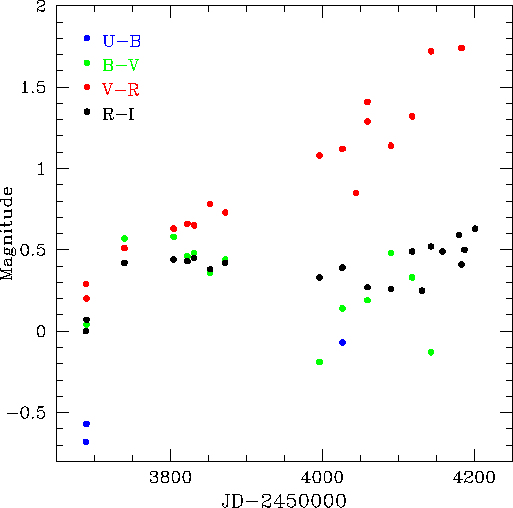
The color curves are presented in Figure 3. The ![]() color
was gradually increasing,
color
was gradually increasing, ![]() remained nearly constant after
its initial increase, while
remained nearly constant after
its initial increase, while ![]() reached its maximum on the
plateau and then was slightly decreasing.
reached its maximum on the
plateau and then was slightly decreasing.
If we adopt the distance modulus ![]() and Galactic
extinction
and Galactic
extinction ![]() from NED3 for PGC 14370, then the
absolute magnitude on 2006 January 3 (day 54) was
from NED3 for PGC 14370, then the
absolute magnitude on 2006 January 3 (day 54) was ![]() .
The real maximum luminosity can be significantly higher because we
missed the peak of the light curve and do not know the extinction
in the host galaxy.
.
The real maximum luminosity can be significantly higher because we
missed the peak of the light curve and do not know the extinction
in the host galaxy.
The absolute ![]() -band light curve of SN 2005kd is shown in Fig. 4
and compared to the light curves of well-studied slowly declining
type IIn SNe: 1997cy (Germany et al., 2000), 1999E (Rigon et al.,
2003), 1995G (Pastorello et al., 2002), 1988Z (Turatto et al.,
1993). The similarity of overall photometric evolution of SNe
2005kd and 1997cy is evident, although the differences are also
noticeable. We note that, for both SNe, the rate of brightness
decline changed at about the same phase, close to day 400. SN
1999E was fainter, but the shape of its light curve is the same as
for SN 1997cy; SNe 1988Z and 1995G were much fainter and have
different light curves. The plateau of SN 2005kd is the unique
feature for SNe IIn, nothing similar can be seen for any of the
other light curves.
-band light curve of SN 2005kd is shown in Fig. 4
and compared to the light curves of well-studied slowly declining
type IIn SNe: 1997cy (Germany et al., 2000), 1999E (Rigon et al.,
2003), 1995G (Pastorello et al., 2002), 1988Z (Turatto et al.,
1993). The similarity of overall photometric evolution of SNe
2005kd and 1997cy is evident, although the differences are also
noticeable. We note that, for both SNe, the rate of brightness
decline changed at about the same phase, close to day 400. SN
1999E was fainter, but the shape of its light curve is the same as
for SN 1997cy; SNe 1988Z and 1995G were much fainter and have
different light curves. The plateau of SN 2005kd is the unique
feature for SNe IIn, nothing similar can be seen for any of the
other light curves.
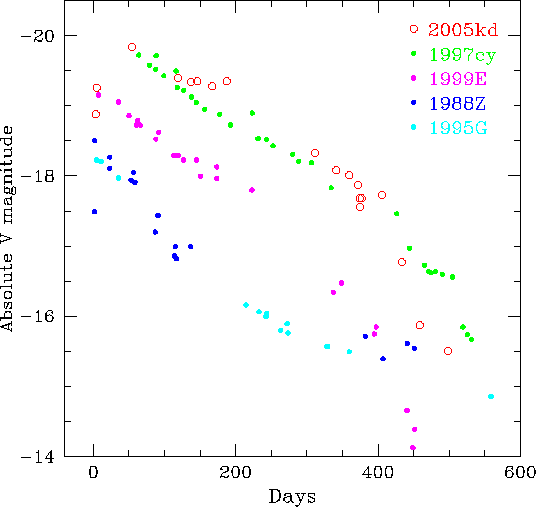 |
Fig. 4.
The absolute |
The ![]() color curves for these SNe are compared in Fig. 5.
SNe 1997cy, 1999E and 1999G had similar color evolution: after an
initial reddening, the
color curves for these SNe are compared in Fig. 5.
SNe 1997cy, 1999E and 1999G had similar color evolution: after an
initial reddening, the ![]() color remained nearly constant,
at about 0
color remained nearly constant,
at about 0![]() 5-0
5-0![]() 6. SNe 2005kd and 1988Z were certainly
bluer, and at the phases after 300 days SN 2005kd was the bluest
among these objects.
6. SNe 2005kd and 1988Z were certainly
bluer, and at the phases after 300 days SN 2005kd was the bluest
among these objects.
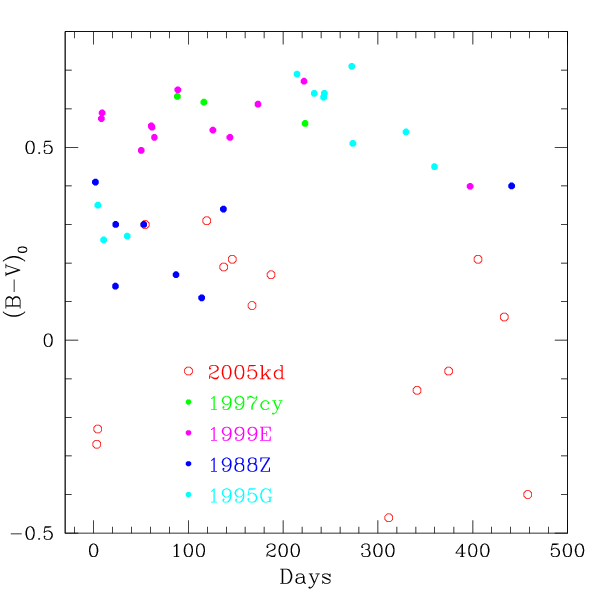 |
Fig. 5. The (B-V)0 color curve for SN 2005kd compared to those for SNe IIn 1997cy, 1999E, 1995G, and 1988Z |
We can roughly estimate the lower limit to the energy radiated by
SN 2005kd in the ![]() bands during the first 500 days of
evolution. Assuming the distance and extinction reported earlier
and using simple linear interpolations in the gaps, we obtain
ergs.
bands during the first 500 days of
evolution. Assuming the distance and extinction reported earlier
and using simple linear interpolations in the gaps, we obtain
ergs.
SN 2005kd is among the most luminous SNe ever observed. As for other SNe IIn, its high energy release is likely due to the interaction of ejecta with a dense circumstellar medium. For all well-studied SNe IIn, the brightness decline was slow but gradual, without periods of constant luminosity. The plateau lasting at least 192 days observed for SN 2005kd is a unique feature for SNe IIn. Unfortunately, the gaps in our data do not allow to trace the peak of the light curve and the end of the plateau.
This research has made use of the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED) which is operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under contract with NASA.
References:
Germany, L.M., Reiss, D.J., Sadler, E.M., et al., 2000, Astrophys. J., 533, 320
Pastorello, A., Turatto, M., Benetti, S., et al., 2002, MNRAS, 330, 844
Prieto, J., 2005, IAU Circ., No. 8630
Puckett, T., Pelloni, A., 2005, IAU Circ., No. 8630
Rigon, L., Turatto, M., Benetti, S., et al., 2003, MNRAS, 340, 191
Tsvetkov, D.Yu., Volnova, A.A., Shulga, A.P., et al., 2006, Astron. Astrophys., 460, 769
Turatto, M., Cappellaro, E., Danziger, I.J., et al., 1993, MNRAS, 262, 128
Footnotes
1
IRAF is distributed by the National Optical Astronomy
Observatory, which is operated by AURA under cooperative agreement
with the National Science Foundation
2
http://www.astrosurf.com/snweb2/2005/05kd/05kdMeas.htm
3
http://nedwww.ipac.caltech.edu