|
Peremennye Zvezdy (Variable Stars) 36, No. 1, 2016 Received 29 September; accepted 4 October. MASTER OT J190519.41+301524.4: A New Eclipsing Cataclysmic Variable of the VY Scl Type
|
Article in PDF |
1. Introduction
MASTER OT J190519.41+301524.4 is an optical transient in Lyra
discovered on March 6, 2014 (Denisenko et al. 2014) by
MASTER-Kislovodsk auto-detection system (Lipunov et al. 2010). The
previously unremarkable star was found to be highly variable on
the digitized Palomar plates. Namely, the star was bright on the
1950 June 17 POSS-I plate, but very faint on the 1987 June 21
POSS-II plate (see Fig. 1). These brightness changes are clearly
seen from the magnitudes reported in different catalogs. Namely,
the USNO-B1.0 catalogue (Monet et al. 2003) is listing USNO-B1.0
1202-0321874 with ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , (
, (![]() magnitude not available),
magnitude not available), ![]() , while GSC 2.3.2 is giving
, while GSC 2.3.2 is giving
![]() measured from the 1987 June 21 Palomar
plate. The star is an ultraviolet source GALEX J190519.4+301525
with the far and near UV magnitudes
measured from the 1987 June 21 Palomar
plate. The star is an ultraviolet source GALEX J190519.4+301525
with the far and near UV magnitudes
![]() ,
,
![]() respectively. Based on this information,
Denisenko et al. suggested that MASTER OT J190519.41+301524.4 was
a cataclysmic variable, most likely an anti-nova of the VY Scl
type in the high state.
respectively. Based on this information,
Denisenko et al. suggested that MASTER OT J190519.41+301524.4 was
a cataclysmic variable, most likely an anti-nova of the VY Scl
type in the high state.
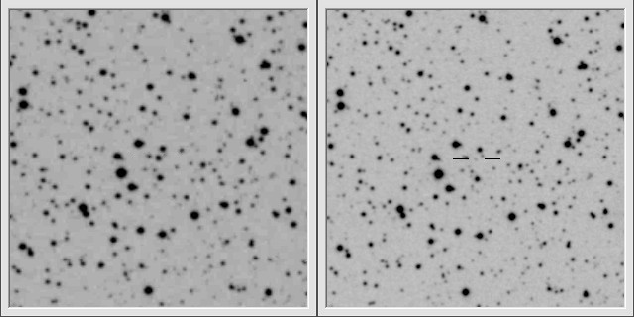 |
Fig. 1.
MASTER OT J190519.41+301524.4 on digitized
Palomar Red plates. Left: 1950 June 17 (bright state); right: 1987
June 21 (faint state). The FOV is |
In this paper, we report the results of our observations of MASTER OT J190519.41+ 301524.4 obtained in June-July, 2015 in the Lajatico Astronomical Center in Italy. We detected deep eclipses in this compact binary system, measured its orbital period, and confirmed its classification as a VY Scl cataclysmic variable.
2. Photometry
Our observations of J1905+3015 were performed in the Lajatico
Astronomical Center in Italy (http://www.astronomicalcentre.org/)
located in Tuscany region, 40 km southeast of Pisa. Data were
taken on seven nights (2015 June 28, 30; July 7, 12, 15, 17, and
18) using the 0.36-m Cassegrain telescope with an SBIG ST-8XME
CCD. A total of 203 unfiltered images with 300-s exposures were
obtained (26, 11, 35, 23, 34, 35, and 37 images covering 2.9, 1.4,
3.7, 2.8, 4.1, 3.0, and 3.8 hours, respectively). A nearby star
USNO-B1.0 1202-0321923 (![]() to the east and
to the east and ![]() to the south
of the variable), with the magnitude
to the south
of the variable), with the magnitude ![]() , was used as a
reference star.
, was used as a
reference star.
The observation times were converted from JD to Barycentric Julian
Date using the online period search service
(http://scan.sai.msu.ru/lk/) by Kirill Sokolovsky. Using the
Lafler-Kinman and Deeming methods, we have obtained the best
period value 0![]() 129694(2), or 3
129694(2), or 3![]() 113. The phased light curve
from our observations is presented in Fig. 2. It shows deep
eclipses with a total amplitude about 2
113. The phased light curve
from our observations is presented in Fig. 2. It shows deep
eclipses with a total amplitude about 2![]() and variations by
0
and variations by
0![]() 3 near the maximum light. Our search for secondary periods
has not detected any additional periodic signals at higher
frequencies.
3 near the maximum light. Our search for secondary periods
has not detected any additional periodic signals at higher
frequencies.
The light elements of J1905+3015 obtained from our observations
are:
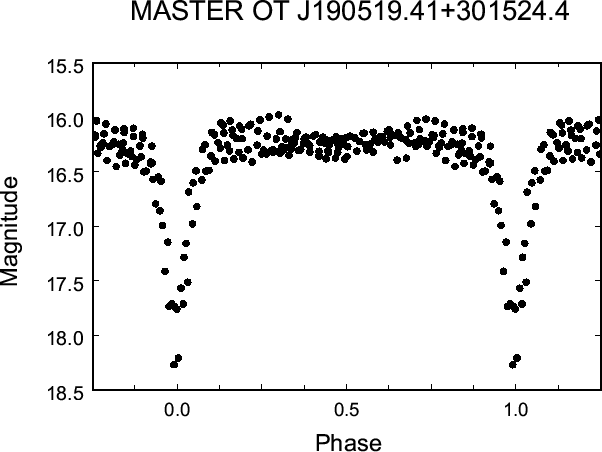 |
Fig. 2.
The light curve of J1905+3015
from Lajatico data (June-July, 2015) folded with the best orbital
period,
|
3. Discussion
The deep fading of J1905+3014 observed on the 1987 POSS-II Red
plate can be explained either with the low state of a polar
(magnetic CV without an accretion disk) or with the drop of
accretion rate in a variable of the VY Scl type ("anti-nova"
with a disk). Our observations are strongly in favor of the second
scenario. The V-shaped eclipse of a long duration (about 20 per
cent of the orbital period) is consistent with the presence of
quite a large accretion disk. The system was not detected by the
ROSAT all-sky survey (Voges et al. 2003). If J1905+3014 were a
magnetic CV with a range of
![]() , it should have been
present in the ROSAT catalog.
, it should have been
present in the ROSAT catalog.
MASTER OT J190519.41+301524.4 turns out to be an eclipsing
cataclysmic variable of the VY Scl type. Such systems are quite
rare. The catalog of cataclysmic binaries by Ritter and Kolb
(2003; Version 7.23 of July 2015) lists only eight nova-like
variables with eclipses (NL+E), but none of them is classified as
an "anti-nova". Interestingly enough, all of them have orbital
periods longer than 0![]() 133. The phased light curve of the
binary system J1905+3015 resembles that of V482 Cam = HS 0728+6738
(Rodriguez-Gil et al. 2004), which belongs to the subgroup of
eclipsing SW Sextantis stars. It is possible that J1905+3015 is
also an SW-type variable. We encourage continued monitoring of
this new CV to follow its return to the low state. When the system
fades back to the
133. The phased light curve of the
binary system J1905+3015 resembles that of V482 Cam = HS 0728+6738
(Rodriguez-Gil et al. 2004), which belongs to the subgroup of
eclipsing SW Sextantis stars. It is possible that J1905+3015 is
also an SW-type variable. We encourage continued monitoring of
this new CV to follow its return to the low state. When the system
fades back to the
![]() level, it will become a good target
to measure the size of the accretion disk and to determine the
orbital inclination from changes in the depth and duration of the
eclipse.
level, it will become a good target
to measure the size of the accretion disk and to determine the
orbital inclination from changes in the depth and duration of the
eclipse.
References:
Denisenko, D., Balanutsa, P., Lipunov, V., et al., 2014, Astronomer's Telegram, No. 5953
Lipunov, V., Kornilov, V., Gorbovskoy, E., et al., 2010, Adv. in Astron., 2010, Art. ID 349171
Monet, D. G., Levine, S. E., Canzian, B., et al., 2003, Astron. J., 125, 984
Ritter, H., Kolb, U., 2003, Astron. & Astrophys., 404, 301
Rodriguez-Gil, P., Gaensicke, B. T., Barwig, H., et al., 2004, Astron. & Astrophys., 424, 647
Voges, W., Aschenbach, B., Boller, T., et al., 1999, Astron. & Astrophys., 349, 389