
|
Astronomy Picture Of the Day (APOD)
 Jupiter, Io, and Shadow
Jupiter, Io, and Shadow
25.12.2000
Just as planets orbit our Sun, Jupiter's Moons orbit Jupiter. Pictured above is the closest of Jupiter's Galilean Satellites, Io, superposed in front of the giant planet it circles. To the left of Io is a dark spot that is its own shadow.
 The Eclipse Tree
The Eclipse Tree
24.12.2000
If you look closely at the shadow of this tree, you will see something quite unusual: it is composed of hundreds of images of a partially eclipsed Sun. Early today, trees across North America will be casting similar shadows as a partial eclipse of the Sun takes place.
 NGC 1850: Gas Clouds and Star Clusters
NGC 1850: Gas Clouds and Star Clusters
23.12.2000
There's nothing like it in our own Galaxy. Globular clusters as young as NGC 1850 don't exist here. Globular clusters only 40 millions of years old can still be found in the neighboring LMC galaxy, though, but perhaps none so unusual as NGC 1850.
 Summer at the South Pole
Summer at the South Pole
22.12.2000
The December solstice brings the beginning of Winter to Earth's Northern Hemisphere and Summer time to the South! This view of Earth's Southern Hemisphere near the beginning of Summer was created using images from the Galileo spacecraft taken during its December 1990 flyby of our fair planet.
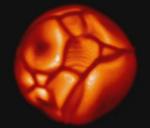 Simulated Supergiant Star
Simulated Supergiant Star
21.12.2000
Looking for that perfect holiday gift for an astronomer? Consider this "star in a box". Of course, the box is actually a computational box consisting of a three dimensional grid of points, and the star is a virtual one whose physical properties and internal dynamics are numerically simulated at the points on the grid.
 Solstice And Season's Eclipse
Solstice And Season's Eclipse
20.12.2000
Today the Sun reaches its southernmost point in planet Earth's sky at 13:37 UT. This celestial event is known as a solstice, marking the beginning of Summer in the Southern Hemisphere and Winter in the North.
 Sgr A: Fast Stars Near the Galactic Center
Sgr A: Fast Stars Near the Galactic Center
19.12.2000
Why are these stars moving so fast? Shown above is a time-lapse movie in infrared light detailing how stars in the central light-year of our Galaxy have moved over the past eight years. The yellow mark at the image center represents the location of a peculiar radio source named Sgr A
 A Close Up of Aurora on Jupiter
A Close Up of Aurora on Jupiter
18.12.2000
Jupiter has aurorae. Like Earth, the magnetic field of the gas giant funnels charged particles released from the Sun onto the poles. As these particles strike the atmosphere, electrons are temporarily knocked away from existing gas molecules. Electric force attracts these electrons back. As the electrons recombine to remake neutral molecules, auroral light is emitted.
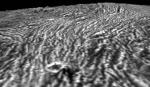 Oceans Under Jupiter's Ganymede
Oceans Under Jupiter's Ganymede
17.12.2000
The search for extraterrestrial life came back into our own Solar System last week with the announcement that there may be liquid oceans under the surface of Jupiter's moon Ganymede. Ganymede now joins Callisto and Europa as moons of Jupiter that may harbor seas of liquid water under layers of surface ice.
 M2 9: Wings of a Butterfly Nebula
M2 9: Wings of a Butterfly Nebula
16.12.2000
Are stars better appreciated for their art after they die? Actually, stars usually create their most artistic displays as they die. In the case of low-mass stars like our Sun and M2-9 pictured above
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||