
|
Astronomy Picture Of the Day (APOD)
 Night Lightning on Jupiter
Night Lightning on Jupiter
16.12.1997
Why is there lightning on Jupiter? Lightning is a sudden rush of electrically charged particles from one location to another. To create lightning, charges must first separate inside a cloud. On Earth, drafts of colliding ice and water droplets usually create this charge separation, but what happens on Jupiter?
 A Farewell to Tails
A Farewell to Tails
15.12.1997
As 1997 fades, so does the Great Comet of 1997: Comet Hale-Bopp. Discovered even before the Great Comet of 1996, Comet Hale-Bopp became the brightest comet since 1976. Many will remember Comet Hale-Bopp as a comet with a coma so bright it could be seen by eye even when near the Moon.
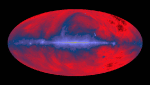 The Radio Sky: Tuned to 408MHz
The Radio Sky: Tuned to 408MHz
14.12.1997
Tune your radio telescope to 408MHz (408 million cycles per second) and check out the Radio Sky! You should find that frequency on your dial somewhere between US broadcast television channels 13 and 14.
 The Coma Cluster of Galaxies
The Coma Cluster of Galaxies
13.12.1997
Almost every object in the above photograph is a galaxy. The Coma Cluster of Galaxies pictured is one of the densest clusters known - it contains thousands of galaxies. Each of these galaxies house billions of stars - just as our own Milky Way Galaxy does.
 Phi Persei: Double Star
Phi Persei: Double Star
12.12.1997
It's clear who is the biggest star in this binary system. Based on recent results, this artist's vision of the double star Phi Persei, 720 light years away, shows a bright, rapidly rotating massive star surrounded by a disk of gas. A small companion star orbits 100 million miles away.
 A Martian Lake Bed
A Martian Lake Bed
11.12.1997
Look closely. In this Mars Global Surveyor image of the Martian surface just south of Schiaparelli crater, dark lines appear to criss-cross light colored depressions. One tantalizing possibility is simply that the feature near...
 Sprint the Flying Space Camera
Sprint the Flying Space Camera
10.12.1997
Yes, but can your soccer ball do this? The ball near the middle of the above photograph is actually a robotic camera designed to float about a Space Shuttle and the International Space Station and take pictures.
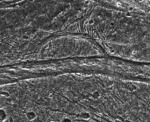 Mysterious Features on Ganymede
Mysterious Features on Ganymede
9.12.1997
Where is the rest of the circle? Jupiter's largest moon Ganymede has some truly unusual terrain, including the pictured half circle above cut by nearly parallel curves. Full circles can be easily explained by impact craters, but partial circles imply that some resurfacing has occurred since the original impact.
 The Trifid Nebula in Red, White and Blue
The Trifid Nebula in Red, White and Blue
8.12.1997
Three dark dust lanes give the picturesque Trifid Nebula its name. The red and blue colors of the Trifid Nebula are present in different regions and are created by different processes. A big bright star near the center of the red region appears white hot and emits light so energetic
 A Distant Cluster of Galaxies
A Distant Cluster of Galaxies
7.12.1997
In this 1994 Hubble Space Telescope photograph, every bright object is a galaxy. Oddly - most of them are spiral galaxies. This rich cluster of galaxies, named CL 0939+4713, is almost half way across the visible universe.
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||