
|
Astronomy Picture Of the Day (APOD)
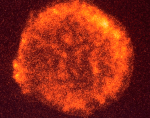 Tychos Supernova Remnant in X ray
Tychos Supernova Remnant in X ray
7.03.1999
How often do stars explode? By looking at external galaxies, astronomers can guess that these events, known as a supernovae, should occur about once every 30 years in a typical spiral galaxy like our MilkyWay.
 Miranda, Chevron, and Alonso
Miranda, Chevron, and Alonso
6.03.1999
Miranda is a bizarre world which surely had a tempestuous past. The innermost of the larger Uranian moons, Miranda is almost 300 miles in diameter and was discovered in 1948 by American planetary astronomer Gerard Kuiper.
 M46 And NGC 2438: Young And Old
M46 And NGC 2438: Young And Old
5.03.1999
Galactic or open star clusters are relatively young. These swarms of bright stars are born near the plane of the Milky Way, but their numbers steadily dwindle as cluster members are strewn through the Galaxy by gravitational interactions.
 Ganymede Mosaic
Ganymede Mosaic
4.03.1999
Ganymede, one of the four Galilean moons of Jupiter, is the largest moon in the Solar System. With a diameter of 5,260 kilometers it is even larger than planets Mercury and Pluto and just over three quarters the size of Mars. Ganymede is locked in synchronous rotation with Jupiter.
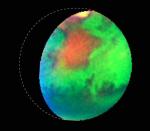 Infrared Mars
Infrared Mars
3.03.1999
Was Mars wetter and more Earth-like in its distant past? This false-color composite image of Mars is part of the mounting evidence that liquid water once did play a significant role in Martian surface geology.
 The Kleinmann Low Nebula
The Kleinmann Low Nebula
2.03.1999
The most active part of the Orion Nebular Cloud Complex is an area known as the Kleinmann-Low Nebula. There, a cluster of young and forming stars is embedded in a molecular cloud filled with dust.
 Reflection Nebula NGC 1435
Reflection Nebula NGC 1435
1.03.1999
Reflection nebulae reflect light from a nearby star. Many small carbon grains in the nebula reflect the light. The blue color typical of reflection nebula is caused by blue light being more efficiently scattered by the carbon dust than red light.
 Trapezium: Teardrops in My Skies
Trapezium: Teardrops in My Skies
28.02.1999
Sometimes the unexpected comes in a familiar shape. In this picture, the seemingly familiar teardrop-shaped object just right of center is actually an unusually situated disk of gas and dust. In fact, the teardrop is about the size of our own Solar System and is racing against time to condense and form planets.
 Hamlet of Oberon
Hamlet of Oberon
27.02.1999
What's in a name? Since 1919, the International Astronomical Union has been charged with the task of establishing "conventional" nomenclature for planets, satellites, and surface features. For the remote Uranian system of moons, namesakes from Shakespearean works have been chosen.
 Dark Cloud
Dark Cloud
26.02.1999
Ominously foreshadowing events to come, a dark cloud of obscuring dust stands out against a luminous star field in the Milky Way. Cataloged as Feitzinger and Stuwe object "1-457" this fuliginous interstellar nebula is relatively close - possibly only 1,000 light-years distant.
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||