
|
Astronomy Picture Of the Day (APOD)
 West Of The Great Red Spot
West Of The Great Red Spot
26.12.1999
The turbulent region West of Jupiter's Great Red Spot is highlighted in this picture constructed from data recorded by the Galileo spacecraft. The image is color coded to show cloud height and thickness; white clouds are high and thick, light blue clouds are high and thin, and reddish clouds are low.
 An Earth Ornament
An Earth Ornament
25.12.1999
The Apollo 8 astronauts spent the 1968 Christmas Season orbiting the Moon, returning with striking images of both Moon and Earth from space - pictures which inspired the world. While in lunar orbit...
 Hubble Holiday
Hubble Holiday
24.12.1999
How would you like to spend your holiday in low earth orbit? That's what the crew of the space shuttle Discovery is doing as they deliver six new gyros and a faster main computer to the orbiting Hubble Space Telescope.
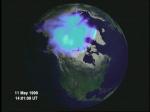 Unusual Aurora During Solar Wind Dropout
Unusual Aurora During Solar Wind Dropout
23.12.1999
On May 10, for some unknown reason, the Solar Wind virtually stopped. Normally our Sun emits a wind of between five and ten energetic particles per cubic centimeter moving outward at about 500 kilometers per second.
 Perigee Moon, Apogee Moon
Perigee Moon, Apogee Moon
22.12.1999
Tonight, those blessed with clear skies can enjoy a glorious full moon, the last full moon of the "Y1.9K"s. In fact, tonight's moon will be a full-perigee-solstice moon, reaching its full phase and perigee (the closest point in its orbit) on the solstice, the first day of northern hemisphere winter.
 XMM Launched
XMM Launched
21.12.1999
X-ray astronomy entered a golden age earlier this month with the successful launch of the X-ray Multi-Mirror (XMM) satellite. XMM's three huge telescope barrels each hold 58 concentric cylindrical mirrors, together totaling a surface area rivaling a tennis court.
 Lava Fountain on Jupiter's Io
Lava Fountain on Jupiter's Io
20.12.1999
A lava fountain shooting over a kilometer high has been discovered on Jupiter's moon Io. The robot Galileo spacecraft orbiting Jupiter photographed the volcanic eruption during its close flyby of the moon late last month. The fountain is visible in the above mosaic of images from the flyby.
 Accretion Disk Binary System
Accretion Disk Binary System
19.12.1999
Our Sun is unusual in that it is alone - most stars occur in multiple or binary systems. In a binary system, the higher mass star will evolve faster and will eventually become a compact object - either a white dwarf star, a neutron star, or black hole.
 Irregular Galaxy Sextans A
Irregular Galaxy Sextans A
18.12.1999
Grand spiral galaxies often seem to get all the glory. Their newly formed, bright, blue star clusters found along beautiful, symmetric spiral arms are guaranteed to attract attention. But small irregular galaxies form stars too, like this lovely, gumdrop-shaped galaxy, Sextans A.
 Hot Gas In Hydra A
Hot Gas In Hydra A
17.12.1999
The Hydra A galaxy cluster is really big. In fact, such clusters of galaxies are the largest gravitationally bound objects in the Universe. But individual galaxies are too cool to be recorded in this false-color Chandra Observatory X-ray image which shows only the 40 million degree gas that permeates the Hydra A cluster.
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||