|
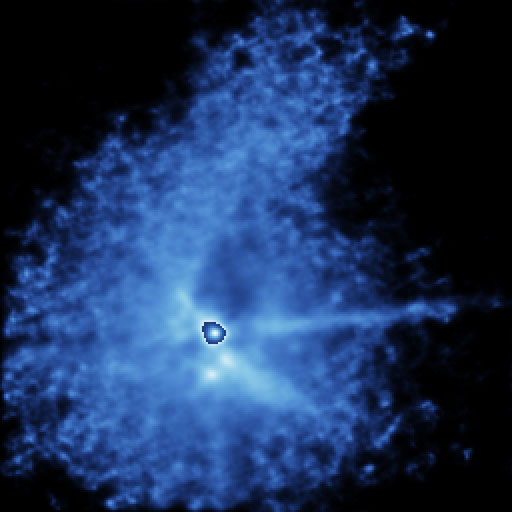
Explanation: What did the Sun look like before there were planets? A prototype laboratory for the formation of low mass stars like our Sun is the T Tauri system, one of the brighter star systems toward the constellation of Taurus. In young systems, gravity causes a gas cloud to condense. The situation then usually becomes quite complex, as some of the infalling gas is heated by collisions so high that it is immediately expelled as an outgoing wind. Complex geometries including jets and disks form as the infalling and outflowing gas collide and interact with a changing magnetic field. Pictured above is a false-color image of the T Tauri system itself, which turns out to be a binary. In a few million years, the central condensate will likely become hot enough to ignite nuclear fusion, by which time much of the surrounding circumstellar material will either have fallen in or have been driven off by the stellar wind. At that time, a new star will shine.
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Based on Astronomy Picture
Of the Day
Publications with keywords: star formation
Publications with words: star formation
See also:
- APOD: 2025 December 9 B The Heart of the Soul Nebula
- APOD: 2025 July 10 B Lynds Dark Nebula 1251
- APOD: 2025 June 23 B W5: Pillars of Star Formation
- APOD: 2025 April 28 B Gum 37 and the Southern Tadpoles
- APOD: 2025 March 26 B Star Formation in the Pacman Nebula
- APOD: 2024 October 22 B M16: Pillars of Star Creation
- Star Factory Messier 17