|
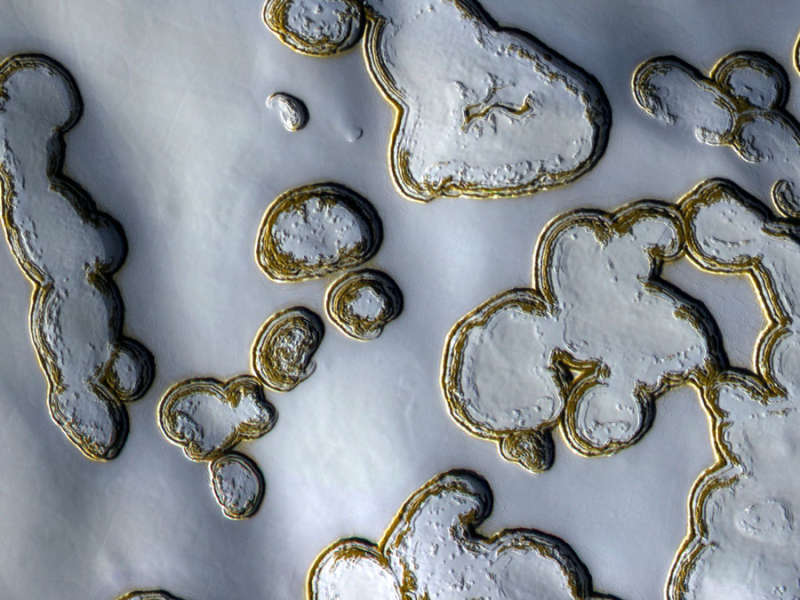
Explanation: Part of Mars is defrosting. Around the South Pole of Mars, toward the end of every Martian summer, the warm weather causes a section of the vast carbon-dioxide ice cap to evaporate. Pits begin to appear and expand where the carbon dioxide dry ice sublimates directly into gas. These ice sheet pits may appear to be lined with gold, but the precise composition of the dust that highlights the pit walls actually remains unknown. The circular depressions toward the image center measure about 60 meters across. The HiRISE camera aboard the Mars-orbiting Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured the above image in late July. In the next few months, as Mars continues its journey around the Sun, colder seasons will prevail, and the thin air will turn chilly enough not only to stop the defrosting but once again freeze out more layers of solid carbon dioxide.
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Based on Astronomy Picture
Of the Day
Publications with keywords: Mars - carbon dioxide - south pole of Mars
Publications with words: Mars - carbon dioxide - south pole of Mars
See also:
- APOD: 2025 September 28 B Leopard Spots on Martian Rocks
- APOD: 2025 July 15 B Collapse in Hebes Chasma on Mars
- APOD: 2025 July 6 B The Spiral North Pole of Mars
- APOD: 2025 June 29 B Dark Sand Cascades on Mars
- APOD: 2025 June 22 B A Berry Bowl of Martian Spherules
- APOD: 2025 June 15 B Two Worlds One Sun
- Perseverance Selfie with Ingenuity